Developing Employee Productivity and Performance through Work Engagement and Organizational Factors in an Educational Society
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Q1. What factors enhance the EPD and EP in HEIs in Saudi Arabia?
- Q2. What is the relationship between EPD and EP in HEIs in Saudi Arabia?
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Construction
2.1. Employee Work Engagement (WEE) and Employee Productivity (EPD)
2.2. Organizational Factors and Employee Performance (EP)
2.3. Employee Productivity (PRD) and Employee Performance (EP)
3. Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. Data Collection Modes and Ethical Protocols
3.3. Instrumental Validation
3.4. Measures
4. Analysis
4.1. Demography
4.2. Measurement of Model Assessment
4.3. Structural Model Assessment
5. Discussion and Conclusions
6. Limitations, Novelty and Future Research Agenda
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Auzina-Emsina, A. Labour productivity, economic growth and global competitiveness in post-crisis period. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 156, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, B.A.; Saraih, U.N.; Ahmad, T.S.T. Personality traits and conflict management styles: Building the relationship through leadership effectiveness. Kybernetes 2022. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.M.; Nguyen, L.V. Employer attractiveness, employee engagement and employee performance. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2022. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.R.; Yu, J.J.; Guo, Q.; Li, J.J. Employee engagement, its antecedents and effects on business performance in hospitality industry: A multilevel analysis. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2022, 34, 4631–4652. [Google Scholar]
- Riwukore, J.R.; Marnisah, L.; Habaora, F. Employee performance analysis based on the effect of discipline, motivation, and organizational commitment at the Regional Secretariat of the Kupang City Government. J. Maksipreneur Manaj. Kop. Dan Entrep. 2022, 12, 76–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Pant, D.; Chopra, P. Work engagement and individual work performance: Research findings and an agenda for employee relationships. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 2019, 6, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zondo, R.W. The influence of employee engagement on labour productivity in an automotive assembly organisation in South Africa. South Afr. J. Econ. Manag. Sci. 2020, 23, a3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, J. Determinants of employee engagement and their impact on employee performance. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2014, 63, 308–323. [Google Scholar]
- Basem, Z.; Zulher; Yusril, M.; Pangestika, N.D. Analysis of discipline, organizational commitment, work environment and their effect on employee performance PT, Adhiyasa Bangkinang. Influ. Int. J. Sci. Rev. 2022, 4, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiing, H.L.; Ahmad, Z.B.K. The moderating effects of organizational culture on the relationships between leadership behaviour and organizational commitment and between organizational commitment and job satisfaction and performance. Leadersh. Organ. Dev. J. 2009, 30, 53–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norawati, S.; Lutfi, A.; Zulher, Z.; Basem, Z. The effect of supervision, work motivation, and interpersonal communication on employee performance and organizational commitment as variables intervening. IJEBD Int. J. Entrep. Bus. Dev. 2022, 5, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amusa, O.I.; Iyoro, A.O.; Olabisi, A.F. Work environments and job performance of librarians in the public universities in South-west Nigeria. Int. J. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 5, 457–461. [Google Scholar]
- Hanaysha, J. Improving employee productivity through work engagement: Evidence from higher education sector. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2016, 6, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simorangkir, S.T.; Karnati, N.; Abdullah, T. The effect of supportive leadership, learning culture, and responsibility on job performance of teacher in junior high schools of South Tangerang. Int. J. Educ. Vocat. Stud. 2019, 1, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, S.D.; Priyono, B.S. The influence of perception of organizational justice, quality of work life and organizational commitment on performance: (Study on Kayen and Jaken Public Health Center Employees). Int. J. Soc. Manag. Stud. 2022, 3, 187–204. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Khalifa, G.S.; Nusari, M.; Ameen, A.; Al-Shibami, A.H.; Abu-Elhassan, A.E. Effect of organizational excellence and employee performance on organizational productivity within healthcare sector in the UAE. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2018, 13, 6199–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cherian, J.; Gaikar, V.; Paul, R.; Pech, R. Corporate culture and its impact on employees’ attitude, performance, productivity, and behavior: An investigative analysis from selected organizations of the United Arab Emirates (UAE). J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2021, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaikhmubarak, A.; Da Camara, N.; Baruch, Y. The impact of high-performance human resource practices on the research performance and career success of academics in Saudi Arabia. Career Dev. Int. 2020, 25, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanzi, A.A.; Sulphey, M.M.; Jnaneswar, K. Can knowledge of administrative law impact constructive deviance and task performance: Empirical evidence from Saudi Arabia. Vision 2022. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, B.A.; Saraih, U.N.; Ahmad, T.S.T. Personality traits and conflict management styles via job performance in higher education. J. Appl. Res. High. Educ. 2022. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, A.S.; Ahmad, A.R. Factors impacting research productivity of academic staff at the Iraqi higher education system. Int. Bus. Educ. J. 2020, 13, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moletsane, M.; Tefera, O.; Migiro, S. The relationship between employee engagement and organisational productivity of sugar industry in South Africa: The employees’ perspective. Afr. J. Bus. Econ. Res. 2019, 14, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, F.; Kadir, A.A.; Alhosani AA, H. Impact of leadership styles toward employee engagement among Malaysian Civil Defence Force. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2021, 22, 1188–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, M.Q.; Chaudhary, N.; Huseynov, R.; Li, M.; Sharma, A.; Jafarova, R.; Huseynova, C. Impact of organisational commitment on employee productivity during COVID-19: Evidence from Afghanistan and India. J. Corp. Gov. Insur. Risk Manag. 2021, 8, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alashab, A.A.; Mohamad, K.A. Performance management in Saudi Arabia: The effects of employee engagement, physical fitness and healthy lifestyle on job performance towards absenteeism. J. Int. Bus. Manag. 2020, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Jose, G.; Nimmi, P.M.; Kuriakose, V. HRM practices and employee engagement: Role of personal resources- a study among nurses. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2022. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, N.; Sharma, S. Drivers of employee engagement in the banking industry: Empirical evidence from fourteen banks. Int. J. Proj. Manag. Product. Assess. (IJPMPA) 2022, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmenas, N.H. Employee engagement: Turn over prevention strategies and the key to improving performance management in a multinational company. J. Econ. Manag. Entrep. Bus. (JEMEB) 2022, 2, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayeola, O.; Sidek, S.; Sanyal, S.; Hasan, M.M.; Singh, A.P.; Hasan, S.I. The nexus between top management support on change management, cloud ERP implementation, and performance of SMEs. Acad. J. Interdiscip. Stud. 2022, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, E.; García-Morales, V.J.; Bolívar-Ramos, M.T. The influence of top management support for ICTs on organisational performance through knowledge acquisition, transfer, and utilization. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2017, 11, 19–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Huang, C.K. Employee turnover intentions and job performance from a planned change: The effects of an organizational learning culture and job satisfaction. Int. J. Manpow. 2021, 42, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I. Moving beyond mandates: Organizational learning culture, empowerment, and performance. Int. J. Public Adm. 2020, 43, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Han, S.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, W. Structural relationships among transformational leadership, affective organizational commitment, and job performance: The mediating role of employee engagement. Eur. J. Train. Dev. 2021, 46, 920–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Q.I.; Mumtaz, R.; Rehan, M.F. How do organizational commitment and work engagement mediate between human resource management practices and job performance? Rev. Econ. Dev. Stud. 2021, 7, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, B.N.; Duy Tung, D.; Hoa, N.D.; Chau, N.T.N.; Tushar, H. An empirical assessment of organizational commitment and job performance: Vietnam small and medium-sized enterprises. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2020, 7, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Hitu, F.; Kusumaningtyas, A.; Ardiana, I.D.K.R. The influence of principal supervision on organizational commitment, and emotional intelligence on work discipline, work motivation and performance of state high school teachers in North Maluku province. J. Asian Multicult. Res. Econ. Manag. Study 2022, 3, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Mydin, Y.O.; Juarez, F.; Rani, D.M.; Hamid, N.A.; Roslan, N.; Ati, N.S.A. Attitude toward poverty among academicians: Social care institution workers and general population in Kuala-Lumpur, Malaysia. In Proceedings of the 4th ASEAN Conference on Psychology, Counselling, and Humanities (ACPCH 2018), George Town, Malaysia, 2–3 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, B.; Kalia, N. Contextual and task performance: Role of employee engagement and organizational culture in hospitality industry. Vilakshan—XIMB J. Manag. 2021, 18, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzee, H.; Kizza, J.; Mugabe, G.M. Organizational compassion and employee engagement in virtual work environments during Covid-19 lockdown in Uganda and Rwanda. Int. J. Manag. Knowl. Learn. 2021, 10, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, I.; Adi, K.R.; Soetjipto, B.E.; Supriyanto, A.S. The mediating role of job satisfaction on compensation, work environment, and employee performance: Evidence from Indonesia. Entrep. Sustain. Issues 2020, 8, 735–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawirosumarto, S.; Sarjana, P.K.; Gunawan, R. The effect of work environment, leadership style, and organizational culture towards job satisfaction and its implication towards employee performance in Parador Hotels and Resorts, Indonesia. Int. J. Law Manag. 2017, 59, 1337–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantidis, A.D.; Chatzoglou, P. Factors affecting employee performance: An empirical approach. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2019, 68, 171–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagliotti, A.L. Work engagement in nursing: A concept analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 2012, 68, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Tian, W.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y. The influence of professional identity on work engagement among nurses working in nursing homes in China. J. Nurs. Manag. 2022, 30, 3022–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkorashy, H.; Alanazi, M. Personal and Job-Related Factors Influencing the Work Engagement of Hospital Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study from Saudi Arabia. Healthcare 2023, 11, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, M.; Pais, L.; Mónico, L.; Santos NR, D.; Ferraro, T.; Berger, R. Decent work and work engagement: A profile study with academic personnel. Appl. Res. Qual. Life 2021, 16, 917–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspitasari, A.S.A.; Darwin, M. Effect of work-life balance and welfare level on millennial employee performance through work engagement. Int. J. Sci. Soc. 2021, 3, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Qiu, Y.; Gan, Y. Workplace incivility and work engagement: The mediating role of job insecurity and the moderating role of self-perceived employability. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2022, 43, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.S.; Ghayas, M.M. Impact of authentic leadership on employee engagement in the banking sector of Karachi. Int. J. Bus. Perform. Manag. 2022, 23, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santalla-Banderali, Z.; Alvarado, J.M. Incidence of Leader–Member Exchange Quality, Communication Satisfaction, and Employee Work Engagement on Self-Evaluated Work Performance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obuma, G.E.; Worlu, G.O. Workplace diversity and employee engagement of banks in rivers state, Nigeria. Int. J. Adv. Acad. Res. 2017, 3, 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, H.H.; Huang, J.T. Why and when are silent employees less satisfied with their jobs? A conservation of resources perspective. J. Manag. Psychol. 2022, 37, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajani, D.; Zaki, M.A. The impact of employee engagement on job performance and organisational commitment in the Egyptian banking sector. J. Bus. Manag. Sci. 2015, 3, 138–147. [Google Scholar]
- Jaya, L.H.S.; Ariyanto, E. The effect of vigor, dedication and absorption on the employee performance of PT Garuda Indonesia Cargo. Eur. J. Bus. Manag. Res. 2021, 6, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeve, Y.B.; Oppenheimer, C.; Konje, J. Employee engagement within the NHS: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Health Policy Manag. 2015, 4, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.; Roberts, R. Employee age and the impact on work engagement. Strateg. HR Rev. 2020, 19, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragu-Nathan, B.S.; Apigian, C.H.; Ragu-Nathan, T.S.; Tu, Q. A path analytic study of the effect of top management support for information systems performance. Omega 2004, 32, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, G.B.; Kim, H. An integrated view of knowledge management for performance. J. Knowl. Manag. 2012, 16, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpkan, L.; Bulut, C.; Gunday, G.; Ulusoy, G.; Kilic, K. Organizational support for intrapreneurship and its interaction with human capital to enhance innovative performance. Manag. Decis. 2010, 48, 732–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, R.Y.Y.; Yang, B.; Lien, B.Y.H.; McLean, G.N.; Kuo, Y.M. Dynamic capability: Impact of process alignment and organizational learning culture on performance. J. World Bus. 2010, 45, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N. Assessing the learning culture and performance of educational institutions. Perform. Improv. 2005, 44, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.A.; Park, S. Factors influencing job performance: Organizational learning culture, cultural intelligence, and transformational leadership. Perform. Improv. Q. 2019, 32, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škerlavaj, M.; Štemberger, M.I.; Dimovski, V. Organizational learning culture—The missing link between business process change and organizational performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2007, 106, 346–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, B.A.; Mangi, S.; Shah, N. Strategic factors and significance of organizational innovation and organizational learning in organizational performance. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2021, 24, 481–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.K.; Soomro, B.A.; Shah, N. Work environment and performance among nurses: A significant way to overcome violation of human rights in the health sector. Int. J. Hum. Rights Healthc. 2022, 15, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.K.; Soomro, B.A.; Shah, N. Predictive power of training design on employee performance: An empirical approach in Pakistan’s health sector. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2022, 71, 3792–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.K.; Soomro, B.A.; Shah, N. Training characteristics and employees’ performance among the nurses in Pakistan. J. Econ. Adm. Sci. 2021. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacmar, K.M.; Collins, B.J.; Harris, K.J.; Judge, T.A. Core self-evaluations and job performance: The role of the perceived work environment. J. Appl. Psychol. 2009, 94, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omari, K.; Okasheh, H. The influence of work environment on job performance: A case study of engineering company in Jordan. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2017, 12, 15544–15550. [Google Scholar]
- Dul, J.; Ceylan, C. The Impact of a creativity-supporting work environment on a firm’s product innovation performance. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2014, 31, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, T. The influence of leadership styles, work environment and job satisfaction of employee performance--studies in the school of SMPN 10 Surabaya. Int. Educ. Stud. 2016, 9, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, B.A.; Shah, N. Entrepreneurial orientation and performance in a developing country: Strategic entrepreneurship as a mediator. Bus. Strategy Dev. 2020, 3, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahed, N.A.A.; Soomro, B.A.; Shah, N. Predicting employee performance through transactional leadership and entrepreneur’s passion among the employees of Pakistan. Asia Pac. Manag. Rev. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, B.A.; Shah, N. Determining the impact of entrepreneurial orientation and organizational culture on job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and employee’s performance. South Asian J. Bus. Stud. 2019, 8, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, B.A.; Zehri, A.W.; Anwar, S.; Abdelwahed, N.A.A.; Shah, N. Developing the relationship between corporate cultural factors and employees’ organizational commitment via self-efficacy. South Asian J. Bus. Stud. 2023. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Jha, S.K.; Prasad, K.D.; Singh, A.K. Productivity, quality and business performance: An empirical study. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2017, 66, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangen, S. Demystifying productivity and performance. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2005, 54, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tjosvold, D. Collectivist Values for Productive Teamwork between Korean and Chinese Employees. Working Paper Series, Centre for Asian Pacific Studies, 2008. Available online: http://commons.ln.edu.hk/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1002&context=capswp (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- Lee, S.Y.; Brand, J.L. Can personal control over the physical environment ease distractions in office workplaces? Ergonomics 2010, 53, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J. The relationship between organizational factors and the transfer of training in the electronics industry in Shenzhen, China. Hum. Resour. Dev. Q. 1996, 7, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sal, A.; Raja, M. The impact of training and development on employees performance and productivity. Int. J. Manag. Sci. Bus. Res. 2016, 5, 37–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H. Performance from building smart factories of small- and medium-sized enterprises: The moderating effects of product complexity and company size. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2022, 42, 1497–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, E.G.; Fleming, D.E. The productive service employee: Personality, stress, satisfaction and performance. J. Serv. Mark. 2017, 31, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyan, A.K. Moderating role of productivity on diversified conglomerates and performance: The case of Malaysia. Asia-Pac. J. Bus. Adm. 2017, 9, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; King, J. Managing the downside effect of a productivity orientation. J. Serv. Mark. 2016, 30, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kengatharan, N. A knowledge-based theory of the firm: Nexus of intellectual capital, productivity and firms’ performance. Int. J. Manpow. 2019, 40, 1056–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahed, N.A.A.; Soomro, B.A.; Shah, N. Determining employee satisfaction, intrapreneurship and firm growth among managers of Pakistan. Heliyon 2022, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmy, A. Employee engagement factors in a higher education institution. Binus Bus. Rev. 2019, 10, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, B.A.; Shah, N. Examining the intention to stay home due to COVID-19: A pandemic’s second wave outlook. Health Educ. 2021, 121, 420–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, R.A.; Gullone, E. Why we should not use 5-point Likert scales: The case for subjective quality of life measurement. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Quality of Life in Cities, Singapore, 8–10 March 2000; Volume 74, pp. 74–93. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, N.; Aggarwal, A. The role of perceived benefits in formation of online shopping attitude among women shoppers in India. South Asian J. Bus. Stud. 2018, 7, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinnell, R.M.; Williams, M. Research in Social Work: A Primer; Wadsworth: Belmont, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, S.P.; Cappellari, L.; Lynn, P.; Jäckle, A.; Sala, E. Patterns of consent: Evidence from a general household survey. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A (Stat. Soc.) 2006, 169, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderson, P.; Mayall, B.; Barker, S.; Henderson, J.; Pratten, B. Childhood immunization: Meeting targets yet respecting consent. Eur. J. Public Health 1997, 7, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautmans, I.; Jansen, B.; Van Keymolen, B.; Mets, T. Reliability and clinical correlates of 3D-accelerometry based gait analysis outcomes according to age and fall-risk. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods; Sage Publication: Thousands Oakes, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collis, J.; Hussey, R. Business Research: A Practical Guide for Undergraduate and Postgraduate Student, 2nd ed.; Palgrave Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- McFadden, D. Quantitative methods for analysing travel behaviour of individuals: Some recent developments. In Behavioural Travel Modelling; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2021; pp. 279–318. [Google Scholar]
- Schaufeli, W.B.; Bakker, A.B. Utrecht Work Engagement Scale: Preliminary Manual; Occupational Health Psychology Unit, Utrecht University: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Swink, M. Technological innovativeness as a moderator of new product design integration and top management support. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2000, 17, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, N.G.; Pérez, M.J.S.; Gutiérrez, J.A.T. Can a good organizational climate compensate for a lack of top management commitment to new product development? J. Bus. Res. 2008, 61, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, T.M.; Yang, B.; Bartlett, K.R. The effects of organizational learning culture and job satisfaction on motivation to transfer learning and turnover intention. Hum. Resour. Dev. Q. 2004, 15, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuei, C.H.; Madu, C.N.; Lin, C. The relationship between supply chain quality management practices and organizational performance. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2001, 18, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Hooff, B.; De Leeuw Van Weenen, F. Committed to share: Commitment and CMC use as antecedents of knowledge sharing. Knowl. Process Manag. 2004, 11, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentler, P.M.; Huang, W. On components, latent variables, PLS and simple methods: Reactions to Rigdon’s rethinking of PLS. Long Range Plan. 2014, 47, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, G.; Paul, J. CB-SEM vs PLS-SEM methods for research in social sciences and technology forecasting. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 173, 121092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarstedt, M.; Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Thiele, K.O.; Gudergan, S.P. Estimation issues with PLS and CBSEM: Where the bias lies! J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 3998–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Hamid, M.R.; Sami, W.; Sidek, M.M. Discriminant validity assessment: Use of Fornell and Larcker criterion versus HTMT criterion. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 890, 012163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Category | Frequency | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 156 | 61.41 |
| Female | 98 | 38.59 | |
| Total | 254 | 100.0 | |
| Age (years) | 18–25 | 10 | 3.94 |
| 26–35 | 70 | 27.56 | |
| 36–45 | 130 | 51.18 | |
| 46 and above | 44 | 17.32 | |
| Total | 254 | 100.0 | |
| Tenure (years) How long have you worked at a specific organization? | 1–5 | 38 | 14.96 |
| 6–10 | 78 | 30.71 | |
| 11–20 | 128 | 50.39 | |
| 21 and above | 10 | 3.94 | |
| Total | 254 | 100.0 |
| Construct | Indicator | Factor Loadings Above 0.5 | CR >0.7 | AVE Above 0.5 | α Above 0.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vigour [vgr] | vgr1 | 0.876 | 0.881 | 0.822 | 0.829 |
| vgr2 | 0.865 | ||||
| vgr4 | 0.860 | ||||
| vgr3 | 0.855 | ||||
| Dedication [ded] | ded1 | 0.880 | 0.852 | 0.832 | 0.819 |
| ded2 | 0.876 | ||||
| ded3 | 0.862 | ||||
| ded5 | 0.850 | ||||
| ded4 | 0.861 | ||||
| Absorption | abr1 | 0.898 | 0.844 | 0.789 | 0.846 |
| abr3 | 0.875 | ||||
| abr4 | 0.866 | ||||
| abr5 | 0.841 | ||||
| Management support [ms] | ms1 | 0.867 | 0.849 | 0.796 | 0.833 |
| ms2 | 0.845 | ||||
| ms4 | 0.833 | ||||
| ms3 | 0.821 | ||||
| ms7 | 0.818 | ||||
| ms6 | 0.791 | ||||
| Learning culture [lc] | lc1 | 0.865 | 0.821 | 0.800 | 0.816 |
| lc4 | 0.854 | ||||
| lc5 | 0.831 | ||||
| lc6 | 0.829 | ||||
| lc7 | 0.810 | ||||
| lc2 | 0.789 | ||||
| Work environment [we] | we1 | 0.872 | 0.801 | 0.815 | 0.861 |
| we2 | 0.856 | ||||
| we3 | 0.842 | ||||
| we4 | 0.821 | ||||
| we5 | 0.802 | ||||
| Organizational commitment [oc] | oc1 | 0.881 | 0.820 | 0.811 | 0.855 |
| oc2 | 0.866 | ||||
| oc4 | 0.856 | ||||
| oc6 | 0.844 | ||||
| oc8 | 0.831 | ||||
| oc7 | 0.821 | ||||
| oc5 | 0.799 | ||||
| Employee productivity [epd] | epd1 | 0.887 | 0.792 | 0.825 | 0.798 |
| epd2 | 0.866 | ||||
| epd3 | 0.852 | ||||
| epd5 | 0.830 | ||||
| epd4 | 0.811 | ||||
| Employee performance [ep] | ep1 | 0.890 | 0.830 | 0.822 | 0.809 |
| ep2 | 0.876 | ||||
| ep3 | 0.851 | ||||
| ep6 | 0.849 | ||||
| ep5 | 0.832 | ||||
| ep4 | 0.811 |
| Factors | 1 VGR | 2 DED | 3 ABR | 4 MS | 5 LC | 6 WE | 7 OC | 8 EPD | 9 EP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VGR | 0.821 | ||||||||
| 2 | DED | 0.421 | 0.799 | |||||||
| 3 | ABR | 0.502 | 0.522 | 0.811 | ||||||
| 4 | MS | 0.402 | 0.519 | 0.499 | 0.778 | |||||
| 5 | LC | 0.488 | 0.398 | 0.424 | 0.463 | 0.808 | ||||
| 6 | WE | 0.511 | 0.376 | 0.415 | 0.500 | 0.382 | 0.784 | |||
| 7 | OC | 0.489 | 0.481 | 0.444 | 0.411 | 0.520 | 0.452 | 0.812 | ||
| 8 | EPD | 0.399 | 0.566 | 0.472 | 0.392 | 0.482 | 0.402 | 0.421 | 0.775 | |
| 9 | EP | 0.380 | 0.520 | 0.388 | 0.326 | 0.462 | 0.327 | 0.488 | 0.318 | 0.798 |
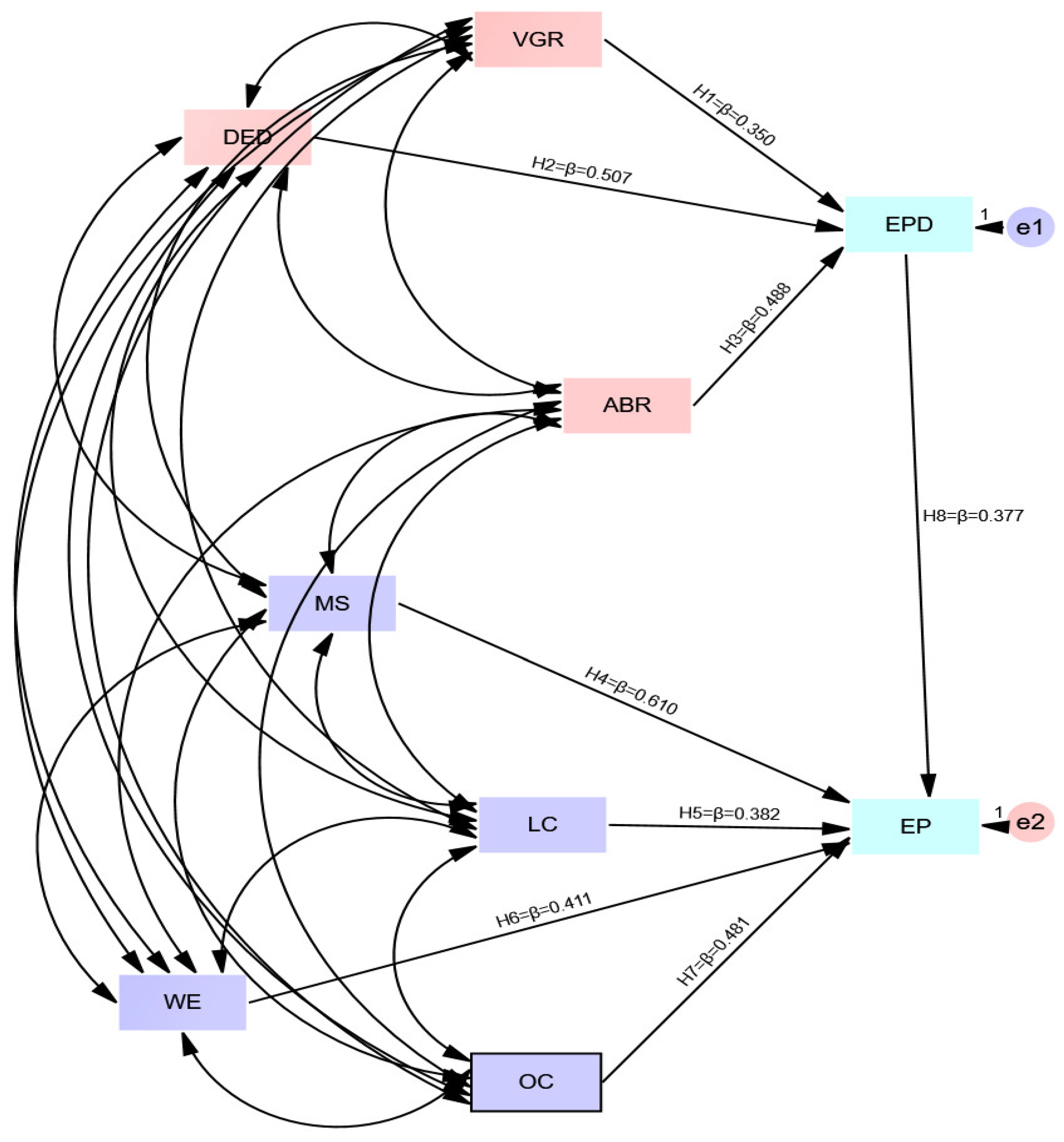
| H.No. | Independent Variables | Path | Dependent Variables | Estimate β (Path Co-efficient) | SE | CR (t-Value) | Result | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | VGR | → | EPD | 0.350 | 0.031 | 5.672 *** | Significant | Supported |
| H2 | DED | → | EPD | 0.507 | 0.060 | 7.090 *** | Significant | Supported |
| H3 | ABR | → | EPD | 0.488 | 0.071 | 7.892 *** | Significant | Supported |
| H4 | MS | → | EP | 0.610 | 0.035 | 6.999 *** | Significant | Supported |
| H5 | LC | → | EP | 0.382 | 0.302 | 5.372 *** | Significant | Supported |
| H6 | WE | → | EP | 0.411 | 0.399 | 6.321 *** | Significant | Supported |
| H7 | OC | → | EP | 0.481 | 0.421 | 5.882 *** | Significant | Supported |
| H8 | EPD | → | EP | 0.377 | 0.449 | 6.222 *** | Significant | Supported |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelwahed, N.A.A.; Doghan, M.A.A. Developing Employee Productivity and Performance through Work Engagement and Organizational Factors in an Educational Society. Societies 2023, 13, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc13030065
Abdelwahed NAA, Doghan MAA. Developing Employee Productivity and Performance through Work Engagement and Organizational Factors in an Educational Society. Societies. 2023; 13(3):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc13030065
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelwahed, Nadia Abdelhamid Abdelmegeed, and Mohammed A. Al Doghan. 2023. "Developing Employee Productivity and Performance through Work Engagement and Organizational Factors in an Educational Society" Societies 13, no. 3: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc13030065
APA StyleAbdelwahed, N. A. A., & Doghan, M. A. A. (2023). Developing Employee Productivity and Performance through Work Engagement and Organizational Factors in an Educational Society. Societies, 13(3), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc13030065






