Effect of Plyometric Training on Speed and Change of Direction Ability in Elite Field Hockey Players
Abstract
1. Introduction
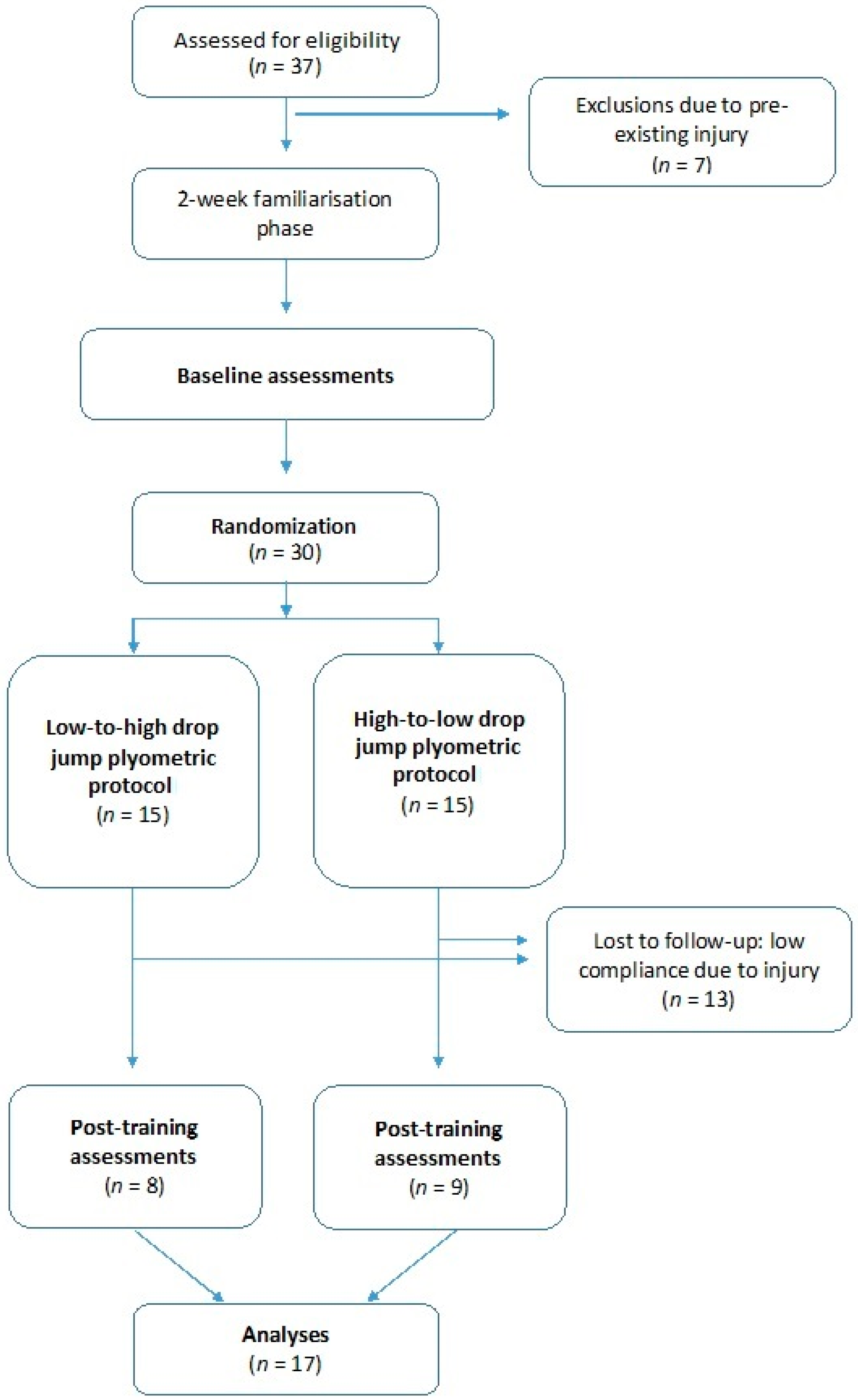
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
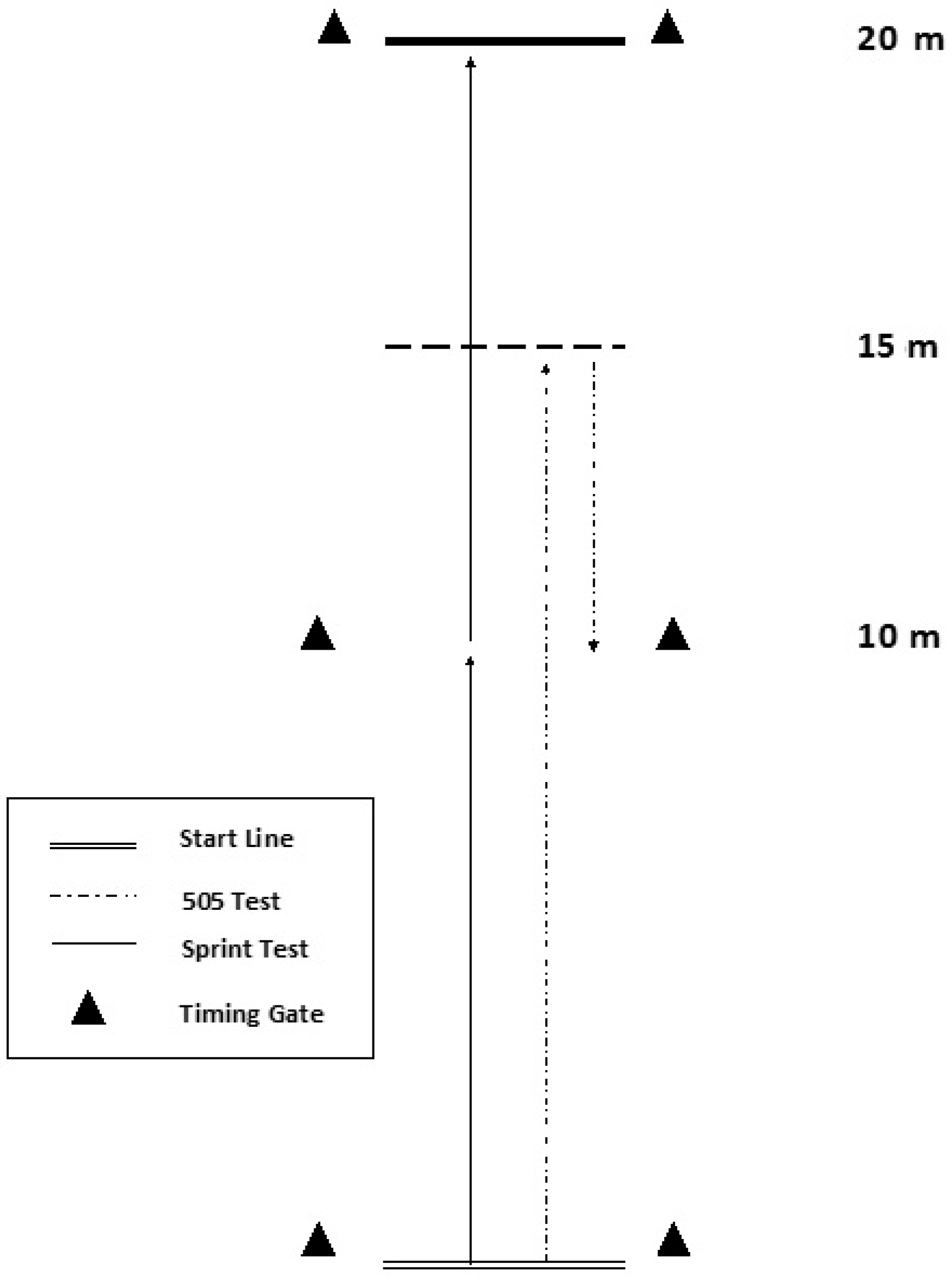
2.3. Assessments
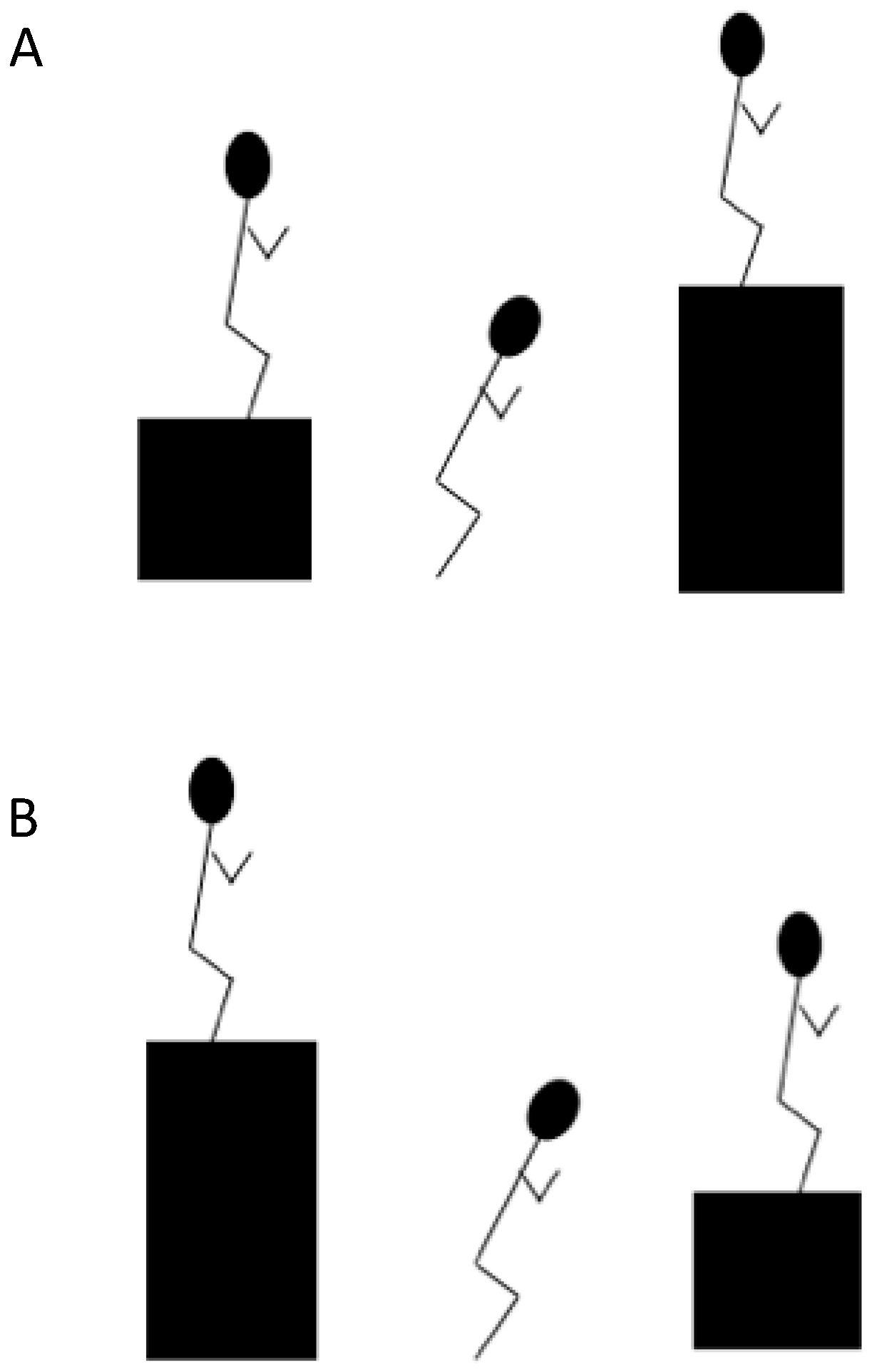
2.4. Training Protocol
2.5. Statistical Analyses
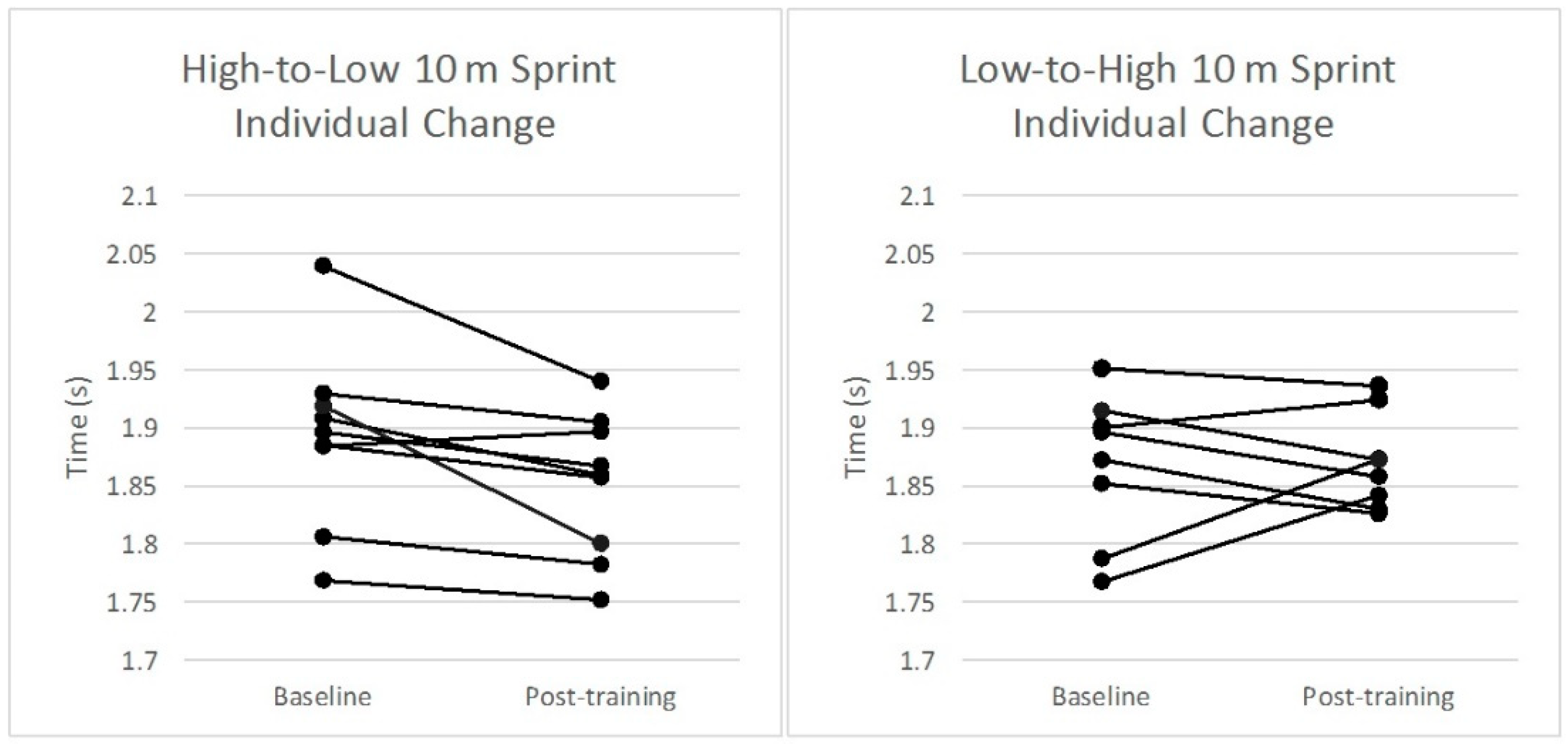
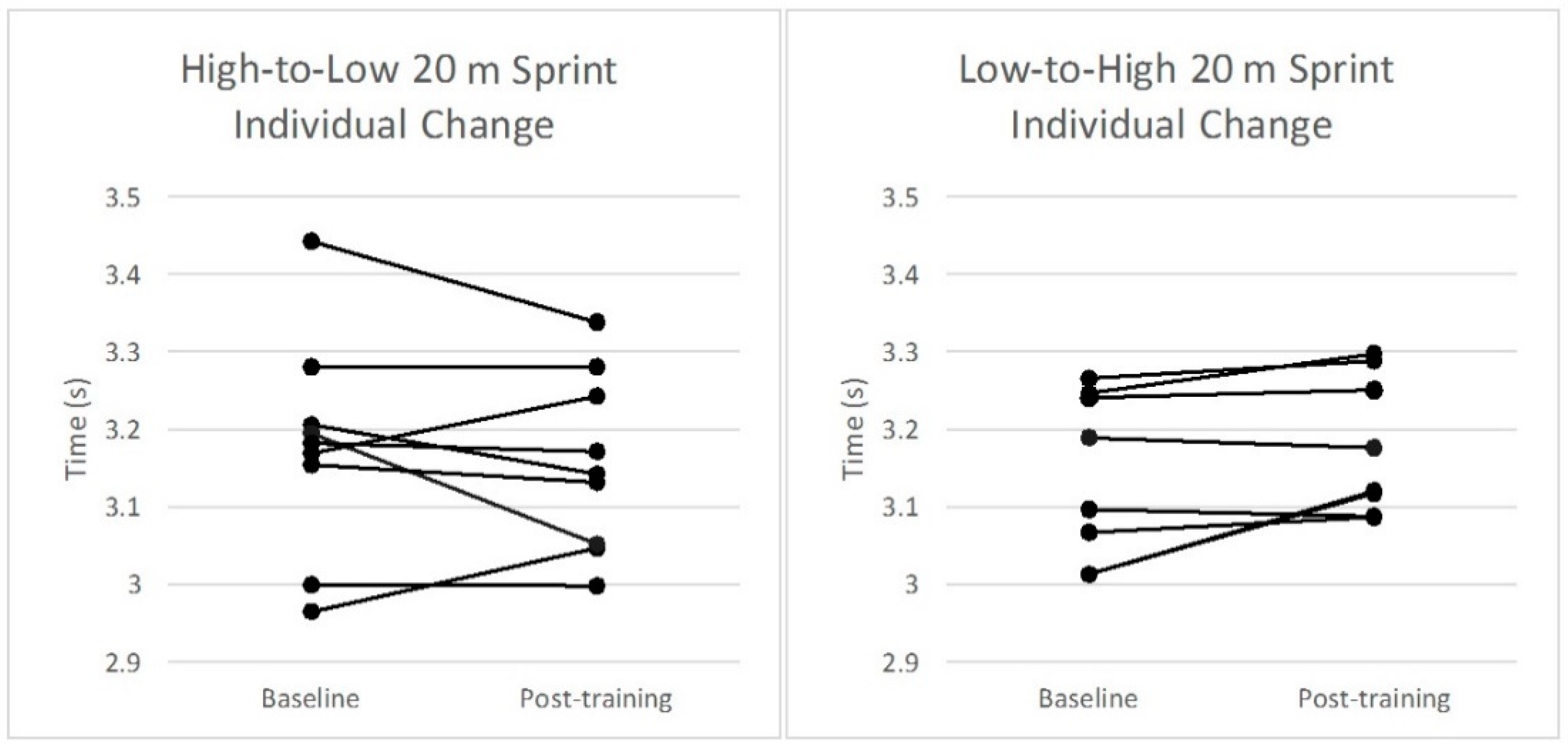
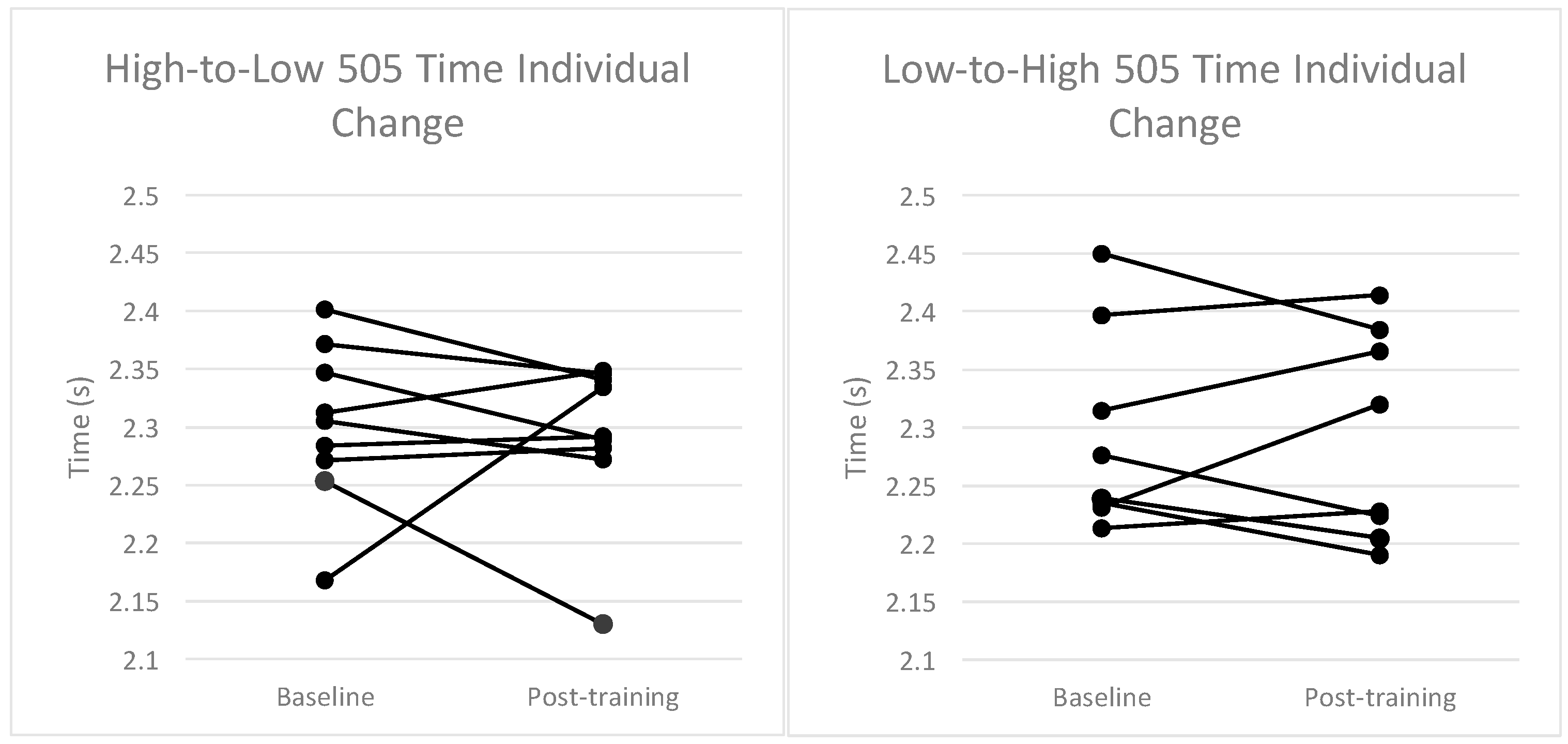
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spiteri, T.; Cochrane, J.L.; Hart, N.H.; Haff, G.G.; Nimphius, S. Effect of strength on plant foot kinetics and kinematics during a change of direction task. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2013, 13, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, M.; Lawrence, S.; Rechichi, C.; Bishop, D.; Dawson, B.; Goodman, C. Time-motion analysis of elite field hockey, with special reference to repeated-sprint activity. J. Sports Sci. 2004, 22, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, J.M.; Dawes, J.J.; Jeffreys, I.; Spiteri, T.; Nimphius, S. Broadening the View of Agility: A Scientific Review of the Literature. J. Aust. Strength Cond. 2014, 22, 6–25. [Google Scholar]
- Spiteri, T.; Newton, R.U.; Binetti, M.; Hart, N.H.; Sheppard, J.M.; Nimphius, S. Mechanical Determinants of Faster Change of Direction and Agility Performance in Female Basketball Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheit, M.; Samozino, P.; Glynn, J.A.; Michael, B.S.; Al Haddad, H.; Mendez-Villanueva, A.; Morin, J.B. Mechanical determinants of acceleration and maximal sprinting speed in highly trained young soccer players. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1906–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.P.; Marshall, R.N.; McNair, P.J. Relationships between ground reaction force impulse and kinematics of sprint-running acceleration. J. Appl. Biomech. 2005, 21, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Bampouras, T.M.; Marrin, K. An investigation into the physical determinants of change of direction speed. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2009, 49, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor, J.; Greig, M. A hierarchical model of factors influencing a battery of agility tests. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2015, 55, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Asadi, A.; Arazi, H.; Young, W.B.; Sáez de Villarreal, E. The Effects of Plyometric Training on Change-of-Direction Ability: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brughelli, M.; Cronin, J.; Levin, G.; Chaouachi, A. Understanding Change of Direction Ability in Sport: A Review of Resistance Training Studies. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 1045–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, E.P.; Comyns, T.M. The use of contact time and the reactive strength index to optimize fast stretch-shortening cycle training. Strength Cond. J. 2008, 30, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelly, M.S.; Ghenem, M.A.; Abid, K.; Hermassi, S.; Tabka, Z.; Shephard, R.J. Effects of in-season short-term plyometric training program on leg power, jump-and sprint performance of soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, J.; Villarreal, E.S.D.; Sanz-Rivas, D.; Moya, M. The Effects of 8-Week Plyometric Training on Physical Performance in Young Tennis Players. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2016, 28, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.G.; Herniman, J.J.; Ricard, M.D.; Cheatham, C.C.; Michael, T.J. The effects of a 6-week plyometric training program on agility. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2006, 5, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vaczi, M.; Tollar, J.; Meszler, B.; Juhasz, I.; Karsai, I. Short-Term High Intensity Plyometric Training Program Improve Strength, Power and Agility in Male Soccer Players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2013, 36, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewit, J.; Cronin, J.; Button, C.; Hume, P. Understanding deceleration in sport. Strength Cond. J. 2011, 33, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, M.S.; Roetert, E.P.; Ellenbecker, T.S. Efficient Deceleration: The Forgotten Factor in Tennis-Specific Training. Strength Cond. J. 2008, 30, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, F.A.; Gamble, P.; Gill, N.D.; McGuigan, M.R. Effects of a Six-Week Strength Training Programme on Change of Direction Performance in Youth Team Sport Athletes. Sports 2017, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalo-Skok, O.; Tous-Fajardo, J.; Valero-Campo, C.; Berzosa, C.; Bataller, A.V.; Arjol-Serrano, J.L.; Moras, G.; Mendez-Villanueva, A. Eccentric-Overload Training in Team-Sport Functional Performance: Constant Bilateral Vertical Versus Variable Unilateral Multidirectional Movements. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.A.; Thomas, C.; Dos’Santos, T.; McMahon, J.J.; Graham-Smith, P. The role of eccentric strength in 180 turns in female soccer players. Sports 2017, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroto-Izquierdo, S.; García-López, D.; de Paz, J.A. Functional and Muscle-Size Effects of Flywheel Resistance Training with Eccentric-Overload in Professional Handball Players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 60, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockie, R.G.; Schultz, A.B.; Callaghan, S.J.; Jeffriess, M.D. The Effects of Traditional and Enforced Stopping Speed and Agility Training on Multidirectional Speed and Athletic Function. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1538–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos’ Santos, T.; Thomas, C.; Jones, P.A.; Comfort, P. Mechanical determinants of faster change of direction speed performance in male athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Hoyo, M.; Sañudo, B.; Carrasco, L.; Mateo-Cortes, J.; Domínguez-Cobo, S.; Fernandes, O.; Del Ojo, J.J.; Gonzalo-Skok, O. Effects of 10-week eccentric overload training on kinetic parameters during change of direction in football players. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, B.X.; Morris, S.; Keogh, J.W.; Appleby, B.; Netto, K. Effects of two neuromuscular training programs on running biomechanics with load carriage: A study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimphius, S.; Callaghan, S.J.; Spiteri, T.; Lockie, R.G. Change of Direction Deficit: A More Isolated Measure of Change of Direction Performance Than Total 505 Time. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 3024–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.-T. Changes in biomechanical properties during drop jumps of incremental height. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 2510–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.-T.; Kernozek, T.W.; Song, C.-Y. Quadricep and hamstring activation during drop jumps with changes in drop height. Phys. Ther. Sport 2011, 12, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, B.J.; Kernozek, T.W.; White, J.M.; Kline, D.E.; Wright, G.A.; Peng, H.-T.; Huang, C.-F. Quantification of vertical ground reaction forces of popular bilateral plyometric exercises. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batterham, A.M.; Cox, A.J. Spreadsheets for analysis of controlled trials, with adjustment for a subject characteristic. Sportscience 2006, 10, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, W.; Marshall, S.; Batterham, A.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arazi, H.; Mohammadi, M.; Asadi, A. Muscular adaptations to depth jump plyometric training: Comparison of sand vs. land surface. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 2014, 6, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, B.; Norasteh, A.A.; de Villarreal, E.S.; Asadi, A. Effects of six weeks of depth jump vs. countermovement jump training on sand on muscle soreness and performance. Kinesiology 2014, 46, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Campillo, R.; Gallardo, F.; Henriquez-Olguín, C.; Meylan, C.M.; Martínez, C.; Álvarez, C.; Caniuqueo, A.; Cadore, E.L.; Izquierdo, M. Effect of vertical, horizontal, and combined plyometric training on explosive, balance, and endurance performance of young soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1784–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleby, B.; Newton, R.U.; Cormie, P. Changes in Strength over a 2-Year Period in Professional Rugby Union Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 2538–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.G.; Newton, R.U. Adaptations in upper-body maximal strength and power output resulting from long-term resistance training in experienced strength-power athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2006, 20, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.M.; Marin, P.J.; Rhea, M.R.; Wilson, S.M.; Loenneke, J.P.; Anderson, J.C. Concurrent training: A meta-analysis examining interference of aerobic and resistance exercises. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 2293–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronnestad, B.R.; Kvamme, N.H.; Sunde, A.; Raastad, T. Short-term effects of strength and plyometric training on sprint and jump performance in professional soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, J.; Pearson, S.; Ross, A.; McGuigan, M. Chronic adaptations to eccentric training: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 917–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tous-Fajardo, J.; Gonzalo-Skok, O.; Arjol-Serrano, J.L.; Tesch, P. Enhancing change-of-direction speed in soccer players by functional inertial eccentric overload and vibration training. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dello Iacono, A.; Martone, D.; Milic, M.; Padulo, J. Vertical-vs. horizontal-oriented drop jump training: Chronic effects on explosive performances of elite handball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.A.; Cipriani, D.J. Comparing preseason frontal and sagittal plane plyometric programs on vertical jump height in high-school basketball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 2109–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loturco, I.; Pereira, L.A.; Kobal, R.; Zanetti, V.; Kitamura, K.; Abad, C.C.C.; Nakamura, F.Y. Transference effect of vertical and horizontal plyometrics on sprint performance of high-level U-20 soccer players. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 2182–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manouras, N.; Papanikolaou, Z.; Karatrantou, K.; Kouvarakis, P.; Gerodimos, V. The efficacy of vertical vs. horizontal plyometric training on speed, jumping performance and agility in soccer players. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2016, 11, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, B.T.; Hannon, J.C.; Newton, M.; Shultz, B.; Detling, N.; Young, W.B. The effects of frontal-and sagittal-plane plyometrics on change-of-direction speed and power in adolescent female basketball players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Singh, S. Effects of vertical and horizontal plyometric exercises on running speed. Hum. Mov. 2013, 14, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, F.J.; Santalla, A.; Carrasquila, I.; Asian, J.A.; Reina, J.I.; Suarez-Arrones, L.J. The effects of unilateral and bilateral eccentric overload training on hypertrophy, muscle power and COD performance, and its determinants, in team sport players. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Performance Measure | High-to-Low (n = 9) | Low-to-High (n = 8) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Post-Training | Baseline | Post-Training | |||
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ES | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ES | |
| 10 m Sprint (s) | 1.893 ± 0.08 | 1.851 ± 0.06 * | −0.44 (−0.75, −0.13) | 1.868 ± 0.06 | 1.870 ± 0.04 | 0.05 (−0.37, 0.47) |
| 20 m Sprint (s) | 3.177 ± 0.14 | 3.155 ± 0.15 | −0.07 (−0.37, 0.23) | 3.141 ± 0.11 | 3.178 ± 0.09 | 0.34 (0.07, 0.61) |
| 505 Time (s) | 2.301 ± 0.07 | 2.293 ± 0.07 | 0.06 (−0.53, 0.65) | 2.295 ± 0.09 | 2.291 ± 0.09 | −0.03 (−0.43, 0.37) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, J.; Appleby, B.B.; Lavender, A.P. Effect of Plyometric Training on Speed and Change of Direction Ability in Elite Field Hockey Players. Sports 2018, 6, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6040144
Singh J, Appleby BB, Lavender AP. Effect of Plyometric Training on Speed and Change of Direction Ability in Elite Field Hockey Players. Sports. 2018; 6(4):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6040144
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Jasdev, Brendyn B. Appleby, and Andrew P. Lavender. 2018. "Effect of Plyometric Training on Speed and Change of Direction Ability in Elite Field Hockey Players" Sports 6, no. 4: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6040144
APA StyleSingh, J., Appleby, B. B., & Lavender, A. P. (2018). Effect of Plyometric Training on Speed and Change of Direction Ability in Elite Field Hockey Players. Sports, 6(4), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6040144






