Countermovement Jump Analysis Using Different Portable Devices: Implications for Field Testing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. Gold-Standard Measurements
2.3.2. Accelerometric System
2.3.3. Switch Mat
2.3.4. Optical Equipment with Light-Emitting Diodes
2.3.5. Smartphone App
2.4. Statistical Analysis
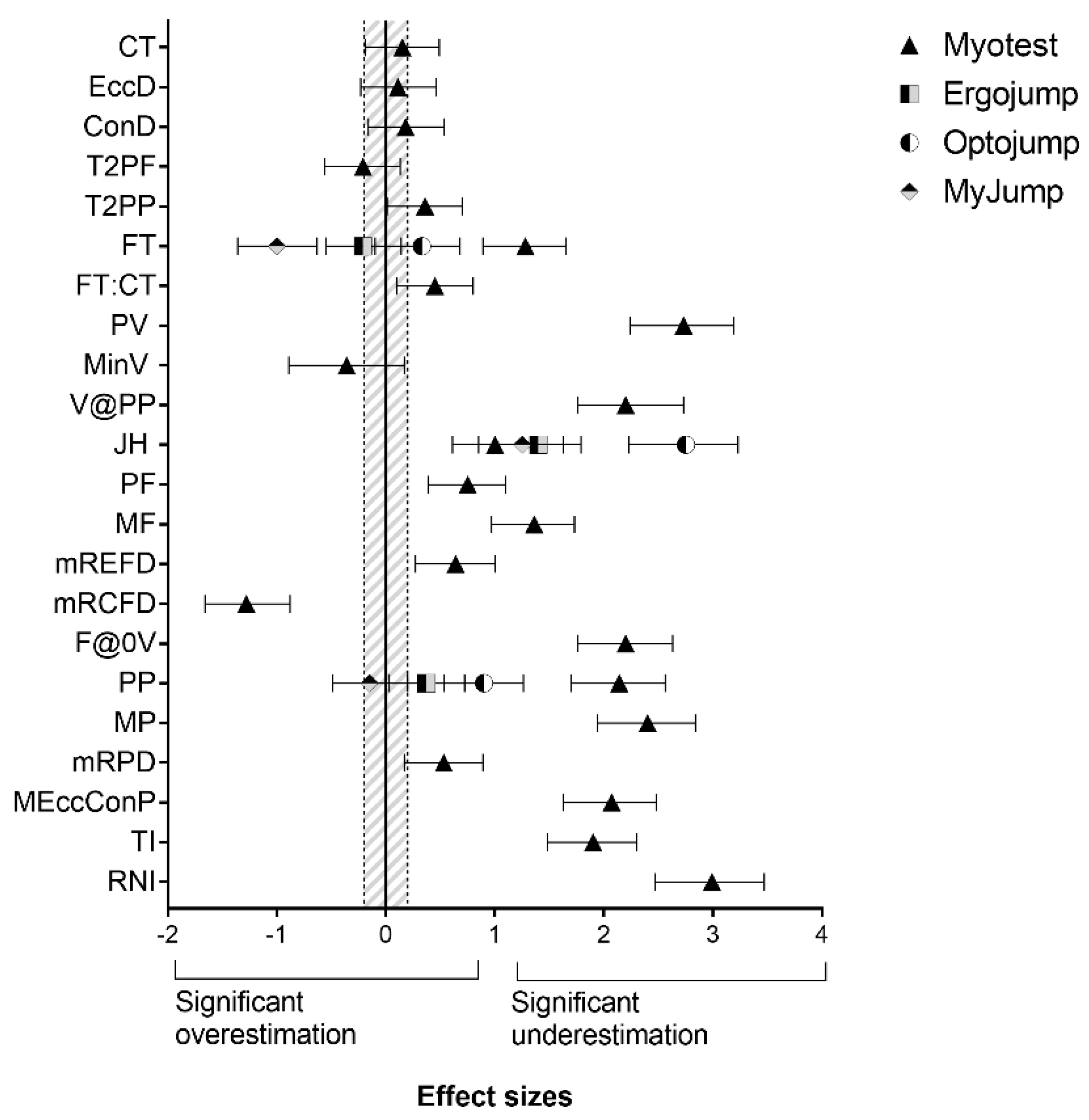
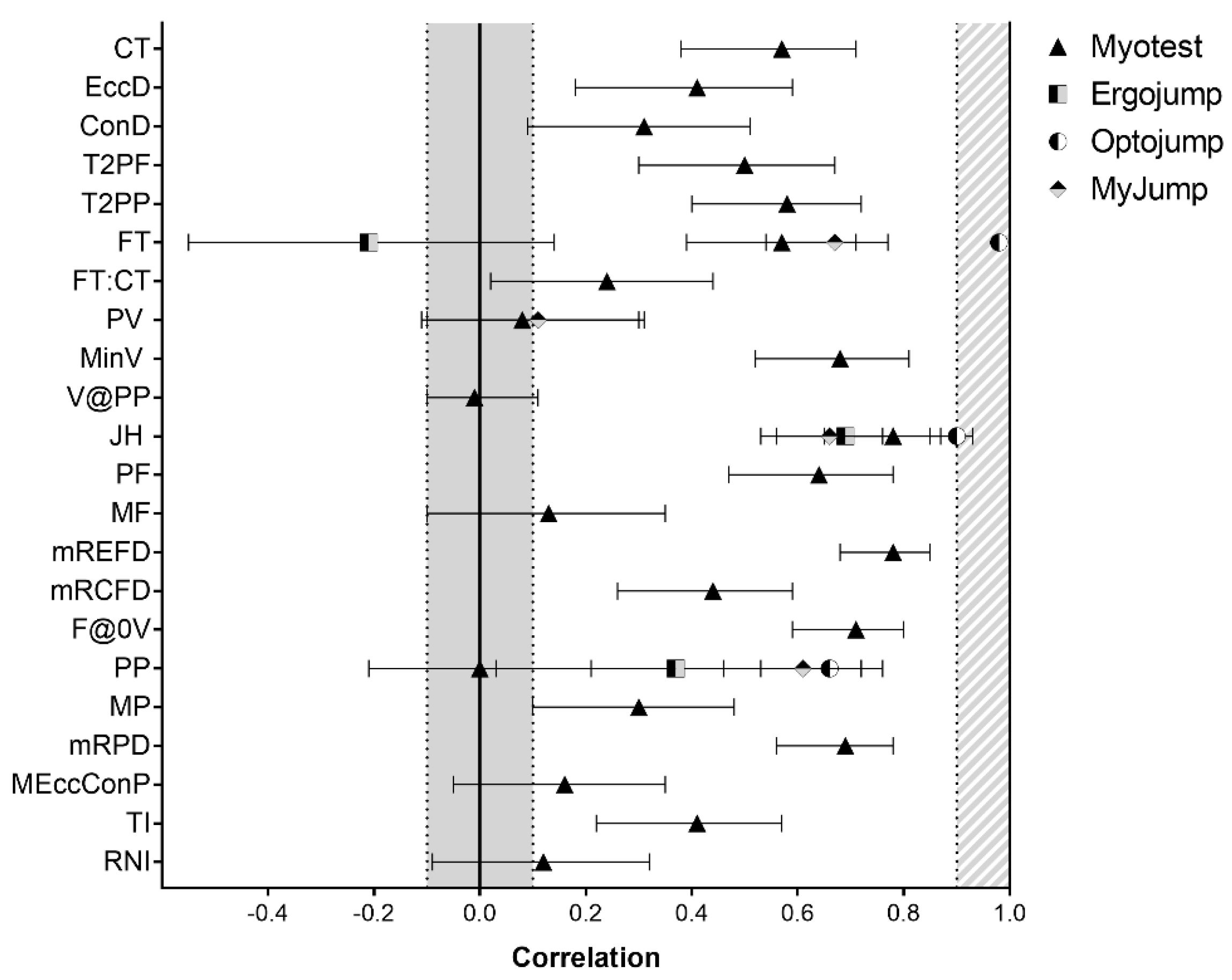
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vanezis, A.; Lees, A. A biomechanical analysis of good and poor performers of the vertical jump. Ergonomics 2005, 48, 1594–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.R.; Magalhaes, J.F.; Ascensao, A.A.; Oliveira, E.M.; Seabra, A.F.; Rebelo, A.N. Individual match playing time during the season affects fitness-related parameters of male professional soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 2729–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, R.T.; Strudwick, A.J.; Buchheit, M.; Atkinson, G.; Drust, B.; Gregson, W. Monitoring Fatigue During the In-Season Competitive Phase in Elite Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2015, 10, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffaye, G.; Wagner, P.P.; Tombleson, T.I. Countermovement jump height: Gender and sport-specific differences in the force-time variables. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Los Arcos, A.; Martinez-Santos, R.; Yanci, J.; Mendiguchia, J.; Mendez-Villanueva, A. Negative Associations between Perceived Training Load, Volume and Changes in Physical Fitness in Professional Soccer Players. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2015, 14, 394–401. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, J.; Krustrup, P.; Rebelo, A. The influence of the playing surface on the exercise intensity of small-sided recreational soccer games. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2012, 31, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebelo, A.N.; Silva, P.; Rago, V.; Barreira, D.; Krustrup, P. Differences in strength and speed demands between 4v4 and 8v8 small-sided football games. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormack, S.J.; Newton, R.U.; McGuigan, M.R.; Cormie, P. Neuromuscular and endocrine responses of elite players during an Australian rules football season. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2008, 3, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gathercole, R.; Sporer, B.; Stellingwerff, T. Countermovement Jump Performance with Increased Training Loads in Elite Female Rugby Athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 36, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linthorne, N.P. Analysis of standing vertical jumps using a force platform. Am. J. Phys. 2001, 69, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón, L.F. Evaluation of Four Vertical Jump Tests: Methodology, Reliability, Validity, and Accuracy. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2000, 4, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gathercole, R.; Sporer, B.; Stellingwerff, T.; Sleivert, G. Alternative countermovement-jump analysis to quantify acute neuromuscular fatigue. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2015, 10, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castagna, C.; Ganzetti, M.; Ditroilo, M.; Giovannelli, M.; Rocchetti, A.; Manzi, V. Concurrent validity of vertical jump performance assessment systems. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casartelli, N.; Muller, R.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Validity and reliability of the Myotest accelerometric system for the assessment of vertical jump height. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 3186–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, C.; Luhtanen, P.; Komi, P.V. A simple method for measurement of mechanical power in jumping. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1983, 50, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatthorn, J.F.; Gouge, S.; Nussbaumer, S.; Stauffacher, S.; Impellizzeri, F.M.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Validity and reliability of Optojump photoelectric cells for estimating vertical jump height. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsalobre-Fernandez, C.; Glaister, M.; Lockey, R.A. The validity and reliability of an iPhone app for measuring vertical jump performance. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 1574–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena, B.; García, I.; Requena, F.; de Villarreal, E.S.S.; Pääsuke, M. Reliability and Validity of a Wireless Microelectromechanicals Based System (Keimove™) for Measuring Vertical Jumping Performance. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2012, 11, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Halvorsen, K.; Eriksson, M.; Gullstrand, L.; Tinmark, F.; Nilsson, J. Minimal marker set for center of mass estimation in running. Gait Posture 2009, 30, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuguchi, S.; Sands, W.A.; Wassinger, C.A.; Lamont, H.S.; Stone, M.H. A new approach to determining net impulse and identification of its characteristics in countermovement jumping: Reliability and validity. Sports Biomech. 2015, 14, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, S.P.; Harackiewicz, D.V.; Harman, E.A.; Frykman, P.N.; Rosenstein, M.T. Cross-validation of three jump power equations. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1999, 31, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portney, L.; Watkins, M. Foundations of Clinical Research: Applications to Practice; Pearson/Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, J.P. Quantifying test-retest reliability using the intraclass correlation coefficient and the SEM. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, W.G. Measures of reliability in sports medicine and science. Sports Med. 2000, 30, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, G.; Davison, R.C.; Nevill, A.M. Performance characteristics of gas analysis systems: What we know and what we need to know. Int. J. Sports Med. 2005, 26 (Suppl. S1), S2–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choukou, M.A.; Laffaye, G.; Taiar, R. Reliability and validity of an accelerometric system for assessing vertical jumping performance. Biol. Sport 2014, 31, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo-Fuentes, F.; Gallardo-Fuentes, J.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Balsalobre-Fernandez, C.; Martinez, C.; Caniuqueo, A.; Canas, R.; Banzer, W.; Loturco, I.; Nakamura, F.Y.; et al. Intersession and Intrasession Reliability and Validity of the My Jump App for Measuring Different Jump Actions in Trained Male and Female Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Abbreviation | Unit of Measure | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kinematic parameters | - | - | - |
| Total contraction time | CT | s | Total duration from jump initiation to take-off |
| Eccentric duration | EccD | s | Time period of the eccentric phase |
| Concentric duration | ConD | s | Time period of the concentric phase |
| Time to peak force | T2PF | s | Time period between jump start and peak force |
| Time to peak power | T2PP | s | Time period between jump start and peak power |
| Flight time | FT | s | Time period of zero force, corresponding to noncontact with the floor |
| Flight time to contraction time ratio | FT:CT | % | Ratio between flight time and contraction time |
| Peak velocity | PV | m∙s−1 | Highest jump velocity during the concentric phase |
| Minimum velocity | MinV | m∙s−1 | Lowest jump velocity during the eccentric phase |
| Velocity at peak power | V@PP | m∙s−1 | Velocity recorded at time point where peak power occurred |
| Jump height | JH | m | Highest height achieved during the jump |
| Kinetic parameters | - | - | - |
| Peak force | PF | N∙kg−1 | Maximum force achieved during the concentric phase |
| Mean force | MF | - | Average force of the concentric phase |
| Maximum rate of eccentric force development | mREFD | N∙s−1∙kg−1 | Maximum force increase within a 30 ms window during the eccentric phase |
| Maximum rate of concentric force development | mRCFD | N∙s−1∙kg−1 | Maximum force increase within a 30 ms window during the concentric phase. |
| Force at zero velocity | F@0V | N∙kg−1 | Force exerted at the end of the countermovement where the jump transitions from eccentric to concentric movement |
| Peak power | PP | W∙kg−1 | Higher power value achieved during the jump |
| Mean power | MP | W∙kg−1 | Average power value obtained during the concentric phase |
| Maximum rate of power development | mRPD | W∙s−1∙kg−1 | Largest power increase within a 30 ms window during the concentric phase |
| Mean eccentric and concentric power over time | MEccConP | W∙kg−1∙s−1 | Power produced during both eccentric (converted to positive values) and concentric phases, divided by contraction duration |
| Total impulse | TI | N∙s−1 | Force exerted concentrically multiplied by the time taken concentrically |
| Relative net impulse | RNI | N∙s∙kg−1 | Impulse between the beginning of the concentric phase and the moment force reached weight level, minus the impulse equivalent to that of the propulsion-deceleration phase |
| Variable | MCAP | Force Platform | Myotest | Ergojump | Optojump | MyJump |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinematic parameters | ||||||
| CT (s) | - | 0.77 ± 0.16 | 0.76 ± 0.09 | - | - | - |
| EccD (s) | - | 0.50 ± 0.15 | 0.50 ± 0.08 | - | - | - |
| ConD (s) | - | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.26 ± 0.04 | - | - | - |
| T2PF (s) | - | 0.55 ± 0.17 | 0.60 ± 0.10 | - | - | - |
| T2PP (s) | - | 0.71 ± 0.16 | 0.67 ± 0.09 | - | - | - |
| FT (s) | - | 0.54 ± 0.03 | 0.49 ± 0.04 | 0.55 ± 0.06 | 0.53 ± 0.03 | 0.57 ± 0.03 |
| FT:CT (%) | - | 0.72 ± 0.16 | 0.66 ± 0.10 | - | - | - |
| PV (m∙s−1) | 3.04 ± 0.23 | - | 2.08 ± 0.39 | - | - | 1.42 ± 0.23 |
| MinV (m∙s−1) | −1.25 ± 0.16 | - | −1.08 ± 0.26 | - | - | - |
| V@PP (m∙s−1) | - | 2.47 ± 0.15 | 1.89 ± 0.34 | - | - | - |
| JH (m) | 0.46 ± 0.04 | - | 0.42 ± 0.04 | 0.38 ± 0.07 | 0.35 ± 0.04 | 0.41 ± 0.04 |
| Kinetic parameters | ||||||
| PF (N∙kg−1) | - | 23.88 ± 1.99 | 22.23 ± 2.37 | - | - | - |
| MF (N∙kg−1) | - | 13.39 ± 1.24 | 11.96 ± 0.82 | - | - | - |
| mREFD (N∙s−1∙kg−1) | - | 136.88 ± 69.88 | 101.27 ± 36.22 | - | - | - |
| mRCFD (N∙s−1∙kg−1) | - | 29.37 ± 19.93 | 57.44 ± 23.82 | - | - | - |
| F@0V (N∙kg−1) | - | 23.16 ± 2.31 | 18.77 ± 3.30 | - | - | - |
| PP (W∙kg−1) | - | 36.01 ± 8.80 | 47.84 ± 10.17 | 46.18 ± 5.38 | 51.47 ± 3.80 | - |
| MP (W∙kg−1) | - | 28.66 ± 2.51 | 18.89 ± 5.17 | - | - | - |
| mRPD (W∙s−1∙kg−1) | - | 345.49 ± 81.79 | 301.08 ± 84.41 | - | - | - |
| MEccConP (W∙kg−1∙s−1) | - | 13.63 ± 2.29 | 9.14 ± 2.04 | - | - | - |
| TI (N∙s−1) | - | 197.00 ± 29.77 | 121.74 ± 47.34 | - | - | - |
| RNI (N∙s−1∙kg−1) | - | 2.61 ± 0.16 | 1.70 ± 0.40 | - | - | - |
| Variable | Reliability Indicators | MCAP | Force Platform | Myotest | Ergojump | Optojump | MyJump |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.84 (0.58; 0.95) | 0.93 (0.83; 0.98) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 120.1 (7.7; 16.5) | 6.8 (4.9; 8.7) | - | - | - | |
| EccD | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.81 (0.51; 0.94) | 0.95 (0.87; 0.98) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 17.5 (10.1; 24.9) | 8.0 (5.7; 10.3) | - | - | - | |
| ConD | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.89 (0.71; 0.96) | 0.72 (0.27; 0.92) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 6.8 (5.2; 8.3) | 12.0 (7.1; 16.9) | - | - | - | |
| T2PF | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.80 (0.48; 0.94) | 0.93 (0.82; 0.98) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 21.1 (14.4; 27.7) | 7.9 (5.8; 10.1) | - | - | - | |
| T2PP | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.82 (0.52; 0.95) | 0.93 (0.83; 0.98) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 13.3 (8.6; 18.1) | 7.0 (5.1; 8.9) | - | - | - | |
| FT | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.97 (0.92; 0.99) | 0.96 (0.91; 0.99) | 0.54 (−0.34; 0.89) | 0.96 (0.91; 0.99) | 0.80 (0.37; 0.96) |
| CV (%) | - | 1.8 (1.3; 2.2) | 3.8 (0.4; 7.2) | 8.2 (0.8; 15.7) | 1.8 (1.4; 2.3) | 3.0 (2.1; 3.8) | |
| FT:CT | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.73 (0.30; 0.92) | 0.92 (0.78; 0.98) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 13.2 (8.0; 18.3) | 8.4 (3.4; 13.4) | - | - | - | |
| PV | ICC (95% CI) | 0.91 (0.78; 0.97) | - | 0.78 (0.44; 0.94) | - | - | 0.74 (0.17; 0.95) |
| CV (%) | 5.2 (3.2; 7.1) | - | 11.6 (7.6; 15.3) | - | - | 3.3 (2.2; 4.4) | |
| MinV | ICC (95% CI) | 0.79 (−39; 0.95) | - | 0.50 (−0.30; 0.86) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | −6.8 (−8.0; −5.6) | - | −18.0 (−24.6; −12.3) | - | - | - | |
| V@PP | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.97 (0.92; 0.99) | 0.79 (0.46; 0.94) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 2.1 (1.54; 2.6) | 11.1 (7.7; 14.5) | - | - | - | |
| JH | ICC (95% CI) | 0.96 (0.90; 0.99) | - | 0.97 (0.92; 0.99) | 0.93 (0.81; 0.98) | 0.87 (0.62; 0.97) | 0.97 (0.91; 0.99) |
| CV (%) | 3.3 (2.2; 4.4) | - | 4.2 (3.2; 5.3) | 3.2 (2.3; 4.1) | 4.2 (3.3; 5.1) | 3.9 (3.0; 4.9) | |
| PF | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.83 (0.57; 0.95) | 0.91 (0.77; 0.97) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 3.4 (2.4; 4.5) | 6.4 (4.4; 8.3) | - | - | - | |
| MF | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.89 (−0.73; 0.96) | 0.89 (0.70; 0.96) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 5.2 (1.9; 8.5) | 4.2 (2.5; 5.9) | - | - | - | |
| mREFD | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.89 (0.71; 0.97) | 0.76 (0.37; 0.93) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 17.1 (10.8; 23.4) | 21.1 (15.3; 26.8) | - | - | - | |
| mRCFD | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.84 (0.62; 0.95) | 0.28 (−0.29; 0.86) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 46.4 (30.4; 62.4) | 30.9 (20.9; 40.9) | - | - | - | |
| F@0V | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| F@0V | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.90 (0.74; 0.97) | 0.91 (0.77; 0.97) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 4.3 (2.7; 5.9) | 8.9 (5.6; 12.2) | - | - | - | |
| PP | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.95 (0.87; 0.98) | 0.81 (0.52; 0.94) | 0.91 (0.79; 0.97) | 0.86 (0.63; 0.96) | 0.84 (0.48; 0.96) |
| CV (%) | - | 3.4 (2.1; 4.7) | 15.8 (11.3; 20.4) | 3.3 (2.3; 4.3) | 4.5 (1.0; 8.1) | 4.0 (3.0; 5.0) | |
| MP | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.91 (0.77; 0.97) | 0.84 (0.59; 0.95) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 3.8 (2.7; 5.0) | 14.8 (10.2; 19.3) | - | - | - | |
| mRPD | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| mRPD | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.75 (0.34; 0.93) | 0.84 (0.58; 0.95) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 10.1 (8.0; 12.3) | 16.0 (10.6; 21.3) | - | - | - | |
| MEccCONP | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.87 (0.65; 0.96) | 0.93 (0.81; 0.98) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 9.0 (5.9; 12.1) | 9.5 (5.8; 13.2) | - | - | - | |
| TI | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.79 (0.44; 0.94) | 0.95 (0.87; 0.98) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 5.6 (1.3; 9.9) | 24.4 (10.8; 37.9) | - | - | - | |
| RNI | ICC (95% CI) | - | 0.97 (0.92; 0.99) | 0.86 (0.63; 0.96) | - | - | - |
| CV (%) | - | 1.7 (1.1; 2.2) | 15.9 (10.1; 21.8) | - | - | - |
| Variable | MCAP | Force Platform | Myotest | Ergojump | Optojump | MyJump | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEM | SWC | MDC | SEM | SWC | MDC | SEM | SWC | MDC | SEM | SWC | MDC | SEM | SWC | MDC | SEM | SWC | MDC | |
| Kinematic parameters | ||||||||||||||||||
| CT (s) | - | - | - | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.012 | 0.018 | 0.033 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| EccD (s) | - | - | - | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.010 | 0.016 | 0.029 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ConD (s) | - | - | - | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.015 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| T2PF (s) | - | - | - | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.013 | 0.021 | 0.038 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| T2PP (s) | - | - | - | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.011 | 0.018 | 0.033 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| FT (s) | - | - | - | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.015 | 0.008 | 0.013 | 0.024 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.010 |
| FT:CT (%) | - | - | - | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.013 | 0.021 | 0.038 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| PV (m∙s−1) | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.11 | - | - | - | 0.050 | 0.078 | 0.14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MinV (m∙s−1) | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 | - | - | - | 0.032 | 0.050 | 0.090 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| V@PP (m∙s−1) | - | - | - | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.056 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.009 | 0.015 | 0.027 | |
| JH (m) | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.015 | - | - | - | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.014 | 0.010 | 0.015 | 0.028 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.016 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.015 |
| Kinetic parameters | ||||||||||||||||||
| PF (N∙kg−1) | - | - | - | 0.26 | 0.40 | 0.73 | 0.30 | 0.47 | 0.84 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MF (N∙kg−1) | - | - | - | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.47 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.47 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| mREFD (N∙s−1∙kg−1) | - | - | - | 9.42 | 1.88 | 26.11 | 4.88 | 0.97 | 13.53 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| mRCFD (N∙s−1∙kg−1) | - | - | - | 2.74 | 0.54 | 7.59 | 3.46 | 0.69 | 9.61 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| F@0V (N∙kg−1) | - | - | - | 0.30 | 0.47 | 0.84 | 0.42 | 0.65 | 1.17 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PP (W∙kg−1) | - | - | - | 0.63 | 0.98 | 1.76 | 1.13 | 1.76 | 3.15 | 1.31 | 2.03 | 3.63 | 0.69 | 1.07 | 1.92 | 0.49 | 0.76 | 1.36 |
| MP (W∙kg−1) | - | - | - | 0.32 | 0.51 | 0.91 | 0.67 | 1.03 | 1.86 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| mRPD (W∙s−1) | - | - | - | 11.38 | 2.27 | 31.54 | 0.30 | 0.06 | 0.84 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MEccConP (W∙kg−1∙s−1) | - | - | - | 0.29 | 0.45 | 0.80 | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.71 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| TI (N∙s−1) | - | - | - | 4.06 | 6.29 | 11.26 | 6.24 | 9.67 | 17.30 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| RNI (N∙s−1∙kg−1) | - | - | - | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rago, V.; Brito, J.; Figueiredo, P.; Carvalho, T.; Fernandes, T.; Fonseca, P.; Rebelo, A. Countermovement Jump Analysis Using Different Portable Devices: Implications for Field Testing. Sports 2018, 6, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6030091
Rago V, Brito J, Figueiredo P, Carvalho T, Fernandes T, Fonseca P, Rebelo A. Countermovement Jump Analysis Using Different Portable Devices: Implications for Field Testing. Sports. 2018; 6(3):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6030091
Chicago/Turabian StyleRago, Vincenzo, João Brito, Pedro Figueiredo, Thiago Carvalho, Tiago Fernandes, Pedro Fonseca, and António Rebelo. 2018. "Countermovement Jump Analysis Using Different Portable Devices: Implications for Field Testing" Sports 6, no. 3: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6030091
APA StyleRago, V., Brito, J., Figueiredo, P., Carvalho, T., Fernandes, T., Fonseca, P., & Rebelo, A. (2018). Countermovement Jump Analysis Using Different Portable Devices: Implications for Field Testing. Sports, 6(3), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports6030091






