Link between Motor Competence and Health Related Fitness in Children and Adolescents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.3. Data Analysis
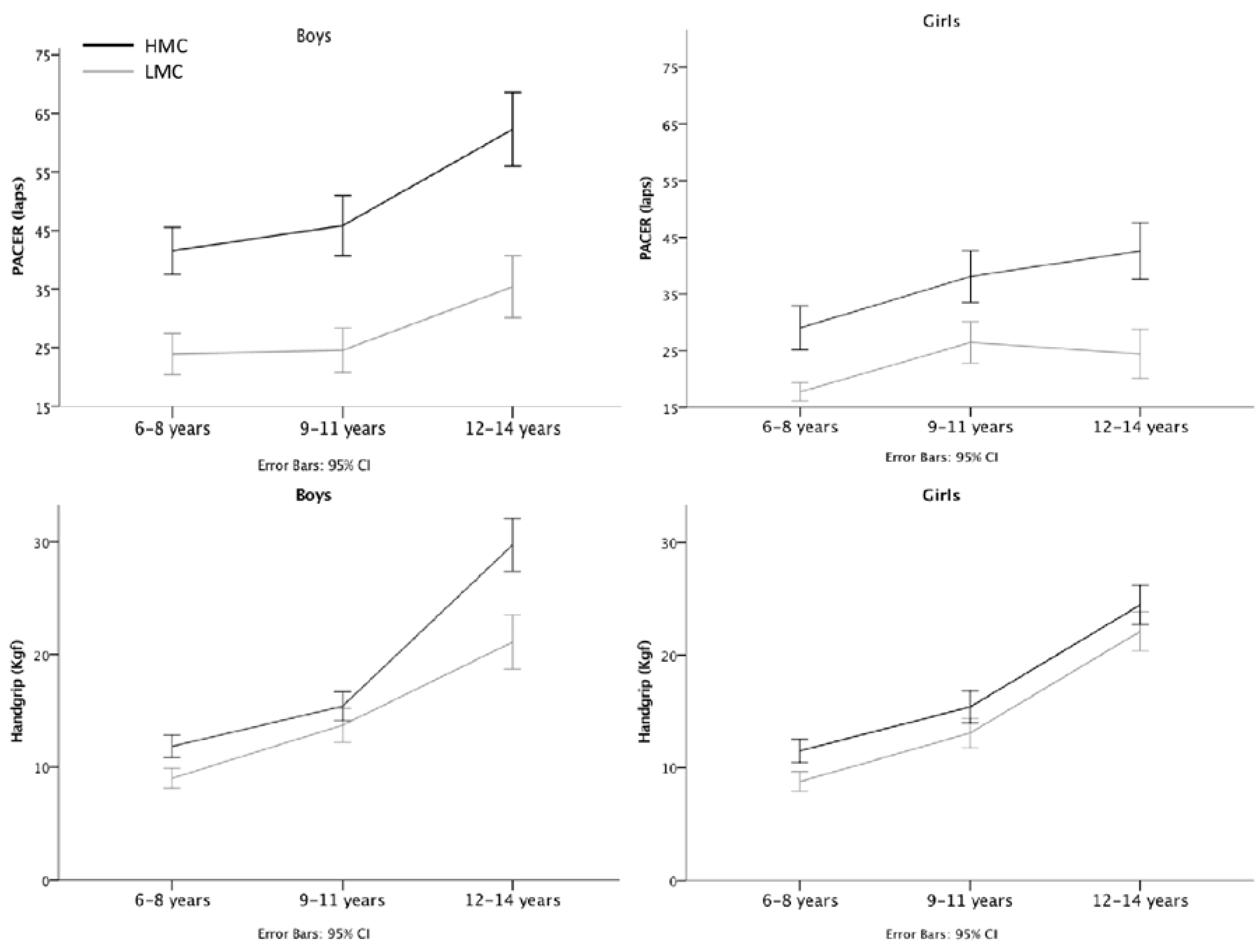
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Low, S.; Chin, M.C.; Deurenberg-Yap, M. Review on epidemic of obesity. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2009, 38, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strong, W.B.; Malina, R.M.; Blimkie, C.J.R.; Daniels, S.R.; Dishman, R.K.; Gutin, B.; Hergenroeder, A.C.; Must, A.; Nixon, P.A.; Pivarnik, J.M.; et al. Evidence Based Physical Activity for School-age Youth. J. Pediatr. 2005, 146, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, L.; Santos, R.; Pereira, B.; Lopes, V.P. Associations between sedentary behavior and motor coordination in children. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2012, 24, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stodden, D.F.; Goodway, J.D.; Langendorfer, S.J.; Roberton, M.A.; Rudisill, M.E.; Garcia, C.; Garcia, L.E. A Developmental Perspective on the Role of Motor Skill Competence in Physical Activity: An Emergent Relationship. Quest 2008, 60, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattuzzo, M.T.; Dos Santos Henrique, R.; Ré, A.H.N.; de Oliveira, I.S.; Melo, B.M.; de Sousa Moura, M.; de Araújo, R.C.; Stodden, D. Motor competence and health related physical fitness in youth: A systematic review. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, L.E.; Stodden, D.F.; Barnett, L.M.; Lopes, V.P.; Logan, S.W.; Rodrigues, L.P.; D’Hondt, E. Motor Competence and its Effect on Positive Developmental Trajectories of Health. Sport Med. 2015, 45, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransen, J.; D’Hondt, E.; Bourgois, J.; Vaeyens, R.; Philippaerts, R.M.; Lenoir, M. Motor competence assessment in children: Convergent and discriminant validity between the BOT-2 Short Form and KTK testing batteries. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallahue, D.; Ozmun, J.; Goodway, J. Understanding Motor Development: Infants, Children, Adolescents, Adults, 7th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Luz, C.; Rodrigues, L.P.; Almeida, G.; Cordovil, R. Development and validation of a model of motor competence in children and adolescents. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catley, M.J.; Tomkinson, G.R. Normative health-related fitness values for children: Analysis of 85347 test results on 9–17-year-old Australians since 1985. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, L.L.; Barnett, L.; Espinel, P.; Okely, A.D. Thirteen-year trends in child and adolescent fundamental movement skills: 1997–2010. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomkinson, G.R.; Olds, T.S. Secular changes in aerobic fitness test performance of Australasian children and adolescents. Med. Sport Sci. 2007, 50, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vandorpe, B.; Vandendriessche, J.; Lefevre, J.; Pion, J.; Vaeyens, R.; Matthys, S.; Philippaerts, R.; Lenoir, M. The KörperkoordinationsTest für Kinder: Reference values and suitability for 6–12-year-old children in Flanders. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2011, 21, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cermak, S.A.; Larkin, D. Developmental Coordination Disorder; Delmar Thomson Learning: Albany, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gillberg, C.; Kadesjö, B. Why bother about clumsiness? The implications of having developmental coordination disorder (DCD). Neural Plast. 2003, 10, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnhart, R.C.; Davenport, M.J.; Epps, S.B.; Nordquist, V.M. Developmental Coordination Disorder. Phys. Ther. 2003, 83, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Cairney, J.; Hay, J.A.; Faught, B.E.; Wade, T.J.; Corna, L.; Flouris, A. Developmental coordination disorder, generalized self-efficacy toward physical activity, and participation in organized and free play activities. J. Pediatr. 2005, 147, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouffard, M.; Watkinson, E.J.; Thompson, L.P.; Causgrove Dunn, J.L.; Romanow, S.K.E. A test of the activity deficit hypothesis with children with movement difficulties. Adapt. Phys. Act. Q. 1996, 13, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Castillo, M.J. Physical activity , physical fitness , and overweight in children and adolescents: Evidence from epidemiologic studies. Med. Intensiva (Eng. Ed.) 2013, 60, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, V.P.; Stodden, D.F.; Bianchi, M.M.; Maia, J.A.; Rodrigues, L.P. Correlation between BMI and motor coordination in children. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2012, 15, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.J.; Eather, N.; Morgan, P.J.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; Lubans, D.R. The Health Benefits of Muscular Fitness for Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sport Med. 2014, 44, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Castillo, M.J.; Sjöström, M. Physical fitness in childhood and adolescence: A powerful marker of health. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairney, J.; Hay, J.A.; Faught, B.E.; Flouris, A.; Klentrou, P. Developmental coordination disorder and cardiorespiratory fitness in children. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2007, 19, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hands, B.; Larkin, D. Physical fitness differences in children with and without motor learning difficulties. Eur. J. Spec. Needs Educ. 2006, 21, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hands, B.; Larkin, D.; Parker, H.; Straker, L.; Perry, M. The relationship among physical activity, motor competence and health-related fitness in 14-year-old adolescents. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2009, 19, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransen, J.; Deprez, D.; Pion, J.; Tallir, I.B.; D’Hondt, E.; Vaeyens, R.; Lenoir, M.; Philippaerts, R.M. Changes in physical fitness and sports participation among children with different levels of motor competence: A 2-year longitudinal study. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2014, 26, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hands, B. Changes in motor skill and fitness measures among children with high and low motor competence: A five-year longitudinal study. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2008, 11, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairney, J.; Hay, J.; Veldhuizen, S.; Faught, B.E. Trajectories of cardiorespiratory fitness in children with and without developmental coordination disorder: A longitudinal analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haga, M. Physical fitness in children with high motor competence is different from that in children with low motor competence. Phys. Ther. 2009, 89, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stodden, D.F.; Gao, Z.; Goodway, J.D.; Langendorfer, S.J. Dynamic Relationships between Motor Skill Competence and Health-Related Fitness in Youth. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2014, 26, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.P.; Stodden, D.F.; Lopes, V.P. Developmental pathways of change in fitness and motor competence are related to overweight and obesity status at the end of primary school. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2015, 19, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welk, G.J.; Meredith, M.D. FITNESSGRAM/ACTIVITYGRAM Reference Guide; Welk, G.J., Meredith, M.D., Eds.; The Cooper Institute: Dalas, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, M.J.; Bryant, E.; Stodden, D.; Duncan, M.J.; Bryant, E.; Stodden, D.; Duncan, M.J. Low fundamental movement skill proficiency is associated with high BMI and body fatness in girls but not boys aged 6–11 years old fatness in girls but not boys aged 6–11 years old. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.G.; Pfeiffer, K.A.; O’Neill, J.R.; Dowda, M.; McIver, K.L.; Brown, W.H.; Pate, R.R. Motor skill performance and physical activity in preschool children. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008, 16, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourtessis, T.; Tsougou, E.; Maheridou, M.; Tsigilis, N.; Psalti, M.; Kioumourtzoglou, E. Developmental coordination disorder in early childhood—A preliminary epidemiological study in greek schools. Int. J. Med. 2008, 1, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988; p. 567. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, L.M.; van Beurden, E.; Morgan, P.J.; Brooks, L.O.; Beard, J.R. Childhood Motor Skill Proficiency as a Predictor of Adolescent Physical Activity. J. Adolesc. Heal. 2009, 44, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milliken, L.A.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; Loud, R.L.; Westcott, W.L. Correlates of upper and lower body muscular strength in children. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | 6–8 Years | 9–11 Years | 12–14 Years | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B n = 94 | G n = 90 | B n = 97 | G n = 94 | B n = 97 | G n = 92 | |
| M ± SD | M ± SD | M ± SD | M ± SD | M ± SD | M ± SD | |
| Stability (pts) | 43.5 ± 7.0 | 41.3 ± 7.1 | 49.2 ± 7.6 | 50.8 ± 8.0 | 59.1 ± 8.2 | 55.5 ± 9.1 |
| Locomotor (pts) | 46.3 ± 6.6 | 40.5 ± 7.9 | 50.7 ± 8.0 | 48.6 ± 7.0 | 61.1 ± 8.8 | 52.0 ± 8.3 |
| Manipulative (pts) | 46.0 ± 4.9 | 38.3 ± 4.8 | 53.7 ± 6.0 | 46.2 ± 4.9 | 64.3 ± 8.6 | 50.4 ± 5.6 |
| MC total (pts) | 44.6 ± 5.8 | 38.8 ± 6.2 | 51.4 ± 6.5 | 48.4 ± 6.0 | 62.9 ± 8.2 | 53.0 ± 7.0 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 17.0 ± 1.9 | 17.4 ± 2.5 | 19.4 ± 3.7 | 18.7 ± 3.4 | 20.3 ± 3.7 | 21.9 ± 4.7 |
| PACER (laps) | 31.8 ± 12.6 | 23.1 ± 9.0 | 35.7 ± 16.0 | 30.9 ± 11.9 | 49.1 ± 19.0 | 32.8 ± 14.6 |
| High MC | 41.5 ± 10.9 | 29.0 ± 10.3 | 45.8 ± 14.3 | 38.1 ± 12.4 | 62.3 ± 17.4 | 42.6 ± 13.6 |
| Low MC | 23.9 ± 9.5 | 17.7 ± 4.4 | 24.6 ± 10.5 | 26.45 ± 9.9 | 35.4 ± 14.7 | 24.4 ± 11.6 |
| Handgrip (Kgf) | 10.4 ± 2.7 | 10.0 ± 2.7 | 14.9 ± 4.1 | 14.6 ± 4.1 | 25.3 ± 7.4 | 22.9 ± 4.7 |
| High MC | 11.8 ± 2.7 | 11.5 ± 2.8 | 15.4 ± 3.6 | 15.4 ± 3.9 | 29.7 ± 6.5 | 24.5 ± 4.8 |
| Low MC | 9.0 ± 2.5 | 8.7 ± 2.4 | 13.7 ± 4.2 | 13.1 ± 3.6 | 21.1 ± 6.6 | 22.1 ± 4.7 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luz, C.; Cordovil, R.; Almeida, G.; Rodrigues, L.P. Link between Motor Competence and Health Related Fitness in Children and Adolescents. Sports 2017, 5, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports5020041
Luz C, Cordovil R, Almeida G, Rodrigues LP. Link between Motor Competence and Health Related Fitness in Children and Adolescents. Sports. 2017; 5(2):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports5020041
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuz, Carlos, Rita Cordovil, Gabriela Almeida, and Luis P. Rodrigues. 2017. "Link between Motor Competence and Health Related Fitness in Children and Adolescents" Sports 5, no. 2: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports5020041
APA StyleLuz, C., Cordovil, R., Almeida, G., & Rodrigues, L. P. (2017). Link between Motor Competence and Health Related Fitness in Children and Adolescents. Sports, 5(2), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports5020041






