Correlation of Body Parameters and Age with Foot Arch Index and Stabilometric Variables in Physically Active Young Males and Females
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Equipment
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
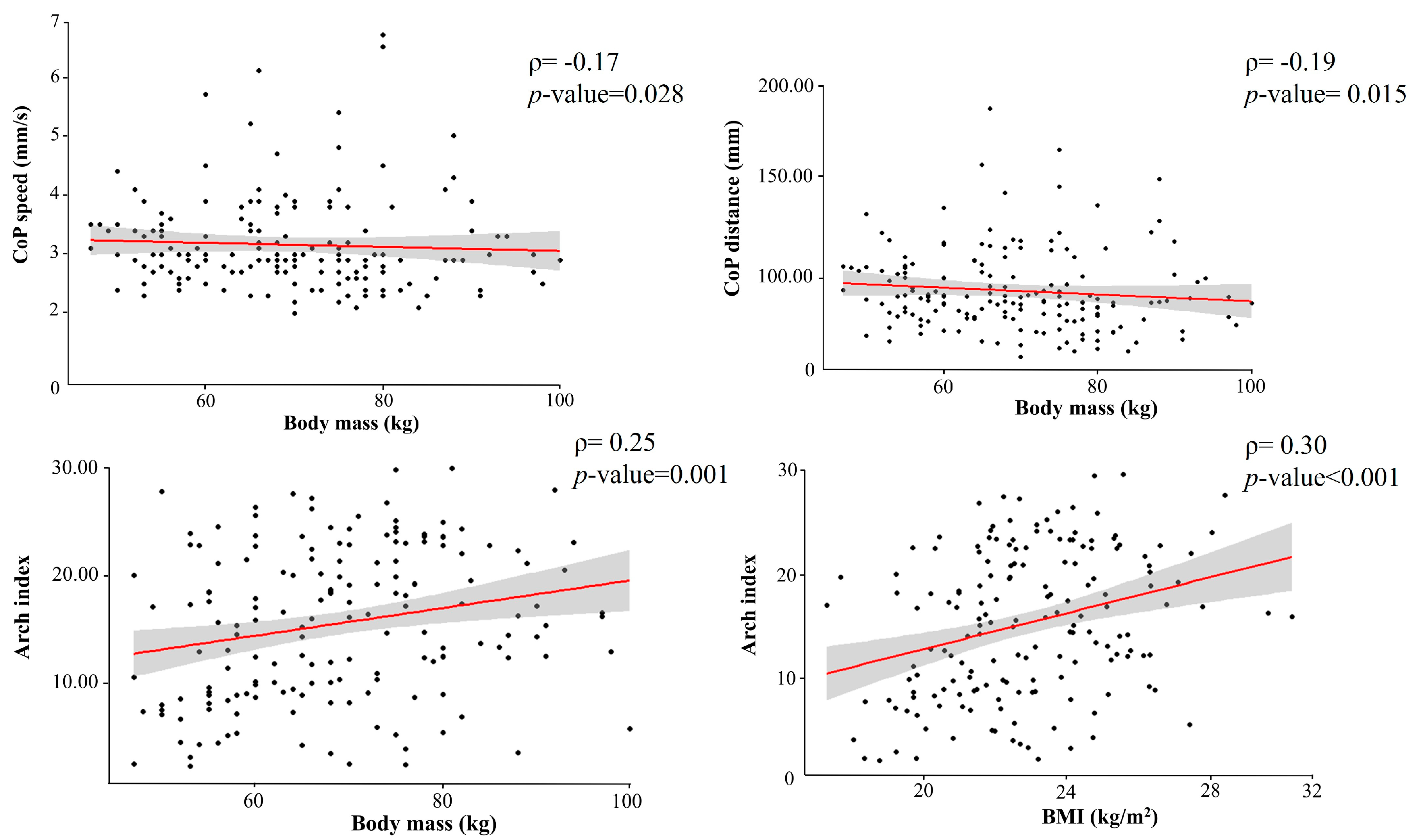
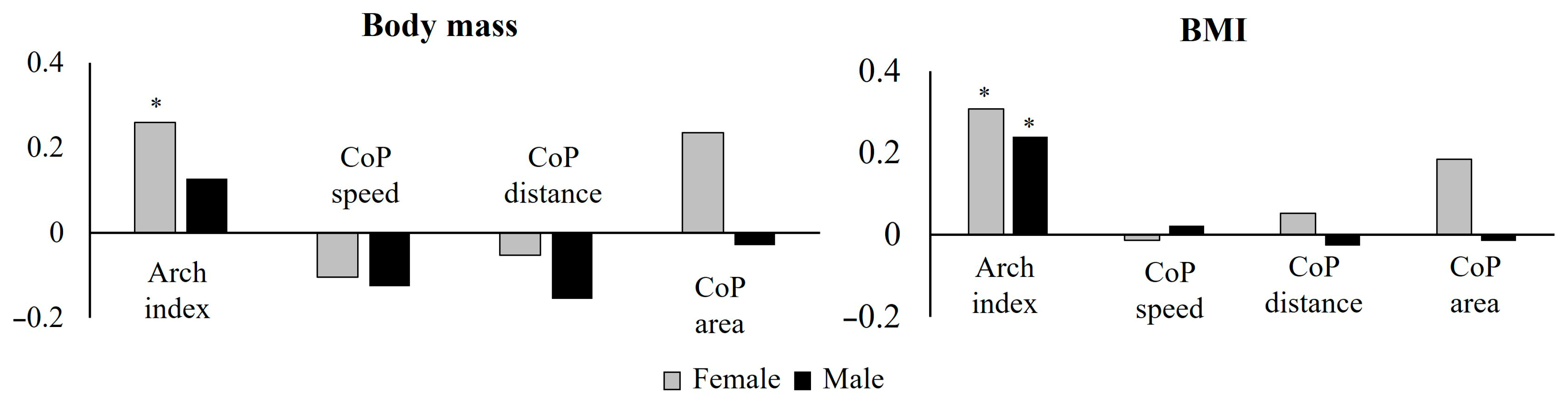
3.1. Body Mass and BMI Correlation with Arch Index and Stabilometric and Baropodometric Variables (CoP Distance, CoP Speed, Arch Index)
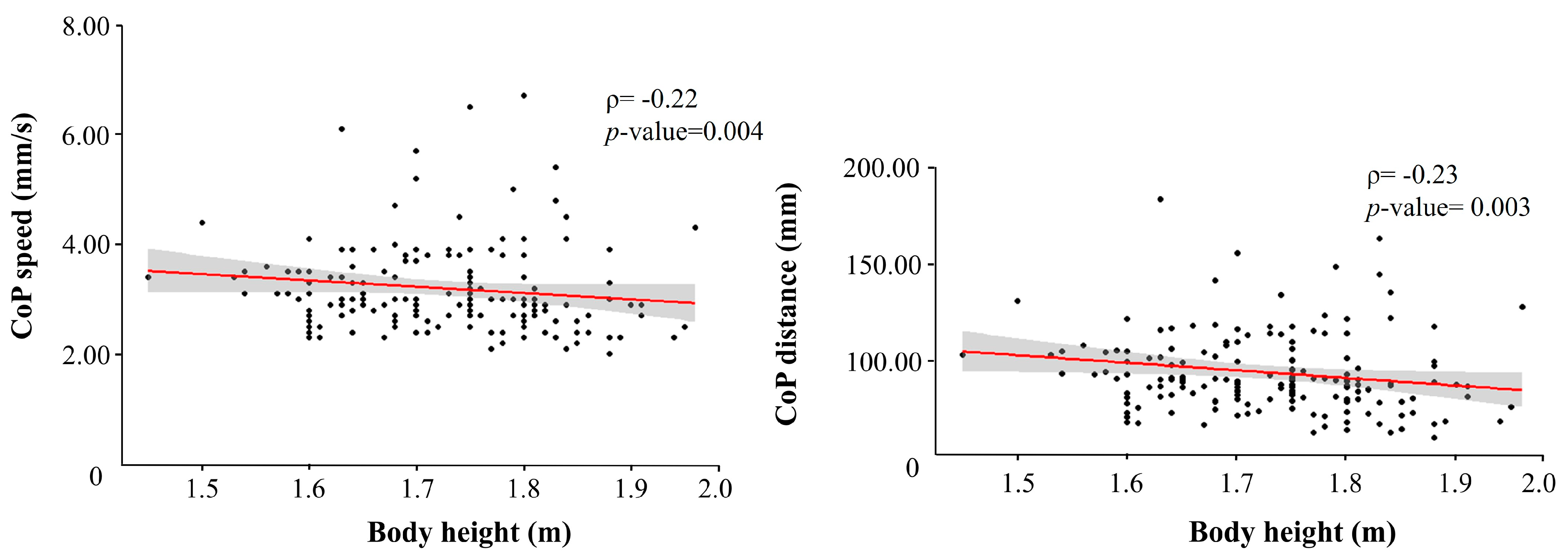
3.2. Height Correlation with Stabilometric Variables (CoP Distance and CoP Speed)
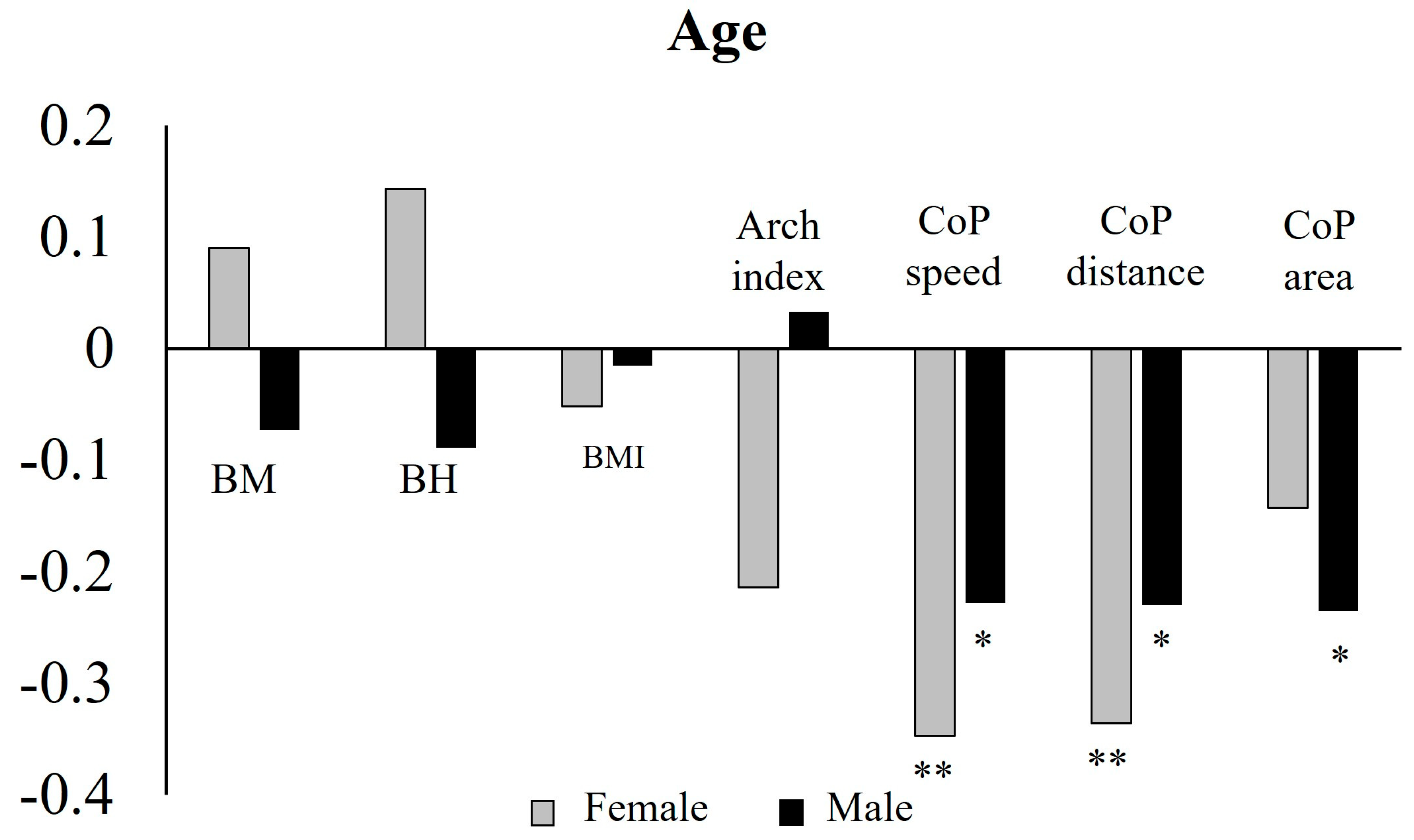
3.3. Age Effect Correlation with Stabilometric Variables (CoP Distance, CoP Speed, and CoP Area)
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CoP | Center of Pressure |
References
- Pojednic, R.; Bantham, A.; Arnstein, F.; Kennedy, M.A.; Phillips, E. Bridging the gap between clinicians and fitness professionals: A challenge to implementing exercise as medicine. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2018, 4, e000369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsapenko, V.; Tereshchenko, M. Criteria of Supporting Characteristics of the Human Foot. Bull. Kyiv Polytech. Inst. Ser. Instrum. Mak. 2022, 63, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.; Naaz, S. The transverse arch in the human feet: A narrative review of its evolution, anatomy, biomechanics and clinical implications. Morphologie 2022, 106, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Howard, D.; Ren, L.-q.; Nester, C.; Tian, L.-m. A Phase-Dependent Hypothesis for Locomotor Functions of Human Foot Complex. J. Bionic Eng. 2008, 5, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Ren, L.; Ren, L. A Coupling Analysis of the Biomechanical Functions of Human Foot Complex during Locomotion. J. Bionic Eng. 2010, 7, S150–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, P.R.; Rodgers, M.M. The arch index: A useful measure from footprints. J. Biomech. 1987, 20, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallashetty, N.; Itagi, V.; Vikas, N.M. Effect of body weight on arches of foot-A correlative study between BMI and arch index. Int. J. Anat. Res. 2019, 7, 6877–6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohatgi, R.; Gupta, N.; Khatri, K. A Comparative Study of Variation of Foot Arch Index with Body Mass Index among Young Adults. Innov. J. Med. Health Sci. 2016, 6, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Rosende-Bautista, C.; Munuera-Martínez, P.V.; Seoane-Pillado, T.; Reina-Bueno, M.; Alonso-Tajes, F.; Pérez-García, S.; Domínguez-Maldonado, G. Relationship of Body Mass Index and Footprint Morphology to the Actual Height of the Medial Longitudinal Arch of the Foot. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suciati, T.; Adnindya, M.; Septadina, I.S.; Pratiwi, P. Correlation between flat feet and body mass index in primary school students. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1246, 012063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, P.A.; Urquhart, D.M.; Landorf, K.B.; Wluka, A.E.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Menz, H.B. Foot posture, range of motion and plantar pressure characteristics in obese and non-obese individuals. Gait Posture 2015, 41, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, B.S.; Griffiths, I.B.; Dowling, G.J.; Murley, G.S.; Munteanu, S.E.; Franettovich Smith, M.M.; Collins, N.J.; Barton, C.J. Foot posture as a risk factor for lower limb overuse injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2014, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagedorn, T.J.; Dufour, A.B.; Riskowski, J.L.; Hillstrom, H.J.; Menz, H.B.; Casey, V.A.; Hannan, M.T. Foot disorders, foot posture, and foot function: The Framingham foot study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, H.B.; Dufour, A.B.; Riskowski, J.L.; Hillstrom, H.J.; Hannan, M.T. Foot posture, foot function and low back pain: The Framingham Foot Study. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 2275–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A.P.C.; Vieira, L.A.; Cruz, J.L.; Rinaldi, N.M. Joint torque parameters of lower limbs and the relationship with postural balance in young adults: A cross-sectional study. Braz. J. Mot. Behav. 2023, 17, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiari, L.; Rocchi, L.; Cappello, A. Stabilometric parameters are affected by anthropometry and foot placement. Clin. Biomech. 2002, 17, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; Mochizuki, L.; Mns, L.; Canonica, A.; Souza, R.; Maifrino, L.; Figueira Junior, A.; Bocalini, D.; Greve, J. Men and women do not have the same relation between body composition and postural sway. J. Morphol. Sci. 2015, 32, 093–097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kwon, Y.; Chung, H.-Y.; Kim, C.-S.; Eom, G.-M.; Jun, J.-H.; Park, B.K. Relationship between body factors and postural sway during natural standing. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2012, 13, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šarabon, N.; Kozinc, Ž.; Marković, G. Effects of age, sex and task on postural sway during quiet stance. Gait Posture 2022, 92, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzo, F.; Nardi, A.; Lamouchideli, N.; Caronti, A.; Alashram, A.; Padua, E.; Annino, G. The effect of age, sex and a firm-textured surface on postural control. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 2181–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, A.; Melnikov, A.; Skvortsov, D.; Akhmerova, K.; Vavaev, A.; Golov, A.; Draugelite, V.; Nikolaev, R.; Chechelnickaia, S.; Zhuk, D.; et al. Postural Stability in Athletes: The Role of Age, Sex, Performance Level, and Athlete Shoe Features. Sports 2020, 8, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leversen, J.S.; Haga, M.; Sigmundsson, H. From children to adults: Motor performance across the life-span. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giorgio, A. The roles of motor activity and environmental enrichment in intellectual disability. Somatosens Mot Res. 2017, 34, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.H. Functional brain development in humans. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Baudry, S. Age-related changes in leg proprioception: Implications for postural control. J. Neurophysiol. 2019, 122, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Humbeeck, N.; Kliegl, R.; Krampe, R.T. Lifespan changes in postural control. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagströmer, M.; Oja, P.; Sjöström, M. The International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ): A study of concurrent and construct validity. Public Health Nutr. 2006, 9, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.H.; Macfarlane, D.J.; Lam, T.H.; Stewart, S.M. Validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form (IPAQ-SF): A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. W.H.O. Global Status Report on Physical Activity 2022. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/363607/9789240059153-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Fullin, A.; Caravaggi, P.; Picerno, P.; Mosca, M.; Caravelli, S.; De Luca, A.; Lucariello, A.; De Blasiis, P. Variability of Postural Stability and Plantar Pressure Parameters in Healthy Subjects Evaluated by a Novel Pressure Plate. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giboin, L.-S.; Gruber, M.; Kramer, A. Motor learning of a dynamic balance task: Influence of lower limb power and prior balance practice. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlroy, W.E.; Maki, B.E. Preferred placement of the feet during quiet stance: Development of a standardized foot placement for balance testing. Clin. Biomech. 1997, 12, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandria, M. Comparison between two different thicknesses in thin mechanical stimulations on the plantar arch: Effects on the gait analysis and balance control. Sport Sci. Health 2024, 20, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandria, M.; Gollin, M. Proprioceptive effects on gait and postural stability through mechanical stimulation with an Internal and External Heel Wedge: An interventional single-arm study. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2020, 24, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalíková, M.; Lucia, B.; Barcalová, M.; Ižaríková, G.; Zivcak, J. Corellation the body weight to selected stabilometric parameters. Lékař A Tech. Clin. Technol. 2022, 52, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, K.D.; Rogers, J.; Winzenberg, T.; van Middelkoop, M. Higher body mass index is associated with plantar fasciopathy/‘plantar fasciitis’: Systematic review and meta-analysis of various clinical and imaging risk factors. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macchi, M.; Spezia, M.; Elli, S.; Schiaffini, G.; Chisari, E. Obesity Increases the Risk of Tendinopathy, Tendon Tear and Rupture, and Postoperative Complications: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour, A.B.; Losina, E.; Menz, H.B.; LaValley, M.P.; Hannan, M.T. Obesity, foot pain and foot disorders in older men and women. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 11, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cen, X.; Xu, D.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Effect of additional body weight on arch index and dynamic plantar pressure distribution during walking and gait termination. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of Dynamic Posture Control when Wearing High-Heeled Shoes Using Star Excursion Balance Test. Phys. Act. Health 2017, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, K.M.; Gaw, R.; MacLean, M.R. Obesity, estrogens and adipose tissue dysfunction—Implications for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2020, 10, 2045894020952019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Au, C.C.; Benito-Martin, A.; Ladumor, H.; Oshchepkova, S.; Moges, R.; Brown, K.A. Estrogens and breast cancer: Mechanisms involved in obesity-related development, growth and progression. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 189, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidi-Ogbolu, N.; Baar, K. Effect of Estrogen on Musculoskeletal Performance and Injury Risk. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orvanová, E. Somatotypes of weight lifters. J. Sports Sci. 1990, 8, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinarli, F.; Kafkas, M.E. The effect of somatotype characters on selected physical performance parameters. Phys. Educ. Stud. 2019, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, C.; Deviterne, D.; Perrin, P. Influence of training on postural and motor control in a combative sport. J. Hum. Mov. Stud. 1998, 35, 119–136. [Google Scholar]
- Mesure, S.; Bonnet, M.; Crémieux, J. L’entraînement sportif peut-il influencer le contrôle postural statique. Sci. Mot. 1994, 21, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Paillard, T. Sport-specific balance develops specific postural skills. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 1019–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, O.; Soylu, Y.; Erkmen, N.; Kaplan, T.; Batalik, L. Effects of proprioceptive training on sports performance: A systematic review. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2024, 16, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Groups | N | Age | Height (cm) | Body Mass (kg) | BMI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||
| Min, Max, Median | Min, Max, Median | Min, Max, Median | Min, Max, Median | ||
| Overall | 169 | 23.1 ± 1.4 | 173 ± 9.7 | 69.0 ± 12.2 | 22.9 ± 2.4 |
| 21, 29, 23 | 145, 196, 175 | 47, 100, 68 | 17.3, 30.2, 22.7 | ||
| Female | 66 | 22.9 ± 1.07 | 164 ± 7.0 | 59.2 ± 8.0 | 21.8 ± 2.2 |
| 21, 27, 23 | 145, 182, 164 | 47, 82, 58 | 17.3, 28.0, 21.9 | ||
| Male | 103 | 23.3 ± 1.7 | 178 ± 6.9 | 75.3 ± 10.1 | 23.6 ± 2.3 |
| 21, 29, 23 | 164, 196, 178 | 54, 100, 75 | 18.0, 30.3, 23.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alessandria, M.; Pivetta, I.; Kuvacic, G.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Angilletta, S.; Giorgio, A.D. Correlation of Body Parameters and Age with Foot Arch Index and Stabilometric Variables in Physically Active Young Males and Females. Sports 2025, 13, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13090324
Alessandria M, Pivetta I, Kuvacic G, Bragazzi NL, Angilletta S, Giorgio AD. Correlation of Body Parameters and Age with Foot Arch Index and Stabilometric Variables in Physically Active Young Males and Females. Sports. 2025; 13(9):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13090324
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlessandria, Marco, Irene Pivetta, Goran Kuvacic, Nicola Luigi Bragazzi, Sonia Angilletta, and Andrea De Giorgio. 2025. "Correlation of Body Parameters and Age with Foot Arch Index and Stabilometric Variables in Physically Active Young Males and Females" Sports 13, no. 9: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13090324
APA StyleAlessandria, M., Pivetta, I., Kuvacic, G., Bragazzi, N. L., Angilletta, S., & Giorgio, A. D. (2025). Correlation of Body Parameters and Age with Foot Arch Index and Stabilometric Variables in Physically Active Young Males and Females. Sports, 13(9), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13090324







