Effects of Arch Support Pad Stiffness on Lower-Limb Biomechanics During Single-Leg Landing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
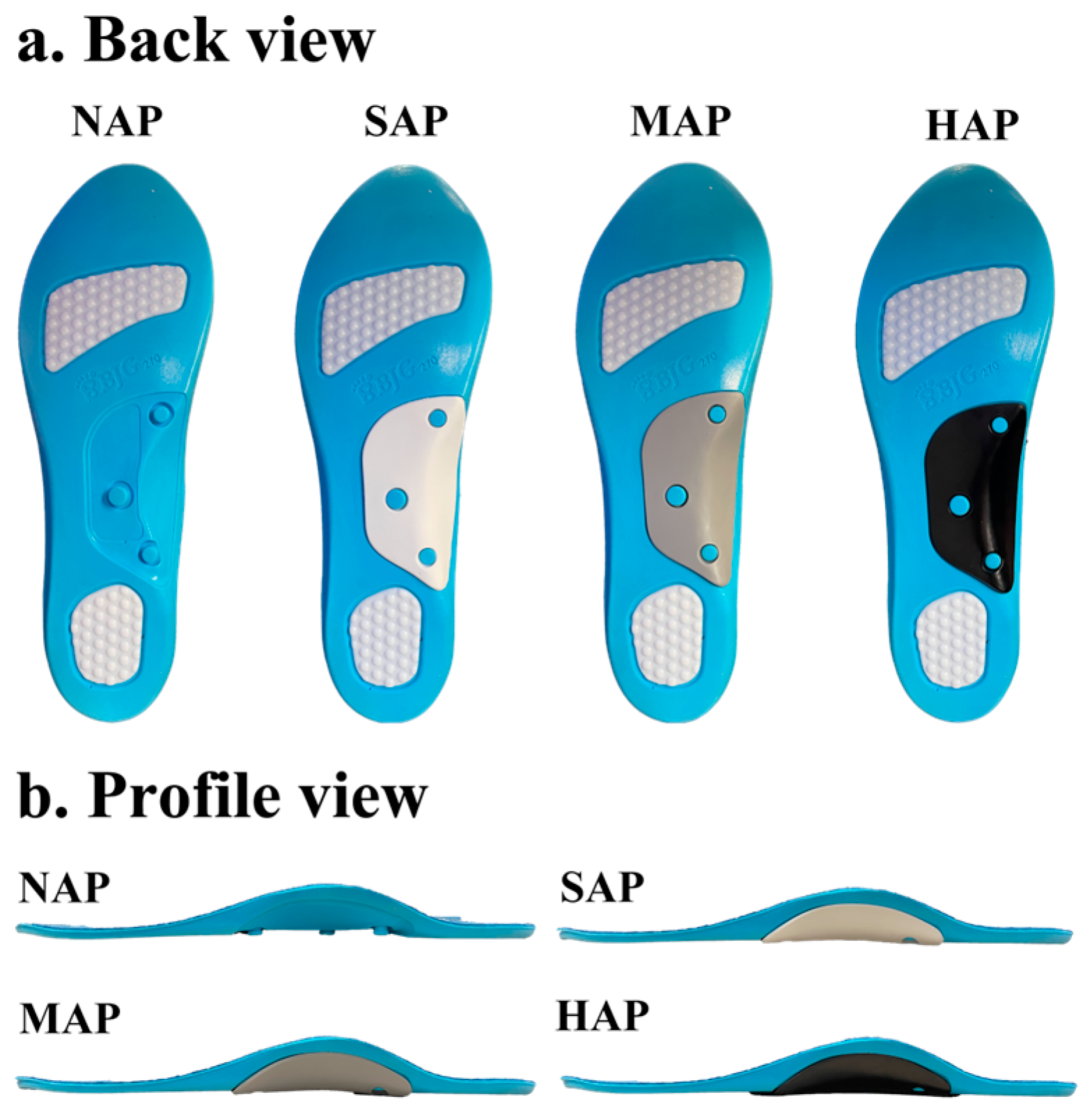
2.2. Arch Support Pads
2.3. Experimental Protocol
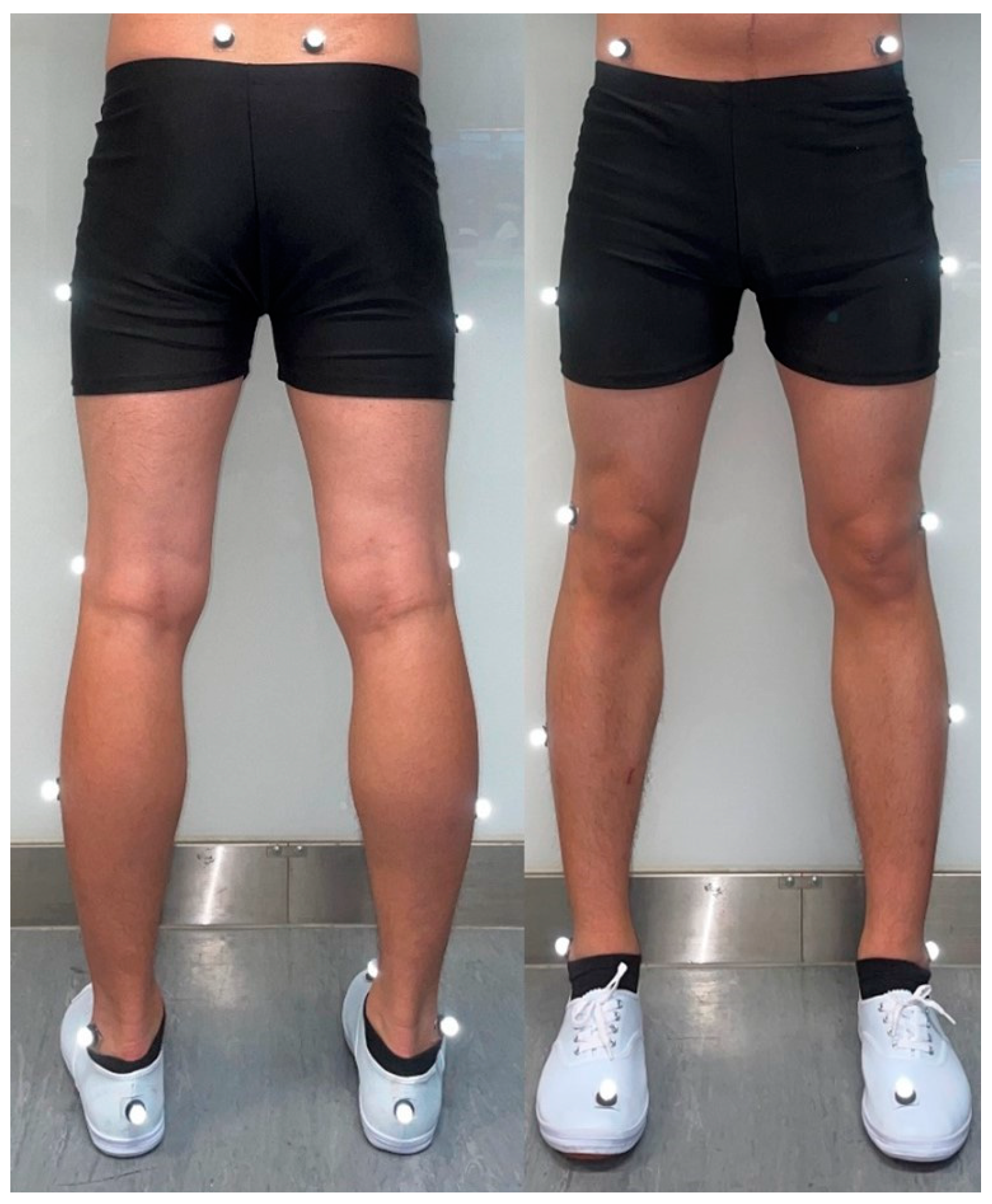
2.4. Data Collection and Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Kinematics
3.2. Kinetics
4. Discussion
4.1. Kinematics
4.2. Kinetics
4.3. Practical Applications
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BW | Body weight |
| CI | Confidence intervals |
| ES | Effect size |
| HAP | High-stiffness arch-support pad |
| MD | Mean difference |
| MCID | Minimal clinically important difference |
| MAP | Medium-stiffness arch-support pad |
| NAP | No arch-support pad |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| ROM | Range of motion |
| SAP | Soft-stiffness arch-support pad |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| vGRF | Vertical ground reaction force |
References
- Mizrahi, J.; Susak, Z. Analysis of Parameters Affecting Impact Force Attenuation during Landing in Human Vertical Free Fall. Eng. Med. 1982, 11, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.W.; Hanson, N.J.; Long, B.; Williams, D.S.B.I. Frontal Plane Landing Mechanics in High-Arched Compared with Low-Arched Female Athletes. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2012, 22, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, M.J.; Torry, M.R.; Wyland, D.J.; Sterett, W.I.; Richard Steadman, J. Gender differences in lower extremity kinematics, kinetics and energy absorption during landing. Clin. Biomech. 2003, 18, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, E.L.; Martin, R.B.; Burr, D.B.; Caterson, B.; Boyd, R.D.; Goodwin, C. Effects of mechanical loading on the tissues of the rabbit knee. J. Orthop. Res. 1984, 2, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Biró, I. Effects of Arch Support Pads and Insoles on Gait Parameters and Plantar Mechanics During Running in Adults with Flatfoot. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 7th International Conference and Workshop Óbuda on Electrical and Power Engineering (CANDO-EPE), Budapest, Hungary, 17–18 October 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hovey, S.; Henry, W.; Judge, L.W.; Avedesian, J.M.; Dickin, D.C. The effect of landing type on kinematics and kinetics during single-leg landings. Sports Biomech. 2021, 20, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hong, Y.; Li, J.-X.; Zhou, J.-H. Comparison of Plantar Loads During Running on Different Overground Surfaces. Res. Sports Med. 2012, 20, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banwell, H.A.; Mackintosh, S.; Thewlis, D. Foot orthoses for adults with flexible pes planus. a systematic review. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2014, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.-K.; Lee, W.C.-C.; Ng, S.-O.; Zheng, Y. Effects of foot orthoses on dynamic balance and basketball free-throw accuracy before and after physical fatigue. J. Biomech. 2019, 96, 109338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, K.; Blanch, P.; Chapman, A.R.; McPoil, T.G.; Vicenzino, B. Foot orthoses and gait. a systematic review and meta-analysis of literature pertaining to potential mechanisms. Br. J. Sports Med. 2010, 44, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.N.; Bates, B.T.; Dufek, J.S. Contributions of lower extremity joints to energy dissipation during landings. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.Q.; Li, P.L.; Yick, K.-L.; Li, N.-W.; Jiao, J. Effects of contoured insoles with different materials on plantar pressure offloading in diabetic elderly during gait. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, Y.; Sugimoto, M.; Iwamoto, K.; Kitsunai, I.; Sugiyama, K.; Kimura, K. Medial longitudinal arch pad influences landing control of the lower limbs during single-leg jump-landing. Health 2020, 12, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.-K.; Cheung, C.C.; Zhiguan, H.; Leung, A.K. Effects of shoe collar height and arch-support orthosis on joint stability and loading during landing. Res. Sports Med. 2022, 30, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Tsai, H.-T.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-N. Effects of orthopedic insoles on postural balance in patients with chronic stroke. A randomized crossover study. Gait Posture 2021, 87, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, M.; Chiaramonte, R.; Alessandro, D.; Buccheri, E.; Finocchiaro, P.; Scaturro, D.; Mauro, G.L.; Cioni, M. Do proprioceptive training strategies with dual-task exercises positively influence gait parameters in chronic stroke? A systematic review. J. Rehabil. Med. 2024, 56, 18396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Effects of footwear on impact forces and soft tissue vibrations during drop jumps and unanticipated drop landings. Int. J. Sports Med. 2013, 34, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Clowers, K.; Kohstall, C.; Yu, Y.-J. Effects of Various Midsole Densities of Basketball Shoes on Impact Attenuation during Landing Activities. J. Appl. Biomech. 2005, 21, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, K.J. The Influence of Variations in Shoe Midsole Density on the Impact Force and Kinematics of Landing in Female Volleyball Players. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Toledo, Toledo, OH, USA, 2004. Available online: http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=toledo1083796438 (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- De Wit, B.; De Clercq, D.; Aerts, P. Biomechanical analysis of the stance phase during barefoot and shod running. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamill, J.; Russell, E.M.; Gruber, A.H.; Miller, R. Impact characteristics in shod and barefoot running. Footwear Sci. 2011, 3, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigoja, S.; Asmussen, M.J.; Firminger, C.R.; Fletcher, J.R.; Edwards, W.B.; Nigg, B.M. The Effects of Increased Midsole Bending Stiffness of Sport Shoes on Muscle-Tendon Unit Shortening and Shortening Velocity. a Randomised Crossover Trial in Recreational Male Runners. Sports Med.-Open 2020, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, M.; Fekete, G.; Baker, J.S.; Wiltshire, H.; Gu, Y. Analyzing the effect of an arch support functional insole on walking and jogging in young, healthy females. Technol. Health Care 2021, 29, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, P.R.; Rodgers, M.M. The arch index. a useful measure from footprints. J. Biomech. 1987, 20, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, A.; Dave, D.; Chockalingam, N. Effect of insole material on plantar pressure. Footwear Sci. 2011, 3 (Suppl. S1), S69–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.; Williams, A.E.; Nester, C. Development and evaluation of a dual density insole for people standing for long periods of time at work. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2020, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Mo, Z.; Guo, J.; Fan, Y. The effect of arch height and material hardness of personalized insole on correction and tissues of flatfoot. J. Healthc. Eng. 2017, 2017, 8614341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPorta, J.W.; Brown, L.E.; Coburn, J.W.; Galpin, A.J.; Tufano, J.J.; Cazas, V.L.; Tan, J.G. Effects of Different Footwear on Vertical Jump and Landing Parameters. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, K.A.; Palmieri, R.M.; Zinder, S.M.; Ingersoll, C.D. Sex differences in valgus knee angle during a single-leg drop jump. J. Athl. Train. 2006, 41, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Shimokochi, Y.; Ambegaonkar, J.P.; Meyer, E.G.; Lee, S.Y.; Shultz, S.J. Changing sagittal plane body position during single-leg landings influences the risk of non-contact anterior cruciate ligament injury. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2013, 21, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, R.; Silvers, H.J.; Gonzales, T.; Mandelbaum, B.R. Gender influences: The role of leg dominance in ACL injury among soccer players. Br. J. Sports Med. 2010, 44, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.A. Biomechanics and Motor Control of Human Movement; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dadfar, M.; Sheikhhoseini, R.; Jafarian, M.; Esmaeili, A. Lower extremity kinematic coupling during single and double leg landing and gait in female junior athletes with dynamic knee valgus. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.C.; Chesterton, P.; Taylor, A.; Evans, W. The effect of surface on knee landing mechanics and muscle activity during a single-leg landing task in recreationally active females. Phys. Ther. Sport 2024, 69, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plug-in Gait Reference Guide. Available online: https://help.vicon.com/download/attachments/11378719/Plug-in%20Gait%20Reference%20Guide.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, D.M. Prefabricated Insoles and Modifications in Sports Medicine. In Athletic Footwear and Orthoses in Sports Medicine; Werd, M.B., Knight, E.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wikstrom, E.A.; Powers, M.E.; Tillman, M.D. Dynamic stabilization time after isokinetic and functional fatigue. J. Athl. Train. 2004, 39, 247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mendiguchia, J.; Ford, K.R.; Quatman, C.E.; Alentorn-Geli, E.; Hewett, T.E. Sex Differences in Proximal Control of the Knee Joint. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiderscheit, B.C. Lower extremity injuries. is it just about hip strength? J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2010, 40, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, K.; Whatman, C. Biomechanics Associated with Patellofemoral Pain and ACL Injuries in Sports. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1325–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmyttere, G.; Leteneur, S.; Hajizadeh, M.; Bleau, J.; Begon, M. Effect of 3D printed foot orthoses stiffness and design on foot kinematics and plantar pressures in healthy people. Gait Posture 2020, 81, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimokochi, Y.; Yong Lee, S.; Shultz, S.J.; Schmitz, R.J. The relationships among sagittal-plane lower extremity moments. implications for landing strategy in anterior cruciate ligament injury prevention. J. Athl. Train. 2009, 44, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Garrett, W.E. Mechanisms of non-contact ACL injuries. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41 (Suppl. S1), i47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zeng, Q.; Lai, J.; Zhang, X. Effects of arch support doses on the center of pressure and pressure distribution of running using statistical parametric mapping. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1051747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, B.M.; Nurse, M.A.; Stefanyshyn, D.J. Shoe inserts and orthotics for sport and physical activities. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1999, 31, S421–S428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mündermann, A.; Nigg, B.M.; Neil Humble, R.; Stefanyshyn, D.J. Foot orthotics affect lower extremity kinematics and kinetics during running. Clin. Biomech. 2003, 18, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piri, E.; Sobhani, V.; Jafarnezhadgero, A.; Arabzadeh, E.; Shamsoddini, A.; Zago, M.; Granacher, U. Effect of double- density foot orthoses on ground reaction forces and lower limb muscle activities during running in adults with and without pronated feet. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2025, 17, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dami, A.; Payen, E.; Farahpour, N.; Robb, K.; Isabelle, P.-L.; Moisan, G. Medially wedged foot orthoses generate greater biomechanical effects than thin-flexible foot orthoses during a unilateral drop jump task on level and inclined surfaces. Clin. Biomech. 2024, 112, 106193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarnezhadgero, A.; Mousavi, S.H.; Madadi-Shad, M.; Hijmans, J.M. Quantifying lower limb inter-joint coordination and coordination variability after four-month wearing arch support foot orthoses in children with flexible flat feet. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2020, 70, 102593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferber, R.; Davis, I.M.; Williams, D.S. Effect of foot orthotics on rearfoot and tibia joint coupling patterns and variability. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | NAP | SAP | MAP | HAP | p | η2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial contact | ||||||
| Ankle | −24.65 ± 4.20 | −21.71 ± 5.74 | −22.04 ± 4.51 | −21.52 ± 4.86 | 0.01 | 0.34 |
| Knee | −0.78 ± 3.84 | 0.20 ± 4.76 | −0.29 ± 4.51 | 0.51 ± 4.46 | 0.23 | 0.13 |
| Hip | 10.86 ± 5.68 | 10.58 ± 4.70 | 11.05 ± 5.38 | 11.46 ± 4.98 | 0.84 | 0.02 |
| Max knee flexion | ||||||
| Ankle | 25.86 ± 4.44 | 25.83 ± 4.59 | 24.92 ± 5.36 | 26.87 ± 4.90 | 0.168 | 0.15 |
| Knee | 31.97 ± 8.09 | 32.40 ± 8.97 | 30.68 ± 8.08 | 34.73 ± 9.66 | <0.05 | 0.25 |
| Hip | 27.08 ± 5.92 | 25.52 ± 6.88 | 25.46 ± 6.12 | 27.57 ± 6.89 | 0.231 | 0.12 |
| Range of motion | ||||||
| Ankle | 51.07 ± 6.65 | 48.06 ± 6.10 | 47.58 ± 6.31 | 48.90 ± 7.59 | 0.056 | 0.22 |
| Knee | 32.75 ± 5.86 | 32.20 ± 6.80 | 30.97 ± 5.84 | 34.23 ± 7.01 | 0.04 | 0.26 |
| Hip | 17.51 ± 3.62 | 16.49 ± 4.20 | 15.57 ± 2.85 | 17.39 ± 3.70 | 0.01 | 0.30 |
| Variable | NAP | SAP | MAP | HAP | p | η2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical GRF (BW) | ||||||
| Time to Peak vGRF (ms) | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.70 | 0.04 |
| Peak vGRF (BW) | 4.04 ± 0.45 | 3.95 ± 0.36 | 3.99 ± 0.36 | 3.99 ± 0.40 | 0.75 | 0.04 |
| Max loading rate (BW/s) | 66.33 ± 11.89 | 66.30 ± 11.47 | 65.55 ± 10.17 | 66.25 ± 9.77 | 0.99 | 0.01 |
| Peak joint moment (Nm/kg) | ||||||
| Ankle dorsiflexion | 3.42 ± 0.53 | 3.33 ± 0.47 | 3.33 ± 0.39 | 3.18 ± 0.44 | 0.04 | 0.25 |
| Knee flexion | 1.36 ± 0.62 | 1.36 ± 0.69 | 1.29 ± 0.63 | 1.41 ± 0.56 | 0.47 | 0.07 |
| Hip flexion | 4.94 ± 1.77 | 4.61 ± 1.74 | 4.40± 1.47 | 4.49 ± 1.47 | 0.31 | 0.10 |
| Ankle plantarflexion | −0.18 ± 0.09 | −0.19 ± 0.08 | −0.18 ± 0.07 | −0.19 ± 0.08 | 0.57 | 0.06 |
| Knee extension | −1.71 ± 0.57 | −1.55 ± 0.61 | −1.48 ± 0.51 | −1.43 ± 0.51 | 0.01 | 0.32 |
| Hip extension | −3.33 ± 2.08 | −3.64 ± 2.75 | −3.23 ± 2.16 | −3.45 ± 2.25 | 0.52 | 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.-H.; Shi, Q.-Q.; Yick, K.-L.; Hu, M.-Y.; Mo, S.-W. Effects of Arch Support Pad Stiffness on Lower-Limb Biomechanics During Single-Leg Landing. Sports 2025, 13, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13090323
Li C-H, Shi Q-Q, Yick K-L, Hu M-Y, Mo S-W. Effects of Arch Support Pad Stiffness on Lower-Limb Biomechanics During Single-Leg Landing. Sports. 2025; 13(9):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13090323
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chu-Hao, Qiu-Qiong Shi, Kit-Lun Yick, Ming-Yu Hu, and Shi-Wei Mo. 2025. "Effects of Arch Support Pad Stiffness on Lower-Limb Biomechanics During Single-Leg Landing" Sports 13, no. 9: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13090323
APA StyleLi, C.-H., Shi, Q.-Q., Yick, K.-L., Hu, M.-Y., & Mo, S.-W. (2025). Effects of Arch Support Pad Stiffness on Lower-Limb Biomechanics During Single-Leg Landing. Sports, 13(9), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13090323






