Comparison of Ultra-Short Race Pace and High-Intensity Interval Training in Age Group Competitive Swimmers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Design
2.2.1. Pre-Test Procedures
2.2.2. Test Protocols
2.2.3. Kinematic Analysis
2.2.4. Biomarkers
2.2.5. Heart Rate
2.2.6. Rate of Perceived Exertion
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Kinematic Characteristics
3.1.1. Distance per Stroke (DPS)
3.1.2. Stroke Rate (SR)
3.1.3. Stroke Index (SI)
3.1.4. Swimming Velocity (SV)
3.2. Biomarkers
3.2.1. Blood Lactate (BL)
3.2.2. Blood Glucose (BG)
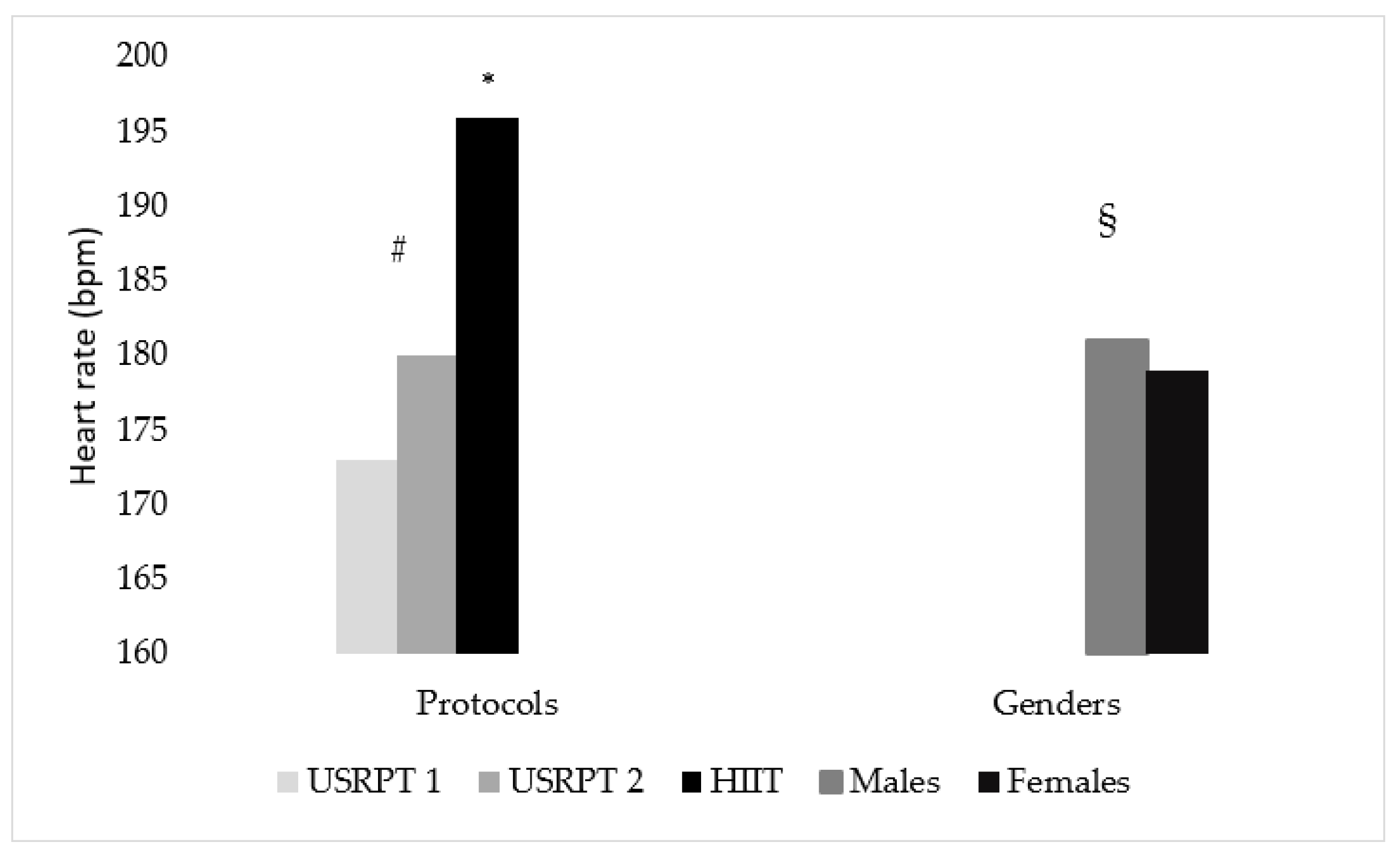
3.3. Heart Rate (HR)
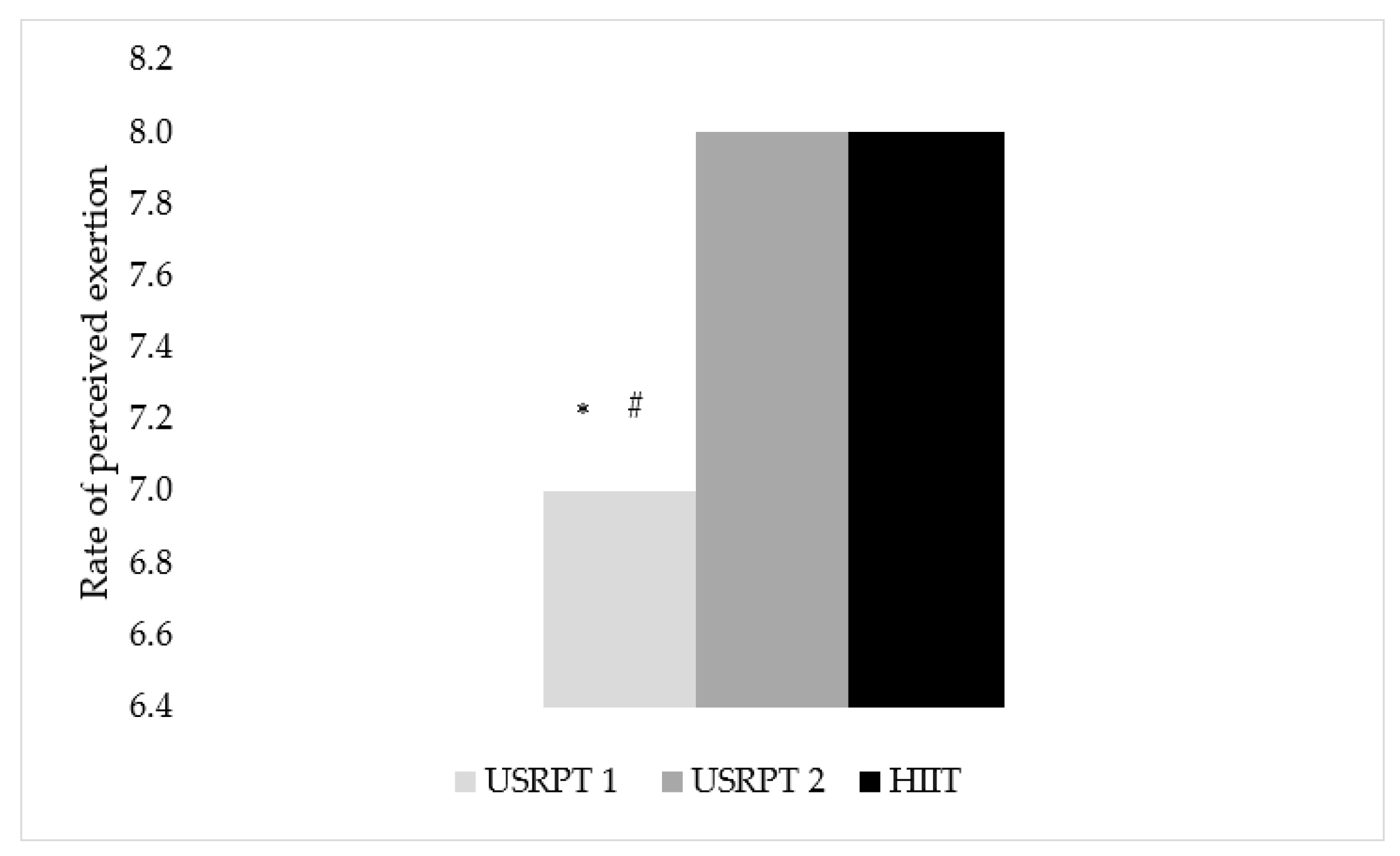
3.4. Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE)
3.5. Correlations
4. Discussion
4.1. Conceptualization of the Study
4.2. Kinematic Characteristics
4.3. Biomarkers
4.4. HR and RPE
4.5. USRPT, a New HIIT’s Approach?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skalidou, S.; Anestis, A.; Bakolas, N.; Tsoulfa, G.; Papadimitriou, K. Swimming Activity Alleviates the Symptoms of Attention: Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) a Case Report. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, K. Effect of Ultra-Short Race Pace Training on Performance of an Adult Middle-Distance Swimmer after Quarantine Period: A Case Study. In Proceedings of the 30th International Congress on Physical Education & Sport Science, Komotini, Greece, 20–22 May 2022; pp. 20–22. Available online: https://www.icpess.gr/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/ICPESS2022-ConferenceBook.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2023).
- Rushall, B.S. Understanding a USRPT Set. Swim. Sci. Bull. 2013, 45e, 1–4. Available online: https://coachsci.sdsu.edu/swim/bullets/45e%20UNDERSTANDING.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2023).
- Astrand, I.; Astrand, P.O.; Christensen, E.H.; Hedman, R. Intermittent Muscular Work. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1960, 48, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beidaris, N.; Botonis, P.; Platanou, T. Physiological and Performance Characteristics of 200 m Continuous Swimming and 4 × 50 m “Broken” Swimming with Different Interval Time Demands. In Proceedings of the XIVth International Symposium of Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming, Oslo, Norway, 16–19 June 2010; pp. 16–19. Available online: https://coachsci.sdsu.edu/swim/training/beidaris.htm (accessed on 11 June 2023).
- Nugent, F.; Comyns, T.; Kearney, P.; Warrington, G. Ultra-Short Race-Pace Training (USRPT) in Swimming: Current Perspectives. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2019, 10, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilen, A.; Larsson, T.H.; Jørgensen, M.; Johansen, L.; Jørgensen, S.; Nordsborg, N.B. Effects of 12 Weeks High-Intensity & Reduced-Volume Training in Elite Athletes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, M.; Nordsborg, N.B.; Lindenskov, A.; Steinholm, H.; Nielsen, H.P.; Mortensen, J.; Weihe, P.; Krustrup, P. High-Intensity Intermittent Swimming Improves Cardiovascular Health Status for Women with Mild Hypertension. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 728289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbe, A.M.; Rasmussen, C.P.; Nielsen, G.; Nordsborg, N.B. High Intensity and Reduced Volume Training Attenuates Stress and Recovery Levels in Elite Swimmers. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2016, 16, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Savvoulidis, S. Does High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) have an effect on young swimmer’s performance? J. Sports Sci. Rec. 2017, 25, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Alansare, A.; Alford, K.; Lee, S.; Church, T.; Jung, H.C. The Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training vs. Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training on Heart Rate Variability in Physically Inactive Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperlich, B.; Zinner, C.; Heilemann, I.; Kjendlie, P.-L.; Holmberg, H.-C.; Mester, J. High-Intensity Interval Training Improves VO2peak, Maximal Lactate Accumulation, Time Trial and Competition Performance in 9–11-Year-Old Swimmers. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Savvoulidis, S. The Effects of Two Different HIIT Resting Protocols on Children’s Swimming Efficiency and Performance. Cent. Eur. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2020, 30, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabasakalis, A.; Nikolaidis, S.; Tsalis, G.; Christoulas, K.; Mougios, V. Effects of Sprint Interval Exercise Dose and Sex on Circulating Irisin and Redox Status Markers in Adolescent Swimmers. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, L. High Intensity Interval Training. ACSM. Available online: https://www.acsm.org/docs/default-source/files-for-resource-library/high-intensity-interval-training.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2023).
- Norberto, M.S.; De Arruda, T.B.; Cursiol, J.A.; De Andrade, V.L.; De Araujo, G.G.; Papoti, M. Metformin Anticipates Peak of Lactate during High-Intensity Interval Training but No Changes Performance or Neuromuscular Response in Amateur Swimmers. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 46, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzi, E.; Skari, A.; Nikolaidis, S.; Papadimitriou, K.; Kabasakalis, A.; Mougios, V. Relevance of a Sprint Interval Swim Training Set to the 100-Meter Freestyle Event Based on Blood Lactate and Kinematic Variables. J. Hum. Kinet. 2021, 80, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenca-Fernández, F.; Boullosa, D.; Ruiz-Navarro, J.J.; Gay, A.; Morales-Ortíz, E.; López-Contreras, G.; Arellano, R. Lower Fatigue and Faster Recovery of Ultra-Short Race Pace Swimming Training Sessions. Res. Sports Med. 2021, 31, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.; McCarthy, E.; Ditroilo, M. Acute Physiological Responses to Ultra Short Race-Pace Training in Competitive Swimmers. J. Hum. Kinet. 2020, 75, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Papadimitriou, N.; Gourgoulis, V.; Barkoukis, V.; Loupos, D. Assessment of Young Swimmers’ Technique with Tec Pa Tool. Cent. Eur. J. Sport Sci. Med. 2021, 34, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Loupos, D. The Effect of an Alternative Swimming Learning Program on Skills, Technique, Performance, and Salivary Cortisol Concentration at Primary School Ages Novice Swimmers. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Loupos, D.; Tsalis, G.; Manou, B. Effects of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) on swimmers leg mobility and performance. J. Phys. Educ. Sport JPES 2017, 17, 663–666. [Google Scholar]
- Zompanakis, I.; Papadimitriou, K.; Georgios, T.; Dimitrios, L. The Effects of Reduced Breathing on Swimming Performance and on Blood Lactate Concentration in 25 and 50 m Breaststroke Swimming at Maximal Intensity. JSR 2020, 27, 2. Available online: https://cdn.ymaws.com/swimmingcoach.org/resource/resmgr/swimresearch/JSR-_Zompanakis_-_Manuscript.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2023).
- Kabasakalis, A.; Nikolaidis, S.; Tsalis, G.; Mougios, V. Response of Blood Biomarkers to Sprint Interval Swimming. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2020, 15, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskinen, K.L. Evaluation of Technique Performances in Freestyle Swimming. Kinesiology 1997, 2, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wądrzyk, Ł.; Staszkiewicz, R.; Strzała, M. Comparison of Race Performance Characteristics for the 50 m and 100 m Freestyle among Regional-Level Male Swimmers. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jürimäe, J.; Haljaste, K.; Cicchella, A.; Lätt, E.; Purge, P.; Leppik, A.; Jürimäe, T. Analysis of Swimming Performance from Physical, Physiological, and Biomechanical Parameters in Young Swimmers. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2007, 19, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, W.; Klarowicz, A.; Rejman, M.; Szczepan, S. An Evaluation of the Usefulness of Stroke Index Values in the Swimming Training of People with Disabilities. Pol. J. Sport Tour. 2016, 23, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.; Arellano, R. Stroke Index Values According to Level, Gender, Swimming Style and Event Race Distance. In Proceedings of the Symposium of the International Society of Biomechanics in Sports, Caceres, Spain, 1–6 July 2002; Available online: https://ojs.ub.unikonstanz.de/cpa/article/view/620 (accessed on 11 June 2023).
- Zwiren, L.D.; Cureton, K.J.; Hutchinson, P. Comparison of Circulatory Responses to Submaximal Exercise in Equally Trained Men and Women. Int. J. Sports Med. 1983, 4, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Spina, R.J.; Martin, W.H.; Kohrt, W.M.; Schechtman, K.B.; O Holloszy, J.; Ehsani, A.A. Effects of Aging, Sex, and Physical Training on Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise. Circulation 1992, 86, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turley, K.R. Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise in Children. Sports Med. 1997, 24, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, I.J.; Sørås, S.E.; Relling, B.E.; Lundgren, K.M.; Kiel, I.A.; Moholdt, T. The Relationship between Maximum Heart Rate in a Cardiorespiratory Fitness Test and in a Maximum Heart Rate Test. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Monahan, K.D.; Seals, D.R. Age-Predicted Maximal Heart Rate Revisited. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; McCrory, J. Validation of Maximal Heart Rate Prediction Equations Based on Sex and Physical Activity Status. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2015, 8, 318–330. [Google Scholar]



| Swimmers | Age (yrs) | Height (m) | Weight (kg) | BMI (kg/m2) | Experience (yrs) | SB 25 m (s) | SB 50 m (s) | SB 100 m (s) | WA Score (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | 13.4 ± 0.2 | 1.67 ± 0.07 | 53.0 ± 3.1 | 18.9 ± 0.7 | 8.3 ± 0.9 | 14.1 ± 0.5 | 30.5 ± 0.8 | 65.0 ± 1.3 | 552 ± 170 |
| Females | 13.5 ± 0.2 | 1.63 ± 0.05 | 50.0 ± 2.4 | 18.8 ± 0.7 | 7.9 ± 0.7 | 14.1 ± 0.2 | 31.4 ± 0.4 | 67.6 ± 0.5 | 580 ± 120 |
| Total Av. | 13.5 ± 0.1 | 1.65 ± 0.06 | 51.5 ± 7.8 | 18.8 ± 1.9 | 8.0 ± 0.5 | 14.1 ± 0.9 | 31.0 ± 1.8 | 66.4 ± 2.8 | 566 ± 145 |
| Swimmer’s SB 100 m (s) | HIIT (s) (≈103% of 100 m SB) | USRPT (s) (100m SB/4 or ≈100% of 100 m SB) |
|---|---|---|
| 68.0 | 32.5 | 17.0 |
| USRPT (USRPT1 & USRPT2) | HIIT | Eta Square (η2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPS (m) | 1.41 ± 0.81 | 1.46 ± 0.23 | 1.63 ± 0.37 * | 0.20 |
| SR (strokes·min−1) | 49.53 ± 0.78 | 49.41 ± 0.78 | 49.70 ± 0.92 | 0.01 |
| SI (m2·s−1) | 1.82 ± 0.70 § | 1.78 ± 0.71 § | 2.26 ± 0.82 * | 0.60 |
| SV (m·s−1) | 1.61 ± 0.20 § | 1.60 ± 0.20 § | 1.56 ± 0.20 * | 0.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papadimitriou, K.; Kabasakalis, A.; Papadopoulos, A.; Mavridis, G.; Tsalis, G. Comparison of Ultra-Short Race Pace and High-Intensity Interval Training in Age Group Competitive Swimmers. Sports 2023, 11, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11090186
Papadimitriou K, Kabasakalis A, Papadopoulos A, Mavridis G, Tsalis G. Comparison of Ultra-Short Race Pace and High-Intensity Interval Training in Age Group Competitive Swimmers. Sports. 2023; 11(9):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11090186
Chicago/Turabian StylePapadimitriou, Konstantinos, Athanasios Kabasakalis, Anastasios Papadopoulos, Georgios Mavridis, and Georgios Tsalis. 2023. "Comparison of Ultra-Short Race Pace and High-Intensity Interval Training in Age Group Competitive Swimmers" Sports 11, no. 9: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11090186
APA StylePapadimitriou, K., Kabasakalis, A., Papadopoulos, A., Mavridis, G., & Tsalis, G. (2023). Comparison of Ultra-Short Race Pace and High-Intensity Interval Training in Age Group Competitive Swimmers. Sports, 11(9), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11090186








