Relationship between Aggressiveness, Self-Confidence, and Perceived Coach Support and Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stern, R.A.; Riley, D.O.; Daneshvar, D.; Nowinski, C.J.; Cantu, R.C.; McKee, A.C. Long-term Consequences of Repetitive Brain Trauma: Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy. PMR 2011, 3, S460–S467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamm, J.M.; Bourlas, A.P.; Baugh, C.M.; Fritts, N.G.; Daneshvar, D.H.; Martin, B.M.; McClean, M.D.; Tripodis, Y.; Stern, R.A. Age of first exposure to football and later-life cognitive impairment in former NFL players. Neurology 2015, 84, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stamm, J.M.; Koerte, I.K.; Muehlmann, M.; Pasternak, O.; Bourlas, A.P.; Baugh, C.M.; Giwerc, M.Y.; Zhu, A.; Coleman, M.J.; Bouix, S.; et al. Age at First Exposure to Football Is Associated with Altered Corpus Callosum White Matter Microstructure in Former Professional Football Players. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alosco, M.L.; Tripodis, Y.; Jarnagin, J.; Baugh, C.M.; Martin, B.; Chaisson, C.E.; Estochen, N.; Song, L.; Cantu, R.C.; Jeromin, A.; et al. Repetitive head impact exposure and later-life plasma total tau in former National Football League players. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2016, 7, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenigro, P.; Alosco, M.L.; Martin, B.M.; Daneshvar, D.; Mez, J.; Chaisson, C.E.; Nowinski, C.J.; Au, R.; McKee, A.C.; Cantu, R.C.; et al. Cumulative Head Impact Exposure Predicts Later-Life Depression, Apathy, Executive Dysfunction, and Cognitive Impairment in Former High School and College Football Players. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagge, C.A.; Fisher, A.M.; Minaeva, O.V.; Gaudreau-Balderrama, A.; Moncaster, J.; Zhang, X.-L.; Wojnarowicz, M.W.; Casey, N.; Lu, H.; Kokiko-Cochran, O.N.; et al. Concussion, microvascular injury, and early tauopathy in young athletes after impact head injury and an impact concussion mouse model. Brain 2018, 141, 422–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guskiewicz, K.M.; Weaver, N.L.; Padua, D.A.; Garrett, W.E. Epidemiology of Concussion in Collegiate and High School Football Players. Am. J. Sports Med. 2000, 28, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.W. Traumatic Brain Injury in High School Athletes. JAMA 1999, 282, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, R.W.; Rowson, S.; Duma, S.M. Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cobb, B.R.; Urban, J.E.; Davenport, E.M.; Rowson, S.; Duma, S.M.; Maldjian, J.; Whitlow, C.T.; Powers, A.K.; Stitzel, J.D. Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football: Elementary School Ages 9–12 Years and the Effect of Practice Structure. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 2463–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelley, M.E.; Kane, J.M.; Espeland, M.A.; Miller, L.E.; Powers, A.K.; Stitzel, J.D.; Urban, J.E. Head impact exposure measured in a single youth football team during practice drills. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 20, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelley, M.E.; Espeland, M.A.; Flood, W.C.; Powers, A.K.; Whitlow, C.T.; Maldjian, J.A.; Stitzel, J.D.; Urban, J.E. Comparison of head impact exposure in practice drills among multiple youth football teams. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2019, 23, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urban, J.E.; Flood, W.C.; Zimmerman, B.J.; Kelley, M.E.; Espeland, M.A.; McNamara, L.; Davenport, E.M.; Powers, A.K.; Whitlow, C.T.; Maldjian, J.A.; et al. Evaluation of head impact exposure measured from youth football game plays. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2019, 24, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campolettano, E.T.; Rowson, S.; Duma, S.M. Drill-specific head impact exposure in youth football practice. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2016, 18, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pop Warner Safety—Play Safer—Health & Safety. Available online: https://www.popwarner.com/Default.aspx?tabid=1579758 (accessed on 6 September 2021).
- HEADS UP | CDC Injury Center. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/HeadsUp/ (accessed on 6 September 2021).
- Kelley, M.E.; Jones, D.A.; Espeland, M.A.; Rosenberg, M.L.; Miles, C.M.; Whitlow, C.T.; Maldjian, J.A.; Stitzel, J.D.; Urban, J.E. Physical Performance Measures Correlate with Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 52, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGuglielmo, D.M.; Kelley, M.E.; Espeland, M.A.; Gregory, Z.A.; Payne, T.D.; Jones, D.A.; Filben, T.M.; Powers, A.K.; Stitzel, J.D.; Urban, J.E. The Effect of Player Contact Characteristics on Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football Games. J. Appl. Biomech. 2021, 37, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.D.; Pierce, A.F.; Guskiewicz, K.M.; Register-Mihalik, J.K.; Pamukoff, D.N.; Mihalik, J.P. Safe-Play Knowledge, Aggression, and Head-Impact Biomechanics in Adolescent Ice Hockey Players. J. Athl. Train. 2016, 51, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelley, M.E.; Urban, J.E.; Miller, L.E.; Jones, D.A.; Espeland, M.A.; Davenport, E.M.; Whitlow, C.T.; Maldjian, J.A.; Stitzel, J.D. Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football: Comparing Age- and Weight-Based Levels of Play. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campolettano, E.T.; Gellner, R.A.; Rowson, S. High-magnitude head impact exposure in youth football. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 20, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellner, R.A.; Campolettano, E.T.; Smith, E.P.; Rowson, S. Are specific players more likely to be involved in high-magnitude head impacts in youth football? J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2019, 24, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Register-Mihalik, J.; Baugh, C.; Kroshus, E.; Kerr, Z.Y.; McLeod, T.C.V. A Multifactorial Approach to Sport-Related Concussion Prevention and Education: Application of the Socioecological Framework. J. Athl. Train. 2017, 52, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerr, Z.Y.; Yeargin, S.W.; McLeod, T.C.V.; Mensch, J.; Hayden, R.; Dompier, T.P. Comprehensive Coach Education Reduces Head Impact Exposure in American Youth Football. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kroshus, E.; Garnett, B.; Hawrilenko, M.; Baugh, C.M.; Calzo, J.P. Concussion under-reporting and pressure from coaches, teammates, fans, and parents. Soc. Sci. Med. 2015, 134, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chrisman, S.; Quitiquit, C.; Rivara, F.P. Qualitative Study of Barriers to Concussive Symptom Reporting in High School Athletics. J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 52, 330–335.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baugh, C.M.; Kroshus, E.; Daneshvar, D.; Stern, R. Perceived Coach Support and Concussion Symptom-Reporting: Differences between Freshmen and Non-Freshmen College Football Players. J. Law Med. Ethics 2014, 42, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltz, D.L. Self-confidence and sports performance. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 1988, 16, 423–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, C.; Lane, A.M.; Brierley, J.H.; Terry, P.C. Anxiety, Self-Confidence and Performance in Tae Kwon-Do. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1997, 85, 1275–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.R.; Nicholls, A.R.; Polman, R.C.J. Pre-competitive confidence, coping, and subjective performance in sport. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 21, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanz, K.; Rimer, B.K.; Viswanath, K. Health Behavior and Health Education: Theory, Research, and Practice, 4th ed.; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith, J.G.; Greenwald, R.M.; Chu, J.J. Measuring Head Kinematics in Football: Correlation Between the Head Impact Telemetry System and Hybrid III Headform. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 40, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crisco, J.J.; Chu, J.J.; Greenwald, R.M. An Algorithm for Estimating Acceleration Magnitude and Impact Location Using Multiple Nonorthogonal Single-Axis Accelerometers. J. Biomech. Eng. 2004, 126, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamkonda, S.; Woodward, S.J.; Campolettano, E.; Gellner, R.; Kelley, M.E.; Jones, D.A.; Genemaras, A.; Beckwith, J.G.; Greenwald, R.M.; Maerlender, A.C.; et al. Head Impact Exposure in Practices Correlates With Exposure in Games for Youth Football Players. J. Appl. Biomech. 2018, 34, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, S.; Hardy, L.; Savage, J.; Woodman, T.; Callow, N. Development and validation of a trait measure of robustness of self-confidence. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2011, 12, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PAS—Sport Climate. Available online: https://selfdeterminationtheory.org/pas-sport-climate/ (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Maxwell, J.; Moores, E. The development of a short scale measuring aggressiveness and anger in competitive athletes. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2007, 8, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, D.R.; Gillespie, D.F. Phrase Completion Scales. J. Soc. Serv. Res. 2007, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, J.E.; Davenport, E.M.; Golman, A.J.; Maldjian, J.; Whitlow, C.T.; Powers, A.K.; Stitzel, J.D. Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football: High School Ages 14 to 18 Years and Cumulative Impact Analysis. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 2474–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campolettano, E.T.; Gellner, R.A.; Smith, E.P.; Bellamkonda, S.; Tierney, C.T.; Crisco, J.J.; Jones, D.A.; Kelley, M.E.; Urban, J.E.; Stitzel, J.D.; et al. Development of a Concussion Risk Function for a Youth Population Using Head Linear and Rotational Acceleration. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 48, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.B. The Influence of Performance Level and Setting on Collegiate Athletes’ Motivational Profiles; Brigham Young University: Provo, UT, USA, 2007; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalik, J.P.; Blackburn, J.T.; Greenwald, R.M.; Cantu, R.C.; Marshall, S.W.; Guskiewicz, K.M. Collision Type and Player Anticipation Affect Head Impact Severity Among Youth Ice Hockey Players. Pediatrics 2010, 125, e1394–e1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, S.M.; Suksreephaisan, T.K.; Perry, B.G.; Palmer, B.R.; Page, R.A. The Effects of Anticipation and Visual and Sensory Performance on Concussion Risk in Sport: A Review. Sports Med. Open 2020, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (Alan) Chu, T.L.; Zhang, X.; Lee, J.; Zhang, T. Perceived coach-created environment directly predicts high school athletes’ physical activity during sport. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2020, 16, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, M.S.; Balaguer, I.; Castillo, I.; Duda, J.L. Coach Autonomy Support and Quality of Sport Engagement in Young Soccer Players. Span. J. Psychol. 2009, 12, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, N.; Vallerand, R.J.; Amoura, S.; Baldes, B. Influence of coaches’ autonomy support on athletes’ motivation and sport performance: A test of the hierarchical model of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2010, 11, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Smoll, F.L. Behavioral research and intervention in youth sports. Behav. Ther. 1991, 22, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broglio, S.P.; Eckner, J.T.; Martini, D.; Sosnoff, J.J.; Kutcher, J.S.; Randolph, C. Cumulative Head Impact Burden in High School Football. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 2069–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| (a) | ||
| Characteristic | Middle School | High School |
| Age (years) | 13.3 ± 0.4 | 16.0 ± 0.9 |
| Height (m) | 1.69 ± 0.07 | 1.79 ± 0.08 |
| Weight (kg) | 63.5 ± 8.1 | 90.0 ± 25.9 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.3 ± 2.9 | 27.8 ± 6.6 |
| (b) | ||
| Race | Middle School (# of Athletes) | High School (# of Athletes) |
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 0 | 0 |
| Asian | 0 | 0 |
| Pacific Islander | 0 | 0 |
| Black/African American | 9 | 11 |
| White | 2 | 7 |
| Two or more of the above races | 1 | 3 |
| Declined | 1 | 0 |
| Survey | Statistic | Middle School | High School |
|---|---|---|---|
| TROSCI | Mean ± SD | 45.3 ± 12.1 | 46.6 ± 9.2 |
| Median [95th %] | 45.0 [70.0] | 45.0 [64.0] | |
| SCQ | Mean ± SD | 5.83 ± 1.13 | 5.75 ± 1.25 |
| Median [95th %] | 5.60 [7.00] | 6.27 [6.93] | |
| CAAS | Mean ± SD | 26.7 ± 9.4 | 31.9 ± 11.4 |
| Median [95th %] | 25.0 [44.0] | 33.0 [52.0] |
| Overall Metric | Session Type | Middle School | High School |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median [95th %] | Median [95th %] | ||
| N | Overall | 247.0 [547.0] | 317.0 [631.0] |
| Practice | 146.0 [282.0] | 169.0 [356.0] | |
| Competition | 92.0 [275.0] | 151.0 [318.0] | |
| Impacts/player/session | Overall | 7.4 [18.2] | 8.8 [19.7] |
| Practice | 6.1 [13.6] | 6.4 [13.9] | |
| Competition | 10.4 [27.5] | 15.4 [32.7] |
| Overall Metric | Session Type | Middle School | High School |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median [95th %] | Median [95th %] | ||
| Median LA | Overall | 18.7 [21.8] | 19.2 [23.8] |
| Practice | 19.1 [22.7] | 18.5 [22.5] | |
| Competition | 18.3 [20.6] | 19.4 [25.8] | |
| LA95 | Overall | 50.9 [67.4] | 47.7 [65.9] |
| Practice | 51.7 [77.1] | 40.1 [61.9] | |
| Competition | 50.8 [62.3] | 53.9 [76.2] | |
| Median RA | Overall | 886.9 [1053] | 994.4 [1133] |
| Practice | 904.4 [1095] | 985.3 [1102] | |
| Competition | 889.2 [1046] | 1024 [1225] | |
| RA95 | Overall | 2330 [3121] | 2493 [3495] |
| Practice | 2475 [3459] | 2224 [3124] | |
| Competition | 2217 [3186] | 2701 [3828] | |
| RWE | Overall | 0.973 [5.575] | 1.358 [4.392] |
| Practice | 0.328 [2.211] | 0.327 [1.192] | |
| Competition | 0.296 [3.364] | 1.164 [3.477] |
| Survey/Metric | p (Survey) | p (Age) | p (BMI) | p (Model) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TROSCI | |||||
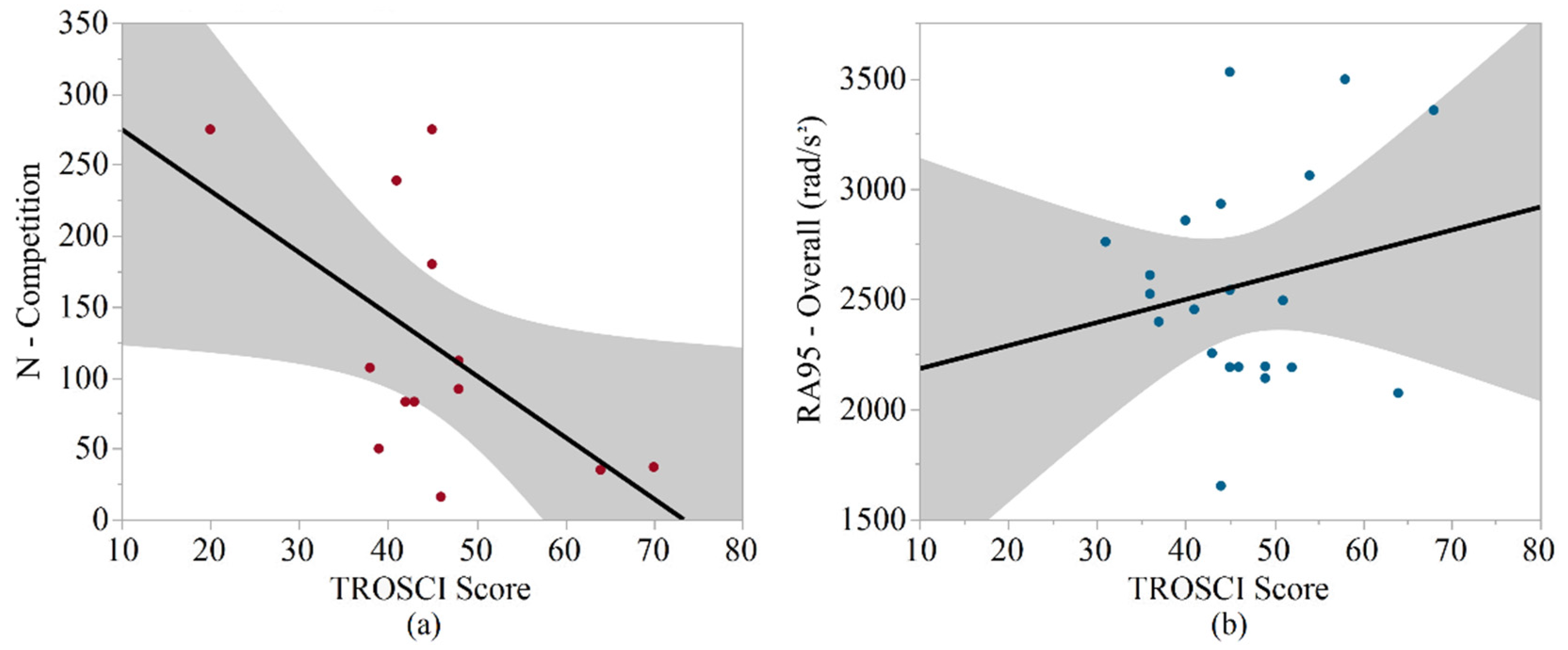
| N-competition | 0.045 | 0.756 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| Impacts/Player/Session-competition | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.999 | 0.153 | 0.508 |
| Median RA-practice | 0.197 | 0.283 | 0.006 | 0.024 | 0.720 |
| SCQ | |||||
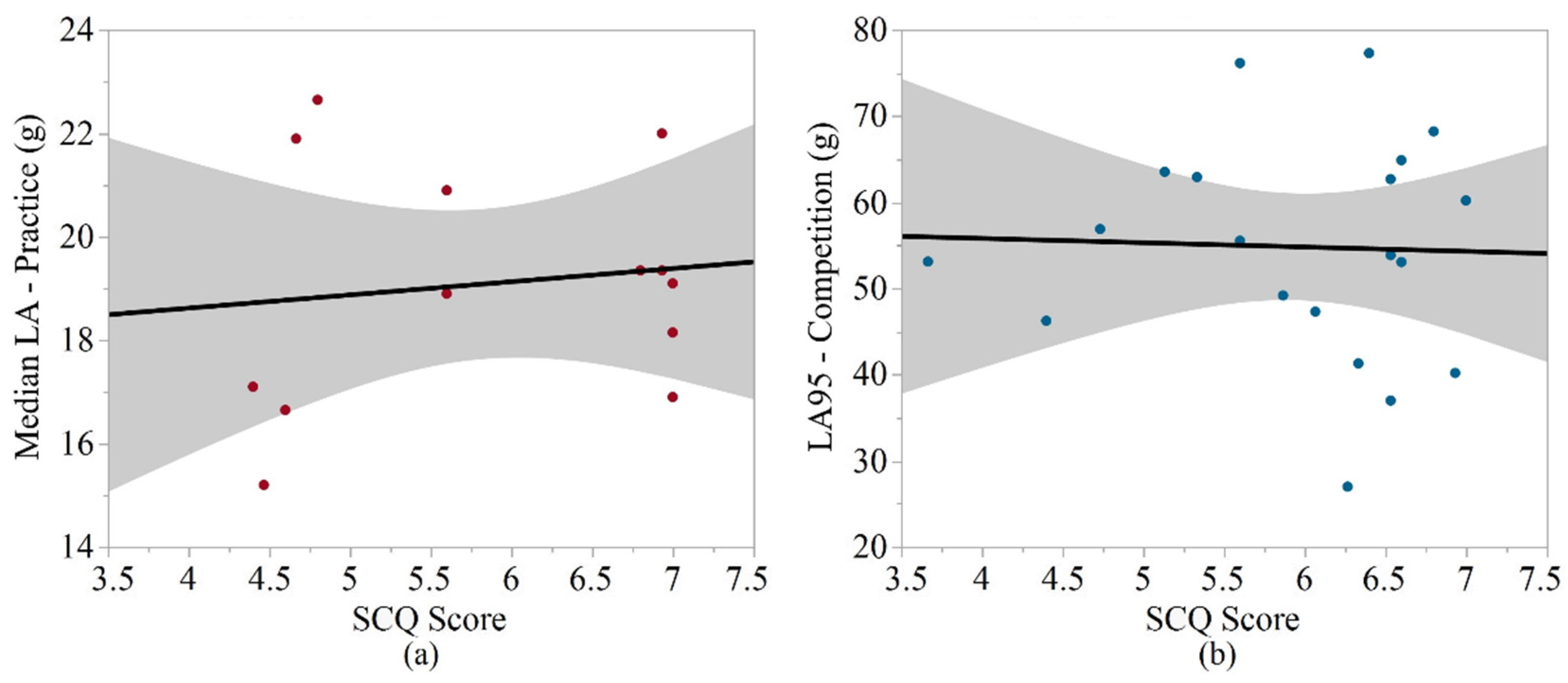
| Median LA-practice | 0.025 | 0.736 | 0.027 | 0.042 | 0.670 |
| Median RA-overall | 0.281 | 0.149 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.851 |
| Median RA-practice | 0.078 | 0.370 | 0.016 | 0.057 | 0.691 |
| RWE-competition | 0.897 | 0.034 | 0.376 | 0.117 | 0.547 |
| Survey/Metric | p (Survey) | p (Age) | p (BMI) | p (Model) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TROSCI | |||||
| N-overall | 0.434 | 0.019 | 0.217 | 0.045 | 0.426 |
| N-practice | 0.267 | 0.037 | 0.079 | 0.041 | 0.436 |
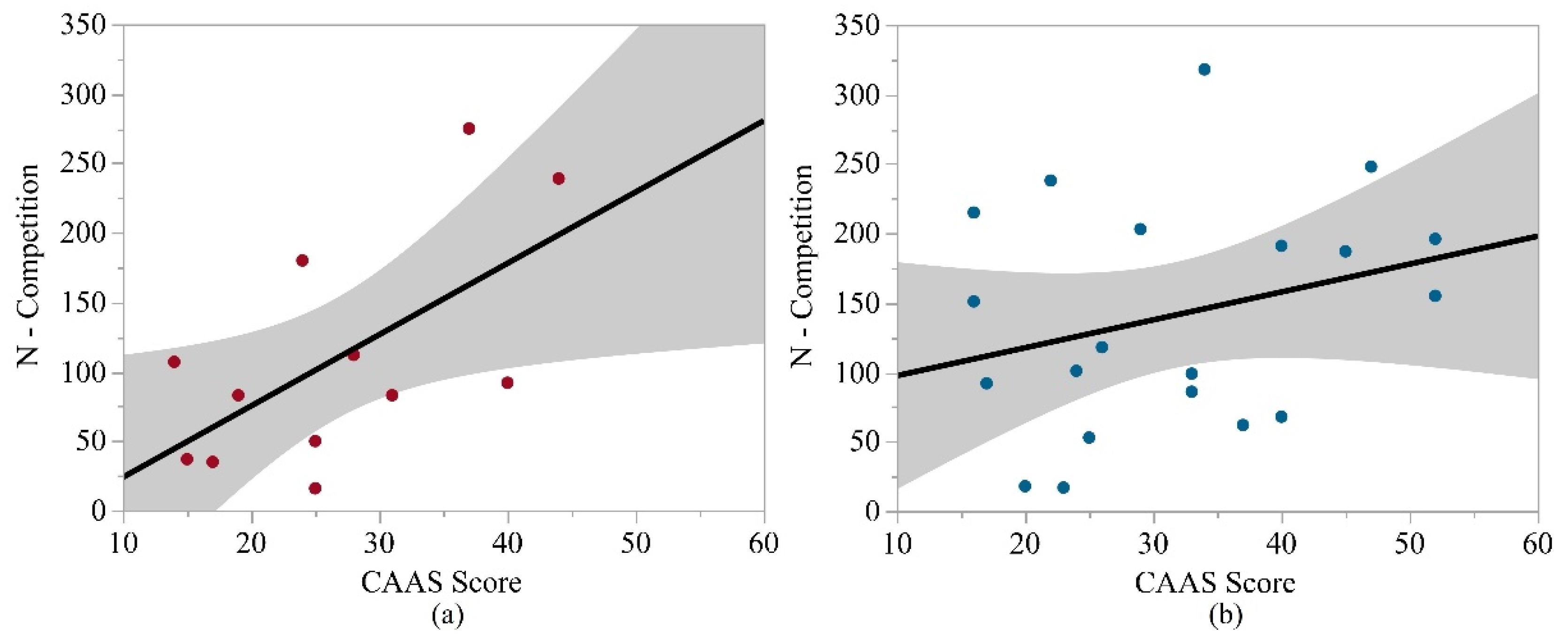
| N-competition | 0.893 | 0.041 | 0.313 | 0.112 | 0.321 |
| Impacts/Player/Session-practice | 0.450 | 0.490 | 0.019 | 0.044 | 0.452 |
| Impacts/Player/Session-competition | 0.810 | 0.025 | 0.571 | 0.046 | 0.403 |
| LA95-overall | 0.212 | 0.611 | 0.018 | 0.059 | 0.363 |
| LA95-competition | 0.091 | 0.911 | 0.034 | 0.053 | 0.392 |
| RA95-overall | 0.222 | 0.409 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.480 |
| RA95-practice | 0.971 | 0.666 | 0.005 | 0.037 | 0.403 |
| RA95-competition | 0.207 | 0.803 | 0.013 | 0.072 | 0.383 |
| RWE-practice | 0.738 | 0.904 | 0.036 | 0.142 | 0.314 |
| SCQ | |||||
| N-overall | 0.421 | 0.019 | 0.505 | 0.045 | 0.428 |
| N-competition | 0.376 | 0.021 | 0.613 | 0.042 | 0.393 |
| Impacts/Player/Session-competition | 0.684 | 0.024 | 0.723 | 0.044 | 0.408 |
| LA95-overall | 0.909 | 0.278 | 0.024 | 0.097 | 0.335 |
| LA95-competition | 0.179 | 0.448 | 0.018 | 0.087 | 0.346 |
| RA95-overall | 0.635 | 0.046 | 0.003 | 0.016 | 0.466 |
| RA95-practice | 0.514 | 0.456 | 0.016 | 0.032 | 0.433 |
| RA95-competition | 0.707 | 0.068 | 0.046 | 0.137 | 0.285 |
| Median RA-overall | 0.579 | 0.023 | 0.176 | 0.070 | 0.349 |
| RWE-overall | 0.314 | 0.062 | 0.035 | 0.150 | 0.291 |
| RWE-practice | 0.322 | 0.743 | 0.025 | 0.121 | 0.351 |
| CAAS | |||||
| N-overall | 0.483 | 0.028 | 0.384 | 0.048 | 0.421 |
| N-competition | 0.146 | 0.015 | 0.666 | 0.024 | 0.436 |
| Impacts/Player/Session-competition | 0.255 | 0.017 | 0.698 | 0.026 | 0.452 |
| LA95-overall | 0.980 | 0.521 | 0.027 | 0.123 | 0.296 |
| RA95-overall | 0.940 | 0.262 | 0.008 | 0.027 | 0.428 |
| RA95-practice | 0.234 | 0.464 | 0.016 | 0.026 | 0.413 |
| Median RA-overall | 0.175 | 0.030 | 0.036 | 0.044 | 0.407 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marks, M.E.; Flood, W.C.; Kelley, M.E.; Espeland, M.A.; Miles, C.M.; Powers, A.K.; Whitlow, C.T.; Maldjian, J.A.; Stitzel, J.D.; Urban, J.E. Relationship between Aggressiveness, Self-Confidence, and Perceived Coach Support and Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football. Sports 2022, 10, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports10080115
Marks ME, Flood WC, Kelley ME, Espeland MA, Miles CM, Powers AK, Whitlow CT, Maldjian JA, Stitzel JD, Urban JE. Relationship between Aggressiveness, Self-Confidence, and Perceived Coach Support and Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football. Sports. 2022; 10(8):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports10080115
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarks, Madison E., William C. Flood, Mireille E. Kelley, Mark A. Espeland, Christopher M. Miles, Alexander K. Powers, Christopher T. Whitlow, Joseph A. Maldjian, Joel D. Stitzel, and Jillian E. Urban. 2022. "Relationship between Aggressiveness, Self-Confidence, and Perceived Coach Support and Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football" Sports 10, no. 8: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports10080115
APA StyleMarks, M. E., Flood, W. C., Kelley, M. E., Espeland, M. A., Miles, C. M., Powers, A. K., Whitlow, C. T., Maldjian, J. A., Stitzel, J. D., & Urban, J. E. (2022). Relationship between Aggressiveness, Self-Confidence, and Perceived Coach Support and Head Impact Exposure in Youth Football. Sports, 10(8), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports10080115






