Abstract
Apple skin color is an important trait for organoleptic quality. In fact, it has a major influence on consumer choice. Skin color is, thus, one of the most important criteria taken into account by breeders. For apples, most novel varieties are so-called “mutants” or “sports” that have been identified in clonal populations. Indeed, many “sports” exist that show distinct phenotypic differences compared to the varieties from which they originated. These differences affect a limited number of traits of economic importance, including skin color. Until recently, the detailed genetic or epigenetic changes resulting in heritable phenotypic changes in sports was largely unknown. Recent technological advances and the availability of several high-quality apple genomes now provide the bases to understand the exact nature of the underlying molecular changes that are responsible for the observed phenotypic changes observed in sports. The present review investigates the molecular nature of sports affected in apple skin color giving arguments in favor of the genetic or epigenetic explanatory models.
1. Introduction
Apple skin color is one of the most important factors determining the acceptance and economic value of apples. The red coloration of the skin of an apple fruit is mainly attributed to anthocyanin pigmentation. Therefore, anthocyanin is key to improving our understanding of the genes and mechanisms involved in this trait.
In Europe, distinctness, uniformity, and stability (DUS) testing of fruit species is long and expensive compared to other crop sectors [1]. This process aims to determine whether a new variety is different from an existing variety within the same species (“distinctness”). Furthermore, it is used to determine whether distinctive traits are expressed uniformly (“uniformity”), and whether subsequent processes will change the phenotype of the generation (“stability”). The DUS test exists to allow new varieties to enter the market legally and allow plant breeders to protect their rights. Apple varieties appear to come about as clearly distinctive mutants, but certain apple mutants, for example derived from the “Gala” variety, may only show subtle phenotypic changes and are difficult to distinguish from each other, thus requiring long and expensive tests. To better distinguish these varieties, it is necessary to decipher the genetic or epigenetic origin of the skin color mutations, then to develop molecular genetic or epigenetic markers to help institutions such as the Community Plant Variety Office (CPVO) to accelerate testing of fruit species.
Recently, numerous studies have investigated the roles of genetics and epigenetics in apple skin color development. The aim of this review is to bring together the findings of these articles and summarize the genetic and epigenetic regulation of apple skin color. This review gives arguments in favor of the genetic and epigenetic explanatory models and gives an overview of the research frontier.
2. Anthocyanin Biosynthesis and Pigment Composition
Apple skin color is determined by the contents of anthocyanins, carotenoids, and chlorophyll, as well as their distribution over the skin surface. Anthocyanin content plays an important role in the degree of coloring of red apples. The content and distribution patterns of anthocyanins in the skin are responsible for the different color phenotypes. With the same anthocyanin content, a higher chlorophyll content will make the skin color dark red, whereas a lower content will cause the skin color to be bright red [2,3].
Anthocyanins are water-soluble flavonoids occurring naturally in plants and are widely distributed. Furthermore, anthocyanins are important in plants as secondary metabolites. So far, twenty-two major types of anthocyanins have been described in more than 250 species [4]. At present, five anthocyanin components have been studied extensively in the skin of apples: cyanidin-3-arabinoside, cyanidin-3-rutinoside, cyanidin 3-galactosides, cyanidin-3-xylosides, and cyanidin-3-glucosides [5]. Among these anthocyanins, cyanidin-3-galactoside was found to be the most abundant in apple skin, accounting for about 80% of the total anthocyanin content [4].
Anthocyanins play numerous roles in plants, most importantly in the reproductive organs. For example, anthocyanins can make flowers appear to be brightly colored to facilitate plant pollination [6]. In addition, anthocyanins can protect plants from low temperatures and other abiotic and biotic stresses [7]. Indeed, when plants are in a stressful environment, the accumulation of anthocyanins can have a protective role [8]. A well-known example is the reddening of the leaves of deciduous trees in autumn, induced by lower temperatures, to protect the plant from freezing damage [9]. In addition, studies have shown that anthocyanins can play an antioxidant role in plants; however, the proportion of anthocyanins with an antioxidant function in apples is only about 1–20% [10]. Anthocyanins are also an important indicator for evaluating fruit maturity. Generally, the content of anthocyanins will be relatively high when the fruit is mature.
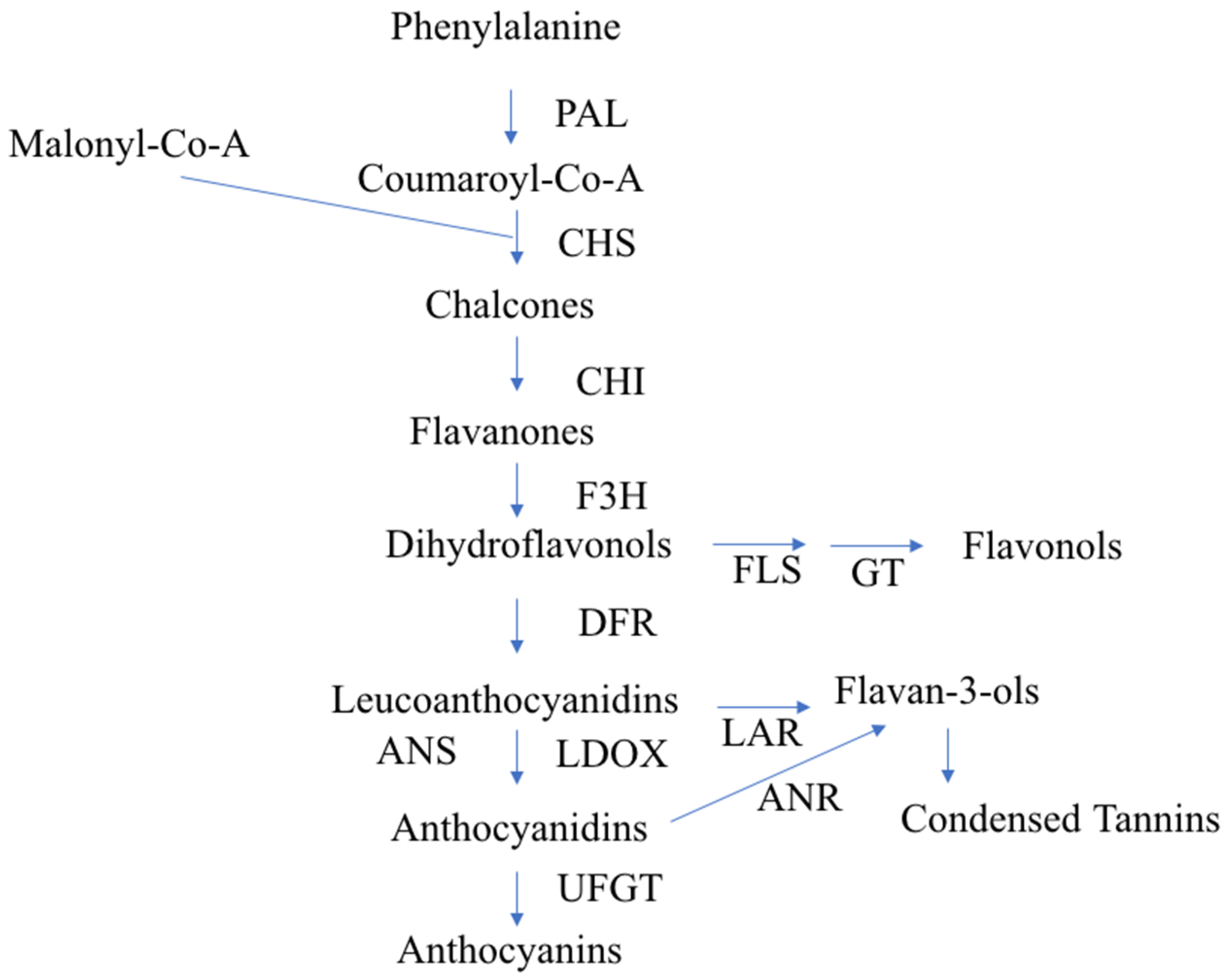
To study fruit color, we first need to inspect the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway. This pathway has already been studied in detail—it starts with the biosynthesis of phenylalanine with the help of different enzymes and transcription factors (TFs) [11] (Figure 1).
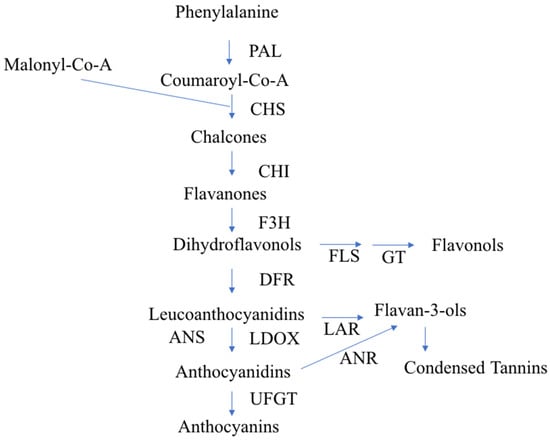
Figure 1.
Diagrammatic representation of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in apples, according to Takos et al. [14]. PAL, Phe ammonia lyase; CHS, Chalcone synthase; CHI, chalcone isomerase; F3H, flavanone-3 b-hydroxylase; DFR, dihydroflavonol-4-reductase; LDOX, leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase. UFGT, UDP-glycose: flavonoid-3-O-glycosyltransferase; FLS, flavonol synthase; GT, glycosyl transferase; LAR, leucoanthocyanidin reductase; ANR, anthocyanidin reductase.
The biosynthesis of anthocyanin pigments is influenced by two categories of genes. To the first category belong structural genes encoding enzymes, such as chalcone synthase (CHS), chalcone isomerase (CHI), flavanone-3-hydroxylase (F3H), dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (DFR), leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase (LDOX), and UDP-glucose: flavonoid-3-O-glycosyltransferase (UFGT). The second category comprises genes coding for regulatory proteins, which include a number of TFs that influence the intensity and pattern of anthocyanin accumulation. At least three protein families, namely MYB, bHLH, and WD40, are involved in the regulation of anthocyanin synthesis, but the specific classes and the genes involved in the biosynthesis vary depending on the species [12,13].
Anthocyanins can accumulate in leaves, roots, and stocks [15], while regulatory proteins which involve in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway are localized in the cytosol. After biosynthesis, flavonoids are transported to vacuoles or cell walls [16]. Anthocyanins are upregulated by maturity and the formation of flavonoids, especially anthocyanin and chlorogenic acid in apple skin, which influence growth regulators and fruit maturity [17]. The signals or metabolite biosynthesis which influence the maturity of fruits also influence anthocyanin accumulation. For example, plant hormones (abscisic acid, ethylene, jasmonates, auxin, gibberellin) have a crucial role in the regulation of fruit development and ripening. They interact with MYB–bHLH–WD40 complexes at either the transcriptional or the post-transcriptional level to control the anthocyanin composite [18]. Espley et al. [15] reported that the increased flux in the anthocyanin pathway was also associated with increases in metabolite concentrations of other polyphenols, including up to a 10-fold increase in quercetin-3-galactoside. Anthocyanins in the vacuole are degraded by peroxidases. The possible involvement of vacuolar peroxidases in anthocyanin degradation may be a component of the adaptation of plants to changing environmental conditions, such as decreased light intensities, but may also be a component of the plant developmental program [19].
Rootstocks also link with apple skin color. From the 20th century, much research has been conducted on the subject. In a study using seven rootstocks, Rogers [20] observed the best color on fruit from “Bramley” trees grafted on “M9”. Tukey and Brase [21] and Blair [22] observed that red-colored cultivars developed higher color on “M”. Hewetson [23] and Upshall [24] found that the increase in red fruit color intensity found on some Malling rootstocks was due to earlier maturity date [25]. The amount of total phenolic compounds and flavonoids increased, which may be due to the influence of different rootstocks and the incompatibility between the rootstock and the scion or grafting wound. In one study, “Bud 9” rootstock generally had a negative effect on the amount of anthocyanin, while M9 increased the amount of anthocyanin [26]. Grafting of “Bekran” on “Bekran” rootstock and “Red Delicious” cultivar on “Bekran” decreased the anthocyanin in scion leaves, but when “Bastam” cultivar was grafted on this rootstock it increased the amount of anthocyanin [26].
3. Genetic Determinants of Apple Skin Color
3.1. MYB Transcription Factors Regulate Apple Skin Color
The genetic mechanisms determining skin color in apple have been investigated in a number of studies [14,27,28]. MYB TFs have been reported to play an important role in plant secondary metabolism, especially the phenylalanine metabolism pathway. In particular, the well-studied MdMYB1, MdMYBA, and MdMYB10 genes code for TFs that were found to control the color of apple skin and flesh [14,27,28].
MdMYB1 (Md: Malus × domestica) is a TF isolated and identified from apples that regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple skins. The transcriptional abundance of this gene was strongly regulated by light and positively correlated with anthocyanin accumulation [14]. Another study confirmed that light can make the MdMYB1 protein more stable, and therefore can enhance the anthocyanin synthesis of apple skin [29]. A further finding was that the promoter region of MdMYB1 is rich in polymorphisms [14]. Based on these polymorphisms, a set of dCAPS markers was designed based on MdMYB1-1, which had a dominant effect on fruit skin color [14]. Apples that have MdMYB1-1 will exhibit a red-skinned phenotype, whereas those that do not have the MdMYB1-1 allele will have yellow or green skin [14]. However, this MdMYB1 dCAPS marker was unable to identify alleles of the MdMYB1 gene in “Fuji” apples [30].
In addition to MdMYB1, MdMYB10 and MdMYBA were isolated and found to be closely associated with the redness of apple skin and flesh [27,28]. Low temperature and UV-B (280 ~ 320nm) induced MdMYBA in different tissues. There were significant differences in expression levels between differently colored varieties [27]. Confirming its direct role in anthocyanin biosynthesis, it was shown that MdMYB10 overexpression could significantly enhance anthocyanin accumulation in transgenic apple seedlings [28].
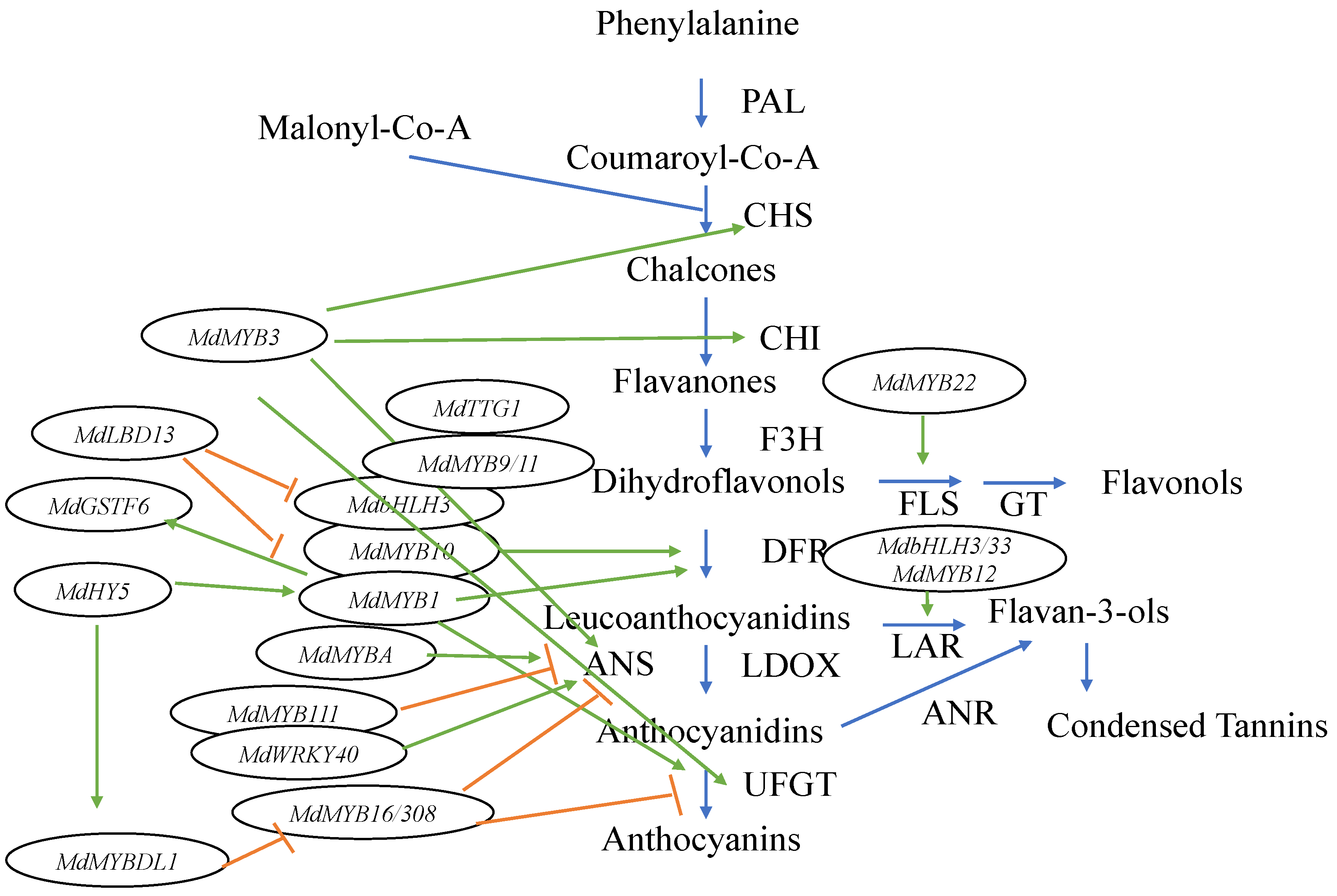
In recent research, the anthocyanin biosynthesis process has been proven to be more complex, with more genes, TFs, and interactions having been discovered. A number of other MYB TFs were found in the apple genome (Figure 2). Among them, MdMYB3 is involved in the transcriptional activation of several flavonoid biosynthesis pathway genes [31]. In addition, it not only regulates anthocyanin accumulation in the apple skin, but also participates in the regulation of flower development [31]. Recently, another MYB TF, MdMYB16, was described, which could form homodimers and directly inhibit anthocyanin synthesis through its C-terminal EAR (ethylene responsive element binding factor-associated amphiphilic repression) repressor [32]. MdMYB16 was shown to interact with a bHLH family TF MdbHLH33 to weaken inhibition of anthocyanin synthesis [32]. More recently, a light-responsive MYB-like gene called MdMYBDL1 was found [33]. It functions downstream of MdHY5, which coordinates light signal transduction and regulates the expression of flower color [33]. MdHY5 activates the expression of MdMYBDL1, while MdMYBDL1 inhibited the transcription of MdMYB16 and its homolog MdMYB308, which are inhibitors of anthocyanin biosynthesis in apples. This means that MdHY5 is able to promote anthocyanin biosynthesis in apples (Figure 2) [32]. These results indicate that MdHY5 enhances apple anthocyanins synthesis by acting on different types of MYB TFs [33]. In addition, MdMYB9 and MdMYB11 were found to bind to the promoters of structural genes, such as a bHLH TF MdbHLH3 and WD repeat protein TTG1 to regulate anthocyanin and PA accumulation [34]. Moreover, two putative flavonoid-related genes, MdMYB12 (proanthocyanidin-specific TF) and MdMYB22 (flavonol-specific TF), were found to directly facilitate the expression of leucoanthocyanidin reductase (LAR) and flavonol synthase (FLS), respectively [35]. MdMYB12 is thought to interact with bHLH3 and bHLH33, which are regulators of anthocyanin synthesis in apples [28], and to facilitate the expression of LAR and promote proanthocyanidin synthesis. Furthermore, MdMYB22 activates flavonol pathways by directly combining with the flavonol synthase (FLS) promoter [35]. Among the MYB TFs, MdMYB111 was found to bind the MYB recognition element (MRE) of the MdANS (anthocyanidin synthase) promoter and to potentially inhibit anthocyanin biosynthesis [36]. MdWRKY40 was found to form homodimers and to bind to the W box of the MdANS promoter. In addition, it was shown to reduce the inhibitory effect of MdMYB111 on anthocyanin biosynthesis. This means that both MdMYB111 and MdWRKY40 are important regulatory elements of the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway (Figure 2) [36].
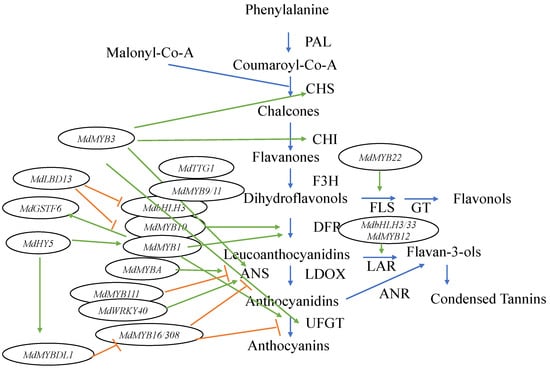
Figure 2.
Diagrammatic representation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway and the related TFs in apples. Green arrows indicate TFs activating enzymes in the pathway, while orange barred lines signify a TF inhibiting enzyme expression in the pathway.
In addition to MYBs, other TFs are involved in regulating anthocyanin synthesis and transport. Anthocyanins are biosynthesized on the cytosolic surface of the endoplasmic reticulum and are then transported into the vacuole for storage [37]. Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) are thought to be responsible for the transport of anthocyanins into the vacuole in apples [38]. MdGSTF6 encodes an important GST transporter of anthocyanins in apple fruit and its expression is activated by MdMYB1, providing evidence for the related regulatory mechanisms [39]. Therefore, MdMYB1 is thought to not only regulate anthocyanin synthesis, but also to control anthocyanin transport in apples [39]. A nitrate-induced LBD (lateral organ boundaries domain) TF gene, MdLBD13, has been discovered, which can repress anthocyanin biosynthesis by downregulating the expression of genes related to anthocyanin biosynthesis, such as MdMYB1, MdMYB9/11, and MdbHLH3/33, resulting in reduced anthocyanin accumulation [40]. MdLBD13 could, thus, play the role of a negative regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis [40].
In conclusion, MYB TFs, especially those encoded by MdMYB1, MdMYBA, and MdMYB10 genes, play important roles in the regulation of apple skin color [14,27,28]. However, a number of other MYB family genes also control the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway, such as the aforementioned MdMYB3, MdMYB9, MdMYB11, MdMYB12, MdMYB16, MdMYB22, MdMYBDL1, MdMYB111, and MdMYB308. Their effects in the anthocyanin pathway are shown in Figure 2.
3.2. Genetic Mapping
Since the 1990s, numerous quantitative genetics studies on apples have allowed the location of a huge number of quantitative trait loci (QTL) and major genes linked to the major agronomical traits. Amongst these, only a few were concerned with polyphenol compounds [41,42,43]. A small number of genetic studies have been performed to decipher red pigmentation in apple. Since apple skin color is one of the main factors defining the commercial value of apples, several genetic studies have been performed to decipher its locations in the genetic maps of apples. These studies have been performed thanks to the availability of different kinds of molecular markers, such as single sequence repeats (SSRs) [44]. However, the bulk of the studies used single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) [41,45,46,47], which are the most abundant type of DNA sequence polymorphisms [48]. These were based on different origins and kinds of plant materials, such as segregating populations [41,45,46,49] and cultivar populations, through genome wide analysis studies (GWAS). The results of all these studies are convergent, showing that MdMYB10 and MdMYB1 are the two main transcription factors involved in the regulation of red skin color in apples [44]. As MdMYB1 and MdMYBA share identical sequences and MdMYB10 and MdMYB1 genes are located at very similar positions, sharing 98% homology on linkage group 9, it was concluded that these genes were allelic [27,28,50,51]. In addition, MYB TFs also influence red-flesh apples, of which there are normally two types. In type 1, red pigmentation is observed from the fruit set through to maturity, exhibiting red fruit skin, leaves, stems, roots, and flowers. In type 2, red pigmentation is only present in the fruit cortex at the late stage of fruit development and the leaves are green [52,53]. Differences in anthocyanin accumulation in the red flesh type 2 apples have been associated with one SNP marker close to the MdMYB10 homolog MdMYB110a, which is physically located on LG 17 [52].
The last genetic mapping results identified alleles of SSRs and SNPs markers that could be used in molecular assisted breeding [42,44,45,47]. However, these studies cannot assist in the distinction of apple mutants (e.g., Gala), which show very tiny differences in skin coloration. For this, new approaches need to be developed.
3.3. Copy Number Variations
Copy number variations (CNVs) are defined as deletions, duplications, or insertions of DNA sequence fragments longer than 50 base pairs in length [54]. CNVs have the potential to influence genes by altering their structure and expression [55]. CNVs are a common feature of plant genomes that include non-global duplication and deletion events [55].
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have greatly facilitated the discovery of CNVs [56]. Using NGS data, copy number variable regions (CNVRs) within the apple genome were detected, as well as examined for their distribution and impact [55]. In total, 876 CNVRs accounting for 3.5% of the apple genome were identified. The enrichment of the CNVRs with gene loci of agronomical significance has drawn attention to these newly discovered forms of genetic variation in apples [55].
Notably, some MYB TFs were found to have CNVs that could be linked to apple fruit coloration. For instance, a rearrangement in the upstream regulatory region of the gene encoding the MdMYB10 was detected [57]. This rearrangement includes a series of multiple repeats, forming a microsatellite-like structure, featuring five direct tandem repeats of a 23 bp sequence. This MdMYB10 rearrangement was only present in red-fleshed apple varieties and was not observed in white-fleshed varieties. Transient analysis showed that the 23 bp sequence motif is a target for the MdMYB10 protein itself, and the number of repeat units is related to the increase in transactivation by MdMYB10 [57]. The red-fleshed phenotype is also associated with enhanced expression of MdMYB110a (paralog of MdMYB10) [52]. Functional characterization of MYB110a showed that it could upregulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). MdMYB10 (LG 9) and MdMYB110a (LG 17) have conserved functions in some varieties, but their expression and response to fruit maturity are different. MdMYB10 was found to be expressed in apple skin, flesh, and foliage, while MdMYB110a was found to only be expressed in the fruit cortex [52]. Other anthocyanin-related MYBs were selected from a number of plant species, including apple, pear, strawberry, petunia, kiwifruit, and Arabidopsis thaliana, to initiate promoters containing the R6 motif, which has six minisatellite repeat units thought to increase anthocyanin pigmentation [58]. Insertion of the apple R6 motif into the MYB10 orthologous promoter of pear (PcMYB10) and Arabidopsis (AtMY75) was able to increase anthocyanin levels [58].
In conclusion, copy number differences could be used as markers for apple color, especially MdMYB10 and MdMYB110a (summarized in Table 1).

Table 1.
Overview of CNVs for apple color characteristics.
3.4. Transposable Elements
Transposable elements (TEs) are ubiquitous mobile genetic factors that can make up more than 50% of a plant’s nuclear genome [59]. They can be divided into two broad classes according to their method of proliferation [60,61]. Class I elements transpose by reverse transcription of RNA intermediates, and once inserted into a new location in the genome they cannot be removed [60,61]. This class includes retrotransposons and potential retroviruses with long terminal repeats (LTR), as well as non-LTR elements, including long and short interspersed nuclear elements (LINE and SINE, respectively) and processed pseudogenes [60,61]. Class II elements (also called DNA transposons) can be excised and inserted, and thus move from one nuclear position to another [60,61]. Some coding factors mediate their own transposition, while others are non-autonomous, depending on the activity of the transposase encoded at a separate site [60,61,62].
TEs are usually methylated via small RNAs, and this methylation can extend to surrounding genes, making them inactive [63,64]. The role played by retrotransposons in plant genomes is well known—by self-replication and insertion into multiple genomic sites [65,66], they have an influence on the size, structure, function, and evolution of plant genomes. Retrotransposons, thus, are an important source of genetic diversity; they may cause changes that could lead to genetic variations within plant species [66,67].
TEs account for 60% of the apple genome in the final assembly and provide insights into its evolution [68]. LTR retrotransposons (LRNs) are the most abundant type of TEs [69,70]. There is evidence that TEs affect the appearance of some genetic variation in the color of pome fruits [71]. Recently, a gypsy-like LTR retrotransposon (denoted as redTE) was found inserted in the upstream of the MdMYB1 promoter and could be associated with red coloration [72]. The redTE controlled the development of red coloration by lowering the threshold of light response. This insertion appears in the HFTH1 (“Hanfu”, which has bright red skin color) genome and is located −3297 bp upstream of the ATG initiation codon of MdMYB1 [72]. This redTE has two target site duplications (TSDs) and two identical flanking LTR sequences (1274 bp). Furthermore, redTE-mediated control of anthocyanin distribution patterns manipulates MdMYB1 function through the creation of genetic and epigenetic alleles under natural conditions [72].
It is noteworthy that TEs were found to be associated with coloration in other fruit species. For example, in blood oranges, two different TE inserts are responsible for the cold-induced Ruby expression, thereby regulating fruit color [73]. In grapes, a Gypsy-like retrotransposon called Gret1 inhibited the expression of MYBA1, while the retrotransposon is linked with the development of white-skinned berries [74,75]. The recombination between Gret1 LTRs caused some restoration of MYB gene function and blush-skinned sports, including “Flame Muscat” and “Chardonnay Rose” [73,76]. Furthermore, it remains to be seen whether similar redTE insertions could enhance MYB transcription in other Rosaceae fruit species [72,73]. These findings strongly suggest that TE insertions may also play key roles in influencing traits of interest in apples.
In conclusion, redTE-mediated control of the distribution patterns of anthocyanin accumulation is exerted through the creation of genetic and epigenetic alleles that manipulate the function of MdMYB1 under natural conditions. This suggests that some TEs and retrotransposon elements are linked with the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway in apple skin. Therefore, we will next look at the epigenetic determinants of apple skin color.
4. Epigenetic Determinants of Apple Skin Color
In addition to genetic factors, some epigenetic factors can also affect apple skin color. Epigenetics describe mitotically or meiotically heritable variations in gene expression that cannot be explained by changes in DNA sequence [77,78,79]. Thus, epigenetics refers to the study of heritable changes in gene transcription that do not involve changes in the DNA sequence. Epigenetic marks can be transferred from one generation to the next [79,80]. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression is achieved through DNA methylation and specific histone modifications [79,81].
4.1. DNA Methylation and Demethylation
DNA methylation can be highly stable and inherited in a mendelian manner. This was demonstrated by experiments with 30 consecutive generations of plants in Arabidopsis thaliana [79,82]. In plants, DNA methylation has three sequence contexts: CG, CHG, and CHH (H = A, T, or C) [83]. One of the key activities of DNA methylation is the silencing of TFs to prevent their transcription and mobility.
Emerging evidence suggests that a modification in DNA methylation is also important for the ripening of fleshy fruits [84]. In tomatoes, the VTE3 gene regulates the vitamin E content in fruits. VTE3 expression is linked with the TE methylation level in the promoter region [85]. In sweet oranges, a DNA methylation inhibitor, by stopping further increase in DNA methylation, could prevent fruit from degreening [86]. Some studies have investigated the role of epigenetics in apples, comparing specific varieties and their mutants that produce fruit with a stable pigment pattern or different skin phenotypes, respectively. For example, mutants of “Honeycrisp” or “Fuji” can produce fruit with two different kinds of patterns,—striped and blushed. In “Honeycrisp”, DNA methylation at the MdMYB10 promoter was detected’ increased DNA methylation levels were observed in green stripes, and a 900 bp long sequence, starting 1400 bp upstream of the translation start site, was highly methylated in MdMYB10 [71]. Another example concerns varieties derived from “Gala”, with “Kidd’s D-8” (KID) being the red-skinned mutant and “Blondee” (BLO) being the yellow-skinned mutant [38]. Two regions, MR3 and MR7, exist in the MdMYB10 promotor that showed significant differences between BLO and KID. Methylation was found to be higher and gradually increased during fruit development of BLO, whereas in KID it was lower and constant. The higher levels of DNA methylation reduced MdMYB10 transcription, and thus anthocyanin production [38]. In “Hanfu”, DNA was also methylated in the MR3 and MR7 regions in MdMYB1; in the MR8-MR11 regions, the degree of methylation of redTE was high. This suggests that redTE-induced epigenetic changes may be related to variable color patterns [72].
DNA methylation could modify both regulatory and structural genes in the anthocyanin pathway. In apple skin, differential changes in methylation patterns related to anthocyanin concentrations have been reported [87]. Two differentially methylated regions (DMRs) and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were linked to the anthocyanin pathway: MdANS and MdF3H. These genes were up regulated in apple mutants, and differences in the methylation patterns of their promoters were observed [87]. The transcription of structural genes may be regulated by both changes in TF levels and DNA methylation. Additionally, the expression of the TF MdMYB114 was upregulated in deep-skinned apples [87]. In “Fuji”, the methylation in three ‘mutants with different colors was detected, and it was found that the CHH methylation level in the MR3 region (–1246 to –780) of the MdMYB1 promoter was negatively correlated with MdMYB1 expression [88]. MdAGO4, which plays a key role in RNA-directed DNA methylation, is required for CHH methylation, which was found to interact with the MdMYB1 promoter. The promoter of MdMYB1 was found to be methylated through binding of MdAGO4 to this gene’s promoter, thereby regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis [88].
Methylation of cytosine in the genome of eukaryotes is often related to repeats, including TEs and their derivatives. Such sequences are usually enriched in centromeres and their vicinity [79]. It was confirmed that the differential accumulation of MdMYB1-specific mRNA was causing the difference in anthocyanin levels between “Granny Smith” and “Golden Delicious” [89]. The methylation level of the promoter region was linked to different levels of MdMYB1 transcripts in the two varieties. The formation of red pigment in the skin of “Granny Smith” is related to the hypomethylation of the MdMYB1 promoter [89].
Whole-genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS) is a useful method of detection for methylation differences between different color mutants. Using this method, Li et al. [90] found the methylation relationship between Red Delicious (G0) and its four-generation bud sport mutants (G1 to G4) [90]. The phenotypes of the mutants were different and the pigmentation in the apple skin gradually increased from G0 to G4 [91]. The phenotype of these mutants in Red Delicious was obviously linked with the difference in DNA methylation [90]. Furthermore, in some flavonoid biosynthetic pathway genes (including CHS, PAL, F3’H, PER, 4CL, CYP98A, and CCoAOMT), the mCHG and mCG contexts are hypomethylated; the mCHG contexts upstream of MdMYB10 especially cause the transcriptional activation and increase anthocyanin accumulation. However, the methylation of the mCG context upstream of bHLH74 causes transcriptional repression and inhibits the accumulation of anthocyanin [90]. In summary, methylation is linked with apple skin coloration and patterning. Furthermore, higher levels of DNA methylation reduced MdMYB10 expression, and thus anthocyanin production [88].
In addition to accumulation of DNA methylation having an influence on the anthocyanin pathway, demethylation is also linked to its regulation. Bagging treatment could induce epigenetic changes. Ma et al. [89] compared DNA methylation levels in the 2 kb upstream region of MdMYB1 in bag-treated apples after removal of the bags and unbagged controls. There was a correlation between hypomethylation and the red-skinned phenotype in “Granny Smith” apples [89]. Granny Smith fruits responded to treatment with an inhibitor of DNA methylation, 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-aza-dC), an analog of cytosine that can inhibit the activity of DNA methyltransferases. These drug treatments effectively limited DNA methylation and induced color phenotype variants [92,93]. In Granny Smith, after bag removal and 5-aza-dC treatments, some MdMYB1 promoter regions showed reduced DNA methylation. This could indicate a 5-aza-dC-treatment-induced activation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Granny Smith skin [89]. Ma et al. [94] performed another study in the same year to compare the transcriptomes of Granny Smith skin with and without 5-aza-dC treatment after bagging [94]. They found many differentially expressed genes through 5-aza-dC-treated and non-treated apples, including TF genes and anthocyanin accumulation-related genes. Demethylation treatments were linked to differential gene expression, while the regulatory mechanisms were associated with red pigmentation in “Granny Smith” apples and other non-red apple fruits [94]. Demethylation also enhanced the expression of MdMYB1-2 and MdMYB1-3 and induced the accumulation of anthocyanin in “Mutsu”, which was obtained from a yellow-skinned cultivar [95]. Some cases of demethylation were documented for Fuji mutants. Usually, Fuji fruit exhibit a striped pattern; however, “Beni Shogun”, one of its mutants, has blushed skin. The difference in methylation between Fuji and Beni Shogun was linked to reduced DNA methylation at MR7 in the MdMYB10 promoter, which increased full redness in the skin of these apples [96].
From this part, we can conclude that both gain and loss of DNA methylation can influence the anthocyanin pathway (Table 2). Furthermore, DNA methylation might inhibit anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple skin, while demethylation seems to induce it. However, epigenetic levels are different in different organizations and in different developmental stages in plants [97]. The methylation is inherited but is less stable which depending upon the environment [97]. For example, the chestnut methylation level decreases with the age of the tree [98]. Epialleles or epimutations can generate stable and heritable changes of fruit phenotypes [99]. However, in some situations epialleles could be less stable and the apple mutant skin color could revert to the original apple color; the reason causing this change is still unknown. These scientific questions still need to be researched in the future.

Table 2.
Overview of methylation and demethylation in apple color characteristics.
4.2. Histone Modifications
In recent years, there has been evidence suggesting that a conserved histone H2 variant, H2A.Z, and histone methylation are associated with the regulation of gene transcription in different organisms throughout the genome [100,101]. However, little is known about the roles of these two types of epigenetic regulation in the control of anthocyanin biosynthesis. The conserved histone H2 variant, H2A.Z, negatively controls the accumulation of anthocyanin in Arabidopsis [102]. H2A.Z and H3K4me3 have an antagonistic effect on the transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes, which highlights a role of chromatin in gene regulation and reflects the complexity of gene regulatory mechanisms [102].
Bagging treatment could induce epigenetic changes and the histone levels could be different in different regions of transcribed genes. This treatment was able to turn the normally non-red apple variety “Mutsu” into a red one. Furthermore, the histone H3K4me3 was found to be higher in the 5′ upstream region of MdMYB1-2/-3, while H3k27me3 was lower [95]. H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 in the 5′ upstream region of MdMYB1-2/-3 were associated with the paper-bagging-induced red pigmentation. The modifications of the H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 could induce the expression of MdMYB1-2/-3 in some regions [95].
An example for the link between histones and anthocyanin accumulation can be found in Arabidopsis. A HD-ZIP II TF HAT1 negatively regulates the accumulation of anthocyanin through post-translational regulation of the MYB-bHLH-WD40 (MBW) protein complex [103]. MYB75 was found to form a transcriptional repressor complex with HAT1-TPL through the deacetylation of histone H3 at the target gene in Arabidopsis [103]. It was indicated that HAT1 inhibited the formation of MBW protein complexes and recruited TPL core inhibitors to epigenetically regulate the anthocyanin late biosynthesis genes (LBGs), thereby inhibiting the activity of MBW protein complexes, and thus anthocyanin accumulation [103]. In maize, the basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) protein R interacts with the MYB TF C1 and R-interacting factor 1 (RIF1) to form a C1-R-RIF1 complex [104]. This complex binds to the A1 promoter and activates A1 expression through increasing H3K9 and H3K14 acetylation levels in the promoter region [104].
In conclusion, identifying the interaction between MBW protein complexes and epigenetic regulators remains challenging [103]. How the histones regulate structural genes or TFs in the anthocyanins biosynthetic pathway in apple skin is still a complex question and an interesting subject that needs to be studied by subsequent researchers.
4.3. Small RNAs
Recently, in various organisms, small RNAs (sRNAs) have been identified as key genetic and epigenetic regulators, being involved in histone methylation and DNA modification to regulate the abundance of coding or non-coding RNAs [105]. In plants, microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are the main regulatory RNA species [105]. The former are mainly involved in post-transcriptional regulation, while the latter are linked with transcriptional regulation [105]. Many of these characteristic sRNAs are related to numerous biological programs, processes, and pathways in response to developmental cues, environmental stress, pathogen infection, and pest infestation [105].
In apples, miR828 and miR858 regulate a large number of MYB genes through targeting the region encoding the conserved R3 domain of the MYB protein [106]. MiR828 triggered the targeting of MYB genes to produce secondary phasiRNAs (phased siRNAs), thereby enhancing its silencing effect. Most MYBs for miR828 are linked with primary and secondary metabolism related to anthocyanin production [106]. Among them, there are nine MYBs co-targeted by miR828 and miR858, which are involved in the regulation of proanthocyanidin biosynthesis [106]. Xia et al. [106] conducted an analysis of 81 MYBs—29 MYBs were identified as targets, most of which are mainly involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis [106]. In tomato, miR858 plays a negative role in anthocyanin biosynthesis—blocking miR858 can increase the accumulation of anthocyanin by regulating the expression of SlMYB7 and SlMYB4861 [107].
The RdDM pathway could influence fruit coloration in different apple mutants. Jiang et al. [88] systematically studied the causes of coloring differences in different apple bud varieties and found that there was a significant negative correlation between the content of anthocyanin in the skin and the CHH methylation level of the TF MdMYB1 promoter. CHH methylation is primarily mediated by the RdDM pathway [88]. The RdDM pathway AGO protein MdAGO4-1/2 was found to interact with the apple MdMYB1 promoter. In the apple callus, overexpression of MdAGO4s and MdDRM2s can increase the CHH methylation level at the MdMYB1 promoter, thus affecting the accumulation of anthocyanins in apples [88]. In summary, apple MdAGO4s bind to ABS (AGO4 binding site) on the MdMYB1 promoter, recruit the DNA methyltransferase MdDRM2, and exert a DNA methylation function. On the other hand, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) mediate the methylation of MdAGO4 binding site, thereby modifying the MdMYB1 promoter, affecting its expression and regulating fruit color [88].
lncRNA could also be linked to anthocyanin biosynthesis in apples [108]. During light-induced rapid anthocyanin accumulation, RNA-seq analysis of apple skin of the “Red Fuji” variety revealed 5297 putative lncRNAs [108]. Differential expression analysis further showed that lncRNAs involved in photosynthesis during light treatment were transcribed [108]. It was predicted that two differentially expressed lncRNAs, MLNC3.2 and MLNC4.6, are potential endogenous target mimics (eTMs) for miRNA156a, which can prevent cleavage of SPL2-like and SPL33 during light-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis [108]. SPL (squamosa promoter-binding protein-like) interacts with MYB TFs and coordinates the biosynthesis of anthocyanins during the exposure of apple skin [108]. This research provides basic insights into the involvement of lncRNA in anthocyanin biosynthesis pathways of apple fruits [108].
In conclusion, small RNAs are now widely recognized as key genetic and epigenetic regulatory factors in various organisms and biosynthesis pathways, including that of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Small RNAs such as miR828 and miR858 seem to synergistically regulate a large number of MYB genes by directly targeting the region encoding the conserved R3 domain of the MYB protein.
5. Conclusions
In this review, we have summarized the recent research on the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms affecting the buildup of apple skin color. Most studies have investigated the genetic part of fruit coloring, with a focus on the genes in the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway, such as the MdMYB1 gene, which is linked with apple skin color. However, evidence on the role of epigenetics in the development of fruit color and patterns is now mounting. A number of tasks remain to be performed in the future—this review has shown a surprisingly large variety of regulatory mechanisms involved in a host of different genetic and epigenetic factors underlying the expression of skin coloration in apple fruit. Although the number of studies dedicated to the topic is impressive, more work still needs to be performed to clarify the roles of certain factors, especially when mechanisms seem to be redundant or complementary. In addition, from a more practical point of view, breeding of certain apple varieties would benefit from the development of genetic and epigenetic markers. This would allow apple breeders to better and more reliably distinguish apple mutants, saving them time and money.
Author Contributions
W.W. wrote the manuscript. J.-M.C., G.B.-S., S.B., E.B., and F.L. reviewed and edited previous versions of the manuscript. G.B.-S. proofread the submitted version. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Community Plant Variety Office (CPVO), an agency of the European Union. W.W. received a personal PhD fellowship from the China Scholarship Council (No. 201706350142).
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to the members of thesis committee for helpful advice in writing this review: Andrea Patocchi, Charles-Eric Durel, David Rousseau, Mohamed Zouine, and Sylvain Guyot. All help is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| 5-aza-dC | 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine |
| ANS | Anthocyanidin synthase |
| CHI | Chalcone isomerase |
| CHS | Chalcone synthase |
| CNV | Copy number variation |
| CNVRs | Copy number variable regions |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| DFR | Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase |
| DMG | Differentially methylated genes |
| DMR | Differentially methylated regions |
| DUS | Distinctness, uniformity, and stability |
| eTMs | Endogenous target mimics |
| F3H | Flavanone-3-hydroxylase |
| FLS | Flavonol synthase |
| GSTs | Glutathione S-transferases |
| LAR | Leucoanthocyanidin reductase |
| LDOX | Leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase |
| LINE, SINE | Long and short interspersed nuclear elements |
| lncRNA | Long non-coding RNA |
| LRNs | LTR retrotransposons |
| LTR | Long terminal repeats |
| miRNAs | MicroRNAs |
| MRE | MYB recognition element |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| PA | Proanthocyanidin |
| phasiRNAs | Phased siRNAs |
| QTL | Quantitative trait locus |
| RdDM pathway | RNA-directed DNA methylation pathway |
| siRNAs | Small interfering RNAs |
| SNPs | Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms |
| sRNAs | Small RNAs |
| TE | Transposable elements |
| TF | Transcription factor |
| TSDs | Target site duplications |
| UFGT | UDP-glucose: flavonoid-3-O-glycosyltransferase |
| WGBS | Whole-genome bisulfite sequencing |
References
- Habben, J.; Schulte, E. Plant breeders’ rights for new fruit cultivars. Acta Hortic. 2000, 538, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, R.N.; Lee, S.K. Influence of chlorophyll, internal ethylene, and PAL on anthocyanin synthesis in “Fuji” apple. J. Korean Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1995, 36, 361–370. [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster, J.E.; Grant, J.E.; Lister, C.E.; Taylor, M.C. Skin Color in Apples—Influence of Copigmentation and Plastid Pigments on Shade and Darkness of Red Color in Five Genotypes. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1994, 119, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treutter, D. Biosynthesis of phenolic compounds and its regulation in apple. Plant Growth Regul. 2001, 34, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Yehudah, G.; Korchinsky, R.; Redel, G.; Ovadya, R.; Oren-Shamir, M.; Cohen, Y. Colour accumulation patterns and the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in “Red Delicious” apple variants. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipollini, M.L.; Levey, D.J. Antifungal activity of Solanum fruit glycoalkaloids: Implications for frugivory and seed dispersal. Ecology 1997, 78, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyn, W.J.; Wand, S.J.E.; Jacobs, G.; Rosecrance, R.C.; Roberts, S.C. Evidence for a photoprotective function of low-temperature-induced anthocyanin accumulation in apple and pear peel. Physiol. Plant. 2009, 136, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, W.A.; Singsaas, E.L.; McCown, B.H. Resorption Protection. Anthocyanins Facilitate Nutrient Recovery in Autumn by Shielding Leaves from Potentially Damaging Light Levels. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W. Anthocyanins in autumn leaf senescence. Adv. Bot. Res. 2002, 37, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, R.; Yang, R.; Xie, S.; Sockovie, E.; Khanizadeh, S. Which polyphenolic compounds contribute to the total antioxidant activities of apple? J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4989–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takos, A.M.; Ubi, B.E.; Robinson, S.P.; Walker, A.R. Condensed tannin biosynthesis genes are regulated separately from other flavonoid biosynthesis genes in apple fruit skin. Plant Sci. 2006, 170, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broun, P. Transcription factors as tools for metabolic engineering in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hichri, I.; Deluc, L.; Barrieu, F.; Bogs, J.; Mahjoub, A.; Regad, F.; Gallois, B.; Granier, T.; Trossat-Magnin, C.; Gomès, E.; et al. A single amino acid change within the R2 domain of the VvMYB5b transcription factor modulates affinity for protein partners and target promoters selectivity. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takos, A.M.; Jaffe, F.W.; Jacob, S.R.; Bogs, J.; Robinson, S.P.; Walker, A.R. Light-Induced Expression of a MYB Gene Regulates Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Red Apples. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 1216–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espley, R.V.; Bovy, A.; Bava, C.; Jaeger, S.R.; Tomes, S.; Norling, C.; Crawford, J.; Rowan, D.; McGhie, T.K.; Brendolise, C.; et al. Analysis of genetically modified red-fleshed apples reveals effects on growth and consumer attributes. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2013, 11, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koes, R.; Verweij, W.; Quattrocchio, F. Flavonoids: A colorful model for the regulation and evolution of biochemical pathways. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.A.; De Jager, A. Formation of flavonoids, especially anthocyanin and chlorogenic acid in “Jonagold” apple skin: Influences of growth regulators and fruit maturity. Sci. Hortic. 2002, 93, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakola, L. New insights into the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in fruits. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipor, G.; Duarte, P.; Carqueijeiro, I.; Shahar, L.; Ovadia, R.; Teper-Bamnolker, P.; Eshel, D.; Levin, Y.; Doron-Faigenboim, A.; Sottomayor, M.; et al. In planta anthocyanin degradation by a vacuolar class III peroxidase in Brunfelsia calycina flowers. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, W.S. Rootstock effect on colour and size of apples. Rep. East Malling Res. Stn. 1926, 2, 16–32. [Google Scholar]
- Tukey, H.B.; Brase, K.D. Three year performance of sixteen varieties of apples on Malling IX rootstocks Proc. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci 1941, 38, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, D.S. Rootstock and scion relationship in apple trees. Sci. Agric. 1938, 19, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Hewetson, F.N. Growth and yield of McIntosh apple trees as influenced by the use of various intermediate stem pieces. Proc. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1944, 45, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Upshalli, W.H. Malling Stocks and French Crab Seedlings as Stocks for Five Varieties of Apples. III. Sci. Agric. 1943, 23, 537–545. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, F.E.; Fritts, R.; Olsen, K.L. Rootstock influence on “delicious” and “golden delicious” apple fruit quality at harvest and after storage. Sci. Hortic. 1985, 26, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvaneh, T.; Abedi, B.; Davarynejad, G.H.; Ganji Moghadam, E. Enzyme activity, phenolic and flavonoid compounds in leaves of Iranian red flesh apple cultivars grown on different rootstocks. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 246, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Y.; Honda, C.; Hatsuyama, Y.; Igarashi, M.; Bessho, H.; Moriguchi, T. Isolation and functional analysis of a MYB transcription factor gene that is a key regulator for the development of red coloration in apple skin. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007, 48, 958–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; Putterill, J.; Stevenson, D.E.; Kutty-Amma, S.; Allan, A.C. Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J. 2007, 49, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Mao, K.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Shu, H.R.; Hao, Y.J. MdCOP1 ubiquitin E3 ligases interact with MdMYB1 to regulate light-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis and red fruit coloration in apple. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Xin, L.; Zhou, G.; Li, L.; Shen, G. Analysis of the MdMYB1 gene sequence and development of new molecular markers related to apple skin color and fruit-bearing traits. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimolmangkang, S.; Han, Y.; Wei, G.; Korban, S.S. An apple MYB transcription factor, MdMYB3, is involved in regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis and flower development. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wang, N.; Liu, J.; Qu, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Lu, N.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. The molecular mechanism underlying anthocyanin metabolism in apple using the MdMYB16 and MdbHLH33 genes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 94, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Jiang, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, N.; Jiang, S.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.L.; et al. MdMYBDL1 employed by MdHY5 increases anthocyanin accumulation via repression of MdMYB16/308 in apple. Plant Sci. 2019, 283, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.H.; Tian, Y.; Chen, K.Q.; Liu, X.J.; Liu, D.D.; Xie, X.-B.; Cheng, C.G.; Cong, P.H.; Hao, Y.J. MdMYB9 and MdMYB11 are involved in the regulation of the ja-induced biosynthesis of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin in apples. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Xu, H.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, N.; Qiu, H.; Qu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, X. MYB12 and MYB22 play essential roles in proanthocyanidin and flavonol synthesis in red-fleshed apple (Malus sieversii f. niedzwetzkyana). Plant J. 2017, 90, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Yang, G.; Wang, N.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Molecular mechanism of MYB111 and WRKY40 involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in red-fleshed apple callus. Plant Cell. Tissue Organ Cult. 2019, 139, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, J.R. Arabidopsis TT19 functions as a carrier to transport anthocyanin from the cytosol to tonoplasts. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharkawy, I.; Liang, D.; Xu, K. Transcriptome analysis of an apple (Malus × domestica) yellow fruit somatic mutation identifies a gene network module highly associated with anthocyanin and epigenetic regulation. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 7359–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, M.; He, N.; Chen, X.; Wang, N.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Fang, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. MdGSTF6, activated by MdMYB1, plays an essential role in anthocyanin accumulation in apple. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H.; Liu, X.; An, J.P.; Hao, Y.J.; Wang, X.F.; You, C.X. Cloning and elucidation of the functional role of apple MdLBD13 in anthocyanin biosynthesis and nitrate assimilation. Plant Cell. Tissue Organ Cult. 2017, 130, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagné, D.; Krieger, C.; Rassam, M.; Sullivan, M.; Fraser, J.; André, C.; Pindo, M.; Troggio, M.; Gardiner, S.E.; Henry, R.A.; et al. QTL and candidate gene mapping for polyphenolic composition in apple fruit. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClure, K.A.; Gong, Y.; Song, J.; Vinqvist-Tymchuk, M.; Campbell Palmer, L.; Fan, L.; Burgher-MacLellan, K.; Zhang, Z.; Celton, J.-M.; Forney, C.F.; et al. Genome-wide association studies in apple reveal loci of large effect controlling apple polyphenols. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunemann, F.; Kahnau, R.; Stange, I. Analysis of complex leaf and flower characters in Rhododendron using a molecular linkage map. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1999, 98, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, S.; Kunihisa, M.; Okada, K.; Shimizu, T.; Honda, C.; Yamamoto, T.; Muranty, H.; Denancé, C.; Katayose, Y.; Iwata, H.; et al. Allelic composition of MdMYB1 drives red skin color intensity in apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.) and its application to breeding. Euphytica 2017, 213, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagné, D.; Kirk, C.; How, N.; Whitworth, C.; Fontic, C.; Reig, G.; Sawyer, G.; Rouse, S.; Poles, L.; Gardiner, S.E.; et al. A functional genetic marker for apple red skin coloration across different environments. Tree Genet. Genomes 2016, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, K.M.; Brown, P.; Cooke, T.F.; Cann, S.; Costa, F.; Bustamante, C.; Velasco, R.; Troggio, M.; Myles, S. Fast and Cost-Effective Genetic Mapping in Apple Using Next-Generation Sequencing. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2014, 4, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, L.; Iglesias, I.; Micheletti, D.; Troggio, M.; Kumar, S.; Volz, R.K.; Allan, A.C.; Chagné, D.; Gardiner, S.E. Feasibility of genome-wide association analysis using a small single nucleotide polymorphism panel in an apple breeding population segregating for fruit skin color. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2014, 139, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijavetzky, D.; Cabezas, J.; Ibáñez, A.; Rodríguez, V.; Martínez-Zapater, J.M. High throughput SNP discovery and genotyping in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) by combining a re-sequencing approach and SNPlex technology. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagné, D.; Carlisle, C.M.; Blond, C.; Volz, R.K.; Whitworth, C.J.; Oraguzie, N.C.; Crowhurst, R.N.; Allan, A.C.; Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; et al. Mapping a candidate gene (MdMYB10) for red flesh and foliage colour in apple. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin-Wang, K.; Bolitho, K.; Grafton, K.; Kortstee, A.; Karunairetnam, S.; Mcghie, T.K.; Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; Allan, A.C. An R2R3 MYB transcription factor associated with regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Rosaceae. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Evans, K.; Peace, C. Utility testing of an apple skin color MdMYB1 marker in two progenies. Mol. Breed. 2011, 27, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagné, D.; Lin-Wang, K.; Espley, R.V.; Volz, R.K.; How, N.M.; Rouse, S.; Brendolise, C.; Carlisle, C.M.; Kumar, S.; De Silva, N.; et al. An Ancient Duplication of Apple MYB Transcription Factors Is Responsible for Novel Red Fruit-Flesh Phenotypes. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volz, R.; Oraguzie, N.; Whitworth, C.; How, N.; Chagné, D.; Carlisle, C.; Gardiner, S. Red flesh breeding in apple—Progress and challenges. Acta Hortic. 2009, 814, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girirajan, S.; Campbell, C.D.; Eichler, E.E. Human Copy Number Variation and Complex Genetic Disease. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2011, 45, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boocock, J.; Chagné, D.; Merriman, T.R.; Black, M.A. The distribution and impact of common copy-number variation in the genome of the domesticated apple, Malus × domestica Borkh. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, R.K.; Nayak, S.N.; May, G.D.; Jackson, S.A. Next-generation sequencing technologies and their implications for crop genetics and breeding. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espley, R.V.; Brendolise, C.; Chagné, D.; Kutty-Amma, S.; Green, S.; Volz, R.; Putterill, J.; Schouten, H.J.; Gardiner, S.E.; Hellens, R.P.; et al. Multiple repeats of a promoter segment causes transcription factor autoregulation in red apples. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brendolise, C.; Espley, R.V.; Lin-Wang, K.; Laing, W.; Peng, Y.; McGhie, T.; Dejnoprat, S.; Tomes, S.; Hellens, R.P.; Allan, A.C. Multiple copies of a simple MYB-binding site confers trans-regulation by specific flavonoid-related R2R3 MYBs in diverse species. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bennetzen, J.L. Plant Retrotransposons. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1999, 33, 479–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnegan, D.J. Transposable elements. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1992, 2, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesworth, B.; Sniegowski, P.; Stephan, W. The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature 1994, 371, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadonou, A.M.; Gittins, J.R.; Hiles, E.R.; James, D.J. Two apple repetitive sequence elements: Characterisation and potential use as genetic markers. Euphytica 2003, 131, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollister, J.D.; Smith, L.M.; Guo, Y.L.; Ott, F.; Weigel, D.; Gaut, B.S. Transposable elements and small RNAs contribute to gene expression divergence between Arabidopsis thaliana and Arabidopsis lyrata. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2322–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-González, L.; Mhiri, C.; Deyholos, M.K.; Grandbastien, M.A. LTR-retrotransposons in plants: Engines of evolution. Gene 2017, 626, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amyotte, S.G.; Tan, X.; Pennerman, K.; del Mar Jimenez-Gasco, M.; Klosterman, S.J.; Ma, L.J.; Dobinson, K.F.; Veronese, P. Transposable elements in phytopathogenic Verticillium spp.: Insights into genome evolution and inter- and intra-specific diversification. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Q.; Qiao, G.; Peng, L.; Wen, X. Transcriptional activation of long terminal repeat retrotransposon sequences in the genome of pitaya under abiotic stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebollo, R.; Romanish, M.T.; Mager, D.L. Transposable Elements: An Abundant and Natural Source of Regulatory Sequences for Host Genes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2012, 46, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daccord, N.; Celton, J.M.; Linsmith, G.; Becker, C.; Choisne, N.; Schijlen, E.; Van De Geest, H.; Bianco, L.; Micheletti, D.; Velasco, R.; et al. High-quality de novo assembly of the apple genome and methylome dynamics of early fruit development. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, R.; Zharkikh, A.; Affourtit, J.; Dhingra, A.; Cestaro, A.; Kalyanaraman, A.; Fontana, P.; Bhatnagar, S.K.; Troggio, M.; Pruss, D.; et al. The genome of the domesticated apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peace, C.P.; Bianco, L.; Troggio, M.; van de Weg, E.; Howard, N.P.; Cornille, A.; Durel, C.E.; Myles, S.; Migicovsky, Z.; Schaffer, R.J.; et al. Apple whole genome sequences: Recent advances and new prospects. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telias, A.; Lin-Wang, K.; Stevenson, D.E.; Cooney, J.M.; Hellens, R.P.; Allan, A.C.; Hoover, E.E.; Bradeen, J.M. Apple skin patterning is associated with differential expression of MYb10. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Richards, C.M.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Y.; Liu, G.; Gul, H.; et al. A high-quality apple genome assembly reveals the association of a retrotransposon and red fruit colour. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butelli, E.; Licciardello, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Mackay, S.; Bailey, P.; Reforgiato-Recupero, G.; Martin, C. Retrotransposons control fruit-specific, cold-dependent accumulation of anthocyanins in blood oranges. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Goto-Yamamoto, N.; Hirochika, H. Retrotransposon-Induced Mutations in Grape Skin Color. Science 2004, 304, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier-Level, A.; Lacombe, T.; Le Cunff, L.; Boursiquot, J.M.; This, P. Evolution of the VvMybA gene family, the major determinant of berry colour in cultivated grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Heredity 2010, 104, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelsy, F. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of diversity within grapevine varieties. Heredity 2010, 104, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.E.; Martienssen, R.A.; Riggs, A.D. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Gene Regulation; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, S.; Whitelaw, E. Epigenetic germline inheritance. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004, 14, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basdeki, L.; Hagidimitriou, M. The Role of DNA Methylation in Perennial Plants. Not. Sci. Biol. 2019, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefsbol, T. Handbook of Epigenetics: The New Molecular and Medical Genetics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 0128054778. [Google Scholar]
- Reinders, J.; Wulff, B.B.H.; Mirouze, M.; Marí-Ordóñez, A.; Dapp, M.; Rozhon, W.; Bucher, E.; Theiler, G.; Paszkowski, J. Compromised stability of DNA methylation and transposon immobilization in mosaic Arabidopsis epigenomes. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederhuth, C.E.; Schmitz, R.J. Covering your bases: Inheritance of DNA methylation in plant genomes. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikaard, C.S.; Scheid, O.M.; Kingston, R.E.; Tamkun, J.W.; Baulcombe, D.C.; Dean, C. Epigenetic Regulation in Plants. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a019315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Lang, Z.; Genetics, P.M. The mechanism and function of active DNA demethylation in plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 62, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quadrana, L.; Almeida, J.; Asís, R.; Duffy, T.; Dominguez, P.G.; Bermúdez, L.; Conti, G.; Corrêa Da Silva, J.V.; Peralta, I.E.; Colot, V.; et al. Natural occurring epialleles determine vitamin e accumulation in tomato fruits. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Liu, R.; Niu, Q.; Tang, K.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Chen, K.; Zhu, J.K.; Lang, Z. Global increase in DNA methylation during orange fruit development and ripening. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.H.; Sun, Q.G.; Chen, M.; Wang, N.; Xu, H.F.; Fang, H.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Chen, X. Sen Methylome and transcriptome analyses of apple fruit somatic mutations reveal the difference of red phenotype. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, N.; Chen, M.; Zhang, R.; Sun, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sui, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Methylation of MdMYB1 locus mediated by RdDM pathway regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Jing, C.; Chang, B.; Yan, J.; Liang, B.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z. The effect of promoter methylation on MdMYB1 expression determines the level of anthocyanin accumulation in skins of two non-red apple cultivars. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.F.; Ning, G.X.; Mao, J.; Guo, Z.G.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, B.H. Whole-genome DNA methylation patterns and complex associations with gene expression associated with anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple fruit skin. Planta 2019, 250, 1833–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.F.; Mao, J.; Yang, S.J.; Guo, Z.G.; Ma, Z.H.; Dawuda, M.M.; Zuo, C.W.; Chu, M.Y.; Chen, B.H. Anthocyanin accumulation correlates with hormones in the fruit skin of “Red Delicious” and its four generation bud sport mutants. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tanino, K.K.; Horner, K.N.; Robinson, S.J. Quantitative trait variation is revealed in a novel hypomethylated population of woodland strawberry (Fragaria vesca). BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossman, D.; Kim, K.T.; Scott, R.J. Demethylation by 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine in colorectal cancer cells targets genomic DNA whilst promoter CpG island methylation persists. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liang, B.; Chang, B.; Liu, L.; Yan, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Transcriptome profiling reveals transcriptional regulation by DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine enhancing red pigmentation in bagged “granny smith” apples (Malus domestica). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Tuan, P.A.; Saito, T.; Honda, C.; Hatsuyama, Y.; Ito, A.; Moriguchi, T. Epigenetic regulation of MdMYB1 is associated with paper bagging-induced red pigmentation of apples. Planta 2016, 244, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Kim, G.H.; Choi, C. Differential gene expression and epigenetic analyses between striped and blushed skinned sports of “Fuji” apple. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, N.M. Epigenetics and crop improvement. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasbún, R.; Valledor, L.; Berdasco, M.; Santamaría, E.; Cañal, M.J.; Rodríguez, R.; Ríos, D.; Sánchez, M. In vitro proliferation and genome dna methylation in adult chestnuts. Acta Hortic. 2005, 693, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, E.; Kong, J.; Teyssier, E.; Gallusci, P. Epigenetic Regulations of Fleshy Fruit Development and Ripening and Their Potential Applications to Breeding Strategies. Adv. Bot. Res. 2018, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Cui, K.; Northrup, D.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Tang, Q.; Ge, K.; Levens, D.; Crane-Robinson, C.; Zhao, K. H2A.Z facilitates access of active and repressive complexes to chromatin in embryonic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, L.; Dou, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Hui, Y.; Huang, X.; et al. H2A.Z Represses Gene Expression by Modulating Promoter Nucleosome Structure and Enhancer Histone Modifications in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1274–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, M.; Chai, M.; He, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhao, L.; Qin, Y. Epigenetic regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis by an antagonistic interaction between H2A.Z and H3K4me3. New Phytol. 2018, 221, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Tan, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, T.; Liu, B.; Zhang, D.; Lin, H. Regulation of anthocyanin accumulation via MYB75/HAT1/TPL-mediated transcriptional repression. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.M.; Feller, A.; Morohashi, K.; Frame, K.; Grotewold, E. The basic helix-loop-helix domain of maize R links transcriptional regulation and histone modifications by recruitment of an EMSY-related factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17222–17227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xia, R. Small RNAs, emerging regulators critical for the development of horticultural traits. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, R.; Zhu, H.; An, Y.-Q.; Beers, E.P.; Liu, Z. Apple miRNAs and tasiRNAs with novel regulatory networks. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Shen, J.; Liu, H.; Li, F.; Ding, N.; Gao, C.; Pattanaik, S.; Patra, B.; Li, R.; Yuan, L. Small tandem target mimic-mediated blockage of microRNA858 induces anthocyanin accumulation in tomato. Planta 2015, 242, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, T.; Song, T.; Tian, J.; Yao, Y. Systematic identification of long noncoding RNAs expressed during light-induced anthocyanin accumulation in apple fruit. Plant J. 2019, 100, 572–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).