Nanomaterial-Mediated RNAi Targeting Chitin Metabolism Genes in MEAM1 Cryptic Species of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Bioinformatic Analysis of Genes
2.3. RT-PCR Analysis of Genes
2.4. Expression Pattern Analysis of Genes
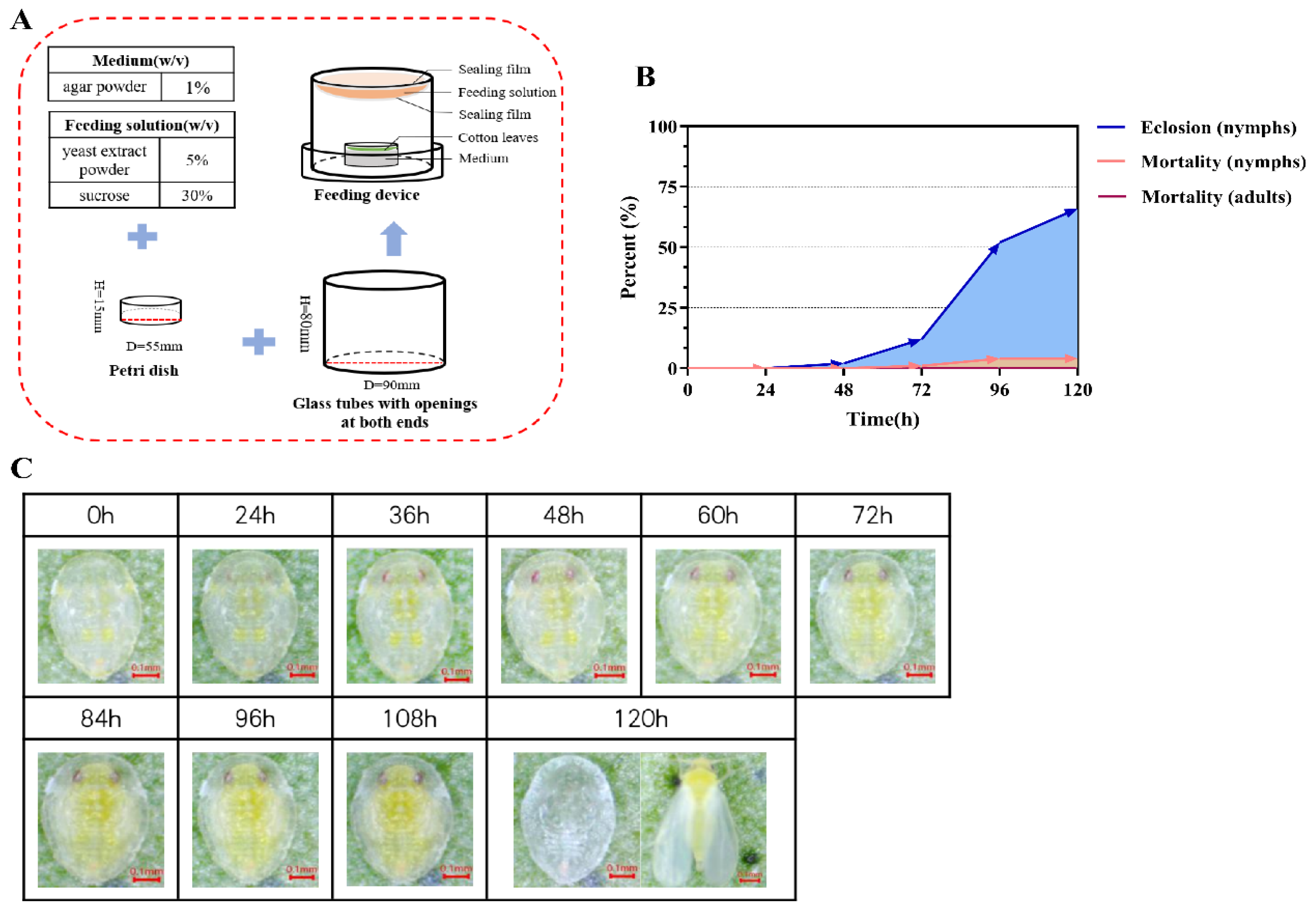
2.5. Design of Device for Insect Rearing and RNAi
2.6. Synthesis of dsRNA and RNA Interference
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bioinformatic Analyses of Genes
3.2. Temporal Gene Expression Profiles
3.3. Validation of Insect Rearing and RNAi Device
3.4. Expression of Target Genes After dsRNA Treatment
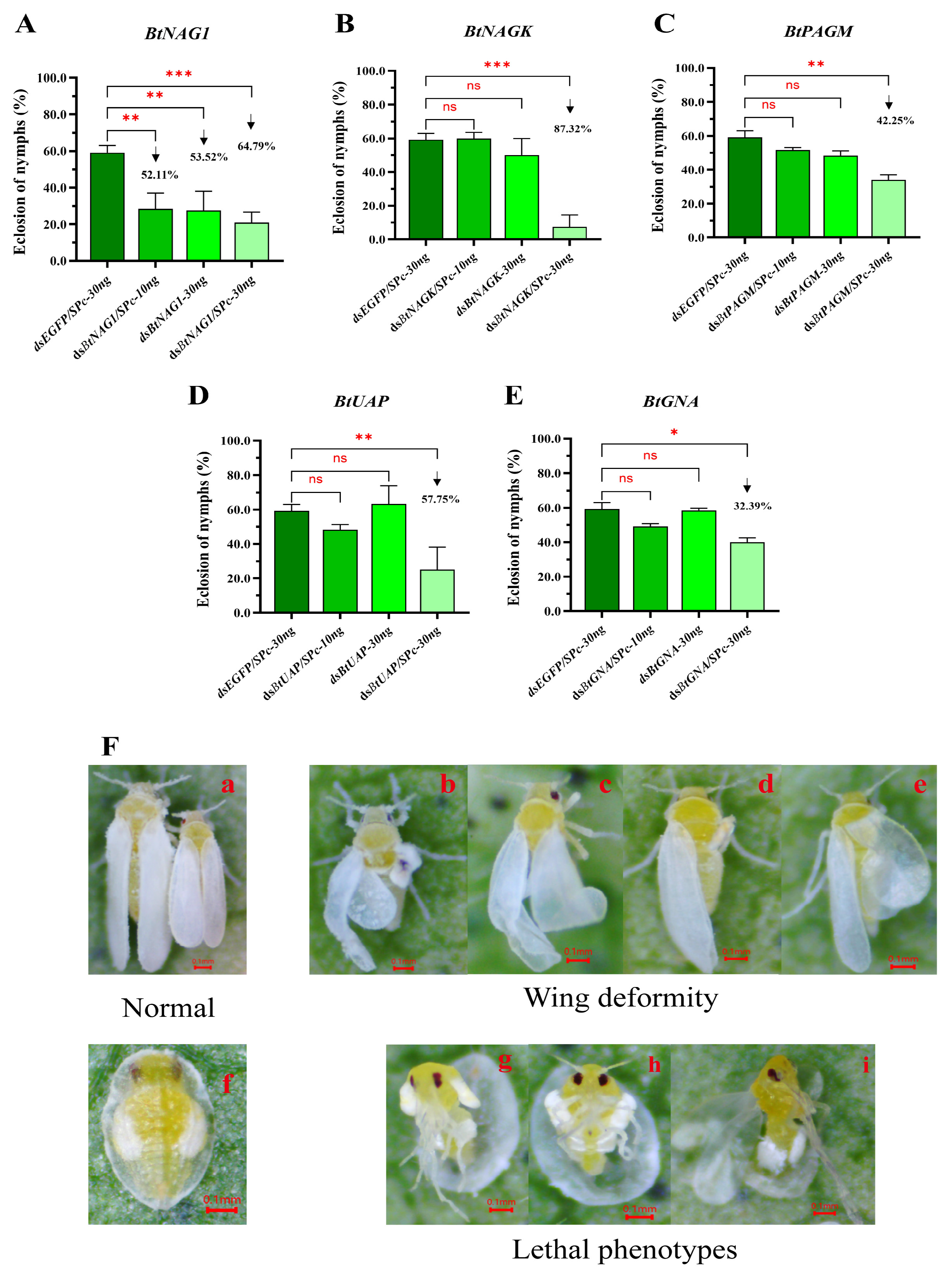
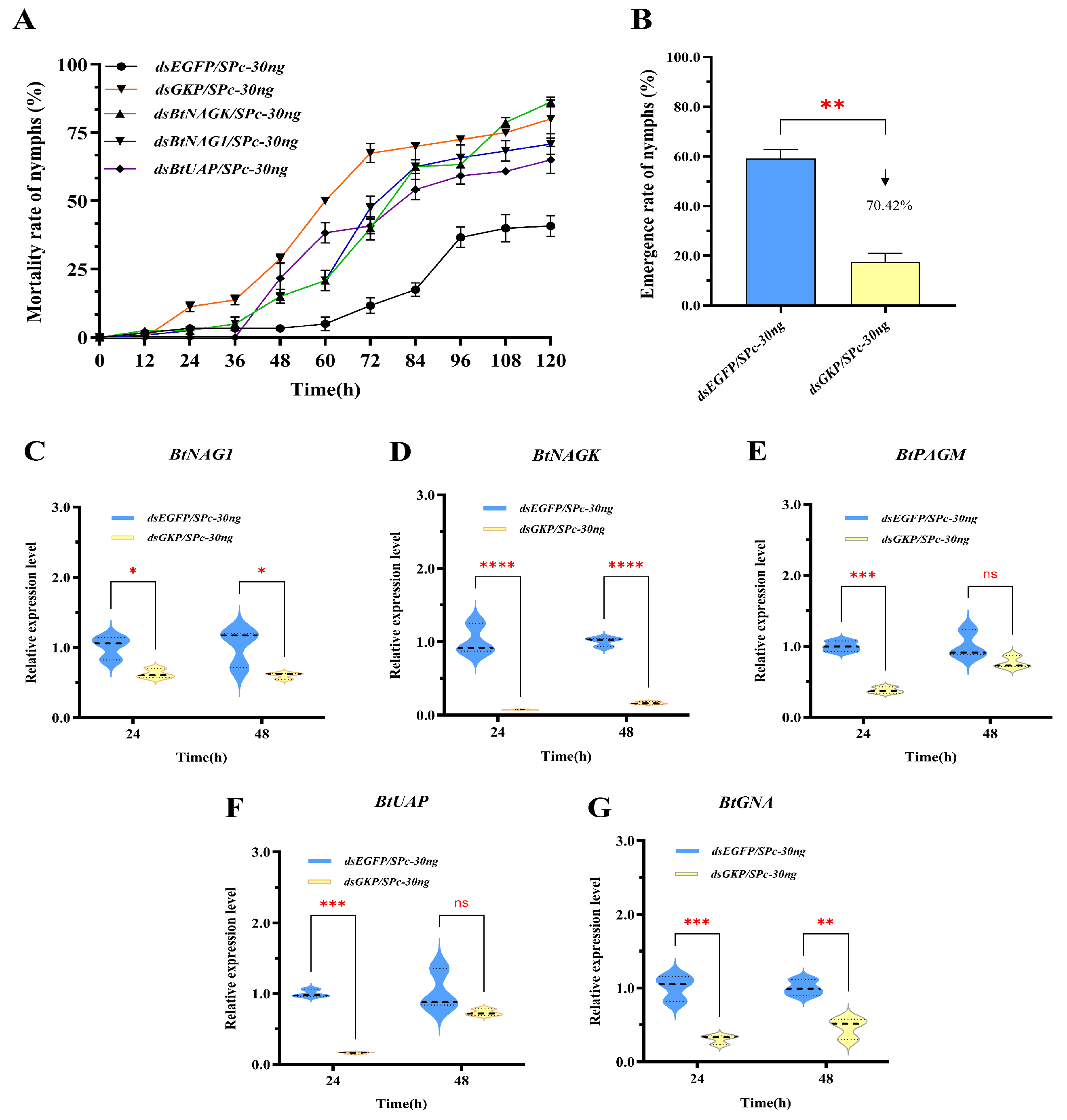
3.5. Mortality and Adult Emergence Rates of Whitefly Nymphs After RNAi
3.6. Fusion Gene RNAi Efficiency
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suhag, A.; Yadav, H.; Chaudhary, D.; Subramanian, S.; Jaiwal, R.; Jaiwal, P.K. Biotechnological interventions for the sustainable management of a global pest, whitefly (Bemisia tabaci). Insect Sci. 2020, 28, 1228–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; De Barro, P.J.; Liu, S.S. Reproductive incompatibility among genetic groups of Bemisia tabaci supports the proposition that the whitefly is a cryptic species complex. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2010, 100, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Luo, C.; Wang, R. Insecticide resistance and its management in two invasive cryptic species of Bemisia tabaci in China. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, E.A.; Moss, J.B.; Andreason, S.A.; Simmons, A.M.; Moore, A.J.; Moore, P.J. Debugging: Strategies and considerations for efficient RNAi-mediated control of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Insects 2020, 11, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Rabou, S.; Simmons, A.M. Survey of reproductive host plants of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) in Egypt, including new host records. Entomol. News 2010, 121, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A.M.; Shaaban, A.R. Populations of predators and parasitoids of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) after the application of eight biorational insecticides in vegetable crops. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, A.R.; Ghanim, M.; Roditakis, E.; Nauen, R.; Ishaaya, I. Insecticide resistance and its management in Bemisia tabaci species. J. Pest Sci. 2020, 93, 893–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chougule, N.P.; Bonning, B.C. Toxins for transgenic resistance to hemipteran pests. Toxins 2012, 4, 405–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, F.J.; Bolckmans, K.; Belda, J.E. Development of a biological control-based integrated pest management method for Bemisia tabaci for protected sweet pepper crops. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2009, 133, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.L.; Beck, M.; Merzendorfer, H.; Yang, Q. Advances in understanding insect chitin biosynthesis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2024, 164, 104058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzendorfer, H. The cellular basis of chitin synthesis in fungi and insects: Common principles and differences. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cooper, A.M.W.; Yu, Z.; Silver, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, K.Y. Progress and prospects of arthropod chitin pathways and structures as targets for pest management. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 161, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harðardóttir, H.M.; Male, R.; Nilsen, F.; Eichner, C.; Dondrup, M.; Dalvin, S. Chitin synthesis and degradation in Lepeophtheirus salmonis: Molecular characterization and gene expression profile during synthesis of a new exoskeleton. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2019, 227, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, D.; Retnakaran, A. Insect chitin: Metabolism, genomics and pest management. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Dhadialla, T.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Kidlington, Oxford, UK, 2012; Volume 43, pp. 437–511. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Chitin synthesis and degradation in crustaceans: A genomic view and application. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, K.H.J.; Waterhouse, P.M. RNAi for insect-proof plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1231–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Khan, S.A.; Heckel, D.G.; Bock, R. Next-generation insect-resistant plants: RNAi-mediated crop protection. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, J.A.; Bogaert, T.; Clinton, W.; Heck, G.R.; Feldmann, P.; Ilagan, O.; Johnson, S.; Plaetinck, G.; Munyikwa, T.; Pleau, M.; et al. Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.B.; Cai, W.J.; Wang, J.W.; Hong, G.J.; Tao, X.Y.; Wang, L.J.; Huang, Y.P.; Chen, X.Y. Silencing a cotton bollworm P450 monooxygenase gene by plant-mediated RNAi impairs larval tolerance of gossypol. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.S.; He, Q.Y.; Lin, X.F.; Smagghe, G. Recent progress in nanoparticle-mediated RNA interference in insects: Unveiling new frontiers in pest control. J. Insect Physiol. 2025, 167, 104884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Z.; Cao, L.J.; Chen, J.C.; Chen, W.B.; Shen, X.J.; Song, W.; Yang, F.Y.; Wei, S.J. A nanocarrier-mediated dsRNA oral delivery enhances RNAi efficiency in thrips. Entomol. Gen. 2024, 44, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E. Chitin synthesis and inhibition: A revisit. Pest Manag. Sci. 2001, 57, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.K.; Ren, J.; Su, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Tian, L.X.; Wang, S.L.; Wu, Q.J.; Liang, P.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Y.J. Genome-Wide identification and analysis of chitinase-like gene family in Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Insects 2021, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, W.J.; Wu, Q.J.; Xu, B.Y.; Chu, D. Analysis of genetic diversity among different geographical populations and determination of biotypes of Bemisia tabaci in China. J. Appl. Entomol. 2005, 129, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.; Frati, F.; Beckenbach, A.; Crespi, B.; Liu, H.; Flook, P. Evolution, weighting, and phylogenetic utility of mitochondrial gene sequences and a compilation of conserved polymerase chain reaction primers. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1994, 87, 651–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatters, R.G., Jr.; Powell, C.A.; Boykin, L.M.; Liansheng, H.; McKenzie, C.L. Improved DNA barcoding method for Bemisia tabaci and related Aleyrodidae: Development of universal and Bemisia tabaci biotype-specific mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase I polymerase chain reaction primers. J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, B.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.J.; Hu, S.; Chen, W.H. Evolview v3: A webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W270–W275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xie, W.; Li, R.M.; Zhou, X.M.; Wang, S.L.; Wu, Q.J.; Yang, N.N.; Xia, J.X.; Yang, Z.Z.; Guo, L.T.; et al. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of the hydroxyacid-oxoacid transhydrogenase gene decreases thiamethoxam resistance in adults of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamatsu, Y.; Yanagisawa, I.; Kimoto, M.; Okamoto, E.; Koga, D. Purification of a chitooligosaccharidolytic beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Bombyx mori larvae during metamorphosis and the nucleotide sequence of its cDNA. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995, 59, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogenkamp, D.G.; Arakane, Y.; Kramer, K.J.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Beeman, R.W. Characterization and expression of the β-N-acetylhexosaminidase gene family of Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.; Li, D.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, K.Y.; Guo, Y.P.; Ma, E.B.; Zhang, J.Z. RNA interference to reveal roles of β-N-acetylglucosaminidase gene during molting process in Locusta migratoria. Insect Sci. 2012, 20, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, T.; Liu, F.Y.; Qu, M.B.; Qian, X.H. A novel β-N-acetyl-d-hexosaminidase from the insect Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée). FEBS J. 2008, 275, 5690–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Yang, Z.Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Q.J.; Wang, S.L.; Guo, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.J. Silencing of the BtTPS genes by transgenic plant-mediated RNAi to control Bemisia tabaci MED. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.X.; Guo, Z.J.; Yang, Z.Z.; Han, H.L.; Wang, S.L.; Xu, H.F.; Yang, X.; Yang, F.S.; Wu, Q.J.; Xie, W.; et al. Whitefly hijacks a plant detoxification gene that neutralizes plant toxins. Cell 2021, 184, 1693–1705.e1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.; Suhag, A.; Jaiwal, R.; Chaudhary, D.; Jaiwal, P.K. Current progress and challenges of horizontal gene transfers in whiteflies (Bemisia tabaci) for their sustainable management. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2024, 27, 102216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civolani, S.; Bariselli, M.; Osti, R.; Bernacchia, G. Insect pest control from chemical to biotechnological approach: Constrains and challenges. Insects 2025, 16, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaens, O.; Niu, J.Z.; Nji Tizi Taning, C. RNAi in insects: A revolution in fundamental research and pest control applications. Insects 2020, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.D.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.R.; Wen, J.X.; Yang, Y.B.; Niu, Z.L.; Guo, W.; Zhao, D. Effects of double-stranded RNA degrading nucleases on RNAi efficiency in beet moth Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Insects 2025, 16, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Palli, S.R. Mechanisms, applications, and challenges of insect RNA interference. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merzendorfer, H.; Zimoch, L. Chitin metabolism in insects: Structure, function and regulation of chitin synthases and chitinases. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 4393–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Merzendorfer, H.; Zhang, W.Q.; Zhang, J.Z.; Muthukrishnan, S. Biosynthesis, turnover, and functions of chitin in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tang, B.; Chen, H.X.; Yao, Q.; Huang, X.F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.W.; Zhang, W.Q. Different functions of the insect soluble and membrane-bound trehalase genes in chitin biosynthesis revealed by RNA interference. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zou, Z.W.; Xin, T.R.; Cai, S.Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.J.; Zhong, L.; Xia, B. Knockdown of hexokinase in Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Liviidae) by RNAi inhibits chitin synthesis and leads to abnormal phenotypes. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 4303–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.H.; Zhang, J.Q.; Liu, X.J.; Liu, Y.Y.; Bi, Y.; Kou, X.J.; McNeill, M.R.; Li, D.Q.; Zhang, J.Z. Disruption of egg and nymph development via RNAi-mediated Glutamine: Fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase knockdown in Locusta migratoria: A promising strategy for pest management. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2025, 214, 106559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.H.; Chen, J.X.; Lyu, J.; Guo, P.P.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, J.H.; Zhang, W.Q. Spraying double-stranded RNA targets UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase in the control of Nilaparvata lugens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakane, Y.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Kramer, K.J.; Specht, C.A.; Tomoyasu, Y.; Lorenzen, M.D.; Kanost, M.; Beeman, R.W. The Tribolium chitin synthase genes TcCHS1 and TcCHS2 are specialized for synthesis of epidermal cuticle and midgut peritrophic matrix. Insect Mol. Biol. 2005, 14, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, X.M.; Liu, Z.R.; Wu, H.; Lu, X.J.; Guo, W. Identification and functional analysis of two potential RNAi targets for chitin degradation in Holotrichia parallela Motschulsky (Insecta Coleoptera). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 188, 105257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, X.J.; Ma, E.B.; Zhang, J.Z. The Characteristics and Biological Function of Glucosamine-6-phosphate-N-acetyltransferase in Locusta migratoria. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2012, 45, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrière, Y.; Crickmore, N.; Tabashnik, B.E. Optimizing pyramided transgenic Bt crops for sustainable pest management. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.R. Gene redundancy and gene compensation: An updated view. J. Genet. Genom. 2019, 46, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Jaouannet, M.; Dempsey, D.M.A.; Imani, J.; Coustau, C.; Kogel, K.H. RNA-based technologies for insect control in plant production. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 39, 107463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Miguel, K.; Scott, J.G. The next generation of insecticides: dsRNA is stable as a foliar-applied insecticide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.S.; Tan, S.Q.; Yan, S.; Li, Z.; Shen, J.; Liu, X.X. Nanocarrier-mediated transdermal dsRNA-NPF1 delivery system contributes to pest control via inhibiting feeding behavior in Grapholita molesta. J. Pest Sci. 2022, 95, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.Y.; Xu, X.N.; Huang, X.X.; Peng, J.; Ma, W.H.; Hull, J.J.; Hua, H.X.; Chen, L.Z. Spray-induced and nanocarrier-delivered gene silencing system targeting juvenile hormone receptor components: Potential application as fertility inhibitors for Adelphocoris suturalis management. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 3743–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Qian, J.; Cai, C.; Ma, Z.Z.; Li, J.H.; Yin, M.Z.; Ren, B.Y.; Shen, J. Spray method application of transdermal dsRNA delivery system for efficient gene silencing and pest control on soybean aphid Aphis glycines. J. Pest Sci. 2020, 93, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Qian, J.; Xu, Y.Y.; Yan, S.; Shen, J.; Yin, M.Z. A facile-synthesized star polycation constructed as a highly efficient gene vector in pest management. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6316–6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Z.; Zheng, Y.; Chao, Z.J.; Chen, H.T.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yin, M.Z.; Shen, J.; Yan, S. Visualization of the process of a nanocarrier-mediated gene delivery: Stabilization, endocytosis and endosomal escape of genes for intracellular spreading. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Ren, B.Y.; Shen, J. Nanoparticle-mediated double-stranded RNA delivery system: A promising approach for sustainable pest management. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Yin, M.Z.; Shen, J. Nanoparticle-based nontransformative RNA insecticides for sustainable pest control: Mechanisms, current status and challenges. Entomol. Gen. 2023, 43, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swevers, L.; Smagghe, G. Use of RNAi for Control of Insect Crop Pests. In Arthropod-Plant Interactions: Novel Insights and Approaches for IPM; Smagghe, G., Diaz, I., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 177–197. [Google Scholar]
- Zand Karimi, H.; Innes, R.W. Molecular mechanisms underlying host-induced gene silencing. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 3183–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
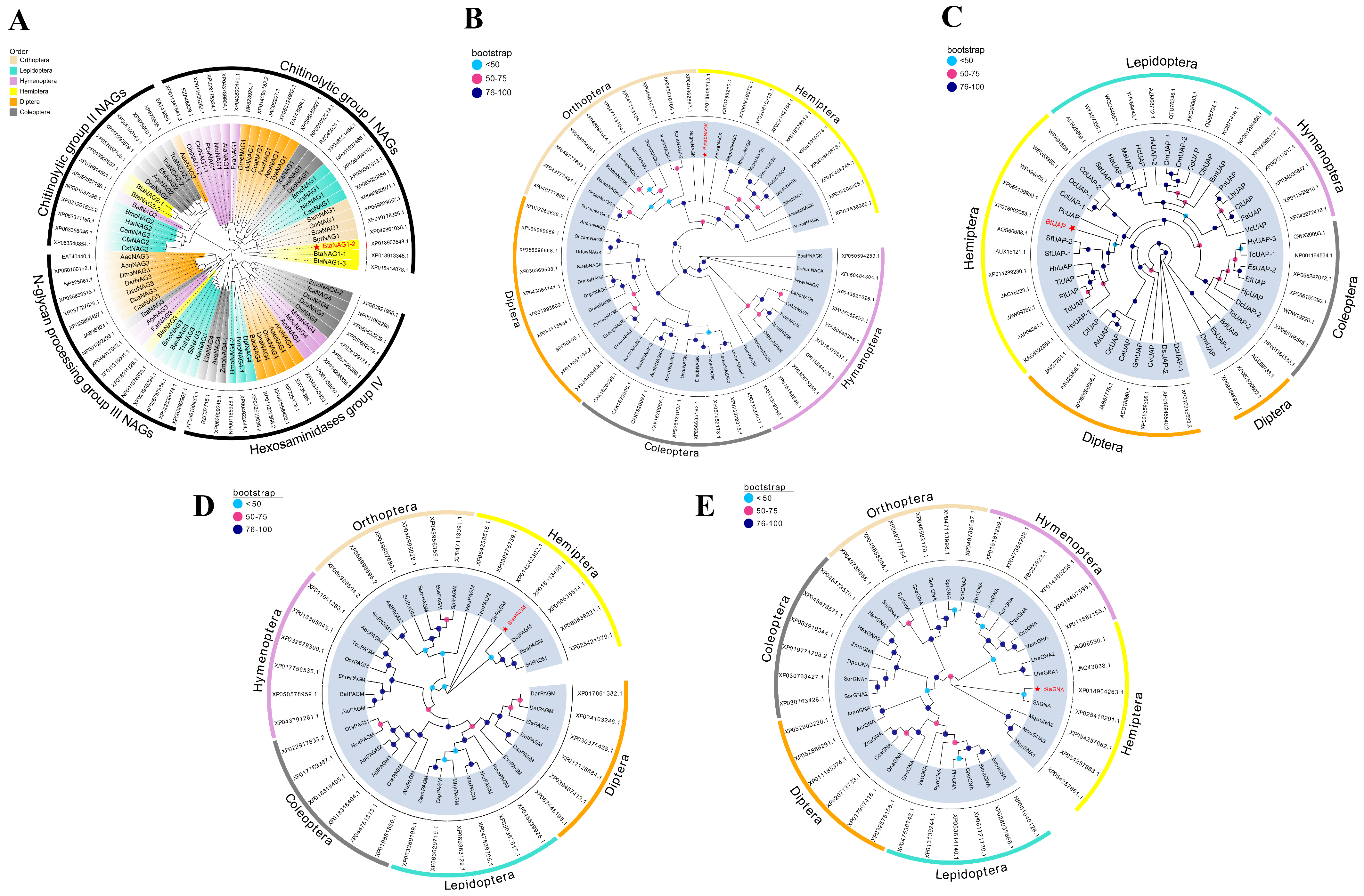




| Gene Name | GenBank Accession | Aa | pI | Subcellular Localization | SP | TMHs | Protein Domain Family |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BtNAG1 | XM019048003 | 622 | 5.62 | lysosome | + | - | GH20 |
| BtNAGK | XM019053168 | 344 | 5.20 | cytoplasm | - | - | ASKHA superfamily |
| BtPAGM | XM019054883 | 567 | 6.29 | cytoplasm | - | - | α-D-phosphohexomutase superfamily |
| BtUAP | XM019046508 | 492 | 6.30 | cytoplasm | - | - | GT superfamily-A |
| BtGNA | XM019048719 | 173 | 7.62 | cytoplasm | - | - | N-Acyltransferase superfamily |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Kong, D.; Gu, H.; Gao, Y.; Hou, Y.; Li, J. Nanomaterial-Mediated RNAi Targeting Chitin Metabolism Genes in MEAM1 Cryptic Species of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Insects 2026, 17, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010002
Kong D, Gu H, Gao Y, Hou Y, Li J. Nanomaterial-Mediated RNAi Targeting Chitin Metabolism Genes in MEAM1 Cryptic Species of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Insects. 2026; 17(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Dejun, Huarong Gu, Yinglu Gao, Yangnan Hou, and Jigang Li. 2026. "Nanomaterial-Mediated RNAi Targeting Chitin Metabolism Genes in MEAM1 Cryptic Species of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae)" Insects 17, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010002
APA StyleKong, D., Gu, H., Gao, Y., Hou, Y., & Li, J. (2026). Nanomaterial-Mediated RNAi Targeting Chitin Metabolism Genes in MEAM1 Cryptic Species of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Insects, 17(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects17010002






