Diversity and Seasonal Abundance of Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Tengchong County of Yunnan, China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Biting Midges
2.2. Sorting the Culicoides
2.3. Extracting DNA from Midges
2.4. Mounting Specimens
2.5. Sequencing
2.6. Weather Data
2.7. Analysis for the Dynamics of Midge Abundance
3. Results
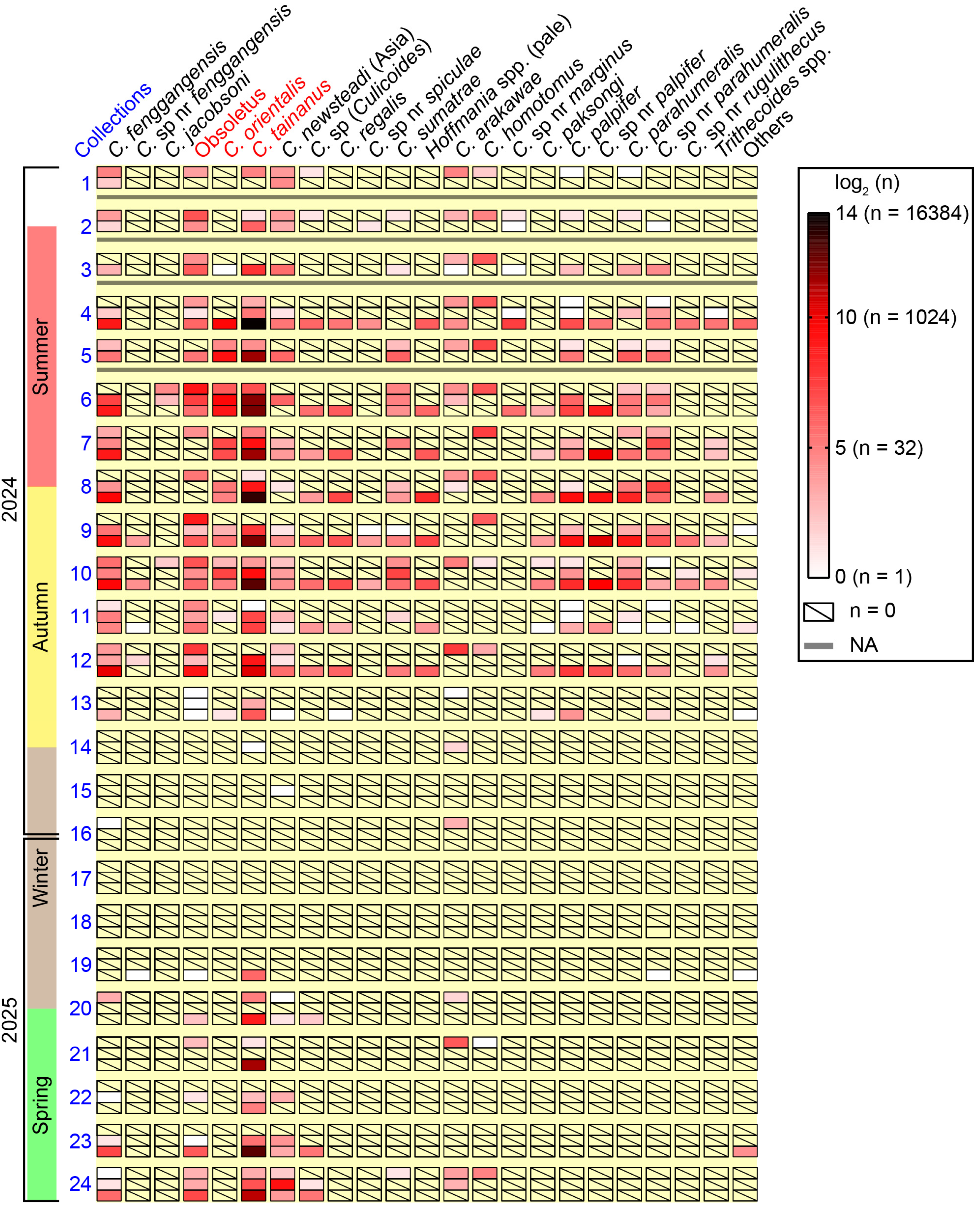
3.1. Diversity of Culicoides
3.2. Seasonal Abundance
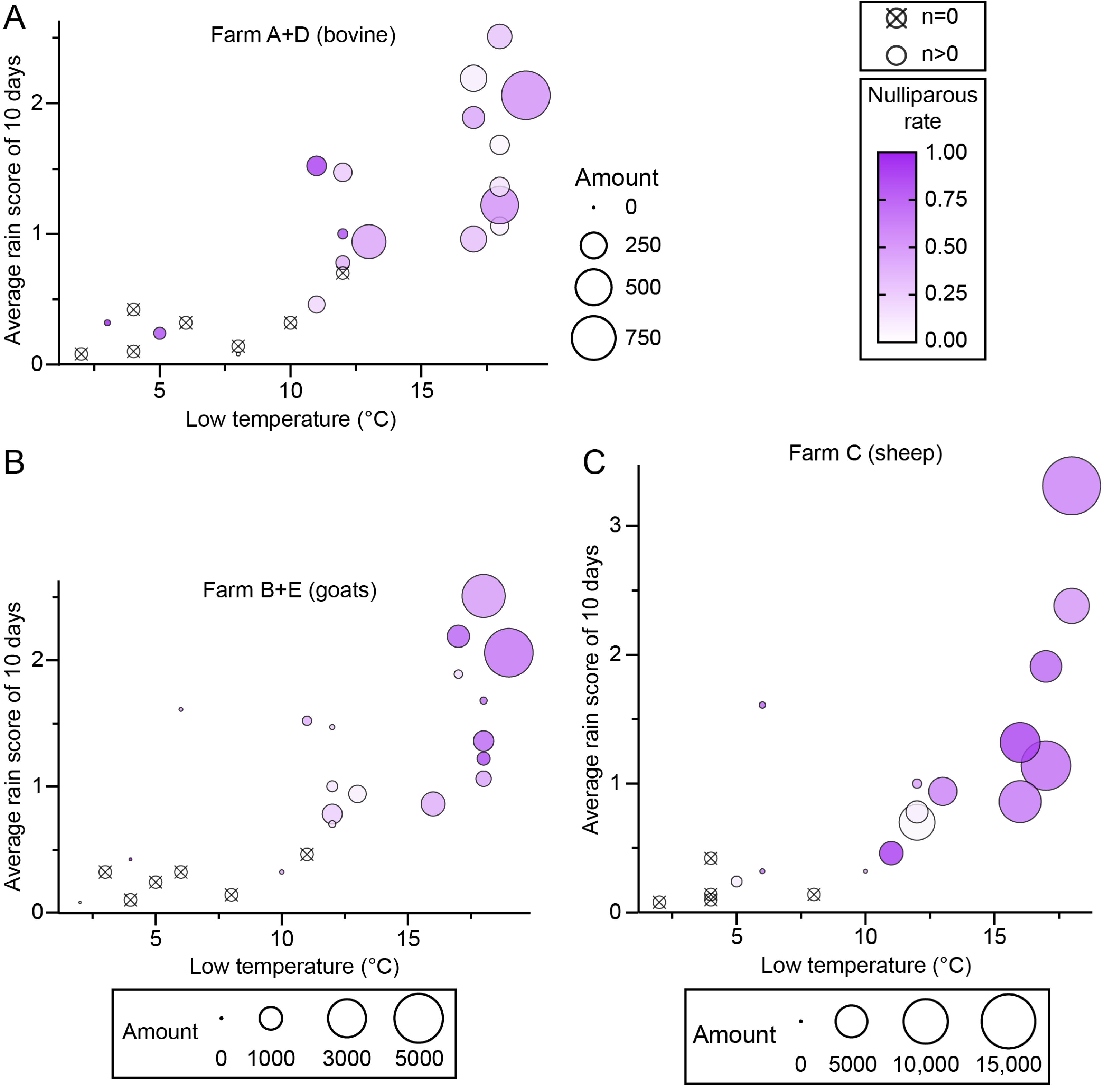
3.3. Effects of Heat and Rainfall on Midge Abundance
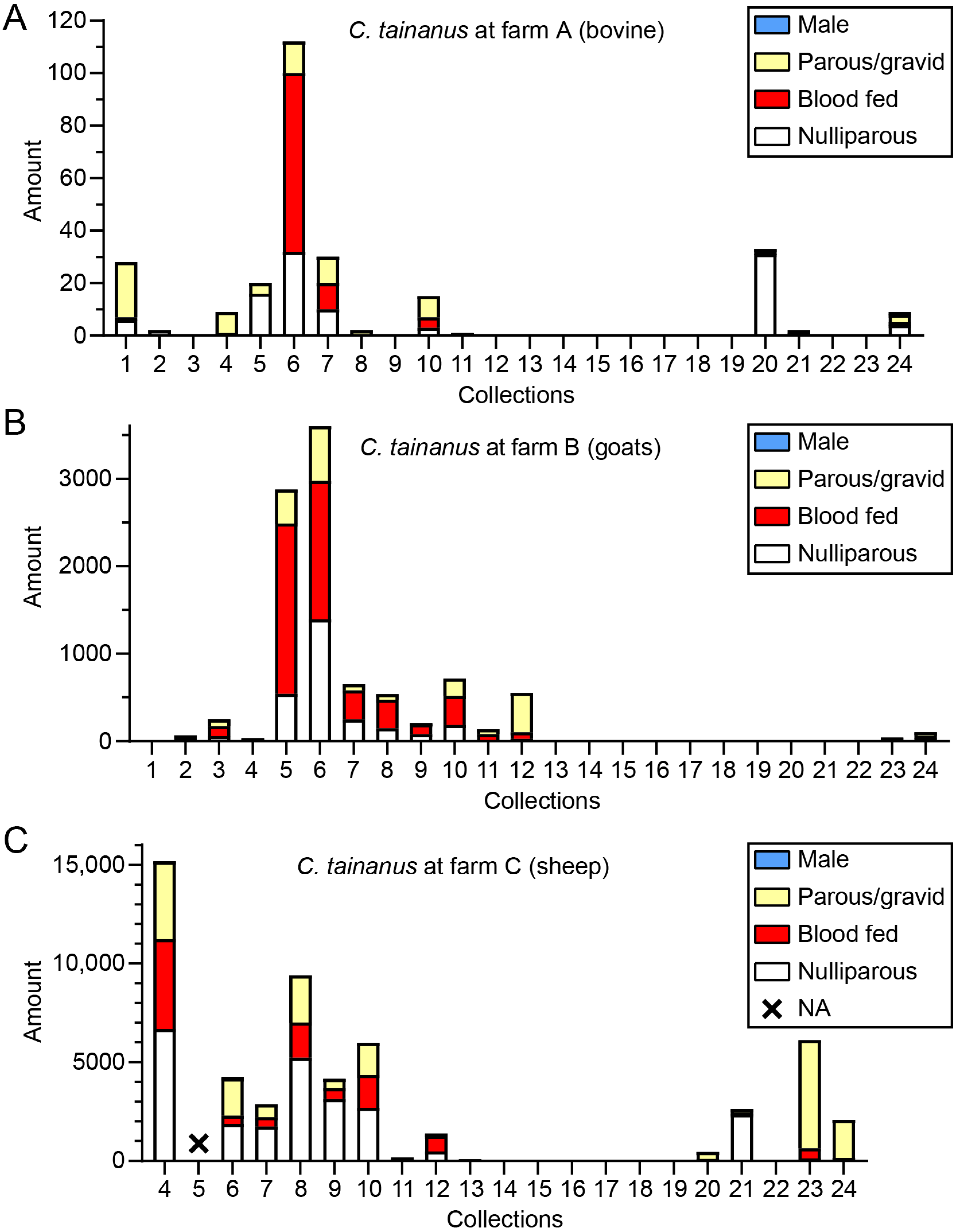
3.4. Midge Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meiswinkel, R.; Venter, G.J.; Nevill, E.M. Vectors: Culicoides spp. In Infectious Diseases of Livestock, 2nd ed.; Coetzer, J.A.W., Tustin, R.C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 93–136. [Google Scholar]
- Borkent, A.; Evenhuis, N.L.; Dominiak, P. The World Catalog of Biting Midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae): Additional Updates and Errata. Zootaxa 2025, 5631, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkent, A.; Dominiak, P. Catalog of the Biting Midges of the World (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). Zootaxa 2020, 4787, zootaxa.4787.1.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.X.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, G.P.; Liu, Z.J.; Yan, G.; Hao, B.S.; Zhao, T.S.; Yu, Y.X. Ceratopogonidae: Culicoides. In Ceratopogonidae of China, 1st ed.; Yu, Y.X., Ed.; Military Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005; Volume 2, pp. 815–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, D.; Zheng, D.C.; Liu, G.P. Classification of Culicoides (Jilinocoides) and a new species from China (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). Chin. J. Front. Health Quaran. 2024, 47, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkent, A. The Subgeneric Classification of Species of Culicoides- Thoughts and a Warning. Available online: https://wwv.inhs.illinois.edu/files/5014/6532/8290/CulicoidesSubgenera.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Wirth, W.W.; Hubert, A.A. The Culicoides of Southeast Asia (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). In Memoirs of the American Entomological Institute; American Entomological Institute: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1989; Volume 44, pp. 1–508. [Google Scholar]
- Janke, L.A.A.; Vigil, S.; Lindsay, K.G.; Furukawa-Stoffer, T.; Colucci, N.; Ambagala, A.; Hanner, R. Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) of Ontario: A Dichotomous Key and Wing Atlas. Can. J. Arthropod. Identif. 2023, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.X.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, G.P.; Liu, Z.J.; Yan, G.; Hao, B.S.; Zhao, T.S.; Yu, Y.X. Ceratopogonidae of China, 1st ed.; Military Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Barcelo, C.; Miranda, M.A. Bionomics of livestock-associated Culicoides (biting midge) bluetongue virus vectors under laboratory conditions. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2018, 32, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Eynde, C.; Sohier, C.; Matthijs, S.; De Regge, N. Temperature and food sources influence subadult development and blood-feeding response of Culicoides obsoletus (sensu lato) under laboratory conditions. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purse, B.V.; Mellor, P.S.; Rogers, D.J.; Samuel, A.R.; Mertens, P.P.; Baylis, M. Climate change and the recent emergence of bluetongue in Europe. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunamaker, R.A.; Sieburth, P.J.; Dean, V.C.; Wigington, J.G.; Nunamaker, C.E.; Mecham, J.O. Absence of transovarial transmission of bluetongue virus in Culicoides variipennis: Immunogold labelling of bluetongue virus antigen in developing oocytes from Culicoides variipennis (Coquillett). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Comp. Physiol. 1990, 96, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, C.J.; Mayo, C.E.; Mullens, B.A.; McDermott, E.G.; Gerry, A.C.; Reisen, W.K.; MacLachlan, N.J. Lack of Evidence for Laboratory and Natural Vertical Transmission of Bluetongue Virus in Culicoides sonorensis (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augot, D.; Hadj-Henni, L.; Strutz, S.E.; Slama, D.; Millot, C.; Depaquit, J.; Millot, J.M. Association between host species choice and morphological characters of main sensory structures of Culicoides in the Palaeartic region. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomontean, B.; Vaisusuk, K.; Chatan, W.; Wongpakam, K.; Sankul, P.; Lachanthuek, L.; Mintara, R.; Thanee, I.; Pramual, P. Diversity, Abundance and Host Blood Meal Analysis of Culicoides Latreille (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) from Cattle Pens in Different Land Use Types from Thailand. Insects 2023, 14, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunantaraporn, S.; Hortiwakul, T.; Kraivichian, K.; Siriyasatien, P.; Brownell, N. Molecular Identification of Host Blood Meals and Detection of Blood Parasites in Culicoides Latreille (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) Collected from Phatthalung Province, Southern Thailand. Insects 2022, 13, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaoka, S.; Morii, T. Observations on the breeding habitats of some biting midges and seasonal population dynamics in the life cycle of Culicoides arakawae in Tokyo and its vicinity. Natl. Inst. Anim. Health Q 1963, 3, 198–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, H. A video clip of the biting midge Culicoides anophelis ingesting blood from an engorged Anopheles mosquito in Hainan, China. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellis, G.A.; Melville, L.F.; Hunt, N.T.; Hearnden, M.N. Temporal activity of biting midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) on cattle near Darwin, Northern Territory, Australia. Vet. Ital. 2004, 40, 324–328. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, T.M.; Hajibabaei, M. Over 2.5 million COI sequences in GenBank and growing. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glockner, F.O.; Yilmaz, P.; Quast, C.; Gerken, J.; Beccati, A.; Ciuprina, A.; Bruns, G.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Westram, R.; et al. 25 years of serving the community with ribosomal RNA gene reference databases and tools. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 261, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrelli, M.T.; Sallum, M.A.; Marinotti, O. The second internal transcribed spacer of nuclear ribosomal DNA as a tool for Latin American anopheline taxonomy—A critical review. Mem. Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2006, 101, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BOLD. BOLD Systems, Version 5. Available online: https://boldsystems.org/ (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. A DNA-baseavaild registry for all animal species: The barcode index number (BIN) system. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Shi, W.Q.; Zhang, Y. Molecular phylogeny of Anopheles hyrcanus group (Diptera: Culicidae) based on mtDNA COI. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Husseneder, C.; Foil, L. Assigning Culicoides larvae to species using DNA barcoding of adult females and phylogenetic associations. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swe, M.M.M.; Phyo, A.P.; Cooper, B.S.; White, N.J.; Smithuis, F.; Ashley, E.A. A systematic review of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) in Myanmar. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyce, A.L. The recognition of nulliparous and parous Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) without dissection. J. Aust. Ent. Soc. 1969, 8, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.L.; Bellis, G.; Yang, Z.X.; Li, Z.H.; Liu, B.G.; Li, L. DNA barcoding and phylogenetic analysis of midges belonging to Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) subgenus Hoffmania in Yunnan, China. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2022, 25, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Wang, Y.N.; Deng, J.M.; Li, L.; Yang, L.J.; Chen, X.Q.; Wang, W.H.; Lu, F.Y.; Tang, Z.J.; Wang, D.M.; et al. Searching for potential Culicoides vectors of four orbiviruses in Yunnan Province, China. Parasites Vectors 2025, 18, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellis, G.A.; Dyce, A.L.; Gopurenko, D.; Mitchell, A. Revision of the Immaculatus Group of Culicoides Latreille (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) from the Australasian Region with descriptions of two new species. Zootaxa 2013, 3680, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhoum, M.T.; Labuschagne, K.; Huber, K.; Fall, M.; Mathieu, B.; Venter, G.; Gardès, L.; Baldet, T.; Bouyer, J.; Fall, A.G.; et al. Phylogenetic relationships and molecular delimitation of Culicoides Latreille (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) species in the Afrotropical region: Interest for the subgenus Avaritia. Syst. Entomol. 2018, 43, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Historical Weather in Kunming. Available online: https://tianqi.2345.com/wea_history/56778.htm (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Greene, C.S.; Tan, J.; Ung, M.; Moore, J.H.; Cheng, C. Big data bioinformatics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1896–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Van der Saag, M.; Nicholas, A.; Ward, M.; Kirkland, P. Evaluation of in vitro methods for assessment of infection of Australian Culicoides spp. with bluetongue viruses. Vet. Ital. 2015, 51, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.L.; Li, L.; Bellis, G.; Yang, Z.X.; Li, H.C. Detection of bluetongue virus in Culicoides spp. in southern Yunnan Province, China. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, Y.; Homat, T.; Thepparat, A.; Changbunjong, T.; Sutummaporn, K.; Kornmatitsuk, S.; Kornmatitsuk, B. DNA barcode identification and molecular detection of bluetongue virus in Culicoides biting midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) from western Thailand. Acta Trop. 2021, 224, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Shirafuji, H.; Tanaka, S.; Sato, M.; Yamakawa, M.; Tsuda, T.; Yanase, T. Bovine Arboviruses in Culicoides Biting Midges and Sentinel Cattle in Southern Japan from 2003 to 2013. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, e160–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Bellis, G.A.; Kim, M.S.; Klein, T.A.; Gopurenko, D.; Cai, D.C.; Seo, H.J.; Cho, I.S.; Park, J.Y. Species Diversity and Seasonal Distribution of Culicoides spp. (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Jeju-do, Republic of Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2015, 53, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, W.W.; Dyce, A.L. The current taxonomic status of the Culicoides vectors of bluetongue viruses. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1985, 178, 151–164. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.L.; Bellis, G.; Liu, B.G.; Li, L. Diversity and seasonal abundance of Culicoides (Diptera, Ceratopogonidae) in Shizong County, Yunnan Province, China. Parasite 2022, 29, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuellar, A.C.; Kjaer, L.J.; Kirkeby, C.; Skovgard, H.; Nielsen, S.A.; Stockmarr, A.; Andersson, G.; Lindstrom, A.; Chirico, J.; Luhken, R.; et al. Spatial and temporal variation in the abundance of Culicoides biting midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in nine European countries. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredo, M.; Meiswinkel, R.; Federici, V.; Di Nicola, F.; Mancini, G.; Ippoliti, C.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Quaglia, M.; Santilli, A.; Conte, A.; et al. The ‘Culicoides obsoletus group’ in Italy: Relative abundance, geographic range, and role as vector for Bluetongue virus. Vet. Ital. 2016, 52, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Vega, C.; Rivera, B.; Lucientes, J.; Gutierrez-Boada, I.; Sanchez-Vizcaino, J.M. A study of the composition of the Obsoletus complex and genetic diversity of Culicoides obsoletus populations in Spain. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augot, D.; Sauvage, F.; Jouet, D.; Simphal, E.; Veuille, M.; Couloux, A.; Kaltenbach, M.L.; Depaquit, J. Discrimination of Culicoides obsoletus and Culicoides scoticus, potential bluetongue vectors, by morphometrical and mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I analysis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluiters, G.; Pages, N.; Carpenter, S.; Gardes, L.; Guis, H.; Baylis, M.; Garros, C. Morphometric discrimination of two sympatric sibling species in the Palaearctic region, Culicoides obsoletus Meigen and C. scoticus Downes & Kettle (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae), vectors of bluetongue and Schmallenberg viruses. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.A.; Kristensen, M. Morphological and molecular identification of species of the Obsoletus group (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Scandinavia. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.L.; Lu, L.C. Female Culicoides of Taiwan with descriptions of new species (Diptera, Ceratopogonidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1972, 9, 396–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.L.; Bellis, G.; Li, L.; Li, H.C.; Miao, H.S.; Kou, M.L.; Liao, F.; Wang, Z.; Gao, L.; Li, J.Z. Potential vectors of bluetongue virus in high altitude areas of Yunnan Province, China. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.Q.; Jiang, X.H.; Liu, G.P.; Li, X.F.; Hou, X.H. A species checklist of the subgenus Culicoides (Avaritia) in China, with a description of a new species (Diptera, Ceratopogonidae). Zookeys 2017, 706, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Banerjee, P.; Sinha, S.K.; Mazumdar, A. A taxonomic revision of the Indian species of the ‘Aterinervis’ group of Culicoides Latreille Subgenus Hoffmania Fox (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). Zootaxa 2023, 5258, 405–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, F.I.; Liu, S.C. A Taxonomic Study of the Genus Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) of Yunnan, with Descriptions of Five New Species. ACTA Entomol. Sin. 1978, 21, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, F.I. Two New Names of Chinese Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). Entomotaxonomia 1984, 6, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.L.; Li, Z.H.; Bellis, G.A.; Li, L.; Liu, B.G.; Wang, J.P.; Liu, J.M.; Liao, D.F.; Zhu, J.B. Culicoides and midge-associated arboviruses on cattle farms in Yunnan Province, China. Parasite 2024, 31, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Bellis, G.A.; Kim, M.S.; Chong, S.T.; Lee, D.K.; Park, J.Y.; Yeh, J.Y.; Klein, T.A. Seasonal abundance of biting midges, Culicoides spp. (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae), collected at cowsheds in the southern part of the Republic of Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2012, 50, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.P.; Deng, C.Y. [A New Species of Culicoides and Newly Found Male of Culicoides pelius Liu et Yu (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) from Tibet, China]. Chin. J. Vect. Biol. Con. 2000, 11, 245–247. [Google Scholar]
- Promrangsee, C.; Sriswasdi, S.; Sunantaraporn, S.; Savigamin, C.; Pataradool, T.; Sricharoensuk, C.; Boonserm, R.; Ampol, R.; Pruenglampoo, P.; Mungthin, M.; et al. Seasonal dynamics, Leishmania diversity, and nanopore-based metabarcoding of blood meal origins in Culicoides spp. in the newly emerging focus of leishmaniasis in Northern Thailand. Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyce, A.L.; Bellis, G.A.; Muller, M.J. Pictorial Atlas of Australasian Culicoides Wings (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae), 1st ed.; Wells, A., Ed.; Australian Biological Resources Study: Canberra, Australia, 2007; p. 88. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, D.L.; Grames, E.M.; Forister, M.L.; Berenbaum, M.R.; Stopak, D. Insect decline in the Anthropocene: Death by a thousand cuts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023989118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibold, S.; Gossner, M.M.; Simons, N.K.; Bluthgen, N.; Muller, J.; Ambarli, D.; Ammer, C.; Bauhus, J.; Fischer, M.; Habel, J.C.; et al. Arthropod decline in grasslands and forests is associated with landscape-level drivers. Nature 2019, 574, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Klink, R.; Bowler, D.E.; Gongalsky, K.B.; Swengel, A.B.; Gentile, A.; Chase, J.M. Meta-analysis reveals declines in terrestrial but increases in freshwater insect abundances. Science 2020, 368, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maclachlan, N.J.; Drew, C.P.; Darpel, K.E.; Worwa, G. The pathology and pathogenesis of bluetongue. J. Comp. Pathol. 2009, 141, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allingham, P.G. Effect of temperature on late immature stages of Culicoides brevitarsis (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1991, 28, 878–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, A.L.; McKenzie, H.J.; Barchia, I.M.; Harris, A.M. Effect of Temperature Regimes on the Development, Survival and Emergence of Culicoides brevitarsis Kieffer (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Bovine Dung. Aust. J. Entom. 1996, 35, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
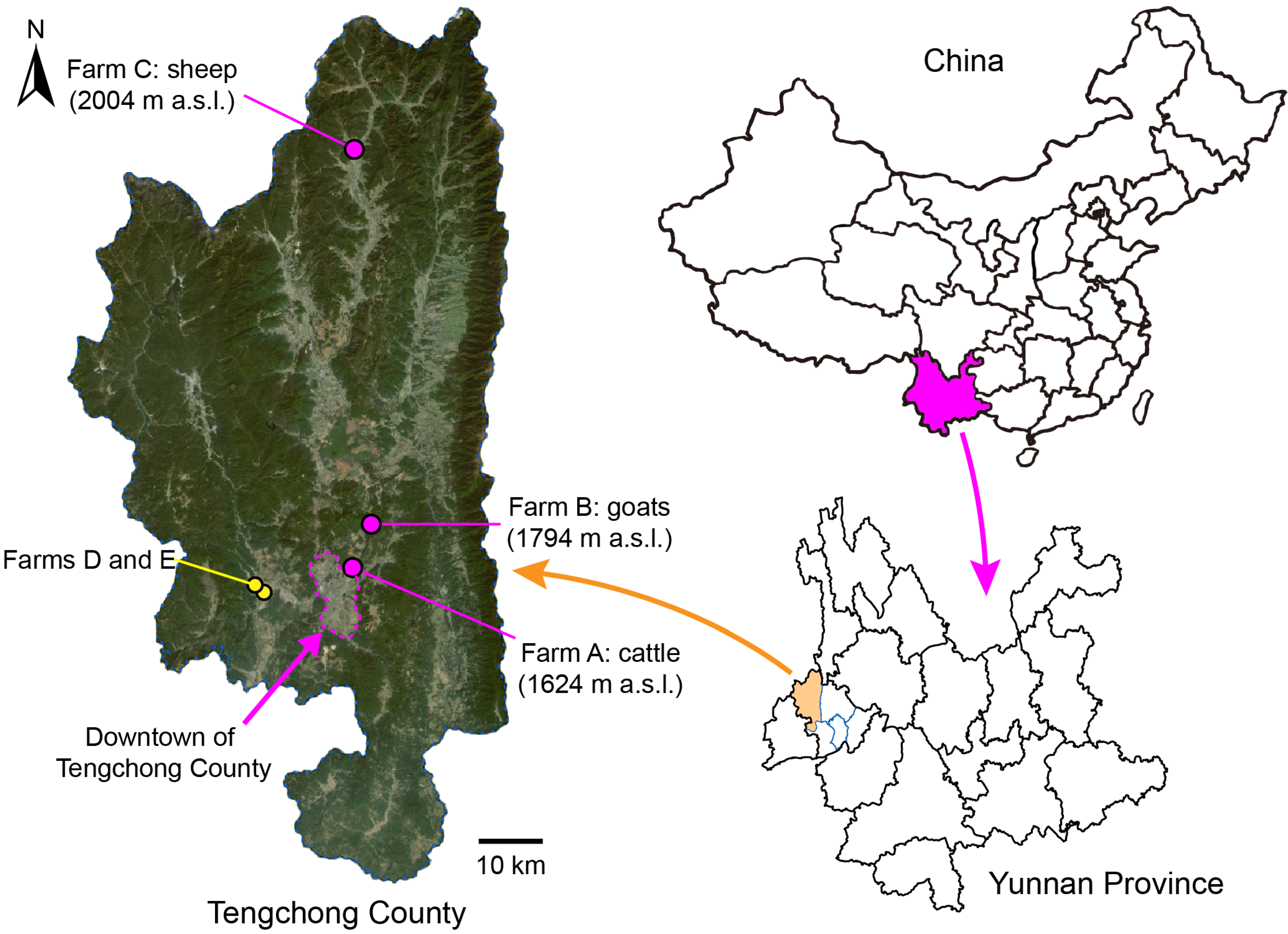
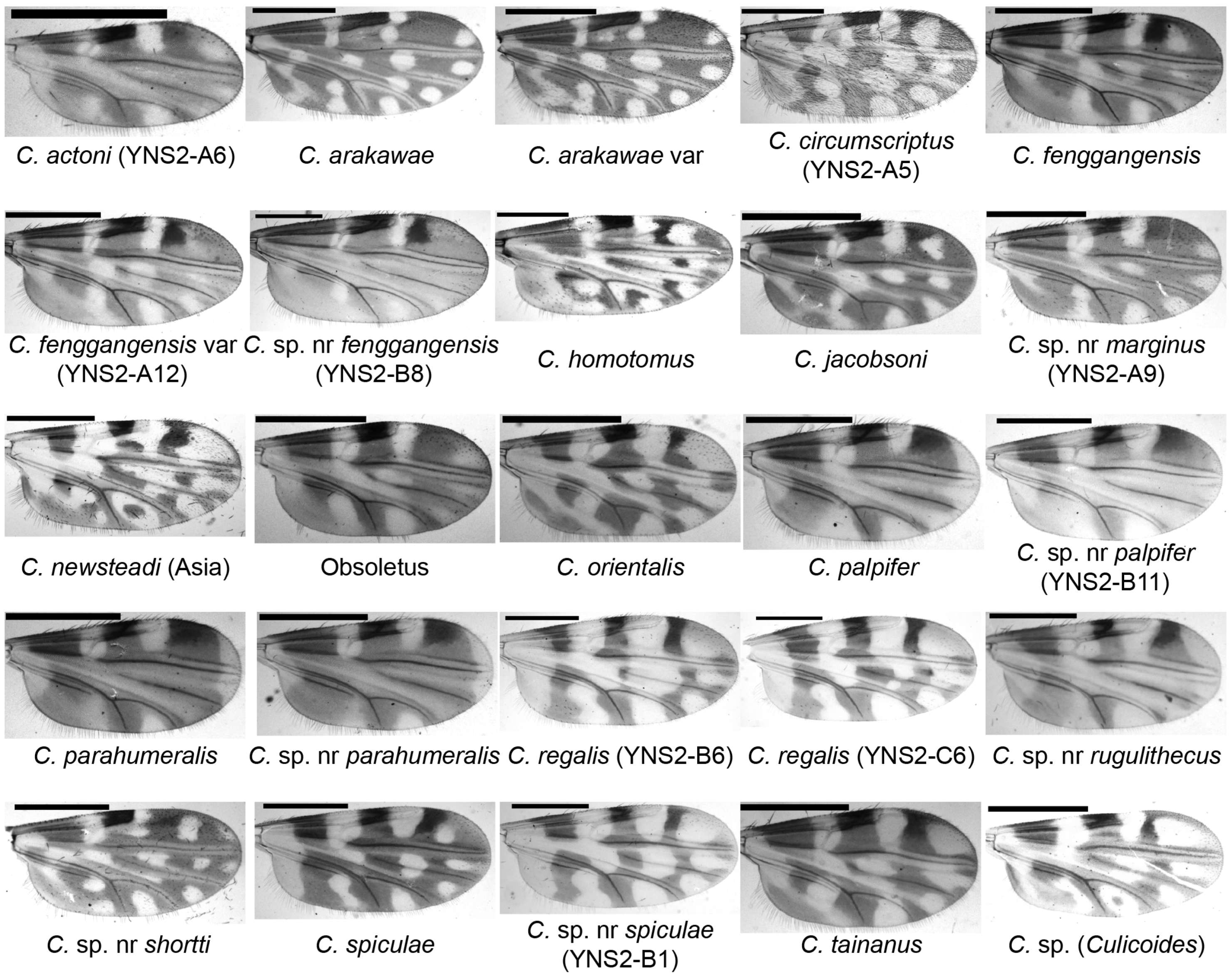
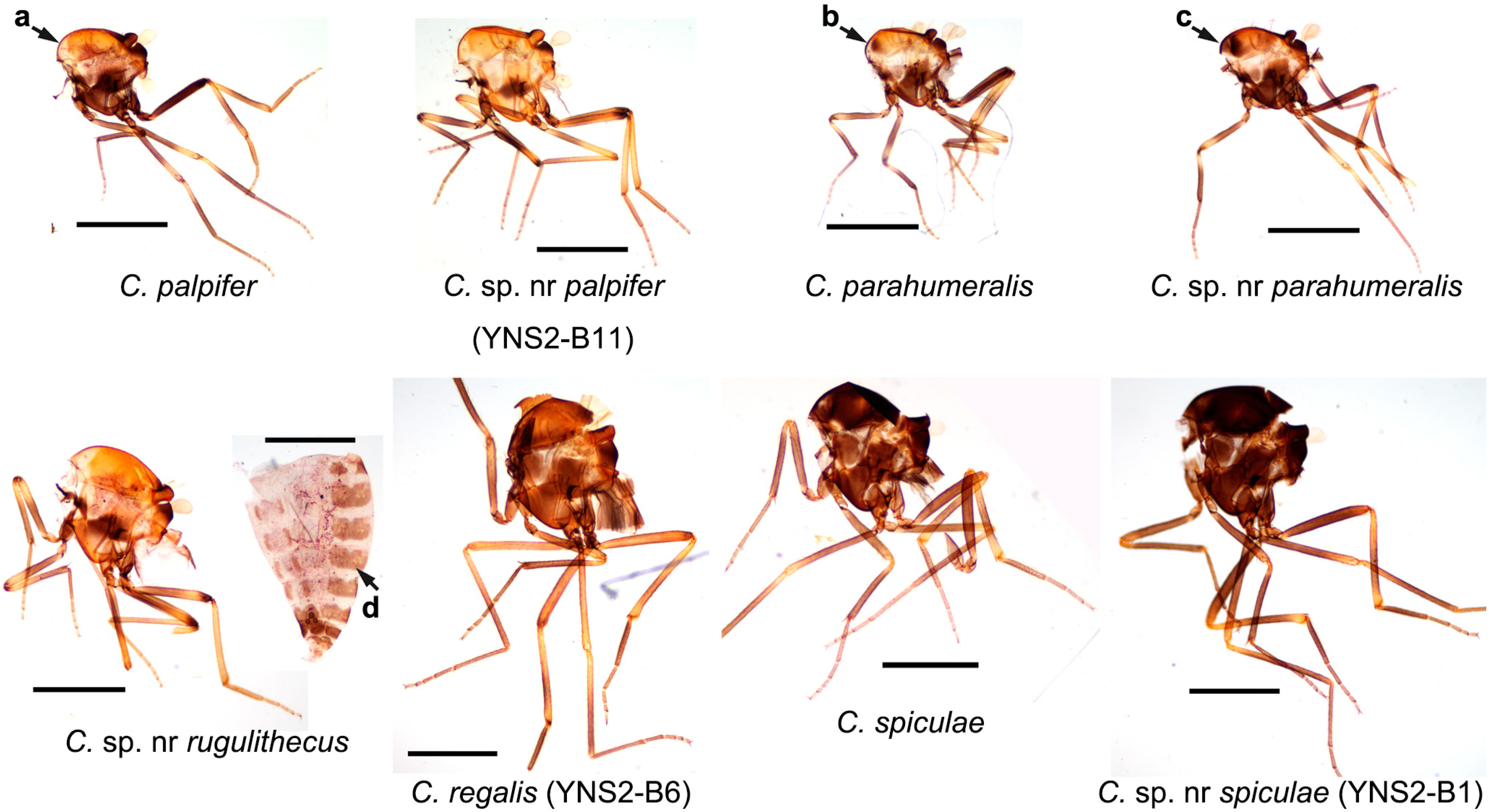
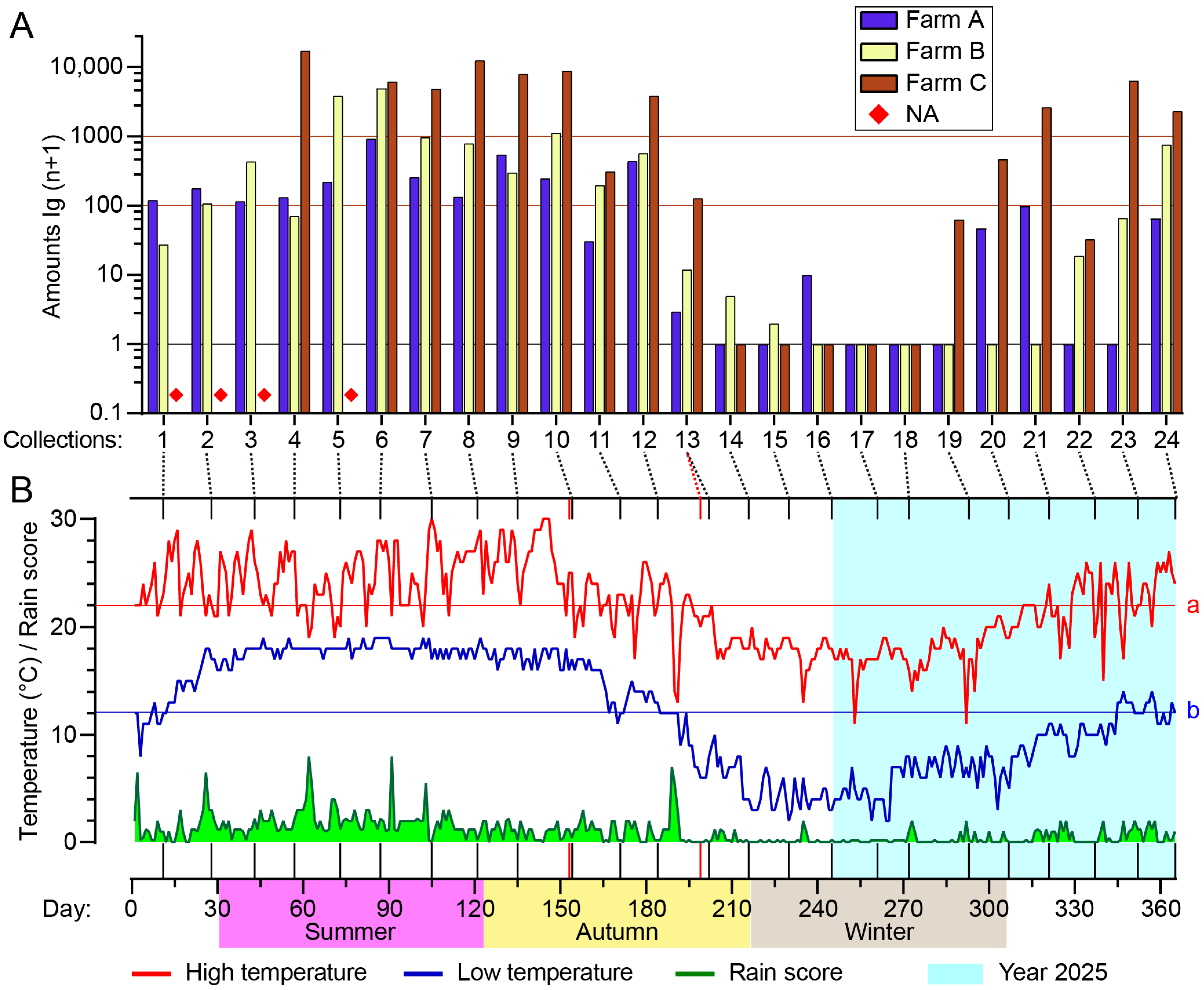
| Farm ID | Town | Major Animals | No. of Pens | Collection Date | Exact Coordinates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Elevation (m a.s.l.) | |||||
| A | Teng-yue | 30 bovine a | 1 | 2024–2025 | 25.062 | 98.542 | 1624 |
| B | Bei-hai | 30 goats | 1 | 2024–2025 | 25.139 | 98.571 | 1794 |
| C | Ming-guang | 50 sheep | 1 | 2024–2025 | 25.717 | 98.545 | 2004 |
| D | Zhong-he | 360 bovine a | 4 | 10 May 2024 | 25.032 | 98.371 | 1397 |
| E | Zhong-he | 80 goats | 2 | 10 May 2024 | 25.021 | 98.394 | 1375 |
| Subgenus and Species | Total Number, Percentage, and Mean ± SD for Each Species | Frequency of Occurrences a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farm A/Bovine (24 Collections) | Farm B/Goats (24 Collections) | Farm C/Sheep (20 Collections) | ||
| Avaritia: | 2125 (59.2%) | 12,400 (86.0%) | 63,155 (84.7%) | |
| C. actoni | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | E (1) |
| C. fenggangensis | 136 (3.8%) 5.7 ± 11.4 | 383 (2.7%) 16.0 ± 33.2 | 5475 (7.3%) 273.8 ± 379.8 | all (38) |
| C. sp. nr fenggangensis | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (<0.1%) 0.1 ± 0.6 | 36 (<0.1%) 1.8 ± 5.2 | ABC (5) |
| C. hui | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (<0.1%) 0.1 ± 0.2 | C (1) |
| C. jacobsoni | 28 (0.8%) 1.2 ± 4.8 | 6 (<0.1%) 0.3 ± 1.2 | 0 (0.0%) | AB (3) |
| Obsoletus | 1583 (44.1%) 66.0 ± 142.8 | 380 (2.6%) 15.8 ± 37.8 | 1112 (1.5%) 55.6 ± 129.6 | ABCD (39) |
| C. orientalis | 115 (3.2%) 4.8 ± 17.2 | 1821 (12.6%) 75.9 ± 205.6 | 1649 (2.2%) 82.5 ± 216.4 | ABC (18) |
| C. tainanus | 263 (7.3%) 11.0 ± 23.5 | 9807 (68.0%) 408.6 ± 887.9 | 54,882 (73.6%) 2744.1 ± 3865.6 | all (45) |
| Beltranmyia: | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| C. circumscriptus | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | E (1) |
| Culicoides: | 48 (1.3%) | 916 (6.4%) | 571 (0.8%) | |
| C. newsteadi (Asia) | 44 (1.2%) 1.8 ± 4.1 | 914 (6.3%) 38.1 ± 126.5 | 177 (0.2%) 8.9 ± 14.2 | ABCD (33) |
| C. sp. (Culicoides) | 4 (0.1%) 0.2 ± 0.6 | 2 (<0.1%) 0.1 ± 0.4 | 394 (0.5%) 19.7 ± 23.3 | ABC (14) |
| Hoffmania: | 58 (1.6%) | 309 (2.1%) | 1742 (2.3%) | |
| C. parabubalus | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (<0.1%) 0.0 ± 0.2 | 0 (0.0%) | B (1) |
| C. regalis | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 657 (0.9%) 32.9 ± 48.1 | C (9) |
| C. spiculae | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (<0.1%) 0.1 ± 0.4 | 1 (<0.1%) 0.1 ± 0.2 | BC (3) |
| C. sp. nr spiculae | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (<0.1%) 0.1 ± 0.4 | 44 (0.1%) 2.2 ± 5.5 | BCD (6) |
| C. sumatrae | 58 (1.6%) 2.4 ± 6.7 | 302 (2.1%) 12.6 ± 34.2 | 147 (0.2%) 7.4 ± 14.1 | ABCE (19) |
| Hoffmania spp. (pale) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 893 (1.2%) 44.7 ± 76.9 | C (8) |
| Meijerehelea: | 463 (12.9%) | 20 (0.1%) | 20 (<0.1%) | |
| C. arakawae | 463 (12.9%) 19.3 ± 43.0 | 20 (0.1%) 0.8 ± 2.0 | 20 (<0.1%) 1.0 ± 4.4 | ABCE (21) |
| Monoculicoides: | 837 (23.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| C. homotomus | 837 (23.3%) 34.9 ± 52.2 | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | A (13) |
| Oecacta: | 2 (0.1%) | 3 (<0.1%) | 230 (0.3%) | |
| C. sp. nr marginus | 2 (0.1%) 0.1 ± 0.4 | 3 (<0.1%) 0.1 ± 0.3 | 230 (0.3%) 11.5 ± 40.2 | ABC (6) |
| Remmia: | 1 (<0.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| C. oxystoma | 1 (<0.1%) 0.0 ± 0.2 | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | A (1) |
| Shortti group: | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (<0.1%) | |
| C. sp. nr shortti | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (<0.1%) 0.3 ± 1.1 | C (1) |
| Trithecoides: | 56 (1.6%) | 772 (5.4%) | 8737(11.7%) | |
| C. paksongi | 2 (0.1%) 0.1 ± 0.4 | 0 (0.0%) | 126 (0.2%) 6.3 ± 11.2 | AC (9) |
| C. palpifer | 9 (0.3%) 0.4 ± 0.7 | 143 (1.0%) 6.0 ± 14.2 | 2148 (2.9%) 107.4 ± 200.2 | ABCD (25) |
| C. sp. nr palpifer | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 4664 (6.3%) 233.2 ± 424.0 | C (8) |
| C. parahumeralis | 26 (0.7%) 1.1 ± 2.5 | 205 (1.4%) 8.5 ± 18.3 | 1310 (1.8%) 65.5 ± 142.8 | all (24) |
| C. sp. nr parahumeralis | 19 (0.5%) 0.8 ± 2.1 | 415 (2.9%) 17.3 ± 38.2 | 282 (0.4%) 14.1 ± 26.4 | ABCD (25) |
| C. sp. nr rugulithecus | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (<0.1%) 0.1 ± 0.4 | 103 (0.1%) 5.2 ± 12.7 | BCD (6) |
| Trithecoides spp. | 0 (0.0%) | 7 (<0.1%) 0.3 ± 0.9 | 104 (0.1%) 5.2 ± 10.1 | BC (9) |
| Others b | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (<0.1%) 0.1 ± 0.4 | 84 (0.1%) 4.2 ± 13.5 | BCD (8) |
| Total | 3590 (100.0%) | 14,423 (100.0%) | 74,544 (100.0%) | |
| Cox1 Sequence of Culicoides Specimen | Best Matched Record on NCBI a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen | Sample ID | BIN No. | Access No. | |
| C. actoni | YNS2-A6 | AAJ7360 | PV636443 | C. actoni, KT352829.1 (99.9%) |
| C. circumscriptus | YNS2-A4 | ACG0258 | PV636441 | C. circumscriptus, OM060694.1 (99.8%) |
| C. circumscriptus | YNS2-A5 | ACG0258 | PV636442 | C. circumscriptus, OM060694.1 (97.7%) |
| C. fenggangensis b | YNS2-A12 | AEB1084 | PV636446 | C. sp., MF709270.1 (86.9%) |
| C. fenggangensis b | YNS2-B10 | AEB1084 | PV690512 | C. sp., KR672173.1 (86.8%) |
| C. sp. nr fenggangensis b | YNS2-B8 | NA | PV636449 | C. brevipalpis, KT352210.1 (86.3%) |
| C. sp. nr marginus b | YNS2-A7 | AGH4070 | PV636444 | C. sp., JN302158.1 (84.5%) |
| C. sp. nr marginus b | YNS2-A9 | AGH4070 | PV636445 | C. sp., JN302158.1 (84.5%) |
| C. sp. nr palpifer | YNS2-B11 | AFK8101 | PV690513 | C. sp., KM992425.1 (82.8%) |
| C. sp. nr palpifer | YNS2-B12 | AFK8101 | PV690514 | C. sp., KM992425.1 (83.8%) |
| C. regalis | YNS2-B6 | AFE7578 | PV636448 | C. regalis, OP405012.1 (94.6%) |
| C. regalis | YNS2-C6 | AFE7578 | PV690515 | C. regalis, OP405012.1 (94.6%) |
| C. sp. nr spiculae b | YNS2-B1 | AFF5003 | PV636447 | C. spiculae, ON002362.1 (86.6%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-N.; Duan, Y.-L.; Li, Z.-H.; Deng, J.-M.; Sun, X.-N.; Shen, X.-Y.; Yang, A.-X.; Li, S.-L. Diversity and Seasonal Abundance of Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Tengchong County of Yunnan, China. Insects 2025, 16, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080780
Wang Y-N, Duan Y-L, Li Z-H, Deng J-M, Sun X-N, Shen X-Y, Yang A-X, Li S-L. Diversity and Seasonal Abundance of Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Tengchong County of Yunnan, China. Insects. 2025; 16(8):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080780
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yi-Nan, Ying-Liang Duan, Zhan-Hong Li, Jia-Ming Deng, Xing-Nan Sun, Xue-Ying Shen, An-Xi Yang, and Shi-Long Li. 2025. "Diversity and Seasonal Abundance of Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Tengchong County of Yunnan, China" Insects 16, no. 8: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080780
APA StyleWang, Y.-N., Duan, Y.-L., Li, Z.-H., Deng, J.-M., Sun, X.-N., Shen, X.-Y., Yang, A.-X., & Li, S.-L. (2025). Diversity and Seasonal Abundance of Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Tengchong County of Yunnan, China. Insects, 16(8), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080780






