Evaluation on Biocontrol Efficacy of Episyrphus balteatus De Geer (Diptera: Syrphidae) Against Aphis craccivora, Myzus persicae, and Megoura crassicauda
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Aphid and Hoverfly
2.2. Predatory Functional Response of E. balteatus to Aphids
2.3. Control Efficacy of E. balteatus to Aphids Under Caged Conditions
2.4. Preference of E. balteatus for A. craccivora, M. persicae, and M. crassicauda
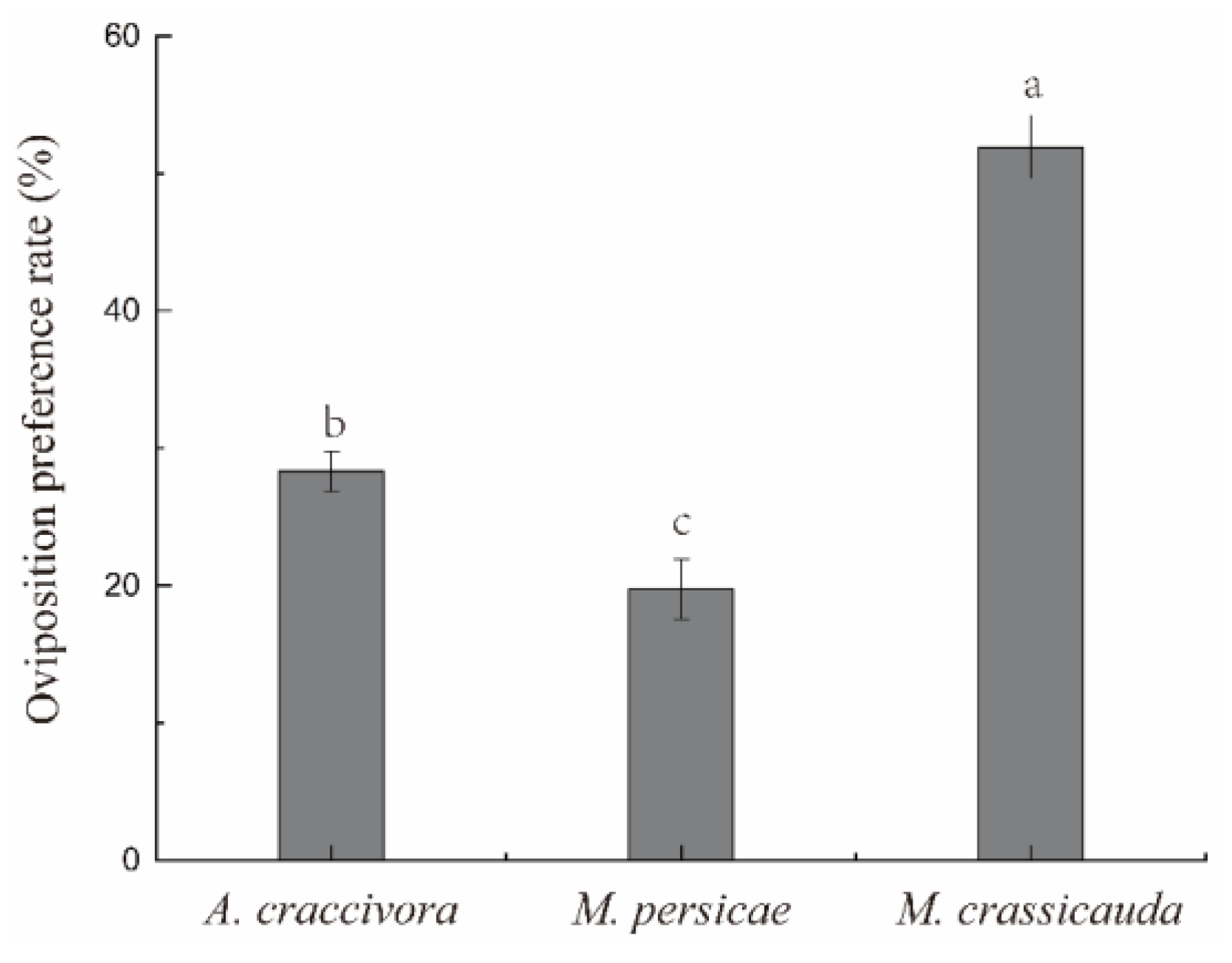
2.4.1. Oviposition Preference
2.4.2. Predatory Preference
2.5. Statistical Methodology
3. Results
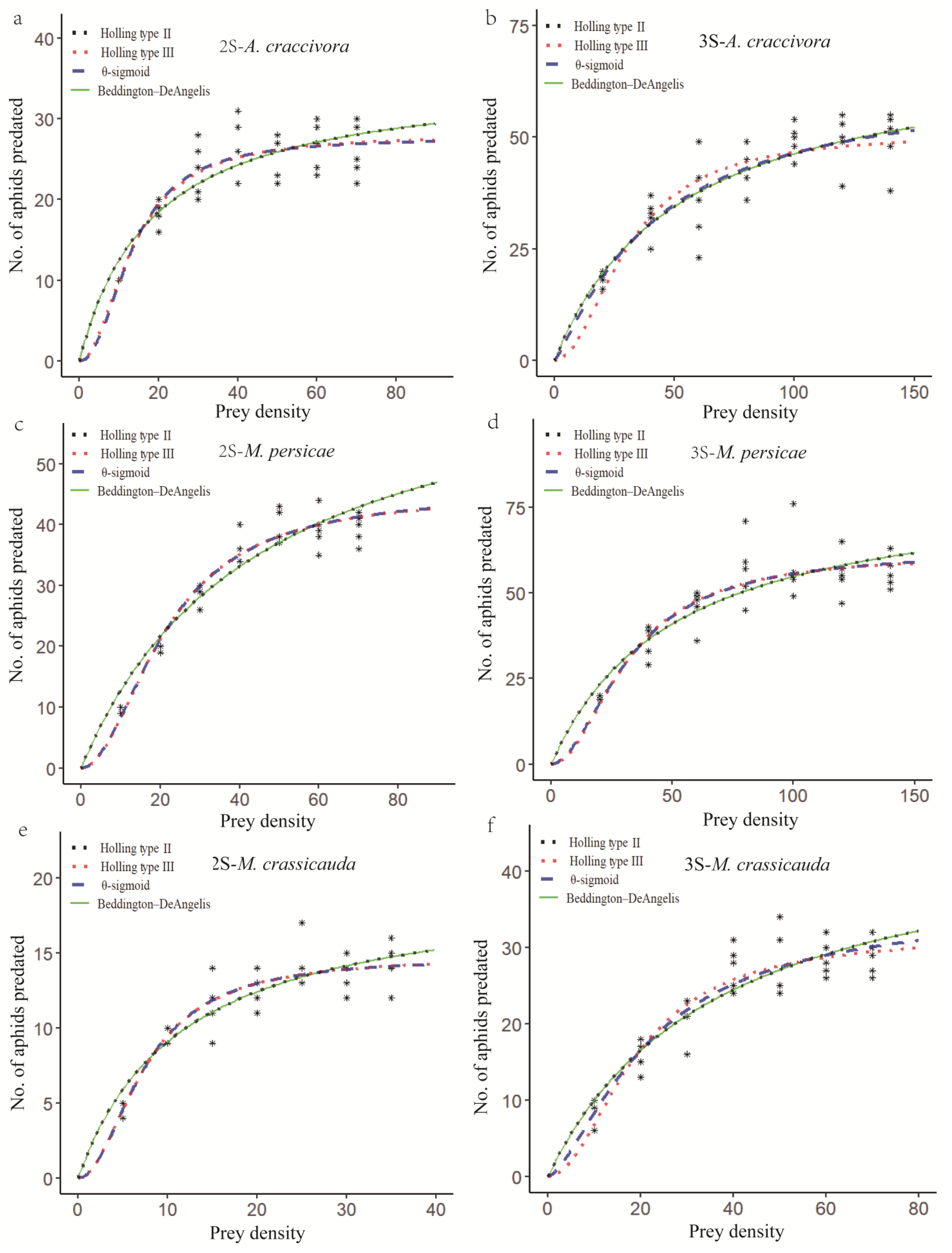
3.1. Predatory Functional Response of E. balteatus to Aphids
3.2. Control Efficacy of E. balteatus to Aphids Under Caged Conditions
3.3. Preference of E. balteatus for A. craccivora, M. persicae, and M. crassicauda
3.3.1. Oviposition Preference
3.3.2. Predatory Preference
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCAs | biological control agents |
| AIC | Akaike information criterion |
References
- Mengual, X.; Ståhls, G.; Rojo, S. Molecular phylogeny of Allograpta (Diptera, Syrphidae) reveals diversity of lineages and non-monophyly of phytophagous taxa. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 49, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengual, X.; Ståhls, G.; Rojo, S. Phylogenetic relationships and taxonomic ranking of pipizine flower flies (Diptera: Syrphidae) with implications for the evolution of aphidophagy. Cladistics 2015, 31, 491–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotton, K.R.; Gao, B.; Menz, M.H.M.; Morris, R.K.A.; Ball, S.G.; Lim, K.S.; Reynolds, D.R.; Hu, G.; Chapman, J.W. Mass seasonal migrations of hoverflies provide extensive pollination and crop protection services. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 2167–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, Y. Study on the predation effect of Eupeodes corollae Fabricius on three species of aphids. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. 2001, 2, 102–104+110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiko, K.; Mitsuhiro, S. Assessment of the maple aphid colony by the hover fly, Episyrphus balteatus (de Geer) (Diptera: Syrphidae) I. J. Ethol. 1986, 4, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, J.; Belliure, B. Impact of syrphid predation on production of migrants in colonies of the brown citrus aphid, Toxoptera citricida (Homoptera: Aphididae). Biol. Control 2001, 21, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, H.; He, L.; Wu, K. Population fitness of the hoverfly, Episyrphus balteatus (De Geer) (Diptera: Syrphidae) fed on different aphid species. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2023, 39, 254–263. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Cao, L.; Liang, D.; Zhang, Z. Control aphids in vegetable fields with Syrphid flies. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2002, 3, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, K. Bidirectional predation between larvae of the hoverfly Episyrphus balteatus (Diptera: Syrphidae) and the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigitie, T. Estimating predatory efficiency of Episyrphus balteatus (Diptera: Syrphidae) in cereal fields. Environ. Entomol. 1995, 24, 687–691. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Li, X. Predatory functional response of Episyrphus balteatus to Myzus persicae. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. 2000, 109–111. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X.; Luo, J.; Cheng, X. Analysis of predatory hoverfly species and their damage control effects on soybean aphids in the northeast soybean ecological region. J. Appl. Entomol. 2011, 48, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H. Episyrphus balteaus (De Geer) and Metasyrphus corollae (Fabricius) attractants. CN103355293B, 18 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cock, M.J.W.; Lenteren, V.; Brodeur, J.C.; Barratt, J.; Bigler, B.I.P.; Bolckmans, F.; Cônsoli, K.; Haas, F.L.; Mason, F.; Parra, P.G.; et al. Do new access and benefit sharing procedures under the convention on biological diversity threaten the future of biological control? BioControl 2010, 55, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clem, C.S.; Hobson, K.A.; Harmon, T.; Alexandra, N. Insights into natal origins of migratory Nearctic hoverflies (Diptera: Syrphidae): New evidence from stable isotope (δ2H) assignment analyses. Ecography 2022, 2023, 06465. [Google Scholar]
- Dedryver, C.A.; Ralec, A.L.; Fabre, F. The conflicting relationships between aphids and men: A review of aphid damage and control strategies. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2010, 333, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ju, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, H.; Wang, J.; Qu, M. Control effects and safety assessment of four insecticideson Aphis craccivora. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2013, 45, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Takemura, M.; Nishida, R.; Mori, N.; Kuwahara, Y. Acylated flavonol glycosides as probing stimulants of a bean aphid, Megoura crassicauda, from Vicia angustifolia. Phytochemistry 2002, 61, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emden, H.F.v.; Eastop, V.F.; Hughes, R.D.; Way, M.J. The ecology of myzus persicae. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1969, 14, 197–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, B.I.P.; Moran, V.C.; Bigler, F.; Lenteren, J.C.V. The status of biological control and recommendations for improving uptake for the future. BioControl 2018, 63, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, T. Research progress, application and prospect of biological control of aphids in major crops in China. J. Plant Prot. 2022, 49, 146–172. [Google Scholar]
- Stiling, P.; Cornelissen, T. What makes a successful biocontrol agent? A meta-analysis of biological control agent performance. Biol. Control 2005, 34, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, G. Aphids and their biocontrol. In Ecofriendly Pest Management for Food Security; Omkar, Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 63–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, C. Methods for determining the quantity of predator selectivity for prey. Acta Ecol. Sinica. 1987, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Okuyama, T.; Ruyle, R.L. Solutions for functional response experiments. Acta Oecologica 2011, 37, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, T. On selection of functional response models: Holling’s models and more. BioControl 2013, 58, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilborn, R.; Mangel, M. The Ecological Detective: Confronting Models with Data; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1997; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Putra, N.S.; Yasuda, H. Effects of prey species and its density on larval performance of two species of hoverfly larvae, Episyrphus balteatus de Geer and Eupeodes corollae Fabricius (Diptera: Syrphidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2006, 41, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryam, S.; Hossein, M.; Babak, G. Host plant effect on functional response and consumption rate of Episyrphus balteatus (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on different densities of Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Crop. Prot. 2013, 2, 375–385. [Google Scholar]
- Baskaran, R.; Sasikumar, S.; SRajavel, D.; Suresh, K. Influence of semi-synthetic diet on fecundity of Paragus serratus. Ann. Plant Prot. Sci. 2009, 17, 235–236. [Google Scholar]
- Torrealba, J.; Arcaya, E. Respuesta funcional de la larva de Pseudodoros clavatus (Fabricius, 1794) (Diptera: Syrphidae) al áfido negro del matarratón Aphis craccivora Koch, 1854 (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Entomotropica 2014, 29, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, R.A.J.; Hussein, S.N. Responses of Episyrphus balteatus DeGeer (Diptera: Syrphidae) in relation to prey density and predator size. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2014, 17, 207–211. [Google Scholar]
- Jalilian, F.; Fathipour, Y.; Talebi, A.A.; Sedaratian, A. Functional response and mutual interference of Episyrphus balteatus and Scaeva albomaculata (Dip.: Syrphidae) fed on Myzus persicae (Hom.: Aphididae). Appl. Entomol. Phytopathol. 2011, 78, 257–274. [Google Scholar]
- Enkegaard, A.; Brødsgaard, H.F.; Hansen, D.L. Macrolophus caliginosus: Functional response to whiteflies and preference and switching capacity between whiteflies and spider mites. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2003, 101, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Wu, K. Predation and control effect of Eupeodes corollae Fabricius (Diptera: Syrphidae) on leguminous plant aphids. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evelin, A.; Celeste, P.-B.; Ximo, M.; Jacobo, Z.-V.J.; Santos, R. Life table and predation rates of the syrphid fly Allograpta exotica, a control agent of the cowpea aphid Aphis craccivora. Biol. Control 2017, 115, 74–84. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Wu, K. Hoverflies provide pollination and biological pest control in greenhouse-grown horticultural crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1118388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelton, D.W.; James, D.H. Temporal dynamics of natural enemy–pest interactions in a changing environment. Biol. Control 2014, 75, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Pan, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhou, X.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Wu, K. Windborne migration amplifies insect-mediated pollination services. Elife 2022, 11, e76230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J. On optimal oviposition behavior in phytophagous insects. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1978, 14, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonebrake, T.C.; Boggs, C.L.; McNally, J.M.; Ranganathan, J.; Ehrlich, P.R. Oviposition behavior and offspring performance in herbivorous insects: Consequences of climatic and habitat heterogeneity. Oikos 2010, 119, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatti-Ricalde, M.G.; de Carvalho Silva, A.; Ricalde, M.P.; Rouws, J.R.C.; Mayhe-Nunes, A.J.; de Souza Abboud, A.C. Abundance of natural enemies and aphids in okra crops (Abelmoschus esculentus—Malvaceae) diversified with Tithonia rotundifolia (Asteraceae). Biol. Control 2023, 187, 105399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, T.; Qin, Z.; Cao, K.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Shi, W. Predation preference and nutritional values of four different aphid species for Orius sauteri (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2022, 32, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, G.H.; Pulliam, H.R.; Charnov, E.L. Optimal foraging:a selective review of theory and tests. Q. Rev. Biol. 2025, 52, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.H.; Hogg, B.N.; Mills, N.J.; Daane, K.M. Syrphid flies suppress lettuce aphids. BioControl 2012, 57, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Larvae of E. balteatus | Aphid Species | Density Settings |
|---|---|---|
| 2nd instar | A. craccivora | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 |
| M. persicae | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 | |
| M. crassicauda | 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 | |
| 3rd instar | A. craccivora | 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120,140 |
| M. persicae | 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120, 140 | |
| M. crassicauda | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 |
| Aphid | Control Group | Hoverfly/Aphid |
|---|---|---|
| A. craccivora | 1000 | 1:500, 1:1000, 1:2000, 1:4000, 1:6000 |
| M. persicae | 2000 | 1:2000, 1:4000, 1:6000, 1:8000, 1:10,000 |
| M. crassicauda | 250 | 1:250, 1:500, 1:1000, 1:1500, 1:2000 |
| Name | Model | z | Q |
|---|---|---|---|
| Holling type II | Na = aN/(1 + aNh) | 1 | 1 |
| Holling type III | Na = aN2/(1 + aN2h) | 2 | 1 |
| θ-sigmoid | Na = aNθ/(1 + aNθh) | θ | 1 |
| Beddington–DeAngelis | Na = aN/(1 + γP + aNh) | 1 | 1 + γP |
| Arditi and Akçakaya | Na = aNP−m /(1 + aNP−mh) | 1 | P −m |
| Arditi and Ginzburg | Na = aN/P/(1 + aNh/P) | 1 | P |
| Model | Attack Rate (a) | Handling Time (h) | SSQ | AIC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. craccivora | |||||
| 2nd instar | |||||
| Holling type II | 1.927 | 0.028 | Z = 1 | 335.934 | 2.640 |
| Holling type III | 0.154 | 0.036 | Z = 2 | 253.395 | 2.518 |
| θ-Sigmoid | 0.097 | 0.036 | Z = 2.179 | 251.719 | 2.572 |
| Beddington– DeAngelis | 1.93 | 0.028 | r = 0.001 | 335.934 | 2.697 |
| 3rd instar | |||||
| Holling type II | 1.353 | 0.014 | Z = 1 | 1085.461 | 3.149 |
| Holling type III | 0.055 | 0.02 | Z = 2 | 1210.885 | 3.197 |
| θ-Sigmoid | 0.739 | 0.016 | Z = 1.195 | 1076.196 | 3.203 |
| Beddington– DeAngelis | 1.416 | 0.014 | r = 0.046 | 1085.461 | 3.207 |
| M. persicae | |||||
| 2nd instar | |||||
| Holling type II | 1.561 | 0.014 | Z = 1 | 419.373 | 2.737 |
| Holling type III | 0.1 | 0.022 | Z = 2 | 256.728 | 2.524 |
| θ-Sigmoid | 0.114 | 0.022 | Z = 1.955 | 256.434 | 2.580 |
| Beddington– DeAngelis | 1.589 | 0.014 | r = 0.018 | 419.373 | 2.794 |
| 3rd instar | |||||
| Holling type II | 1.625 | 0.012 | Z = 1 | 1754.829 | 3.358 |
| Holling type III | 0.06 | 0.016 | Z = 2 | 1493.542 | 3.288 |
| θ-Sigmoid | 0.092 | 0.016 | Z = 1.873 | 1488.689 | 3.344 |
| Beddington– DeAngelis | 1.658 | 0.012 | r = 0.02 | 1754.829 | 3.416 |
| M. crassicauda | |||||
| 2nd instar | |||||
| Holling type II | 1.694 | 0.051 | Z = 1 | 77.833 | 2.005 |
| Holling type III | 0.265 | 0.068 | Z = 2 | 60.272 | 1.894 |
| θ-Sigmoid | 0.258 | 0.068 | Z = 2.015 | 60.269 | 1.951 |
| Beddington– DeAngelis | 1.7 | 0.051 | r = 0.004 | 77.833 | 2.062 |
| 3rd instar | |||||
| Holling type II | 1.275 | 0.021 | Z = 1 | 328.515 | 2.631 |
| Holling type III | 0.087 | 0.032 | Z = 2 | 323.501 | 2.624 |
| θ-Sigmoid | 0.339 | 0.028 | Z = 1.508 | 302.637 | 2.652 |
| Beddington– DeAngelis | 1.293 | 0.021 | r = 0.015 | 328.515 | 2.688 |
| Hoverfly/Aphid | Population Decline Rate (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3rd Day | 6th Day | 9th Day | 12th Day | |
| A. craccivora | ||||
| CK | −179.00 ± 1.89c | −208.67 ± 6.43c | −378.67 ± 16.73c | −449.67 ± 27.86c |
| 1:500 | −186.67 ± 6.69c | −210.67 ± 8.13c | −18.00 ± 14.24a | 94.67 ± 2.88a |
| 1:1000 | −176.67 ± 12.53c | −203.33 ± 6.43c | −66.66 ± 17.74b | 100.00 ± 0.00a |
| 1:2000 | −104.00 ± 3.27b | −109.67 ± 3.65b | −36.50 ± 6.13ab | 77.50 ± 5.18ab |
| 1:4000 | −108.67 ± 6.88b | −134.92 ± 7.33b | −93.58 ± 3.37b | 35.58 ± 5.51ab |
| 1:6000 | −28.50 ± 2.75a | −42.44 ± 3.85a | −91.67 ± 7.20b | 24.72 ± 4.61b |
| M. persicae | ||||
| CK | −46.83 ± 3.81bc | −59.50 ± 5.67bc | −131.5 ± 6.28b | −152.50 ± 2.62d |
| 1:2000 | −59.33 ± 6.95c | −71.33 ± 5.20c | 1.33 ± 14.74a | 96.67 ± 0.76a |
| 1:4000 | −17.67 ± 1.72a | −36.50 ± 0.93ab | 16.42 ± 6.14a | 95.42 ± 0.95a |
| 1:6000 | −19.61 ± 2.57a | −40.00 ± 4.35ab | 20.67 ± 6.30a | 60.72 ± 1.99b |
| 1:8000 | −25.54 ± 3.62ab | −22.83 ± 4.98a | −1.96 ± 4.16a | 40.25 ± 5.31bc |
| 1:10,000 | −17.17 ± 2.76a | −27.23 ± 4.81a | −6.37 ± 7.83a | 21.10 ± 7.02c |
| M. crassicauda | ||||
| CK | −34.67 ± 2.88ab | −108.00 ± 5.66abc | −244.00 ± 16.11c | −304.00 ± 21.75c |
| 1:250 | −25.33 ± 4.74a | −77.33 ± 10.38a | 100.00 ± 0.00a | — — |
| 1:500 | −60.00 ± 6.53b | −182.00 ± 17.99c | −100.00 ± 36.48b | 84.67 ± 7.56a |
| 1:1000 | −32.67 ± 1.90ab | −154.33 ± 22.29bc | −45.67 ± 14.32b | 40.33 ± 16.98a |
| 1:1500 | −43.55 ± 8.41ab | −89.33 ± 7.10ab | −128.89 ± 4.28b | −98.22 ± 5.28b |
| 1:2000 | −52.83 ± 5.30ab | −102.00 ± 1.65ab | −128.67 ± 4.28b | −98.17 ± 5.27b |
| Larva | Aphid Species | No. of Predatory | Ci |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd instar | A. craccivora | 9.33 ± 0.66a | 0.04 ± 0.01a |
| M. persicae | 7.67 ± 0.34a | −0.06 ± 0.01b | |
| M. crassicauda | 9.00 ± 0.58a | 0.02 ± 0.01a | |
| 3rd instar | A. craccivora | 16.67 ± 0.88a | 0.17 ± 0.01a |
| M. persicae | 6.33 ± 0.34c | −0.30 ± 0.02c | |
| M. crassicauda | 12.33 ± 0.66b | 0.02 ± 0.01b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Wu, K. Evaluation on Biocontrol Efficacy of Episyrphus balteatus De Geer (Diptera: Syrphidae) Against Aphis craccivora, Myzus persicae, and Megoura crassicauda. Insects 2025, 16, 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080774
Jiang S, Li H, Wu K. Evaluation on Biocontrol Efficacy of Episyrphus balteatus De Geer (Diptera: Syrphidae) Against Aphis craccivora, Myzus persicae, and Megoura crassicauda. Insects. 2025; 16(8):774. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080774
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shanshan, Hui Li, and Kongming Wu. 2025. "Evaluation on Biocontrol Efficacy of Episyrphus balteatus De Geer (Diptera: Syrphidae) Against Aphis craccivora, Myzus persicae, and Megoura crassicauda" Insects 16, no. 8: 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080774
APA StyleJiang, S., Li, H., & Wu, K. (2025). Evaluation on Biocontrol Efficacy of Episyrphus balteatus De Geer (Diptera: Syrphidae) Against Aphis craccivora, Myzus persicae, and Megoura crassicauda. Insects, 16(8), 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080774





