Host-Dependent Variation in Tetranychus urticae Fitness and Microbiota Composition Across Strawberry Cultivars
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Cultivation of Tetranychus urticae
2.2. Fitness Assessment of T. urticae on Different Strawberry Cultivars
2.2.1. Pre-Adult Development Period and Longevity
2.2.2. Fecundity Assessment
2.3. Microbiota Analysis of T. urticae on Different Strawberry Cultivars
3. Results
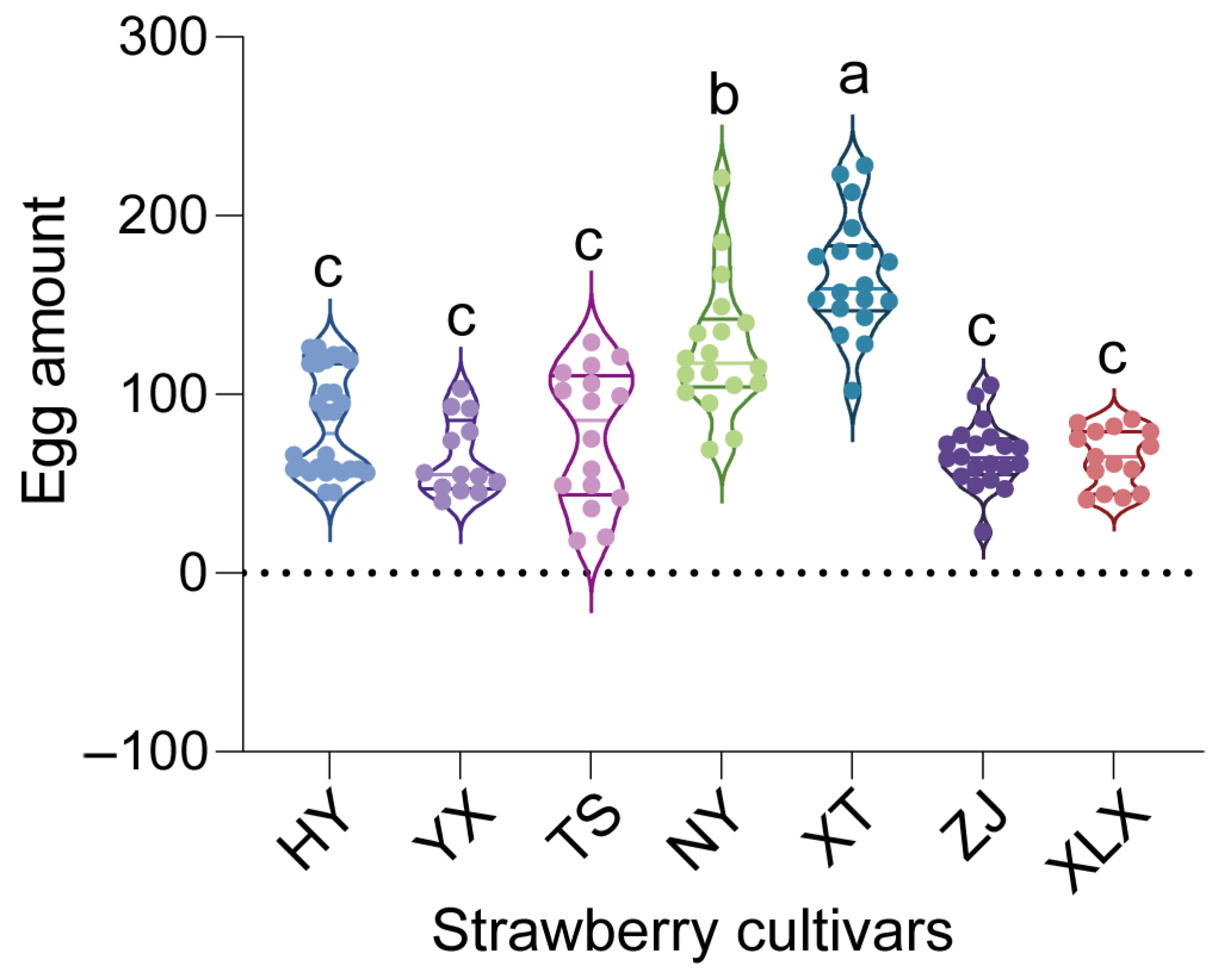
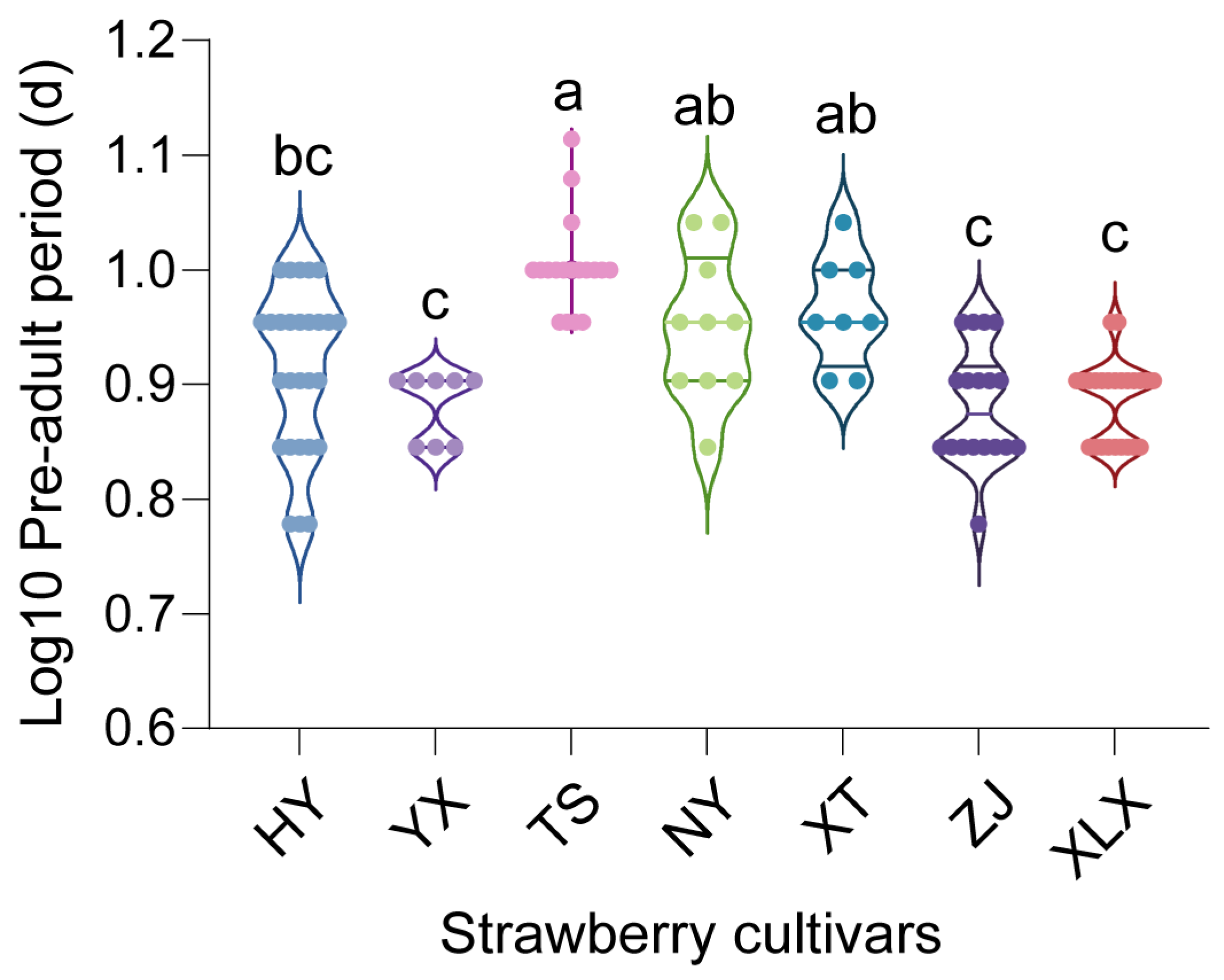
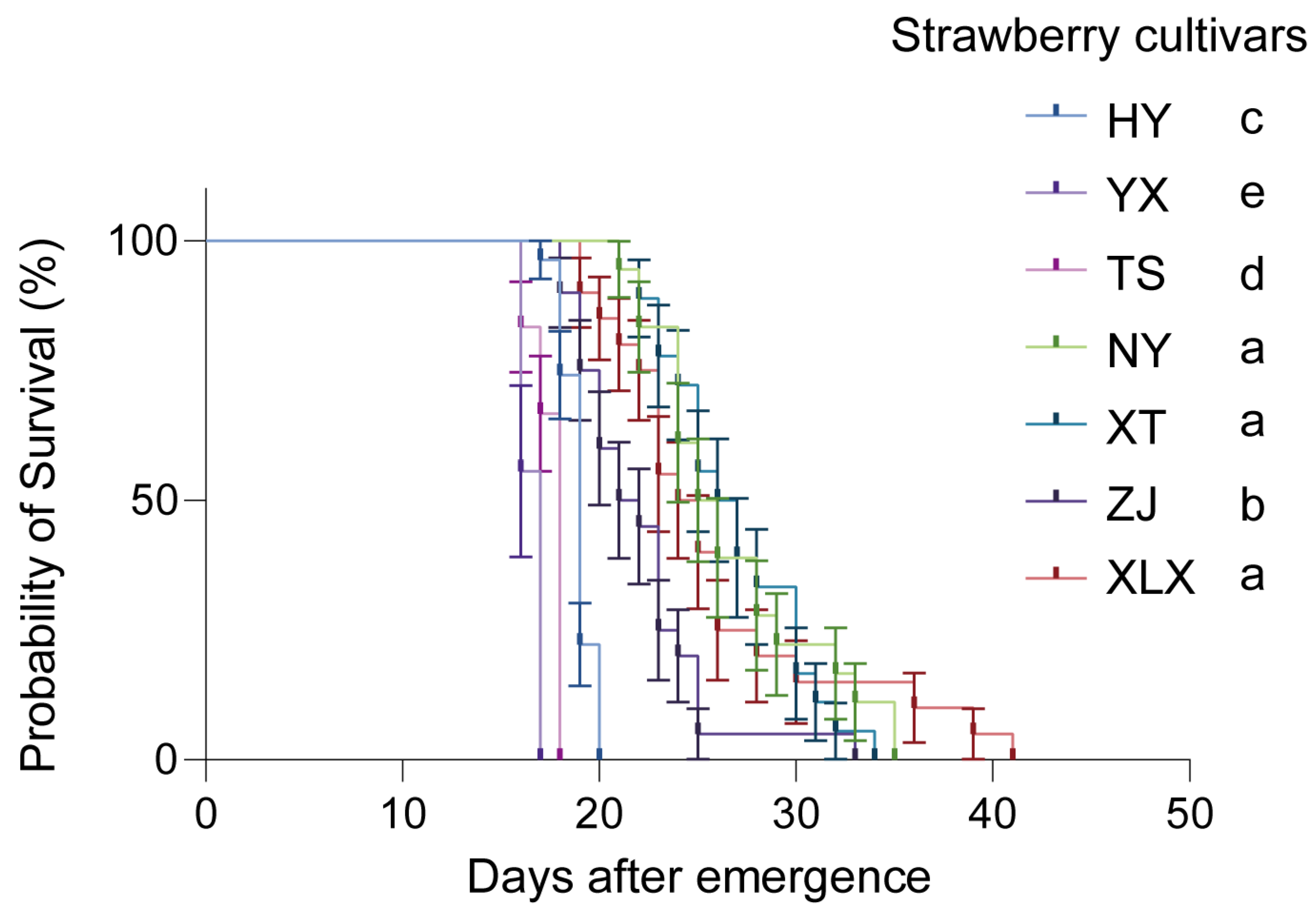
3.1. Tetranychus urticae Fitness on Various Strawberry Cultivars
3.2. Tetranychus urticae Bacterial Microbiota Changed in Various Strawberry Cultivars
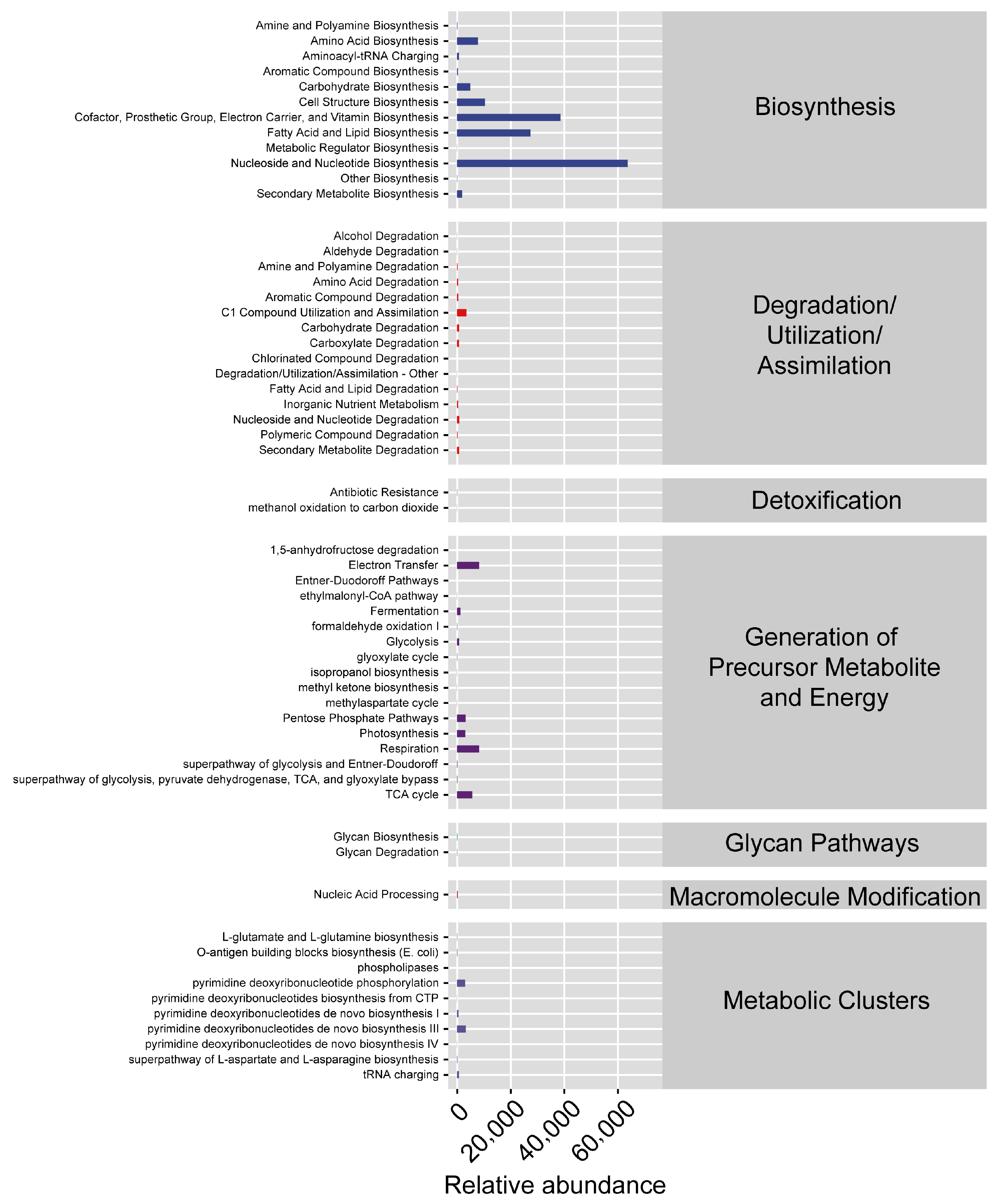
3.2.1. Sequencing Data of Bacterial Microbiota in Tetranychus urticae
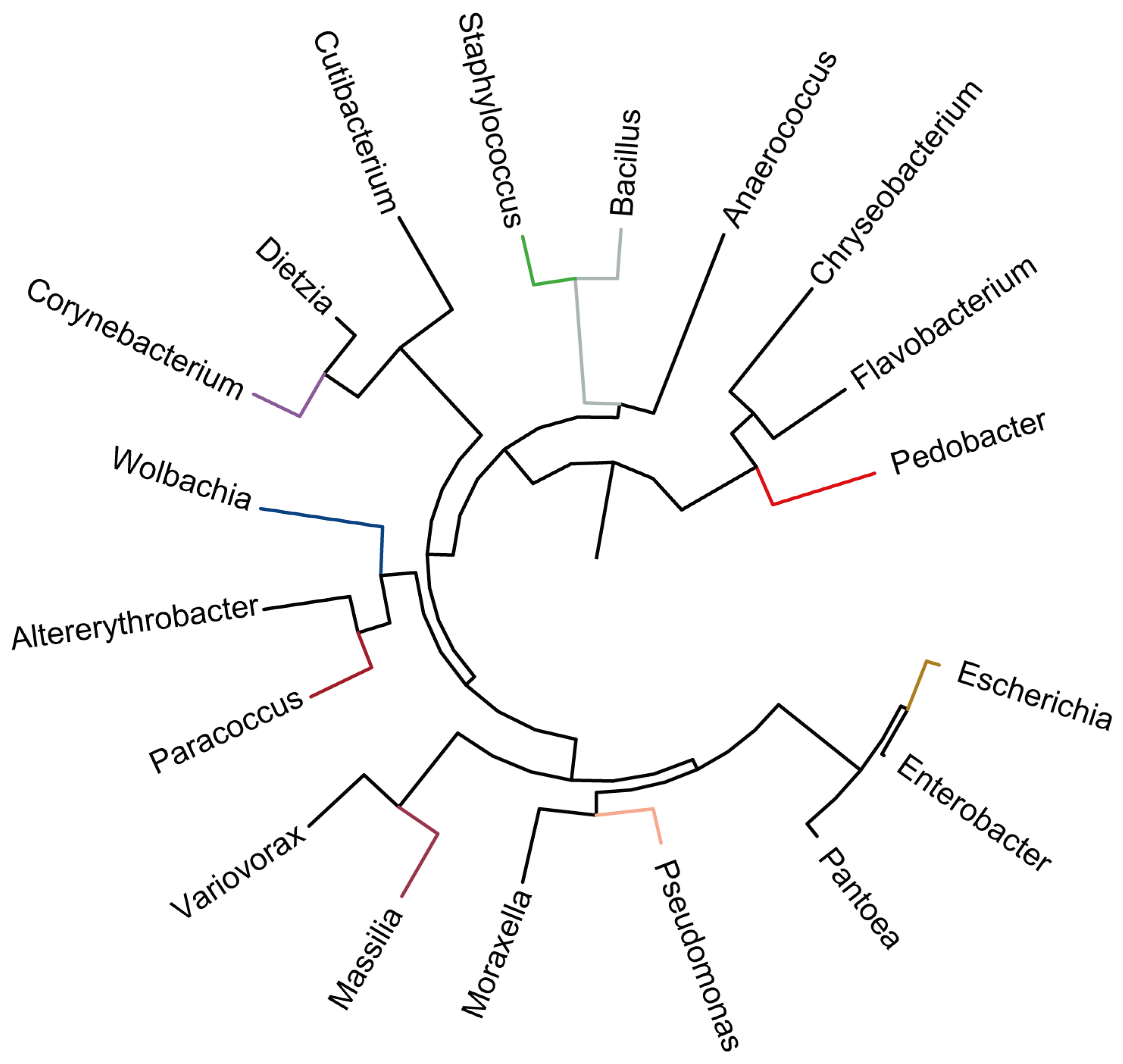
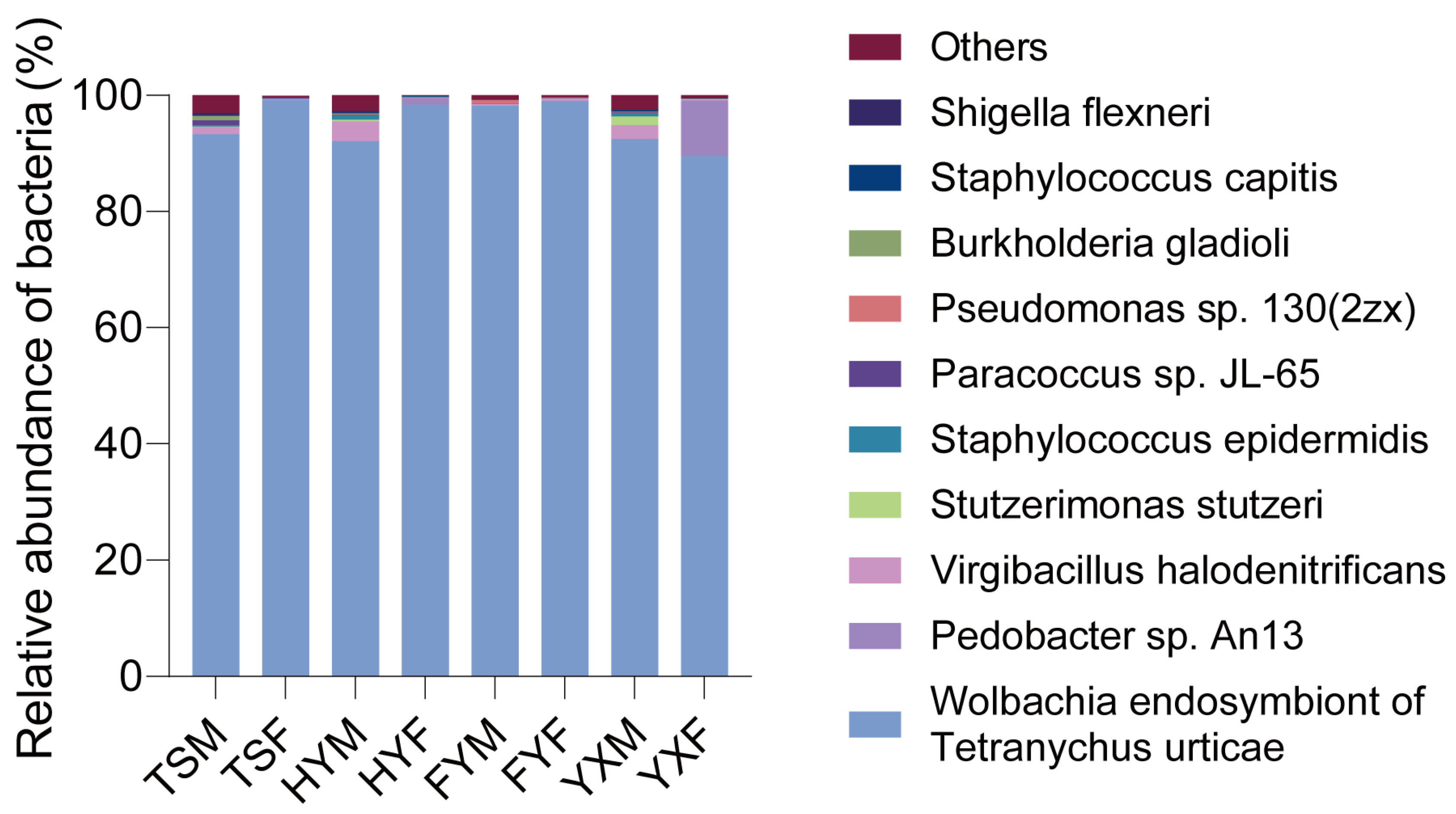
3.2.2. Bacterial Communities in Tetranychus urticae Reared on Different Strawberry Cultivars
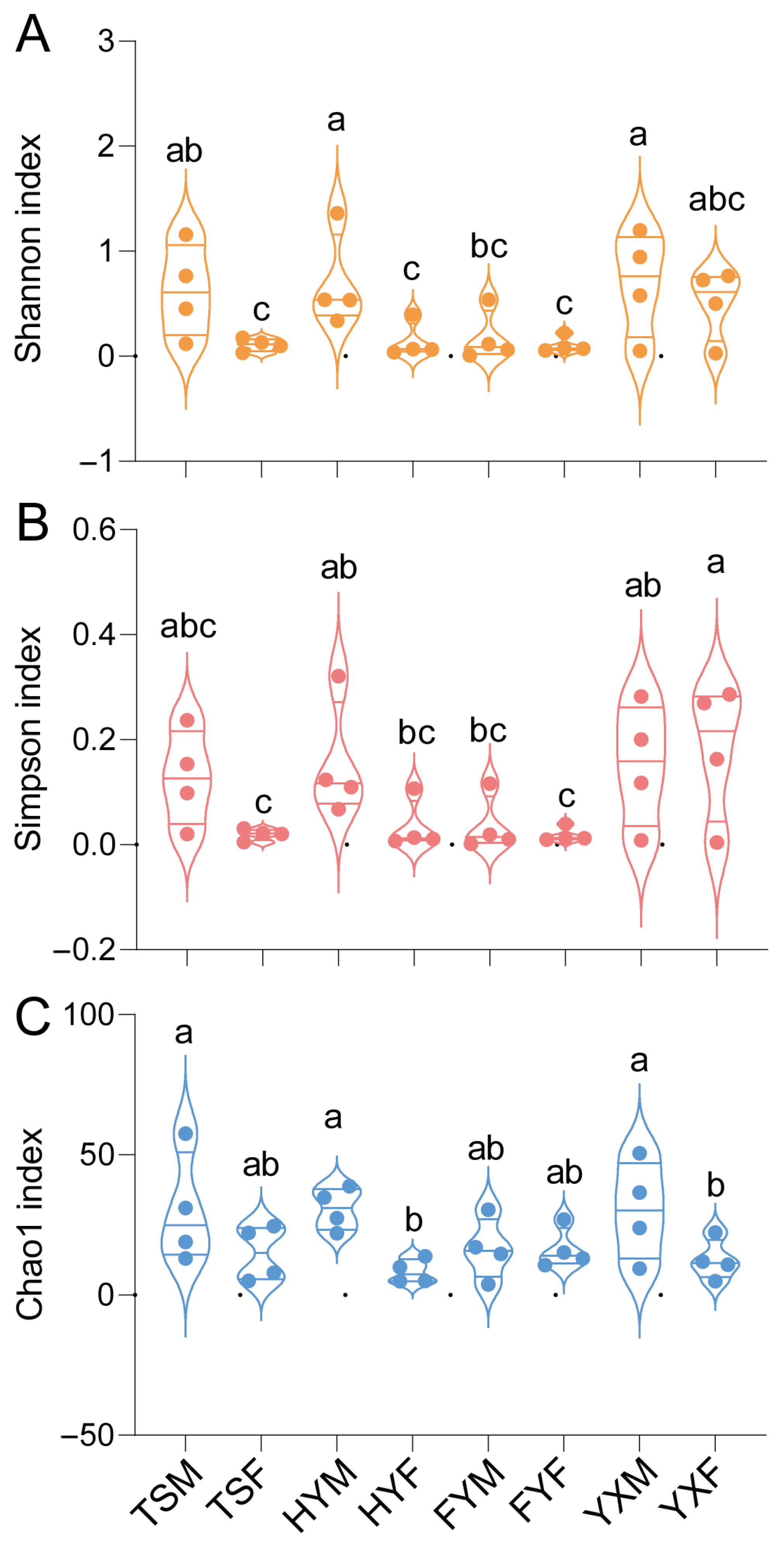
3.2.3. Bacterial Microbiota Varied in Tetranychus urticae Reared on Different Strawberry Cultivars
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Strawberry Cultivars on T. urticae Fitness
4.2. Microbiota Composition and Its Modulation by Host Plants
4.3. Sex-Based Differences in Microbial Diversity
4.4. Implications for Integrated Pest Management
4.5. Future Research Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Guo, L.X.; Yu, X.Y.; Huo, S.M.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Zhou, J.Y.; Sun, J.T.; Hong, X.Y. Decoding plant-induced transcriptomic variability and consistency in two related polyphagous mites differing in host ranges. Mol. Ecol. 2024, 34, e17521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grbić, M.; Van Leeuwen, T.; Clark, R.M.; Rombauts, S.; Rouzé, P.; Grbić, V.; Osborne, E.J.; Dermauw, W.; Thi Ngoc, P.C.; Ortego, F.; et al. The genome of Tetranychus urticae reveals herbivorous pest adaptations. Nature 2011, 479, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmagnani, A.S.; Mannino, G.; Brillada, C.; Novero, M.; Dall’Osto, L.; Maffei, M.E. Biology of two-spotted spider mite (Tetranychus urticae): Ultrastructure, photosynthesis, guanine transcriptomics, carotenoids and chlorophylls metabolism, and decoyinine as a potential acaricide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, T.; Vontas, J.; Tsagkarakou, A.; Dermauw, W.; Tirry, L. Acaricide resistance mechanisms in the two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae and other important Acari: A review. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S. Status of pesticide resistance and associated mutations in the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae, in China. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 150, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E. Multiorganismal insects: Diversity and function of resident microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Moran, N.A. The gut microbiota of insects: Diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 699–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Yuan, M.Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, C.L.; Liu, T.X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chu, D. First evidence for thermal tolerance benefits of the bacterial symbiont Cardinium in an invasive whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 5021–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Song, Z.R.; Song, Y.L.; Zhao, D.S.; Hong, X.Y. The microbiota in spider mite feces potentially reflects intestinal bacterial communities in the host. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E.; Minto, L.B.; Wilkinson, T.L. Quantifying nutrient production by the microbial symbionts in an aphid. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballinger, M.J.; Perlman, S.J. The defensive Spiroplasma. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 32, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbutsu, H.; Moriyama, M.; Nikoh, N.; Hosokawa, T.; Futahashi, R.; Tanahashi, M.; Meng, X.Y.; Kuriwada, T.; Mori, N.; Oshima, K.; et al. Small genome symbiont underlies cuticle hardness in beetles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8382–E8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltenpoth, M.; Flórez, L.V. Versatile and dynamic symbioses between insects and Burkholderia bacteria. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 145–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xie, K.; Zhu, Y.X.; Huo, S.M.; Hoffmann, A.; Hong, X.Y. Wolbachia dominate Spiroplasma in the co-infected spider mite Tetranychus truncatus. Insect Mol. Biol. 2020, 29, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Peng, C.W.; Cui, J.R.; Jin, P.Y.; Yang, K.; Hong, X.Y. Wolbachia affects reproduction in the spider mite Tetranychus truncatus (Acari: Tetranychidae) by regulating chorion protein S38-like and Rop. Insect Mol. Biol. 2021, 30, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Song, Z.R.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Hong, X.Y. Spider mites singly infected with either Wolbachia or Spiroplasma have reduced thermal tolerance. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 706321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, X.L.; Xia, C.B.; Ye, Q.T.; Gong, X.; Cui, J.R.; Peng, C.W.; Hong, X.Y. Wolbachia manipulates reproduction of spider mites by influencing herbivore salivary proteins. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, M.E.; Arnaiz, A.; Rosa-Diaz, I.; González-Melendi, P.; Romero-Hernandez, G.; Ojeda-Martinez, D.A.; Garcia, A.; Contreras, E.; Martinez, M.; Diaz, I. Plant defenses against Tetranychus urticae: Mind the gaps. Plants 2020, 9, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, W.; Tayyab, M.; Khalil, F.; Hua, Z.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H.Y.H. Silicon-mediated plant defense against pathogens and insect pests. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 168, 104641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljbory, Z.; Chen, M.S. Indirect plant defense against insect herbivores: A review. Insect Sci. 2018, 25, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- War, A.R.; Paulraj, M.G.; Ahmad, T.; Buhroo, A.A.; Hussain, B.; Ignacimuthu, S.; Sharma, H.C. Mechanisms of plant defense against insect herbivores. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1306–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Z.; Han, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, F.; Wu, Q.; Xie, W.; et al. Whitefly hijacks a plant detoxification gene that neutralizes plant toxins. Cell 2021, 184, 1693–1705.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechaine, J.M.; Burger, J.C.; Chapman, M.A.; Seiler, G.J.; Brunick, R.; Knapp, S.J.; Burke, J.M. Fitness effects and genetic architecture of plant-herbivore interactions in sunflower crop-wild hybrids. New Phytol. 2009, 184, 828–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Z.; Fang, C.; Liu, K. Transcriptome and metabolome analyses reveal the responses of brown planthoppers to RH resistant rice cultivar. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1018470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabelo, M.M.; Paula-Moraes, S.V.; Pereira, E.J.G.; Siegfried, B.D. Demographic performance of Helicoverpa zea populations on dual and triple-gene Bt cotton. Toxins 2020, 12, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Gu, Z.; Shen, J.; Wang, C.; Zeng, L.; Reitz, S.R.; Cao, Y. Rosa chinensis cultivars affect fitness-related characteristics and digestive physiology of the western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis Pergande (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 1620–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, I.A.; Silveira, E.C.; Souza, D.C.; Bernardi, L.; Souza, B.H.S.; Resende, L.V. Resistance of strawberry genotypes to the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Persian J. Acarol. 2022, 11, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, X.L.; Lu, Y.J.; Xia, C.B.; Xia, X.; Hong, X.Y. Transcriptome of Tetranychus urticae embryos reveals insights into Wolbachia-induced cytoplasmic incompatibility. Insect Mol. Biol. 2020, 29, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.X.; Sun, J.T.; Witters, J.; Vandenhole, M.; Dermauw, W.; Bajda, S.A.; Simma, E.A.; Wybouw, N.; Villacis-Perez, E.; Van Leeuwen, T. Incomplete reproductive barriers and genomic differentiation impact the spread of resistance mutations between green- and red-colour morphs of a cosmopolitan mite pest. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 4278–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.T.; Gong, X.; Liu, H.H.; Wu, B.X.; Peng, C.W.; Hong, X.Y.; Bing, X.L. The symbiont Wolbachia alleviates pesticide susceptibility in the two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae through enhanced host detoxification pathways. Insect Sci. 2024, 31, 1822–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, X.B.; Zhang, T.T.; Bai, S.X.; He, K.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Francis, F.; Wang, Z.Y. Effects of host plants on aphid feeding behavior, fitness, and Buchnera aphidicola titer. Insect Sci. 2024, 32, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skidmore, I.H.; Hansen, A.K. The evolutionary development of plant-feeding insects and their nutritional endosymbionts. Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 910–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Li, C.; Yan, J.Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Yao, Y.L.; Ren, F.R.; Luan, J.B. Autophagy regulates whitefly-symbiont metabolic interactions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0208921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.P.; Yang, Q.Y.; Liu, J.X.; Haq, I.U.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Attia, K.A.; Abushady, A.M.; Liu, C.Z.; Lv, N. Host plant-mediated effects on Buchnera symbiont: Implications for biological characteristics and nutritional metabolism of pea aphids (Acyrthosiphon pisum). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1288997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Cao, W.J.; Zhong, L.R.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Liu, X.D. Host plant determines the population size of an obligate symbiont (Buchnera aphidicola) in aphids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 2336–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matchado, M.S.; Rühlemann, M.; Reitmeier, S.; Kacprowski, T.; Frost, F.; Haller, D.; Baumbach, J.; List, M. On the limits of 16S rRNA gene-based metagenome prediction and functional profiling. Microb. Genom. 2024, 10, 001203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Mo, B.T.; Li, G.C.; Li, Z.L.; Huang, L.Q.; Sun, Y.L.; Dong, J.F.; Smith, D.P.; Wang, C.Z. Sex pheromone communication in an insect parasitoid, Campoletis chlorideae Uchida. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2215442119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, S.E.; Jeon, C.O.; Hyun, S. Comparative analysis of Drosophila melanogaster gut microbiota with respect to host strain, sex, and age. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 74, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, V.B.; Bachtrog, D. Evolution of sex chromosomes in insects. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2010, 44, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.D.; Stoehr, A.M.; Nunn, C.; Smyth, K.N.; Prokop, Z.M. Sexual dimorphism in immunity across animals: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.T.; Li, T.P.; Wang, M.K.; Hong, X.Y. Wolbachia-based strategies for control of agricultural pests. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2023, 57, 101039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.L. Wolbachia mosquito control: Tested. Science 2016, 352, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Name | Input | Filtered | Denoised | Phylum | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSM1 | 9454 | 9454 | 9369 | 4 | 9 |
| TSM2 | 10,303 | 10,303 | 10,196 | 4 | 21 |
| TSM3 | 14,999 | 14,999 | 14,876 | 4 | 38 |
| TSM4 | 15,463 | 15,463 | 15,387 | 5 | 16 |
| TSF1 | 15,050 | 15,050 | 14,992 | 5 | 20 |
| TSF2 | 14,562 | 14,562 | 14,555 | 2 | 4 |
| TSF3 | 14,019 | 14,019 | 13,936 | 6 | 20 |
| TSF4 | 13,536 | 13,536 | 13,524 | 4 | 7 |
| HYM1 | 14,520 | 14,520 | 14,486 | 3 | 14 |
| HYM2 | 14,892 | 14,892 | 14,512 | 4 | 25 |
| HYM3 | 13,410 | 13,410 | 13,348 | 4 | 17 |
| HYM4 | 15,636 | 15,636 | 15,502 | 5 | 25 |
| HYF1 | 12,979 | 12,979 | 12,965 | 4 | 10 |
| HYF2 | 12,687 | 12,687 | 12,663 | 4 | 9 |
| HYF3 | 12,352 | 12,352 | 12,282 | 2 | 4 |
| HYF4 | 14,573 | 14,573 | 14,570 | 2 | 4 |
| FYM1 | 13,989 | 13,989 | 13,952 | 2 | 4 |
| FYM2 | 15,759 | 15,759 | 15,593 | 4 | 11 |
| FYM3 | 15,138 | 15,138 | 15,080 | 4 | 21 |
| FYM4 | 14,878 | 14,878 | 14,793 | 5 | 13 |
| FYF1 | 14,918 | 14,918 | 14,862 | 4 | 11 |
| FYF2 | 12,277 | 12,277 | 12,194 | 4 | 22 |
| FYF3 | 13,397 | 13,397 | 13,349 | 4 | 9 |
| FYF4 | 13,533 | 13,533 | 13,457 | 4 | 11 |
| YXM1 | 15,624 | 15,624 | 15,614 | 4 | 9 |
| YXM2 | 14,113 | 14,113 | 14,102 | 3 | 11 |
| YXM3 | 15,449 | 15,449 | 15,061 | 5 | 32 |
| YXM4 | 14,191 | 14,191 | 14,144 | 5 | 24 |
| YXF1 | 15,636 | 15,636 | 15,610 | 2 | 4 |
| YXF2 | 14,354 | 14,354 | 14,291 | 4 | 15 |
| YXF3 | 13,540 | 13,540 | 13,477 | 4 | 11 |
| YXF4 | 15,975 | 15,975 | 15,942 | 4 | 11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huo, S.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, J.; Yang, K. Host-Dependent Variation in Tetranychus urticae Fitness and Microbiota Composition Across Strawberry Cultivars. Insects 2025, 16, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080767
Zhang X, Yang H, Yan Z, Wang Y, Wang Q, Huo S, Chen Z, Cheng J, Yang K. Host-Dependent Variation in Tetranychus urticae Fitness and Microbiota Composition Across Strawberry Cultivars. Insects. 2025; 16(8):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080767
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xu, Hongjun Yang, Zhiming Yan, Yuanhua Wang, Quanzhi Wang, Shimei Huo, Zhan Chen, Jialong Cheng, and Kun Yang. 2025. "Host-Dependent Variation in Tetranychus urticae Fitness and Microbiota Composition Across Strawberry Cultivars" Insects 16, no. 8: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080767
APA StyleZhang, X., Yang, H., Yan, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, Q., Huo, S., Chen, Z., Cheng, J., & Yang, K. (2025). Host-Dependent Variation in Tetranychus urticae Fitness and Microbiota Composition Across Strawberry Cultivars. Insects, 16(8), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080767







