Comparative Toxicity and P450-Mediated Detoxification of Flonicamid in Lygus lineolaris and Lygus hesperus
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Populations and Insecticides
2.2. Spray and Dipping Bioassay
2.3. Synergistic Experiments
2.4. Detoxification Enzyme Activity Assays
2.4.1. Chemicals
2.4.2. Enzyme Preparation
2.4.3. Esterase Activity Assays
2.4.4. Glutathione S-Transferase (GST) Activity Assays
2.4.5. Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenase (P450) Assays
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
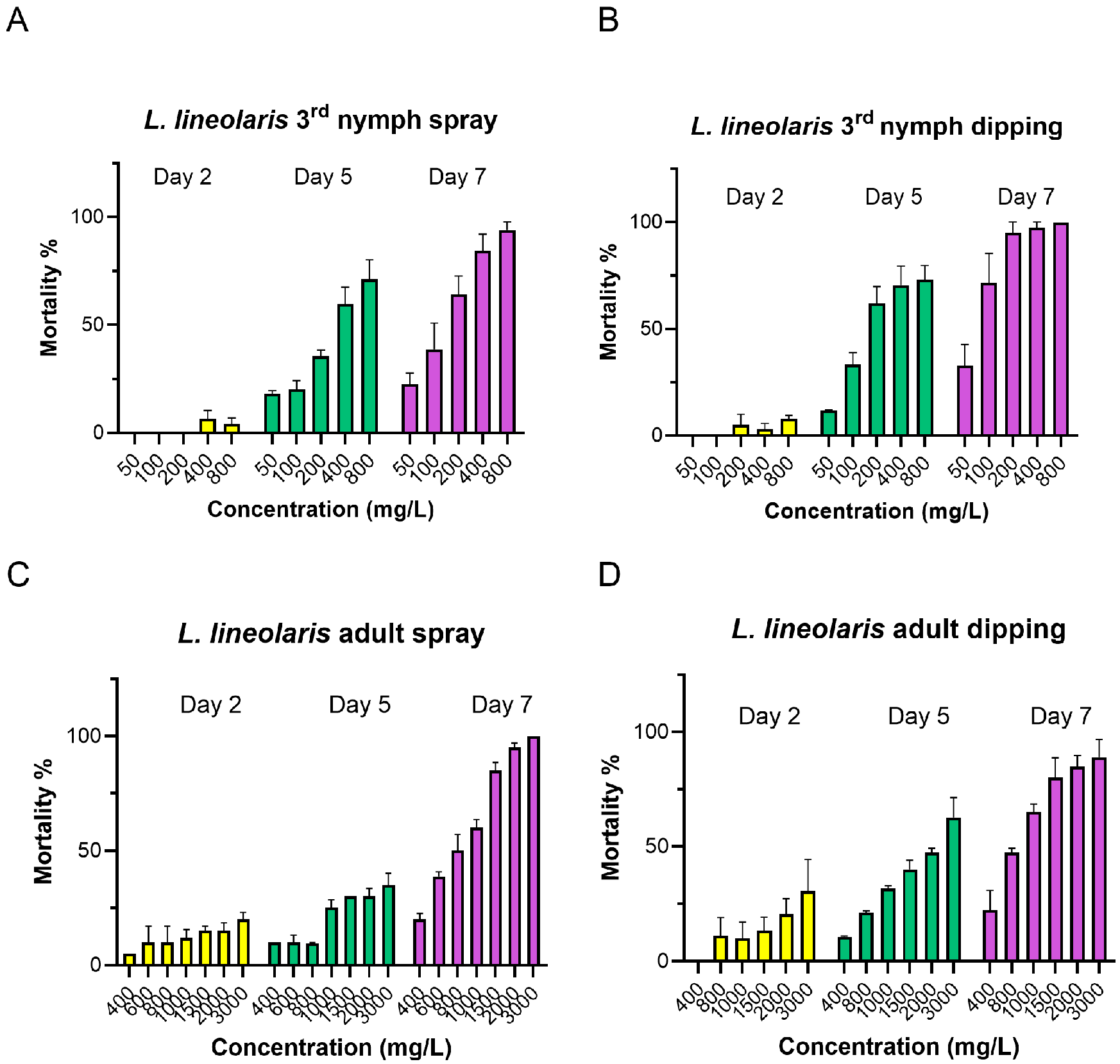
3.1. Toxicity of Flonicamid to L. lineolaris and L. hesperus
3.2. Synergistic Effects of Enzyme Inhibitors on Flonicamid Toxicity
3.3. Detoxification Enzyme Activity Following Exposure to Sublethal Dose of Flonicamid
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutierrez, A.P.; Leigh, T.F.; Wang, Y.H.; Cave, R.D. An analysis of cotton production in california: Lygus hesperus (Heteroptera: Miridae) injury—An evaluation. Can. Entomol. 1977, 109, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmer, J.L.; Rodriguez-Saona, C.; Byers, J.A.; Shope, K.L.; Smith, J.P. Behavioral response of Lygus hesperus to conspecifics and headspace volatiles of alfalfa in a Y-tube olfactometer. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 1547–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parajulee, M.; Shrestha, R.; Barman, A.; Carroll, S. Ecologically intensive pest management in cotton agroecosystems: Lygus hesperus as a model system. Egypt. J. Agricul. Res. 2008, 86, 57–81. [Google Scholar]
- George, J.; Glover, J.P.; Gore, J.; Crow, W.D.; Reddy, G.V.P. Biology, ecology, and pest management of the tarnished plant bug, Lygus lineolaris (Palisot de Beauvois) in southern row crops. Insects 2021, 12, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenheim, J.A.; Steinmann, K.; Langellotto, G.A.; Zink, A.G. Estimating the impact of Lygus hesperus on cotton: The insect, plant, and human observer as sources of variability. Envir. Entomol. 2006, 35, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, G.; Scott, W.; Smith, J. Host plants and seasonal distribution of the tarnished plant bug (Hemiptera: Miridae) in the Delta of Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi. Envir. Entomol. 1984, 13, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, G.L.; Elzen, G.W. Insecticide resistance in a tarnished plant bug population in cotton in the Mississippi Delta. Southwest. Entomol. 1995, 20, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth, P. Lygus management: A western perspective. In Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conferences, Nashville, TN, USA, 8–11 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kandasamy, R.; London, D.; Stam, L.; von Deyn, W.; Zhao, X.; Salgado, V.L.; Nesterov, A. Afidopyropen: New and potent modulator of insect transient receptor potential channels. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 84, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Yoneda, T.; Akiyoshi, N. Research and development of a novel insecticide, flonicamid. J. Pestic. Sci. 2014, 39, 179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalthoff, C.; Salgado, V.L.; Theis, M.; Geurten, B.R.; Göpfert, M.C. Flonicamid metabolite 4-trifluoromethylnicotinamide is a chordotonal organ modulator insecticide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 4802–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Ueda, T.; Yoneda, T.; Koyanagi, T.; Haga, T. Flonicamid, a novel insecticide with a rapid inhibitory effect on aphid feeding. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insecticide Resistance Action Committee. Mode of Action Classification Scheme. 2024. Available online: https://irac-online.org/mode-of-action/ (accessed on 8 March 2025).
- Hancock, H. Field performance of flonicamid (F1785) in cotton. In Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conferences, Nashville, TN, USA, 6–10 January 2003; pp. 1629–1636. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Schuler, M.A.; Berenbaum, M.R. Molecular mechanisms of metabolic resistance to synthetic and natural xenobiotics. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, R.; Bass, C.; Feyereisen, R.; Vontas, J. The role of cytochrome P450s in insect toxicology and resistance. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2022, 67, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, C.; Field, L.M. Gene amplification and insecticide resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guengerich, F.P. Common and uncommon cytochrome P450 reactions related to metabolism and chemical toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 611–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittapelly, P.; Bansal, R.; Michel, A. Differential expression of cytochrome P450 CYP6 genes in the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Scheibener, S.; Zhu, Y.; Portilla, M.; Reddy, G.V.P. Biochemical and molecular characterization of neonicotinoids resistance in the tarnished plant bug, Lygus lineolaris. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 275, 109765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodhue, R.; Mace, K.; Rudder, J.; Tolhurst, T.; Tregeagle, D.; Wei, H.; Zheng, Y.; Grafton-Cardwell, B.; Grettenberger, I.; Wilson, H. Economic and Pest Management Evaluation of Proposed Regulation of Nitroguanidine-Substituted Neonicotinoid Insecticides: Eight Major California Commodities; California Department of Food and Agriculture’s Office of Pesticide Consultation and Analysis: Sacramento, CA, USA; The University of California Cooperative Extension: Davis, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri, S.; Smith, H.A.; Gireesh, M.; Kaur, G.; Montemayor, J.D. Arthropod pest management in strawberry. Insects 2022, 13, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodell, P.; Ellsworth, P.C. Second international Lygus symposium asilomar conference grounds, Pacific Grove, California, April 15–19 2007. J. Insect Sci. 2008, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.; Cook, D.; Dodds, D.; Gore, J.; Irby, T.; Larson, E.; Layton, B.; Meyers, S.; Musser, F. 2015 Insect Control Guide for Agronomic Crops; Mississippi State University Extension Service: Starkville, MS, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Crow, W.; Catchot, A.; Gore, J.; Cook, D.; Layton, B.; Musser, F.; Pieralisi, B.; Larson, E.; Irby, T. 2021 Insect Control Guide for Agronomic Crops; Mississippi State University Extension Service: Starkville, MS, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Crow, W.; Catchot, A.; Gore, J.; Cook, D.; Layton, B.; Musser, F.; Towles, T. 2022 Insect Control Guide for Agronomic Crops; Mississippi State University Extension Service: Starkville, MS, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Zhu, Y.C.; Portilla, M.; Zhang, M.; Reddy, G.V.P. The mechanisms of metabolic resistance to pyrethroids and neonicotinoids fade away without selection pressure in the tarnished plant bug Lygus lineolaris. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 3893–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Yao, J.; Adamczyk, J.; Luttrell, R. Feeding toxicity and impact of imidacloprid formulation and mixtures with six representative pesticides at residue concentrations on honeybee physiology (Apis mellifera). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, S.J.; Gross, A.D.; Musser, F.R.; Catchot, B.D.; Smith, R.H.; Reisig, D.D.; Reay-Jones, F.P.; Greene, J.K.; Roberts, P.M.; Taylor, S.V. Resistance monitoring to four insecticides and mechanisms of resistance in Lygus lineolaris Palisot de Beauvois (Hemiptera: Miridae) populations of southeastern USA cotton. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 3935–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leeuwen, T.; Van Pottelberge, S.; Tirry, L. Biochemical analysis of a chlorfenapyr-selected resistant strain of Tetranychus urticae Koch. Pest Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.; Bibb, J.; Catchot, A.; Cook, D.; Crow, W.; Dean, J.; Fleming, D.; Gore, J.; Layton, B.; Little, N.; et al. 2017 Insect Control Guide for Agronomic Crops; Mississippi State University Extension Service: Starkville, MS, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, C.; Bibb, J.; Catchot, A.; Cook, D.; Crow, W.; Dean, J.; Fleming, D.; Gore, J.; Layton, B.; Little, N.; et al. 2018 Insect Control Guide for Agronomic Crops; Mississippi State University Extension Service: Starkville, MS, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, C.; Catchot, A.; Cook, D.; Dodds, D.; Gore, J.; Irby, T.; Larson, E.; Layton, B.; Little, N.; MacGown, J.; et al. 2019 Insect Control Guide for Agronomic Crops; Mississippi State University Extension Service: Starkville, MS, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, C.; Dodds, D.; Larson, E.; Meyers, S.; Bibb, J.; Gore, J.; Layton, B.; Cook, D.; IRby, T.; MacGown, J. 2016 Insect Control Guide for Agronomic Crops; Mississippi State University Extension Service: Starkville, MS, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Catchot, A.; Crow, W.; Dodds, D.; Gore, J.; Musser, F.; Irby, T.; Cook, D.; Layton, B.; Larson, E. 2020 Insect Control Guide for Agronomic Crops; Mississippi State University Extension Service: Starkville, MS, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Barkley, V.; Ellsworth, P.C. Search for effective chemical controls for Lygus bugs and whiteflies in Arizona cotton. In Cotton: A College of Agriculture Report; Series P-138; University of Arizona, College of Agriculture: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2004; pp. 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Roditakis, E.; Fytrou, N.; Staurakaki, M.; Vontas, J.; Tsagkarakou, A. Activity of flonicamid on the sweet potato whitely Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) and its natural enemies. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, J.; Cook, D.; Catchot, A.; Leonard, B.R.; Stewart, S.D.; Lorenz, G.; Kerns, D. Cotton aphid (Heteroptera: Aphididae) susceptibility to commercial and experimental insecticides in the southern United States. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frewin, A.J.; Schaafsma, A.W.; Hallett, R.H. Susceptibility of Aphelinus certus to foliar-applied insecticides currently or potentially registered for soybean aphid control. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Razzaq, F.; Razzaq, A.; Gogi, M.D.; Fernández-Grandon, G.M.; Tayib, M.; Ayub, M.A.; Sufyan, M.; Shahid, M.R.; Qayyum, M.A.; et al. Compatibility and synergistic interactions of fungi, Metarhizium anisopliae, and insecticide combinations against the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Yuan, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, H.; Zou, J.; Liu, Z. Reducing expression of salivary protein genes by flonicamid partially contributed to its feeding inhibition of the brown planthopper on rice. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2023, 71, 6032–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Gong, C.; Pu, J.; Peng, A.; Yang, J.; Wang, X. Enhancement of tolerance against flonicamid in Solenopsis invicta queens through overexpression of CYP6AQ83. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Scheibener, S.; Zhu, Y.; Portilla, M.; Zhang, M. Resistance risk assessment of six pyrethroids and acephate toward the resistant adult tarnished plant bug, Lygus lineolaris. Insect Sci. 2024, 31, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, L.; Wu, W.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Montell, C.; Huang, J. An insecticide target in mechanoreceptor neurons. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, D.; Kinsey, M. A technique for electronically recording aphid feeding and salivation. Nature 1964, 202, 1358–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjallingii, W.F.; Gabryś, B. Anomalous stylet punctures of phloem sieve elements by aphids. In Series Entomologica, Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Insect-Plant Relationships, Oxford, UK, 4–10 July 1998; Simpson, S.J., Mordue, A.J., Hardie, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Wu, Z.; Yang, X.; Qian, K.; Zhang, N.; Jiang, H.; Yin, X.; Guan, D.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J. Flonicamid and knockdown of inward rectifier potassium channel gene CsKir2B adversely affect the feeding and development of Chilo suppressalis. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Species (L. hesperus) | Days | n | Slope | LC50 (μg/mL) a | 95% Confidence Limits (μg/mL) a | χ2 b | df c | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3rd nymph | Day 5 | 279 | 1.21 ± 0.14 | 36.25 | 25.89–49.59 cd | 5.63 | 5 | 0.35 |
| (Spray) | Day 7 | 279 | 1.34 ± 0.16 | 20.72 | 14.53–27.96 d | 7.88 | 5 | 0.16 |
| 3rd nymph | Day 5 | 276 | 1.58 ± 0.19 | 45.74 | 34.67–58.22 c | 5.98 | 4 | 0.20 |
| (Dipping) | Day 7 | 276 | 1.92 ± 0.23 | 29.59 | 22.48–36.98 cd | 3.89 | 4 | 0.42 |
| Adult (Spray) | Day 5 | 274 | 3.37 ± 0.59 | 316.35 | 274.83–370.18 ab | 3.54 | 4 | 0.32 |
| Day 7 | 274 | 2.18 ± 0.53 | 226.76 | 156.34–297.78 b | 1.70 | 4 | 0.64 | |
| Adult (Dipping) | Day 5 | 272 | 3.37 ± 0.59 | 376.91 | 334.51–441.21 a | 2.58 | 4 | 0.28 |
| Day 7 | 272 | 2.51 ± 0.62 | 302.61 | 224.83–414.09 ab | 2.75 | 4 | 0.25 |
| Species (L. lineolaris) | Days | n | Slope | LC50 (μg/mL) a | 95% Confidence Limits (μg/mL) a | χ2 b | df c | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3rd nymph | Day 5 | 250 | 1.51 ± 0.19 | 398.25 | 305.02–522.74 b | 1.53 | 5 | 0.91 |
| (Spray) | Day 7 | 250 | 2.18 ± 0.53 | 105.00 | 70.43–140.44 c | 3.98 | 5 | 0.55 |
| 3rd nymph | Day 5 | 217 | 1.39 ± 0.23 | 348.11 | 239.07–467.12 ab | 2.06 | 5 | 0.84 |
| (Dipping) | Day 7 | 217 | 2.44 ± 0.38 | 130.12 | 85.98–169.98 c | 5.40 | 5 | 0.25 |
| Adult (Spray) | Day 7 | 302 | 2.15 ± 0.37 | 620.90 | 463.26–786.85 ab | 0.93 | 6 | 0.98 |
| Adult (Dipping) | Day 7 | 298 | 2.11 ± 0.35 | 742.13 | 547.73–949.36 a | 1.19 | 5 | 0.95 |
| Species | Days | n | Slope | LC50 (μg/mL) a | 95% Confidence Limits (μg/mL) a | χ2 b | df c | p | SR d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. hesperus | Day 5 | 274 | 3.37 ± 0.59 | 316.35 | 274.83–370.18 | 3.54 | 4 | 0.32 | -- |
| Day 7 | 274 | 2.18 ± 0.53 | 226.76 | 156.34–297.78 | 1.70 | 4 | 0.64 | -- | |
| +PBO (Day 5) | 186 | 1.95 ± 0.45 | 97.18 | 60.09–138.82 * | 1.02 | 3 | 0.62 | 3.26 | |
| +PBO (Day 7) | 186 | 1.76 ± 0.44 | 81.94 | 43.12–120.83 * | 0.28 | 3 | 0.87 | 2.77 | |
| +DEM (Day 5) | 246 | 6.99 ± 1.31 | 320.12 | 281.96–356.57 | 0.85 | 4 | 0.65 | 0.99 | |
| +DEM (Day 7) | 246 | 5.83 ± 1.16 | 295.14 | 251.83–333.98 | 0.15 | 4 | 0.93 | 0.77 | |
| +TPP (Day 5) | 232 | 2.89 ± 0.36 | 288.56 | 248.14–331.82 | 0.74 | 4 | 0.58 | 1.10 | |
| +TPP (Day 7) | 232 | 2.59 ± 0.49 | 238.13 | 196.14–342.28 | 0.64 | 4 | 0.76 | 0.95 | |
| L. lineolaris | Day 7 | 302 | 2.15 ± 0.37 | 620.90 | 463.26–786.85 | 0.93 | 6 | 0.98 | -- |
| +PBO (Day 5) | 200 | 2.59 ± 0.46 | 103.78 | 73.46–137.16 * | 4.20 | 3 | 0.24 | 5.98 | |
| +PBO (Day 7) | 200 | 3.75 ± 0.78 | 82.02 | 62.33–103.23 * | 0.91 | 3 | 0.64 | 7.58 | |
| +DEM (Day 7) | 192 | 2.53 ± 0.48 | 800.36 | 690.49–1263.61 | 2.81 | 4 | 0.59 | 0.78 | |
| +TPP (Day 7) | 202 | 2.36 ± 0.43 | 523.93 | 376.61–684.75 | 3.09 | 4 | 0.38 | 1.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Scheibener, S.; Zhu, Y.-C.; Pierce, C.; Perera, O.P.; Portilla, M. Comparative Toxicity and P450-Mediated Detoxification of Flonicamid in Lygus lineolaris and Lygus hesperus. Insects 2025, 16, 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080757
Du Y, Scheibener S, Zhu Y-C, Pierce C, Perera OP, Portilla M. Comparative Toxicity and P450-Mediated Detoxification of Flonicamid in Lygus lineolaris and Lygus hesperus. Insects. 2025; 16(8):757. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080757
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yuzhe, Shane Scheibener, Yu-Cheng Zhu, Calvin Pierce, Omaththage P. Perera, and Maribel Portilla. 2025. "Comparative Toxicity and P450-Mediated Detoxification of Flonicamid in Lygus lineolaris and Lygus hesperus" Insects 16, no. 8: 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080757
APA StyleDu, Y., Scheibener, S., Zhu, Y.-C., Pierce, C., Perera, O. P., & Portilla, M. (2025). Comparative Toxicity and P450-Mediated Detoxification of Flonicamid in Lygus lineolaris and Lygus hesperus. Insects, 16(8), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080757









