Identification and Quantification of Pteridines in the Wild Type and the ambar Mutant of Orius laevigatus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Insects and Pteridine Standards
2.2. Separation of Fluorescent Compounds by Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC)
2.3. Partial Purification of ambar Nymph Extracts by Column Chromatography
2.4. Identification of Fluorescent Compounds by LC/MS/MS
2.5. Quantification of Fluorescent Compounds
2.6. Analysis of Xanthine Dehydrogenase (XDH) Activity
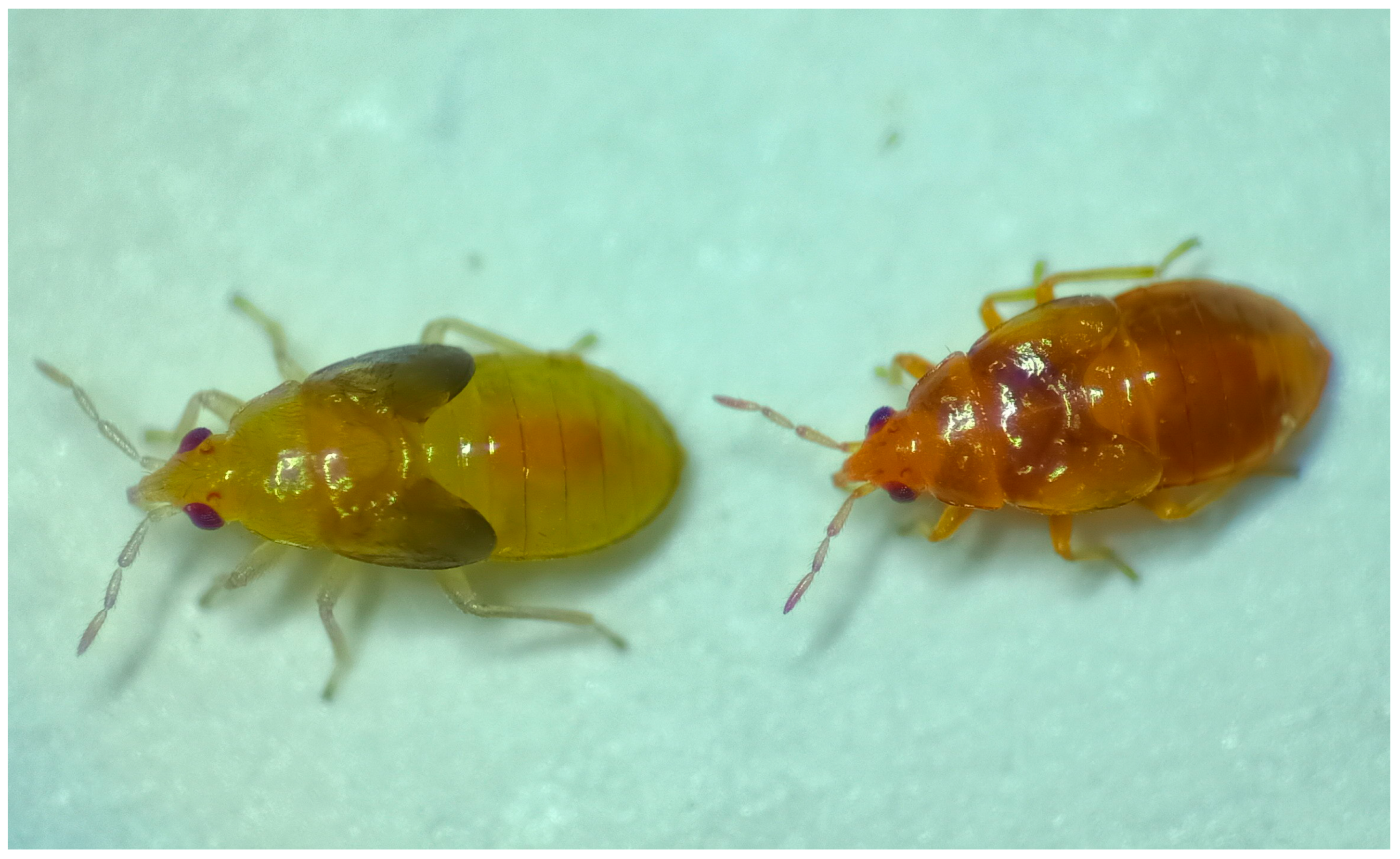
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Fluorescent Compounds Separated by TLC
3.2. Identification of Fluorescent Compounds Separated by SEC
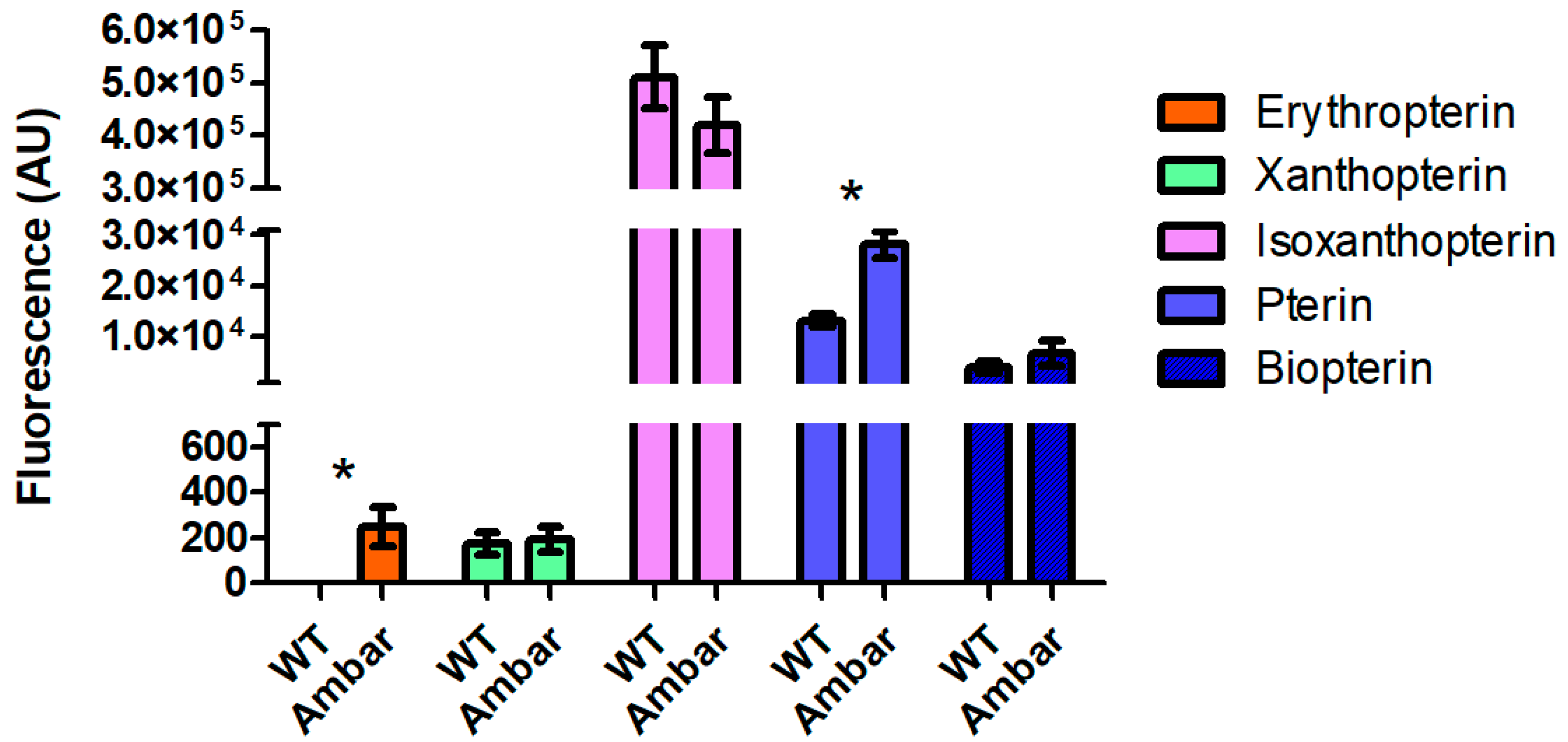
3.3. Quantification of Fluorescent Compounds
3.4. XDH Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Van Lenteren, J.C.; Bolckmans, K.; Köhl, J.; Ravensberg, W.J.; Urbaneja, A. Biological control using invertebrates and microorganisms: Plenty of new opportunities. BiolControl 2018, 63, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouagga, S.; Urbaneja, A.; Rambla, J.L.; Granell, A.; Pérez-Hedo, M. Orius laevigatus strengthens its role as a biological control agent by inducing plant defenses. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanza, V.; Mendoza, J.E.; Cifuentes, D.; Bielza, P. Selection for resistance to pyrethroids in the predator Orius laevigatus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 2539–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balanza, V.; Mendoza, J.E.; Cifuentes, D.; Bielza, P. Genetic improvement of spinosad resistance in the biocontrol agent Orius laevigatus. BioControl 2021, 66, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, J.E.; Balanza, V.; Cifuentes, D.; Bielza, P. Genetic improvement of Orius laevigatus for better fitness feeding on pollen. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, J.E.; Balanza, V.; Cifuentes, D.; Bielza, P. Selection for larger body size in Orius laevigatus: Intraspecific variability and effects on reproductive parameters. BiolControl 2020, 148, 104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, J.E.; Balanza, V.; Rodríguez-Gómez, A.; Cifuentes, D.; Bielza, P. Enhanced biocontrol services in artificially selected strains of Orius laevigatus. J. Pest Sci. 2022, 95, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gómez, A.; Donate, A.; Sánchez-Martínez, I.; Balanza, V.; Abelaira, A.B.; Reche, M.D.C.; Bielza, P. Inheritance and biological characterization of an orange-nymph mutant in Orius laevigatus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Insects 2022, 13, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futahashi, R.; Osanai-Futahashi, M. Pigments in insects. In Pigments, Pigment Cells and Pigment Patterns; Hashimoto, H., Goda, M., Futahashi, R., Kelsh, R., Akiyama, T., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 3–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Lowman, A.; Armisen, D.; Burguez Floriano, C.F.; da Rocha Silva Cordeiro, I.; Viala, S.; Bouchet, M.; Bernard, M.; Le Bouquin, A.; Santos, M.E.; Berlioz-Barbier, A.; et al. Cooption of the pteridine biosynthesis pathway underlies the diversification of embryonic colors in water striders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 19046–19054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferré, J.; Silva, F.J.; Real, M.D.; Ménsua, J.L. Pigment patterns in mutants affecting the biosynthesis of pteridines and xanthommatin in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem. Genet. 1986, 24, 545–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melber, C.H.; Schmidt, G.H. Quantitative variations in the pteridines during the post-embryonic development of Dysdercus species (Heteroptera: Pyrrhocoridae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1994, 108, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, J. Biosynthesis of pteridines in insects: A review. Insects 2024, 15, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bel, Y.; Porcar, M.; Socha, R.; Němec, V.; Ferré, J. Analysis of pteridines in Pyrrhocoris apterus (L.) (Heteroptera, Pyrrhocoridae) during development and in body-color mutants. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1997, 34, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, E.R.; Blau, N.; Thony, B. Tetrahydrobiopterin: Biochemistry and pathophysiology. Biochem. J. 2011, 438, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichwald, T.; da Silva, L.B.; Staats Pires, A.C.; Niero, L.; Schnorrenberger, E.; Filho, C.C.; Espíndola, G.; Huang, W.L.; Guillemin, G.J.; Abdenur, J.E.; et al. Tetrahydrobiopterin: Beyond its traditional role as a cofactor. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlini, L.; Nasini, G. Insect pigments-IV. Pteridines and color in some Hemiptera. J. Insect Physiol. 1966, 12, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, P.B.; Purrmann, R.; Schmitt, W.; Hitchings, G.H. The synthesis of pterorhodin (rhodopterin). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1949, 71, 3412–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descimon, H. Les ptérines des Pieridae (Lepidoptera) et leur biosynthèse: I—Identification des principales ptérines de Colias croceus (Fourcroy) et de quelques autres espèces de Pieridae. Biochimie 1971, 53, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descimon, H. Biology of pigmentation in Pieridae butterflies. In Chemistry and Biology of Pteridines; Pfleiderer, W., Ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1975; pp. 805–840. [Google Scholar]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bel, Y.; Rodríguez-Gómez, A.; Bielza, P.; Ferré, J. Identification and Quantification of Pteridines in the Wild Type and the ambar Mutant of Orius laevigatus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Insects 2025, 16, 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080756
Bel Y, Rodríguez-Gómez A, Bielza P, Ferré J. Identification and Quantification of Pteridines in the Wild Type and the ambar Mutant of Orius laevigatus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Insects. 2025; 16(8):756. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080756
Chicago/Turabian StyleBel, Yolanda, Amador Rodríguez-Gómez, Pablo Bielza, and Juan Ferré. 2025. "Identification and Quantification of Pteridines in the Wild Type and the ambar Mutant of Orius laevigatus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae)" Insects 16, no. 8: 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080756
APA StyleBel, Y., Rodríguez-Gómez, A., Bielza, P., & Ferré, J. (2025). Identification and Quantification of Pteridines in the Wild Type and the ambar Mutant of Orius laevigatus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Insects, 16(8), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16080756







