Evolutionary Dynamics of Glycoside Hydrolase Family 1 Provide Insights into Insect–Plant Interactions in Lepidoptera
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Genome-Wide Identification of GH1
2.3. Gene Tree Inference
2.4. Gene Duplication and Loss Inference
2.5. Duplicate Mode Inference and Collinearity Analysis
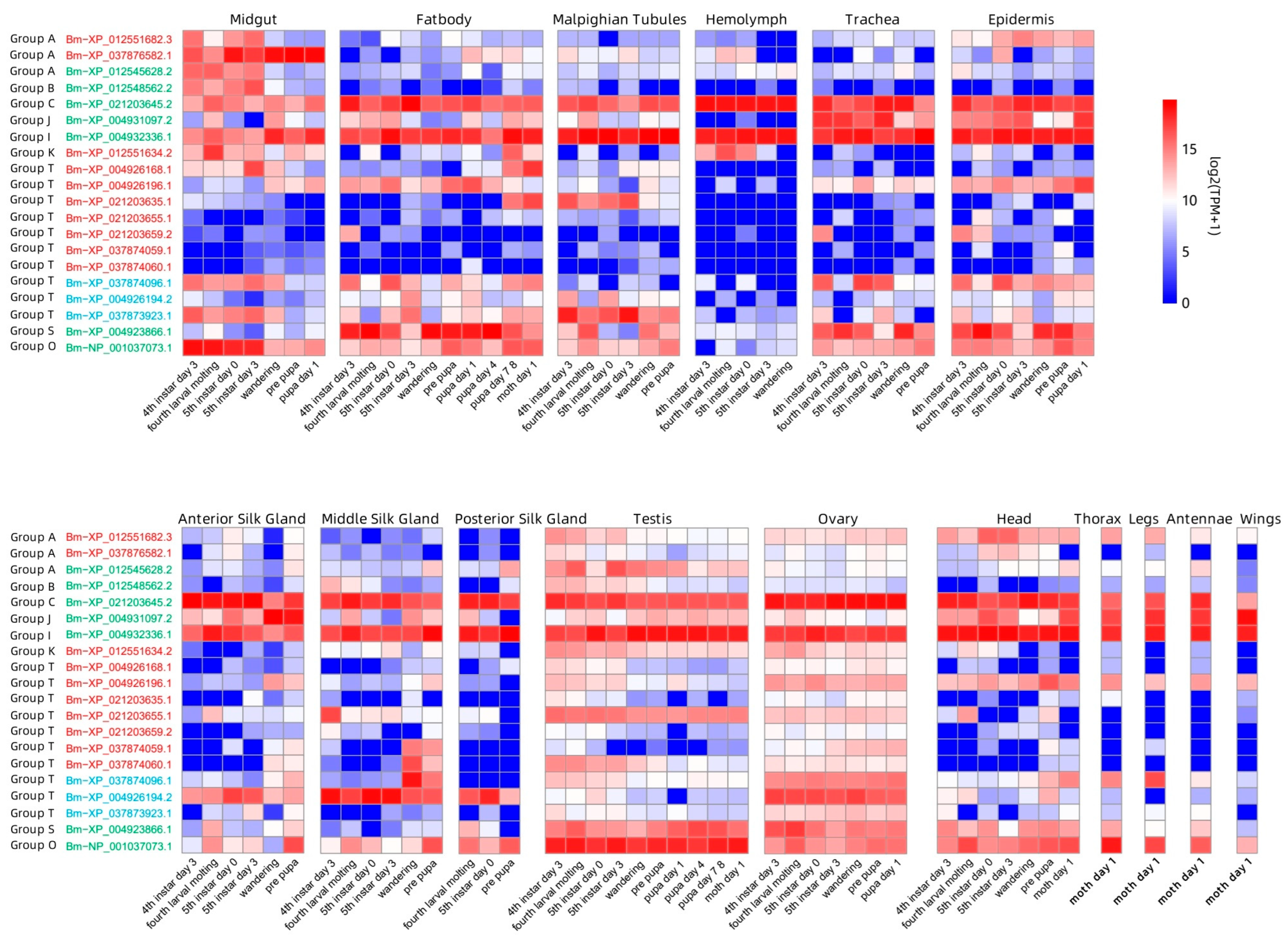
2.6. Expression of GH1 Genes in Developmental Stages and Tissues of B. mori
| Superfamily | Family | Genus | Species | Accession No. | GH1 | Feeding Habit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bombycoidea | Bombycidae | Bombyx | mori | GCF_014905235.1 | 20 | M |
| Bombycoidea | Bombycidae | Trilocha | varians | GCA_030269945.2 | 18 | P |
| Bombycoidea | Lasiocampidae | Dendrolimus | pini | GCA_949752895.1 | 10 | P |
| Copromorphoidea | Carposinidae | Carposina | sasakii | GCA_014607495.2 | 10 | P |
| Cossoidea | Cossidae | Zeuzera | pyrina | GCA_907165235.1 | 9 | P |
| Gelechioidea | Coleophoridae | Coleophora | deauratella | GCA_958295455.1 | 10 | M |
| Gelechioidea | Coleophoridae | Coleophora | flavipennella | GCA_947284805.1 | 13 | |
| Gelechioidea | Cosmopterigidae | Hyposmocoma | kahamanoa | GCF_003589595.1 | 15 | |
| Gelechioidea | Gelechiidae | Anarsia | innoxiella | GCA_947563765.1 | 18 | |
| Gelechioidea | Gelechiidae | Athrips | mouffetella | GCA_947532105.1 | 14 | M |
| Gelechioidea | Gelechiidae | Carpatolechia | fugitivella | GCA_951230895.1 | 8 | P |
| Gelechioidea | Gelechiidae | Pectinophora | gossypiella | GCF_024362695.1 | 10 | P |
| Gelechioidea | Gelechiidae | Scrobipalpa | costella | GCA_949820665.1 | 10 | M |
| Geometroidea | Geometridae | Biston | stratarius | GCA_950106695.1 | 12 | |
| Geometroidea | Geometridae | Eulithis | testata | GCA_947507515.1 | 11 | P |
| Geometroidea | Geometridae | Hemistola | chrysoprasaria | GCA_947063395.1 | 14 | M |
| Geometroidea | Geometridae | Horisme | vitalbata | GCA_951804965.1 | 9 | M |
| Geometroidea | Geometridae | Lampropteryx | suffumata | GCA_948098915.1 | 16 | M |
| Hesperioidea | Hesperiidae | Carterocephalus | palaemon | GCA_944567765.1 | 18 | M |
| Hesperioidea | Hesperiidae | Erynnis | tages | GCA_905147235.1 | 22 | M |
| Hesperioidea | Hesperiidae | Pyrgus | malvae | GCA_911387765.1 | 16 | M |
| Hesperioidea | Hesperiidae | Thymelicus | acteon | GCA_951805285.1 | 22 | M |
| Hesperioidea | Hesperiidae | Thymelicus | sylvestris | GCA_911387775.1 | 19 | M |
| Incurvarioidea | Adelidae | Nematopogon | swammerdamellus | GCA_946902875.1 | 13 | |
| Incurvarioidea | Incurvariidae | Incurvaria | masculella | GCA_946894095.1 | 14 | M |
| Noctuoidea | Erebidae | Euproctis | similis | GCA_905147225.2 | 11 | P |
| Noctuoidea | Erebidae | Leucoma | salicis | GCA_948253155.1 | 13 | P |
| Noctuoidea | Erebidae | Lymantria | dispar | GCA_016802235.1 | 14 | P |
| Noctuoidea | Erebidae | Lymantria | monacha | GCA_905163515.2 | 17 | P |
| Noctuoidea | Erebidae | Orgyia | antiqua | GCA_916999025.1 | 13 | P |
| Noctuoidea | Notodontidae | Clostera | curtula | GCA_905475355.2 | 8 | M |
| Noctuoidea | Notodontidae | Furcula | furcula | GCA_911728495.1 | 17 | P |
| Noctuoidea | Notodontidae | Notodonta | dromedarius | GCA_905147325.1 | 14 | P |
| Noctuoidea | Notodontidae | Phalera | bucephala | GCA_905147815.2 | 9 | P |
| Noctuoidea | Notodontidae | Ptilodon | capucinus | GCA_914767695.1 | 10 | |
| Papilionoidea | Lycaenidae | Aricia | agestis | GCF_905147365.1 | 29 | P |
| Papilionoidea | Lycaenidae | Celastrina | argiolus | GCA_905187575.2 | 13 | P |
| Papilionoidea | Lycaenidae | Cyaniris | semiargus | GCA_905187585.1 | 18 | P |
| Papilionoidea | Lycaenidae | Lycaena | phlaeas | GCA_905333005.2 | 21 | P |
| Papilionoidea | Lycaenidae | Polyommatus | icarus | GCA_937595015.1 | 24 | P |
| Papilionoidea | Nymphalidae | Bicyclus | anynana | GCF_947172395.1 | 35 | M |
| Papilionoidea | Nymphalidae | Danaus | plexippus | GCF_009731565.1 | 19 | M |
| Papilionoidea | Nymphalidae | Melitaea | cinxia | GCF_905220565.1 | 26 | M |
| Papilionoidea | Nymphalidae | Nymphalis | io | GCF_905147045.1 | 13 | P |
| Papilionoidea | Nymphalidae | Pararge | aegeria | GCF_905163445.1 | 17 | M |
| Papilionoidea | Papilionidae | Battus | philenor | GCA_028537555.1 | 18 | P |
| Papilionoidea | Papilionidae | Iphiclides | podalirius | GCA_933534255.1 | 20 | P |
| Papilionoidea | Papilionidae | Papilio | machaon | GCF_912999745.1 | 18 | M |
| Papilionoidea | Pieridae | Colias | croceus | GCF_905220415.1 | 22 | M |
| Papilionoidea | Pieridae | Leptidea | sinapis | GCF_905404315.1 | 42 | M |
| Papilionoidea | Pieridae | Pieris | rapae | GCF_905147795.1 | 21 | M |
| Papilionoidea | Pieridae | Pieris | brassicae | GCF_905147105.1 | 25 | P |
| Papilionoidea | Pieridae | Pieris | napi | GCF_905475465.1 | 27 | M |
| Pyraloidea | Crambidae | Calamotropha | paludella | GCA_927399485.1 | 11 | M |
| Pyraloidea | Crambidae | Chilo | suppressalis | GCA_902850365.2 | 18 | M |
| Pyraloidea | Crambidae | Cnaphalocrocis | medinalis | GCA_014851415.1 | 12 | P |
| Pyraloidea | Crambidae | Ostrinia | furnacalis | GCF_004193835.3 | 15 | P |
| Sesioidea | Choreutidae | Choreutis | nemorana | GCA_949316135.1 | 9 | M |
| Yponomeutoidea | Argyresthiidae | Argyresthia | goedartella | GCA_949825045.1 | 13 | M |
| Yponomeutoidea | Lyonetiidae | Leucoptera | coffeella | GCA_030578115.1 | 10 | M |
| Zygaenoidea | Limacodidae | Apoda | limacodes | GCA_946406115.1 | 23 | M |
3. Results
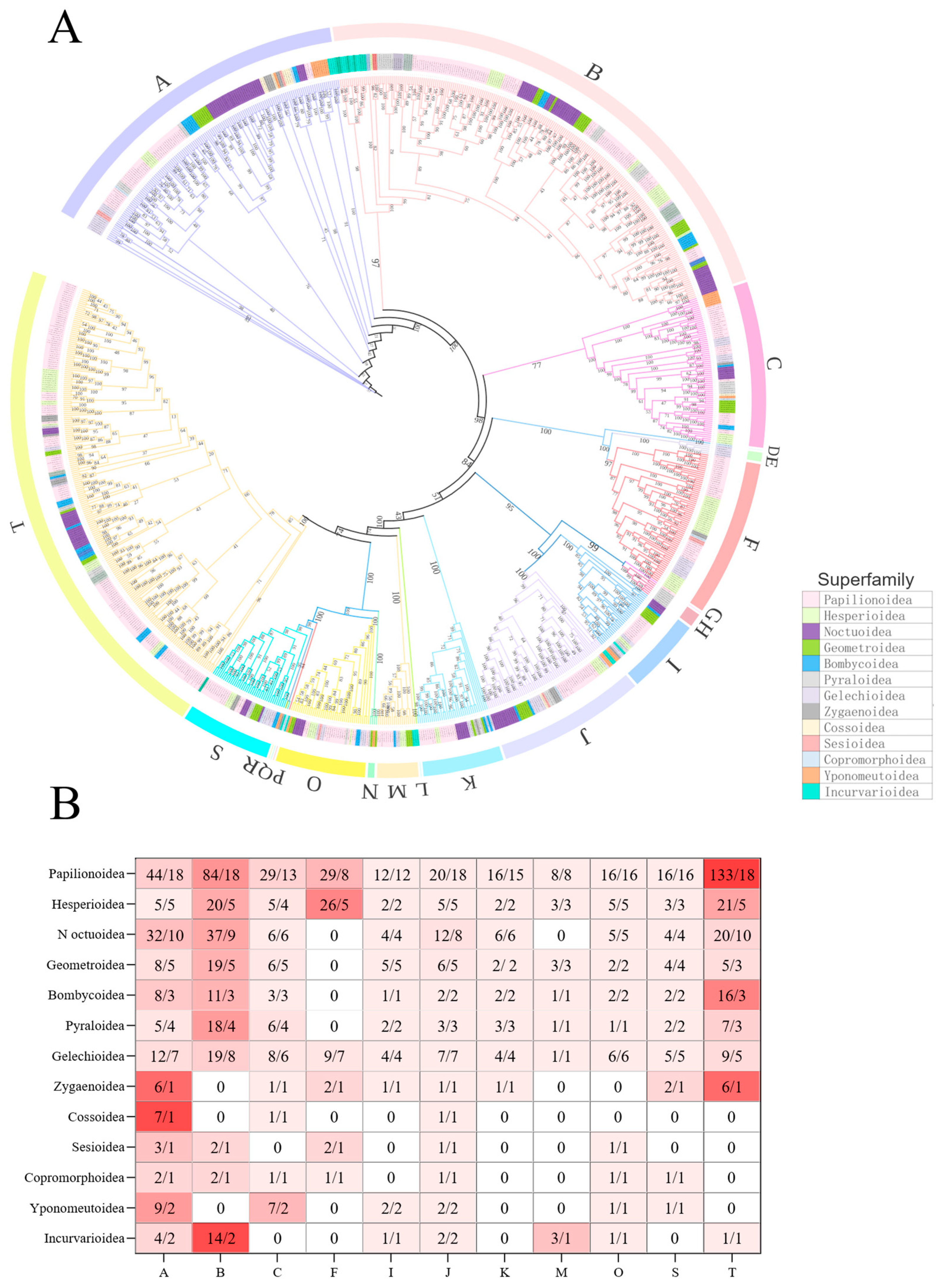
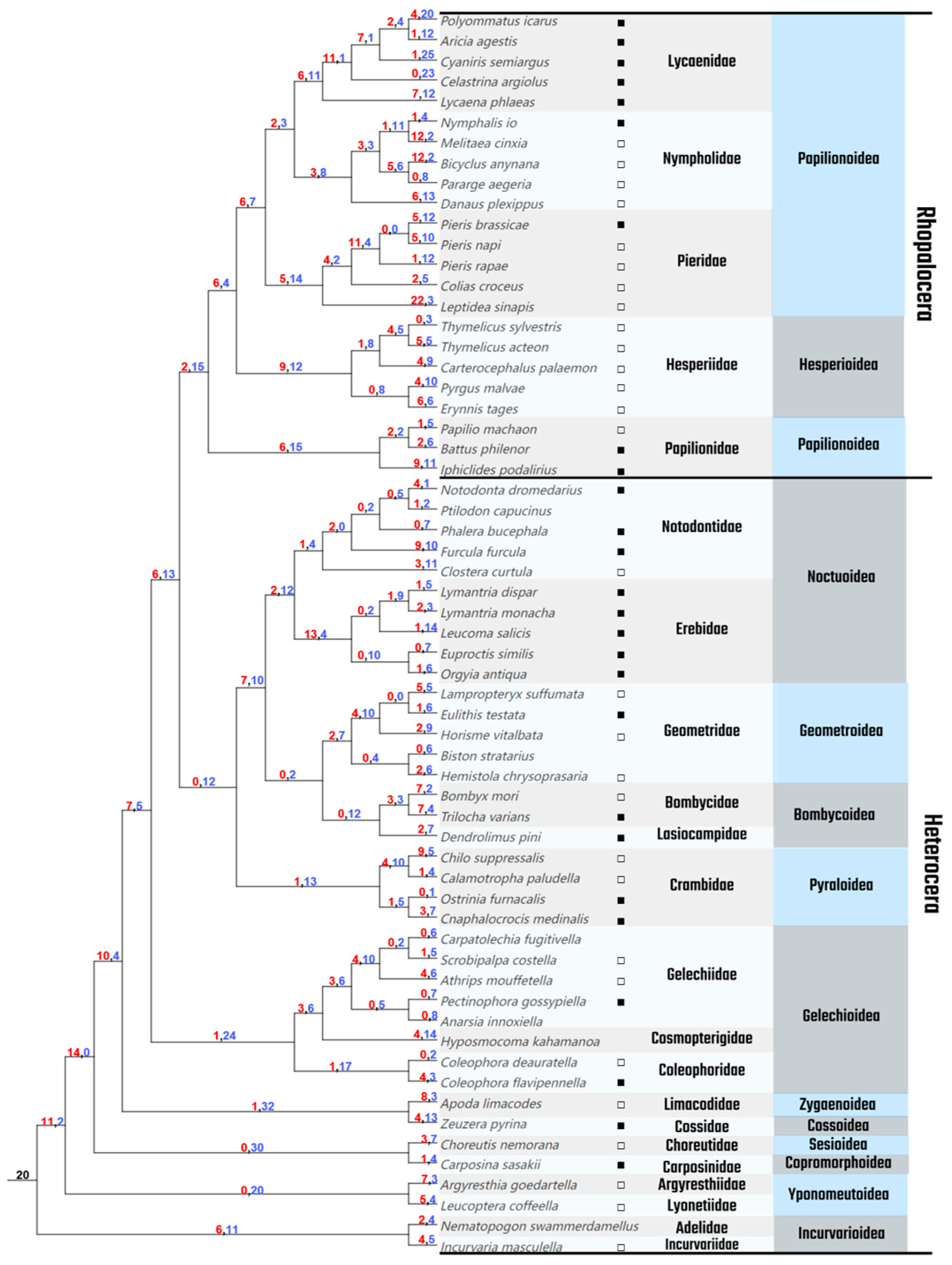
3.1. Phylogenetic Tree of Lepidoptera
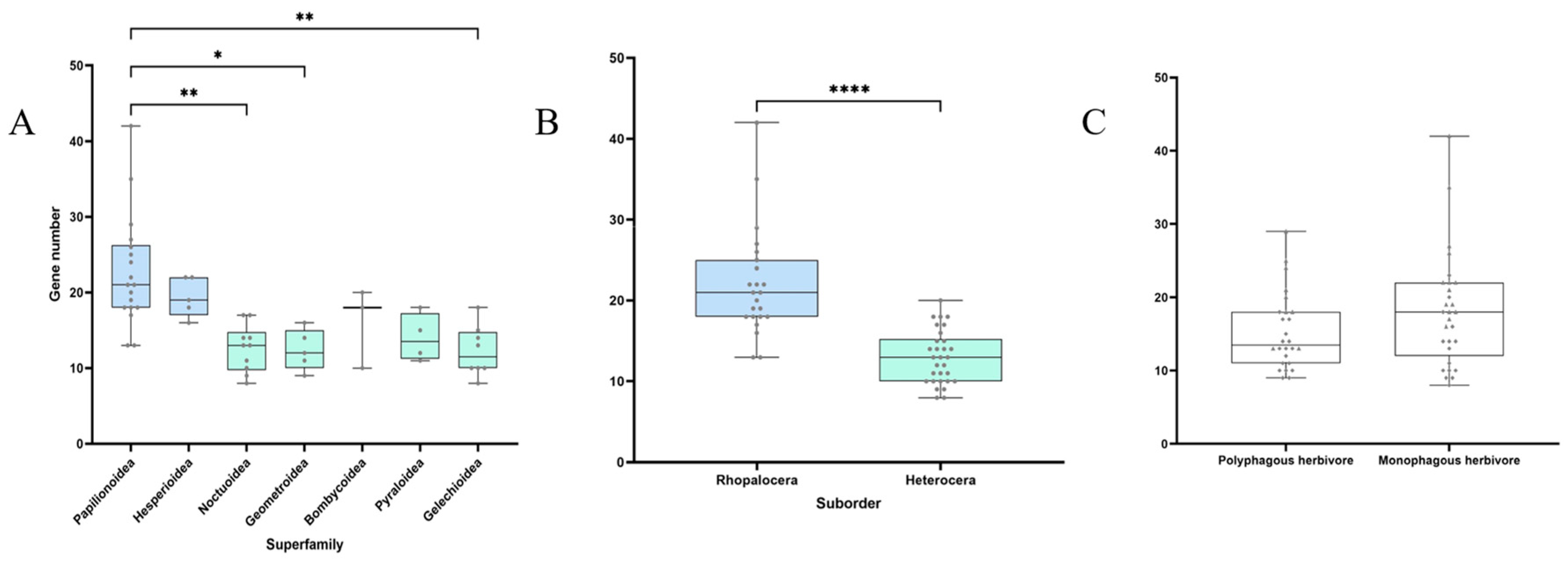
3.2. Gene Duplications and Losses
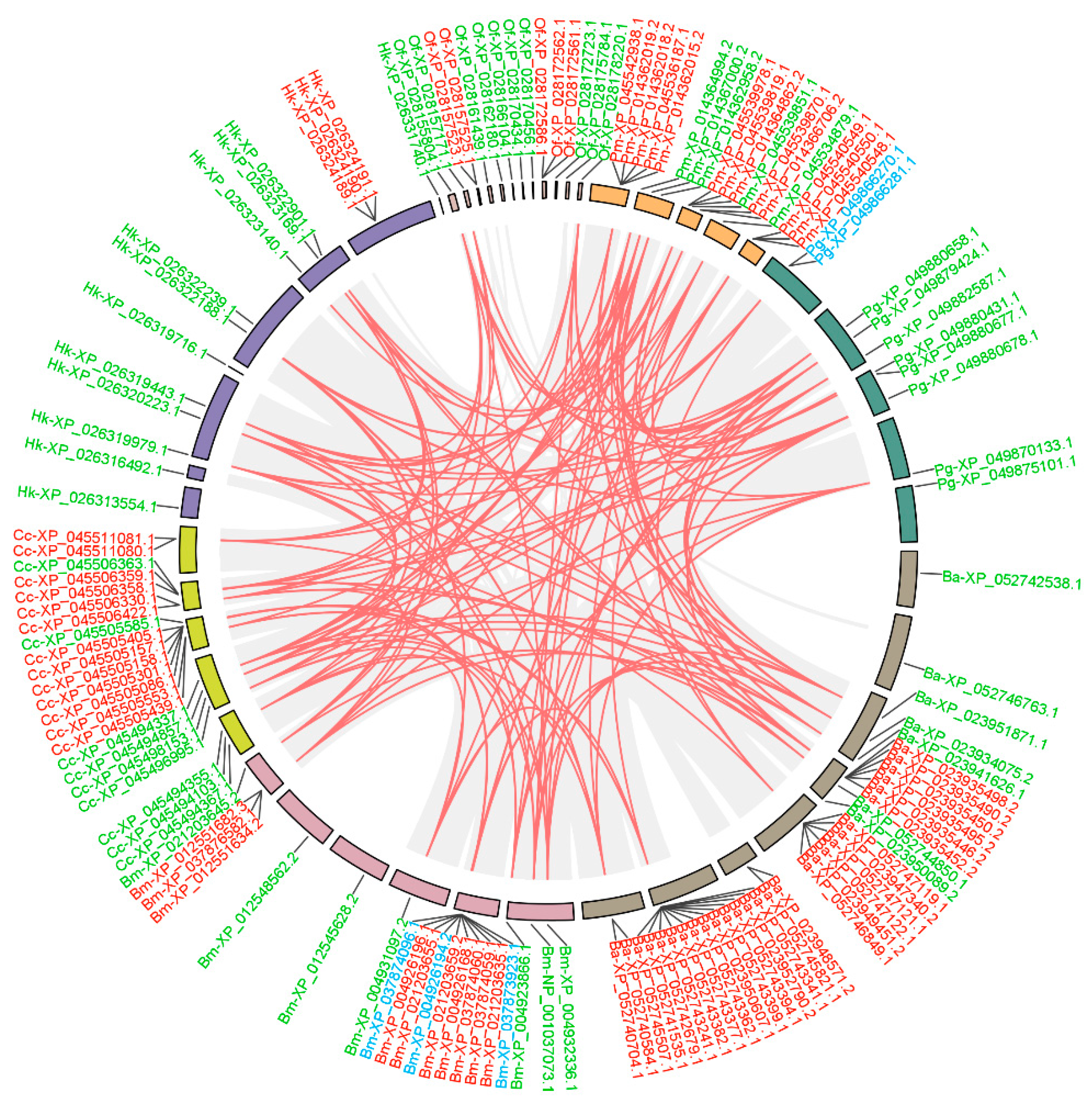
3.3. Duplication Modes and Collinearity Analysis
3.4. Expression of GH1 Genes in the Developmental Stages and Tissues of B. mori
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.Q. Animal biodiversity: An outline of higher-level classification and survey of taxonomic richness (Addenda 2013). Zootaxa 2013, 3703, 1–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, D.; Saviane, A.; Cappellozza, S.; Sandrelli, F. The Circadian Clock in Lepidoptera. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 776826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, G.A.; Jander, G. Plant immunity to insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackman, L.M.; Cullerne, D.P.; Hardham, A.R. Bioinformatic characterisation of genes encoding cell wall degrading enzymes in the Phytophthora parasitica genome. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, C.M.; Knott, B.C.; Mayes, H.B.; Hansson, H.; Himmel, M.E.; Sandgren, M.; Ståhlberg, J.; Beckham, G.T. Fungal cellulases. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1308–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Li, Y.; Liao, H.; Yang, Y. De novo transcriptome assembly of the bamboo snout beetle Cyrtotrachelus buqueti reveals ability to degrade lignocellulose of bamboo feedstock. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentzold, S.; Zagrobelny, M.; Rook, F.; Bak, S. How insects overcome two-component plant chemical defence: Plant β-glucosidases as the main target for herbivore adaptation. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2014, 89, 531–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentzold, S.; Zagrobelny, M.; Bjarnholt, N.; Kroymann, J.; Vogel, H.; Olsen, C.E.; Møller, B.L.; Bak, S. Metabolism, excretion and avoidance of cyanogenic glucosides in insects with different feeding specialisations. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 66, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrissat, B.; Davies, G. Structural and sequence-based classification of glycoside hydrolases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1997, 7, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Aparicio, J.; Hermoso, J.A.; Martínez-Ripoll, M.; Lequerica, J.L.; Polaina, J. Crystal structure of beta-glucosidase A from Bacillus polymyxa: Insights into the catalytic activity in family 1 glycosyl hydrolases. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 275, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, G.; Henrissat, B. Structures and mechanisms of glycosyl hydrolases. Structure 1995, 3, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarel, B.L.; Coutinho, P.M.; Rancurel, C.; Bernard, T.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B. The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): An expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D233–D238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotliński, M.; Knizewski, L.; Muszewska, A.; Rutowicz, K.; Lirski, M.; Schmidt, A.; Baroux, C.; Ginalski, K.; Jerzmanowski, A. Phylogeny-Based Systematization of Arabidopsis Proteins with Histone H1 Globular Domain. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, R.M.; Seppey, M.; Simão, F.A.; Manni, M.; Ioannidis, P.; Klioutchnikov, G.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO Applications from Quality Assessments to Gene Prediction and Phylogenomics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Wei, Z.; Luo, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, G.; Xia, Q.; Wang, Y. SilkDB 3.0: Visualizing and exploring multiple levels of data for silkworm. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D749–D755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drost, H.G.; Gabel, A.; Grosse, I.; Quint, M. Evidence for active maintenance of phylotranscriptomic hourglass patterns in animal and plant embryogenesis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Ge, Q.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Yin, Y. dbCAN3: Automated carbohydrate-active enzyme and substrate annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W115–W121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, G.; Pertea, M. GFF utilities: GffRead and GffCompare. F1000Research 2020, 9, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Thierry, J.C.; Poch, O. RASCAL: Rapid scanning and correction of multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grau-Bové, X.; Sebé-Pedrós, A. Orthology Clusters from Gene Trees with Possvm. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5204–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, A.Y.; Plotkin, D.; Espeland, M.; Meusemann, K.; Toussaint, E.F.A.; Donath, A.; Gimnich, F.; Frandsen, P.B.; Zwick, A.; Dos Reis, M.; et al. Phylogenomics reveals the evolutionary timing and pattern of butterflies and moths. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22657–22663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, D.; Halldórsson, B.V.; Vernot, B. A hybrid micro-macroevolutionary approach to gene tree reconstruction. J. Comput. Biol. 2006, 13, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S. Ultrafast one-pass FASTQ data preprocessing, quality control, and deduplication using fastp. Imeta 2023, 2, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breeschoten, T.; van der Linden, C.F.; Ros, V.I.; Schranz, M.E.; Simon, S. Expanding the menu: Are polyphagy and gene family expansions linked across Lepidoptera? Genome Biol. Evol. 2022, 14, evab283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, V.D. Deterrents and Their Effects on the Feeding Behavior and Sensory Physiology of Insects. In Arthropods-New Advances and Perspectives; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alhassan, I.; Çoklar, H.; Akbulut, M. Determination of some physical, chemical and nutritional properties in the peel and flesh of three crab apple species at five edible maturity stages. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2023, 66, e23220427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labandeira, C.C.; Dilcher, D.L.; Davis, D.R.; Wagner, D.L. Ninety-seven million years of angiosperm-insect association: Paleobiological insights into the meaning of coevolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12278–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.H.; Abdelrahman, M.; El-Sayed, M.A. Alkaloid role in plant defense response to growth and stress. In Bioactive Molecules in Plant Defense: Signaling in Growth and Stress; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, J. The role of terpenoids in plants and its application. Bot. Res. 2013, 2, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.; Serk, H.; Granlund, I.; Pesquet, E. The cell biology of lignification in higher plants. Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 1053–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, P.R.; Raven, P.H. Butterflies and plants: A study in coevolution. Evolution 1964, 18, 586–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidel-Fischer, H.M.; Vogel, H. Molecular mechanisms of insect adaptation to plant secondary compounds. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 8, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loehlin, D.W.; Carroll, S.B. Expression of tandem gene duplicates is often greater than twofold. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5988–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, E.D.; Hoover, K.; Carlson, J.E.; Tien, M.; Geib, S.M. Midgut transcriptome profiling of Anoplophora glabripennis, a lignocellulose degrading cerambycid beetle. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra-Peralbo, E.; Talamillo, A.; Barrio, R. Origin and Development of the Adipose Tissue, a Key Organ in Physiology and Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 786129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Li, J.; Zong, Z.; Liu, X.; Song, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Cloning, expression, and characteristic analysis of the novel β-galactosidase from silkworm, Bombyx mori. Genesis 2021, 59, e23446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albalat, R.; Cañestro, C. Evolution by gene loss. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.; Conery, J.S. The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes. Science 2000, 290, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; He, Z.; Fu, W.; Chakraborty, A.; He, S. Evolutionary Dynamics of Glycoside Hydrolase Family 1 Provide Insights into Insect–Plant Interactions in Lepidoptera. Insects 2025, 16, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070727
Yuan Y, Zhang X, Wu J, Li J, He Z, Fu W, Chakraborty A, He S. Evolutionary Dynamics of Glycoside Hydrolase Family 1 Provide Insights into Insect–Plant Interactions in Lepidoptera. Insects. 2025; 16(7):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070727
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yanping, Xidan Zhang, Jinyu Wu, Jun Li, Zhengbo He, Wenbo Fu, Amrita Chakraborty, and Shulin He. 2025. "Evolutionary Dynamics of Glycoside Hydrolase Family 1 Provide Insights into Insect–Plant Interactions in Lepidoptera" Insects 16, no. 7: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070727
APA StyleYuan, Y., Zhang, X., Wu, J., Li, J., He, Z., Fu, W., Chakraborty, A., & He, S. (2025). Evolutionary Dynamics of Glycoside Hydrolase Family 1 Provide Insights into Insect–Plant Interactions in Lepidoptera. Insects, 16(7), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16070727







