Reproduction and Wing Differentiation of Gynoparae Are Regulated by Juvenile Hormone Signaling in Aphis gossypii
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Gynoparae in Aphids
2.2. Gynoparae Induction
2.3. Morphological Characteristics and Fertility
2.4. Preparation of RNA Sequencing Samples
2.5. Transcriptome Assembly and Gene Annotation
2.6. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
2.7. Validation of RNA-Seq Data by Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.8. Effects of JH Analogue Kinoprene on Gynoparae
3. Results
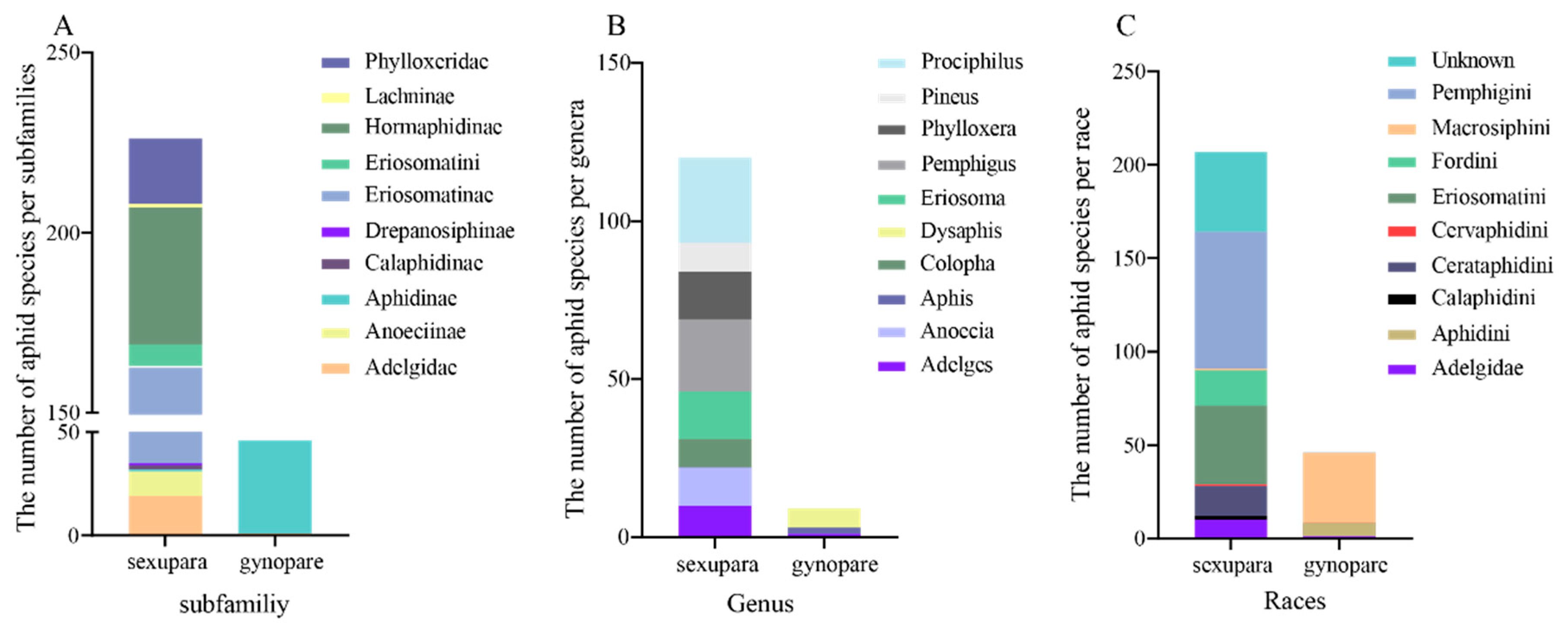
3.1. Distribution of Gynoparae in Aphididae
3.2. Morphology and Embryogenesis of Gynoparae
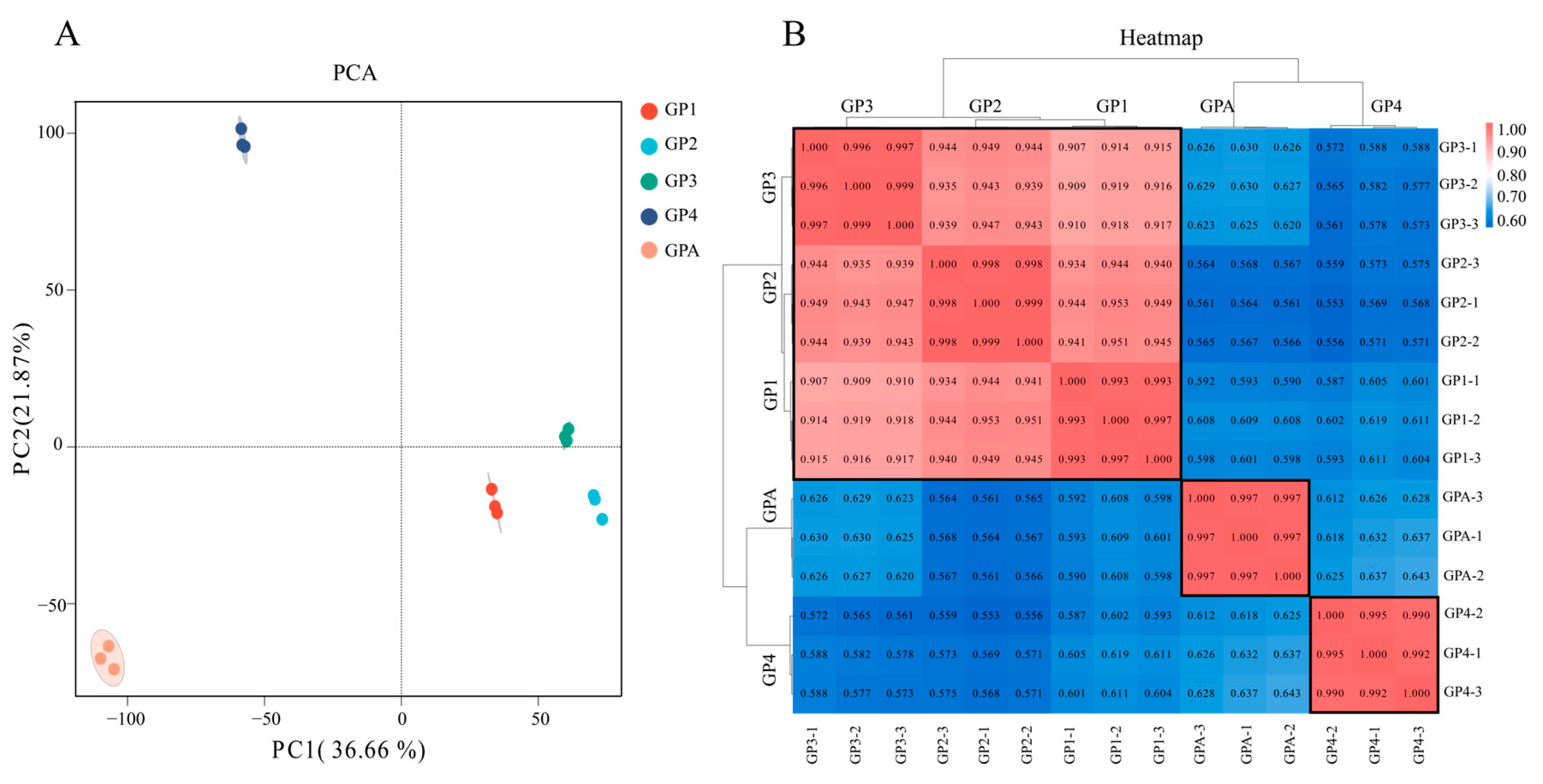
3.3. Transcriptome Data and Their Reliability Analysis
3.4. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
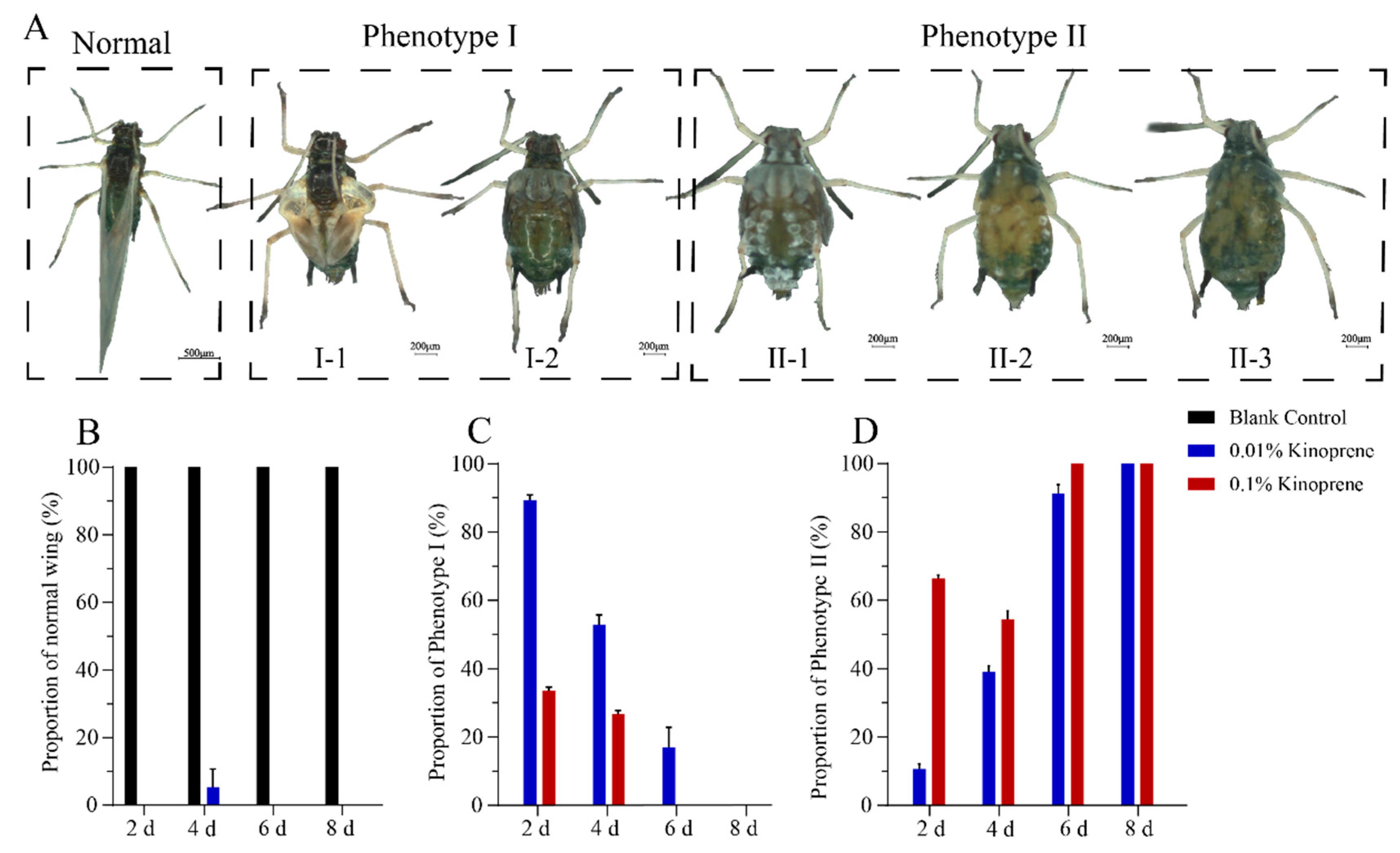
3.5. Effects of Kinoprene on Wing Differentiation and Reproduction of Gynoparae
3.6. Response of JH Biosynthesis-Related Genes to Kinoprene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Approval
References
- Mistral, P.; Vanlerberghe-Masutti, F.; Elbelt, S.; Boissot, N. Aphis gossypii/Aphis frangulae collected worldwide: Microsatellite markers data and genetic cluster assignment. Data Brief 2021, 36, 106967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbanhawy, A.A.; Elsherbiny, E.A.; Abd El-Mageed, A.E.; Abdel-Fattah, G.M. Potential of fungal metabolites as a biocontrol agent against cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover and the possible mechanisms of action. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 159, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilsnis, B.; Mahas, J.B.; Conner, K.; Pandey, S.; Clark, W.; Koebernick, J.; Srinivasan, R.; Martin, K.; Jacobson, A.L. Characterizing the vector competence of Aphis gossypii, Myzus persicae and Aphis craccivora (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to transmit cotton leafroll dwarf virus to cotton in the United States. J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 13, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.Y.; Park, Y.; Lee, J.H. Population Genetic Structure of Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in Korea. Insects 2019, 26, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Qiao, X.; Chen, M. Responses of holocyclic and anholocyclic Rhopalosiphum padi populations to low-temperature and short-photoperiod induction. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 19, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Trionnaire, G.; Hardie, J.; Jaubert-Possamai, S.; Simon, J.; Tagu, D. Shifting from clonal to sexual reproduction in aphids: Physiological and developmental aspects. Biol. Cell 2008, 100, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Thieme, T.; Kim, H. Complex evolution in Aphis gossypii group (Hemiptera: Aphididae), evidence of primary host shift and hybridization between sympatric species. PLoS ONE 2021, 4, e0245604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrock, C.; Razmjou, J.; Vorburger, C. Climate effects on life cycle variation and population genetic architecture of the black bean aphid, Aphis fabae. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 4165–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emden, H.F.; Harrington, R. Aphids as Crop Pests; CAB International: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, N.A. The evolution of aphid life cycles. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1992, 37, 321–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, D.F.; Wellings, P.W.; Parkes, R.A. Investment in gynoparae and males by Myzus persicae (Sulzer). Funct. Ecol. 1989, 3, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.J.; Hardie, J. Chemical aspects of host-acceptance behaviour in the bird cherry-oat aphid Rhopalosiphum padi: Host-acceptance signals used by different morphs with the same genotype. Physiol. Entomol. 2014, 39, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.Q.; Wang, S.J.; Bai, B.; Liu, J.; Zhao, K.J. A morphological study on autumnal morphs of Aphis glycines (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2018, 21, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.K.; Pan, B.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Ren, Q.Q.; Li, C. Roles of the PTP61F Gene in Regulating Energy Metabolism of Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Front. Physiol. 2020, 20, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horodyski, F. Molecular Analysis of an Allatotropin in Manduca Sexta; National Science Foundation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, L.; He, Q.; Zhou, S. Regulatory Mechanisms of Vitellogenesis in Insects. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 28, 593613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Zhou, S.; Feng, Q.; Palli, S.R.; Wang, J.; Roth, S.; et al. Juvenile hormone signaling promotes ovulation and maintains egg shape by inducing expression of extracellular matrix genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 28, e2104461118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyria, J.; Benrabaa, S.; Nouzova, M.; Noriega, F.G.; Tose, L.V.; Fernandez-Lima, F.; Orchard, I.; Lange, A.B. Crosstalk between Nutrition, Insulin, Juvenile Hormone, and Ecdysteroid Signaling in the Classical Insect Model, Rhodnius prolixus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, I.A.; Attardo, G.M.; Rodriguez, S.D.; Drake, L.L. Four-way regulation of mosquito yolk protein precursor genes by juvenile hormone-, ecdysone-, nutrient-, and insulin-like peptide signaling pathways. Front. Physiol. 2014, 20, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Saha, T.T.; Zou, Z.; Raikhel, A.S. Regulatory Pathways Controlling Female Insect Reproduction. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 7, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smykal, V.; Raikhel, A.S. Nutritional Control of Insect Reproduction. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Guo, H.J.; Sun, Y.C.; Ge, F. Juvenile hormone mediates the positive effects of nitrogen fertilization on weight and reproduction in pea aphid. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2511–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, J.; Lees, A.D. The induction of normal and teratoid viviparae by a juvenile hormone and kinoprene in two species of aphids. Physiol. Entomol. 1985, 10, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, T.E.; Nassar, S.G.; Staal, G.B. Wing development and parthenogenesis induced in progenies of kinoprene-treated gynoparae of Aphis fabae and Myzus persicae. J. Insect Physiol. 1976, 22, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zera, A.J.; Denno, R.F. Physiology and ecology of dispersal polymorphism in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1997, 42, 207–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingle, H.; Winchell, R. Juvenile hormone as a mediator of plasticity in insect life histories. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1997, 35, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaffery, A.R.; Page, W.W. Factors influencing the production of long-winged Zonocerus variegatus. J. Insect Physiol. 1978, 24, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.; Gotoh, H.; Abe, T.; Miura, T. Juvenile hormone titer and wing-morph differentiation in the vetch aphid Megoura crassicauda. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niitsu, S.; Lobbia, S.; Kamito, T. In vitro effects of juvenile hormone analog on wing disc morphogenesis under ecdysteroid treatment in the female-wingless bagworm moth Eumeta variegata (Insecta: Lepidoptera, Psychidae). Tissue Cell 2011, 43, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Shahin, R.; Fujimoto, S. Proliferative and preparative cell divisions in wing discs of the last larval instar are regulated by different hormones and determine the size and differentiation of the wing of Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 2023, 145, 104476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.D.; Lavine, L.C. Endocrine regulation of a dispersal polymorphism in winged insects: A short review. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 25, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, J. Juvenile hormone and photoperiodically controlled polymorphism in Aphis fabae: Prenatal effects on presumptive oviparae. J. Insect Physiol. 1981, 27, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Herbaceous Plants and Shrubs; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.C.; Huangfu, N.B.; Luo, J.Y.; Gao, X.K.; Niu, L.; Zhang, S.; Cui, J.J. Insights into wing dimorphism in worldwide agricultural pest and host-alternating aphid Aphis gossypii. J. Cotton Res. 2021, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, N.B.; Shi, Q.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhang, K.X.; Li, D.Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, X.Z.; Ji, J.C.; Luo, J.Y.; et al. Comparative transcriptional analysis and identification of hub genes associated with wing differentiation of male in Aphis gossypii. J. Cotton Res. 2022, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.C.; Shi, Q.Y.; Zhang, K.X.; Chen, L.L.; Zhu, X.Z.; Li, D.Y.; Gao, X.K.; Niu, L.; Wang, L.; Luo, J.Y.; et al. Sexually dimorphic morphology, feeding behavior and gene expression profiles in cotton aphid Aphis gossypii. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 5152–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, K.X.; Li, D.Y.; Gao, M.X.; Guo, L.X.; Tang, Z.J.; Gao, X.K.; Zhu, X.Z.; Wang, L.; et al. Morphological characteristics, developmental dynamics, and gene temporal expressions across various development stages of Aphis gossypii sexual female. J. Cotton Res. 2024, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, X.K.; Wang, L.; Jiang, W.L.; Su, H.H.; Jing, T.X.; Cui, J.J.; Zhang, L.J.; Yang, Y.Z. Chromosome-level genome assemblies of two cotton-melon aphid Aphis gossypii biotypes unveil mechanisms of host adaption. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 1120–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, S.R. Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.S.; Li, F.; Liang, P.Z.; Chen, X.W.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.W. Identification and Validation of Reference Genes for the Normalization of Gene Expression Data in qRT-PCR Analysis in Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Insect Sci. 2016, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Hoelmer, K.A.; Lee, W.; Kwon, Y.D.; Lee, S. Molecular and Morphological Identification of the Soybean Aphid and Other Aphis Species on the Primary Host Rhamnus davurica in Asia. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2010, 103, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.Q.; Cai, J.Y.; Deng, X.Q.; Liang, W.W.; Hu, X.L. Growth, Reproduction, and Transgenerational Effects of Kinoprene on Moina macrocopa. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 110, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.H.; Li, Z.X.; Cheng, J.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Lin, T. Suppression of Gene Juvenile Hormone Diol Kinase Delays Pupation in Heortia vitessoides Moore. Insects 2019, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Liu, X.J.; Shiotsuki, T.; Wang, Z.S.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.P.; Li, M.W.; Li, K.; Tan, A.J. Depletion of juvenile hormone esterase extends larval growth in Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 81, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.J.; Zhang, J.L.; Ma, W.J.; Wu, H.J.; Li, Y.; Shen, X.X.; Xu, H.J. FoxO and rotund form a binding complex governing wing polyphenism in planthoppers. iScience 2023, 26, 107182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yan, R.; Qian, J.; Chen, D.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wu, H.; Chen, M. RNAi-mediated knockdown of juvenile hormone esterase causes mortality and malformation in Tribolium castaneum. Entomol. Res. 2022, 52, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Kalia, V.K. Silencing of juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase gene in Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) by oral delivery of double-stranded RNA. Biologia 2023, 78, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanparast, M.; Kazzazi, M.; Mirzaie-asl, A.; Hosseininaveh, V. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of some genes involved in digestion and development of Helicoverpa armigera. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2017, 107, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Qiu, Y.W.; Huang, J.; Tobe, S.S.; Chen, S.S.; Kai, Z.P. Enzymes in the juvenile hormone biosynthetic pathway can be potential targets for pest control. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.F.; Gao, Q.; Cheng, H.H.; Peng, F.; Wang, C.L.; Xu, B.P. Molecular cloning and expression pattern of the juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase gene from the giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii during larval development and the moult cycle. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 3890–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Transcriptomic and proteomic effects of gene deletion are not evolutionarily conserved. Genome Res. 2025, 35, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Lv, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, K.; Shi, Q.; Wang, L.; Ma, W.; Ji, J.; Luo, J.; Cui, J. Reproduction and Wing Differentiation of Gynoparae Are Regulated by Juvenile Hormone Signaling in Aphis gossypii. Insects 2025, 16, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060559
Wang L, Lv J, Zhu X, Zhang K, Shi Q, Wang L, Ma W, Ji J, Luo J, Cui J. Reproduction and Wing Differentiation of Gynoparae Are Regulated by Juvenile Hormone Signaling in Aphis gossypii. Insects. 2025; 16(6):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060559
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liuyu, Jingli Lv, Xiangzhen Zhu, Kaixin Zhang, Qingyu Shi, Li Wang, Weihua Ma, Jichao Ji, Junyu Luo, and Jinjie Cui. 2025. "Reproduction and Wing Differentiation of Gynoparae Are Regulated by Juvenile Hormone Signaling in Aphis gossypii" Insects 16, no. 6: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060559
APA StyleWang, L., Lv, J., Zhu, X., Zhang, K., Shi, Q., Wang, L., Ma, W., Ji, J., Luo, J., & Cui, J. (2025). Reproduction and Wing Differentiation of Gynoparae Are Regulated by Juvenile Hormone Signaling in Aphis gossypii. Insects, 16(6), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16060559






