Aprostocetus nitens (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), an Ectoparasitoid Proposed for Biological Control of the Destructive Erythrina Gall Wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae, in Hawaiʻi
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
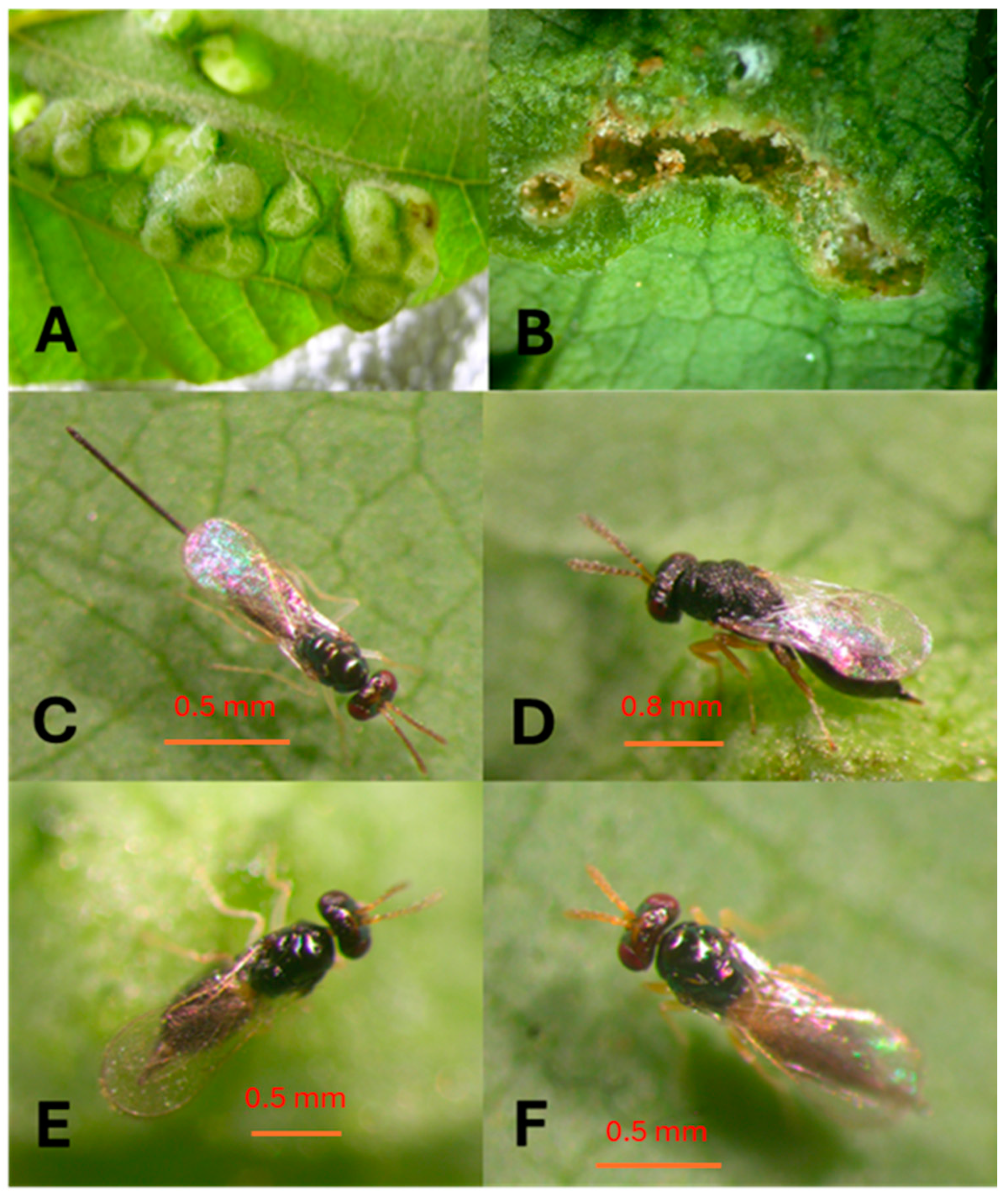
2.1. Explorations and Origin of the Parasitoid Colony
2.2. Propagation of Host Plants and EGW
2.3. Rearing of A. nitens
2.4. Longevity and Life-Time Fecundity of A. nitens
2.5. Host Specificity Testing of A. nitens
2.6. Intersepcific Competition Between A. nitens and E. erythrinae
- Control: Plants with Erythrina gall wasp only, no parasitoids;
- Galled Erythrina were exposed to 10 females of E. erythrinae only, for 72 h;
- Galled Erythrina were exposed to 10 A. nitens only, for 72 h;
- Galled Erythrina were exposed to 10 females of E. erythrinae and 10 females of A. nitens concurrently for 72 h;
- Galled Erythrina were exposed to 10 females of E. erythrinae for 72 h. Then, after 4 days, the same plants were exposed to 10 A. nitens for 72 h;
- Galled Erythrina were exposed to 10 females of A. nitens for 72 h. Then, after 4 days, the same plants were exposed to 10 females of E. erythrinae for 72 h.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
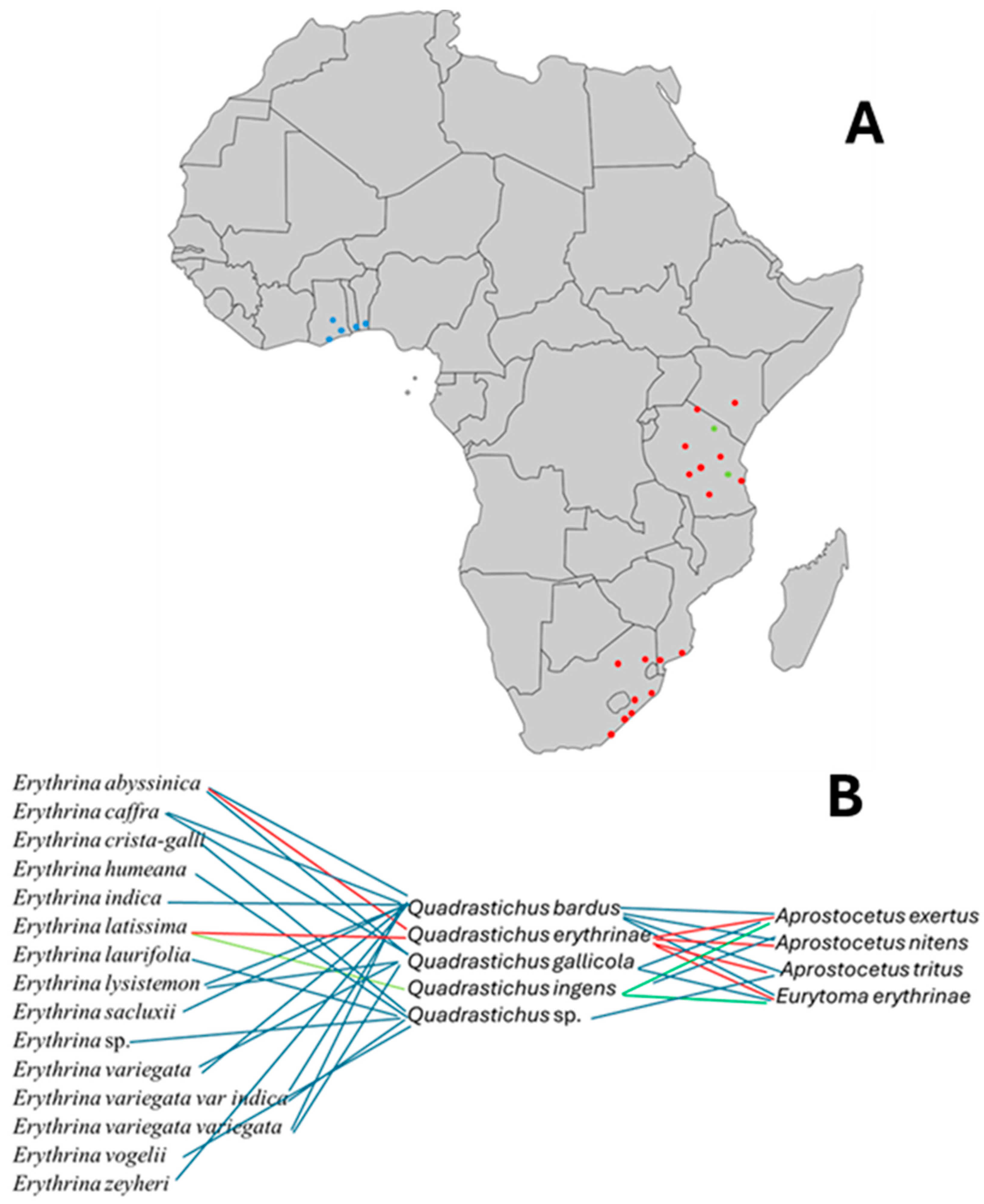
3.1. Explorations and Acquiring Parasitoids
3.2. Tri-Trophical Associations of Native Erythrina, Gall Wasps, and Their Parasitoids
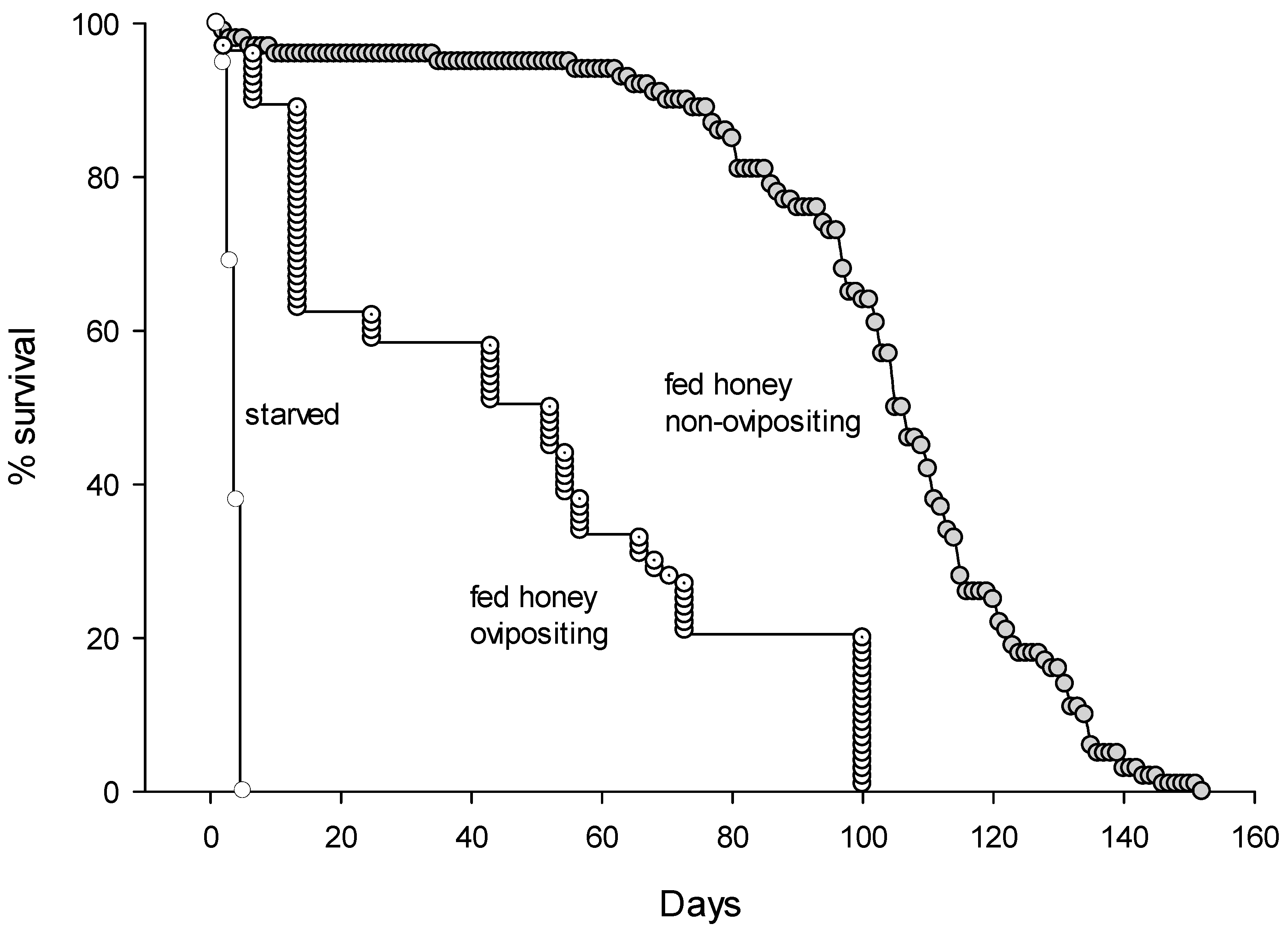
3.3. Longevity and Life-Time Fecundity of A. nitens
3.4. Host Specificity of A. nitens
3.5. Interspecific Competition Between A. nitens and E. erythrinae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heu, R.; Tsuda, D.; Nagamine, W.; Yalemar, J.; Suh, T. Erythrina Gall Wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Hawaii Department of Agriculture, New Pest Advisory, 2006, No. 05-03. Available online: http://www.hawaiiag.org/hdoa/npa/npa05-03-EGW.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2024).
- Wagner, W.L.; Herbst, D.R.; Sohmer, S.H. Manual of the Flowering Plants of Hawaii; Erythrina; University of Hawaii Press: Honolulu, HI, USA; Bishop Museum Press: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1990; Volume 2, pp. 671–672. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.-M.; Tung, G.-S.; LaSalle, J.; Wu, M.-L. Outbreak of Erythrina gall wasp (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) on Erythrina spp. (Fabaceae) in Taiwan. For. Plant Prot. Bul. 2004, 46, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yu, D.; Kang, L.; Yang, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X. Bionomics of the erythrina gall wasp, Quadristichus erythrinae Kim (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2007, 50, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.-M.; Xiao, H.; Peng, H.-X.; Han, X.D. Potential global range expansion of a new invasive species, the erythrina gall wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Raffles Bul. Zool. 2006, 54, 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Messing, R.H.; Noser, S.; Hunkeler, J. Using host plant relationships to help determine origins of the invasive Erythrina gall wasp Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae. Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinoff, D.; Holland, B.S.; Shibata, A.; Messing, R.H.; Wright, M.G. Rapid invasion despite lack of genetic variation in the Erythrina gall wasp (Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim). Pac. Sci. 2010, 64, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre for Agricultural Bioscience International (CABI) Invasive Species Specialist Group. Quadrastichus erythrinae (Erythrina Gall Wasp). 2015. Available online: http://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/46220 (accessed on 6 October 2016).
- Brannon, J. Dying Trees Cost $1M a Year. The Honolulu Advertiser. 2007. Available online: http://the.honoluluadvertiser.com/article/2007/Mar/23/ln/FP703230359.html (accessed on 14 October 2024).
- Smith, S.; Strom, B.; Medeiros, A.; von Allmen, E. Systemically Applied Insecticides for Treatment of Erythrina Gall Wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Arboric. Urban For. 2009, 35, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizal, M.H.; Prathapan, K.D.; Anith, K.N.; Mary, C.A.; Lekha, M.; Rini, C.R. Erythrina gall wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae, yet another invasive pest new to India. Curr. Sci. 2006, 90, 1061–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Nami, U.; Takumi, U.; Yukawa, J. Detection of an invasive gall-inducing pest, Quadrastichus erythrinae (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), causing damage to Erythrina variegata L. (Fabaceae) in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. Entomol. Sci. 2007, 10, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, F.W.; Pemberton, R.R.; Liu, H. Erythrina Gall Wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) in Florida, and Susceptibility of Erythrina herbacea (Fabaceae). Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 2008, 121, 363–369. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.F.; Tung, G.S.; Yang, M.M. The Erythrina gall wasp Quadrastichus erythrinae (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Eulophidae): Invasion history, ecology, infestation and management. Forests 2021, 12, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.F.; Tung, G.S.; Yang, M.M. Out of Africa: Origin of the Erythrina gall wasp Quadrastichus erythrinae (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea: Eulophidae). Formos. Entomol. 2021, 41, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, K.R.; Kester, K.M.; Hoelmer, K.A. XIV International Entomophagous Insects Workshop. 25PP. J. Insect Sci. 2007, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, M.; Delvare, G. A new species of Eurytoma (Hymenoptera: Eurytomidae) attacking Quadrastichus spp. (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) galling Erythrina spp. (Fabaceae), with a summary of African Eurytoma biology and species checklist. Zootaxa 2008, 1751, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaSalle, J.; Ramadan, M.; Kumashiro, B.R. A new parasitoid of the Erythrina gall wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Zootaxa 2009, 2083, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinsloo, G.L.; Kelly, J.A. The Tetrastichine Wasps (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea: Eulophidae) associated with galls on Erythrina species (Fabaceae) in South Africa, with the description of five new species. Zootaxa 2009, 45, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.C.; Belmaker, A.; Couch, C.S.; Marchetto, K.M.; Simonis, J.L.; Thomas, Q.; Sparks, J. Effectiveness of Erythrina gall wasp biocontrol and implications for the recovery of threatened Wiliwili trees (Fabaceae: Erythrina sandwicensis). J. Torrey Bot. Soc. 2013, 140, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, L.V.; Yalemar, J.; Wright, M.G. Classical biological control of the erythrina gall wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae, in Hawaii: Conserving an endangered habitat. Biol. Control 2020, 142, 104161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.M.; Kaufman, L.V.; Wright, M.G. Insect and weed biological control in Hawaii: Recent case studies and trends. Biol. Control 2023, 179, 105170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamine, W.T.; Yalemar, J.A.; Wright, M.G.; Ramadan, M.M. Reproductive parameters and host specificity of Eurytoma erythrinae (Hymenoptera: Eurytomidae), a biological control agent of the Erythrina gall wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Insects 2023, 14, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hogg, B.N.; Wang, X.G.; Levy, K.; Mills, N.J.; Daane, K.M. Complementary effects of resident natural enemies on the suppression of the introduced moth Epiphyas postvittana. Biol. Control 2013, 64, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Hogg, B.N.; Hougardy, E.; Nance, A.H.; Daane, K.M. Potential competitive outcomes among three solitary larval endoparasitoids as candidate agents for classical biological control of Drosophila suzukii. Biol. Control 2019, 130, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JMP®; Version 11; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2023; pp. 1989–2023.
- LaSalle, J. Taxonomic notes on African Aprostocetus Westwood (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Afr. Entomol. 1994, 2, 107–109. [Google Scholar]
- LaSalle, J.; Delvare, G. Aprostocetus procerae (Risbec): A senior synonym of Tetrastichus pachydiplosisae Risbec (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Afr. Entomol. 1994, 2, 133–135. [Google Scholar]
- Noyes, J.S. Universal Chalcidoidea Database. World Wide Web Electronic Publication. 2020. Available online: https://www.nhm.ac.uk/chalcidoids (accessed on 14 October 2024).
- Stouthamer, R.; Pinto, J.D.; Platner, G.R.; Luck, R.F. Taxonomic status of thelytokous forms of Trichogramma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1990, 83, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, H.F.; Mason, A.C. Parasitization of the Mediterranean Fruit Fly in Hawaii, 1937, 1914–1933; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1937; Volume 439, pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bess, H.A.; Van Den Bosch, R.; Haramoto, F.H. Fruit fly parasites and their activities in Hawaii. Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 1961, 17, 367–578. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, T.T.Y.; Ramadan, M.M. Parasization of the Mediterranean and oriental fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) in the Kula area of Maui, Hawaii. J. Econ. Entomol. 1987, 80, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemberton, C.E.; Willard, H.F. Interrelations of fruit fly parasites in Hawaii. J. Agric. Res. 1918, 12, 285–303. [Google Scholar]
- Ramadan, M.M.; Wong, T.T.Y.; Beardsley, J.W. Survivorship, potential, and realized fecundity of Biosteres tryoni (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a larval parasitoid of Ceratitis capitata (Diptera: Tephritidae). Entomophaga 1989, 34, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, R.A. Classical biological control of fruit infesting Tephritidae. In World Crop Pests. Fruit Flies: Their Biology, Natural Enemies, and Control; Robinson, A., Harper, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 3b, pp. 303–313. [Google Scholar]
- Bokonon-Ganta, A.H.; Wang, X.G.; Messing, R.H. Biological control of tephritid fruit flies in Hawaii with special reference to the newly discovered egg-larval parasitoid, Fopius ceratitivorus (Wharton). Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 2007, 39, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, M.F. Contribution of biological control to integrated pest management of tephritid fruit flies in the tropic and subtropics. Integr. Pest Manag. 1998, 3, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, R.I.; Ramadan, M.; Hussain, T.; Mochizuki, N.; Bautista, R.C.; Stark, J.D. Comparative demography of six fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Biol. Control 2002, 25, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Messing, R.H. Intra- and interspecific competition by Fopius arisanus and Diachasmimorpha tryoni (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), parasitoids of tephritid fruit flies. Biol. Control 2003, 27, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Ramadan, M.M.; Guerrieri, E.; Messing, R.H.; Johnson, M.W.; Daane, K.M.; Hoelmer, K.A. Early-acting competitive superiority in opiine parasitoids of fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae): Implications for biological control of invasive tephritid pests. Biol. Control 2021, 162, 104725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Reproductive Parameter | n | Mean ± SEM | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Survival of non-ovipositing females, fed honey (days) | 100 | 102.5 ± 2.3 a | 1–152 |
| Survival of ovipositing females, fed honey (days) | 44 | 46.9 ± 3.5 b | 22–97 |
| Survival of starved females (days) | 58 | 4.0 ± 3.0 c | 2–5 |
| Oviposition period (days) | 7 | 25.1 ± 2.3 | 17–34 |
| Realized fecundity | 7 | 156.7 ± 22.3 | 107–282 |
| Daily progeny | 216 | 5.9 ± 0.45 | 0–53 |
| Female lifecycle (days) | 11 | 20.1 ± 0.28 | 19–22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramadan, M.M.; Yalemar, J.A.; Rubinoff, D.; Wright, M.G.; Bokonon-Ganta, A.H.; Wang, X. Aprostocetus nitens (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), an Ectoparasitoid Proposed for Biological Control of the Destructive Erythrina Gall Wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae, in Hawaiʻi. Insects 2025, 16, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050519
Ramadan MM, Yalemar JA, Rubinoff D, Wright MG, Bokonon-Ganta AH, Wang X. Aprostocetus nitens (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), an Ectoparasitoid Proposed for Biological Control of the Destructive Erythrina Gall Wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae, in Hawaiʻi. Insects. 2025; 16(5):519. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050519
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamadan, Mohsen M., Juliana A. Yalemar, Daniel Rubinoff, Mark G. Wright, Aimé H. Bokonon-Ganta, and Xingeng Wang. 2025. "Aprostocetus nitens (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), an Ectoparasitoid Proposed for Biological Control of the Destructive Erythrina Gall Wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae, in Hawaiʻi" Insects 16, no. 5: 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050519
APA StyleRamadan, M. M., Yalemar, J. A., Rubinoff, D., Wright, M. G., Bokonon-Ganta, A. H., & Wang, X. (2025). Aprostocetus nitens (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), an Ectoparasitoid Proposed for Biological Control of the Destructive Erythrina Gall Wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae, in Hawaiʻi. Insects, 16(5), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050519






