microRNA Targeting Cytochrome P450 Is Involved in Chlorfenapyr Tolerance in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects and Chemicals
2.2. Bioassays
2.3. Analysis of Chlorfenapyr Biotransformation Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.4. RNA Extraction and Library Construction
2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.7. Vector Construction and Luciferase Assay
2.8. miRNA Mimics/Inhibitor Injection and Bioassays of Chlorfenapyr and Tralopyril
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Susceptibility of Silkworm Exposed to Chlorfenapyr and Tralopyril
3.2. Quantification of Chlorfenapyr and Tralopyril Residues in the Body
3.3. Illumina Sequencing and Sequence Alignment Analysis
3.4. ncRNA Analysis
3.5. Identification of miRNAs
3.6. Screening of Differentially Expressed miRNAs in Silkworm Larvae After Chlorfenapyr Treatment
3.7. Predictions and Functional Annotation of the miRNA Target Genes
3.8. Expression Patterns of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
3.9. Screening of Differentially Expressed miRNA Targeting P450s
3.10. Bmo-miR-6497-5P Regulates CYP337A2 Expression
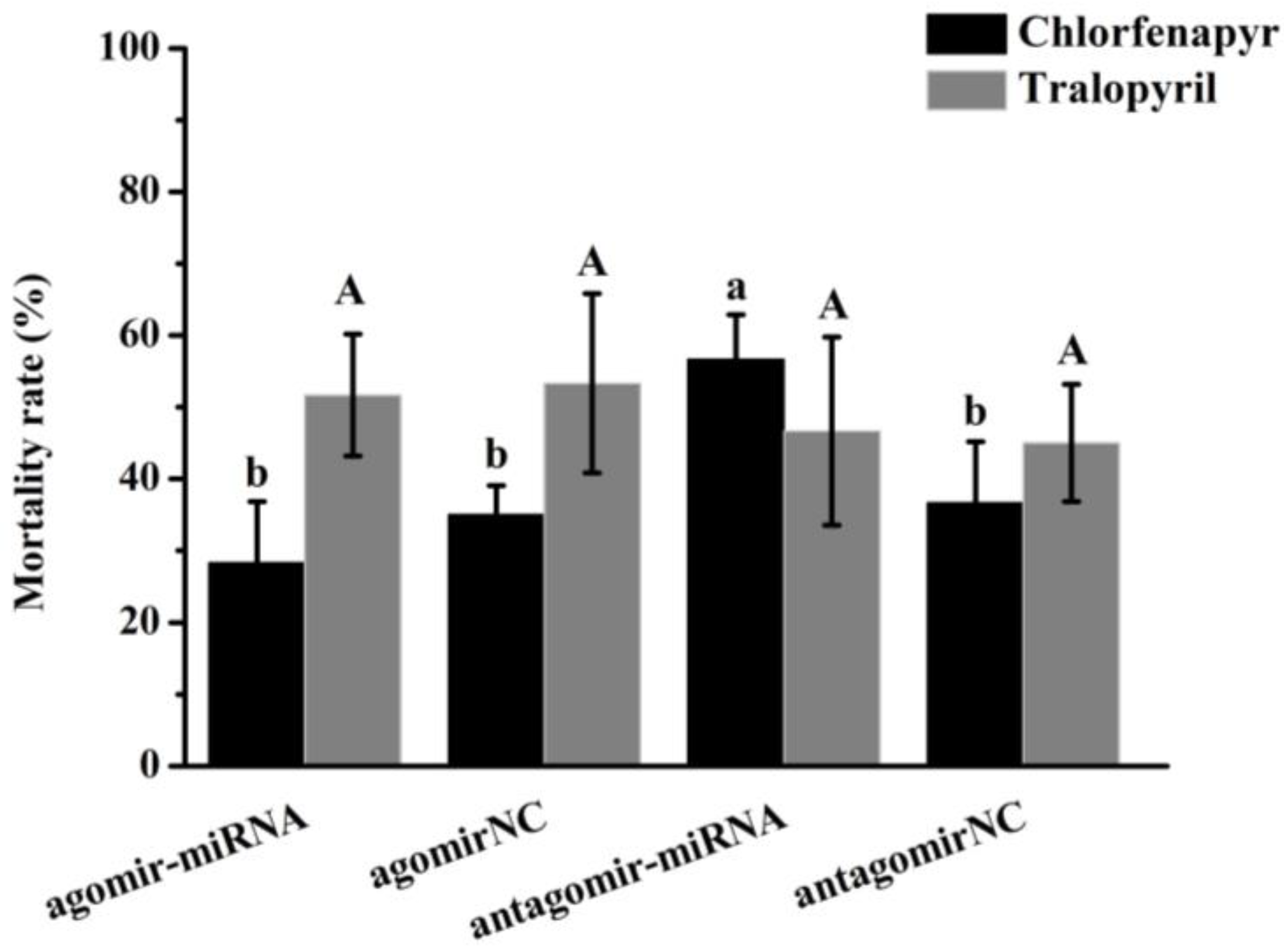
3.11. miRNA Mimics/Inhibitor Injection and Bioassays of Chlorfenapyr and Tralopyril
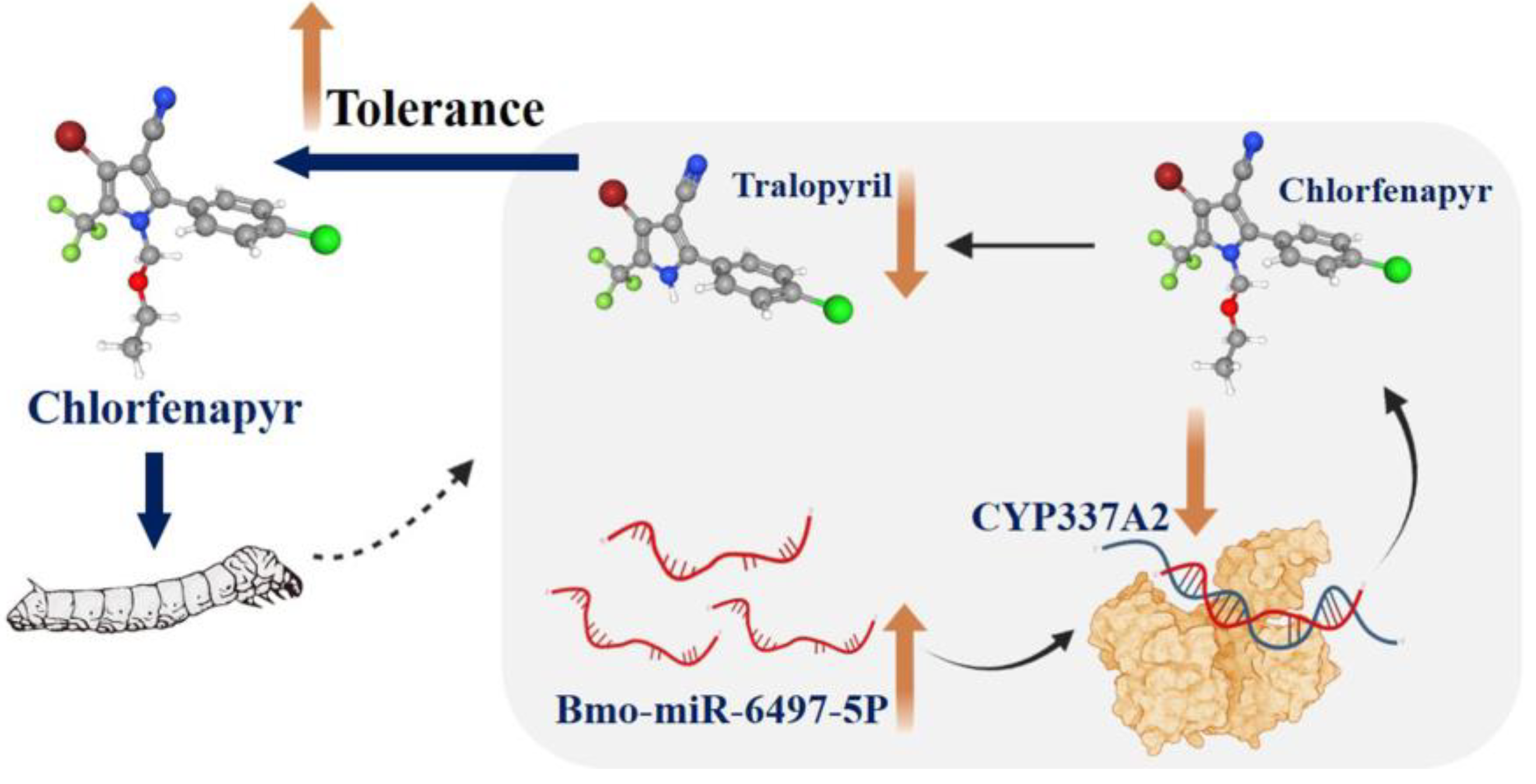
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, L.; Xie, Y.; Gu, Z.Y.; Wang, B.B.; Li, F.C.; Xu, K.Z.; Shen, W.D.; Li, B. Characteristics of phoxim-exposed gene transcription in the silk gland of silkworms. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 107, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Xin, X.D.; Liu, Z.X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Gui, Z.Z. Transcriptional response of detoxifying enzyme genes in Bombyx mori under chlorfenapyr exposure. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 177, 104899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Xie, Y.; Li, F.C.; Ma, L.; Sun, S.S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.B.; Wang, J.M.; Hong, F.S.; et al. The adverse effects of phoxim exposure in the midgut of silkworm, Bombyx mori. Chemosphere 2013, 96, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Wang, J.; Cao, X.W.; Wang, F.L.; Yang, Y.H.; Wu, S.W.; Wu, Y.D. Long-term monitoring and characterization of resistance to chlorfenapyr in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) from China. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.R.; Liu, Z.X.; Yan, M.W.; Shao, Y.; Zhou, J.C.; Wu, F.A.; Wang, J. Evaluation of sensitivity to phoxim and cypermethrin in an endoparasitoid, Meteorus pulchricornis (Wesmael) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), and its parasitization efficiency under insecticide stress. J. Insect Sci. 2021, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, K.; Barik, T.K.; Sharma, P.; Bhatt, R.M.; Srivastava, H.C.; Sreehari, U.; Dash, A.P. Chlorfenapyr: A new insecticide with novel mode of action can control pyrethroid resistant malaria vectors. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zeng, B.; Du, X.G.; Yan, S.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J.Z. Detoxification of Chlorfenapyr by a Parkin-GSTd2 Module in Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Agri. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 25490–25499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchouakui, M.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Mangoua, M.K.; Thiomela, R.F.; Assatse, T.; Ngongang-Yipmo, S.L.; Muhammad, A.; Mugenzi, L.J.M.; Menze, B.D.; Mzilahowa, T.; et al. Substrate promiscuity of key resistance P450s confers clothianidin resistance while increasing chlorfenapyr potency in malaria vectors. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunta, C.; Ooi, J.M.F.; Oladepo, F.; Grafanaki, S.; Pergantis, S.A.; Tsakireli, D.; Ismail, H.M.; Paine, M.J.I. Chlorfenapyr metabolism by mosquito P450s associated with pyrethroid resistance identifies potential activation markers. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.B.; Zhou, Y.F. Effects of introducing theanine or glutamic acid core to tralopyril on systemicity and insecticidal activity. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 141, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z.H.; Chen, A.L.; Liao, P.F.; Yang, H.; Dong, Z.P. Correlation Between Chlorfenapyr Tolerance and Contents of Cytochrome P450 and b5 in Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Sci. Seric. 2017, 43, 436–441. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Hasan, G.; Pikielny, C.W. Preferential expression of biotransformation enzymes in the olfactory organ of Drosophila melanogaster, the antennae. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 27, 10309–10315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, C.T.; Garrood, W.T.; Singh, K.S.; Randall, E.; Lueke, B.; Gutbrod, O.; Matthiesen, S.; Kohler, M.; Nauen, R.; Davis, T.G.E.; et al. Neofunctionalization of Duplicated P450 Genes Drives the Evolution of Insecticide Resistance in the Brown Planthopper. Cur. Biol. 2018, 28, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, R.; Vontas, J.; Kaussmann, M.; Wölfel, K. Pymetrozine is hydroxylated by CYP6CM1, a cytochrome P450 conferring neonicotinoid resistance in Bemisia tabaci. Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.N.; Li, M.; Gong, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, T. Cytochrome P450s-their expression, regulation, and role in insecticide resistance. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 120, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, A.C.; Dugas, D.V.; Bartel, D.P.; Bartel, B. MicroRNA regulation of NAC-domain targets is required for proper formation and separation of adjacent embryonic, vegetative, and floral organs. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, S. MicroRNA functions in insects. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Cheng, H.H.; Tewari, M. MicroRNA profifiling: Approaches and considerations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamasi, V.; Monostory, K.; Prough, R.A.; Falus, A. Role of xenobiotic metabolism in cancer: Involvement of transcriptional and miRNA regulation of P450s. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Liu, B.; Hu, H.; Li, X.X.; Guo, Q.; Zou, F.F.; Liu, X.M.; Hu, M.X.; Guo, J.X.; Ma, L.; et al. MiR-285 targets P450 (CYP6N23) to regulate pyrethroid resistance in Culex pipiens pallens. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 4511–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedländer, M.R.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Li, N. miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tino, P. Basic properties and information theory of Audic-Claverie statistic for analyzing cDNA arrays. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enright, A.J.; John, B.; Gaul, U.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol. 2003, 5, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta C (T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.X.; Bacigalupe, L.D.; Luna-Rudloff, M.; Figueroa, C.C. Insecticide resistance mechanisms in the green peach aphid Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) II: Costs and benefits. PLoS ONE 2012, 27, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Ran, L.; Zhu, B.; Gao, X.W.; Liang, P. Overexpression of cytochrome P450 CYP6BG1 may contribute to chlorantraniliprole resistance in Plutella xylostella (L). Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 74, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gong, Y.; Shahbaz, A.; Hou, M.L. Mechanisms of resistance to thiamethoxam and dinotefuran compared to imidacloprid in the brown planthopper: Roles of cytochrome P450 monooxygenase and a P450 gene CYP6ER1. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 150, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.R.; Yan, M.W.; Pang, H.L.; Wu, F.A.; Wang, J.; Sheng, S. Cytochrome P450s Are Essential for Insecticide Tolerance in the Endoparasitoid Wasp Meteorus pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Insects 2021, 12, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, R.S.; Hart-Smith, G.; Eamens, A.L. MicroRNA regulatory mechanisms play different roles in arabidopsis. J. Proteome. Res. 2015, 6, 4743–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouzova, M.; Etebari, K.; Noriega, F.G.; Asgari, S. A comparative analysis of corpora allata-corpora cardiaca microRNA repertoires revealed significant changes during mosquito metamorphosis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 96, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitamura, T.; Watari, H.; Wang, L.; Kanno, H.; Hassan, M.K.; Miyazaki, M.; Karoh, Y.; Kimura, T.; Tanino, M.; Nishihara, H.; et al. Downregulation of miRNA-31 induces taxane resistance in ovarian cancer cells through increase of receptor tyrosine kinase MET. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.X.; Guo, L.; Zhou, X.G.; Gao, X.W.; Liang, P. miRNAs regulated overexpression of ryanodine receptor is involved in chlorantraniliprole resistance in Plutella xylostella. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Zhang, P.; Su, X.; Guo, T.X.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhang, B.Z.; Wang, H.L. MicroRNA-190-5p confers chlorantraniliprole resistance by regulating CYP6K2 in Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 184, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chao, X.; Zhao, Y.X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.H. A microRNA, PC-5p-30_205949, regulates triflumezopyrim susceptibility in Laodelphax striatellus (Fallen) by targeting CYP419A1 and ABCG23. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 192, 105413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Lv, Y.; Wang, W.; Guo, Q.; Zou, F.F.; Hu, S.L.; Fang, F.J.; Tian, M.M.; Liu, B.Q.; Liu, X.M.; et al. MiR-278-3p regulates pyrethroid resistance in Culex pipiens pallens. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, S.; Komagata, O.; Itokawa, K.; Shono, T.; Ng, L.C.; Kobayashi, M.; Tomita, T. Mechanisms of Pyrethroid Resistance in the Dengue Mosquito Vector, Aedes aegypti: Target Site Insensitivity, Penetration, and Metabolism. PLoS Negl. Trop. D 2014, 8, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komagata, O.; Kasai, S.; Tomita, T. Overexpression of cytochrome P450 genes in pyrethroid-resistant Culex Quinquefasciatus. Insect Biochem. Molec. Biol. 2010, 40, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hu, G.; Lu, L.; Hu, S.; Li, Y.; Su, X.; Dong, W.Y.; Zhen, C.A.; Liu, R.Q.; Kong, F.B.; et al. Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs under imidacloprid exposure in Sitobion miscanthi. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 177, 104885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.S.; Cui, L.L.; Hu, G.L.; Jiang, Y.T.; Lv, Y.P.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, J.S.; Zhang, B.Z.; Liu, R.Q. Overexpression of CYP6CY1 is Involved in Imidacloprid Resistance in Sitobion miscanthi (Takahashi) (Homoptera: Aphidae). Neotrop. Entomol. 2025, 54, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenhole, M.; Lu, X.P.; Tsakireli, D.; Mermans, C.; De Rouck, S.; De Beer, B.; Simma, E.; Pergantis, S.A.; Jonckheere, W.; Vontas, J.; et al. Contrasting roles of cytochrome P450s in amitraz and chlorfenapyr resistance in the crop pest Tetranychus urticae. Insect Biochem. Molec. Biol. 2024, 164, 104039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, K.K.; Jin, R.H.; Ren, Z.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, Z.; He, S.; Ma, K.S.; Wan, H.; Li, J.H. miRNAs targeting CYP6ER1 and CarE1 are involved in nitenpyram resistance in Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Sci. 2021, 29, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ding, W.; Taning, C.N.T.; Smagghe, G.; Wang, J.J. Regulatory roles of microRNAs in insect pests: Prospective targets for insect pest control. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2021, 70, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.X.; Wang, A.Y.; Xue, C.; Tian, H.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.L.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhang, J.H. MicroRNA PC-5p-3991_515 mediates triflumezopyrim susceptibility in the small brown planthopper through regulating the post-transcriptional expression of P450 CYP417A2. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 80, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.T.; Kong, F.B.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, M.Y.; Su, X.; Zhang, B.Z.; Ji, X.; Wang, H.L. MicroRNA-23a changes chlorantraniliprole susceptibility by targeting CYP9F1 in Spodoptera frugiperda. Entomol. Gen. 2023, 43, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Z.; Jiang, Y.T.; Cui, L.L.; Hu, G.L.; Li, X.A.; Zhang, P.; Ji, X.; Ma, P.C.; Kong, F.B. microRNA-3037 targeting CYP6CY2 confers imidacloprid resistance to Sitobion miscanthi (Takahashi). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 202, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

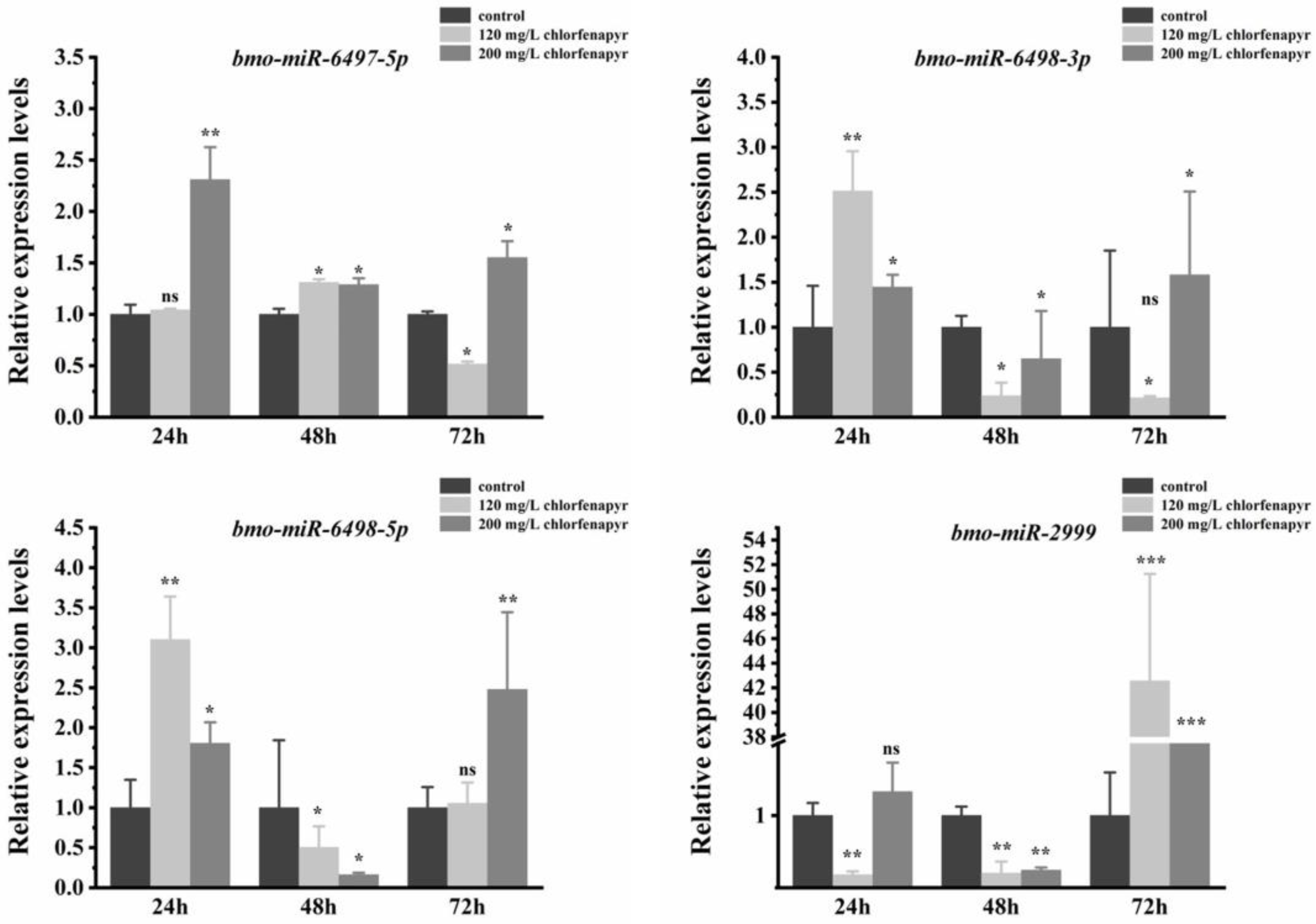
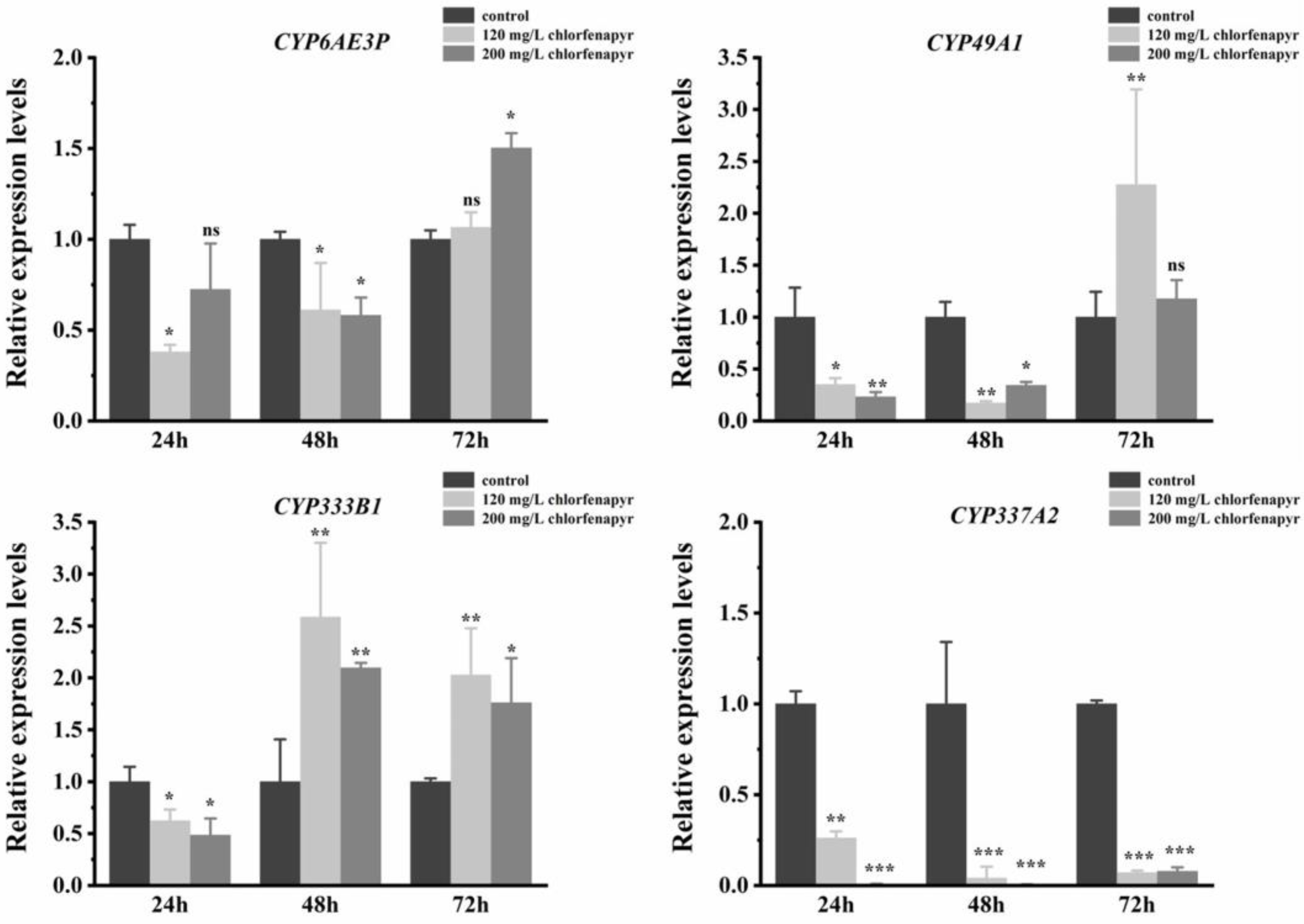
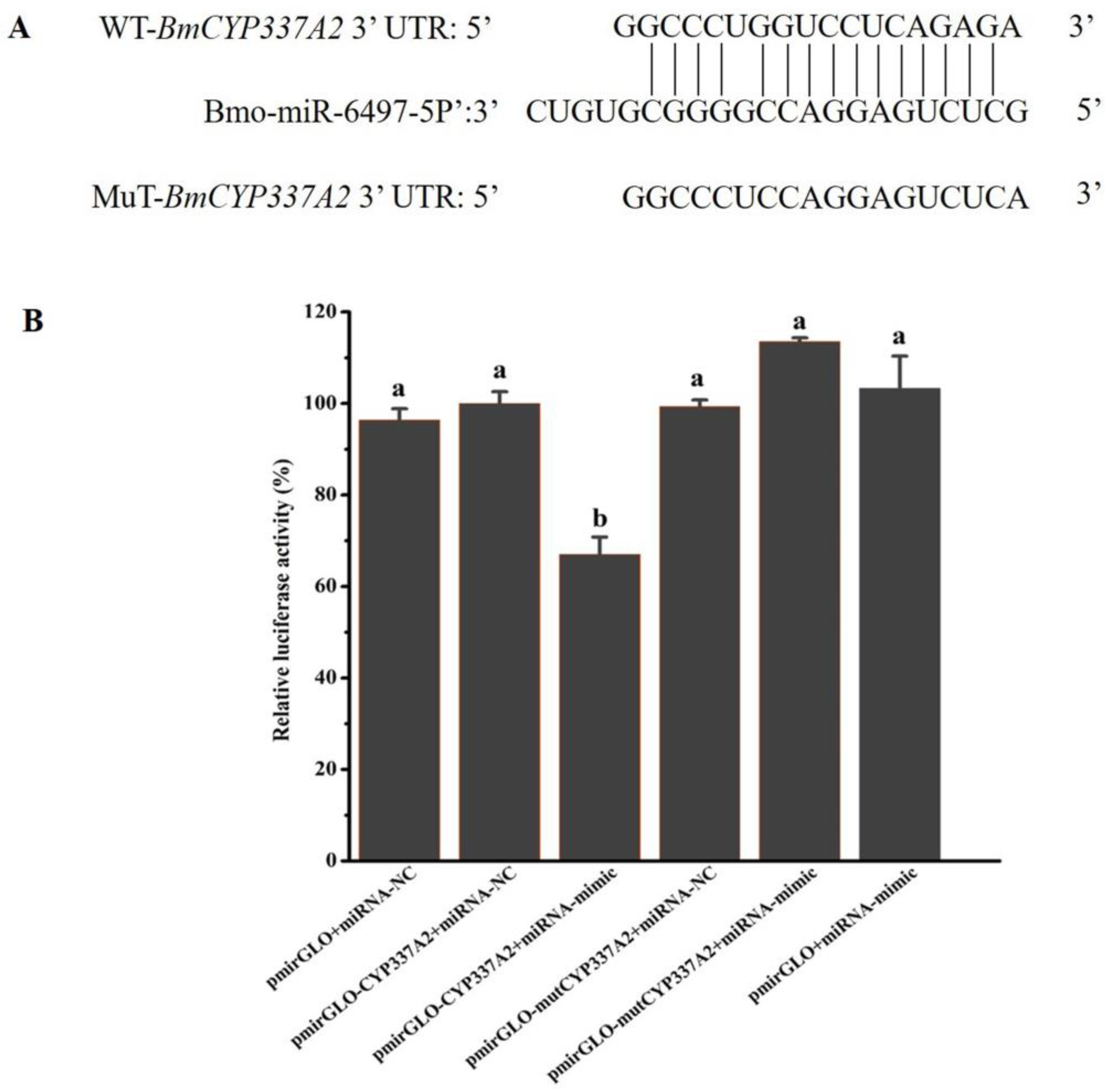
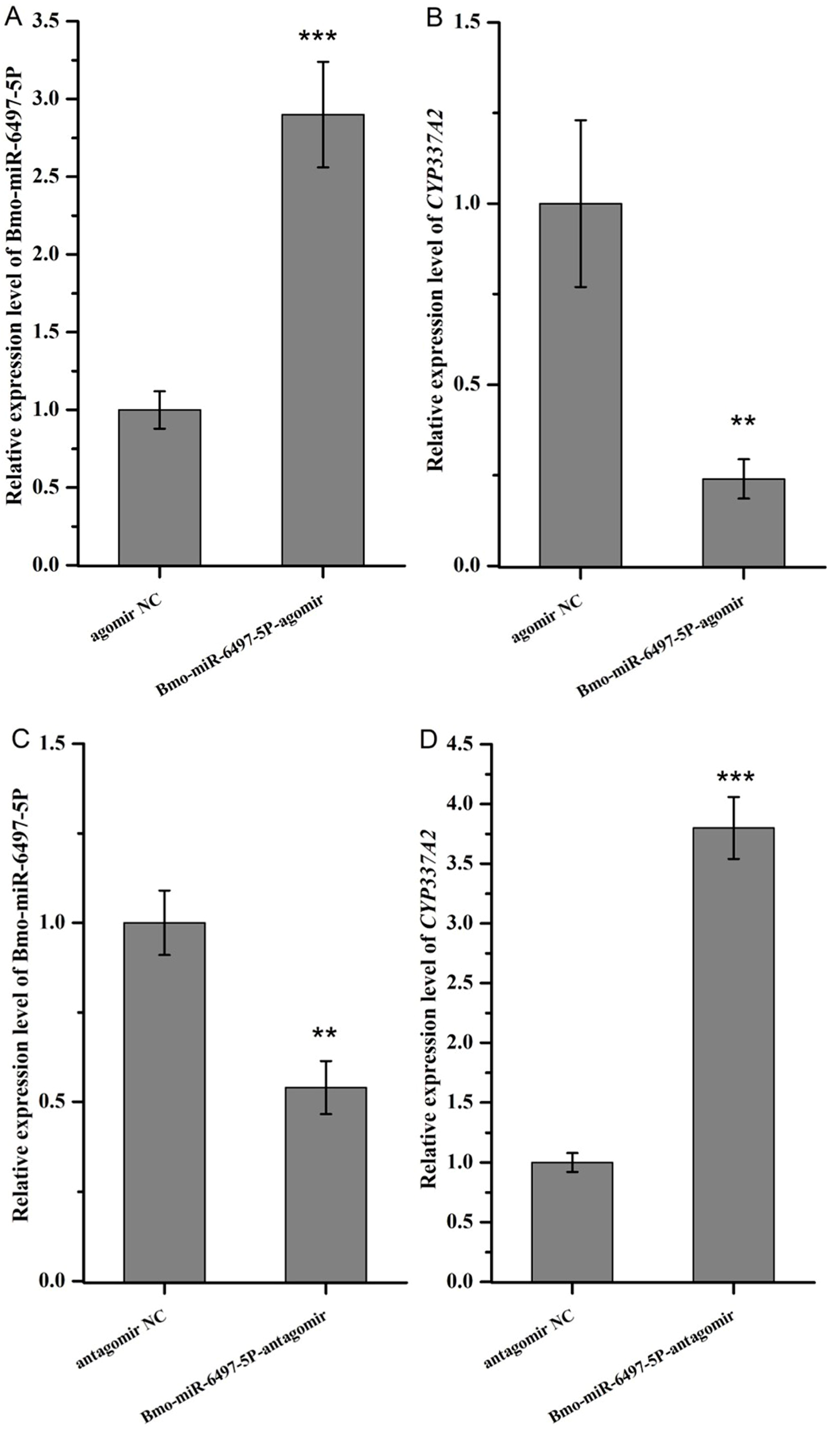
| Chemicals | Slope ± SE | χ2 | p Value | LC50 (95% CI) * (mg/L) | LC30 (95% CI) * (mg/L) | LC10 (95% CI) * (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorfenapyr | 5.38 ± 0.025 | 35.26 | 0.28 | 274.52 (215.42–342.55) | 197.26 (129.16–241.03) | 116.72 (97.35–125.54) |
| Tralopyril | 2.23 ± 0.076 | 8.77 | 0.54 | 8.24 (5.38–13.87) | 4.94 (0.29–10.25) | 1.85 (0.92–2.34) |
| miRNAs | Sequence | Length | Log2FC | p Value | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bmo-miR-275-5p | CGCGCTACTCCGGCGCCAGGACT | 23 | −1.02 | 2.77 × 10−5 | Down |
| Bmo-miR-2792-3p | TAGATTAGATAGCGATTCCATT | 22 | −1.94 | 4.60 × 10−2 | Down |
| Bmo-miR-2999 | CTGCGACGGACTAGACGCGCA | 21 | 2.18 | 1.22 × 10−2 | Up |
| Bmo-miR-3000 | CTGCGCTTAGATGAAGACACTA | 22 | 1.52 | 3.02 × 10−2 | Up |
| Bmo-miR-308-3p | AATCACAGGATAATACTGCGAG | 22 | 1.12 | 1.12 × 10−4 | Up |
| Bmo-miR-6497-5p | GCTCTGAGGACCGGGGCGTGTC | 22 | 3.11 | 1.37 × 10−3 | Up |
| Bmo-miR-6498-3p | AACGTCTGCGATGATACAGTT | 21 | 4.27 | 1.00 × 10−6 | Up |
| Bmo-miR-6498-5p | CGCGTCTGTTGTCGCAGCCGTGC | 23 | 3.49 | 1.86 × 10−3 | Up |
| Bmo-miR-79-5p | CTTTGGCGATTTAGCTCCGTGA | 22 | −1.10 | 3.91 × 10−6 | Down |
| novel-47 | CATGGTCTCATCATTCACA | 19 | −5.90 | 8.93 × 10−5 | Down |
| miRNA | P450 Target Genes | Acc. Number in Gene Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Bmo-miR-6497-5P | CYP337A2 | NM_001279385.1 |
| Bmo-miR-6497-5P | CYP333B1 | AK343202.1 |
| Bmo-miR-6497-5P | CYP6AE3P | AK289290.1 |
| Bmo-miR-6497-5P | CYP49A1 | NM_001279490.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, Y.; Ding, J.-H.; Miao, W.-L.; Wang, Y.-R.; Pei, M.-M.; Sheng, S.; Gui, Z.-Z. microRNA Targeting Cytochrome P450 Is Involved in Chlorfenapyr Tolerance in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Insects 2025, 16, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050515
Shao Y, Ding J-H, Miao W-L, Wang Y-R, Pei M-M, Sheng S, Gui Z-Z. microRNA Targeting Cytochrome P450 Is Involved in Chlorfenapyr Tolerance in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Insects. 2025; 16(5):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050515
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Ying, Jian-Hao Ding, Wang-Long Miao, Yi-Ren Wang, Miao-Miao Pei, Sheng Sheng, and Zhong-Zheng Gui. 2025. "microRNA Targeting Cytochrome P450 Is Involved in Chlorfenapyr Tolerance in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae)" Insects 16, no. 5: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050515
APA StyleShao, Y., Ding, J.-H., Miao, W.-L., Wang, Y.-R., Pei, M.-M., Sheng, S., & Gui, Z.-Z. (2025). microRNA Targeting Cytochrome P450 Is Involved in Chlorfenapyr Tolerance in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Insects, 16(5), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050515






