Development of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Tests for the Identification of Biting Midge Species and Clades (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) of the Obsoletus Group (Subgenus Avaritia), Including Important Viral Vectors in Europe
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Collection and Morphologic Pre-Identification
2.2. Extraction of Genomic DNA
2.3. DNA Amplification and Sequencing
2.4. Data Analysis and PCR Design
2.5. Modular Real-Time PCR
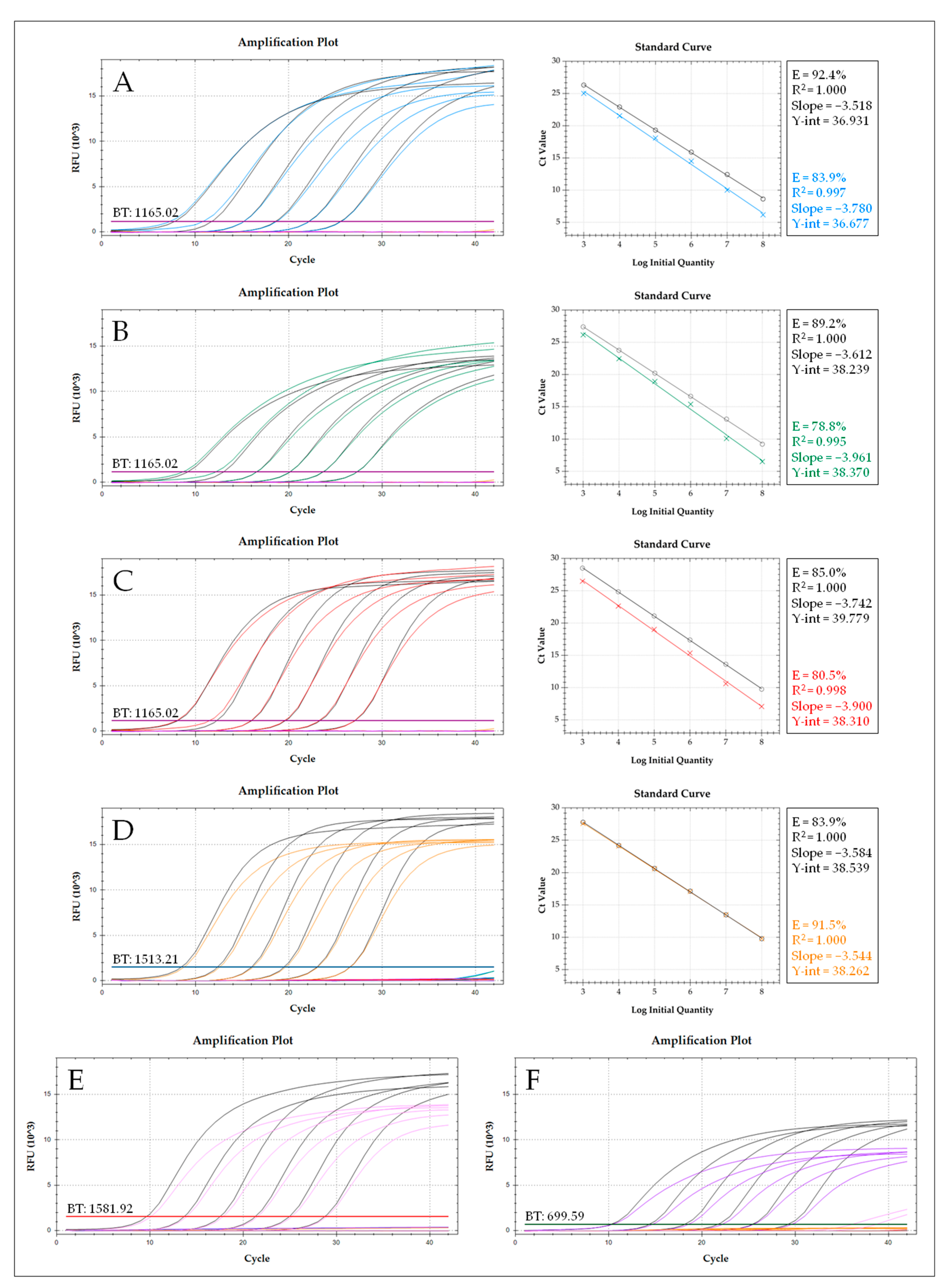
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 28S rDNA | structural ribosomal RNA (large subunit) |
| bp | base pairs |
| BT | baseline threshold |
| BTD | bluetongue disease |
| BTV | bluetongue virus |
| CAD | carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 2 |
| COI | mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I |
| Ct | cycle threshold |
| Cy5 | cyanine5 |
| cytb | mitochondrial cytochrome b |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| dSe | diagnostic sensitivity |
| dSp | diagnostic specificity |
| EHD | epizootic hemorrhagic disease |
| EHDV | epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus |
| FAM | 6-carboxyfluorescein |
| HEX | hexachlorofluorescein |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| ITS-1 | internal transcribed spacer 1 |
| ITS-2 | internal transcribed spacer 2 |
| mt | mitochondrial |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| RFU | relative fluorescence unit |
| s.s. | sensu stricto |
| SBD | Schmallenberg disease |
| SBV | Schmallenberg virus |
| TEX | Texas Red (sulforhodamine 101 acid chloride) |
References
- Vasconcelos, P.F.; Calisher, C.H. Emergence of human arboviral diseases in the Americas, 2000–2016. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catenacci, L.S.; Nunes-Neto, J.; Deem, S.L.; Palmer, J.L.; Travassos-da Rosa, E.S.; Tello, J.S. Diversity patterns of hematophagous insects in Atlantic Forest fragments and human-modified areas of southern Bahia, Brazil. J. Vector Ecol. 2018, 43, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, P.S.; Boorman, J.; Baylis, M. Culicoides biting midges: Their role as arbovirus vectors. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 307–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, S.; Groschup, M.H.; Garros, C.; Felippe-Bauer, M.L.; Purse, B.V. Culicoides biting midges, arboviruses and public health in Europe. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLachlan, N.J. The pathogenesis and immunology of bluetongue virus infection of ruminants. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1994, 17, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclachlan, N.J.; Drew, C.P.; Darpel, K.E.; Worwa, G. The pathology and pathogenesis of bluetongue. J. Comp. Pathol. 2009, 141, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampen, H.; Werner, D. Biting midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) as vectors of viruses. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, P.; Stokstad, M.; Venter, E.H.; Myrmel, M.; Van Vuuren, M. Bluetongue: A historical and epidemiological perspective with the emphasis on South Africa. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zientara, S.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. Control of bluetongue in Europe. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhamis, M.A.; Aguilar-Vega, C.; Fountain-Jones, N.M.; Lin, K.; Perez, A.M.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. Global emergence and evolutionary dynamics of bluetongue virus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Brom, R.; Santman-Berends, I.; van der Heijden, M.G.; Harders, F.; Engelsma, M.; van Gennip, R.G.P.; Maris-Veldhuis, M.A.; Feddema, A.-J.; Peterson, K.; Golender, N.; et al. Bluetongue virus serotype 12 in sheep and cattle in the Netherlands in 2024–a BTV serotype reported in Europe for the first time. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 110365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holwerda, M.; Santman-Berends, I.; Harders, F.; Engelsma, M.; Vloet, R.; Dijkstra, E.; van Gennip, R.G.P.; Mars, M.H.; Roos, L.; van den Brom, R.; et al. Emergence of bluetongue virus serotype 3, the Netherlands, September 2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ProMED-Mail. Bluetongue–Europe (13): Belgium (Antwerp) Serotype 3, Suspected, Request for Information. 9 October 2023: 20231009.8712543. Available online: https://www.promedmail.org/ (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Newbrook, K.; Obishakin, E.; Jones, L.A.; Waters, R.; Ashby, M.; Batten, C.; Sanders, C. Clinical disease in British sheep infected with an emerging strain of bluetongue virus serotype 3. Vet. Rec. 2024, e4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, A.; Kampen, H.; Heuser, E.; Zeiske, S.; Hoffmann, B.; Höper, D.; Holsteg, M.; Sick, F.; Ziegler, S.; Wernike, K.; et al. Bluetongue virus serotype 3 and Schmallenberg virus in Culicoides biting midges, western Germany, 2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 1438–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, C.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, B. Bluetongue virus infection of goats: Re-emerged European serotype 8 vs. two atypical serotypes. Viruses 2022, 14, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhadra, S.; Sreenivasulu, D.; Pattnaik, R.; Panda, B.K.; Kumar, S. Bluetongue virus: Past, present, and future scope. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2023, 17, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijn, P.A. Prospects of next-generation vaccines for bluetongue. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shope, R.E.; Lester, G.M.; Robert, M. Deer mortality–epizootic hemorrhagic disease of deer. N. J. Outdoors 1955, 6, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lorusso, A.; Cappai, S.; Loi, F.; Pinna, L.; Ruiu, A.; Puggioni, G.; Guercio, A.; Purpari, G.; Vicari, D.; Sghaier, S.; et al. Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serotype 8, Italy, 2022. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maan, S.; Maan, N.S.; Ross-smith, N.; Batten, C.A.; Shaw, A.E.; Anthony, S.J.; Samuel, A.R.; Darpel, K.E.; Veronesi, E.; Oura, C.A.; et al. Sequence analysis of bluetongue virus serotype 8 from the Netherlands 2006 and comparison to other European strains. J. Virol. 2008, 377, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulletins Hebdomadaires de Veille Sanitaire Internationale–Sainté Animale (plateforme-esa.fr). Available online: https://www.plateforme-esa.fr/fr/bulletins-hebdomadaires-de-veille-sanitaire-internationale-du-28-11-2023 (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Hoffmann, B.; Scheuch, M.; Höper, D.; Jungblut, R.; Holsteg, M.; Schirrmeier, H.; Eschbaumer, M.; Goller, K.V.; Wernike, K.; Fischer, M.; et al. Novel orthobunyavirus in cattle, Europe, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernike, K.; Conraths, F.; Zanella, G.; Granzow, H.; Gache, K.; Schirrmeier, H.; Valas, S.; Staubach, C.; Marianneau, P.; Kraatz, F.; et al. Schmallenberg virus–two years of experiences. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 116, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernike, K.; Beer, M. Schmallenberg virus: A novel virus of veterinary importance. Adv. Virus Res. 2017, 99, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, S.; Lunt, H.L.; Arav, D.; Venter, G.J.; Mellor, P.S. Oral susceptibility to bluetongue virus of Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) from the United Kingdom. J. Med. Entomol. 2006, 43, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.; McArthur, C.; Selby, R.; Ward, R.; Nolan, D.V.; Luntz, A.J.; Dallas, J.F.; Tripet, F.; Mellor, P.S. Experimental infection studies of UK Culicoides species midges with bluetongue virus serotypes 8 and 9. Vet. Rec. 2008, 163, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, V.; Ippoliti, C.; Goffredo, M.; Catalani, M.; Di Provvido, A.; Santilli, A.; Quaglia, M.; Mancini, G.; Di Nicola, F.; Di Gennaro, A.; et al. Epizootic haemorrhagic disease in Italy: Vector competence of indigenous Culicoides species and spatial multicriteria evaluation of vulnerability. Vet. Ital. 2016, 52, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, L.M.; Paslaru, A.; Torgerson, P.R.; Veronesi, E.; Mathis, A. Vector competence of Culicoides biting midges from Switzerland for African horse sickness virus and epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2022, 164, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiswinkel, R.; van Rijn, P.; Leijs, P.; Goffredo, M. Potential new Culicoides vector of bluetongue virus in northern Europe. Vet. Rec. 2007, 161, 564–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredo, M.; Catalani, M.; Federici, V.; Portanti, O.; Marini, V.; Mancini, G.; Quaglia, M.; Santilli, A.; Teodori, L.; Savini, G. Vector species of Culicoides midges implicated in the 2012–2014 bluetongue epidemics in Italy. Vet. Ital. 2015, 51, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, E.; van der Ven, I.J.K.; Meiswinkel, R.; Hölzel, D.R.; van Rijn, P.A. Culicoides chiopterus as a potential vector of bluetongue virus in Europe. Vet. Rec. 2008, 162, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlhorn, H.; Walldorf, V.; Klimpel, S.; Jahn, B.; Jaeger, F.; Eschweiler, J.; Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M. First occurrence of Culicoides obsoletus-transmitted bluetongue virus epidemic in Central Europe. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, B.; Bauer, B.; Bauer, C.; Bätza, H.J.; Beer, M.; Clausen, P.H.; Geier, M.; Gethmann, J.M.; Kiel, E.; Liebisch, G.; et al. Monitoring of putative vectors of bluetongue virus serotype 8, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foxi, C.; Delrio, G.; Falchi, G.; Marche, M.G.; Satta, G.; Ruiu, L. Role of different Culicoides vectors (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in bluetongue virus transmission and overwintering in Sardinia (Italy). Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.D.; Kristensen, B.; Kirkeby, C.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Belsham, G.J.; Bødker, R.; Bøtner, A. Culicoids as vectors of Schmallenberg virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1204–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Regge, N.; Deblauwe, I.; de Deken, R.; Vantieghem, P.; Madder, M.; Geysen, D.; Smeets, F.; Losson, B.; van den Berg, T.; Cay, A.B. Detection of Schmallenberg virus in different Culicoides spp. by real-time RT-PCR. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2012, 59, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbers, A.R.W.; Meiswinkel, R.; van Weezep, E.; van Sloet Oldruitenborgh-Oosterbaan, M.M.; Kooi, E.A. Schmallenberg virus in Culicoides spp. biting midges, The Netherlands, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredo, M.; Monaco, F.; Capelli, G.; Quaglia, M.; Federici, V.; Catalani, M.; Montarsi, F.; Polci, A.; Pinoni, C.; Calistri, P.; et al. Schmallenberg virus in Italy: A retrospective survey in Culicoides stored during the bluetongue Italian surveillance program. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 111, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larska, M.; Polak, M.P.; Grochowska, M.; Lechowski, L.; Związek, J.S.; Zmudziński, J.F. First report of Schmallenberg virus infection in cattle and midges in Poland. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larska, M.; Lechowski, L.; Grochowska, M.; Żmudziński, J.F. Detection of the Schmallenberg virus in nulliparous Culicoides obsoletus/scoticus complex and C. punctatus—The possibility of transovarial virus transmission in the midge population and of a new vector. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balenghien, T.; Pagès, N.; Goffredo, M.; Carpenter, S.; Augot, D.; Jacquier, E.; Talavera, S.; Monaco, F.; Depaquit, J.; Grillet, C.; et al. The emergence of Schmallenberg virus across Culicoides communities and ecosystems in Europe. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 116, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.D.; Kirkeby, C.; Bødker, R.; Kristensen, B.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Belsham, G.J.; Bøtner, A. Rapid spread of Schmallenberg virus-infected biting midges (Culicoides spp.) across Denmark in 2012. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2014, 61, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbers, A.R.W.; Meiswinkel, R.; van Weezep, E.; Kooi, E.A.; van der Poel, W.H.M. Schmallenberg virus in Culicoides biting midges in the Netherlands in 2012. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Regge, N.; de Deken, R.; Fassotte, C.; Losson, B.; Deblauwe, I.; Madder, M.; Vantieghem, P.; Tomme, M.; Smeets, F.; Cay, A.B. Culicoides monitoring in Belgium in 2011: Analysis of spatiotemporal abundance, species diversity and Schmallenberg virus detection. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2015, 29, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagès, N.; Talavera, S.; Verdún, M.; Pujol, N.; Valle, M.; Bensaid, A.; Pujols, J. Schmallenberg virus detection in Culicoides biting midges in Spain: First laboratory evidence for highly efficient infection of Culicoides of the Obsoletus Complex and Culicoides imicola. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ségard, A.; Gardès, L.; Jacquier, E.; Grillet, C.; Mathieu, B.; Rakotoarivony, I.; Setier-Rio, M.-L.; Chavernac, D.; Cêtre-Sossah, C.; Balenghien, T.; et al. Schmallenberg virus in Culicoides Latreille (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) populations in France during 2011–2012 outbreak. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, e94–e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, M.; Foxi, C.; Satta, G.; Puggioni, G.; Bechere, R.; De Ascentis, M.; D’Alessio, S.G.; Spedicato, M.; Leone, A.; Pisciella, M.; et al. Culicoides species responsible for the transmission of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV) serotype 8 in Italy. Vet. Ital. 2023, 59, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.A.; Kristensen, M. Morphological and molecular identification of species of the Obsoletus Group (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Scandinavia. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredo, M.; Meiswinkel, R.; Federici, V.; Di Nicola, F.; Mancini, G.; Ippoliti, C.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Quaglia, M.; Santilli, A.; Conte, A.; et al. The ‘Culicoides obsoletus group’ in Italy: Relative abundance, geographic range, and role as vector for bluetongue virus. Vet. Ital. 2016, 52, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenkenbecher, J.M.; Mordue, A.J.; Piertney, S.B. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that Culicoides dewulfi should not be considered part of the Culicoides obsoletus complex. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2009, 99, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ander, M.; Troell, K.; Chirico, J. Barcoding of biting midges in the genus Culicoides: A tool for species determination. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2013, 27, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvašová, A.; Kočišová, A.; Halán, M.; Delécolle, J.-C.; Mathieu, B. Morphological and molecular analysis of the genus Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Slovakia with five new records. Zootaxa 2014, 3872, 541–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augot, D.; Mathieu, B.; Hadj-Henni, L.; Barriel, V.; Zapata, M.S.; Smolis, S.; Augot, D.; Mathieu, B.; Hadj-Henni, L.; Barriel, V.; et al. Molecular phylogeny of 42 species of Culicoides (Diptera, Ceratopogonidae) from three continents. Parasite 2017, 24, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, B.; Garros, C.; Balenghien, T.; Candolfi, E.; Delécolle, J.-C.; Cêtre-Sossah, C. A phylogenetic analysis of the biting midges belonging to Culicoides Latreille (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) subgenus Avaritia using molecular data. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajd-Henni, L.; Sauvage, F.; Ninio, C.; Depaquit, J.; Augot, D. Wing geometry as a tool for discrimination of Obsoletus Group (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae: Culicoides) in France. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, B.; Perrin, A.; Baldet, T.; Delécolle, J.-C.; Albina, E.; Cêtre-Sossah, C. Molecular identification of western European species of Obsoletus Complex (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) by an internal transcribed spacer-1 rDNA multiplex polymerase chain reaction assay. J. Med. Entomol. 2007, 44, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignotte, A.; Garros, C.; Gardès, L.; Balenghien, T.; Duhayon, M.; Rakotoarivony, I.; Tabourin, L.; Poujol, L.; Mathieu, B.; Ibañez-Justicia, A.; et al. The tree that hides the forest: Cryptic diversity and phylogenetic relationships in the Palaearctic vector Obsoletus/Scoticus Complex (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) at the European level. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dähn, O.; Werner, D.; Mathieu, B.; Kampen, H. Large-scale cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene data analysis for the development of a multiplex polymerase chain reaction test capable of identifying biting midge vector species and haplotypes (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) of the Culicoides subgenus Avaritia Fox, 1955. Genes 2024, 15, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiehl, E.; Walldorf, V.; Klimpel, S.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Mehlhorn, H. The European vectors of bluetongue virus: Are there species complexes, single species or races in Culicoides obsoletus and C. pulicaris detectable by sequencing ITS-1, ITS-2 and 18S-rDNA? Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiswinkel, R.; De Bree, F.; Bossers-de Vries, R.; Elbers, A.R. An unrecognized species of the Culicoides obsoletus complex feeding on livestock in the Netherlands. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 207, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenk, C.E.; Kaufmann, C.; Schaffner, F.; Mathis, A. Molecular characterization of Swiss Ceratopogonidae (Diptera) and evaluation of real-time PCR assays for the identification of Culicoides biting midges. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 184, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbers, A.R.W.; Meiswinkel, R. Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) host preferences and biting rates in the Netherlands: Comparing cattle, sheep and the black-light suction trap. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, J.Y.; Brostaux, Y.; Haubruge, E.; Francis, F. Larval development sites of the main Culicoides species (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in northern Europe and distribution of coprophilic species larvae in Belgian pastures. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninio, C.; Augot, D.; Delecolle, J.C.; Dufour, B.; Depaquit, J. Contribution to the knowledge of Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) host preferences in France. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garros, C.; Gardès, L.; Allène, X.; Rakotoarivony, I.; Viennet, E.; Rossi, S.; Balenghien, T. Adaptation of a species-specific multiplex PCR assay for the identification of blood meal source in Culicoides (Ceratopogonidae: Diptera): Applications on Palaearctic biting midge species, vectors of Orbiviruses. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettle, D.S.; Lawson, J.W.H. The early Stages of British biting midges Culicoides Latreille (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) and allied genera. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1952, 43, 421–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gethmann, J.; Probst, C.; Conraths, F.J. Economic impact of a bluetongue serotype 8 epidemic in Germany. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrup, L.E.; Bellis, G.A.; Balenghien, T.; Garros, C. Culicoides Latreille (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) taxonomy: Current challenges and future directions. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 30, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, N.; Sarto i Monteys, V. Differentiation of Culicoides obsoletus and Culicoides scoticus (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) based on mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deblauwe, I.; de Witte, J.C.; de Deken, G.; de Deken, R.; Madder, M.; van Erk, S.; Hoza, F.A.; Lathouwers, D.; Geysen, D. A new tool for the molecular identification of Culicoides species of the Obsoletus group: The glass slide microarray approach. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2012, 26, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, C.; Steinmann, I.C.; Hegglin, D.; Schaffner, F.; Mathis, A. Spatio-temporal occurrence of Culicoides biting midges in the climatic regions of Switzerland, along with large scale species identification by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Parasit. Vectors 2012, 5, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, B.; Delecolle, J.-C.; Garros, C.; Balenghien, T.; Setier-Rio, M.-L.; Candolfi, E.; Cêtre-Sossah, C. Simultaneous quantification of the relative abundance of species complex members: Application to Culicoides obsoletus and Culicoides scoticus (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae), potential vectors of bluetongue virus. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 182, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dähn, O.; Werner, D.; Mathieu, B.; Kampen, H. Development of conventional multiplex PCR assays for the identification of 21 west Palaearctic biting midge taxa (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) belonging to the Culicoides subgenus Culicoides, including recently discovered species and genetic variants. Diversity 2023, 15, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorsprach, B.; Meiser, C.K.; Werner, D.; Balczun, C.; Schaub, G.A. Monitoring of Ceratopogonidae in southwest Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenkenbecher, J.M.; Mordue, A.J.; Switek, K.; Piertney, S.B. Discrimination of Culicoides midge larvae using multiplex polymerase chain reaction assays based on DNA sequence variation at the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase I gene. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, K.; Werner, D.; Hoffmann, B.; Kampen, H. PCR identification of culicoid biting midges (Diptera, Ceratopogonidae) of the Obsoletus Complex including putative vectors of bluetongue and Schmallenberg viruses. Parasit. Vectors 2012, 5, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, F.; Benedetto, L.; Di Marcello, V.; Lelli, R.; Goffredo, M. Development and preliminary evaluation of a real-time polymerase chain reaction for the identification of Culicoides obsoletus sensu stricto, C. scoticus and C. montanus in the Obsoletus Complex in Italy. Vet. Ital. 2010, 46, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Delécolle, J.-C. Nouvelle Contribution à L’étude Systématique et Iconographique des Espèces du Genre Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) du Nord-Est de la France. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Strasbourg, Strasbourg, France, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.A.; Pelham-Clinton, E.C. A taxonomic review of the British species of Culicoides Latreille (Diptera, Ceratopogonidae). Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. B Biol. Sci. 1960, 67, 181–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glukhova, V.M. Krovososuščie Mokrecy Rodov Culicoides i Forcipomyia (Ceratopogonidae); Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1989; ISBN 9785020257603. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, B.; Cêtre-Sossah, C.; Garros, C.; Chavernac, D.; Balenghien, T.; Carpenter, S.; Setier-Rio, M.L.; Vignes-Lebbe, R.; Ung, V.; Candolfi, E.; et al. Development and validation of IIKC: An interactive identification key for Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) females from the western Palaearctic region. Parasit. Vectors 2012, 5, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, C.; Sharav, T.; Tseren-Ochir, E.-O.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, B. Putative novel serotypes ‘33’ and ‘35’ in clinically healthy small ruminants in Mongolia expand the group of atypical BTV. Viruses 2021, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, M.; Córdoba, J.J.; Andrade, M.J. Design of primers and probes for quantitative real-time PCR methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1275, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T. Parameters for successful PCR primer design. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2065, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkent, A.; Dominiak, P. Catalog of the biting midges of the world (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). Zootaxa 2020, 4787, 1–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garros, C.; Balenghien, T.; Carpenter, S.; Delécolle, J.-C.; Meiswinkel, R.; Pédarrieu, A.; Rakotoarivony, I.; Gardès, L.; Golding, N.; Barber, J.; et al. Towards the PCR-based identification of Palaearctic Culicoides biting midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae): Results from an international ring trial targeting four species of the subgenus Avaritia. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, D.V.; Carpenter, S.; Barber, J.; Mellor, P.S.; Dallas, J.F.; Mordue Luntz, A.J.; Piertney, S.B. Rapid diagnostic PCR assays for members of the Culicoides obsoletus and Culicoides pulicaris species complexes, implicated vectors of bluetongue virus in Europe. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 124, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomulski, L.M.; Meiswinkel, R.; Delécolle, J.C.; Goffredo, M.; Gasperi, G. Phylogenetic relationships of the subgenus Avaritia Fox, 1955 including Culicoides obsoletus (Diptera, Ceratopogonidae) in Italy based on internal transcribed spacer 2 ribosomal DNA sequences. Syst. Entomol. 2005, 30, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New England Biolabs–Guidelines for PCR Optimization with Taq DNA Polymerase. Available online: https://www.neb.com/en/tools-and-resources/usage-guidelines/guidelines-for-pcr-optimization-with-taq-dna-polymerase (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Garibyan, L.; Avashia, N. Polymerase chain reaction. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Life Technologies Real-Time PCR Handbook. Available online: https://www.gene-quantification.de/real-time-pcr-handbook-life-technologies-update-flr.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Longo, M.C.; Berninger, M.S.; Hartley, J.L. Use of uracil DNA glycosylase to control carry-over contamination in polymerase chain reactions. Gene 1990, 93, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Vega, C.; Rivera, B.; Lucientes, J.; Gutiérrez-Boada, I.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. A study of the composition of the Obsoletus Complex and genetic diversity of Culicoides obsoletus populations in Spain. Parasit. Vectors. 2021, 14, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Taxon | Oligo Name | 5′-Modification | Sequence (5′ > 3′) | 3′-Modification | Amplicon Size (bp) | Sixplex | Fourplex | Triplex | Singleplex |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. obsoletus clade O1 | CobsO1_F | none | AGAAAAYGGRGCAGGAACC | none | 89 | x | x | x | x |
| CobsO1_R | none | AAATAGCCAAATCTACAGAAG | none | x | x | x | x | ||
| CobsO1_P-Atto | Atto647N | CCCTCCCTTTCRTCTAATATCTCT | BHQ-2 | x | - | - | x | ||
| CobsO1_P-HEX | HEX | CCCTCCCTTTCRTCTAATATCTCT | BHQ-1 | - | x | x | x | ||
| C. obsoletus clade O2 | CobsO2_F | none | AGCCGTTAATTTTATTACAACC | none | 127 | x | x | x | x |
| CobsO2_R | none | TAATACAGGTAAAGATAGYAGG | none | x | x | x | x | ||
| CobsO2_P-Atto | Atto647N | ACGATCATATGGAATAAMTTTCGATC | BHQ-2 | x | - | - | x | ||
| CobsO2_P-TEX | TEX | ACGATCATATGGAATAAMTTTCGATC | BHQ-2 | - | x | x | x | ||
| C. obsoletus clade O3 | CobsO3_F | none | GCTCTATTTTAGGTGCTGTT | none | 107 | x | x | x | x |
| CobsO3_R | none | AGTAATTAATACAGATCATACG | none | x | x | x | x | ||
| CobsO3_P-Atto | Atto647N | TATTATCAATATRCGATCATACGGGA | BHQ-2 | x | x | x | x | ||
| C. scoticus clade 1 | Csco_F | none | CACTTTATTATTAATTAGAAGTTTAGTT | none | 116 | x | x | - | x |
| Csco_R | none | AAATTGCTAAGTCAACTGAGG | none | x | x | - | x | ||
| Csco_P-FAM | FAM | ACCCTCCACTTTCAGCAAATGTCT | BHQ-1 | x | x | - | x | ||
| C. chiopterus | Cchi_F | none | CCCTGATATAGCTTTTCCA | none | 86 | x | - | - | x |
| Cchi_R | none | CTAAGCTACTTAYTAATAGTAG | none | x | - | - | x | ||
| Cchi_P-TEX | TEX | TGAATACTRCCRCCCTCTATCACC | BHQ-2 | x | - | - | x | ||
| C. dewulfi | Cdew_F | none | ACAATCATTAATATACGACCAA | none | 118 | x | - | - | x |
| Cdew_R | none | TARCTCCTGCTAAAACTGGA | none | x | - | - | x | ||
| Cdew_P-HEX | HEX | CACAGCTATTCTTTTACTTCTGTCAC | BHQ-1 | x | - | - | x |
| Taxon | Samples Tested (n) 1 | Sixplex PCR (n) 2 | Triplex PCR (n) 2 | dSe | dSp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. obsoletus clade O1 | 39 | 70 | 39 | 39/39 (100%) | 38/39 (97.4%) |
| C. obsoletus clade O2 | 28 | 29 3 | 28/28 (100%) | 28/28 (100%) | |
| C. obsoletus clade O3 | 3 | 3 | 3/3 (100%) | 3/3 (100%) | |
| C. scoticus clade 1 | 10 | 10 | - | 10/10 (100%) | 10/10 (100%) |
| C. chiopterus | 4 | 4 | - | 4/4 (100%) | 4/4 (100%) |
| C. dewulfi | 7 | 7 | - | 7/7 (100%) | 7/7 (100%) |
| Total | 91 | 91 | 71 | 91/91 (100%) | 91/92 (98.9%) |
| Subgenus | Taxon | GenBank Accession No. | Real-Time PCR Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avaritia Fox, 1955 | C. imicola2 | OQ789072 | negative (Ct 36.79) 4 |
| C. montanus2 | OQ789074 | positive (Ct 19.54) 5 | |
| C. sanguisuga2 | MK760238 | negative | |
| C. scoticus clade 2 2 | OQ789084 | positive (Ct 19.97) 6 | |
| C. sinanoensis2 | MK760244 | negative | |
| Beltranmyia Vargas, 1953 | C. salinarius2 | OQ789083 | negative |
| Culicoides Latreille, 1809 | C. boyi3 | - | negative |
| C. bysta3 | - | negative | |
| C. cryptipulicaris3 | - | negative | |
| C. delta2 | OQ789035 | negative | |
| C. fagineus haplotype F1 3 | - | negative | |
| C. fagineus haplotype F2 2 | OQ789036 | negative | |
| C. flavipulicaris3 | - | negative | |
| C. grisescens haplotype G1 2 | OQ789037 | negative (Ct 38.25) 7 | |
| C. grisescens haplotype G2 2 | OQ789038 | negative (Ct 36.27) 7 | |
| C. kalix3 | - | negative | |
| C. lupicaris haplotype L1 2 | OQ789039 | negative | |
| C. lupicaris haplotype L2 2 | OQ789041 | negative | |
| C. newsteadi s.s. 3 | - | negative (Ct 32.40) 6 | |
| C. newsteadi haplotype N1 2 | OQ789045 | negative (Ct 36.09) 4 | |
| C. newsteadi haplotype N2 3 | - | positive (Ct 27.12) 6 | |
| C. newsteadi haplotype N3 2 | OQ789048 | negative | |
| C. pulicaris 2 | OQ789058 | negative | |
| C. punctatus2 | OQ789064 | negative | |
| C. selandicus2 | OQ789052 | negative | |
| C. subfagineus3 | - | negative | |
| Monoculicoides Khalaf, 1954 | C. riethi2 | OQ789081 | negative |
| Sensiculicoides Shevchenko, 1977 | C. alazanicus2 | OQ789067 | negative |
| C. festivipennis2 | OQ789070 | negative (Ct 34.85) 7 | |
| C. griseidorsum2 | OQ789071 | negative | |
| C. kibunensis2 | OQ789073 | negative | |
| C. pictipennis2 | OQ789079 | negative (Ct 34.72) 7 | |
| C. poperinghensis2 | OQ789080 | negative | |
| Silvaticulicoides Glukhova, 1977 | C. achrayi2 | OQ789066 | negative |
| Wirthomyia Vargas, 1973 1 | C. riouxi2 | OQ789082 | negative |
| Unplaced | C. pallidicornis2 | OQ789078 | negative (Ct 34.63) 4 |
| dSp (other Culicoides taxa): | n = 36 | 33/36 (91.7%) |
| Taxon/Genus | GenBank Accession No. | Real-Time PCR Result |
|---|---|---|
| Alluaudomyia spec. | PP110213 | negative |
| Camptocladius stercorarius | PP110214 | negative |
| Chironomus lugubris | PP110215 | negative |
| Clogmia albipunctata | PP110216 | negative (Ct 36.40) 1 |
| Desmometopa sordida | PP110227 | negative |
| Forcipomyia spec. | PP110217 | negative (Ct 35.83) 1 |
| Nemotelus notatus | PP110218 | negative |
| Nilotanypus dubius | PP110219 | negative |
| Physiphora alceae | PP110220 | negative |
| Psychoda cinerea | PP110221 | negative |
| Sepsis violacea | PP110222 | negative |
| Smittia spec. | PP110223 | negative |
| Spelobia luteilabris | PP110224 | negative |
| Sphaerocera curvipes | PP110225 | negative |
| Tephrochlamys rufiventris | PP110226 | negative (Ct 36.89) 2 |
| dSp (other Diptera taxa): | n = 15 | 15/15 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dähn, O.; Hoffmann, B.; Werner, D.; Mathieu, B.; Kampen, H. Development of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Tests for the Identification of Biting Midge Species and Clades (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) of the Obsoletus Group (Subgenus Avaritia), Including Important Viral Vectors in Europe. Insects 2025, 16, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050500
Dähn O, Hoffmann B, Werner D, Mathieu B, Kampen H. Development of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Tests for the Identification of Biting Midge Species and Clades (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) of the Obsoletus Group (Subgenus Avaritia), Including Important Viral Vectors in Europe. Insects. 2025; 16(5):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050500
Chicago/Turabian StyleDähn, Oliver, Bernd Hoffmann, Doreen Werner, Bruno Mathieu, and Helge Kampen. 2025. "Development of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Tests for the Identification of Biting Midge Species and Clades (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) of the Obsoletus Group (Subgenus Avaritia), Including Important Viral Vectors in Europe" Insects 16, no. 5: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050500
APA StyleDähn, O., Hoffmann, B., Werner, D., Mathieu, B., & Kampen, H. (2025). Development of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Tests for the Identification of Biting Midge Species and Clades (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) of the Obsoletus Group (Subgenus Avaritia), Including Important Viral Vectors in Europe. Insects, 16(5), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050500







