The Role of Chemosensory Proteins in Insecticide Resistance: A Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
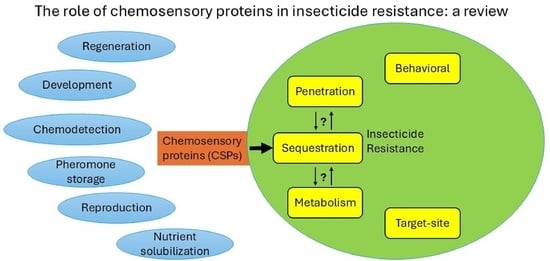
2. CSPs Have Been Implicated to Several Different Functions
3. Evidence for an Insecticide Resistance Function of CSPs
3.1. Gene Expression
3.1.1. Certain CSPs Are Upregulated Following Insecticide Treatment
| CSP Name | Organism | Insecticide (s) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| BtabCSP1 | Bemisia tabaci | Thiamethoxam | [44,45] |
| SAP2, CSP6, SAP3, CSP4 | Anopheles gambiae | Deltamethrin | [56] |
| DcitCSP8 | Diaphorina citri | Thiamethoxam | [58] |
| TcCSP10 | Tribolium castaneum | Dichlorvos, Carbofuran | [54] |
| RpCSP1, RpCSP2, RpCSP4, RpCSP5, RpCSP6, RpCSP7, RpCSP8, RpCSP10 | Rhopalosiphum padi | Imidacloprid, β-cypermethrin | [48] |
| RpCSP1, RpCSP5, RpCSP7 RpCSP4, RpCSP10 | Rhopalosiphum padi | Thiamethoxam | [49] |
| RpCSP6, RpCSP7, RpCSP8 | Rhopalosiphum padi | Deltamethrin | [50] |
| CsCSP1, CsCSP2, CsCSP9, CsCSP12 | Conopomorpha sinensis | λ-cyhalothrin | [52] |
| PxCSP1 | Plutella xylostella | Indoxacarb | [53] |
| PxCSP8 | Plutella xylostella | Permethrin | [47] |
| BmorCSP1, BmorCSP2, BmorCSP4, BmorCSP7, BmorCSP10, BmorCSP9, BmorCSP13, BmorCSP11, BmorCSP12, BmorCSP15, BmorCSP19, BmorCSP14, BmorCSP17, BmorCSP20 | Bombyx mori | Avermectins | [46] |
| AgosCSP5, AgosCSP4, AgosCSP6 | Aphis gossypii | Omethoate | [57] |
| SlituCSP1, SlituCSP3, SlituCSP4, SlituCSP5, SlituCSP11, SlituCSP12, SlituCSP13, SlituCSP18, SlituCSP19, SlituCSP20 | Spodoptera litura | Chlorpyrifos | [55] |
| SlituCSP2, SlituCSP3, SlituCSP4, SlituCSP5, SlituCSP6, SlituCSP11, SlituCSP12, SlituCSP13, SlituCSP20 | Spodoptera litura | Emamectin benzoate | [55] |
| SlituCSP1, SlituCSP2, SlituCSP3, SlituCSP4, SlituCSP5, SlituCSP6, SlituCSP7, SlituCSP8, SlituCSP9, SlituCSP10, SlituCSP11, SlituCSP12, SlituCSP13, SlituCSP19, SlituCSP20 | Spodoptera litura | Fipronil | [55] |
| SfruCSP1, SfruCSP2 | Spodoptera frugiperda | Spinetoram, Cypermethrin, Chlorantraniliprole, Chlorfenapyr, Chlorpyrifos, Indoxacarb | [34] |
| SfruCSP22 | Spodoptera frugiperda | Cypermethrin | [34] |
| unigene 3898 | Ostrinia furnacalis | Flubendiamide | [51] |
3.1.2. Some CSPs Are Constitutively Overexpressed in Resistant Populations
3.1.3. CSP Silencing May Lead to Increased Insecticide Toxicity
3.2. Functional Assays: In Vitro Insecticide Binding and Molecular Docking Simulations
3.3. In Vivo Evidence in Transgenic Insects
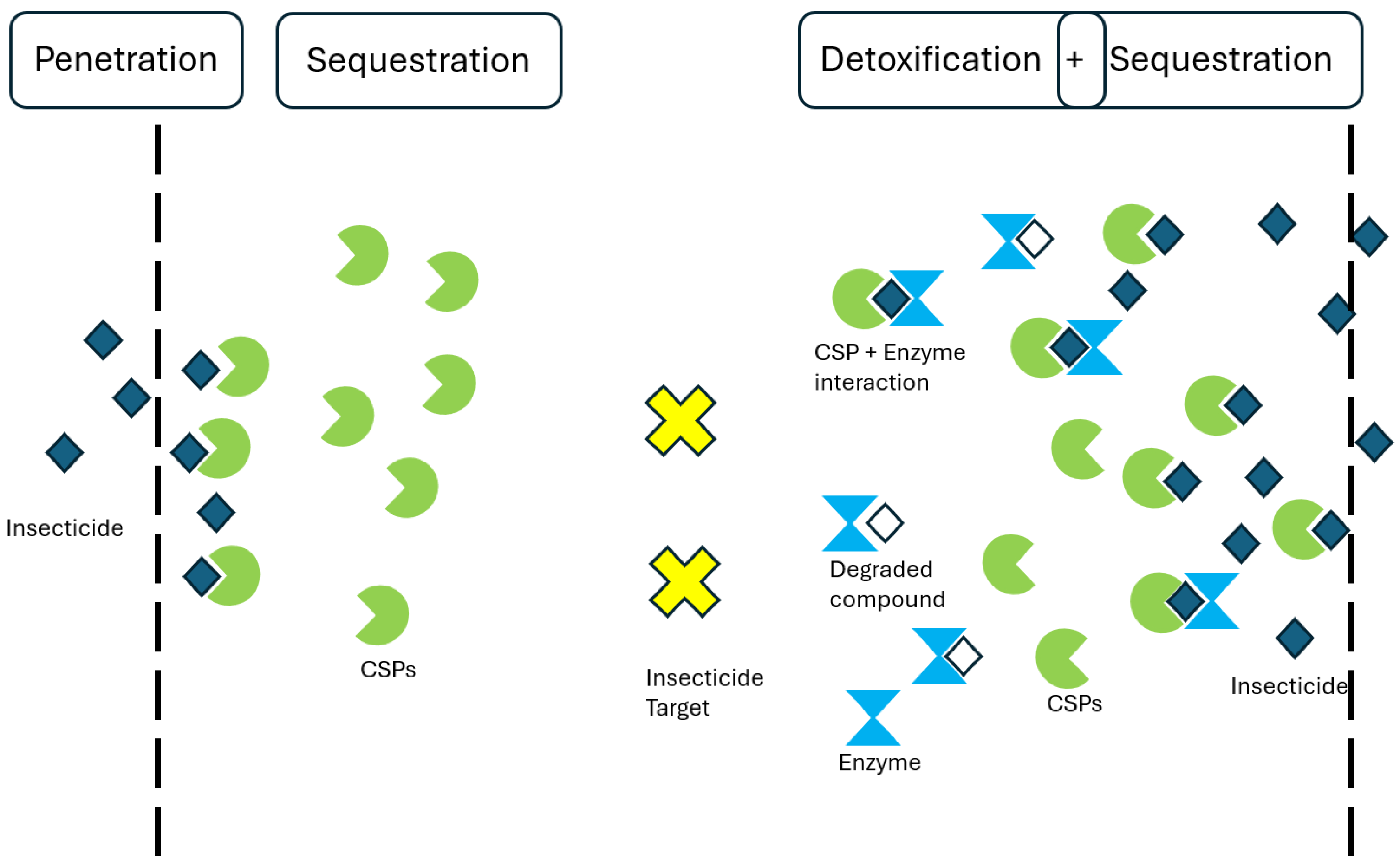
4. A Sequestration Resistance Mechanism and Possible Interactions
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angeli, S.; Ceron, F.; Scaloni, A.; Monti, M.; Monteforti, G.; Minnocci, A.; Petacchi, R.; Pelosi, P. Purification, structural characterization, cloning and immunocytochemical localization of chemoreception proteins from Schistocerca gregaria. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 262, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, K.W.; Willis, L.G.; Theilmann, D.A.; Isman, M.B.; Feng, Q.; Plettner, E. Analysis of the insect OS-D-like gene family. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 889–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, F.G.; Rozas, J. Comparative genomics of the odorant-binding and chemosensory protein gene families across Arthropoda: Origin and evolutionary history of the chemosensory system. Genome Biol. Evol. 2011, 3, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Felicioli, A.; Dani, F.R. Soluble proteins of chemical communication: An overview across arthropods. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Dani, F.R. Beyond chemoreception: Diverse tasks of soluble olfactory proteins in insects. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2018, 93, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, A.; Kawasaki, K.; Kubo, T.; Natori, S. Purification and localization of p10, a novel protein that increases in nymphal regenerating legs of Periplaneta americana American cockroach. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1992, 36, 391–398. [Google Scholar]
- Mckenna, M.P.; Hekmat-Scafe, D.S.; Gaines, P.; Carlson, J.R. Putative Drosophila pheromone-binding proteins expressed in a subregion of the olfactory system. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 16340–16347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanacci, V.; Lartigue, A.; Hallberg, B.M.; Jones, T.A.; Giudici-Orticoni, M.T.; Tegoni, M.; Cambillau, C. Moth chemosensory protein exhibits drastic conformational changes and cooperativity on ligand binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5069–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegoni, M.; Campanacci, V.; Cambillau, C. Structural aspects of sexual attraction and chemical communication in insects. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmuni, J.; Havukainen, H. Insights into the evolution of the CSP gene family through the integration of evolutionary analysis and comparative protein modeling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, J.; Gao, S.; Xiao, N.; Tang, J.; Dong, X.; Xie, W. The Crystal Structure of the Spodoptera litura Chemosensory Protein CSP8. Insects 2021, 12, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lartigue, A.; Campanacci, V.; Roussel, A.; Larsson, A.M.; Jones, T.A.; Tegoni, M.; Cambillau, C. X-ray structure and ligand binding study of a moth chemosensory protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32094–32098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaselli, S.; Crescenzi, O.; Sanfelice, D.; Ab, E.; Wechselberger, R.; Angeli, S.; Scaloni, A.; Boelens, R.; Tancredi, T.; Pelosi, P.; et al. Solution structure of a chemosensory protein from the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 10606–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, S.; Chmelik, J.; Zidek, L.; Padrta, P.; Novak, P.; Zdrahal, Z.; Picimbon, J.F.; Lofstedt, C.; Sklenar, V. Structure of Bombyx mori chemosensory protein 1 in solution. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2007, 66, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Iovinella, I.; Dani, F.R.; Liu, Y.L.; Huang, L.Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.Z.; Pelosi, P.; Wang, G. Conserved chemosensory proteins in the proboscis and eyes of Lepidoptera. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 11, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xuan, N.; Rajashekar, B.; Arnaud, P.; Offmann, B.; Picimbon, J.-F. Comprehensive History of CSP Genes: Evolution, Phylogenetic Distribution and Functions. Genes 2020, 11, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.C.; Sánchez-Gracia, A.; Campos, J.L.; Rozas, J. Family size evolution in Drosophila chemosensory gene families: A comparative analysis with a critical appraisal of methods. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 1669–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, F.R.; Iovinella, I.; Felicioli, A.; Niccolini, A.; Calvello, M.A.; Carucci, M.G.; Qiao, H.; Pieraccini, G.; Turillazzi, S.; Moneti, G.; et al. Mapping the expression of soluble olfactory proteins in the honeybee. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 1822–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Xu, X.; Xiao, T.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Pan, B.; He, Z.; et al. Chemosensory proteins protect Nilaparvata lugens from Imidacloprid by sequestering the insecticide and facilitating metabolic detoxification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 3951–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, A.; Liu, N.; Xu, W. Chemosensory Proteins in the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera. Insects 2022, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.H.; Ban, L.P.; Iovinella, I.; Zhao, L.J.; Gao, Q.; Felicioli, A.; Sagona, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Pelosi, P.; Zhang, L.; et al. Diversity, abundance and sex-specific expression of chemosensory proteins in the reproductive organs of the locust Locusta migratoria manilensis. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitabayashi, A.N.; Arai, T.; Kubo, T.; Natori, S. Molecular cloning of cDNA for p10, a novel protein that increases in the regenerating legs of Periplaneta americana American cockroach. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 28, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, P.; Zhou, J.J.; Ban, L.P.; Calvello, M. Soluble proteins in insect chemical communication. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 1658–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iovinella, I.; Bozza, F.; Caputo, B.; della Torre, A.; Pelosi, P. Ligand-Binding Study of Anopheles gambiae Chemosensory Proteins. Chem. Senses 2013, 38, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.F.; Liu, H.; Zhang, A.; Lu, Z.X.; Leal, W.S.; Abdelnabby, H.; Wang, M.Q. Three chemosensory proteins from the rice leaf folder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis involved in host volatile and sex pheromone reception. Insect Mol. Biol. 2018, 27, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.L.; Pan, Y.F.; Ma, Y.F.; Wang, J.; He, M.; He, P. Binding affinity characterization of an antennae-enriched chemosensory protein from the white-backed planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Horvath), with host plant volatiles. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 152, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.L.; Lin, J.H.; Lin, J.T.; Wu, Z.Z. Odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory proteins potentially involved in host plant recognition in the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.X.; Wang, S.J.; Li, D.X.; Chen, S.T.; Simon, J.C.; Qu, M.J.; Chen, M.H. Involvement of chemosensory proteins in host plant searching in the bird cherry-oat aphid. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 1338–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, N.N.; Yao, Y.J.; Liang, Y.L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, N.Y. Functional characterization of four antenna-biased chemosensory proteins in Dioryctria abietella reveals a broadly tuned olfactory DabiCSP1 and its key residues in ligand-binding. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 197, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Q.; Zhu, R.; Yao, W.C.; Yu, H.P.; Huang, J.R.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X.Y.; Yuan, D.H.; Sun, Y.Y.; Emam, S.S.; et al. Chemosensory Protein 2 of Male Athetis lepigone Is Involved in the Perception of Sex Pheromones and Maize Volatiles. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 6277–6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Liu, X.; Francis, F.; Fan, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. SmCSP4 from aphid saliva stimulates salicylic acid-mediated defence responses in wheat by interacting with transcription factor TaWKRY76. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 2389–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forêt, S.; Wanner, K.W.; Maleszka, R. Chemosensory proteins in the honey bee: Insights from the annotated genome, comparative analyses and expressional profiling. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, Y.T.; Wu, Q.J.; Wang, S.L.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Y.J. Genome-wide analysis of odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory proteins in the sweet potato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. Insect Sci. 2019, 26, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, R.; Gao, J.; Xiao, X.; Yin, X.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, P.; Gu, S. Two cuticle-enriched chemosensory proteins confer multi-insecticide resistance in Spodoptera frugiperda. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 130941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquin-Joly, E.; Vogt, R.G.; François, M.C.; Nagnan-Le Meillour, P. Functional and expression pattern analysis of chemosensory proteins expressed in antennae and pheromonal gland of Mamestra brassicae. Chem. Senses 2001, 26, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisana, P.; Muñoz, C.; Mutis, A.; Velasco, L.; Palma-Millanao, R.; Quiroz, A.; Venthur, H. Knockdown of a chemosensory protein disrupts soil-guided behavior of a subterranean larval pest. J. Insect Physiol. 2025, 162, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Merchant, A.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Kong, L.; Zhou, X.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Y. A chemosensory protein BtabCSP11 mediates reproduction in Bemisia tabaci. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Cui, S.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Gao, X.; Tian, Z.; Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Zhou, Z. OcomCSP12, a chemosensory protein expressed specifically by ovary, mediates reproduction in Ophraella communa (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.Y.; Li, G.C.; Wang, Z.Q.; Guo, Y.R.; Liu, N.Y. Combined transcriptomic, proteomic and genomic analysis identifies reproductive-related proteins and potential modulators of female behaviors in Spodoptera litura. Genomics 2021, 113, 1876–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.H.; He, Y.; Ma, Y.; Guo, J.M.; Wei, Z.Q.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Dong, S.L. Identification and expression specificity of chemosensory genes in the male reproductive system of Spodoptera exigua. J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2023, 26, 102097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleszka, J.; Forêt, S.; Saint, R.; Maleszka, R. RNAi-induced phenotypes suggest a novel role for a chemosensory protein CSP5 in the development of embryonic integument in the honeybee Apis mellifera. Dev. Genes Evol. 2007, 217, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Liang, G.; He, X. Si-CSP9 regulates the integument and moulting process of larvae in the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.L.; Guo, H.; Huang, L.Q.; Pelosi, P.; Wang, C.Z. Unique function of a chemosensory protein in the proboscis of two Helicoverpa species. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 1821–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.X.; Xuan, N.; Chu, D.; Xie, H.Y.; Fan, Z.X.; Bi, Y.P.; Picimbon, J.F.; Qin, Y.C.; Zhong, S.T.; Li, Y.F.; et al. Biotype expression and insecticide response of Bemisia tabaci chemosensory protein-1. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 85, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Ma, H.; Xie, H.; Xuan, N.; Guo, X.; Fan, Z.; Rajashekar, B.; Arnaud, P.; Offmann, B.; Picimbon, J.-F. Biotype characterization, developmental profiling, insecticide response and binding property of Bemisia tabaci chemosensory proteins: Role of CSP in insect defense. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, N.; Guo, X.; Xie, H.Y.; Lou, Q.N.; Lu, X.B.; Liu, G.X.; Picimbon, J.F. Increased expression of CSP and CYP genes in adult silkworm females exposed to avermectins. Insect Sci. 2015, 22, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, M.A.M.; Bhandary, B.; Wijeratne, A.J.; Michel, A.P.; Hoy, C.W.; Mittapalli, O. Evidence for trade-offs in detoxification and chemosensation gene signatures in Plutella xylostella. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Qu, M.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, M. Chemosensory proteins participate in insecticide susceptibility in Rhopalosiphum padi, a serious pest on wheat crops. Insect Mol. Biol. 2021, 30, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, S.; Tan, J.; Li, X.; Chen, M. Chemosensory proteins are associated with thiamethoxam tolerance in bird cherry-oat aphid Rhopalosiphum padi. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 192, 105393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Tan, J.; Peng, X.; Song, Y.; Qu, M.; Chen, M. Expression pattern of RpCSP6 from Rhopalosiphum padi and its binding mechanism with deltamethrin: Insights into chemosensory protein mediated insecticide resistance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 17847–17857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Rui, C.; Yang, D.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, H. De novo transcriptome and expression profile analyses of the Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis) reveals relevant flubendiamide response genes. BMC Genomics 2017, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Liang, Z.; Chen, B. Evidence for the participation of chemosensory proteins in response to insecticide challenge in Conopomorpha sinensis. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2023, 71, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ni, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Sun, H.; Ye, X.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. The chemosensory protein 1 contributes to indoxacarb resistance in Plutella xylostella (L.). Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 2456–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Gao, S.; Lu, Y.; Wei, L.; Mao, J.; Xie, J.; Cao, Q.; Liu, J.; Bi, J.; Song, X.; et al. Latrophilin participates in insecticide susceptibility through positively regulating CSP10 and partially compensated by OBPC01 in Tribolium castaneum. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 159, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Y. Effects of insecticides chlorpyrifos, emamectin benzoate and fipronil on Spodoptera litura might be mediated by OBPs and CSPs. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2018, 108, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, V.A.; Anthousi, A.; Douris, V.; Harding, N.J.; Lycett, G.; Morris, M.; Vontas, J.; Ranson, H. A sensory appendage protein protects malaria vectors from pyrethroids. Nature 2020, 577, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Venthur, H.; Wang, S.; Homem, R.A.; Zhou, J.-J. Evidence for the involvement of the chemosensory protein AgosCSP5 in resistance to insecticides in the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii. Insects 2021, 12, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hu, W.W.; Fang, A.; Wang, Z.B.; Yuan, X.F.; Sun, Y.; Zou, Z.H.; Chen, N.; Jing, T.X.; Liu, Y.X.; et al. Chemosensory protein 8 confers thiamethoxam resistance in Diaphorina citri. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2025, 208, 106264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, V.; Wagstaff, S.; Ranson, H. Transcriptomic meta- signatures identified in Anopheles gambiae populations reveal previously undetected insecticide resistance mechanisms. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefi, M.; Charamis, J.; Balabanidou, V.; Ioannidis, P.; Ranson, H.; Ingham, V.; Vontas, J. Transcriptomic analysis of resistance and short-term induction response to pyrethroids, in Anopheles coluzzii legs. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Wen, S.; Shang, Q. Chemosensory proteins confer adaptation to the ryanoid anthranilic diamide insecticide cyantraniliprole in Aphis gossypii glover. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 184, 105076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yan, K.; Ding, Y.; Lv, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Pan, Y.; Shang, Q. Chemosensory proteins are associated with thiamethoxam and spirotetramat tolerance in Aphis gossypii Glover. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Tan, J.J.; Su, S.; Wang, S.J.; Peng, X.; Chen, M.H. Overexpression of the chemosensory protein CSP7 gene contributed to lambda-cyhalothrin resistance in the bird cherry-oat aphid Rhopalosiphum padi. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2023, 71, 17005–17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Tan, J.; Song, X.; Wu, F.; Tang, M.; Hua, Q.; Zheng, H.; Hu, F. Sublethal doses of neonicotinoid imidacloprid can interact with honey bee chemosensory protein 1 (CSP1) and inhibit its function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2017, 486, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, N.; Shen, D.; Liang, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, N. A female-biased chemosensory protein PxutCSP19 in the antennae of Papilio xuthus tuned to host volatiles and insecticides. Insects 2024, 15, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, L. Binding properties of four antennae-expressed chemosensory proteins (CSPs) with insecticides indicates the adaption of Spodoptera litura to environment. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 146, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.-J.; Yin, N.-N.; Pu, L.-M.; Yang, A.-J.; Liu, N.-Y. Three chemosensory proteins enriched in antennae and tarsi of Rhaphuma horsfieldi differentially contribute to the binding of insecticides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 199, 105797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, A.H.; Perrimon, N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 1993, 118, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, V.A.; Grigoraki, L.; Ranson, H. Pyrethroid resistance mechanisms in the major malaria vector species complex. Entomol. Gen. 2023, 43, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Chung, H. New and emerging mechanisms of insecticide resistance. Curr. Op. Insect Sci. 2024, 63, 101184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantsidis, G.R.; Panteleri, R.; Denecke, S.; Kounadi, S.; Christou, I.; Nauen, R.; Douris, V.; Vontas, J. ‘What I cannot create, I do not understand’: Functionally validated synergism of metabolic and target site insecticide resistance. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20200838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CSP Name | Organism | Insecticide (s) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAP2 | Anopheles gambiae | Deltamethrin, α-Cypermethrin, Permethrin | [56] |
| AgoCSP1, AgoCSP4 | Aphis gossypii | Thiamethoxam | [62] |
| AgoCSP4 | Aphis gossypii | Spirotetramat | [62] |
| AgoCSP1, AgoCSP4, AgoCSP5 | Aphis gossypii | Cyantraniliprole | [61] |
| RpCSP4, RpCSP5 | Rhopalosiphum padi | Thiamethoxam | [49] |
| RpCSP7 | Rhopalosiphum padi | λ-cyalothrin | [63] |
| RpCSP6 | Rhopalosiphum padi | Deltamethrin | [50] |
| RpCSP4, RpCSP5, RpCSP6, RpCSP10 | Rhopalosiphum padi | Imidacloprid | [48] |
| RpCSP4, RpCSP6 | Rhopalosiphum padi | β-cypermethrin | [48] |
| PxCSP1 | Plutella xylostella | Indoxacarb | [53] |
| SlituCSP18 | Spodoptera litura | Chlorpyrifos, Fipronil | [55] |
| SfruCSP1, SfruCSP2 | Spodoptera frugiperda | Chlorfenapyr, Chlorpyrifos, Indoxacarb | [34] |
| TcCSP10 | Tribolium castaneum | Dichlorvos, Carbofuran | [54] |
| DcitCSP8 | Diaphorina citri | Thiamethoxam | [58] |
| NluCSP2, NluCSP4, NluCSP5, NluCSP7, NluCSP12, NluCSP15 | Nilaparvata lugens | Imidacloprid | [19] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsouri, A.; Douris, V. The Role of Chemosensory Proteins in Insecticide Resistance: A Review. Insects 2025, 16, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050496
Tsouri A, Douris V. The Role of Chemosensory Proteins in Insecticide Resistance: A Review. Insects. 2025; 16(5):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050496
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsouri, Angeliki, and Vassilis Douris. 2025. "The Role of Chemosensory Proteins in Insecticide Resistance: A Review" Insects 16, no. 5: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050496
APA StyleTsouri, A., & Douris, V. (2025). The Role of Chemosensory Proteins in Insecticide Resistance: A Review. Insects, 16(5), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16050496