Wolbachia Screening in Aedes aegypti and Culex pipiens Mosquitoes from Madeira Island, Portugal
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
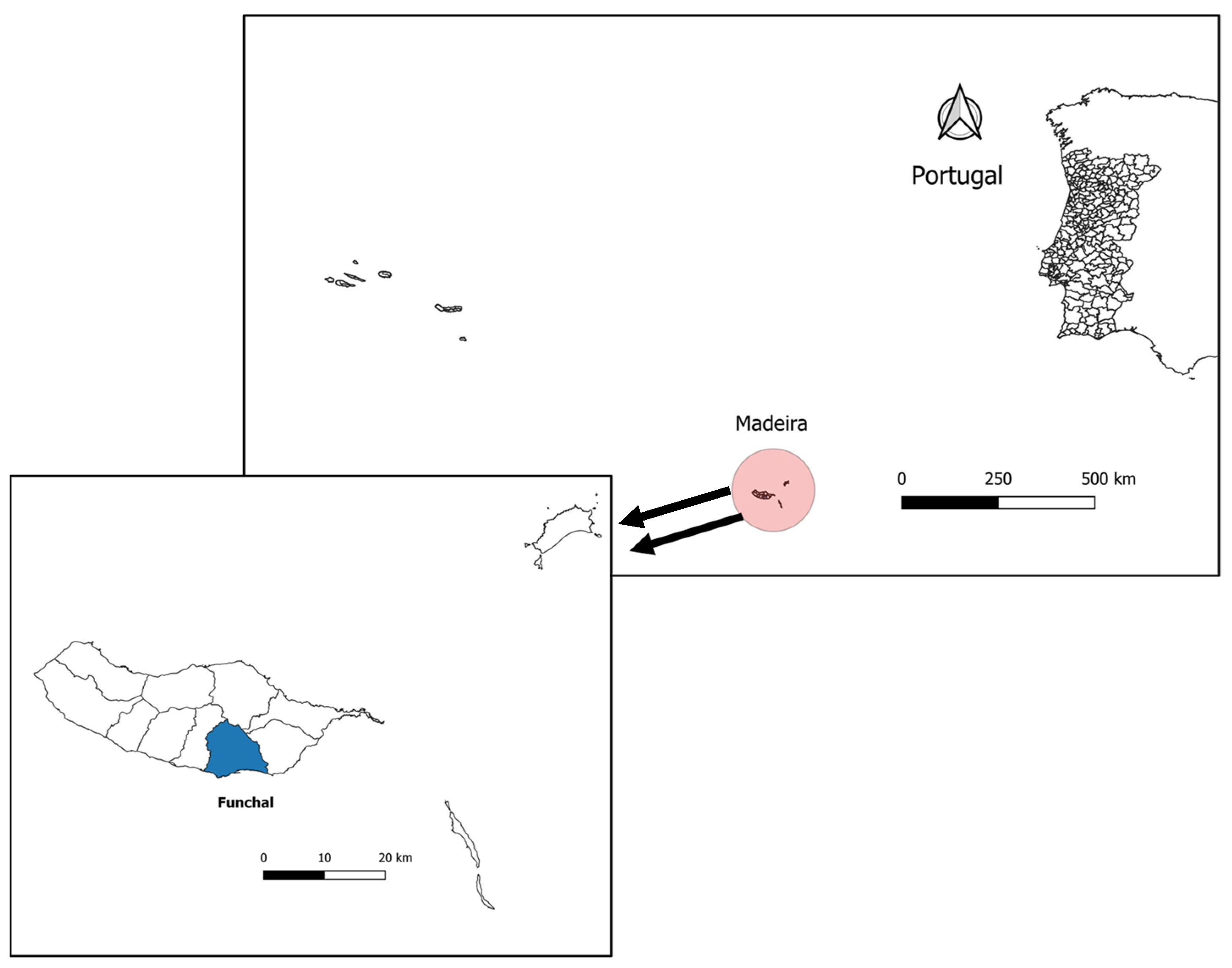
2.1. Mosquito Collection
2.2. Wolbachia Detection
2.3. Multilocus Sequence Typing
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mosquito Morphological Identification
3.2. Wolbachia Screening Through Amplification of the Wsp Gene
3.3. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
4. Discussion
4.1. The Prevalence of Wolbachia in Ae. aegypti
4.2. High Wolbachia Prevalence in Cx. pipiens
4.3. Implications for Vector Competence and Control
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ace-2 | Acetylcholinesterase-2 |
| IIT | Incompatible Insect Technique |
| MBDs | Mosquito-borne diseases |
| MLST | Multilocus Sequence Typing |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| qPCR | Quantitative PCR |
| ST | Sequence type |
| WNV | West Nile virus |
| wsp | Wolbachia surface protein gene |
Appendix A
| Target | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| wsp | 81F-TGGTCCAATAAGTGATGAAGAAA 691R-AAAAATTAAACGCTACTCCA | [2] |
| coxA | wsp_F1: GTCCAATARSTGATGARGAAAC wsp_R1: CYGCACCAAYAGYRCTRTAAA | [3] |
| gatB | gatB_F1: GAKTTAAAYCGYGCAGGBGTT gatB_R1: TGGYAAYTCRGGYAAAGATGA | [3] |
| ftsZ | ftsZ_F1: ATYATGGARCATATAAARGATAG ftsZ_R1: TCRAGYAATGGATTRGATAT | [3] |
| hcpA | hcpA_F1: GAAATARCAGTTGCTGCAAA hcpA_R1: GAAAGTYRAGCAAGYTCTG | [3] |
| fbpA | fbpA_F1: GCTGCTCCRCTTGGYWTGAT fbpA_R1: CCRCCAGARAAAAYYACTATTC | [3] |
| wspHVR | wsp_F1: GTCCAATARSTGATGARGAAAC wsp_R1: CYGCACCAAYAGYRCTRTAAA | [3] |
| Sex | Year | gatB | coxA | hcpA | ftsZ | fbpA | HVR1 | HVR2 | HVR3 | HVR4 | ST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 2023 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 22 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 9 |
| 2024 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 22 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 9 | |
| Male | 2023 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 22 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 9 |
| 2024 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 22 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 8 | 9 |
References
- Souza-Neto, J.A.; Powell, J.R.; Bonizzoni, M. Aedes aegypti vector competence studies: A review. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 67, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farajollahi, A.; Fonseca, D.M.; Kramer, L.D.; Kilpatrick, A.M. Bird biting mosquitoes and human disease: A review of the role of Culex pipiens complex mosquitoes in epidemiology. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challenges in combating arboviral infections. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3350. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubler, D. Dengue, urbanization and globalization: The unholy trinity of the 21st century. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemingway, J.; Ranson, H.; Magill, A.; Kolaczinski, J.; Fornadel, C.; Gimnig, J.; Coetzee, M.; Simard, F.; Roch, D.K.; Hinzoumbe, C.K.; et al. Averting a malaria disaster: Will insecticide resistance derail malaria control? Lancet 2016, 387, 1785–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyes, C.L.; Vontas, J.; Martins, A.J.; Ng, L.C.; Koou, S.Y.; Dusfour, I.; Raghavendra, K.; Pinto, J.; Corbel, V.; David, J.P.; et al. Contemporary Status of Insecticide Resistance in the Major Aedes Vectors of Arboviruses Infecting Humans. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranson, H.; N’Guessan, R.; Lines, J.; Moiroux, N.; Nkuni, Z.; Corbel, V. Pyrethroid resistance in African anopheline mosquitoes: What are the implications for malaria control? Trends Parasitol. 2011, 27, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhav, M.; Blasdell, K.R.; Trewin, B.; Paradkar, P.N.; López-Denman, A.J. Culex-transmitted diseases: Mechanisms, impact, and future control strategies using Wolbachia. Viruses 2024, 16, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, G.; Salgueiro, P.; Bronzato-Badial, A.; Gonçalves, Y.; Reyes-Lugo, M.; Gordicho, V.; Ribolla, P.; Viveiros, B.; Silva, A.C.; Pinto, J.; et al. Origin and expansion of the mosquito Aedes aegypti in Madeira Island (Portugal). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakonyi, T.; Haussig, J.M. West Nile virus keeps on moving up in Europe. Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 2001938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, H.A.; O’Neill, S.L. Controlling vector-borne diseases by releasing modified mosquitoes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Shropshire, J.D.; Cross, K.L.; Leigh, B.; Mansueto, A.J.; Stewart, V.; Bordenstein, S.R.; Bordenstein, S.R. Living in the endosymbiotic world of Wolbachia: A centennial review. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 879–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, M.; Hochstrasser, M. The biochemistry of cytoplasmic incompatibility caused by endosymbiotic bacteria. Genes 2020, 11, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mains, J.W.; Kelly, P.H.; Dobson, K.L.; Petrie, W.D.; Dobson, S.L. Localized control of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) in Miami, FL, via inundative releases of Wolbachia-infected male mosquitoes. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.B.; Riback, T.I.S.; Sylvestre, G.; Costa, G.; Peixoto, J.; Dias, F.B.S.; Tanamas, S.K.; Simmons, C.P.; Dufault, S.M.; Ryan, P.A.; et al. Effectiveness of Wolbachia-infected mosquito deployments in reducing the incidence of dengue and other Aedes-borne diseases in Niterói, Brazil: A quasi-experimental study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputo, B.; Moretti, R.; Virgillito, C.; Manica, M.; Lampazzi, E.; Lombardi, G.; Serini, P.; Pichler, V.; Beebe, N.W.; Della Torre, A.; et al. A bacterium against the tiger: Further evidence of the potential of non inundative releases of males with manipulated Wolbachia infection in reducing fertility of Aedes albopictus field populations in Italy. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 4145–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.L.; Ryan, P.A.; Turley, A.P.; Wilson, G.; Hurst, T.P.; Retzki, K.; Brown-Kenyon, J.; Hodgson, L.; Kenny, N.; Cook, H.; et al. Establishment of wMel Wolbachia in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes and reduction of local dengue transmission in Cairns and surrounding locations in northern Queensland, Australia. Gates Open Res. 2019, 3, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, H.L.; Nguyen, T.Y.; Vu, S.N.; Tran, N.D.; Le, T.N.; Vien, Q.M.; Bui, T.C.; Le, H.T.; Kutcher, S.; et al. Field evaluation of the establishment potential of wMelPop Wolbachia in Australia and Vietnam for dengue control. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indriani, C.; Tantowijoyo, W.; Rancès, E.; Andari, B.; Prabowo, E.; Yusdi, D.; Ansari, M.R.; Wardana, D.S.; Supriyati, E.; Nurhayati, I.; et al. Reduced dengue incidence following deployments of Wolbachia-infected Aedes aegypti in Yogyakarta, Indonesia: A quasi-experimental trial using controlled interrupted time series analysis. Gates Open Res. 2020, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.T.; Bansal, S.; Chong, C.S.; Dickens, B.; Ng, Y.; Deng, L.; Lee, C.; Tan, L.Y.; Chain, G.; Ma, P.; et al. Efficacy of Wolbachia-mediated sterility to reduce the incidence of dengue: A synthetic control study in Singapore. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, e29–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Wu, Y.; Liang, X.; Liang, Y.; Pan, X.; Hu, L.; Sun, Q.; et al. Incompatible and sterile insect techniques combined eliminate mosquitoes. Nature 2019, 572, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.A.; Ahmad, N.W.; Keong, W.M.; Ling, C.Y.; Ahmad, N.A.; Golding, N.; Tierney, N.; Jelip, J.; Putit, P.W.; Mokhtar, N.; et al. Introduction of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes carrying wAlbB Wolbachia sharply decreases dengue incidence in disease hotspots. iScience 2024, 27, 108942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, G.; Jupille, H.; Yen, P.-S.; Viveiros, B.; Failloux, A.-B.; Sousa, C.A. Potential of Aedes aegypti Populations in Madeira Island to Transmit Dengue and Chikungunya Viruses. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, G.; Grigoraki, L.; Weetman, D.; Vicente, J.L.; Silva, A.C.; Pinto, J.; Vontas, J.; Sousa, C.A. Insecticide resistance is mediated by multiple mechanisms in recently introduced Aedes aegypti from Madeira Island (Portugal). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, H.; Ramos, H.C. Identification keys of the mosquitoes of Continental Portugal, Azores and Madeira. Eur. Mosq. Bull. 1999, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.L.; Fonseca, D.M. Rapid assays for identification of members of the Culex (Culex) pipiens complex, their hybrids, and other sibling species (Diptera: Culicidae). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 70, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahnck, C.M.; Fonseca, D.M. Rapid assay to identify the two genetic forms of Culex (Culex) pipiens L. (Diptera: Culicidae) and hybrid populations. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Rousset, F.; O’Neill, S. Phylogeny and PCR-based classification of Wolbachia strains using wsp gene sequences. Proc. Biol. Sci. 1998, 265, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawasdichai, S.; Chaumeau, V.; Dah, T.; Kulabkeeree, T.; Kajeechiwa, L.; Phanaphadungtham, M.; Trakoolchengkaew, M.; Kittiphanakun, P.; Akararungrot, Y.; Oo, K.; et al. Detection of diverse Wolbachia 16S rRNA sequences at low titers from malaria vectors in Kayin State, Myanmar. Wellcome Open Res. 2019, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, L.; Hotopp, J.C.D.; Jolley, K.A.; Bordenstein, S.R.; Biber, S.A.; Choudhury, R.R.; Hayashi, C.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Tettelin, H.; Werren, J.H. Multilocus sequence typing system for the endosymbiont Wolbachia pipientis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7098–7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderheyden, A.; Smitz, N.; De Wolf, K.; Deblauwe, I.; Dekoninck, W.; Meganck, K.; Gombeer, S.; Vanslembrouck, A.; De Witte, J.; Schneider, A.; et al. DNA Identification and Diversity of the Vector Mosquitoes Culex pipiens s.s. and Culex torrentium in Belgium (Diptera: Culicidae). Diversity 2022, 14, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourtzis, K. Wolbachia-based technologies for insect pest population control. In Transgenesis and the Management of Vector-Borne Disease; Aksoy, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 627, pp. 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloria-Soria, A.; Chiodo, T.G.; Powell, J.R. Lack of evidence for natural Wolbachia infections in Aedes aegypti. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1307–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, T.M.; Hashimoto, K.; Harnandika, R.K.; Amalin, D.M.; Watanabe, K. Detection of Wolbachia in Field-Collected Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes in Metropolitan Manila, Philippines. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, S.; Jayachandran, S.; Prabagaran, S.R. Evidence for the natural occurrence of Wolbachia in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayagam, S.; Nirmolia, T.; Chetry, S.; Kumar, N.P.; Saini, P.; Bhattacharyya, D.R.; Bhowmick, I.P.; Sattu, K.; Patgiri, S.J. Molecular Evidence of Wolbachia Species in Wild-Caught Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes in Four States of Northeast India. J. Trop. Med. 2023, 2023, 6678627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, P.A.; Callahan, A.G.; Yang, Q.; Jasper, M.; Arif, M.A.K.; Afizah, A.N.; Nazni, W.A.; Hoffmann, A.A. An elusive endosymbiont: Does Wolbachia occur naturally in Aedes aegypti? Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minwuyelet, A.; Petronio, G.P.; Yewhalaw, D.; Sciarretta, A.; Magnifico, I.; Nicolosi, D.; Di Marco, R.; Atenafu, G. Symbiotic Wolbachia in mosquitoes and its role in reducing the transmission of mosquito-borne diseases: Updates and prospects. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1267832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.A.; Robinson, K.L.; Yang, Q.; Callahan, A.G.; Schmidt, T.L.; Axford, J.K.; Coquilleau, M.P.; Staunton, K.M.; Townsend, M.; Ritchie, S.A.; et al. A decade of stability for wMel Wolbachia in natural Aedes aegypti populations. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, J.I.L.; Suzuki, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Watanabe, K. Detection and quantification of natural Wolbachia in Aedes aegypti in Metropolitan Manila, Philippines using locally designed primers. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inácio da Silva, L.M.; Dezordi, F.Z.; Paiva, M.H.S.; Wallau, G.L. Systematic review of Wolbachia symbiont detection in mosquitoes: An entangled topic about methodological power and true symbiosis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, E.; Atyame, C.M.; Milesi, P.; Fonseca, D.M.; Shaikevich, E.V.; Unal, S.; Makoundou, P.; Weill, M.; Duron, O. Population structure of Wolbachia and cytoplasmic introgression in a complex of mosquito species. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atyame, C.M.; Delsuc, F.; Pasteur, N.; Weill, M.; Duron, O. Diversification of Wolbachia endosymbiont in the Culex pipiens mosquito. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2761–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Moura, A.J.F.; Valadas, V.; da Veiga Leal, S.; Montalvo Sabino, E.; Sousa, C.A.; Pinto, J. Screening of natural Wolbachia infection in mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) from the Cape Verde islands. Parasit. Vectors 2023, 16, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, R.L.; Meola, M.A. The native Wolbachia endosymbionts of Drosophila melanogaster and Culex quinquefasciatus increase host resistance to West Nile virus infection. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.; Ferreira, Á.; Ashburner, M. The bacterial symbiont Wolbachia induces resistance to RNA viral infections in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e1000002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, B.L.; Hughes, G.L.; Paul, O.; Matacchiero, A.C.; Kramer, L.D.; Rasgon, J.L. Wolbachia enhances West Nile virus (WNV) infection in the mosquito Culex tarsalis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.L.J.; Cook, A.R.; Bansal, S.; Chow, J.Y.; Lim, J.T. Wolbachia incompatible insect technique program optimization over large spatial scales using a process-based model of mosquito metapopulation dynamics. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atyame, C.M.; Pasteur, N.; Dumas, E.; Tortosa, P.; Tantely, M.L.; Pocquet, N.; Licciardi, S.; Bheecarry, A.; Zumbo, B.; Weill, M.; et al. Cytoplasmic incompatibility as a means of controlling Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus in the southwestern Indian Ocean islands. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padde, J.R.; Lu, Q.; Long, Y.; Zhang, D.; Hou, M.; Chen, L.; Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Ji, M. The Impact of Environmental and Host Factors on Wolbachia Density and Efficacy as a Biological Tool. Decod. Infect. Transm. 2023, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes, R.; Melo, T.; Zé-Zé, L.; Freitas, I.C.; Silva, M.; Dias, E.; Santos, N.C.; Gouveia, B.R.; Seixas, G.; Osório, H.C. Wolbachia Screening in Aedes aegypti and Culex pipiens Mosquitoes from Madeira Island, Portugal. Insects 2025, 16, 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040418
Fernandes R, Melo T, Zé-Zé L, Freitas IC, Silva M, Dias E, Santos NC, Gouveia BR, Seixas G, Osório HC. Wolbachia Screening in Aedes aegypti and Culex pipiens Mosquitoes from Madeira Island, Portugal. Insects. 2025; 16(4):418. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040418
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes, Rita, Tiago Melo, Líbia Zé-Zé, Inês C. Freitas, Manuel Silva, Eva Dias, Nuno C. Santos, Bruna R. Gouveia, Gonçalo Seixas, and Hugo Costa Osório. 2025. "Wolbachia Screening in Aedes aegypti and Culex pipiens Mosquitoes from Madeira Island, Portugal" Insects 16, no. 4: 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040418
APA StyleFernandes, R., Melo, T., Zé-Zé, L., Freitas, I. C., Silva, M., Dias, E., Santos, N. C., Gouveia, B. R., Seixas, G., & Osório, H. C. (2025). Wolbachia Screening in Aedes aegypti and Culex pipiens Mosquitoes from Madeira Island, Portugal. Insects, 16(4), 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040418







