Adipokinetic Hormones and Their Receptor Regulate the Locomotor Behavior in Tribolium castaneum
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing and Cell Line Maintenance
2.2. Sequence Analysis of Tc-AKHR and Its Ligands in T. castaneum
2.3. Structural Modeling and Molecular Docking
2.4. Functional Calcium Reporter Assays
2.5. Gene Expression in Different Tissues
2.6. Total RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.7. Synthesis of Double-Stranded RNA
2.8. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR
2.9. RNA Interference and Movement Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Analysis and Molecular Characterization of AKHs and AKHR in T. castaneum
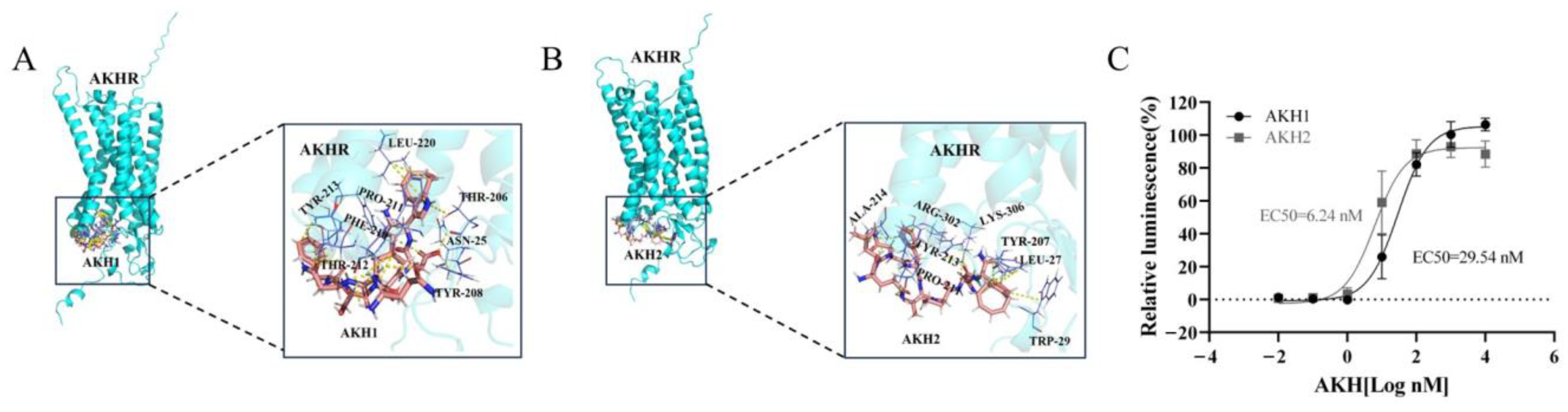
3.2. Activity Determination of Tc-AKHs on Tc-AKHR
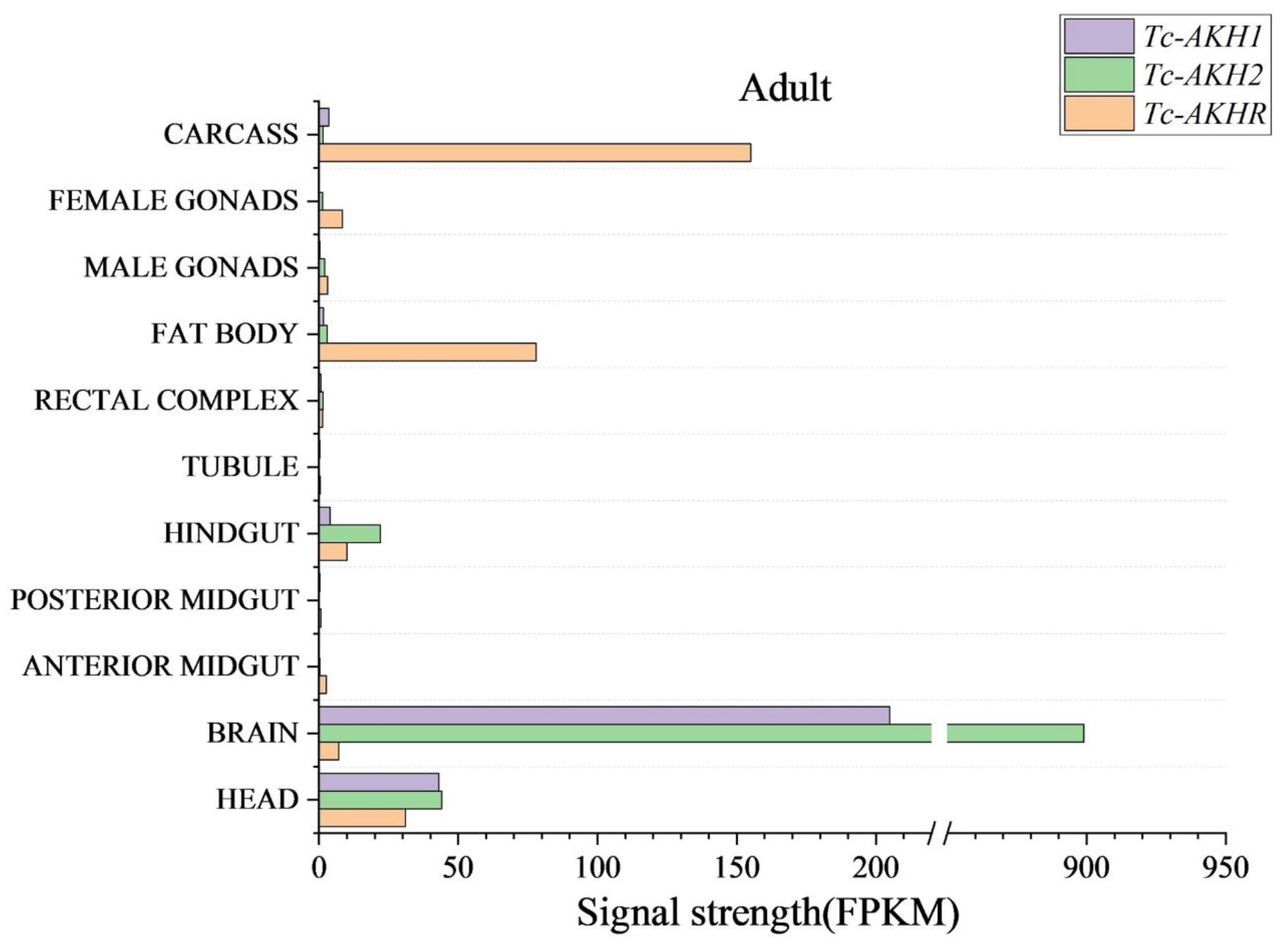
3.3. Expression of Tc-AKHs and Tc-AKHR in Different Tissues of T. castaneum
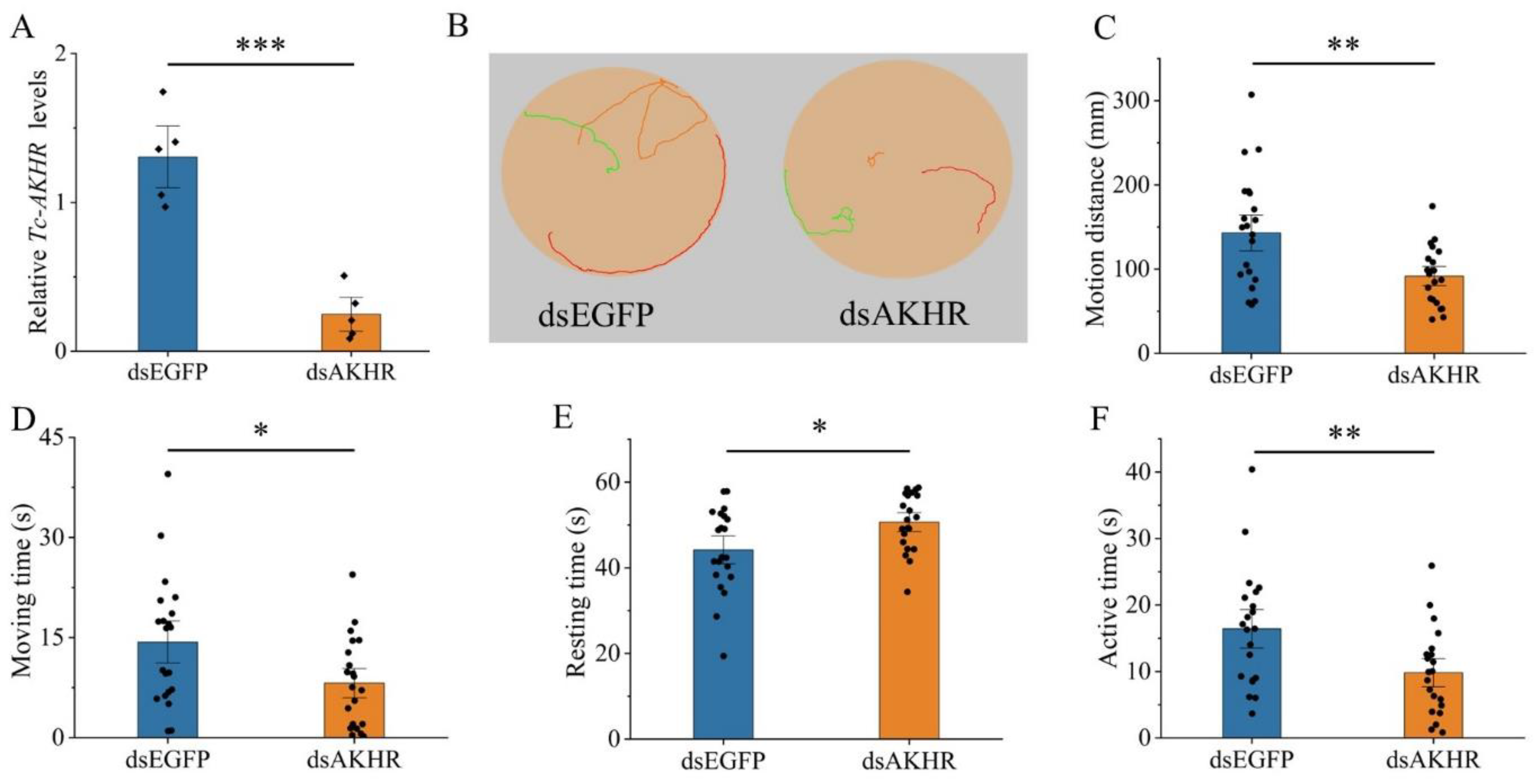
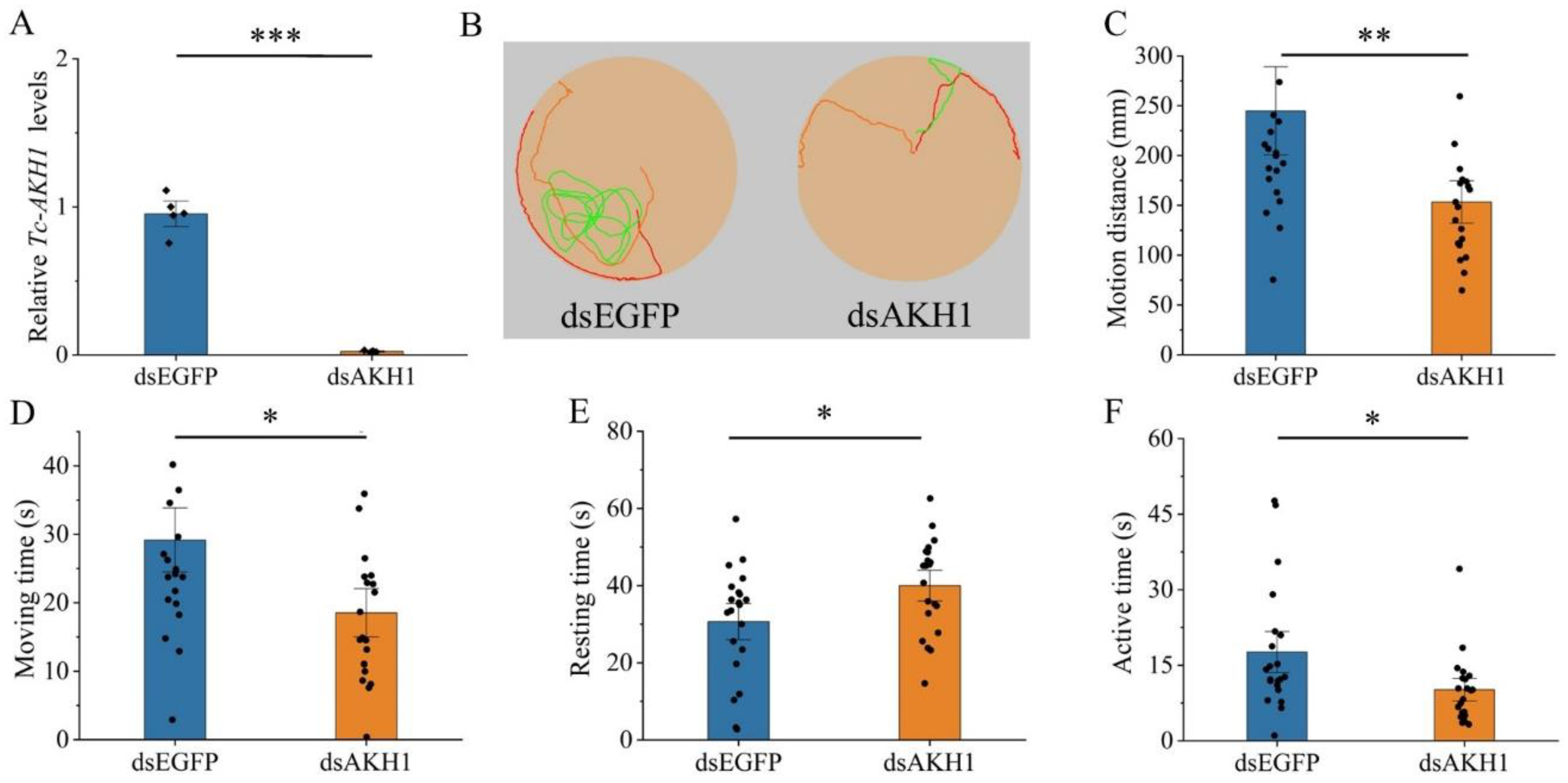
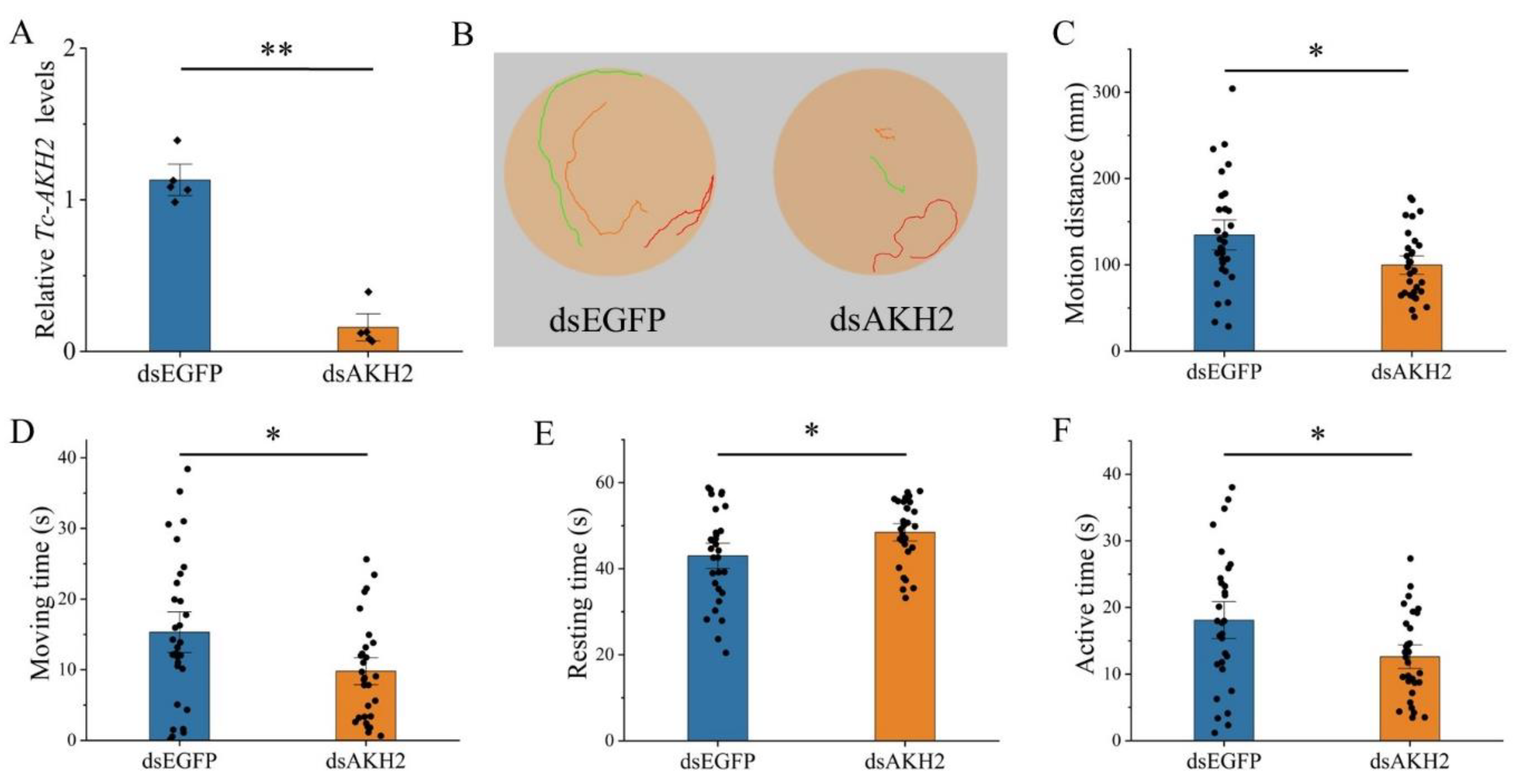
3.4. Effects of Tc-AKH and Tc-AKHR Knockdown on Locomotion
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huston, S.J.; Jayaraman, V. Studying sensorimotor integration in insects. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2011, 21, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, M.H.; Farley, C.T.; Full, R.J.; Koehl, M.A.; Kram, R.; Lehman, S. How animals move: An integrative view. Science 2000, 288, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Peterson, J.; Nachman, R.J.; Ganetzky, B. Drosulfakinin activates CCKLR-17D1 and promotes larval locomotion and escape response in Drosophila. Fly 2012, 6, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nässel, D.R.; Zandawala, M. Recent advances in neuropeptide signaling in Drosophila, from genes to physiology and behavior. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 179, 101607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Yang, P.; Jiang, F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Kang, L. The neuropeptide F/nitric oxide pathway is essential for shaping locomotor plasticity underlying locust phase transition. eLife 2017, 6, e22526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, M.; Wang, N.; Song, Y.; Peng, X.; Chen, M. Functional characterization of two DH44R genes associated with starvation and desiccation in Rhopalosiphum padi (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 201, 105902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahsai, L.; Martin, J.R.; Winther, A.M. Neuropeptides in the Drosophila central complex in modulation of locomotor behavior. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 2256–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.V.; Mordue, W.; Batley, K.E.; Morris, H.R. Structure of locust adipokinetic hormone, a neurohormone that regulates lipid utilisation during flight. Nature 1976, 263, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, H.G.; Gäde, G. Structure and function of adipokinetic hormones of the large white butterfly Pieris brassicae. Physiol. Entomol. 2017, 42, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Xie, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, Z.; Xia, B.; Xin, T. Expression and functional analysis of adipokinetic hormone reveal its different roles in larval development and female fecundity in Panonychus citri (McGregor) (Acari: Tetranychidae). Insect Mol. Biol. 2024, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.L.; Chen, E.H.; Jiang, H.B.; Wei, D.D.; Gui, S.H.; Wang, J.J.; Smagghe, G. Adipokinetic hormone receptor gene identification and its role in triacylglycerol mobilization and sexual behavior in the oriental fruit fly (Bactrocera dorsalis). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 90, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajwan, S.; Sidorov, R.; Stašková, T.; Žaloudíková, A.; Takasu, Y.; Kodrík, D.; Zurovec, M. Targeted mutagenesis and functional analysis of adipokinetic hormone-encoding gene in Drosophila. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 61, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, K. Adipokinetic hormone regulates cytochrome P450-mediated imidacloprid resistance in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Marco, H.G.; Scheich, N.; He, S.; Wang, Z.; Gäde, G.; McMahon, D.P. Comparative analysis of adipokinetic hormones and their receptors in Blattodea reveals novel patterns of gene evolution. Insect Mol. Biol. 2023, 32, 615–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Gibbs, R.A.; Weinstock, G.M.; Brown, S.J.; Denell, R.; Beeman, R.W.; Gibbs, R.; Bucher, G.; Friedrich, M.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J.; et al. The genome of the model beetle and pest Tribolium castaneum. Nature 2008, 452, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walski, T.; Van Damme, E.J.M.; Smargiasso, N.; Christiaens, O.; De Pauw, E.; Smagghe, G. Protein N-glycosylation and N-glycan trimming are required for postembryonic development of the pest beetle Tribolium castaneum. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.D.; Li, Y.S.; Lu, R.H.; Smagghe, G.; Liu, T.X.; Gui, S.H. miR-7977 regulates the locomotor behavior by targeting diuretic hormone and SIFamide receptors in Tribolium castaneum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.H.; Jiang, H.B.; Liu, X.Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.J. Molecular characterizations of natalisin and its roles in modulating mating in the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Insect Mol. Biol. 2017, 26, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, J.C.; Hartzer, K.; Toutges, M.; Oppert, B. Evaluation of quantitative PCR reference genes for gene expression studies in Tribolium castaneum after fungal challenge. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 80, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, M.Y.; Beeman, R.W.; Arakane, Y. RNAi-based functional genomics in Tribolium castaneum and possible application for controlling insect pests. Entomol. Res. 2012, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Adams, M.E. Identification of G protein-coupled receptors for Drosophila PRXamide peptides, CCAP, corazonin, and AKH supports a theory of ligand-receptor coevolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11423–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staubli, F.; Jorgensen, T.J.; Cazzamali, G.; Williamson, M.; Lenz, C.; Sondergaard, L.; Roepstorff, P.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J. Molecular identification of the insect adipokinetic hormone receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3446–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, R.; Isoe, J.; Moore, W.; Riehle, M.A.; Wells, M.A. The putative AKH receptor of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta, and its expression. J. Insect Sci. 2011, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konuma, T.; Morooka, N.; Nagasawa, H.; Nagata, S. Knockdown of the adipokinetic hormone receptor increases feeding frequency in the two-spotted cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3111–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Bezerra, M.; De Paula, I.F.; Medina, J.M.; Silva-Oliveira, G.; Medeiros, J.S.; Gäde, G.; Gondim, K.C. Adipokinetic hormone receptor gene identification and its role in triacylglycerol metabolism in the blood-sucking insect Rhodnius prolixus. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 69, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, M.W. Adipokinetic hormone inhibits the formation of energy stores and egg production in the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 136, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, M.; Witten, J.; Schaffer, M. Isolation and characterization of two myoactive neuropeptides: Further evidence of an invertebrate peptide family. J. Neurosci. 1984, 4, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarborough, R.M.; Jamieson, G.C.; Kalish, F.; Kramer, S.J.; McEnroe, G.A.; Miller, C.A.; Schooley, D.A. Isolation and primary structure of two peptides with cardioacceleratory and hyperglycemic activity from the corpora cardiaca of Periplaneta americana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 5575–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Horst, D.J. Insect adipokinetic hormones: Release and integration of flight energy metabolism. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 136, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, U. The role of peptide hormones in insect lipid metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrese, E.L.; Patel, R.T.; Soulages, J.L. The main triglyceride-lipase from the insect fat body is an active phospholipase A (1): Identification and characterization. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 2656–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrese, E.L.; Soulages, J.L. Insect fat body: Energy, metabolism, and regulation. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönke, S.; Mildner, A.; Fellert, S.; Tennagels, N.; Petry, S.; Müller, G.; Jäckle, H.; Kühnlein, R.P. Brummer lipase is an evolutionary conserved fat storage regulator in Drosophila. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönke, S.; Müller, G.; Hirsch, J.; Fellert, S.; Andreou, A.; Haase, T.; Jäckle, H.; Kühnlein, R.P. Dual lipolytic control of body fat storage and mobilization in Drosophila. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavoso, L.E.; Wells, M.A. Role of lipid transfer particle in delivery of diacylglycerol from midgut to lipophorin in larval Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 31, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrese, E.L.; Mirza, S.; Rivera, L.; Howard, A.D.; Chetty, P.S.; Soulages, J.L. Expression of lipid storage droplet protein-1 may define the role of AKH as a lipid mobilizing hormone in Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, R.-H.; Pang, X.-D.; Wen, S.-Q.; Smagghe, G.; Liu, T.-X.; Gui, S.-H. Adipokinetic Hormones and Their Receptor Regulate the Locomotor Behavior in Tribolium castaneum. Insects 2025, 16, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040407
Lu R-H, Pang X-D, Wen S-Q, Smagghe G, Liu T-X, Gui S-H. Adipokinetic Hormones and Their Receptor Regulate the Locomotor Behavior in Tribolium castaneum. Insects. 2025; 16(4):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040407
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Rui-Han, Xu-Dong Pang, Shuang-Qin Wen, Guy Smagghe, Tong-Xian Liu, and Shun-Hua Gui. 2025. "Adipokinetic Hormones and Their Receptor Regulate the Locomotor Behavior in Tribolium castaneum" Insects 16, no. 4: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040407
APA StyleLu, R.-H., Pang, X.-D., Wen, S.-Q., Smagghe, G., Liu, T.-X., & Gui, S.-H. (2025). Adipokinetic Hormones and Their Receptor Regulate the Locomotor Behavior in Tribolium castaneum. Insects, 16(4), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040407





