Direct and Indirect Effects of Ivermectin on Phytophagous, Frugivorous and Parasitoid Insects
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Does the uptake of IVM directly affect the growth and development of chewing herbivores?
- Does IVM in soil indirectly affect the establishment and growth of aphid colonies on plants growing in IVM-treated soil?
- Does the uptake of sublethal doses of IVM by host insects indirectly affect the development of parasitoids feeding on these hosts?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ivermectin
2.2. Direct Effects of Ivermectin on Lepidopteran Larvae
2.2.1. Test Species
2.2.2. Artificial Diet
2.2.3. Feeding Experiment with L3-L4 Spodoptera frugiperda
2.2.4. Feeding Experiment with L1 Spodoptera frugiperda and Helicoverpa armigera
2.3. Host Plant-Mediated Effects of Ivermectin on the Phloem-Feeding Herbivore Acyrthosiphon pisum
2.4. Host-Mediated Effects of Ivermectin on the Parasitoid Pachycrepoideus vindemmiae
Parasitisation Experiment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Ivermectin Concentration on Larval Performance (Development Time and Pupal Mass) of a Chewing Herbivore
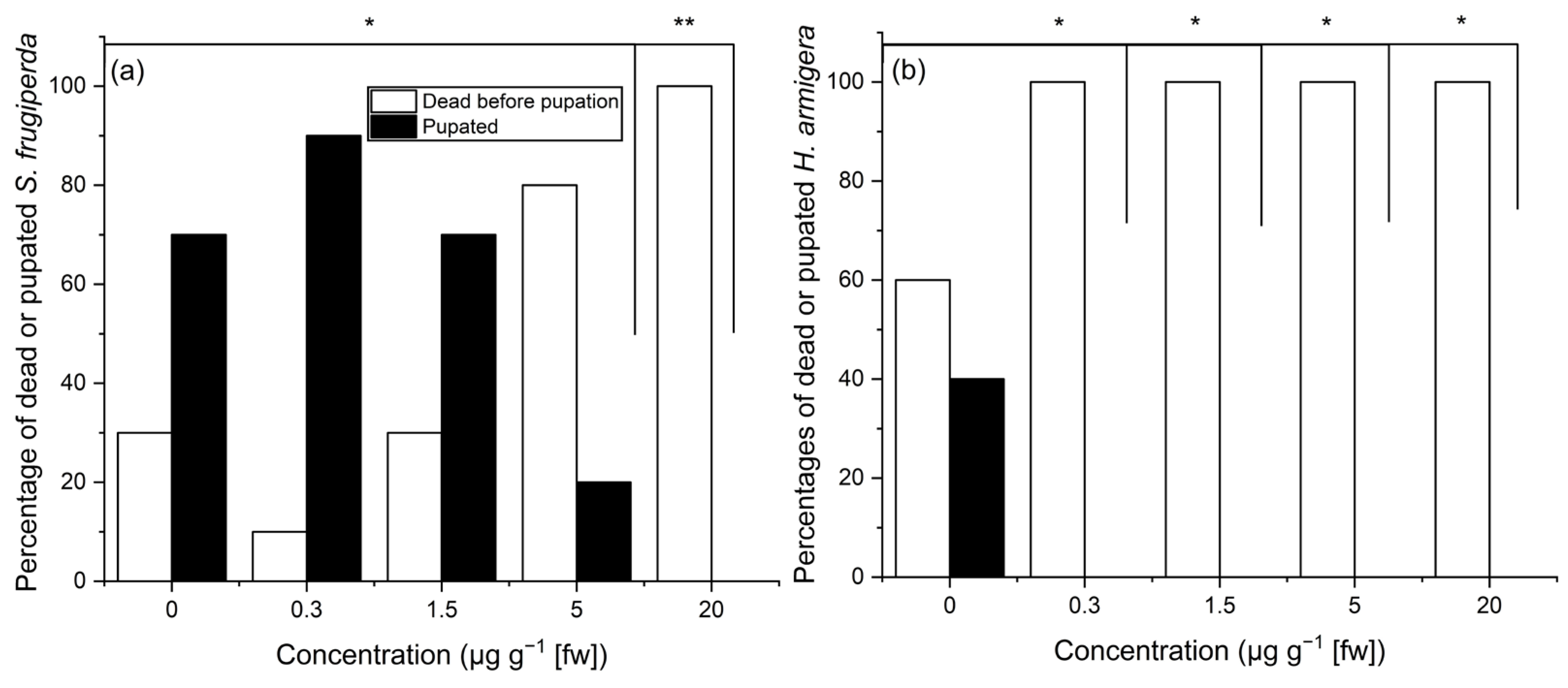
3.2. Effects of Ivermectin Concentration on Larval Mortality of Two Chewing Herbivores
3.3. Host Plant-Mediated Effects of Ivermectin Concentration on Colony Establishment of a Sucking Herbivore
3.4. Host-Mediated Effects of Ivermectin on Parasitoid Development
4. Discussion
4.1. Improving the Understanding of the Environmental Impact of Ivermectin
4.2. Direct Diet-Mediated Effects of IVM on Lepidoptera Larvae
4.3. Indirect Plant-Mediated Effects of IVM on Aphids
4.4. Indirect Host-Mediated Effects of IVM on Hymenopteran Parasitoids
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| IVM | Ivermectin |
References
- Geary, T.G.; Moreno, Y. Macrocyclic Lactone Anthelmintics: Spectrum of Activity and Mechanism of Action. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Õmura, S. Ivermectin: 25 Years and Still Going Strong. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 31, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoop, W.L.; Mrozik, H.; Fisher, M.H. Structure and Activity of Avermectins and Milbemycins in Animal Health. Vet. Parasitol. 1995, 59, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prichard, R.; Ménez, C.; Lespine, A. Moxidectin and the Avermectins: Consanguinity but Not Identity. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2012, 2, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffont, C.M.; Alvinerie, M.; Bousquet-Mélou, A.; Toutain, P.-L. Licking Behaviour and Environmental Contamination Arising from Pour-on Ivermectin for Cattle. Int. J. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, C.; Steffansen, B.; Nielsen, B.O.; Grønvold, J.; Jensen, K.-M.V.; Jespersen, J.B.; Springborg, J.; Nansen, P. Ivermectin Excreted in Cattle Dung after Subcutaneous Injection or Pour-on Treatment: Concentrations and Impact on Dung Fauna. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1992, 82, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herd, R.P.; Sams, R.A.; Ashcraft, S.M. Persistence of Ivermectin in Plasma and Faeces Following Treatment of Cows with Ivermectin Sustained-Release, Pour-on or Injectable Formulations. Int. J. Parasitol. 1996, 26, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena-Díaz, F.; Martínez-M, I.; Gil-Pérez, Y.; González-Tokman, D. Trans-Generational Effects of Ivermectin Exposure in Dung Beetles. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumaret, J.P.; Galante, E.; Lumbreras, C.; Mena, J.; Bertrand, M.; Bernal, J.L.; Cooper, J.F.; Kadiri, N.; Crowe, D. Field Effects of Ivermectin Residues on Dung Beetles. J. Appl. Ecol. 1993, 30, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, C.T.; Scholtz, C.H. A Review on the Effect of Macrocyclic Lactones on Dung-Dwelling Insects: Toxicity of Macrocyclic Lactones to Dung Beetles: Review Article. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2015, 82, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, K.A.; Jensen, G.G.; Schneider, M.K.; Fenner, K.; Halling-Sørensen, B. Analysis of the Dissipation Kinetics of Ivermectin at Different Temperatures and in Four Different Soils. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohde, M.; Blanckenhorn, W.U.; Floate, K.D.; Lahr, J.; Lumaret, J.-P.; Römbke, J.; Scheffczyk, A.; Tixier, T.; Düring, R.-A. Analysis and Dissipation of the Antiparasitic Agent Ivermectin in Cattle Dung under Different Field Conditions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, R.A.; Matheson, J.C. Environmental Assessment of Avermectins by the US Food and Drug Administration. Vet. Parasitol. 1993, 48, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoud, D.; McCarthy, A.; Dubetz, C.; Barker, D.E. The Effects of Emamectin Benzoate or Ivermectin Spiked Sediment on Juvenile American Lobsters (Homarus americanus). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, I.M.; Gillibrand, P.A.; McHenery, J.G.; Rae, G.H. Environmental Risk of Ivermectin to Sediment Dwelling Organisms. Aquaculture 1998, 163, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navrátilová, M.; Raisová Stuchlíková, L.; Moťková, K.; Szotáková, B.; Skálová, L.; Langhansová, L.; Podlipná, R. The Uptake of Ivermectin and Its Effects in Roots, Leaves and Seeds of Soybean (Glycine max). Molecules 2020, 25, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vokřál, I.; Michaela, Š.; Radka, P.; Jiří, L.; Lukáš, P.; Dominika, S.; Kateřina, L.; Barbora, S.; Lenka, S. Ivermectin Environmental Impact: Excretion Profile in Sheep and Phytotoxic Effect in Sinapis Alba. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuchlíková, L.R.; Skálová, L.; Szotáková, B.; Syslová, E.; Vokřál, I.; Vaněk, T.; Podlipná, R. Biotransformation of Flubendazole and Fenbendazole and Their Effects in the Ribwort Plantain (Plantago lanceolata). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhansová, L.; Navrátilová, M.; Skálová, L.; Moťková, K.; Podlipná, R. The Effect of the Manure from Sheep Treated with Anthelmintics on Clover (Trifolium pratense). Agronomy 2021, 11, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laber, L.; Eichberg, C.; Zimmerbeutel, A.; Düring, R.-A.; Donath, T.W. Effects of Macrocyclic Lactone Anthelmintics on Seed Germination of Temperate Grassland Species. Plant Biol. 2023, 25, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laber, L.; Jandowsky, A.; Frölich, K.; Heinrich, A.P.; Düring, R.-A.; Donath, T.W.; Eichberg, C. Dose-Dependent in Vivo Effects of Formulated Moxidectin on Seedling Emergence of Temperate Grassland Species. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laber, L.; Donath, T.W.; Junck, J.; Düring, R.-A.; Eichberg, C. Competition Moderates Impact of Anthelmintic-Contaminated Soil on Growth and Fitness of Temperate Grassland Species. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 968, 178786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navrátilová, M.; Raisová Stuchlíková, L.; Skálová, L.; Szotáková, B.; Langhansová, L.; Podlipná, R. Pharmaceuticals in Environment: The Effect of Ivermectin on Ribwort Plantain (Plantago lanceolata L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 31202–31210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, L.E.; Junco, M.; Lifschitz, A.L.; Sallovitz, J.M.; Saumell, C.A. An Environmental Concern: Uptake of Ivermectin from Growing Substrate to Plant Species. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2022, 11, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrožová, L.; Sládeček, F.X.J.; Zítek, T.; Perlík, M.; Kozel, P.; Jirků, M.; Čížek, L. Lasting Decrease in Functionality and Richness: Effects of Ivermectin Use on Dung Beetle Communities. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 321, 107634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandara, L.; Jacoby, R.; Laurent, F.; Spatuzzi, M.; Vlachopoulos, N.; Borst, N.O.; Ekmen, G.; Potel, C.M.; Garrido-Rodriguez, M.; Böhmert, A.L.; et al. Pervasive Sublethal Effects of Agrochemicals on Insects at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations. Science 2024, 386, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Gong, P.; Wu, K. Life Table Studies of the Cotton Bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), on Different Host Plants. Environ. Entomol. 2004, 33, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Bentivenha, J.P.F.; Paula-Moraes, S.V.; Baldin, E.L.L.; Specht, A.; da Silva, I.F.; Hunt, T.E. Battle in the New World: Helicoverpa armigera versus Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capinera, J.L. Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). EDIS 2002, 2002, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubiales, D.; Fernández-Aparicio, M.; Moral, A.; Barilli, E.; Sillero, J.C.; Fondevilla, S. Disease Resistance in Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Types for Autumn Sowings in Mediterranean Environments. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2009, 45, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smýkal, P.; Aubert, G.; Burstin, J.; Coyne, C.J.; Ellis, N.T.H.; Flavell, A.J.; Ford, R.; Hýbl, M.; Macas, J.; Neumann, P.; et al. Pea (Pisum sativum L.) in the Genomic Era. Agronomy 2012, 2, 74–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubiales, D.; Fondevilla, S.; Chen, W.; Gentzbittel, L.; Higgins, T.J.V.; Castillejo, M.A.; Singh, K.B.; Rispail, N. Achievements and Challenges in Legume Breeding for Pest and Disease Resistance. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2015, 34, 195–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.S. Host-Feeding and Egg Maturation by Pachycrepoideus vindemiae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1993, 69, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.S.B.D.; Price, B.E.; Soohoo-Hui, A.; Walton, V.M. Factors Affecting the Biology of Pachycrepoideus vindemmiae (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae), a Parasitoid of Spotted-Wing Drosophila (Drosophila Suzukii). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, M.D.W.; Skorupa, D.; Partridge, L. Diet, Metabolism and Lifespan in Drosophila. Exp. Gerontol. 2005, 40, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergs, A.; Baden, C.U. A Dynamic Energy Budget Approach for the Prediction of Development Times and Variability in Spodoptera frugiperda Rearing. Insects 2021, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcott, P.H.; Raymond, O.; Fatig, I. Inhibition of Chitin Metabolism by Avermectin in Susceptible Organisms. J. Antibiot. 1984, 37, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachendorff, U.; Koellen, A. Production of chitin in insect cell-lines. Mitt. Dtsch. Ges. Allg. Angew. Entomol. 1987, 5, 211–215. [Google Scholar]
- Halley, B.A.; Jacob, T.A.; Lu, A.Y.H. The Environmental Impact of the Use of Ivermectin: Environmental Effects and Fate. Chemosphere 1989, 18, 1543–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, N.; Bachmann, J.; Blanckenhorn, W.U.; Floate, K.D.; Jensen, J.; Römbke, J. Effects of Ivermectin Application on the Diversity and Function of Dung and Soil Fauna: Regulatory and Scientific Background Information. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1914–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, N.-F.; Fu, L.; Dainese, M.; Kiær, L.P.; Hu, Y.-Q.; Xin, F.; Goulson, D.; Woodcock, B.A.; Vanbergen, A.J.; Spurgeon, D.J.; et al. Pesticides Have Negative Effects on Non-Target Organisms. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Change in Weight | Days to Pupation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DF | MQ | F | p | MQ | F | p | |
| Ivermectin concentration (IVM) | 5 | 29,794.3 | 17.8 | ≤0.0001 | 14.1 | 10.7 | ≤0.0001 |
| Sex (S) | 1 | 201.8 | 0.1 | 0.73 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.52 |
| IVM × S | 5 | 2353.3 | 1.4 | 0.23 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 0.26 |
| Error | 102 | 1674.2 | 1.3 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laber, L.; Blüthgen, N.; Mody, K. Direct and Indirect Effects of Ivermectin on Phytophagous, Frugivorous and Parasitoid Insects. Insects 2025, 16, 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040366
Laber L, Blüthgen N, Mody K. Direct and Indirect Effects of Ivermectin on Phytophagous, Frugivorous and Parasitoid Insects. Insects. 2025; 16(4):366. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040366
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaber, Lars, Nico Blüthgen, and Karsten Mody. 2025. "Direct and Indirect Effects of Ivermectin on Phytophagous, Frugivorous and Parasitoid Insects" Insects 16, no. 4: 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040366
APA StyleLaber, L., Blüthgen, N., & Mody, K. (2025). Direct and Indirect Effects of Ivermectin on Phytophagous, Frugivorous and Parasitoid Insects. Insects, 16(4), 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040366







