Population Genetics, Demographic History, and Potential Distributions of the New Important Pests Monolepta signata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on Corn in China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
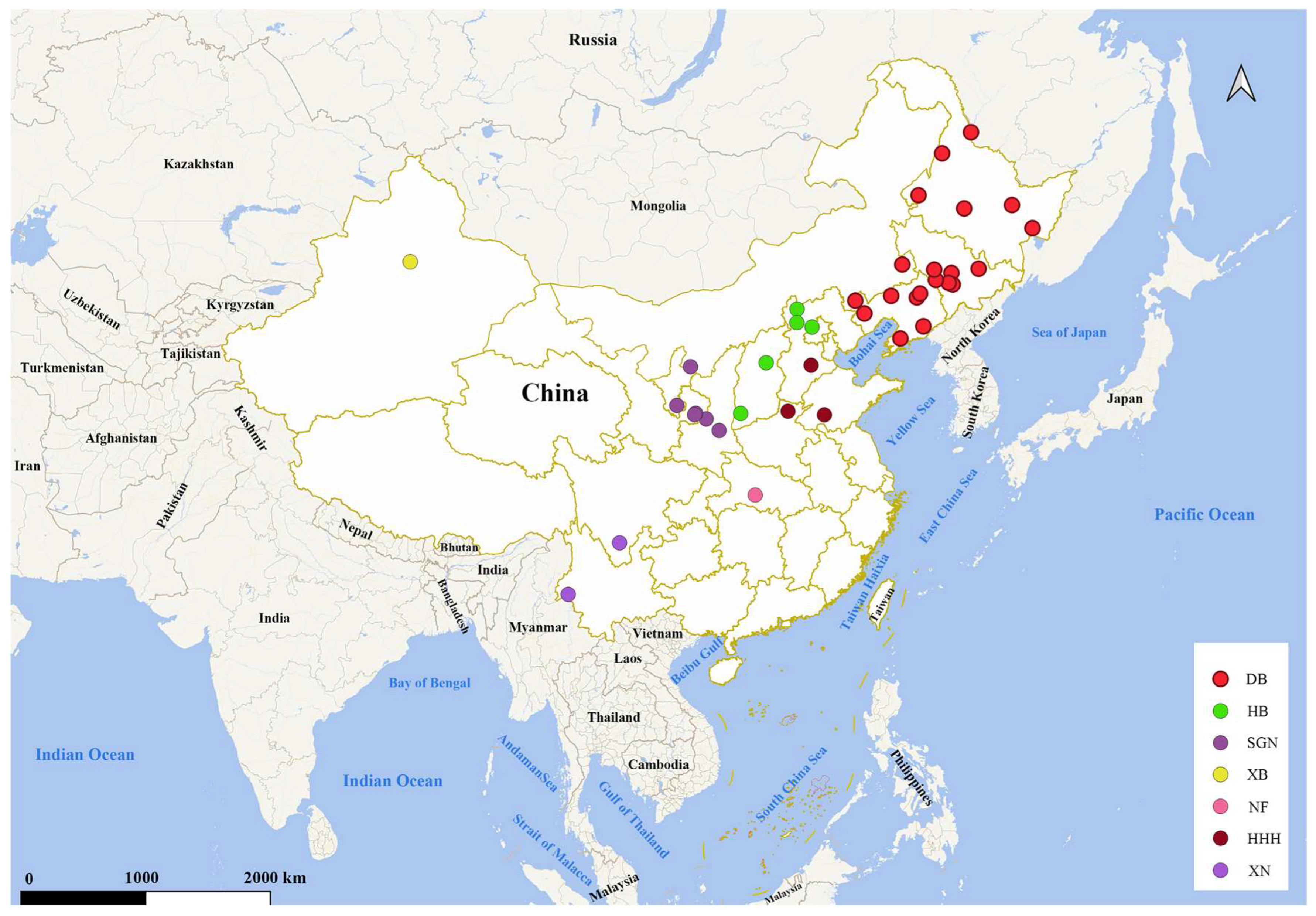
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Genetic Diversity and Historical Dynamics Analysis
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Divergence Time Analysis
2.6. Potential Distribution of M. signata
3. Results
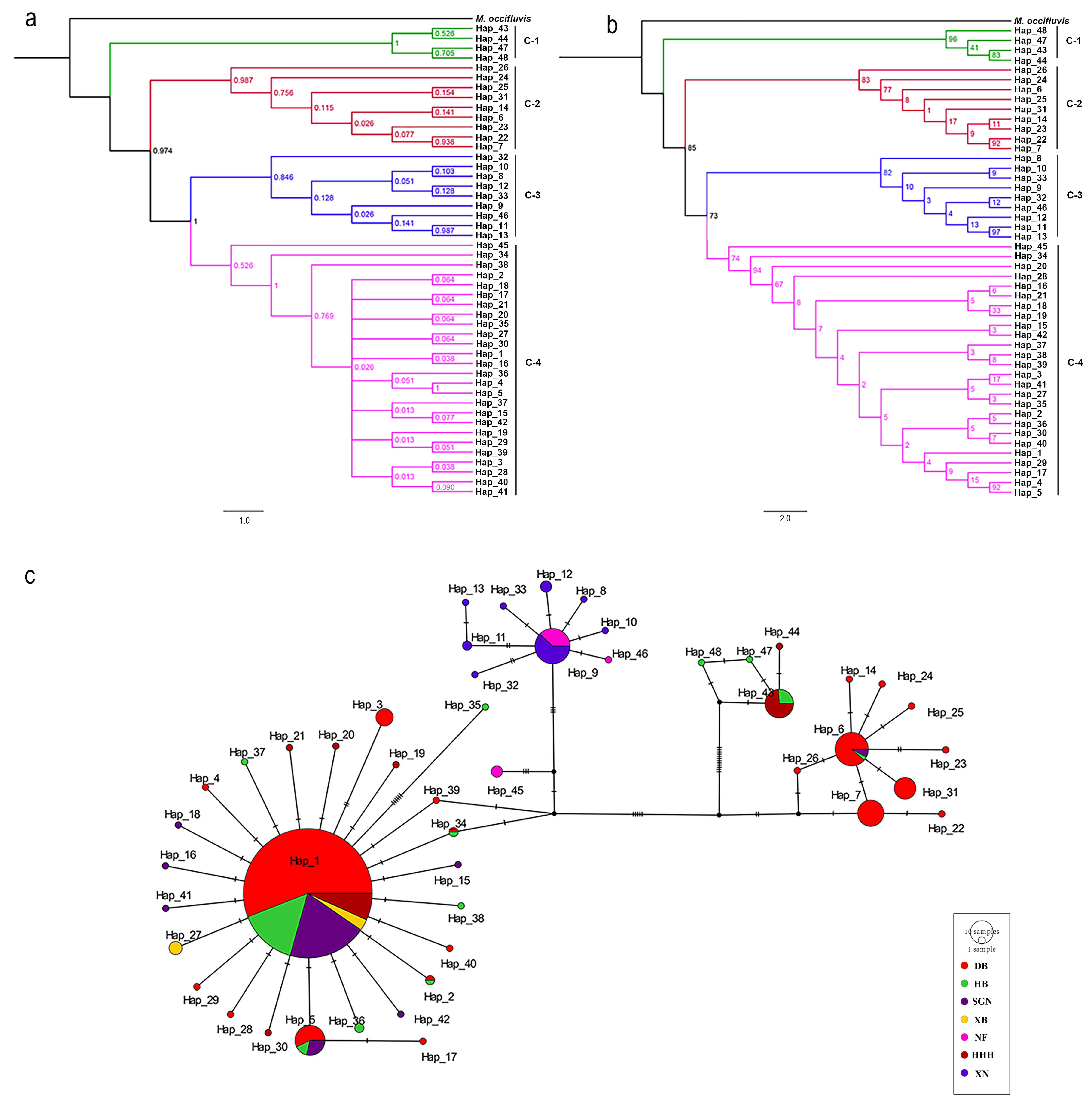
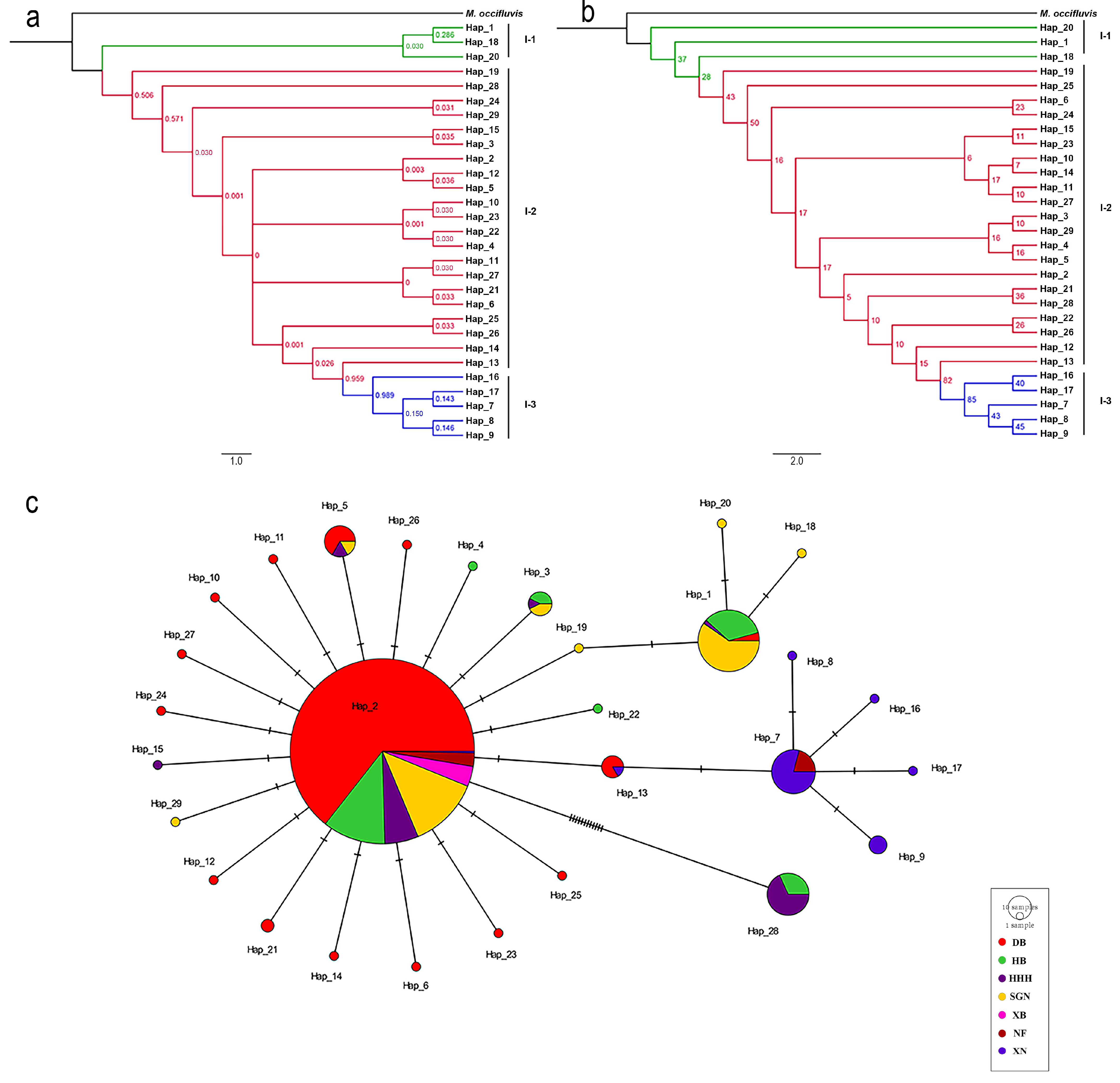
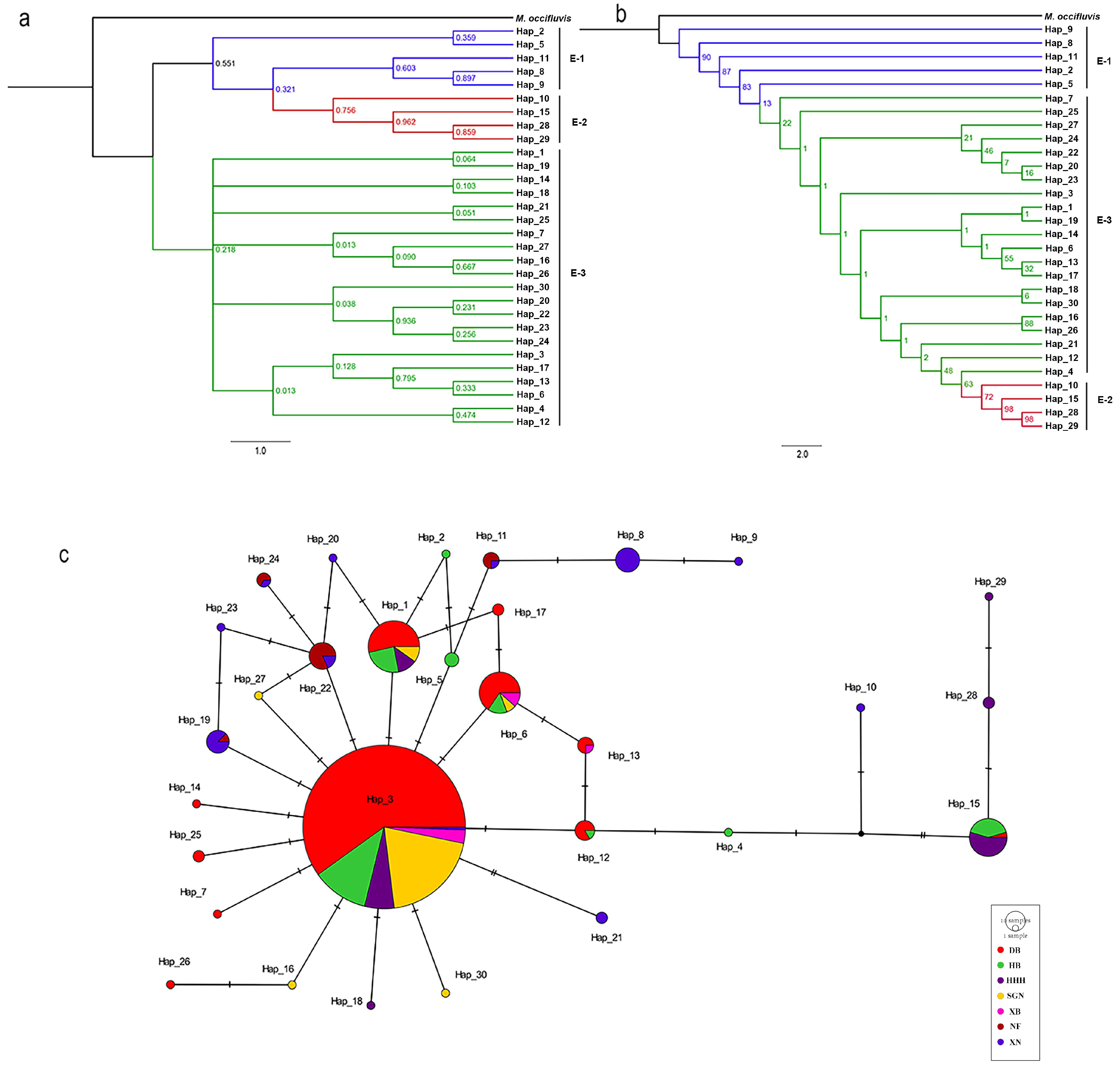
3.1. Genetic Structure
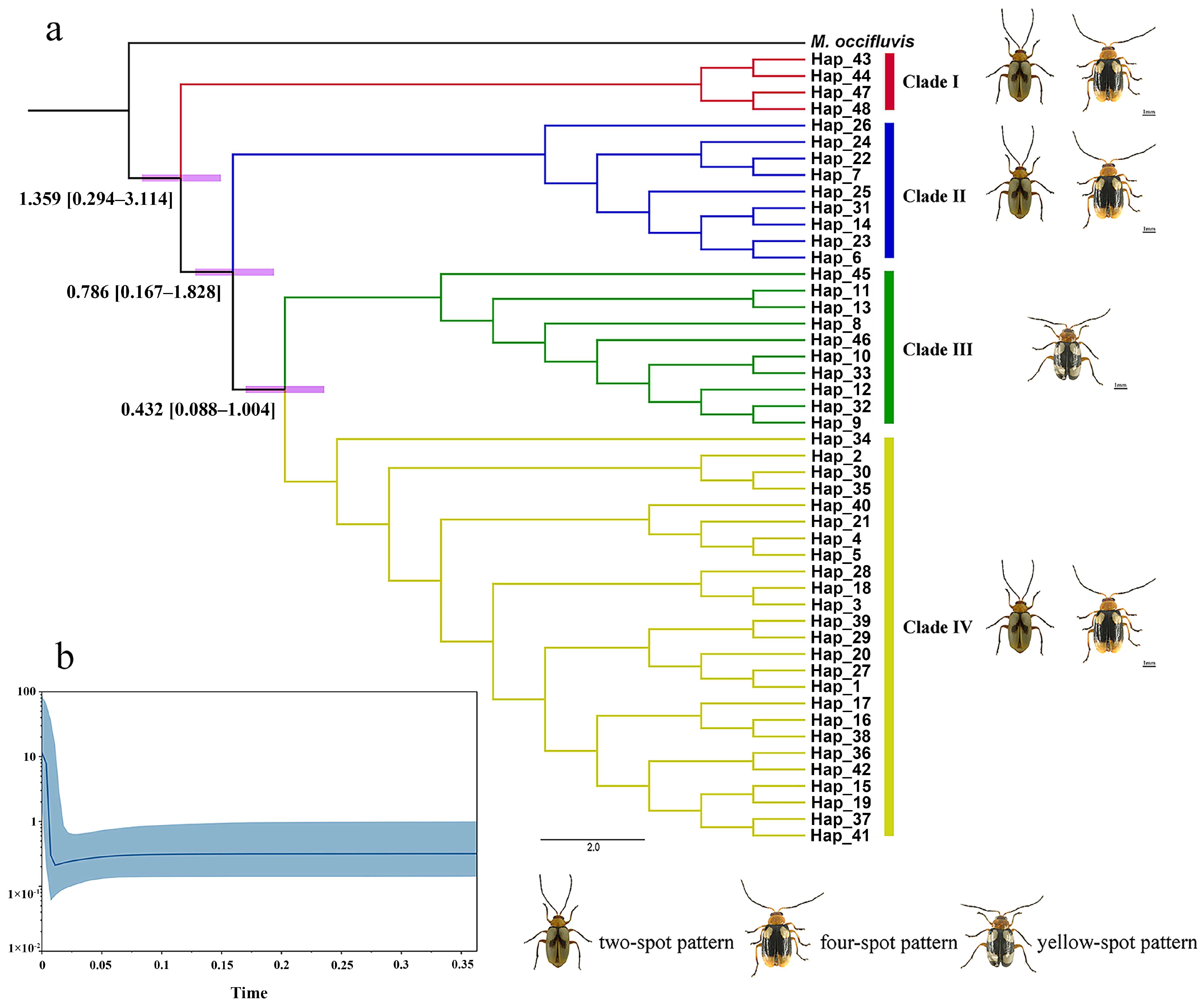
3.2. Phylogenetic Analyses
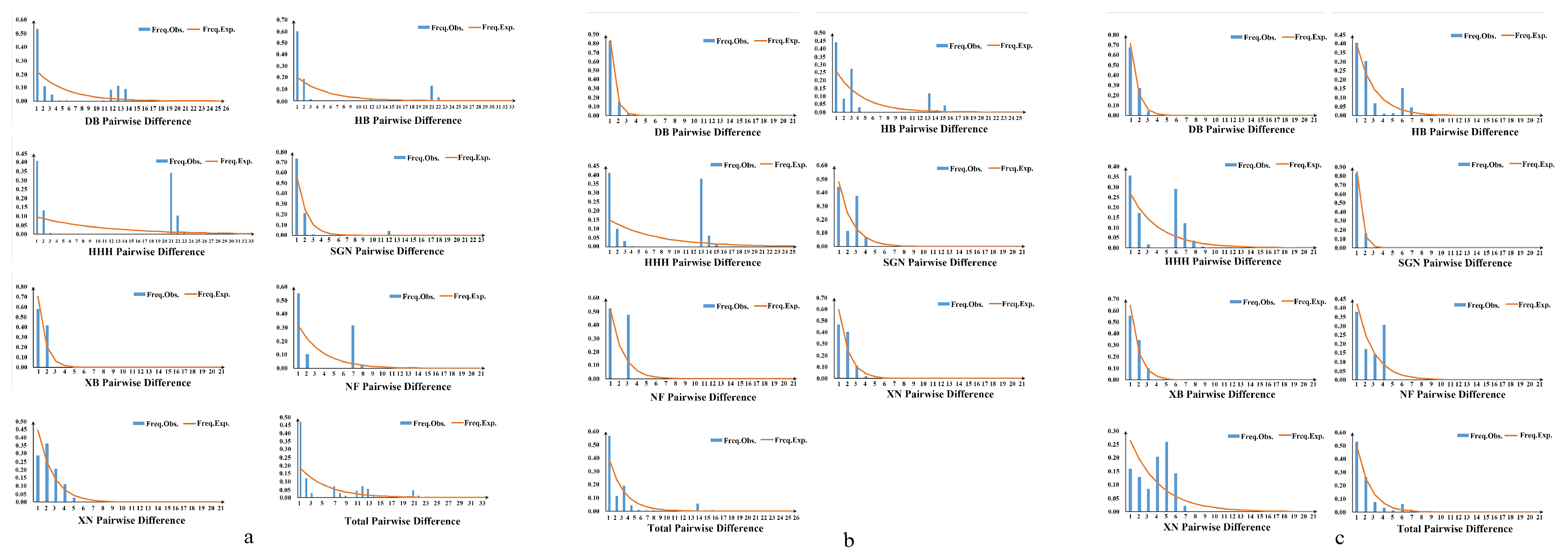
3.3. Population Genetic Analysis
3.4. Divergence Time and Historical Demographic Reconstruction
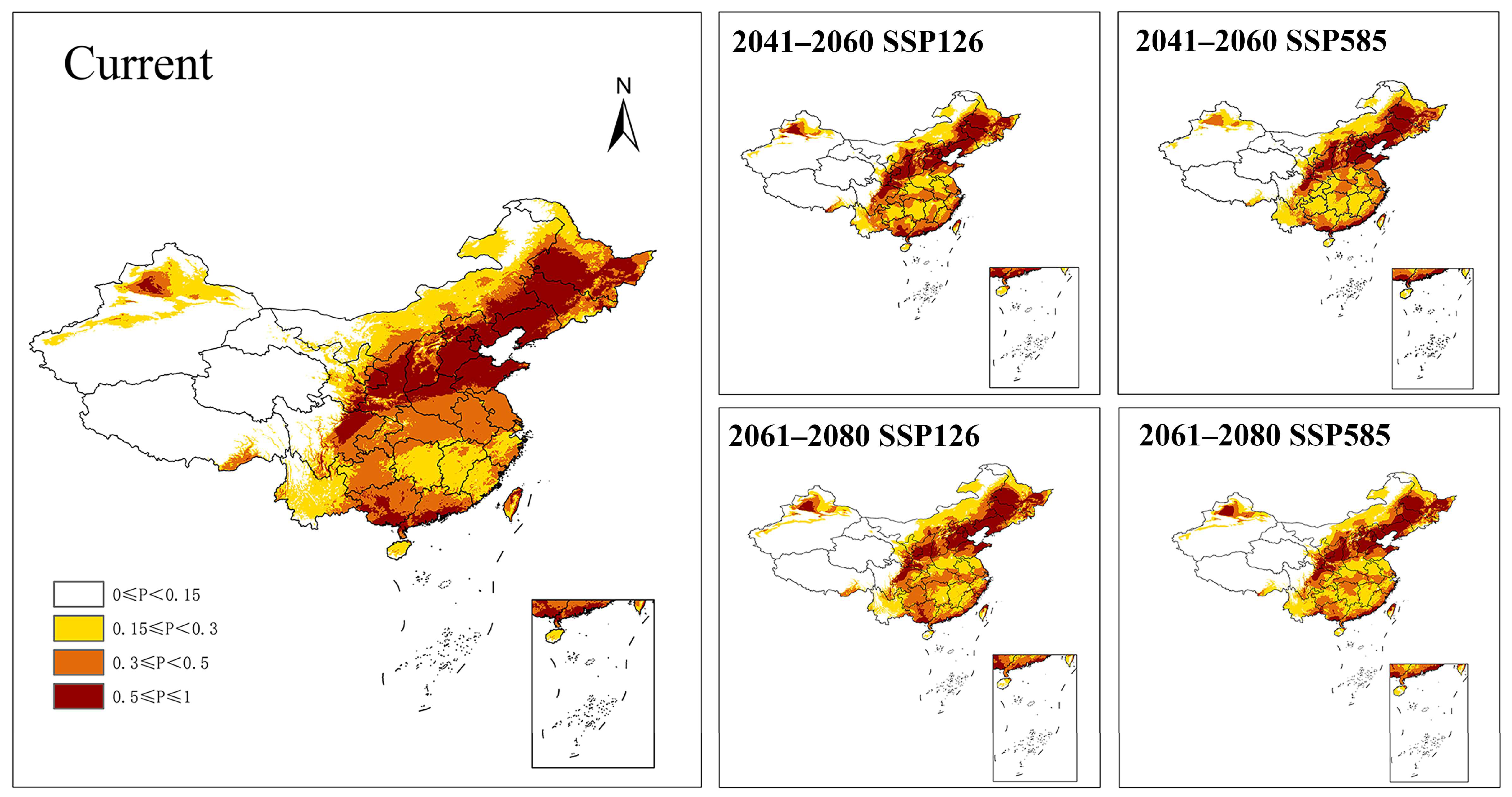
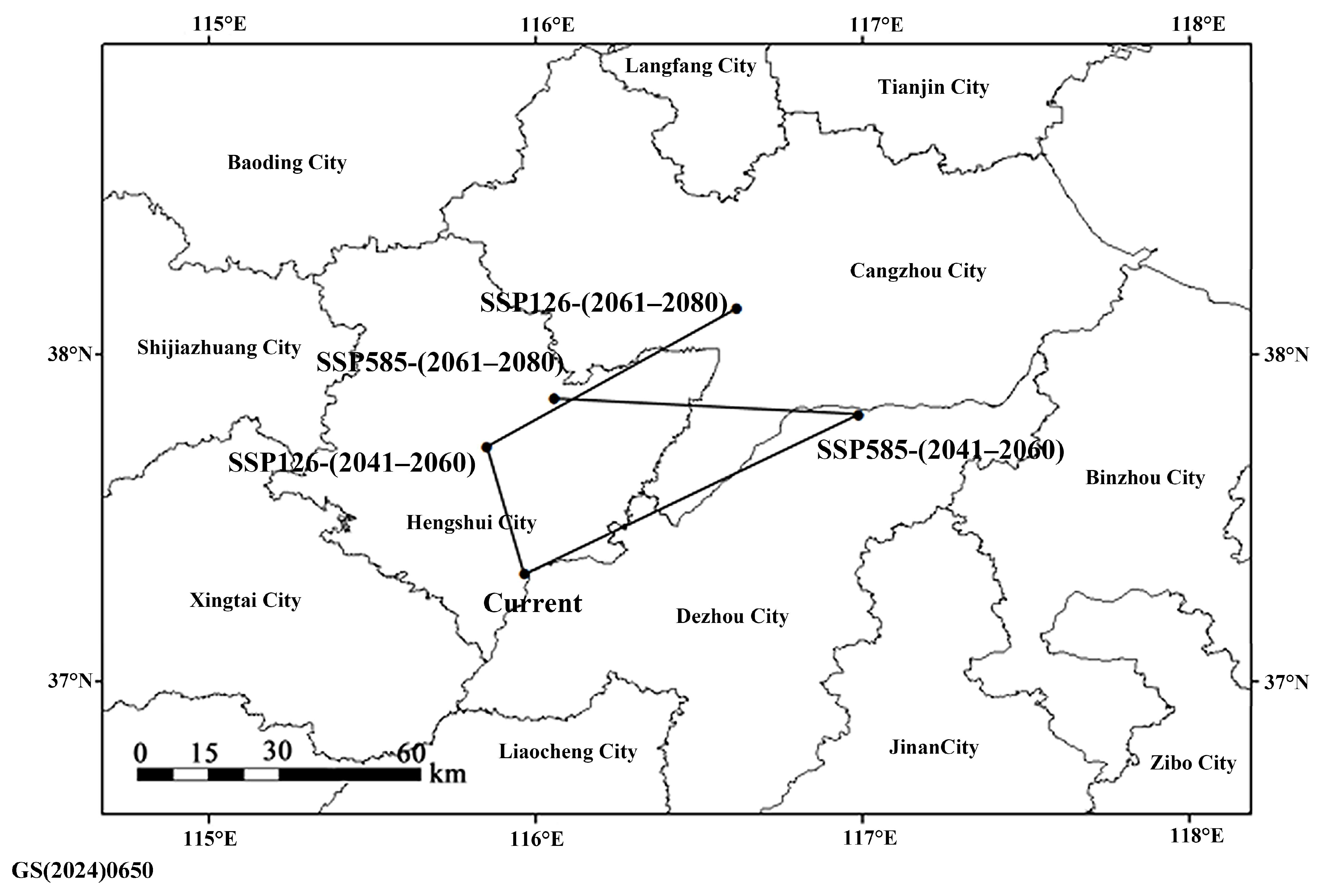
3.5. Potential Distribution Prediction
4. Discussion
4.1. Mitochondrial–Nuclear Discordance in Phylogenetic Resolution of M. signata
4.2. Phenotypic Variation and Phylogeographic Patterns
4.3. Mitochondrial–Nuclear Discordance and Demographic History
4.4. Genetic Differentiation and Gene Flow Barriers
4.5. Human Impacts and Host-Associated Differentiation
4.6. Environmental Constraints and Future Distribution
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Y.; Xu, W.; Shi, S.S.; Cui, J.; Xu, B. A list of the host plants of the Monolepta hieroglyphica. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2017, 56, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.X.; Chen, J. Effects of brief exposure to high temperature on free amino acids, total sugar and trehalose of female adult Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky). Plant Prot. 2018, 44, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.R.; Liu, B.X.; Fu, H. Occurrence, damage and control measures of the leaf beetle of the long-tarsometatarsus in maize field. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2006, 2, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.R.; Liu, B.X.; Fu, H. Occurrence, damage and control of Monolepta hieroglyphica in maize field. China Agric. Technol. Promot. 2006, 22, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Zhao, W.Q. Analysis the causes and control measures of corn northern leaf blight and Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky) insect pest. China Agric. Inf. 2013, 25, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L. Occurrence trend and cause analysis of summer corn diseases and insect pests in Huang-Huai-Hai area. Plant Prot. 2005, 5, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.M.; Xu, Z.; Guo, J.F.; Wang, L.D.; Luo, B.J.; Wang, L.X.; Li, Q.C.; Liu, Y.; Han, Y.H.; Wang, Z.Y. Influences of damaged silks by Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky) on corn yield. Plant Prot. 2021, 47, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H. A research on laws of host selection migration and optimum period of chemical to Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky). Master’s Thesis, Jilin Agricultural University, Jilin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.W. Occurrence and control of Monolepta hieroglyphica in cotton fields in Shihezi General Field of Xinjiang Corps. China Cotton 2014, 41, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Guan, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, A.; Wen, H. Negligible transcriptome and metabolome alterations in RNAi insecticidal maize against Monolepta hieroglyphica. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Yang, X.K. Economic Insect Fauna of China. In Coleoptera: Chrysomeloidea (II); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1996; Volume 54, p. 166. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, P.K. Seasonal diversity with incidence and damage of insect pests in groundnut under red and laterite zone of West Bengal. Environ. Ecol. 2004, 22, 565–570. [Google Scholar]
- Neupane, F.P.; Sharma, M.D.; Neupane, K.R. Incidence of insect pests on chaoyote, Sechium edule (Swartz.) in Nepal. J. Inst. Agric. Anim. Sci. 2006, 27, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharjee, P.; Mandal, S.K. Pest complex of some summer season flowers in West Bengal. Environ. Ecol. 2008, 26, 2385–2389. [Google Scholar]
- Boopathi, T. Influence of weather factors on the population dynamics of chewing pests of lowland paddy. Indian J. Entomol. 2012, 74, 329–335. [Google Scholar]
- Boopathi, T.; Singh, S.B.; Manju, T.; Dutta, S.K.; Saha, S.; Singh, A.R.; Ramakrishna, Y.; Chowdhury, S.; Lungmuana, D.V.; Ngachan, S.V. Effect of weather factors on the population of Chaetocnema spp., Monolepta signata Oliver and Aulacophora foveicollis (Lucas) on paddy under rainfed lowland conditions in Mizoram, India. J. Agrometeorol. 2017, 19, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, L.K.; Das, P.; Mohanasundaram, A.; Saikia, R.; Islam, A.N. A comprehensive study on pest complex of Flemingia spp. from Jorhat, Assam. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 506–511. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.L.; Wang, D.M.; Wang, B.F.; Song, X.Y. Genome survey and mitochondrial genome analysis of Monolepta hieroglyphica. J. Environ. Insects 2019, 41, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Yin, W.; Li, Q.; Hu, H. Research progress on Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky). China Plant Prot. 2016, 36, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, R.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L.; Cong, B.; Li, J. Genetic diversity of geographic populations of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) from North China estimated by mitochondrial COII gene sequences. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2011, 54, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.F.; Xu, L.L.; Shen, Y.Y.; Li, X.X.; Wang, Z.Y. Genetic structure and Wolbachia infection in geographical populations of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in South China. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2021, 64, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.M.; Liu, Z.Y.; Yang, Q.Y. Reasons for the Severe Occurrence of Monolepta hieroglyphica in Corn Fields in Chencang District, Baoji City and Control Countermeasures. J. Agric. 2009, 4, 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.M.; Liu, Y.; Tan, K.F.; Chai, L.L. Occurrence Situation and Control Measures of Monolepta hieroglyphica in Maize Field. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci. 2011, 6, 51–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M.; Zhao, B.J.; Liu, Q.R. Occurrence Regularity and Control Method of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky) in Corn Field in Xinxiang Country. J. Agric. Catastrophology 2015, 5, 3–4+14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.S.; Yang, F.J.; Qu, M.J.; Wang, S.L.; Li, X.; Gao, H.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Zhu, X.M.; Du, L. Investigation on harmful biology species and their occurrence and damage to peanut in Jilin. J. Peanut Sci. 2017, 46, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.S.; Wang, X.Q.; Tian, J.; Gao, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhu, S.Y. Occurrence regularity and economic threshold of Monolepta hieroglyphica adults in soybean fields. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2017, 39, 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, X.M. Current status and management strategies for corn pests and diseases in China. Plant Prot. 2019, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q. Study on Biological Characteristics and Control Strategy of Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky). Master’s Thesis, Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural Reclamation University, Heilongjiang, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Cui, J.; Wu, L.; Xu, W.; Chen, B.C.; Shi, S.S. Screening of Pesticides for Controlling Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky). Agrochemicals 2014, 53, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.H.; Zhou, K.D.; Yu, Y.F.; Peng, L.Y.; Ye, Y.X.; Lin, C.Y.; Xu, C.; Shen, Z.C. RNAi-based transgenic maize to control double-spotted leaf beetle (Monolepta hieroglyphica). Pest Manag. Sci. 2025, 81, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.C.; Shi, C.M.; Bai, M.; Cao, Z.Y.; Cao, L.P.; Wang, Z.Y.; Dong, J.G.; Wang, Y.Y. Molecular data confirm Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky, 1858) and M. quadriguttata (Motschulsky, 1860) being synonyms of M. signata (Oliver, 1808). Insect Syst. Evol. 2023, 54, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satsuki, T.; Naoki, S.; Ryutei, I.; Ryohei, N.; Yoshihisa, A.; Katsutoshi, W. Environmental DNA phylogeography: Successful reconstruction of phylogeographic patterns of multiple fish species from cups of water. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2023, 23, 1050–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.T.; Lu, M.X.; Du, Y.Z. Molecular phylogeography and evolutionary history of the pink rice borer (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): Implications for refugia identification and pest management. Syst. Entomol. 2022, 47, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shi, Q.; Liu, D.G.; Yang, Y.J.; Shang, Z.M. Genetic Divergence of Two Sitobion avenae Biotypes on Barley and Wheat in China. Insects 2020, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, S.; Ciplak, B. Phylogeography and taxonomy of the Psorodonotus caucasicus (Orthoptera, Tettigoniidae) group: Independent double invasion of the Balkans from the Caucasus: Phylogeography and taxonomy of the Psorodonotus caucasicus group. Syst. Entomol. 2017, 42, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.F.; Chen, Z.; Cao, L.M.; Tadashi, I.; Satoshi, K.; Teiji, S.; Song, F.; Li, T.; Cai, W.Z.; et al. Global phylogeography and invasion history of the spotted lanternfly revealed by mitochondrial phylogenomics. Evol. Appl. 2021, 14, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zou, X.; Yuan, F.; Luo, Y.; Shi, J. Predicting the current and future distribution of Monochamus carolinensis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) based on the maximum entropy model. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 5393–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, Q.D.; Heller, K.G.; Zhou, Z.J.; Shi, F.M. Phylogenetic relationships and phylogeography of the genus Sinocyrtaspis Liu, 2000 (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae: Meconematinae) reveal speciation processes related to climate change. Syst. Entomol. 2020, 45, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.J.; Tay, W.T.; McGaughran, A.; Gordon, K.; Walsh, T.K. Population structure and gene flow in the global pest, Helicoverpa armigera. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 5296–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Penton, E.H.; Burns, J.M.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W. Ten species in one: DNA barcoding reveals cryptic species in the neotropical skipper butterfly Astraptes fulgerator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14812–14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombaert, E.; Guillemaud, T.; Thomas, C.E.; Handley, L.J.L.; Estoup, A. Inferring the origin of populations introduced from a genetically structured native range by approximate Bayesian computation: Case study of the invasive ladybird Harmonia axyridis. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 4654–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Sun, J.T.; Xue, X.F.; Li, J.B.; Hong, X.Y.; Crandall, K.A. Invasion genetics of the western flower thrips in China: Evidence for genetic bottleneck, hybridization and bridgehead effect. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, K.; Chakraborty, R.; Cameron, S.L.; Sweet, A.D.; Kumar, V. Rearrangement and evolution of mitochondrial genomes in Thysanoptera (Insecta). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.Z.; Wu, K.M. Genetic diversity and demographic history of globe skimmers (Odonata: Libellulidae) in China based on microsatellite and mitochondrial DNA markers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrich, L.; Pons, J.; Ribera, I.; Michael, B.; Carles, L.F. Mitochondrial cox1 sequence data reliably uncover patterns of insect diversity but suffer from high lineage-idiosyncratic error rates. PLoS ONE 2017, 5, e14448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobelmann, J.; Alexander, A.; Baty, J.W.; Gemmell, N.J.; Lesterv, P.J. The association between mitochondrial genetic variation and reduced colony fitness in an invasive wasp. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 3324–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, T.; Sugita, N.; Someya, S.; Iwami, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Kamigaichi, H.; Higuchi, A.; Asai, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nishiumi, I. DNA barcoding reveals 24 distinct lineages as cryptic bird species candidates in and around the Japanese Archipelago. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. Study on Genetic Diversity and Molecular Phylogenetic Relationships of Partial Species in Nymphalidae in China. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gallego, D.; Galián, J. The internal transcribed spacers (ITS1 and ITS2) of the rDNA differentiates the bark beetle forest pests Tomicus destruens and T. piniperda. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 10, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Pan, J.Y.; Wang, X.Z.; Zhou, S.S.; Zhang, G.Q.; Tang, L.H. Species identification of Anopheles maculatus complex in malaria endemic area Motuo County, Tibet. Insect Mol. Biol. 2008, 26, 286–289. [Google Scholar]
- Mukha, D.; Wiegmann, B.M.; Schal, C. Evolution and phylogenetic information content of the ribosomal DNA repeat unit in the Blattodea (Insecta). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.S.; Tang, L.H.; Gu, Z.C.; Wang, Y. Sequence difference of ribosomal DNA second internal transcribed spacer in Anopheles minimus in different localities. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2002, 20, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, D.R.; Zhang, H.R.; Li, Z.R.; Dong, K.; He, S.Y. Genetic diversity and population expansion in different geographic populations of Frankliniella occidentalis in Yunnan, China. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2011, 48, 504–512. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, S.; Anand, N.; Purcell, D.; Lee, J. Not just for housekeeping: Protein initiation and elongation factors in cell growth and tumorigenesis. J. Mol. Med. 2003, 81, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, I.R.; Emerson, B.C.; Borges, P.A.V.; Wayne, R.K. Phylogeography and molecular phylogeny of Macaronesian island Tarphius (Coleoptera: Zopheridae): Why are there so few species in the Azores? Phylogenetics and diversification of Azorean Tarphius. J. Biogeogr. 2012, 39, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letsch, H.; Balke, M.; Toussaint, E.F.A.; Riedel, A. Historical biogeography of the hyperdiverse hidden snout weevils (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Cryptorhynchinae). Syst. Entomol. 2020, 45, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Dong, W.W.; Jiang, G.F.; Hong, F.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, W.W. Analysis of the genetic differentiation among geographical populations of Luehdorfia chinensis chinensis (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae) based on mitochondrial gene and nuclear genes. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2020, 63, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar]
- QGIS Development Team. QGIS Geographic Information System, Version 3.28; Open Source Geospatial Foundation: Beaverton, OR, USA, 2023; Available online: https://www.qgis.org (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Timmermans, M.; Dodsworth, S.; Culverwell, C.; Bocak, L.; Ahrens, D.; Littlewood, D.; Pons, J.; Vogler, A.P. Why barcode? High-throughput multiplex sequencing of mitochondrial genomes for molecular systematics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 28, e197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swigoňová, Z.; Kjer, K.M. Phylogeny and host-plant association in the leaf beetle genus Trirhabda LeConte (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2004, 32, 358–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.J.; Li, W.Z.; Nie, R.E.; Yang, X.K. Recent speciation in three closely related sympatric specialists: Inferences using multi-locus sequence, post-mating isolation and endosymbiont data. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.Q. Vector NTI, a balanced all-in-one sequence analysis suite. Brief. Bioinform. 2004, 5, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajima, F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 1997, 147, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, A.; Anastasiou, I.; Vogler, A.P. Revisiting the insect mitochondrial molecular clock: The mid-aegean trench calibration. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.L.; Ivan, J.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An inteegrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Molecuar Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von, H.A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree; Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2009; Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- Warren, D.L.; Glor, R.E.; Turelli, M. ENMTools: A toolbox for comparative studies of environmental niche models. Ecography 2010, 33, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscarella, R.; Galante, P.J.; Soley-Guardia, M.; Boria, R.A.; Kass, J.M.; Uriarte, M.; Anderson, R.P. ENMeval: An R package for conducting spatially independent evaluations and estimating optimal model complexity for MAXENT ecological niche models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.L. SDM toolbox: A python-based GIS toolkit for landscape genetic, biogeographic and species distribution model analyses. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, V.A.; Lobo, J.M. Threshold criteria for conversion of probability of species presence to either-or presence-absence. Acta Oecologica 2007, 31, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avise, J.C. Phylogeography: The History and Formation of Species; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Funk, D.J.; Omland, K.E. Species-level paraphyly and polyphyly: Frequency, causes, and consequences, with insights from animal mitochondrial DNA. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2003, 34, 397–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, Y.; Sota, T. Population genetic structure underlying the geographic variation in beetle structural colour with multiple transition zones. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, E. Population, Species, and Evolution: An Abridgment of Animal Species and Evolution; Belknap Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.J.; Chen, X.X. Progress in research on the comparative mitogenomics of insects. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2011, 48, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Avise, J.C.; Neigel, J.E.; Arnold, J. Demographic influences on mitochondrial DNA lineage survivorship in animal populations. J. Mol. Evol. 1984, 20, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.R.; Harpending, H. Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1992, 9, 552–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avise, J.C.; Arnold, J.; Ball, R.M.; Bermingham, E.; Lamb, T.; Neigel, J.E.; Reeb, C.A.; Saunders, N.C. Intraspecific phylogeography: The mitochondrial DNA bridge between population genetics and systematics. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1987, 18, 489–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birky, C.W.; Fuerst, P.; Maruyama, T. Organelle gene diversity under migration, mutation, and drift: Equilibrium expectations, approach to equilibrium, effects of heteroplasmic cells, and comparison to nuclear genes. Genetics 1989, 121, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, J.W.O.; Whitlock, M.C. The incomplete natural history of mitochondria. Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.M.; George, M., Jr.; Wilson, A.C. Rapid evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 1967–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.Z.; Li, J.B.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, G.J. Preliminary studies on two-spotted leaf beetle, Monolepta hieroglyphica on cotton. Plant Prot. 2007, 1, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Slatkin, M. Gene flow and selection in a cline. Genetics 1973, 81, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vialatte, A.; Dedryver, C.A.; Simon, J.C.; Galman, M.; Plantegenest, M. Limited genetic exchanges between populations of an insect pest living on uncultivated and related cultivated host plants. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.W.; Chen, X.L. Investigation and study on the living habits and dynamics of the growth and decline of the long-tarsal beetle in Xinjiang cotton region. China Plant Prot. 2010, 30, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Han, X.Q. Effects of high temperature stress on the total protein and two protective enzymes of adults of the tarsal beetle. J. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 40, 440–445. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.M.; Zheng, X.; Wang, L.X.; Yang, D.B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.D.; Li, Q.C.; Wang, Z.Y. Control effect of seed coating agents against Monolepta hieroglyphica (Motschulsky) in corn fields. Plant Prot. 2021, 48, 337–341+348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandweiss, D.H.; Maasch, K.A.; Anderson, D.G. Climate and culture-Transitions in the mid-Holocene. Science 1999, 283, 499–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B. Genetic Structure, Suitability and Demographic History of Scythropus yasumatsui Populations in China. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Lin, H.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu, X. Impact of climate change on cotton growth and yields in Xinjiang, China. Field Crops Res. 2020, 247, 107590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ning, S.; Hu, X.; Yuan, S. Growth and yield response and water use efficiency of cotton under film-mulched drip irrigation to magnetized ionized water and bacillus subtilis in saline soil in Xinjiang. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Population Code | Haplotype Diversity (Hd) | Nucleotide Diversity (π) | Average Number of Nucleotide Differences (k) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COI | ||||
| DB | 0.467 | 0.005 | 3.616 | |
| HB | 0.420 | 0.006 | 3.918 | |
| HHH | 0.593 | 0.013 | 9.358 | |
| SGN | 0.265 | 0.001 | 0.720 | |
| XB | 0.419 | 0.001 | 0.419 | |
| NF | 0.543 | 0.003 | 2.324 | |
| XN | 0.712 | 0.002 | 1.238 | |
| Total | 0.526 | 0.006 | 4.237 | |
| ITS2 | ||||
| DB | 0.171 | 0.000 | 0.192 | |
| HB | 0.559 | 0.007 | 2.870 | |
| HHH | 0.590 | 0.014 | 5.719 | |
| SGN | 0.561 | 0.003 | 1.080 | |
| XB | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| NF | 0.476 | 0.002 | 0.952 | |
| XN | 0.532 | 0.002 | 0.677 | |
| Total | 0.433 | 0.004 | 1.591 | |
| EF-1α | ||||
| DB | 0.325 | 0.001 | 0.409 | |
| HB | 0.595 | 0.003 | 1.563 | |
| HHH | 0.643 | 0.005 | 2.691 | |
| SGN | 0.189 | 0.000 | 0.197 | |
| XB | 0.448 | 0.001 | 0.552 | |
| NF | 0.619 | 0.003 | 1.371 | |
| XN | 0.841 | 0.005 | 2.788 | |
| Total | 0.472 | 0.002 | 1.026 |
| Gene | Source of Variation | d.f. | Sum of Squares | Variance Components | Percentage of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COI | among populations | 6 | 298.476 | 0.75918 Va | 30.75 |
| within populations | 561 | 958.970 | 1.70939 Vb | 69.25 | |
| total | 567 | 1257.445 | 2.46857 | ||
| ITS2 | among populations | 6 | 127.046 | 0.32550 Va | 36.01 |
| within populations | 561 | 324.526 | 0.57848 Vb | 63.99 | |
| total | 567 | 451.572 | 0.90398 | ||
| EF-1α | among populations | 6 | 52.872 | 0.13262 Va | 23.97 |
| within populations | 561 | 236.038 | 0.42075 Vb | 76.03 | |
| total | 567 | 288.910 | 0.55336 |
| Population Code | COI | ITS2 | EF-1α | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tajima’s D Test | Fu’s Fs Test | Tajima’s D Test | Fu’s Fs Test | Tajima’s D Test | Fu’s Fs Test | |
| DB | −0.511 | −1.887 | −2.245 * | −26.425 * | −1.756 * | −9.543 * |
| HB | −0.811 | 0.992 | −0.513 | 3.403 | 0.224 | −0.741 |
| HHH | 1.914 | 8.077 | 1.497 | 6.584 | 0.878 | 2.111 |
| SGN | −2.249 * | −3.556 * | −0.198 | −1.882 | −1.574 * | −4.741 * |
| XB | 0.742 | 0.909 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −0.268 | −0.248 |
| NF | 0.063 | 2.996 | 1.443 | 2.520 | 0.368 | 0.376 |
| XN | −1.982 * | −7.460 * | −1.628 * | −4.386 * | −0.044 | −2.844 |
| ALL | −1.412 * | −21.491 * | −1.869 * | −17.613 * | −1.681 * | −26.827 * |
| Period | Scenario | Area (×104 km2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginally Suitable Region | Moderately Suitable Region | Highly Suitable Region | ||
| Present | - | 192.80 | 195.86 | 148.59 |
| 2041–2060 | SSP126 | 193.03 (+0.12%) | 183.54 (−6.29%) | 136.48 (−8.15%) |
| SSP585 | 218.07 (+13.11%) | 165.48 (−15.51%) | 126.49 (−14.87%) | |
| 2061–2080 | SSP126 | 210.60 (+9.24%) | 182.67 (−6.77%) | 128.60 (−13.45%) |
| SSP585 | 225.66 (+17.04%) | 168.15 (−14.15%) | 126.98 (−14.54%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wang, L.; Dong, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Population Genetics, Demographic History, and Potential Distributions of the New Important Pests Monolepta signata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on Corn in China. Insects 2025, 16, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030323
Liu Y, Ge Y, Wang L, Dong J, Wang Z, Wang Y. Population Genetics, Demographic History, and Potential Distributions of the New Important Pests Monolepta signata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on Corn in China. Insects. 2025; 16(3):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030323
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yang, Yacong Ge, Liming Wang, Jingao Dong, Zhenying Wang, and Yuyu Wang. 2025. "Population Genetics, Demographic History, and Potential Distributions of the New Important Pests Monolepta signata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on Corn in China" Insects 16, no. 3: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030323
APA StyleLiu, Y., Ge, Y., Wang, L., Dong, J., Wang, Z., & Wang, Y. (2025). Population Genetics, Demographic History, and Potential Distributions of the New Important Pests Monolepta signata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on Corn in China. Insects, 16(3), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030323









