Efficacy of Indigenous Strains of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Controlling the Eggplant Fruit and Shoot Borer Leucinodes orbonalis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Survey
2.2. Isolation of Entomopathogenic Nematodes
2.3. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Reproductive Potential
2.6. Rearing of Leucinodes Orbonalis
2.7. Laboratory Experiment
2.8. Microplot Experiment
2.9. Meteorological Data for the Experimental Area
2.10. Statistical Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Field Surveys
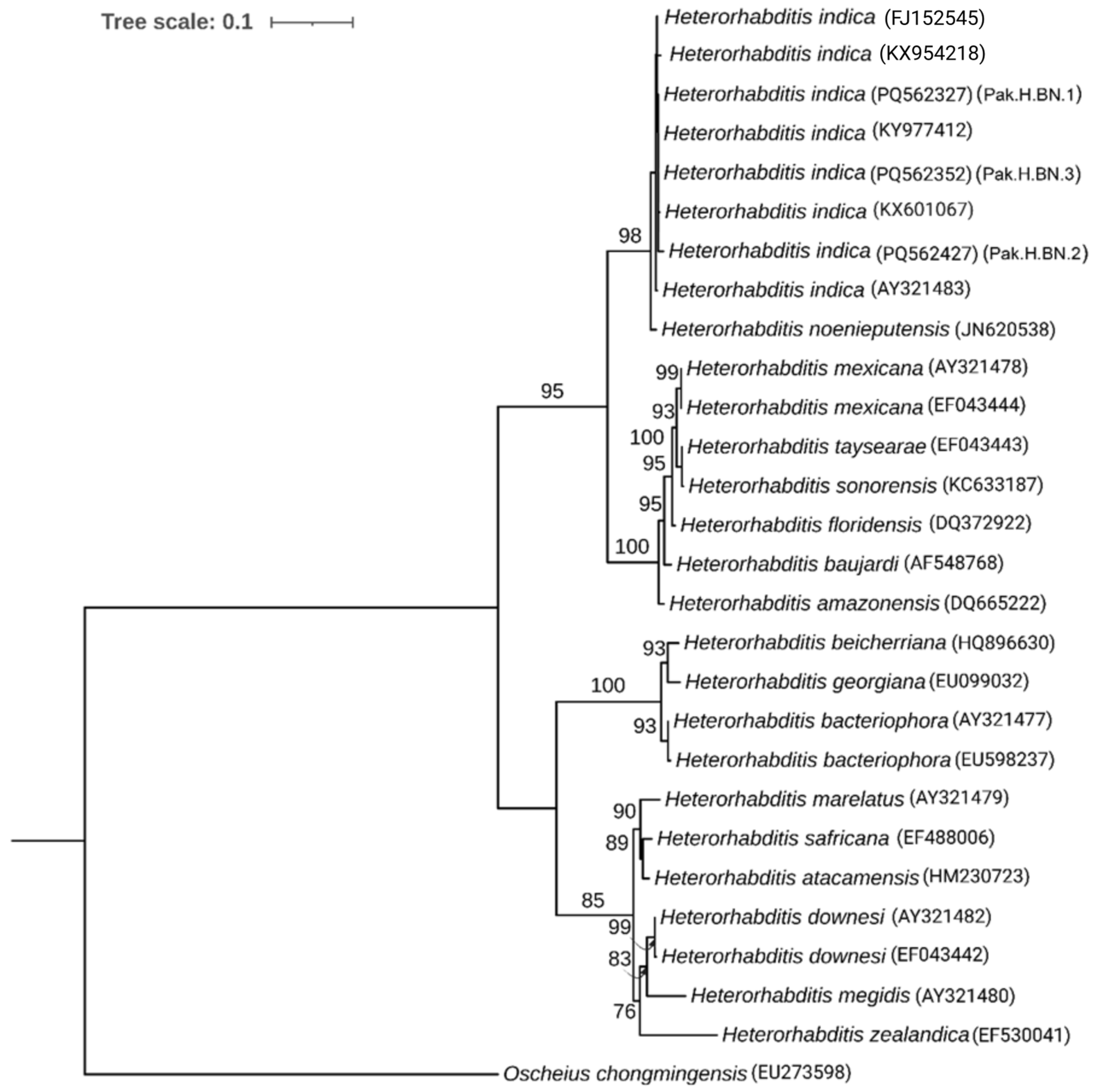
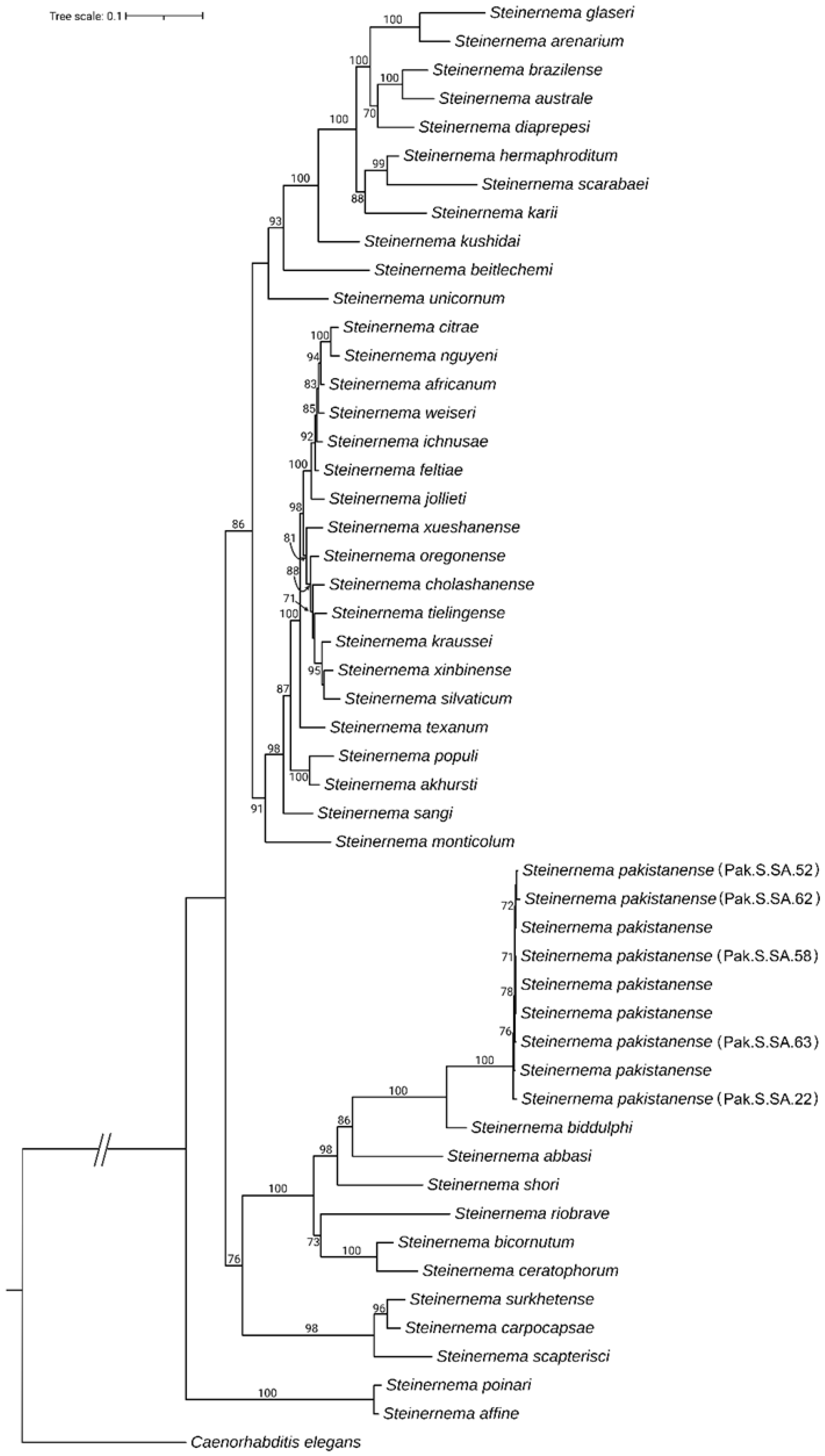
3.2. Molecular Identification and Phylogenic Analysis
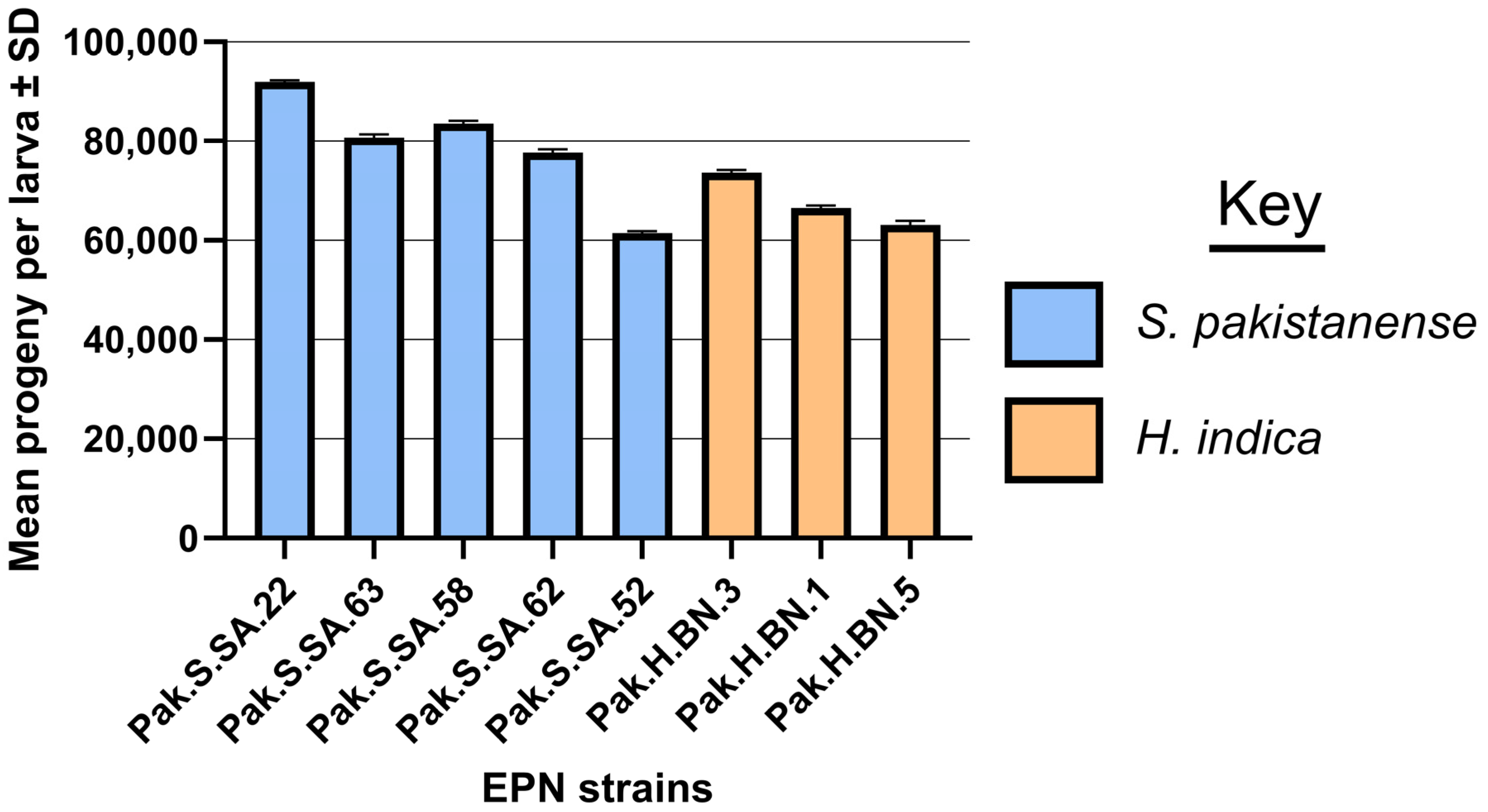
3.3. Reproductive Potential
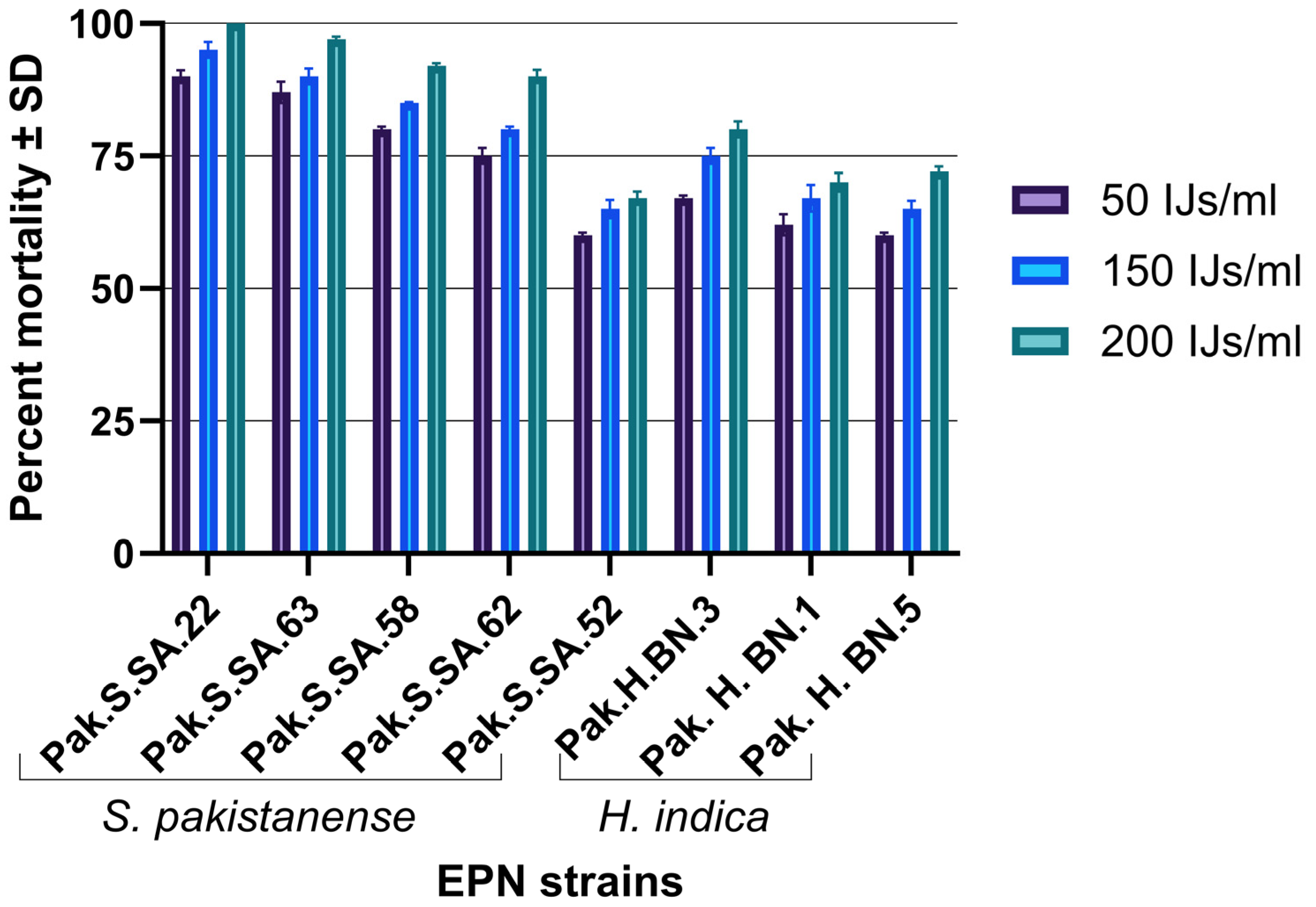
3.4. Laboratory Experiment
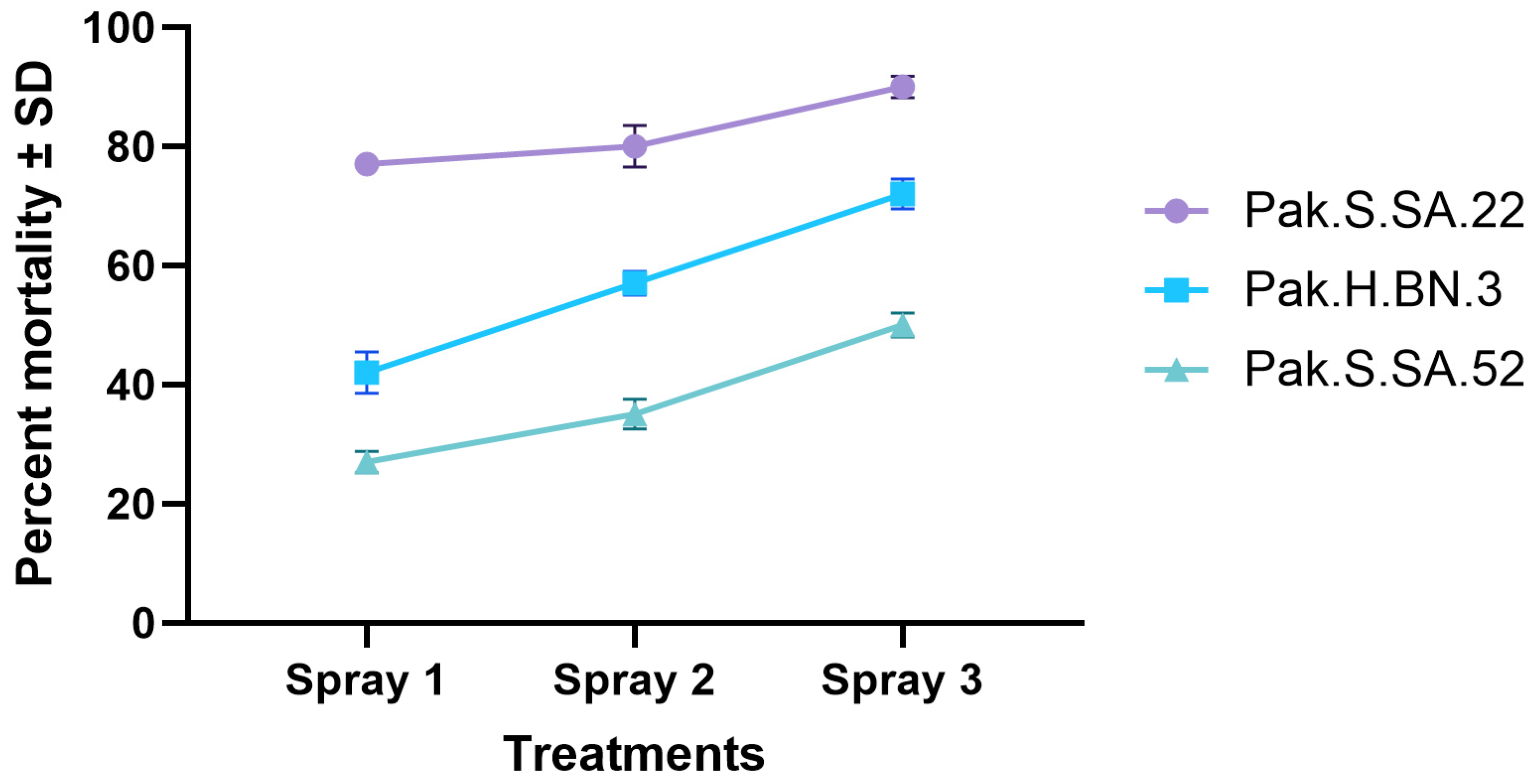
3.5. Microplot Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plazas, M.; Prohens, J.; Cuñat, A.N.; Vilanova, S.; Gramazio, P.; Herraiz, F.J.; Andújar, I. Reducing Capacity, Chlorogenic Acid Content and Biological Activity in a Collection of Scarlet (Solanum aethiopicum) and Gboma (S. macrocarpon) Eggplants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 17221–17241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylo, L.; Sison, M.L.; Hautea, D. Use of Artificial Infestation for Field Bioefficacy Assessment of Bt Eggplant against the Eggplant Fruit and Shoot Borer, Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Philipp. Agric. Sci. 2016, 99, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaliwal, G.S.; Singh, R.; Chhillar, B.S. (Eds.) Essentials of Agricultural Entomology; Kalyani Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2016; ISBN 9789327264531. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, H.; Mukhtar, T.; Javed, K.; Moshin, A. Management of Eggplant Shoot and Fruit Borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee) by Integrating Different Non-Chemical Approaches. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 54, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, D.; Pandey, R.; Dhakal, R.; Neupane, N.; Shrestha, A.; Nepali Joseph, M.; Paudel, A.; Pandey, M. Efficacy of Bio-Rational Pesticides for the Management of Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee in Rupandehi, Nepal. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, K. Probabilistic Assessment of Acute Health Symptoms Related to Pesticide Use under Intensified Nepalese Agriculture. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2008, 18, 187–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Macchietto, M.; Chang, D.; Barros, M.M.; Baldwin, J.; Mortazavi, A.; Dillman, A.R. Activated Entomopathogenic Nematode Infective Juveniles Release Lethal Venom Proteins. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengal, M.A.; Javed, S.; Majeed, S. Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Laboratory and Field Conditions of Cicer arietinum against Cotton Bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera Hübner (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest. Control 2024, 34, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, S.; Javed, S.; Rumbos, C.I.; Athanassiou, C.G. Control of Stored Grain Pests by Entomopathogenic Nematodes. In Biocontrol Agents: Entomopathogenic and Slug Parasitic Nematodes; Abd-Elgawad, M.M.M., Askary, T.H., Coupland, J., Eds.; CABI International: Wallingford, UK, 2017; pp. 208–222. ISBN 9781786390004. [Google Scholar]
- Bedding, R.; Akhurst, R. A Simple Technique for the Detection of Insect Parasitic Rhabditid Nematodes in Soil. Nematologica 1975, 21, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.K.; Patricia Stock, S. Techniques in Insect Nematology. In Manual of Techniques in Insect Pathology; Lacey, L.A., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1997; pp. 281–324. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, K.B. Methodology, Morphology and Identification. In Nematology Monograph and Perspectives: Entomopathogenic Nematodes: Systematics, Phylogeny and Bacterial Symbionts; Nguyen, K., Hunt, D., Eds.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 5, pp. 59–119. ISBN 9789047422396. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, B.J.; Peat, S.M.; Dillman, A.R. Phylogeny And Evolution. In Entomopathogenic Nematodes: Systematics, Phylogeny and Bacterial Symbionts; Nguyen, K., Hunt, D., Eds.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 5, pp. 693–733. ISBN 9789047422396. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, S.; Reid, A.; Driver, F.; Curran, J. Application of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Methods to the Identification of Entomopathogenic Nematodes. In Genetics of Entomopathogenic Nematode-Bacterium Complexes. Proceedings and National Reports 1990–1993, St. Patrick’s College, Maynooth, Co. Kildare, Ireland; Burnell, A.M., Ehlers, R.-U., Masson, J.P., Eds.; European Commission, DG XII: Luxembourg, 1994; pp. 178–187. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, K.B.; Malan, A.P.; Gozel, U. Steinernema khoisanae n. Sp. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae), a New Entomopathogenic Nematode from South Africa. Nematology 2006, 8, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Solan, N.; Pradesh, H.; Rajinder Singh Rana, I.; Chander Sharma, K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, A.; Aarti Sharma, C.; Singh Rana, R. Biology of Brinjal Shoot and Fruit Borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee) on Brinjal Crop under Laboratory Conditions. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 415–419. [Google Scholar]
- White, G.F. A Method for Obtaining Infective Nematode Larvae from Cultures. Science 1927, 66, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, D.J.; Subbotin, S.A. Taxonomy and Systematics. In Advances in Entomopathogenic Nematode Taxonomy and Phylogeny; Hunt, D.J., Nguyen, K.B., Eds.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 12, pp. 13–58. ISBN 978-90-04-28534-7. [Google Scholar]
- Grewal, P.S.; Ehlers, R.U.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I. (Eds.) Nematodes as Biocontrol Agents; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2005; ISBN 9780851990170. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elgawad, M.M.M. Status of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Integrated Pest Management Strategies in Egypt. In Biocontrol Agents: Entomopathogenic and Slug Parasitic Nematodes; Abd-Elgawad, M.M.M., Askary, T.H., Coupland, J., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2017; pp. 473–501. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Javed, S.; Khanum, T.A.; Kazi, N. Entomopathogenic Nematode (Nematoda: Rhabditida) Survey and Their Occurrence in Soil of District Lakki Marwat, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan. Punjab Uni. J. Zool. 2021, 36, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganga Visalakshy, P.N.; Krishnamoorthy, A.; Hussaini, S.S. Field Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Nematode Steinernema carpocapsae (Weiser, 1955) against Brinjal Shoot and Fruit Borer, Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee. Nematol. Mediterr. 2009, 37, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Banu, G.; Gulsarbanu, J.; Subaharan, K.; Iyer, R. Occurrence and Distribution of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in White Grub Endemic Areas. Occurrence and Distribution of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in White Grub Endemic Areas of Kerala. J. Plant Crops 2004, 32, 333–334. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elgawad, M.M.M.; Spiridonov, S.E. Entomopathogenic Nematode Application in Egypt and Russia: Challenges and Opportunities. Egypt. J. Agron. 2014, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patuwatha Withanage, D.B.M.; Briar, S.S.; Edeogu, I. Efficacy of Commercially Available Entomopathogenic Nematodes against Insect Pests of Canola in Alberta, Canada. J. Helminthol. 2024, 98, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataullah, M.; Riaz, S.; Tariq, M.; Aslam, A.; Qadir, A.; Asghar, A.; Shehzad, M.; Akhtar, M.F. In Vitro Exploration of Entomopathogenic Nematodes as Potential Biocontrol Agents of Brinjal Borer Leucinodes orbonalis Guenée (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Plant Prot. 2024, 8, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussaini, S.S.; Singh, S.P.; Nagesh, M. In Vitro and Field Evaluation of Some Indigenous Isolates of Steinernema and Heterorhabditis indica against Shoot and Fruit Borer, Leucinodes orbonalis. Indian J. Nematol. 2002, 32, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lola-Luz, T.; Downes, M.; Dunne, R. Control of Black Vine Weevil Larvae Otiorhynchus sulcatus (Fabricius) (Coleoptera:Curculionidae) in Grow Bags Outdoors with Nematodes. Agric. For. Entomol. 2005, 7, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lola-Luz, T.; Downes, M. Biological Control of Black Vine Weevil Otiorhynchus sulcatus in Ireland Using Heterorhabditis megidis. Biol. Control 2007, 40, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallet, P.; Bazagwira, D.; Ruzzante, L.; Ingabire, G.; Levivier, S.; Bustos-Segura, C.; Kajuga, J.; Toepfer, S.; Turlings, T.C.J. Entomopathogenic Nematodes as an Effective and Sustainable Alternative to Control the Fall Armyworm in Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Nexus 2024, 3, pgae122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Leite, L.G.; Han, R. Production of Entomopathogenic Nematodes. In Mass Production of Beneficial Organisms: Invertebrates and Entomopathogens; Morales-Ramos, J.A., Rojas, M.G., Shapiro-Ilan, D.I., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 293–315. ISBN 9780128221068. [Google Scholar]
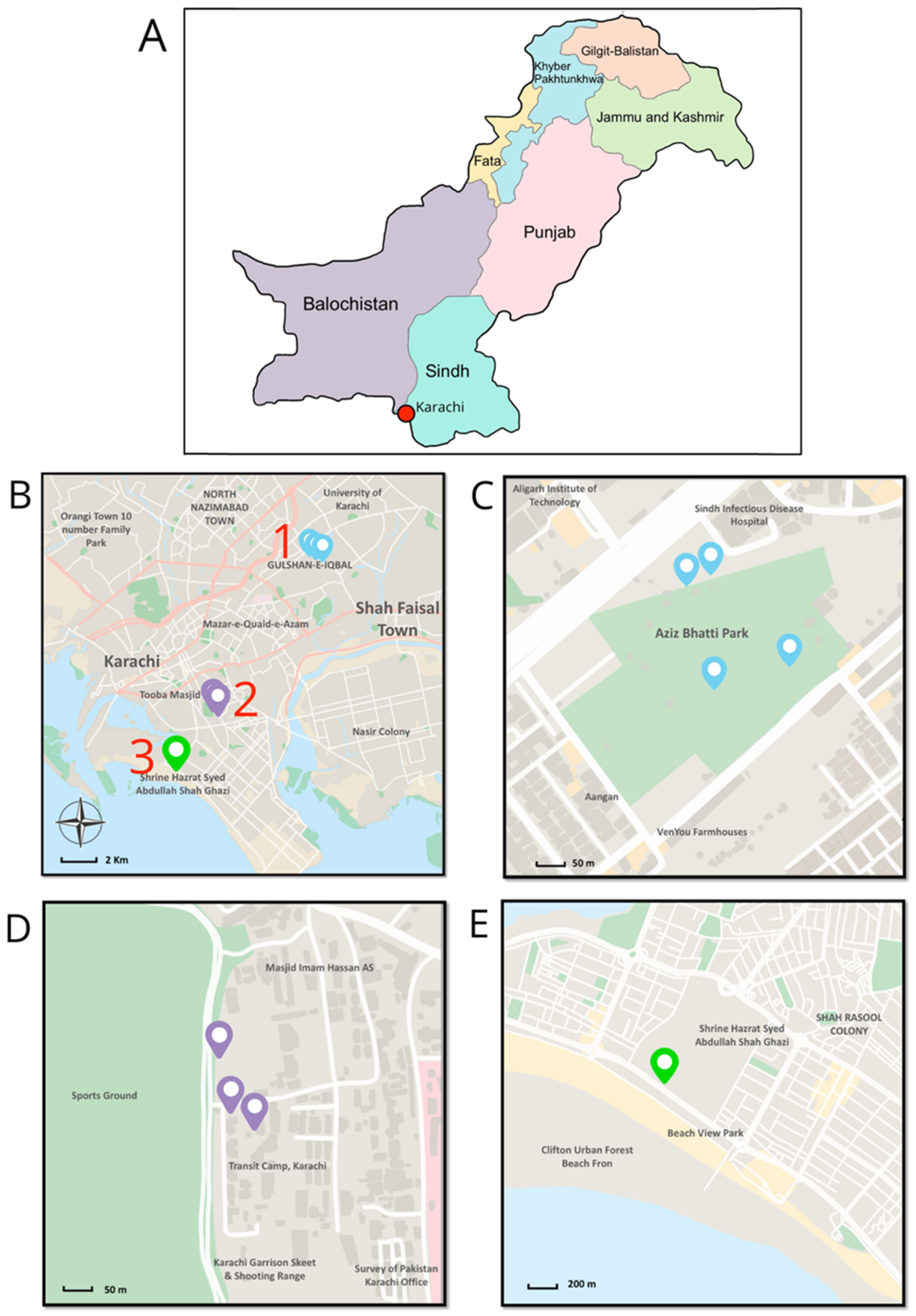
| Species Code | Vegetation | Location | GPS Coordinates | IJ Length (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pak. H. BN.1 | Zoysia japonica | Sabir Sre, DHA | 24.8388° | 528 |
| 67.0439° | (479–573) | |||
| Pak.S.SA.58 | Pongemia pinnata | Aziz Public Bhatti Park | 24.9152° | 662 |
| 67.0948° | (649–716) | |||
| Pak.H.BN.3 | Zoysia japonica | Sabir Sre, DHA | 24.8379° | 511 |
| 67.0441° | (479–573) | |||
| Pak.S.SA.62 | Conocarpus erectus | Aziz Bhatti Public Park | 24.9153° | 678 |
| 67.0952° | (649–716) | |||
| Pak.H.BN.2 | Zoysia japonica | Sabir Sre, DHA | 24.8378° | 525 |
| 67.0444° | (479–573) | |||
| Pak.S.SA.52 | Cassia fistula | Aziz Bhatti Public | 24.9139° | 663 |
| 67.0965° | (649–716) | |||
| Pak.S.SA.63 | Ficus carica | Aziz Bhatti Public Park | 24.9134° | 681 |
| 67.0953° | (649–716) | |||
| Pak.S.SA.22 | Pongemia pinnata | BAGH Ibn-E-Qasim | 24.8078° | 669 |
| 67.0225° | (649–716) |
| Nematode Species | Geographic Origin (28S) | Geographic Origin (ITS) | GenBank Accession No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28S | ITS | |||
| S. abbasi | - | Pakistan | MN533913 | EF469773 |
| S. affine | UK | Turkey | AF331899 | PP538017 |
| S. africanum | Rwanda | Rwanda | OM423154 | ON041032 |
| S. akhursti | China | China | GU395638 | DQ375757 |
| S. arenarium | Slovakia | Russia | KU194619 | KU194614 |
| S. australe | Chile | Chile | FJ235126 | FJ235125 |
| S. beitlechemi | South Africa | South Africa | KT580949 | KT373856 |
| S. bicornutum | Serbia | Yugoslavia | GU569045 | AF121048 |
| S. biddulphi | South Africa | South Africa | KT580950 | KT373857 |
| S. brazilense | Brazil | Brazil | FJ410326 | FJ410325 |
| S. carpocapsae | Colombia | Bulgaria | MK558056 | AF121049 |
| S. ceratophorum | - | China | MW029452 | AY230165 |
| S. cholashanense | China | India | EF520284 | MH065747 |
| S. citrae | South Africa | South Africa | MF540676 | FJ235074 |
| S. diaprepesi | USA | USA | GU177828 | AF122021 |
| S. feltiae | USA | USA | AF331906 | AF121050 |
| S. glaseri | USA | USA | GU177831 | AF122015 |
| S. hermaphroditum | India | India | MF693228 | MF663703 |
| S. ichnusae | Sardinia | Sardinia | EU421130 | EU421129 |
| S. jollieti | USA | USA | GU569051 | AY171265 |
| S. karii | - | Kenya | AF331902 | AY230173 |
| S. kraussei | Poland | Germany | KC631424 | AY230175 |
| S. kushidai | Japan | China | AF331897 | GQ497741 |
| S. monticolum | - | Korea | GU395647 | AF122017 |
| S. nguyeni | South Africa | South Africa | KR815816 | KP325084 |
| S. oregonense | USA | USA | GU569055 | AF122019 |
| S. pakistanense | India | India | MF289982 | MK491798 |
| S. pakistanense | India | Pakistan | MF289983 | JN157771 |
| S. pakistanense | - | - | KC625523 | GQ497273 |
| S. pakistanense | India | Pakistan | PP334013 | JX135548 |
| S. pakistanense Pak.S.SA.58 | Pakistan * | Pakistan * | PQ566940 | PQ562434 |
| S. pakistanense Pak.S. SA.62 | Pakistan * | Pakistan * | PQ566941 | PQ562435 |
| S. pakistanense Pak.S. SA.52 | Pakistan * | Pakistan * | PQ566942 | PQ562445 |
| S. pakistanense Pak.S. SA.63 | Pakistan * | Pakistan * | PQ566943 | PQ562446 |
| S. pakistanense Pak.S. SA.22 | Pakistan * | Pakistan * | PQ566944 | PQ562447 |
| S. poinari | Czech Republic | Czech Republic | KF241750 | KF241753 |
| S. populi | China | China | MZ367685 | MZ367621 |
| S. riobrave | USA | USA | GU177834 | GU174000 |
| S. sangi | India | Vietnam | MF620997 | AY355441 |
| S. scapterisci | - | Uruguay | GU395646 | AF122020 |
| S. scarabaei | USA | Chile | AY172023 | FJ263673 |
| S. shori | India | India | OR194555 | OR194554 |
| S. silvaticum | Poland | Poland | KC631426 | MG543848 |
| S. surkhetense | India | India | KU187262 | MF919614 |
| S. texanum | USA | USA | EF152569 | EF152568 |
| S. tielingense | China | China | GU994202 | GU994201 |
| S. unicornum | Chile | Chile | GU191462 | GQ497167 |
| S. weiseri | France | Czech Republic | FJ165549 | KJ696685 |
| S. xinbinense | China | China | GU994204 | JN171593 |
| S. xueshanense | China | China | FJ666053 | FJ666052 |
| Caenorhabditis elegans | - | - | X03680 | MW646314 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javed, S.; Ali, S.; Goldy, C.J.; Nawab, B.; Baniya, A.; Dillman, A.R. Efficacy of Indigenous Strains of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Controlling the Eggplant Fruit and Shoot Borer Leucinodes orbonalis. Insects 2025, 16, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030272
Javed S, Ali S, Goldy CJ, Nawab B, Baniya A, Dillman AR. Efficacy of Indigenous Strains of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Controlling the Eggplant Fruit and Shoot Borer Leucinodes orbonalis. Insects. 2025; 16(3):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030272
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaved, Salma, Sajjad Ali, Connor J. Goldy, Bushra Nawab, Anil Baniya, and Adler R. Dillman. 2025. "Efficacy of Indigenous Strains of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Controlling the Eggplant Fruit and Shoot Borer Leucinodes orbonalis" Insects 16, no. 3: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030272
APA StyleJaved, S., Ali, S., Goldy, C. J., Nawab, B., Baniya, A., & Dillman, A. R. (2025). Efficacy of Indigenous Strains of Entomopathogenic Nematodes in Controlling the Eggplant Fruit and Shoot Borer Leucinodes orbonalis. Insects, 16(3), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16030272







