Risk Assessment of RNAi-Based Potential Pesticide dsNlAtg3 and Its Homologues for Nilaparvata lugens and Non-Target Organisms
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Double-Stranded RNA Synthesis and Microinjection
2.3. Effect of RNA Interference on the Survival of N. lugens
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis Using RT-qPCR
2.5. Effect of RNAi on the Survival of Non-Target Organisms
2.6. Effect of RNAi on Natural Enemies Feeding dsRNA-Treated N. lugens
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Expression Patterns of NlATG3 Gene in N. lugens
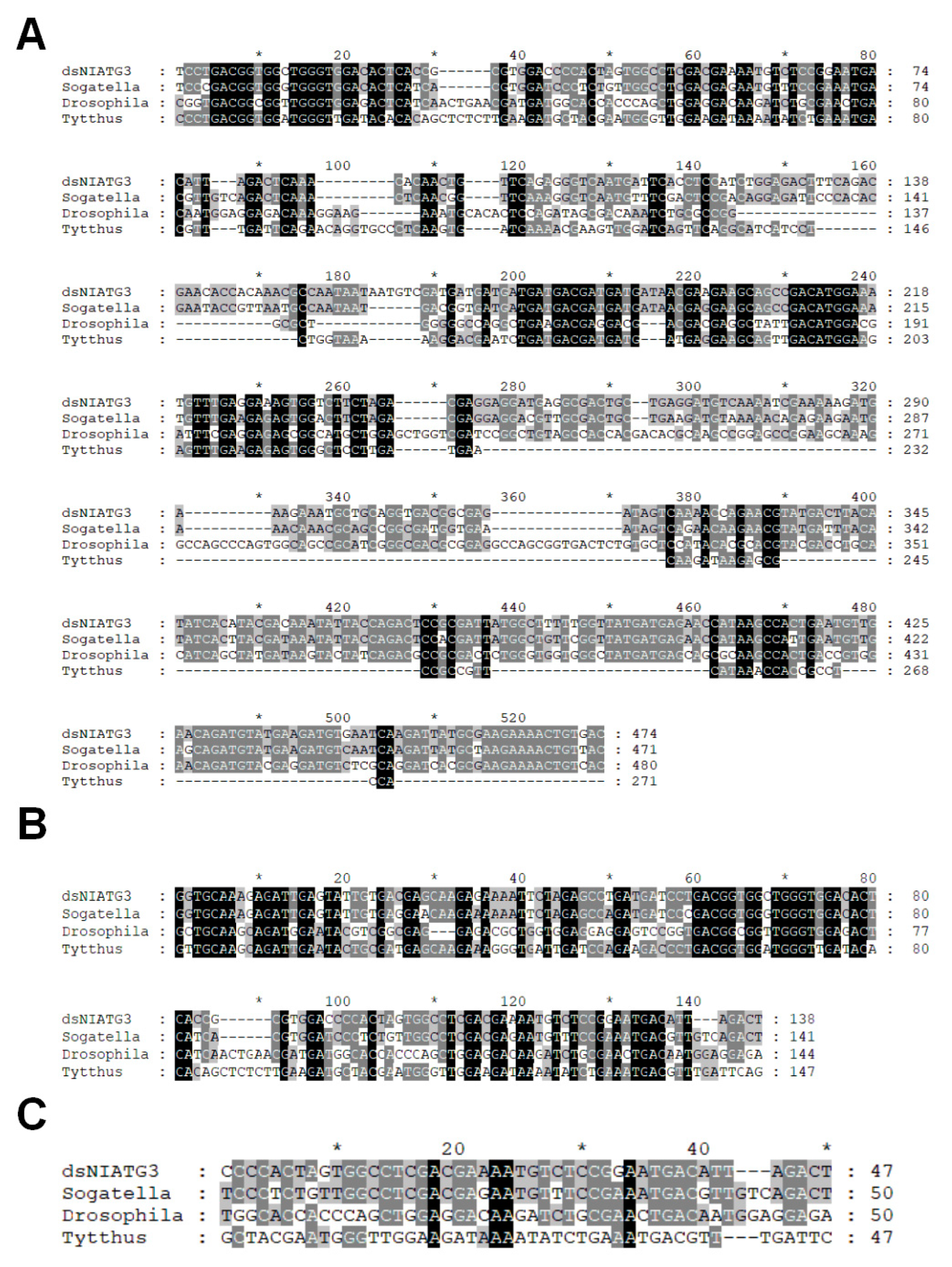
3.2. Sequence Analysis of dsNlAtg3 Fragments with Different Lengths
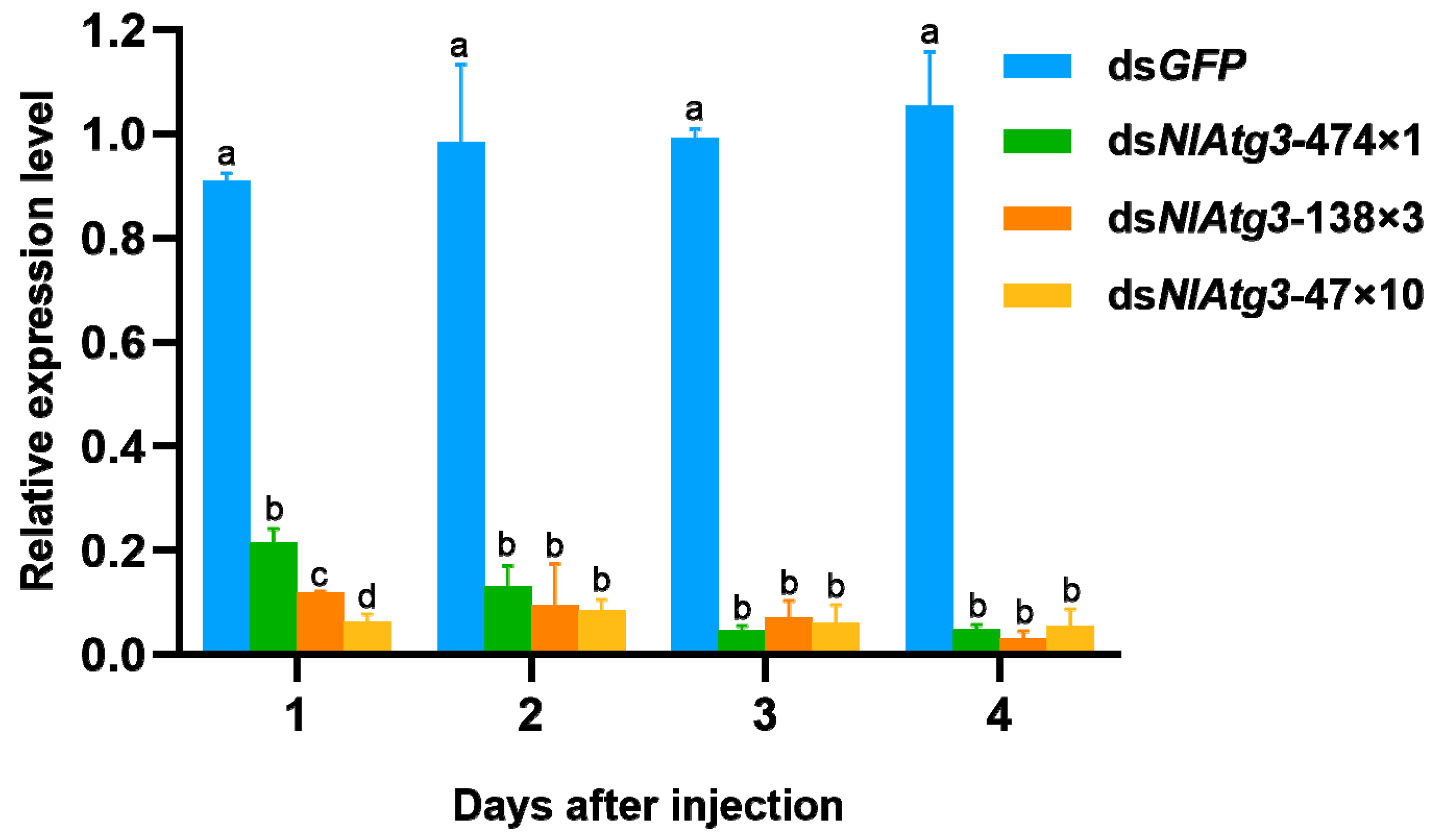
3.3. RNAi Efficiency of Different dsRNA Fragments on the Expression of NlAtg3 in N. lugens
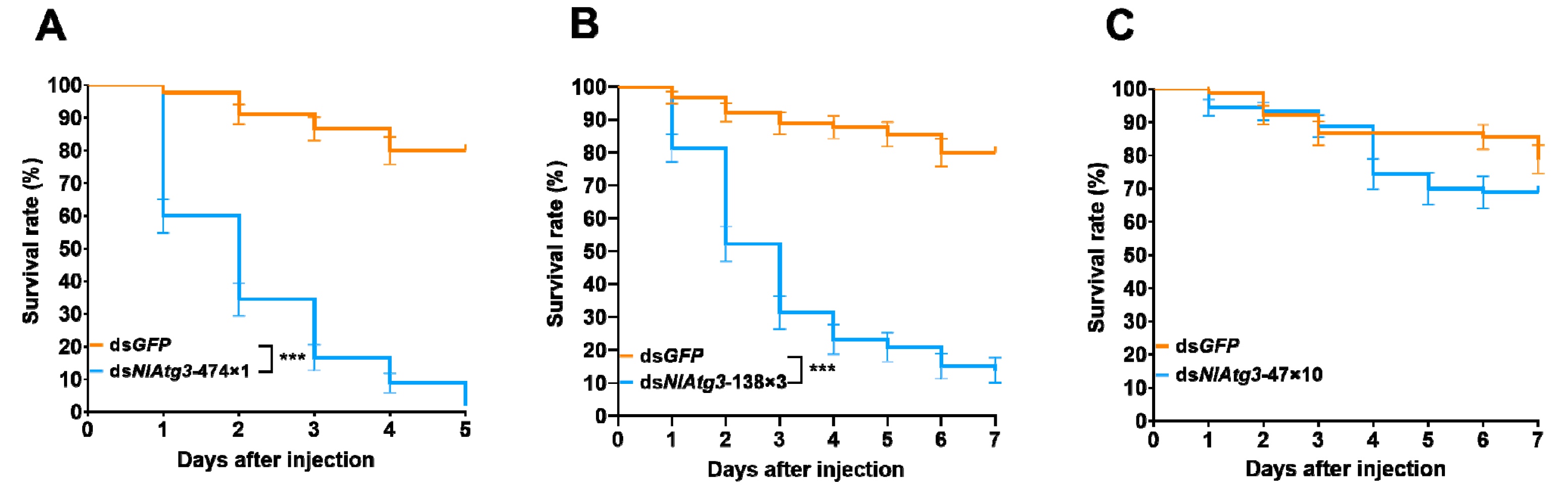
3.4. Effect of Different dsRNA Fragments on the Survival of N. lugens
3.5. Effects of Different dsNlAtg3 Fragments on the Closely Related Species S. furcifera
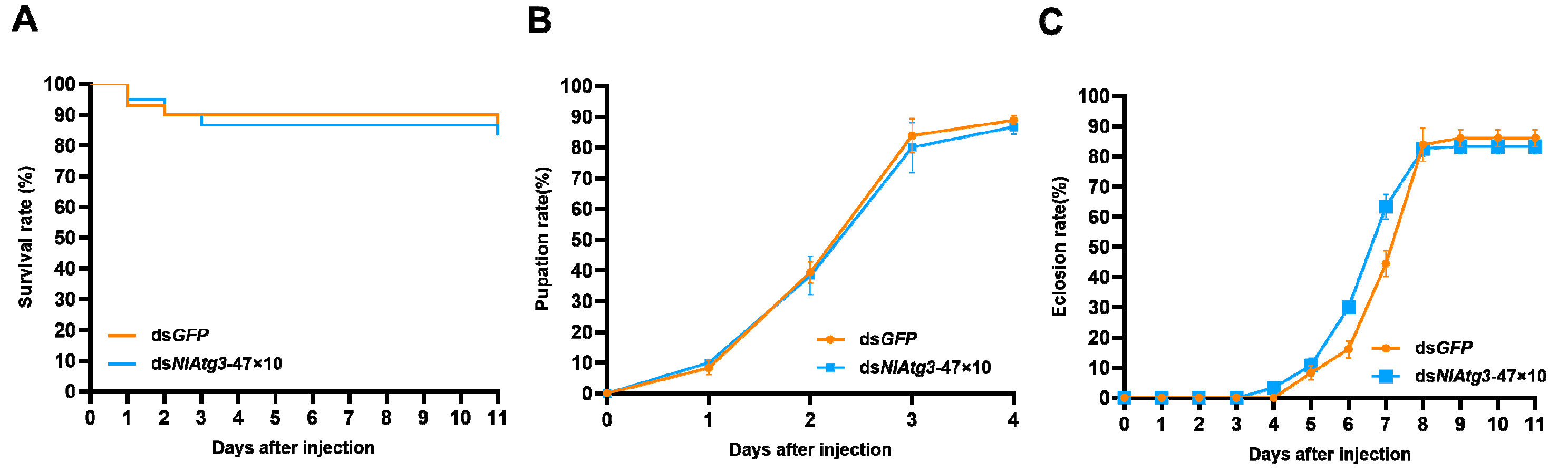
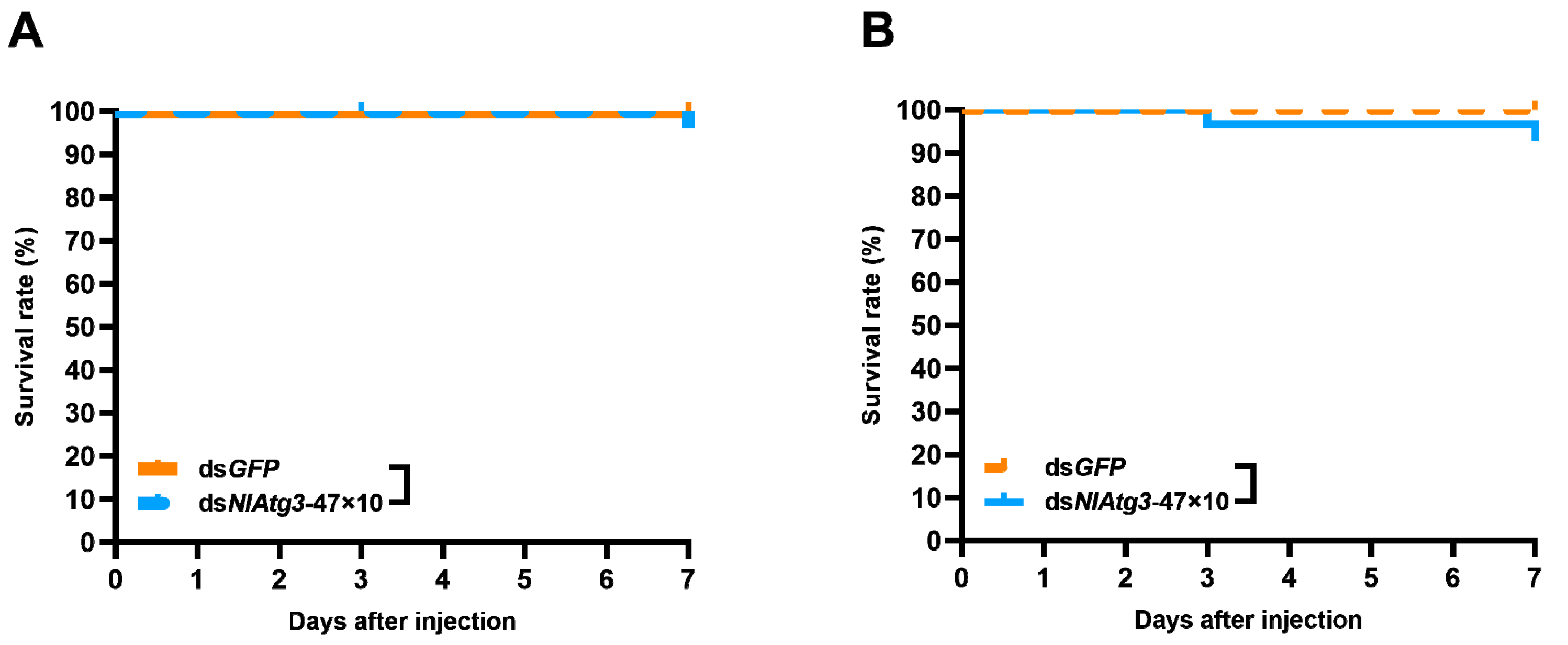
3.6. Effects of Short Concatemerized dsNlAtg3-47×10 on Non-Target Organism D. melanogaster
3.7. Effects of dsNlAtg3-47×10 on Natural Enemies of N. lugens
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foissac, X.; Thi Loc, N.; Christou, P.; Gatehouse, A.M.R.; Gatehouse, J.A. Resistance to Green Leafhopper (Nephotettix virescens) and Brown Planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) in Transgenic Rice Expressing Snowdrop Lectin (Galanthus nivalis Agglutinin; GNA). J. Insect Physiol. 2000, 46, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.A. Rice Planthopper Problems and Relevant Causes in China. In Planthoppers: New Threats to the Sustainability of Intensive Rice Production Systems in Asia; International Rice Research Institute: Manila, Philippines, 2009; Volume 157, p. 178. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, C.T.; Ou, S.H.; Iida, T.T. Grassy Stunt Disease of Rice and Its Transmission by the Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stal. Plant Dis. Report. 1966, 50, 453–456. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, T.; Sanada-Morimura, S.; Oe, T.; Ide, M.; Van Thanh, D.; Van Chien, H.; Van Tuong, P.; Loc, P.M.; Cuong, L.Q.; Liu, Z.; et al. Long-term Field Insecticide Susceptibility Data and Laboratory Experiments Reveal Evidence for Cross Resistance to Other Neonicotinoids in the Imidacloprid-resistant Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, K.; Liu, Z.; Denholm, I.; Brüggen, K.-U.; Nauen, R. Neonicotinoid Resistance in Rice Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Pest. Manag. Sci. Former. Pestic. Sci. 2008, 64, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and Specific Genetic Interference by Double-Stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, B.A.; Fetter, R.D.; Davis, G.W. Dynactin Is Necessary for Synapse Stabilization. Neuron 2002, 34, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.D.; Campbell, L.A.; Lepping, M.D.; Rule, D.M. Field Trial Performance of Herculex XTRA (Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1) and SmartStax (Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 + Cry3Bb1) Hybrids and Soil Insecticides Against Western and Northern Corn Rootworms (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, P.M.; Huizinga, K.M.; Jensen, P.D.; Mueller, G.; Tan, J.; Uffman, J.P.; Levine, S.L. Ecological risk assessment for DvSnf7 RNA: A plant-incorporated protectant with targeted activity against western corn rootworm. Regulatory toxicology and pharmacology. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; Peng, X.; Chen, R.; Du, B.; Zhu, L.; He, G. Knockdown of Midgut Genes by dsRNA-Transgenic Plant-Mediated RNA Interference in the Hemipteran Insect Nilaparvata lugens. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Cao, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Li, J.-F. Overexpression of an Osa-miR162a Derivative in Rice Confers Cross-Kingdom RNA Interference-Mediated Brown Planthopper Resistance without Perturbing Host Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Sun, X.-Q.; Zhu-Salzman, K.; Qin, Q.-M.; Feng, H.-Q.; Kong, X.-D.; Zhou, X.-G.; Cai, Q.-N. Host-Induced Gene Silencing of Brown Planthopper Glutathione S-Transferase Gene Enhances Rice Resistance to Sap-Sucking Insect Pests. J. Pest. Sci. 2021, 94, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Miao, X. Feasibility, Limitation and Possible Solutions of RNAi-based Technology for Insect Pest Control. Insect Sci. 2013, 20, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoch, R.; Sethi, A.; Thakur, N.; Murdock, L.L. RNAi for Insect Control: Current Perspective and Future Challenges. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2013, 171, 847–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.-W. RNA-Based Antiviral Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandety, R.S.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Nouri, S.; Falk, B.W. Emerging Strategies for RNA Interference (RNAi) Applications in Insects. Bioengineered 2015, 6, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenius, O.; Papanicolaou, A.; Garbutt, J.S.; Eleftherianos, I.; Huvenne, H.; Kanginakudru, S.; Albrechtsen, M.; An, C.; Aymeric, J.-L.; Barthel, A.; et al. RNA Interference in Lepidoptera: An Overview of Successful and Unsuccessful Studies and Implications for Experimental Design. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.C.; Van Rij, R.P.; Hekele, A.; Gillis, A.; Foley, E.; O’Farrell, P.H.; Andino, R. The Endocytic Pathway Mediates Cell Entry of dsRNA to Induce RNAi Silencing. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Wang, L.; Ho, M.S.; Zhang, S. The autophagy protein Atg9 functions in glia and contributes to parkinsonian symptoms in a Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, A.R.; Sun, J.; Petitgas, C.; Mesquita, A.; Dulac, A.; Robin, M.; Mollereau, B.; Jenny, A.; Chérif-Zahar, B.; Birman, S. The lysosomal membrane protein LAMP2A promotes autophagic flux and prevents SNCA-induced Parkinson disease-like symptoms in the Drosophila brain. Autophagy 2021, 14, 1898–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Xie, H.; Hu, T.; Shan, H.; Li, M. Binding Features and Functions of ATG3. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 685625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Feng, Y.; Yu, F.; Jiao, Q.; Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, P.; Sun, C.; Pang, K.; Hao, P.; et al. RNAi-mediated Silencing of the Autophagy-related GeneNIATG3 Inhibits Survival and Fecundity of the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 4658–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yang, B.; Liu, Z. Gene Knockdown by Intro-Thoracic Injection of Double-Stranded RNA in the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Tian, P.; Yang, L.; Qiu, L.; He, H.; Ding, W.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Knockdown of Methoprene-Tolerant Arrests Ovarian Development in the Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). J. Insect Sci. 2019, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhou, C.; Yang, W.; Jin, D.; Long, G. Molecular Cloning, Expression, and Functional Analysis of the Chitin Synthase 1 Gene and Its Two Alternative Splicing Variants in the White-Backed Planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.; Pyati, P.; Cao, M.; Bell, H.; Gatehouse, J.A.; Fitches, E. Insecticidal Effects of dsRNA Targeting the Diap1 Gene in Dipteran Pests. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W. The Effects of dsRNA Molecule on the RNAi Efficiency Against Leptinotarsa decemlineata and Its Application in Plastid-Mediated RNAi for Pest Control. Doctoral Dissertation, Hubei University, Wuhan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, S.; Widmer, F.; Siegfried, B.D.; Zhuo, X.; Romeis, J. Responses of two ladybird beetle species (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to dietary RNAi. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2652–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poreddy, S.; Li, J.; Baldwin, I.T. Plant-mediated RNAi silences midgut-expressed genes in congeneric lepidopteran insects in nature. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Li, R.; Wang, F.; Fang, Q.; Yao, H.; Stanley, D.; Ye, G. dsRNAs Targeted to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens: Assessing Risk to a Non-Target, Beneficial Predator, Cyrtorhinus lividipennis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Nanda, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yang, C.; Pan, H. Risk assessment of RNAi-based biopesticides. New Crops 2024, 1, 2949–9526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Levine, S.L.; Bachman, P.M.; Jensen, P.D.; Mueller, G.M.; Uffman, J.P.; Meng, C.; Song, Z.; Richards, K.B.; Beevers, M.H. No impact of DvSnf7 RNA on honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) adults and larvae in dietary feeding tests. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, N.L.; Smagghe, G.; Taning, C.N.T.; Oliveira, E.E.; Christiaens, O. Risk assessment of RNAi-based pesticidesto non-target organisms: Evaluating the effects of sequence similarity in the parasitoid wasp Telenomus podisi. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 154746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, G.; Du, L.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Han, L. Consumption of miRNA-Mediated Insect-Resistant Transgenic Rice Pollen Does Not Harm Apis mellifera Adults. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 4234–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, J.A.; Bogaert, T.; Clinton, W.; Heck, G.R.; Feldmann, P.; Ilagan, O.; Johnson, S.; Plaetinck, G.; Munyikwa, T.; Pleau, M.; et al. Control of Coleopteran Insect Pests through RNA Interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Sun, K.; Pang, K.; Yu, X.; Hao, P. Risk Assessment of RNAi-Based Potential Pesticide dsNlAtg3 and Its Homologues for Nilaparvata lugens and Non-Target Organisms. Insects 2025, 16, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020225
Li K, Chen T, Li Y, Sun K, Pang K, Yu X, Hao P. Risk Assessment of RNAi-Based Potential Pesticide dsNlAtg3 and Its Homologues for Nilaparvata lugens and Non-Target Organisms. Insects. 2025; 16(2):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020225
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kai, Tongtong Chen, Yuliang Li, Kai Sun, Kun Pang, Xiaoping Yu, and Peiying Hao. 2025. "Risk Assessment of RNAi-Based Potential Pesticide dsNlAtg3 and Its Homologues for Nilaparvata lugens and Non-Target Organisms" Insects 16, no. 2: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020225
APA StyleLi, K., Chen, T., Li, Y., Sun, K., Pang, K., Yu, X., & Hao, P. (2025). Risk Assessment of RNAi-Based Potential Pesticide dsNlAtg3 and Its Homologues for Nilaparvata lugens and Non-Target Organisms. Insects, 16(2), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020225






