Identification and Analysis of the GMC Oxidoreductase Family Genes in Cnaphalocrocis medinalis and Their Response to Spinetoram
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Identification and Nomenclature of GMC Oxidoreductase Genes
2.3. Analysis of Basic Information and Physicochemical Properties of the C. medinalis GMC Gene Family
2.4. Chromosomal Localization, Motif, and Conserved Domain Analysis of the C. medinalis GMC Gene Family
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of the C. medinalis GMC Oxidoreductase Family
2.6. Spatiotemporal Expression of CmGMC Oxidoreductase Family Genes
2.7. Insecticide Treatment
2.8. Measurement of Relative Expression Levels of CmGMC Oxidoreductase Family Genes
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the GMC Gene Family in Cnaphalocrocis medinalis
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of the C. medinalis GMC Gene Family
3.3. Chromosomal Localization, Motif, and Conserved Domain Analysis of GMC Genes in C. medinalis
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of the C. medinalis GMC Oxidoreductase Family
3.5. Spatiotemporal Expression Analysis of the GMC Gene Family
3.6. Response of the C. medinalis GMC Family Genes to Spinetoram
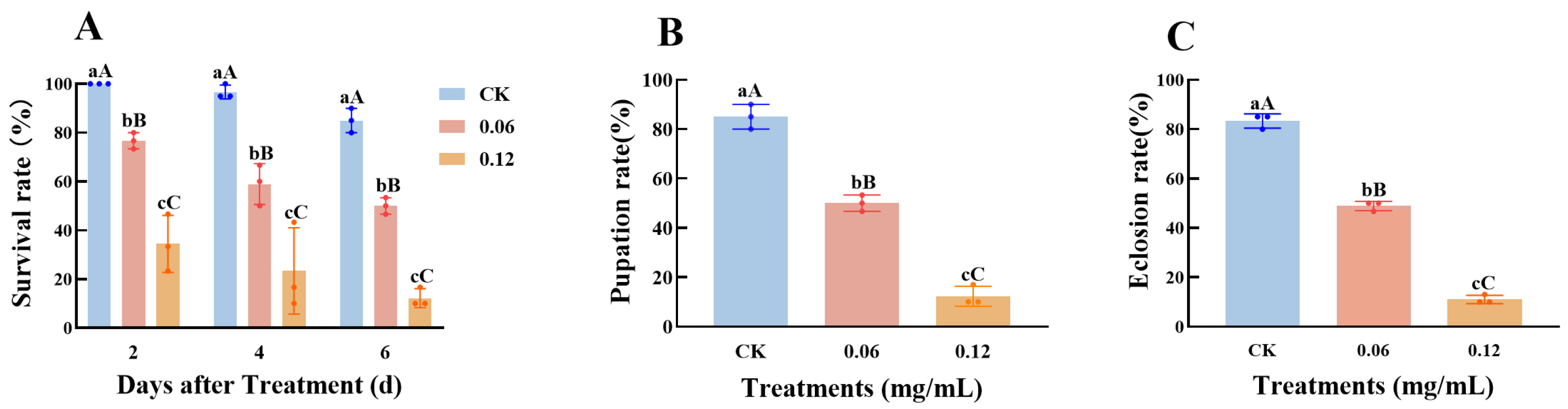
3.6.1. Biological Determination of Spinetoram on C. medinalis
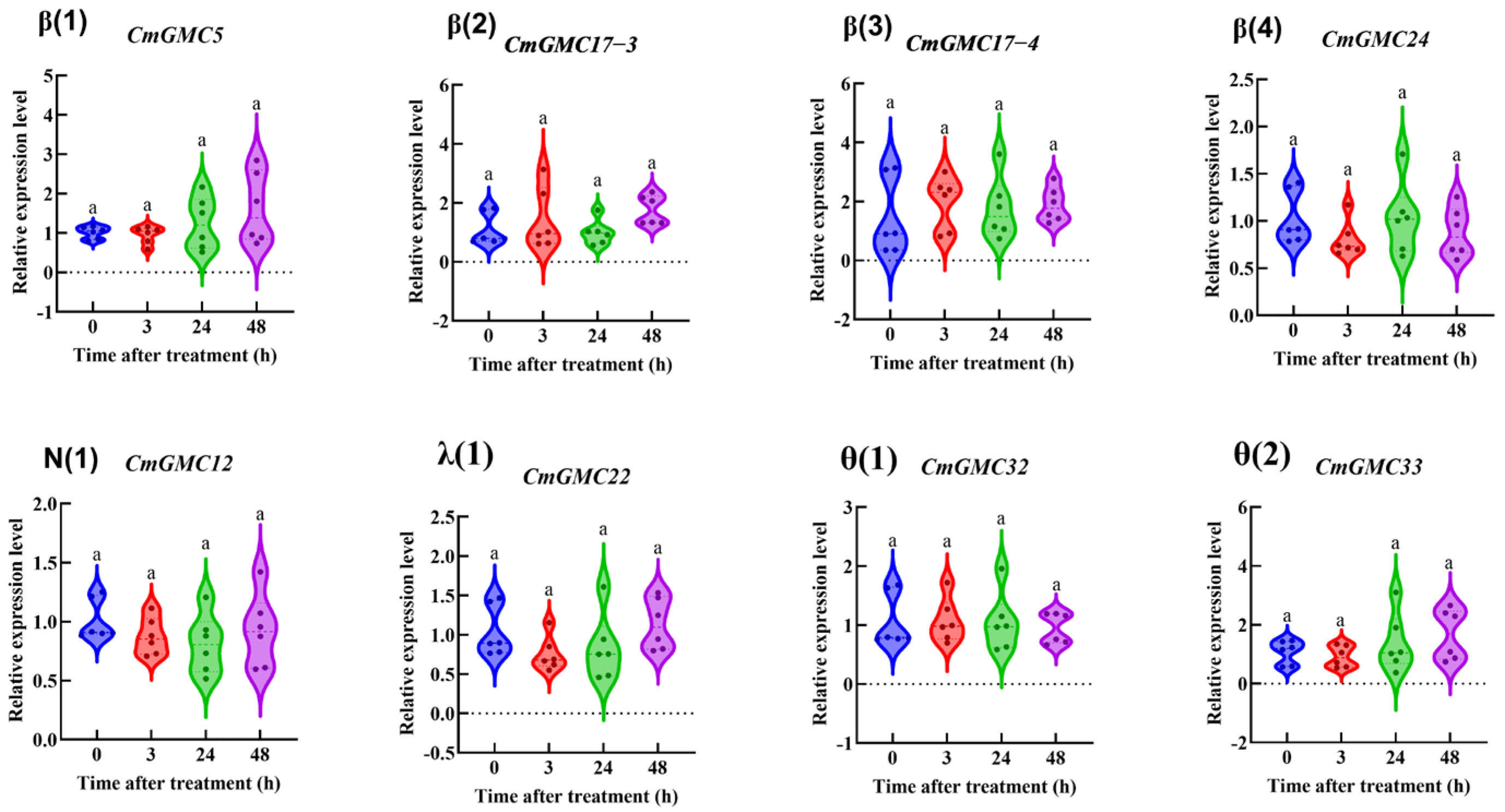
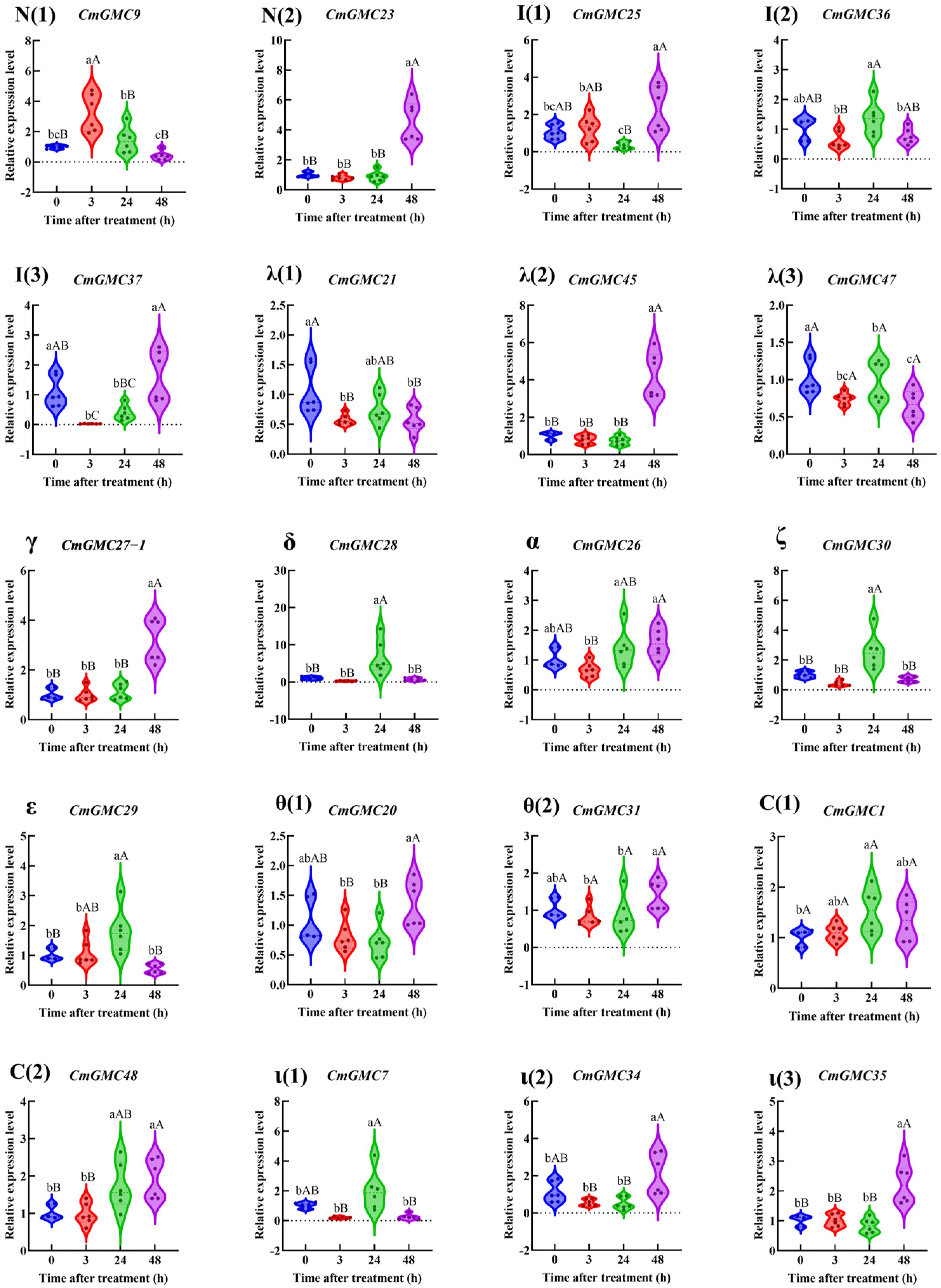
3.6.2. The Relative Expression of CmGMC Against to Spinetoram in C. medinalis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GMC | Glucose–Methanol–Choline |
| CmGMC | Glucose–Methanol–Choline of Cnaphalocrocis medinalis. |
| LC50 | Lethal Concentration 50 |
| hpt | hours post treatment |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Primers Used in the Study
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | ATGGTCGGCATGGGACAG | GAGTTCATTGTAGAAGGTGT |
| RPs15 | ACGTACCCGCTTACAAACCC | TGACCAAGGTGAGCAACAGAG |
| CmGMC1 | GGAAGGGGCGGATACCTAGA | CCGTTCGGGTCTCTCCATTT |
| CmGMC2 | ATCGGTCTTCCATCCATTGAC | AAAAAACCACGAGCTGTGCTC |
| CmGMC3 | CAGGCCCCTCGTTTGACTTC | TAGGGTCGTCACCAGCTTCT |
| CmGMC4 | CAGGTGCCTTTGCGATTGTT | TTGCTTCCACTCGATCCACC |
| CmGMC5 | TATCGCCCCAATCTGCATG | TTTCCCGTTTGACAAAGCC |
| CmGMC6 | GAAGAATCCAACATTCTCCCCATTG | TATGTTGAACAGTCTTTGATCGTCG |
| CmGMC7 | GGAATCCCAGTCATTGCCGA | GGGCTCAAGTAAGCTGGCAT |
| CmGMC8 | TGCCAGTGCCATGCCTAAT | TGCGCCAGTGTCCTTTTTAA |
| CmGMC9 | TGCCAGTGCCATGCCTAAT | ATCAAAGTCCCGAGGGTTGC |
| CmGMC10 | GTCTGCCACTCGCAGTTTGT | GGGACTGCTAGAATGGGTGAT |
| CmGMC11 | GCTATCAATGGACGCGTTGG | GGTGGGCAGGCAAAGACATA |
| CmGMC12 | CTGGCATTTATTGGAGCCTCA | GCCCCCACTTTCACTATCTTG |
| CmGMC14 | CTTCATCGTTGTCGGAGCTG | CTATTGATTCCAAGGGTGGGT |
| CmGMC15 | GGTTGCAGATGGAATGCGTC | CTTTGTCGCCGTTGTGTGTT |
| CmGMC16 | TATGTGAGTACGTGTCGGATGG | GGTGTTACCGCTGGTGATGG |
| CmGMC17-1 | ACAACCACCTGCACATGACT | TCCCCAGTCATATCAGCCCA |
| CmGMC17-2 | TGCCTGGAACTACACCAACG | GCTCTTGTGACACCGACGTA |
| CmGMC17-3 | CGTTCGAGGAGACCCTTACG | GGATCTTCCAGCCTTTCGCT |
| CmGMC17-4 | ATGGCCTTCGTCAAGGTAGC | AGCTTGGACTGTGATGGTGT |
| CmGMC18 | AAACACCACCAACCCCCAT | CGACAAATCTTTAGCAAACGACAC |
| CmGMC19 | TTATGGAAGCCGTAGCTCGC | GGCATCTCCAATACTCCGCA |
| CmGMC20 | CGTCCCTACGAAAGACTACCG | CTCCCAACACCTTCCCAGAT |
| CmGMC21 | ATGAGCGATGTTGCTCCAGT | GGCGCACTAACGCTTTCATA |
| CmGMC22 | CTGAACGGAAACGATGGTTG | AAGGTCCCTGCGTGGAATG |
| CmGMC23 | TCGTATGTGTTCGCCGTTG | ATATCTCTTTTCCGCTTTCCCT |
| CmGMC24 | GATCGAGTCGGGGTTCCTT | CGCGCACACGCTTATAATAA |
| CmGMC25 | ATGCCCACAGTCGTTACTGG | ACTTCGGGACGGTTCTTCAC |
| CmGMC26 | TGCTGTTGGAAGCTGGTGG | CCTTGGGGCTCAGTCTTGTACT |
| CmGMC27-1 | ACAGCATGATGGAAGCGGAA | CAGCCCATTAGCTCGTTTGC |
| CmGMC27-2 | CAACGCAAGCGGTCATCAAA | TAGTAGGGTTCCCTCCAGCC |
| CmGMC27-3 | CTGGGCAGCTATTCGCAAAC | CCCGACCACGATGAAGTCAA |
| CmGMC28 | GGGGCTATAGGATCCCCACA | TGGAACACAAGCCCTCCAAT |
| CmGMC29 | GGCCAAGACACCGTATCACA | TCGCGCCGTTTATATCACGA |
| CmGMC30 | ACGGGCAGATCGTGAGAAA | GGACGCAACAATAAAGGCA |
| CmGMC31 | CCATTACAAGTACGATATACCACCA | ACTCTCAAACCCTTCACGCC |
| CmGMC32 | CAGAACACCGACCCCATCTC | TCGTACTCGGTGAGGAGGTT |
| CmGMC33 | CATGCTCCTTTCAGAACAACGA | AACGATACGCCTGACGGAAA |
| CmGMC34 | AAGGCCAGCTGTATTCCGTC | CAGAGGACCCCAACGTAACC |
| CmGMC35 | ATGGAAAACGAGCGTTGCT | CGATCCTATCCCAGTCTTGAGG |
| CmGMC36 | GCCCTACTTCCTCAAGTCCG | TAGCTCAAAGGCGGGTGGTA |
| CmGMC37 | AACTACCAACCCAAAGAGACAAAAG | CGACCATGAACCCAACAGGA |
| CmGMC38 | TATGCAGCCGTATTCAACTGG | AGCGAGCGAAGTCTTTAAGGTA |
| CmGMC39 | GCAAAAACCTCCACGACCAC | GGCACTGGGAATAGGTGAGG |
| CmGMC40 | ATCACGGGACTCCAGCTCA | TCCATCGTTTTCGGAGGTGA |
| CmGMC41 | CTGTGCTTCCAGGTCTGTTTCC | GCTGTCATTCCAGGCTTGTTC |
| CmGMC42 | CTGAAACCACTTATTGAACGC | AATCCAAACTCCAACACCTT |
| CmGMC43 | GTTGGAATCAGTGCTGCCT | TCCTTGAACGTTCTGTGCG |
| CmGMC44 | GCAGATAAATTAACGCACGCTT | TAACTCGTCTGCCTTTGTGC |
| CmGMC45 | GTATGGTGTTCACGGGCTCA | AAAACGAACGCCACTCCTCT |
| CmGMC46 | TGGCCACGTGGAAAAACATT | CCCCAACCAAGGTTACCGAG |
| CmGMC47 | GCAATTCCACAGTTACGGGC | TGCCAGGTTTGTATCCTTCGT |
| CmGMC48 | CATGGTGGAAGGAGTACGATTAG | GGAAAGGGCACTGTGTGGA |
| CmGMC49 | ATGGACTGGAACTACACGGC | CTGGTCGGTCTTGTGTCCTC |
| CmGMC50 | TACCGGTATCCTTTGCCAGC | AGGGTCACCACCAGCTTCTA |
Appendix A.2. The LC50 Value of Spinetoram Against Cnaphalocrocis medinalis
| Pesticide | Y = a + bx | Slope ± SE | X2 (df) | R2 | LC50 (95%CL) (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| spinetoram | y = 1.78 + 1.84x | 1.78 ± 0.201 | 1.594 (3) | 0.987 | 0.109 (0.88–0.133) |
Appendix A.3. Location of CmGMC in Cnaphalocrocis medinalis
| Sequence ID | Chr | Start | End | Length | ±Chain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CmGMC1 | Chr4 | 12,031,548 | 12,037,042 | 5494 | − |
| CmGMC2 | Chr6 | 153,967 | 158,617 | 4650 | − |
| CmGMC3 | Chr6 | 158,719 | 160,568 | 1849 | − |
| CmGMC4 | Chr10 | 55,831 | 58,252 | 2421 | + |
| CmGMC5 | Chr10 | 1,592,434 | 1,601,435 | 9001 | − |
| CmGMC6 | Chr10 | 1,601,490 | 1,605,747 | 4257 | − |
| CmGMC7 | Chr10 | 8,676,573 | 8,682,633 | 6060 | + |
| CmGMC8 | Chr12 | 10,471,975 | 10,474,609 | 2634 | − |
| CmGMC9 | Chr13 | 1,419,404 | 1,422,747 | 3343 | + |
| CmGMC10 | Chr16 | 632,936 | 643,480 | 10,544 | + |
| CmGMC11 | Chr16 | 645,155 | 647,221 | 2066 | − |
| CmGMC12 | Chr16 | 2,478,010 | 2,483,491 | 5481 | − |
| CmGMC14 | Chr16 | 2,993,030 | 2,997,453 | 4423 | + |
| CmGMC15 | Chr16 | 3,081,455 | 3,084,711 | 3256 | + |
| CmGMC16 | Chr16 | 3,093,006 | 3,097,729 | 4723 | − |
| CmGMC17−1 | Chr16 | 3,141,854 | 3,145,582 | 3728 | − |
| CmGMC17−2 | Chr16 | 3,147,393 | 3,149,605 | 2212 | − |
| CmGMC17−3 | Chr16 | 3,151,400 | 3,154,375 | 2975 | − |
| CmGMC17−4 | Chr16 | 3,155,559 | 3,158,119 | 2560 | − |
| CmGMC18 | Chr16 | 3,187,948 | 3,194,577 | 6629 | − |
| CmGMC19 | Chr16 | 3,201,984 | 3,208,334 | 6350 | + |
| CmGMC20 | Chr18 | 337,806 | 346,801 | 8995 | + |
| CmGMC21 | Chr18 | 346,848 | 347,911 | 1063 | + |
| CmGMC22 | Chr18 | 347,773 | 350,514 | 2741 | − |
| CmGMC23 | Chr19 | 9,029,185 | 9,036,379 | 7194 | + |
| CmGMC24 | Chr20 | 13,117,124 | 13,120,747 | 3623 | − |
| CmGMC25 | Chr23 | 169,852 | 183,234 | 13,382 | + |
| CmGMC26 | Chr23 | 2,013,736 | 2,017,128 | 3392 | + |
| CmGMC27−1 | Chr23 | 2,021,147 | 2,024,758 | 3611 | + |
| CmGMC27−2 | Chr23 | 2,027,013 | 2,030,765 | 3752 | + |
| CmGMC27−3 | Chr23 | 2,032,287 | 2,035,200 | 2913 | + |
| CmGMC28 | Chr23 | 2,057,813 | 2,063,102 | 5289 | + |
| CmGMC29 | Chr23 | 2,109,580 | 2,121,828 | 12,248 | + |
| CmGMC30 | Chr23 | 2,218,730 | 2,221,531 | 2801 | + |
| CmGMC31 | Chr23 | 2,246,861 | 2,251,496 | 4635 | + |
| CmGMC32 | Chr23 | 2,276,183 | 2,276,614 | 431 | + |
| CmGMC33 | Chr23 | 2,276,628 | 2,277,380 | 752 | + |
| CmGMC34 | Chr23 | 2,287,382 | 2,294,626 | 7244 | + |
| CmGMC35 | Chr23 | 2,296,315 | 2,304,712 | 8397 | + |
| CmGMC36 | Chr23 | 5,982,685 | 5,992,924 | 10,239 | − |
| CmGMC37 | Chr23 | 6,339,412 | 6,349,616 | 10,204 | + |
| CmGMC38 | Chr24 | 9,639,738 | 9,643,575 | 3837 | − |
| CmGMC39 | Chr24 | 9,654,959 | 9,655,795 | 836 | − |
| CmGMC40 | Chr24 | 9,656,209 | 9,657,796 | 1587 | − |
| CmGMC41 | Chr24 | 9,709,590 | 9,720,736 | 11,146 | − |
| CmGMC42 | Chr24 | 9,743,549 | 9,747,716 | 4167 | − |
| CmGMC43 | Chr24 | 9,750,697 | 9,753,458 | 2761 | + |
| CmGMC44 | Chr26 | 7,721,527 | 7,722,002 | 475 | + |
| CmGMC45 | Chr28 | 5,613,898 | 5,633,044 | 19,146 | − |
| CmGMC46 | Chr28 | 5,679,905 | 5,681,963 | 2058 | + |
| CmGMC47 | Chr28 | 7,652,152 | 7,679,704 | 27,552 | − |
| CmGMC48 | ctg1590 | 27,242 | 32,075 | 4833 | + |
| CmGMC49 | ctg7278 | 862 | 2515 | 1653 | + |
| CmGMC50 | ctg7917 | 15 | 4822 | 4807 | + |
References
- Yuan, B.; Doxsey, W.; Tok, O.; Kwon, Y.Y.; Liang, Y.S.; Inouye, K.E.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Hui, S. An organism-level quantitative flux model of metabolism in mice. Cell Metab. 2025, 37, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerch, L.B.; Massaro, D. Oxidation-resuction-sensitive binding of lung protrin to rat catalase messenger-RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 2853–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavener, D.R. GMC oxidoreductases: A newly defned family of homologous proteins with diverse catalytic activities. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 223, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Z.; Liu, L.Q.; Chen, D.J.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.L.; Shao, L. Co-expression of the recombined alcohol dehydrogenase and glucose dehydrogenase and cross-linked enzyme aggregates stabilization. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sützl, L.; Foley, G.; Gillam, E.M.J.; Bodén, M.; Haltrich, D. The GMC superfamily of oxidoreductases revisited: Analysis and evolution of fungal GMC oxidoreductases. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouche, C.B.; Picard, L.; Cochet, C.; Paris, C.; Oger, P.; Turpault, M.P.; Uroz, S. Acidification-based mineral weathering mechanism involves a glucose/methanol/choline oxidoreductase in Caballeronia mineralivorans PML1(12). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e0122124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiess, M.; Hecht, H.J.; Kalisz, H.M. Glucose oxidase from Penicillium amagasakiense—Primary structure and comparison with other glucose-methanol-choline (GMC) oxidoreductases. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 252, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strecker, H.J.; Korkes, S. Glucose dehydrogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 1952, 192, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, W.; Rezende, G.L.; Abreu, L.; Moraes, J.; Lemos, F.J.A.; Vaz, I.D.S., Jr.; Logullo, C. Germ band retraction as a landmark in glucose metabolism during Aedes aegypti embryogenesis. BMC Dev. Biol. 2010, 10, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Wu, Y.; You, L.L.; Xu, B.; Ge, L.Q.; Yang, G.Q.; Wu, J.C. Jinggangmycin-suppressed reproduction in the small brown planthopper (SBPH), Laodelphax striatellus (Fallen), is mediated by glucose dehydrogenase (GDH). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 139, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, K.; Cavener, D.R. Glucose dehydrogenase is required for normal sperm storage and utilization in female Drosophila melanogaster. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.S.; Singh, K.V.; Bansal, S.K. Changes in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity in Indian desert malaria vector Anopheles stephensi during aging. Acta Trop. 2012, 123, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legan, S.K.; Rebrin, I.; Mockett, R.J.; Radyuk, S.N.; Klichko, V.I.; Sohal, R.S.; Orr, W.C. Overexpression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase extends the life span of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 32492–32499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox Foster, D.L.; Stehr, J.E. Induction and localization of FAD-glucose dehydrogenase (GLD) during encapsulation of abiotic implants in Manduca sexta larvae. J. Insect Physiol. 1994, 40, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovallo, N.; Cox-Foster, D.L. Alteration in FAD–glucose dehydrogenase activity and hemocyte behavior contribute to initial disruption of Manduca sexta immune response to Cotesia congregata parasitoids. J. Insect Physiol. 1999, 45, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, T.; Ito, H.; Yatsunami, K.; Echigo, T. Changes of glucose-oxidase activity and amount of gluconic acid formation in the Hypopharyngeal glands during the lifespan of honey bee workers (Apis mellifera L.). Agric. Biol. Chem. 1990, 54, 2133–2134. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sherif, A.A.; Mazeed, A.M.; Ewis, M.; Nafea, E.; Hagag, E.E.; Kamel, A. Activity of salivary glands in secreting honey-elaborating enzymes in two subspecies of honeybee (Apis mellifera L.). Physiol. Entomol. 2017, 42, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.B.; Hu, Y.H.; Kang, L.; Wang, C.Z. For: Archives of insect biochemistry and physiology characterization of glucose-induced glucose oxidase gene and protein expression in Helicoverpa armigera larvae. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 79, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.C.; Lin, P.; Peiffer, M.; Felton, G. Caterpillar salivary glucose oxidase decreases green leaf volatile emission and increases terpene emission from maize. J. Chem. Ecol. 2023, 49, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfare, S.; Ahmad, S.T.; Joyce, M.V.; Boggess, B.; O’Tousa, J.E. The Drosophila ninaG oxidoreductase acts in visual pigment chromophore production. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11895–11901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.T.; Joyce, M.V.; Boggess, B.; O’Tousa, J.E. The role of Drosophila ninaG oxidoreductase in visual pigment chromophore biogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 9205–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Rigden, D.J.; Ebrahimi, B.; Turner, P.C.; Rees, H.H. Regulation of ecdysteroid signalling during Drosophila development: Identification, characterization and modelling of ecdysone oxidase, an enzyme involved in control of ligand concentration. Biochem. J. 2005, 389, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weirich, G.F.; Thompson, M.J.; Svoboda, J.A. Ecdysone oxidase and 3-oxoecdysteroid reductases in Manduca sexta midgut: Kinetic parameters. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1989, 12, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.N.; Zhu, L.H.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Bai, Y.; Li, P.X.; Yang, H.C.; Tang, S.W.; Crickmore, N.; Zhou, X.G.; Zhang, Y.J. Characterization of an ecdysone oxidase from Plutella xylostella (L.) and its role in Bt Cry1Ac resistance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, S.; Tapadia, M.G. Transcriptome profiling identifies multistep regulation through E93, forkhead and ecdysone oxidase in survival of malpighian tubules during metamorphosis in Drosophila. Int. Dev. Biol. 2020, 64, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavigliasso, F.; Savitsky, M.; Koval, A.; Erkosar, B.; Savary, L.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Katanaev, V.L.; Kawecki, T.J. Cis-regulatory polymorphism at fiz ecdysone oxidase contributes to polygenic evolutionary response to malnutrition in Drosophila. PLoS Genet. 2024, 20, e1011204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, W. Ecdysone oxidase and 3-dehydroecdysone-3β-reductase contribute to the synthesis of ecdysone during early embryonic development of the silkworm. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, K.; Cox-Foster, D.; Yang, X.L.; Ko, W.Y.; Cavener, D.R. Expansion and evolution of insect GMC oxidoreductases. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shen, Y.H.; Yang, W.J.; Cao, Y.F.; Xiang, Z.X.; Zhang, Z. Expansion of the silkworm GMC oxidoreductase genes is associated with immunity. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.H.; Silven, J.J.M.; Wybouw, N.; Fandino, R.A.; Dekker, H.L.; Vogel, H.; Wu, Y.-L.; De Koster, C.; Große-Wilde, E.; Haring, M.A.; et al. A salivary GMC oxidoreductase of Manduca sexta re-arranges the green leaf volatile profile of its host plant. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmavathi, C.H.; Katti, G.; Padmakumari, A.P.; Voleti, S.R.; Subba Rao, L.V. The effect of leaffolder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guenee) [Lepidoptera: Pyralidae] injury on the plant physiology and yield loss in rice. J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 137, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.S.; Ren, X.B.; Su, J.Y. Insecticide susceptibility of Cnaphalocrocis medinalia (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in Chian. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, S.T.; Ling, Y.; Wang, L.; Ni, H.; Guo, D.; Dong, B.B.; Huang, Q.; Long, L.P.; Zhang, S.; et al. Insecticide resistance monitoring of Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) and its mechanism to chlorantraniliprole. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 3290–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Fang, Y.; Ha, K.B.; Park, D.H.; Park, M.G.; Woo, R.M.; Kim, W.J.; et al. Laboratory evaluation of transgenic Bt rice resistance against rice leaf roller, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.K.; Liu, B.; Wang, L.; Parajulee, M.N.; Megha, N.; Chen, F.J. Effects of seed mixture sowing with transgenic Bt rice and its parental line on the population dynamics of target stemborers and leafrollers, and non-target planthoppers. Insect Sci. 2019, 26, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Li, S.G.; Rao, X.J.; Liu, S. Molecular characterization of a NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase gene from the rice leaffolder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2018, 53, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Yang, Z.F. Identification and Expression of Two Novel Cytochrome P450 Genes, CYP6CV1 and CYP9A38, in Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Insect Sci. 2015, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Rao, X.J.; Li, M.Y.; Feng, M.F.; He, M.Z.; Li, S.G. Glutathione S-transferase genes in the rice leaffolder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae): Identification and expression profiles. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 90, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhagan, S.R.; Pathrose, B.; Chellappan, M.; Smitha, M.S.; Ranjith, M.T.; Nair, S.; Dhalin, D. Multiple detoxification enzymes mediate resistance to anticholinesterase insecticides in Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Crop Prot. 2015, 195, 107261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, W.L.; Li, M.Y.; Li, S.G.; Liu, S. Identification of putative carboxylesterase and aldehyde oxidase genes from the antennae of the rice leaffolder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Z.; Wen, D.F.; Wang, W.L.; Geng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.P. Identification of genes putatively involved in chitin metabolism and insecticide detoxification in the rice leaf folder (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis) larvae through transcriptomic analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21873–21896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, V.L.; Sparks, T.C.; Gilbert, L.I.; Gill, S.S. The spinosyns: Chemistry, biochemistry, mode of action, and resistance. In Insect Control: Biological and Synthetic Agents; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 207–243. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.G. Unraveling the mystery of spinosad resistance in insects. J. Pestic. Sci. 2008, 33, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Lin, W.; Lin, Q.; Li, Z.; Hang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y. Baseline susceptibility of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) to the novel insecticide spinetoram in China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, E.C.; Bolzan, A.; Nascimento, A.R.; Amaral, F.S.; Kanno, R.H.; Kaiser, I.S.; Omoto, C. resistance of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to spinetoram: Inheritance and cross—Resistance to spinosad. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2674–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.K.; Ren, X.B.; Wang, Y.C.; Su, J. resistance in Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) to new chemistry insecticides. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, P.Q.; Li, M.Z.; Wang, G.R.; Gu, L.L.; Liu, X.D. Comparative transcriptome analysis of the rice leaf folder (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis) to heat acclimation. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.X.; Xu, H.X.; He, K.; Shi, Z.M.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.H.; Mei, Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Li, M.Z.; Gao, L.B.; et al. A chromosome-level genome assembly of rice leaffolder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.R.; Yao, X.J.; Ni, Z.H.; Zhao, H.F.; Yang, Y.J.; Xu, H.X.; Lu, Z.X.; Zhu, P.Y. Identification of salivary proteins in the rice leaf folder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis by transcriptome and LC-MS/MS analyses. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2024, 174, 104–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.T.; Lu, J.Q.; Ji, K.; Wang, C.C.; Yao, Z.C.; Liu, F.; Li, Y. Comparative transcriptomic assessment of chemosensory genes in adult and larval olfactory organs of Cnaphalocrocis medinalis. Genes 2023, 14, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.X.; Zhao, X.X.; Yang, Y.J.; Chen, X.; Mei, Y.; He, K.; Xu, L.; Ye, X.H.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; et al. Chromosome-level genome assembly of an agricultural pest, the rice leaffolder Cnaphalocrocis exigua (Crambidae, Lepidoptera). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Sanderford, M.; Sharma, S.; Tamura, K. MEGA12: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 12 for adaptive and green computing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.Q.; Gascuel, O. An Improved general amino acid replacement matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 147–164. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies:An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Qian, Q.; Liu, X.D.A. Method for rearing the rice leaf folder (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis) using wheat seedlings. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2015, 52, 883–889. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.Y.; Zhang, C.X. Data Processing System (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research. Insect Sci. 2013, 20, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orengo, C.A.; Thornton, J.M. Protein families and their evolution—A structural perspective. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2005, 74, 867–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.E.; Agresti, A. HMG proteins: Dynamic players in gene regulation and differentiation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmamaw, M.D.; He, A.; Zhang, L.R.; Liu, H.M.; Gao, Y. Histone deacetylase complexes: Structure, regulation and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, C.R.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, H.X.; Zheng, X.H. Identification and expression analysis of heat shock protein superfamily genes in Callosobruchus chinensis. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2023, 56, 3814–3828. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Tan, R.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.X.; Diao, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, P.; Ma, L. Analysis of structures and expression patterns of the flavin-containing monooxygenase family genes in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Zhejiang Univ. Agric. Life Sci. 2023, 49, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Thoris, K.; Marrero, M.C.; Fiers, M.; Lai, X.L.; Zahn, I.E. Uncoupling FRUITFULL’s functions through modification of a protein motif identified by co-ortholog analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 13290–13304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, S.; Murthy, M.R.N. Protein thermal stability: Insights from atomic displacement parameters (B values). Protein Eng. 2000, 13, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Su, C.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, R.; He, B.; Hao, J. Genome-wide identification, gene duplication, and expression pattern of NPC2 Gene Family in Parnassius glacialis. Genes 2025, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, H.M.; Warr, C.G.; Carlson, J.R. Molecular evolution of the insect chemoreceptor gene superfamily in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14537–14542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Lu, J.J.; Wu, L.Y.; Cheng, Z.T.; Qiao, G.X.; Huang, X.L. Genomic and transcriptomic analyses of a social hemipteran provide new insights into insect sociality. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2024, 24, e14019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Hua, G.S.; Chen, C.J.; Shen, G.W.; Li, Z.Q.; Hua, X.T.; Lin, P.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q.Y. Metabolic benefits conferred by duplication of the facilitated trehalose transporter in Lepidoptera. Insect Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, D.D.; Scully, E.D.; Pauchet, Y.; Hoover, K.; Kirsch, R.; Geib, S.M.; Mitchell, R.F.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ahn, S.J.; Arsala, D.; et al. Genome of the Asian longhorned beetle (Anoplophora glabripennis), a globally significant invasive species, reveals key functional and evolutionary innovations at the beetle–plant interface. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracheva, E.O.; Ingolia, N.T.; Kelly, Y.M.; Cordero-Morales, J.F.; Hollopeter, G.; Chesler, A.T.; Sánchez, E.E.; Perez, J.C.; Weissman, J.S.; Julius, D. Molecular basis of infrared detection by snakes. Nature 2010, 464, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, P.Q.; Li, J.R.; Liu, X.D. Glucose dehydrogenases-mediated acclimation of an important rice pest to global warming. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyereisen, R. Insect P450 enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1999, 44, 507–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachepilo, T.G.; Pribyshina, A.K. Heat shock proteins in normal insect physiology. Integr. Physiol. 2022, 3, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daborn, P.J.; Yen, J.L.; Bogwitz, M.R.; Goff, G.L.; Feil, E.; Jeffers, S.; Tijet, N.; Perry, T.; Heckel, D.; Batterham, P.; et al. A single P450 allele associated with insecticide resistance in Drosophila. Science 2002, 297, 2253–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.C.; Li, Y.; Li, W.R.; Zhou, Q. Characterization and functional analysis of a carboxylesterase gene associated with chlorpyrifos resistance in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 203, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Z.; Kong, F.C.; Cui, R.K.; Zeng, X.N. Gene expression of detoxification enzymes in insecticide-resistant and insecticide-susceptible Bemisia tabaci strains after diafenthiuron exposure. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 154, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Després, L.; David, J.P.; Gallet, C. The evolutionary ecology of insect resistance to plant chemicals. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.N.; Li, M.; Gong, Y.H.; Liu, F.; Li, T. Cytochrome P450s–Their expression, regulation, and role in insecticide resistance. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 120, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kong, X.D.; Zhu-Salzman, K.; Qin, Q.M.; Cai, Q.N. The key glutathione S-transferase family genes involved in the detoxification of rice gramine in brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Insects 2021, 12, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montella, I.R.; Schama, R.; Valle, D. The classification of esterases: An important gene family involved in insecticide resistance—A review. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2012, 107, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Q.X.; Feng, H.T.; Jiao, L.; Zaheer, U.; Zheng, C.Q.; Zhou, L.; Lin, G.F.; Xiang, X.J.; Liao, H.; Li, S.Y.; et al. Bacteria derived from diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae), gut regurgitant negatively regulate glucose oxidase-mediated anti-defense against host plant. Insects 2024, 15, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.J.; Zhu, L.H.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Dong, L.N.; Guo, L.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Q.J.; Wang, S.L.; Yang, X.; Xie, W.; et al. A midgut transcriptional regulatory loop favors an insect host to withstand a bacterial pathogen. Innovation 2024, 5, 100675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gene ID | Gene Name | AA | MW | PI | II | AI | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmed12162 | CmGMC1 | 638 | 70,952.5 | 9.2 | 31.0 | 84.3 | −0.198 |
| Cmed14810 | CmGMC2 | 770 | 85,725.5 | 5.3 | 28.6 | 92.2 | −0.178 |
| Cmed14811 | CmGMC3 | 406 | 44,942.7 | 5.0 | 33.3 | 90.8 | −0.136 |
| Cmed12844 | CmGMC4 | 617 | 69,151.7 | 8.3 | 32.7 | 97.2 | −0.092 |
| Cmed12391 | CmGMC5 | 570 | 63,769.6 | 8.6 | 38.6 | 80.9 | −0.385 |
| Cmed12392 | CmGMC6 | 574 | 63,690.0 | 5.9 | 44.1 | 84.9 | −0.315 |
| Cmed07297 | CmGMC7 | 720 | 80,319.7 | 6.8 | 41.2 | 83.0 | −0.373 |
| Cmed04604 | CmGMC8 | 582 | 63,256.7 | 5.8 | 39.0 | 90.8 | −0.096 |
| Cmed21934 | CmGMC9 | 596 | 65,188.4 | 6.1 | 23.6 | 92.0 | −0.071 |
| Cmed03671 | CmGMC10 | 1131 | 127,085.0 | 8.8 | 36.5 | 85.7 | −0.368 |
| Cmed03670 | CmGMC11 | 607 | 68,535.8 | 9.3 | 33.9 | 85.8 | −0.401 |
| Cmed13421 | CmGMC12 | 757 | 85,214.7 | 6.2 | 43.3 | 90.0 | −0.134 |
| Cmed16067 | CmGMC14 | 249 | 27,478.8 | 4.6 | 16.9 | 77.2 | −0.325 |
| Cmed17247 | CmGMC15 | 582 | 64,279.7 | 5.1 | 33.9 | 85.1 | −0.274 |
| Cmed17244 | CmGMC16 | 586 | 64,749.0 | 8.9 | 26.6 | 86.8 | −0.250 |
| Cmed15861.1 | CmGMC17−1 | 585 | 65,046.3 | 9.0 | 34.4 | 87.3 | −0.280 |
| Cmed15861.2 | CmGMC17−2 | 582 | 64,833.4 | 5.9 | 35.7 | 82.6 | −0.304 |
| Cmed15861.3 | CmGMC17−3 | 426 | 47,104.8 | 9.1 | 35.9 | 87.9 | −0.256 |
| Cmed15861.4 | CmGMC17-4 | 579 | 64,737.8 | 8.8 | 44.7 | 82.2 | −0.266 |
| Cmed15863 | CmGMC18 | 937 | 104,026.8 | 8.9 | 35.5 | 87.9 | −0.319 |
| Cmed15865 | CmGMC19 | 585 | 65,085.5 | 7.0 | 34.5 | 91.0 | −0.192 |
| Cmed00507 | CmGMC20 | 286 | 32,065.3 | 6.2 | 27.3 | 76.6 | −0.395 |
| Cmed00506 | CmGMC21 | 332 | 36,709.6 | 8.6 | 37.4 | 105.1 | −0.031 |
| Cmed00509 | CmGMC22 | 593 | 66,415.3 | 6.2 | 29.8 | 88.3 | −0.191 |
| Cmed07035 | CmGMC23 | 614 | 68,822.4 | 9.6 | 42.9 | 84.5 | −0.219 |
| Cmed01344 | CmGMC24 | 625 | 69,630.7 | 8.5 | 41.6 | 89.3 | −0.224 |
| Cmed05264 | CmGMC25 | 716 | 79,697.7 | 5.7 | 42.1 | 68.1 | −0.452 |
| Cmed14944 | CmGMC26 | 195 | 21,903.8 | 6.7 | 32.3 | 73.5 | −0.492 |
| Cmed14940.1 | CmGMC27−1 | 802 | 90,806.6 | 5.6 | 37.3 | 80.3 | −0.449 |
| Cmed14940.2 | CmGMC27−2 | 625 | 69,200.3 | 8.9 | 27.6 | 81.0 | −0.320 |
| Cmed14940.3 | CmGMC27−3 | 578 | 64,439.1 | 5.8 | 35.2 | 94.5 | −0.156 |
| Cmed14941 | CmGMC28 | 485 | 54,007.8 | 8.4 | 39.6 | 88.7 | −0.188 |
| Cmed14939 | CmGMC29 | 819 | 91,141.9 | 8.8 | 37.5 | 85.6 | −0.209 |
| Cmed07555 | CmGMC30 | 618 | 69,003.5 | 9.3 | 33.1 | 91.0 | −0.183 |
| Cmed07559 | CmGMC31 | 506 | 56,640.1 | 9.3 | 32.3 | 79.8 | −0.347 |
| Cmed07562 | CmGMC32 | 143 | 15,617.8 | 6.1 | 36.7 | 90.7 | −0.068 |
| Cmed07560 | CmGMC33 | 250 | 28,430.6 | 9.7 | 33.1 | 79.5 | −0.457 |
| Cmed07563 | CmGMC34 | 192 | 21,392.6 | 9.1 | 40.3 | 74.2 | −0.398 |
| Cmed07558 | CmGMC35 | 749 | 82,434.1 | 5.1 | 33.7 | 81.3 | −0.250 |
| Cmed00473 | CmGMC36 | 608 | 65,919.9 | 6.9 | 40.1 | 71.6 | −0.274 |
| Cmed14455 | CmGMC37 | 604 | 67,148.4 | 7.2 | 35.9 | 76.4 | −0.397 |
| Cmed06630 | CmGMC38 | 538 | 59,350.0 | 5.2 | 44.0 | 86.8 | −0.283 |
| Cmed06631 | CmGMC39 | 278 | 30,434.6 | 5.7 | 50.3 | 89.1 | −0.072 |
| Cmed06632 | CmGMC40 | 124 | 13,947.8 | 5.2 | 43.8 | 86.5 | −0.173 |
| Cmed06636 | CmGMC41 | 1036 | 113,781.1 | 5.8 | 35.1 | 85.8 | −0.220 |
| Cmed06637 | CmGMC42 | 611 | 66,566.3 | 6.8 | 40.4 | 93.4 | −0.101 |
| Cmed06633 | CmGMC43 | 539 | 59,604.8 | 6.2 | 39.0 | 87.7 | −0.176 |
| Cmed16057 | CmGMC44 | 151 | 17,369.3 | 5.8 | 10.0 | 61.3 | −0.837 |
| Cmed22270 | CmGMC45 | 620 | 69,341.7 | 8.2 | 28.2 | 81.6 | −0.394 |
| Cmed22269 | CmGMC46 | 616 | 68,593.7 | 5.3 | 34.6 | 87.7 | −0.173 |
| Cmed06807 | CmGMC47 | 962 | 108,670.7 | 9.2 | 40.7 | 74.4 | −0.443 |
| Cmed04144 | CmGMC48 | 635 | 70,851.6 | 9.5 | 32.5 | 84.1 | −0.224 |
| Cmed18776 | CmGMC49 | 409 | 45,325.4 | 4.9 | 39.1 | 77.5 | −0.357 |
| Cmed19817 | CmGMC50 | 525 | 58,163.6 | 9.1 | 37.1 | 84.9 | −0.310 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, C.; Quan, P.; Zhu, J.; Lei, H.; Li, K.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, D.; Zeng, Y.; Ma, M. Identification and Analysis of the GMC Oxidoreductase Family Genes in Cnaphalocrocis medinalis and Their Response to Spinetoram. Insects 2025, 16, 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121272
Xiao C, Quan P, Zhu J, Lei H, Li K, Zhao X, Zhu D, Zeng Y, Ma M. Identification and Analysis of the GMC Oxidoreductase Family Genes in Cnaphalocrocis medinalis and Their Response to Spinetoram. Insects. 2025; 16(12):1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121272
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Conghui, Pengqi Quan, Jian Zhu, Haixia Lei, Kailong Li, Xin Zhao, Daohong Zhu, Yang Zeng, and Mingyong Ma. 2025. "Identification and Analysis of the GMC Oxidoreductase Family Genes in Cnaphalocrocis medinalis and Their Response to Spinetoram" Insects 16, no. 12: 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121272
APA StyleXiao, C., Quan, P., Zhu, J., Lei, H., Li, K., Zhao, X., Zhu, D., Zeng, Y., & Ma, M. (2025). Identification and Analysis of the GMC Oxidoreductase Family Genes in Cnaphalocrocis medinalis and Their Response to Spinetoram. Insects, 16(12), 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121272





