Adaptation and Invasion Dynamics of Rhipicephalus microplus in South Africa: Ecology, Resistance, and Management Implications
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Invasion History and Current Distribution in South Africa
3. Drivers of Spread and Establishment
3.1. Climate: Warm, Humid Zones
3.2. Cattle Movement and Communal Grazing Practices
3.3. Vegetation Index: NDVI as an Indicator
3.4. Rainfall Seasonality
3.5. Ecological Niche and Climate-Change Projections
4. Diagnostic Advances
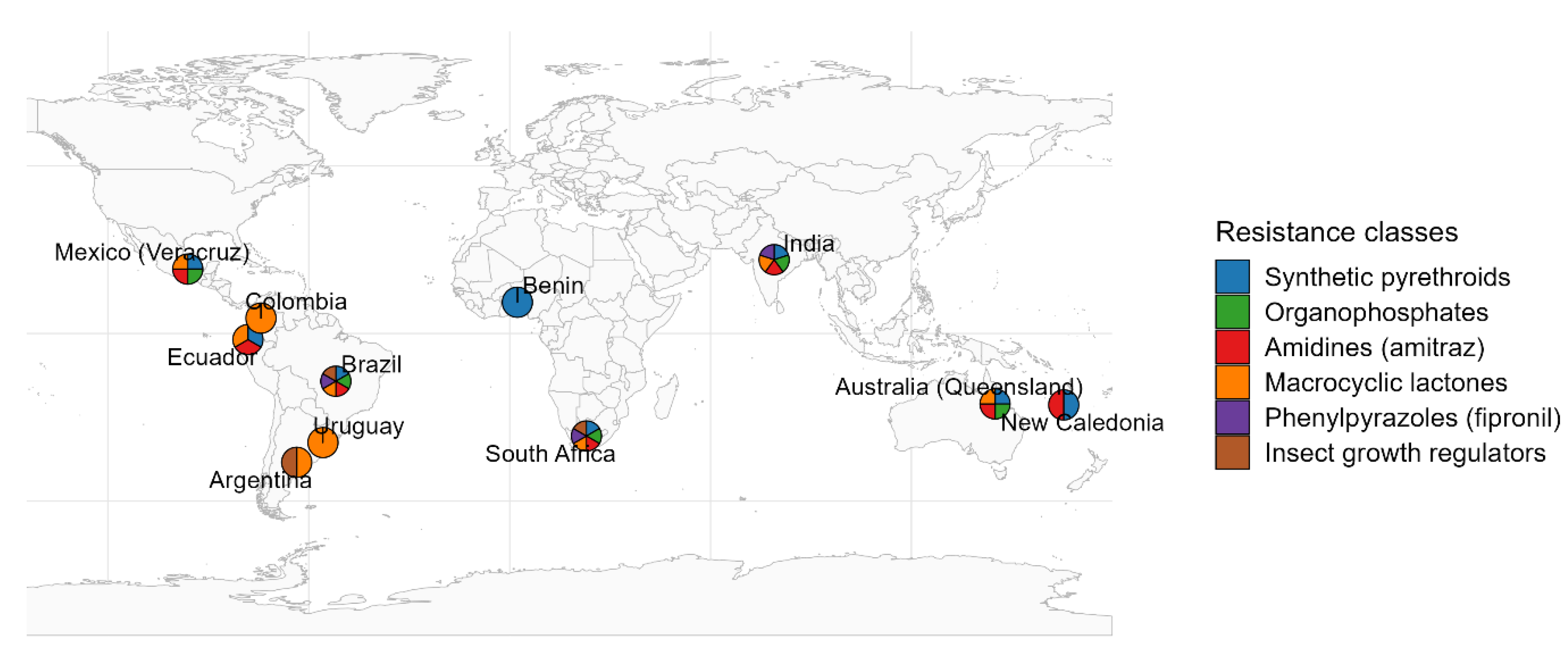
5. Acaricide Resistance Landscape
6. Population Genetics and Adaptation
7. Integrated Management Approaches for R. microplus
8. Knowledge Gaps and Future Directions
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIT | Adult Immersion Test |
| AM | Amitraz (formamidine) |
| B. bigemina | Babesia bigemina |
| B. bovis | Babesia bovis |
| BVDV | Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus |
| COI | Cytochrome Oxidase I gene |
| ECP | Eastern Cape Province |
| FIP | Fipronil (phenylpyrazole) |
| IPM | Integrated Pest Management |
| ITS/ITS2 | Internal Transcribed Spacer/ITS2 |
| kdr | Knockdown Resistance |
| KZN | KwaZulu-Natal |
| LIT | Larval Immersion Test |
| LPT | Larval Packet Test |
| LTT | Larval Tarsal Test |
| ML | Macrocyclic Lactone |
| NDVI | Normalised Difference Vegetation Index |
| OP | Organophosphate |
| PCR-RFLP | Polymerase Chain Reaction–Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| R. australis | Rhipicephalus australis |
| R. decoloratus | Rhipicephalus decoloratus |
| R. microplus | Rhipicephalus microplus |
| 16S rRNA | 16S Ribosomal RNA |
| SNP | Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| SP | Synthetic Pyrethroid |
| SSP5-8.5 | Shared Socio-Economic Pathway 5/RCP 8.5 |
References
- Madder, M.; Thys, É.; Achi, L.Y.; Touré, A.A.; De Deken, R. Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus: A most successful invasive tick species in West Africa. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2010, 53, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyangiwe, N.; Yawa, M.; Muchenje, V. Driving forces for changes in geographic range of cattle ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Africa: A review. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 48, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Fernández, J.M.; Gutiérrez-Ortega, A.; Rosario-Cruz, R.; Camberos, E.P.; Álvarez, Á.H.; Martínez-Velázquez, M. Molecular cloning and characterization of two novel autophagy-related genes belonging to the ATG8 family from the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2014, 64, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, J.M.; Ueti, M.W.; Palmer, G.H.; Scoles, G.A.; Knowles, D.P. Transovarial transmission efficiency of Babesia bovis tick stages acquired by Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus during acute infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista-Garfias, C.R.; Martínez-Ibañez, F.; García-Ortíz, M.Á.; Camarillo, S.D.R. Rhipicephalus microplus: Tick classification, morphological identification and life cycle. In A Laboratory Manual on R. microplus; Salinas-Estrella, E., Ed.; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2023; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Oyen, K.; Poh, K.C. Rhipicephalus microplus (southern cattle tick; Asian blue tick). Trends Parasitol. 2025, 41, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastropaolo, M.; Mangold, A.J.; Guglielmone, A.A.; Nava, S. Non-parasitic life cycle of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in Panicum maximum pastures in northern Argentina. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 115, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, A.; Ren, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yin, H.; Guan, G.; Luo, J. Biological parameters of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) fed on rabbits, sheep, and cattle. Korean J. Parasitol. 2016, 54, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senbill, H.; Hazarika, L.; Baruah, A.; Borah, D.; Bhattacharyya, B.; Rahman, S. Life cycle of the southern cattle tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Canestrini, 1888 (Acari: Ixodidae) under laboratory conditions. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 23, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, B.; Thomas, D.B.; Dearth, R.K. Population dynamics of off-host Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) larvae in response to habitat and seasonality in South Texas. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, D.P.; Silva-Junior, M.H.S.; Tavares, C.P.; Sousa, I.C.; Sousa, D.M.; Brito, D.R.B.; Camargo, A.M.; Leite, R.C.; Faccini, J.L.H.; Lopes, W.D.Z.; et al. Biology of the non-parasitic phase of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in an area of Amazon influence. Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduma, E.G.; Emery, D.; Githaka, N.W.; Nguu, E.K.; Bishop, R.P.; Šlapeta, J. Molecular evidence confirms occurrence of Rhipicephalus microplus Clade A in Kenya and sub-Saharan Africa. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyangiwe, N.; Horak, I.G.; Van der Mescht, L.; Matthee, S. Range expansion of the economically important Asiatic blue tick, Rhipicephalus microplus, in South Africa. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2017, 88, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, Z.I.; Hu, S.H.; Chen, W.J.; Arijo, A.G.; Xiao, C.W. Importance of ticks and their chemical and immunological control in livestock. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2006, 7, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo-Ríos, C.; Betancur, O. Economic and health impact of ticks in production animals. In Ticks and Tick-Borne Pathogens; Abubakar, M., Kanchana Perera, P., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, W.; Fumagalli, M.; Carrasco, A.; Romeiro, M.; Modha, S.; Seki, M.; Gheller, J.; Daffre, S.; Nunes, M.; Murcia, P.; et al. Viral diversity of Rhipicephalus microplus parasitizing cattle in southern Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagunes-Quintanilla, R.; Gómez-Romero, N.; Mendoza-Martínez, N.; Castro-Saines, E.; Galván-Arellano, D.; Basurto-Alcantara, F.J. Perspectives on using integrated tick management to control Rhipicephalus microplus in a tropical region of Mexico. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1497840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, S.; Van der Merwe, N.A.; Maritz-Olivier, C. The genetic relationship between Rhipicephalus microplus and Rhipicephalus decoloratus ticks in South Africa and their population structure. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 129, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozipho, K.; Chaisi, M.; Magoro, R.; Mwale, M. An analysis of the gaps in the South African DNA barcoding library of ticks of veterinary and public health importance. Genome 2024, 67, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottinger, M. The Distribution of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) decoloratus on a Farm in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Master’s Thesis, University of Fort Hare, Alice, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Motloung, R.; Chaisi, M.; Sibiya, M.; Nyangiwe, N.; Shivambu, T. Predicting tick distributions in a changing climate: An ensemble approach for South Africa. Vet. Parasitol. 2025, 338, 110528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Rodriguez-Mallon, A.; Bermúdez, S.; de la Fuente, J.; Domingos, A.; Estrada, M.; Labruna, M.B.; Merino, J.; Mosqueda, J.; Nava, S.; et al. One Health approach to identify research needs on Rhipicephalus microplus ticks in the Americas. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, E.J.; Leal, B.; Thomas, D.B.; Dearth, R.K. Survival of off-host unfed Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus (Acari: Ixodidae) larvae in study arenas in relation to climatic factors and habitats in South Texas, USA. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndoro, J.T.; Mudhara, M.; Chimonyo, M. Cattle commercialization in rural South Africa: Livelihood drivers and implications for livestock marketing extension. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2014, 9, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, A.R.; Shively, G.E.; Masters, W.A. Farm productivity and household market participation: Evidence from LSMS data. Agric. Econ. 2009, 40, 539–552. [Google Scholar]
- Ndoro, J.T.; Mudhara, M.; Chimonyo, M. Farmers’ choice of cattle marketing channels under transaction cost in rural South Africa: A multinomial logit model. Afr. J. Range Forage Sci. 2015, 32, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monakale, K.S.; Ledwaba, M.B.; Smith, R.M.; Gaorekwe, R.M.; Malatji, D.P. A systematic review of ticks and tick-borne pathogens of cattle reared by smallholder farmers in South Africa. Curr. Res. Parasitol. Vector Borne Dis. 2024, 6, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyangiwe, N.; Matthee, S. Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) and tick-borne diseases affecting communal cattle and the control methods practiced by farmers in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. Vet. World 2025, 18, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollong, E.; Lébri, M.; Marie-Magdeleine, C.; Lagou, S.M.; Naves, M.; Bambou, J.-C. Sustainable management of tick infestations in cattle: A tropical perspective. Parasites Vectors 2025, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slayi, M.; Mpisana, Z. Prevalence and diversity of gastrointestinal parasites and tick species in communal feedlots compared to rural free-grazing cattle in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Parasitologia 2025, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makwarela, T.G.; Djikeng, A.; Masebe, T.M.; Nkululeko, N.; Nesengani, L.T.; Mapholi, N.O. Vector abundance and associated abiotic factors that influence the distribution of ticks in six provinces of South Africa. Vet. World 2024, 17, 1765–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolino, C.A.; Paranhos, R.M.; Maciel, W.G. Avaliação in vitro de fitoterápicos no controle de Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Nucleus Anim. 2013, 5, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, A.P.M.; Santos, M.D.C.; Santos, M.C.D.; Botura, M.B. Molecular targets for the development of new acaricides against Rhipicephalus microplus: A review. Parasitology 2022, 149, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.C.; Pérez de León, A.A.; Leite, F.P.L.; Pinto, L.D.S.; Gonçalves dos Santos, J.A.; Andreotti, R. Bovine immunoprotection against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus with recombinant Bm86-Campo Grande antigen. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2012, 21, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almazán, C.; Lagunes, R.; Villar, M.; Canales, M.; Rosario-Cruz, R.; Jongejan, F.; de la Fuente, J. Identification and characterization of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus candidate protective antigens for the control of cattle tick infestations. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 106, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etiang, P.; Atim, S.; Nkamwesiga, J.; Nalumenya, D.; Byaruhanga, C.; Odongo, S.; Vudriko, P.; Ademun, A.R.; Biryomumaisho, S.; Erume, J.; et al. Identification and distribution of Rhipicephalus microplus in selected high-cattle density districts in Uganda. Res. Sq. Preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Ghosh, S. Cloning and molecular analysis of Voraxin-α gene of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. J. Parasitol. Dis. 2014, 40, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neis, L.P.H.; Souza, A.P.D.; Bellato, V.; Sartor, A.A.; de Oliveira, A.P.; Cardoso, H.M. Resistance to cypermethrin and amitraz in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus on the Santa Catarina Plateau, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2012, 21, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães da Rocha, C.M.B.; Leite, R.C.; Bruhn, F.R.P.; Guimarães, A.M.; Furlong, J. Perceptions about the biology of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus among milk producers in Divinópolis, Minas Gerais. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2011, 20, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacarias do Amaral, M.A.; Magalhães da Rocha, C.M.B.; Faccini, J.L.H.; Furlong, J.; de Oliveira, C.M.; de Azevedo, M.C. Perceptions and attitudes among milk producers in Minas Gerais regarding cattle tick biology and control. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2011, 20, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showler, A.T.; de León, A.P.; Saelao, P. Biosurveillance and research needs involving area wide systematic active sampling to enhance integrated cattle fever tick eradication. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzemo, W.D.; Vudriko, P.; Ramatla, T.; Thekisoe, O. Acaricide resistance development in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) populations against amitraz and deltamethrin on communal farms of the King Sabata Dalindyebo Municipality, South Africa. Pathogens 2023, 12, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ellie, M.S.P.; Van der Rensburg, C.J. Competitive displacement and acaricide resistance of two Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) species collected on commercial farms in South Africa. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2023, 92, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makenov, M.T.; Toure, A.H.; Korneev, M.G.; Sacko, N.; Porshakov, A.M.; Yakovlev, S.A.; Radyuk, E.V.; Zakharov, K.S.; Shipovalov, A.V.; Boumbaly, S.; et al. Rhipicephalus microplus and its vector borne haemoparasites in Guinea: Further species expansion in West Africa. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yawa, M.; Nyangiwe, N.; Kadzere, C.T.; Muchenje, V.; Mpendulo, C.T.; Marufu, M.C. In search of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in the western central regions of the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyangiwe, N.; Harrison, A.; Horak, I.G. Displacement of Rhipicephalus decoloratus by Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2013, 61, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, I.G.; Boshoff, C.R.; Cooper, D.V.; Foggin, C.M.; Govender, D.; Harrison, A.; Hausler, G.; Hofmeyr, M.; Kilian, J.W.; MacFadyen, D.N.; et al. Parasites of domestic and wild animals in South Africa. XLIX. Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting white and black rhinoceroses in southern Africa. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2017, 84, e1–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, A.; Nyangiwe, N.; Mukaratirwa, S. Low genetic diversity and population structuring of Amblyomma hebraeum and Rickettsia africae from coastal and inland regions in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2022, 37, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhanguzi, D.; Byaruhanga, J.; Amanyire, W.; Ndekezi, C.; Ochwo, S.; Nkamwesiga, J.; Mwiine, F.N.; Tweyongyere, R.; Fourie, J.; Madder, M.; et al. Invasive cattle ticks in East Africa: Morphological and molecular confirmation of the presence of Rhipicephalus microplus in south-eastern Uganda. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduma, E.; Emery, D.L.; Githaka, N.; Nguu, E.K.; Bishop, R.P.; Šlapeta, J. Molecular evidence confirms occurrence of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in Kenya and suggests that an undifferentiated genotype is prevalent in the African continent. Res. Sq. Prepr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Vivas, R.I.; Jonsson, N.N.; Bhushan, C. Strategies for the control of Rhipicephalus microplus ticks in a world of conventional acaricide and macrocyclic lactone resistance. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiring, C.; Labuschagne, M. Genomic assessment of targets implicated in Rhipicephalus microplus acaricide resistance. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapholi, N.; Banga, C.B.; Dzama, K.; Matika, O.; Riggio, V.; Nyangiwe, N.; Maiwashe, A. Prevalence and tick loads in Nguni cattle reared in different environmental conditions across four provinces of South Africa. Vet. World 2022, 15, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tønnesen, M.; Penzhorn, B.; Bryson, N.; Stoltsz, W.; Masibigiri, T. Displacement of Boophilus decoloratus by Boophilus microplus in the Soutpansberg region, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2004, 32, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzemo, W.D.; Mavundela, S. Progression of deltamethrin resistance in Rhipicephalus microplus populations on communal farms of South Africa. Parasitol. Res. 2025, 124, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbertse, L.; Baron, S.; Van der Merwe, N.A.; Madder, M.; Stoltsz, W.H.; Maritz-Olivier, C. Genetic diversity, acaricide resistance status and evolutionary potential of a Rhipicephalus microplus population from a disease-controlled cattle farming area in South Africa. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, S.; Van der Merwe, N.A.; Madder, M.; Maritz-Olivier, C. SNP analysis infers that recombination is involved in the evolution of amitraz resistance in Rhipicephalus microplus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nchu, F.; Nyangiwe, N.; Muhanguzi, D.; Nzalawahe, J.; Nagagi, Y.P.; Msalya, G.; Joseph, N.A.; Kimaro, E.G.; Mollel, M.; Temba, V.; et al. Development of a practical framework for sustainable surveillance and control of ticks and tick-borne diseases in Africa. Vet. World 2020, 13, 1910–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannou, O.M.; Ouedraogo, A.S.; Biguezoton, A.S.; Abatih, E.; Coral-Almeida, M.; Farougou, S.; Yao, K.P.; Lempereur, L.; Saegerman, C. Models for studying the distribution of ticks and tick-borne diseases in animals: A systematic review and a meta-analysis with a focus on Africa. Pathogens 2021, 10, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Kim, G.; Lim, J.A.; Song, S.; Yoo, D.S.; Cho, H.S.; Oh, Y. Tick diversity and pathogen transmission in Daejeon, Korea: Implications from companion animals and walking trails. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemiya-Shirafuji, R. Distribution, seasonal occurrence and biological characteristics of Haemaphysalis longicornis, a vector of bovine piroplasmosis in Japan. In Climate, Ticks and Disease; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2021; pp. 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.; Krüger, R.F.; Peterson, A.T.; de Melo, L.F.; Vicenzi, N.; Jiménez-García, D. Climate change implications for the distribution of the babesiosis and anaplasmosis tick vector, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sruthy, S.; Asha, K.; Prejit, N.; Das, G.; Verma, R.; Sunanda, C.; Vinod, V.K.; Vergis, J.; Rajasekhar, R.; Milton, A.A.P.; et al. Prevalence of Crimean–Congo haemorrhagic fever virus and Ganjam virus among livestock and ticks in Wayanad, Kerala. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 49, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byaruhanga, C.; Akure, P.C.; Lubembe, D.M.; Sibeko-Matjila, K.; Troskie, M.; Oosthuizen, M.C.; Stoltsz, H. Molecular detection and characterisation of protozoan and rickettsial pathogens in ticks from cattle in the pastoral area of Karamoja, Uganda. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, J.; Shams, S.; Ayaz, S.; Din, I.U.; Khan, A.; Adil, N.; Ullah, H.; Raza, A. Epidemiology of ticks and molecular characterization of Rhipicephalus microplus in cattle population in north-western Pakistan. Int. J. Acarol. 2020, 46, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dalen, E.; Van Rensburg, C.J. Evolution of acaricide resistance of Rhipicephalus decoloratus on commercial farms in South Africa. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2023, 90, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahta, S.; Malope, P. Measurement of competitiveness in smallholder livestock systems and emerging policy advocacy: An application to Botswana. Food Policy 2014, 49, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xulu, S.; Peerbhay, K.; Gebreslasie, M.; Ismail, R. Drought influence on forest plantations in Zululand, South Africa, using MODIS time series and climate data. Forests 2018, 9, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippon, N.; Martiny, N.; Camberlin, P.; Hoffman, M.T.; Gond, V. Timing and patterns of the ENSO signal in Africa over the last 30 years: Insights from Normalized Difference Vegetation Index data. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2509–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannou, O.M.; Re, D.D.; Ouedraogo, A.S.; Biguezoton, A.S.; Abatih, E.; Yao, K.P.; Farougou, S.; Lempereur, L.; Vanwambeke, S.; Saegerman, C. Modelling habitat suitability of the invasive tick Rhipicephalus microplus in West Africa. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 2938–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, I.G.; Heyne, H.; Halajian, A.; Booysen, S.; Smit, W.J. Parasites of domestic and wild animals in South Africa. L. Ixodid ticks infesting horses and donkeys. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2017, 84, e1–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biguezoton, A.S.; Noël, V.; Adehan, S.; Adakal, H.; Dayo, G.K.; Zoungrana, S.; Farougou, S.; Chevillon, C. Ehrlichia ruminantium infects Rhipicephalus microplus in West Africa. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousseu, F.S.; Tchetgna, H.S.; Kamgang, B.; Djonabaye, D.; McCall, P.J.; Ndip, R.N.; Wondji, C.S. Infestation rates, seasonal distribution, and genetic diversity of ixodid ticks from livestock of various origins in two markets of Yaoundé, Cameroon. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2022, 36, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, M.D.; Hoffman, M.T. The consequences of precipitation seasonality for Mediterranean ecosystem vegetation of South Africa. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, B.; Zamora, E.; Fuentes, A.; Thomas, D.B.; Dearth, R.K. Questing by tick larvae (Acari: Ixodidae): A review of the influences that affect off-host survival. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2020, 113, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thekisoe, O.; Mofokeng, L.S.; Smit, N.J.; Taioe, M.O. Parasites of veterinary importance from domestic animals in uMkhanyakude District of KwaZulu-Natal Province. J. South Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2020, 91, e1–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yawa, M.; Nyangiwe, N.; Jaja, I.F.; Kadzere, C.T.; Marufu, M.C. Prevalence of serum antibodies of tick-borne diseases and the presence of Rhipicephalus microplus in communal grazing cattle in the north-eastern region of the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nxumalo, G.; Bashir, B.; Alsafadi, K.; Bachir, H.; Harsányi, E.; Arshad, S.; Mohammed, S. Meteorological drought variability and its impact on wheat yields across South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanjuntak, C.; Gaiser, T.; Ahrends, H.E.; Ceglar, A.; Singh, M.; Ewert, F.; Srivastava, A.K. Impact of climate extreme events and their causality on maize yield in South Africa. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 38921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, E.M.; Leta, S.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Madder, M.; Adehan, S.; Vanwambeke, S.O. Species distribution modelling for Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) in Benin, West Africa: Comparing datasets and modelling algorithms. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 118, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungirai, M.; Moyo, D.; De Clercq, P.; Madder, M.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; De Clercq, E.M. Modelling the distribution of Rhipicephalus microplus and Rhipicephalus decoloratus in Zimbabwe. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2018, 14, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempereur, L.; Geysen, D.; Madder, M. Development and validation of a PCR–RFLP test to identify African Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) ticks. Acta Trop. 2010, 114, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makwarela, T.G.; Nyangiwe, N.; Masebe, T.M.; Djikeng, A.; Nesengani, L.T.; Smith, R.M.; Mapholi, N.O. Morphological and molecular characterization of tick species infesting cattle in South Africa. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etiang, P.; Atim, S.A.; Nkamwesiga, J.; Nalumenya, D.; Byaruhanga, C.; Odongo, S.; Vudriko, P.; Ademun, A.R.; Biryomumaisho, S.; Erume, J.; et al. Identification and distribution of Rhipicephalus microplus in selected high-cattle density districts in Uganda: Signaling future demand for novel tick control approaches. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; Jin, Y.T.; Zhao, J.; Xu, A.C.; Luo, Y.Y. A PCR method that can be further developed into PCR-RFLP assay for eight animal species identification. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2018, 2018, 5890140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahma, R.K.; Dixit, V.; Sangwan, A.K.; Doley, R. Identification and characterization of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and Haemaphysalis bispinosa ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) of north-eastern India by ITS2 and 16S rDNA sequences and morphological analysis. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2014, 62, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, S.M.K.; Hossain, M.A.M.; Chowdhury, Z.Z.; Johan, M.R. Detection and discrimination of seven highly consumed meat species simultaneously in food products using a heptaplex PCR-RFLP assay. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 100, 103938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesson, L.; Heslan, J.M.; Ménoret, S.; Anegon, I. Rapid and accurate determination of zygosity in transgenic animals by real-time quantitative PCR. Transgenic Res. 2002, 11, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tupperwar, N.; Vineeth, V.; Rath, S.; Vaidya, T. Development of a real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for the quantification of Leishmania species and the monitoring of systemic distribution of the pathogen. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Su, J. Cyprinid viral diseases and vaccine development. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 83, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silatsa, B.A.; Kuiate, J.R.; Njiokou, F.; Simo, G.; Feussom, J.K.; Tunrayo, A.; Amzati, G.S.; Bett, B.; Bishop, R.; Githaka, N.; et al. A countrywide molecular survey leads to the identification of the invasive cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in Cameroon, a decade after it was reported in Côte d’Ivoire. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hector, E.; Elelu, N.; Ferrolho, J.; Couto, J.; Sanches, G.; Antunes, S.; Domingos, A.; Eisler, M. PCR detection of Ehrlichia ruminantium and Babesia bigemina in cattle from Kwara State, Nigeria: Unexpected absence of infection. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, L.N.; Diarra, A.Z.; Pham, Q.L.; Le-Viet, N.; Berenger, J.M.; Ho, V.H.; Nguyen, X.Q.; Parola, P. Morphological, molecular and MALDI-TOF MS identification of ticks and tick-associated pathogens in Vietnam. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GilArriortua, M.; Saloña-Bordas, M.I.; Cainé, L.M.; Pinheiro, F.; de Pancorbo, M.M. Technical note: “Mitochondrial and nuclear DNA approaches for reliable identification of Lucilia (Diptera, Calliphoridae) species of forensic interest from southern Europe”. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 257, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, C.; Yuan, X.; Jia, G.; Deng, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; et al. Assessment of four DNA fragments (COI, 16S rDNA, ITS2, 12S rDNA) for species identification of the Ixodida (Acari: Ixodida). Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zeng, W.; Wang, S.; Tan, W.; Lu, X.; Kairullayev, K.; Mi, L.; Hazihan, W.; Liu, G.; Yang, M.; et al. Application of DNA barcodes in the genetic diversity of hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Kazakhstan. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2024, 92, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathirvelpandian, A.; Chowdhury, L.M.; Sanjeev Kumar, M. Species-specific molecular signatures for the commercially important scombrids using mitochondrial gene analysis: A tool for fisheries management. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2022, 15, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuperfain, A.B.; Zhang, Z.L.; Kennedy, J.L.; Gonçalves, V.F. The complex interaction of mitochondrial genetics and mitochondrial pathways in psychiatric disease. Mol. Neuropsychiatry 2018, 4, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, R.A.; Armstrong, K.F.; Meier, R.; Yi, Y.; Brown, S.D.J.; Cruickshank, R.H.; Keeling, S.; Johnston, C. Barcoding and border biosecurity: Identifying cyprinid fishes in the aquarium trade. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e28381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrutha, B.M.; Kumar, K.G.A.; Kurbet, P.S.; Varghese, A.; Deepa, C.K.; Pradeep, R.K.; Nimisha, M.; Asaf, M.; Juliet, S.; Ravindran, R.; et al. Morphological and molecular characterization of Rhipicephalus microplus and Rhipicephalus annulatus from selected states of southern India. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monakale, K.S.; Smith, R.M.; Gaorekwe, R.M.; Ledwaba, M.B.; Malatji, D.P. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of ticks and tick-borne pathogens from cattle in selected villages of Greater Letaba Municipality in Limpopo Province, South Africa. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawana, M.; Onyiche, T.E.; Ramatla, T.; Mtshali, S.; Thekisoe, O. Epidemiology of ticks and tick-borne pathogens in domestic ruminants across the Southern African Development Community (SADC) region from 1980 until 2021: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongejan, F.; Berger, L.; Busser, S.; Deetman, I.; Jochems, M.; Leenders, T.; Sitter, B.; Steen, F.; Wentzel, J.; Stoltsz, H. Amblyomma hebraeum is the predominant tick species on goats in the Mnisi Community Area of Mpumalanga Province, South Africa, and is co-infected with Ehrlichia ruminantium and Rickettsia africae. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona-Guerrero, I.; Maitre, A.; Abuin-Denis, L.; Morales-García, R.; Almazán, C.; Obregón, D.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Mosqueda, J. Babesia bovis infection alters the composition and assembly of Rhipicephalus microplus midgut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1608409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githaka, N.W.; Kanduma, E.G.; Wieland, B.; Darghouth, M.A.; Bishop, R.P. Acaricide resistance in livestock ticks infesting cattle in Africa: Current status and potential mitigation strategies. Curr. Res. Parasitol. Vector Borne Dis. 2022, 2, 100090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heylen, D.J.A.; Labuschagne, M.; Meiring, C.; Van der Mescht, L.; Klafke, G.; Costa Junior, L.M.; Strydom, T.; Wentzel, J.; Shacklock, C.; Halos, L.; et al. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of acaricide resistance in Rhipicephalus microplus field isolates from South Africa and Brazil. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2024, 24, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dalen, E.M.S.P.; Van Rensburg, C.J. Acaricide resistance of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) decoloratus (Acari: Ixodidae) on commercial farms in South Africa: Filling a gap in historical data. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2023, 90, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agwunobi, D.O.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J. A retrospective review on ixodid tick resistance against synthetic acaricides: Implications and perspectives for future resistance prevention and mitigation. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 173, 104776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzemo, W.D.; Thekisoe, O.; Vudriko, P. Risk factors contributing to tick–acaricide control failure in communal areas of the Oliver Tambo District, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2024, 93, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Zhu, G.-D.; Zhou, H.-Y.; Tang, J.-X.; Li, J.-L.; Xu, S.; Zhang, M.-H.; Yao, L.-N.; Huang, G.-Q.; Wang, Y.-B.; et al. Development and application of an AllGlo probe-based qPCR assay for detecting knockdown resistance (kdr) mutations in Anopheles sinensis. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhrahmad, F.; Rakhshandehroo, E.; Ghaemi, M. Molecular evidence on the emergence of benzimidazole resistance SNPs in field isolates of Marshallagia marshalli (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae) in sheep. J. Parasitol. Dis. 2021, 45, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, M.K.; Islam, N.; Alouffi, A.; Khan, A.Z.; da Silva Vaz, I., Jr.; Tanaka, T.; Ali, A. Acaricides resistance in ticks: Selection, diagnosis, mechanisms, and mitigation. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 941831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, N.E.; Olafson, P.U.; Davey, R.B.; Buckmeier, G.; Bodine, D.; Sidak-Loftis, L.C.; Giles, J.R.; Duhaime, R.; Miller, R.J.; Mosqueda, J.; et al. Multiple mutations in the para-sodium channel gene are associated with pyrethroid resistance in Rhipicephalus microplus from the United States and Mexico. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Souza Higa, L.; Garcia, M.; Barros, J.; Koller, W.; Andreotti, R. Acaricide resistance status of the Rhipicephalus microplus in Brazil: A literature overview. Med. Chem. 2015, 5, 326–333. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero, F.D.; Lovis, L.; Martins, J.R. Acaricide resistance mechanisms in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2012, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Canal, L.H.; Dall’Agnol, B.; Webster, A.; Reck, J.; Martins, J.R.; Klafke, G.M. Mechanisms of amitraz resistance in a Rhipicephalus microplus strain from southern Brazil. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vudriko, P.; Umemiya-Shirafuji, R.; Tayebwa, D.S.; Byaruhanga, J.; Byamukama, B.; Tumwebaze, M.; Xuan, X.; Suzuki, H. Molecular characterization of octopamine/tyramine receptor gene of amitraz-resistant Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) decoloratus ticks from Uganda. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hove, P.; Khumalo, Z.T.H.; Chaisi, M.E.; Oosthuizen, M.C.; Brayton, K.A.; Collins, N.E. Detection and characterisation of Anaplasma marginale and A. centrale in South Africa. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzemo, W.D.; Thekisoe, O.; Vudriko, P. Development of acaricide resistance in tick populations of cattle: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, S.S.; Shakya, M.; Singh, M.; Bagherwal, R.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Mehta, H.K. Phytochemical and acaricidal analysis of lavender (Lavandula angustifolia) and sage (Salvia officinalis) essential oils against Rhipicephalus microplus ticks: An in vitro and in vivo study. Vet. Parasitol. 2025, 338, 110523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makwarela, T.G.; Seoraj-Pillai, N.; Nangammbi, T.C. Tick control strategies: Critical insights into chemical, biological, physical, and integrated approaches for effective hard tick management. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovis, L.; Reggi, J.; Berggoetz, M.; Betschart, B.; Sager, H. Determination of acaricide resistance in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) field populations of Argentina, South Africa, and Australia with the larval tarsal test. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Janer, E.; Martins, J.R.; Mendes, M.C.; Namindome, A.; Klafke, G.M.; Schumaker, T.T. Diagnosis of fipronil resistance in Brazilian cattle ticks (Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus) using in vitro larval bioassays. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 173, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrents, J.; Sarli, M.; Sarmiento, N.F.; Rossner, M.V.; Morel, N.; Guglielmone, A.A.; Nava, S. Resistance of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus to fluazuron in Argentina. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2022, 86, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrents, J.; Sarli, M.; Rossner, M.V.; Toffaletti, J.R.; Morel, N.; Martínez, N.C.; Webster, A.; Mangold, A.J.; Guglielmone, A.A.; Nava, S. Resistance of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus to ivermectin in Argentina. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 132, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, J.; Klafke, G.M.; Webster, A.; Dall’Agnol, B.; Scheffer, R.; Souza, U.A.; Corassini, V.B.; Vargas, R.; Dos Santos, J.S.; De Souza Martins, J.R. First report of fluazuron resistance in Rhipicephalus microplus: A field tick population resistant to six classes of acaricides. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 201, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Vivas, R.I.; Pérez-Cogollo, L.C.; Rosado-Aguilar, J.A.; Ojeda-Chi, M.M.; Trinidad-Martinez, I.; Miller, R.J.; Li, A.Y.; de León, A.P.; Guerrero, F.; Klafke, G. Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus resistant to acaricides and ivermectin in cattle farms of Mexico. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2014, 23, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Salas, A.; Rodríguez-Vivas, R.I.; Alonso-Díaz, M.A.; Basurto-Camberos, H. Ivermectin resistance status and associated factors in Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) populations from Veracruz, Mexico. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 190, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Hidalgo, R.; Pérez-Otáñez, X.; Garcés-Carrera, S.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Madder, M.; Benítez-Ortiz, W. The current status of resistance to alpha-cypermethrin, ivermectin, and amitraz of the cattle tick (Rhipicephalus microplus) in Ecuador. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Otáñez, X.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Orozco-Alvarez, G.; Arciniegas-Ortega, S.; Ron-Garrido, L.; Rodríguez-Hidalgo, R. Widespread acaricide resistance and multi-resistance in Rhipicephalus microplus in Ecuador and associated environmental and management risk factors. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2024, 15, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagar, S.V.; Saini, K.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, R.; Fular, A.; Shakya, M.; Upadhaya, D.; Nagar, G.; Ghosh, S.; et al. Acaricide resistance in Rhipicephalus microplus collected from selected districts of Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Punjab states of India. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Singh, H.; Singh, N.K.; Rath, S.S. Multiple mutations in the acetylcholinesterase 3 gene associated with organophosphate resistance in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus ticks from Punjab, India. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 216, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khating, S.; Jadhav, N.; Vijay, M.; Sharma, A.K.; Srivastava, A.; Jadhao, S.; Kumar, S.; Kalwaghe, S.; Siddiqui, M.F.M.F.; Narawade, M.; et al. Current profile of phenotypic pyrethroid resistance in Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) populations sampled from Marathwada region of Maharashtra state, India. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barré, N.; Li, A.; Miller, R.; Gaïa, H.; Delathière, J.-M.; Davey, R.; George, J. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of deltamethrin and amitraz mixtures for the control of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) in New Caledonia. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 155, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro Janer, E.; Klafke, G.M.; Capurro, M.L.; Schumaker, T.T.S. Cross-resistance between fipronil and lindane in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 210, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temnykh, S.; DeClerck, G.; Lukashova, A.; Lipovich, L.; Cartinhour, S.; McCouch, S. Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poćwierz-Kotus, A.; McQuaid, C.D.; Lipinski, M.R.; Zbawicka, M.; Wenne, R. SNPs analysis indicates non-uniform origins of invasive mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) on the Southern African coast. Animals 2024, 14, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, A.; Liu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Xu, S.; Lu, Y. Genomic insights into vector–pathogen adaptation in Haemaphysalis longicornis and Rhipicephalus microplus. Pathogens 2025, 14, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sungirai, M.; Baron, S.; Van der Merwe, N.A.; Moyo, D.Z.; De Clercq, P.; Maritz-Olivier, C.; Madder, M. Population structure and genetic diversity of Rhipicephalus microplus in Zimbabwe. Acta Trop. 2018, 180, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biguezoton, A.S.; Adakal, H.; Noel, V.; Zoungrana, S.; Chevillon, C. Population genetics of the invasive tick Rhipicephalus microplus in Benin and Burkina Faso (West Africa). Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2023, 17, 2747–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corley, S.W.; Jonsson, N.N.; Piper, E.K.; Cutullé, C.; Stear, M.J.; Seddon, J.M. Mutation in the RmβAOR gene is associated with amitraz resistance in the cattle tick Rhipicephalus microplus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16772–16777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, M.; Kumar, B.; Manjunathachar, H.V.; Parthasarathi, B.C.; Nandi, A.; Neethu, C.K.S.; Nagar, G.; Ghosh, S. Genetic diversity of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus for a global scenario: A comprehensive review. Pathogens 2024, 13, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz González, G.; Pinos-Rodriguez, J.; Alonso-Díaz, M.; Romero-Salas, D.; Vicente-Martínez, J.; Fernandez Salas, A.; Rodríguez, J.; Castillo-Gallegos, E. Rotational grazing modifies Rhipicephalus microplus infestation in cattle in the humid tropics. Animals 2023, 13, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-González, G.; Pinos-Rodríguez, J.M.; Alonso-Díaz, M.; Romero-Salas, D.; Vicente-Martínez, J.G.; Fernández-Salas, A.; Jarillo-Rodríguez, J.; Castillo-Gallegos, E. Efficacy of rotational grazing on the control of Rhipicephalus microplus infesting calves in humid tropical conditions. J. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 2024, 7558428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeba, S.; Mahmmod, Y.; Mohammed, H.; Amer, H.; Moustafa, M.; Sobhi, A.; El-Sokary, M.; Hussein, M.; Tolba, A.; Al Hammadi, Z.; et al. In vitro detection of acaricide resistance in Hyalomma species ticks with emphasis on farm management practices associated with acaricide resistance in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpeku, M.; Ogah, D.; Adeleke, M. A review of challenges to genetic improvement of indigenous livestock for improved food production in Nigeria. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2019, 19, 13959–13978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.W.; Van Wyk, J.A.; Hamie, J.C.; Byaruhanga, C.; Kenyon, F. Refugia-based strategies for parasite control in livestock. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2020, 36, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolenga, C.J.R.; Anjos, A.D.; Barbosa, V.H.G.; Yoshitani, U.Y.; Castilho, P.; Miyakawa, V.I.; Molento, M.B. Acaricidal effect of major compounds to control Rhipicephalus microplus (Canestrini, 1887) in dairy cows and possible alternatives for reversing multidrug resistance. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2022, 31, e005422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesquita, E.; Da Costa, D.P.; Meirelles, L.N.; Camargo, M.G.; Corrêa, T.A.; Bittencourt, V.; Da Silva Coelho, I.; Santos, H.A.; Humber, R.A.; Golo, P.S. Entomopathogenic fungus treatment changes the gut bacterial diversity of Rhipicephalus microplus ticks. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bório, V.S.; Corrêa, T.A.; Fiorotti, J.; Mesquita, E.; Meirelles, L.N.; Camargo, M.G.; Bittencourt, V.; Golo, P.S. Inhibition of dopamine activity and response of Rhipicephalus microplus challenged with Metarhizium anisopliae. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeshma Rao, U.B.; Narladkar, B.W. First report on the use of bio-fungal agent Verticillium lecanii against tropical cattle tick, Rhipicephalus microplus (Acarina: Ixodidae). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Oundo, J.W.A.A.; Kalayou, S.; Gort, G.; Bron, G.M.; Koenraadt, C.J.M.; Ten Bosch, Q.; Masiga, D. A randomized controlled trial of Tickoff® (Metarhizium anisopliae ICIPE 7) for control of tick infestations and transmission of tick-borne infections in extensively grazed zebu cattle in coastal Kenya. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2024, 27, e00384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oundo, J.W.A.A.; Masiga, D.; Okal, M.N.A.; Bron, G.M.; Akutse, K.S.; Subramanian, S.; Ten Bosch, Q.; Koenraadt, C.J.M.; Kalayou, S. Evaluating the efficacy of Mazao Tickoff (Metarhizium anisopliae ICIPE 7) in controlling natural tick infestations on cattle in coastal Kenya: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Țopa, D.-C.; Căpșună, S.; Calistru, A.-E.; Ailincăi, C. Sustainable practices for enhancing soil health and crop quality in modern agriculture: A review. Agriculture 2025, 15, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, S.; Morse, S.; Bonifacio, A.; Chancellor, T.; Condori, B.; Crespo-Pérez, V.; Hobbs, S.; Kroschel, J.; Ba, M.; Rebaudo, F.; et al. Obstacles to integrated pest management adoption in developing countries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3889–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaija, P.D.; Contreras, M.; Kirunda, H.; Nanteza, A.; Kabi, F.; Mugerwa, S.; De La Fuente, J. Inspiring anti-tick vaccine research, development and deployment in tropical Africa for the control of cattle ticks: Review and insights. Vaccines 2022, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klafke, G.M.; Golo, P.S.; Monteiro, C.M.O.; Costa-Júnior, L.M.; Reck, J. Brazil’s battle against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus ticks: Current strategies and future directions. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2024, 33, e005124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year/Period | Province/Region | Locality/Site | Evidence/Method | Classes | Example Actives | Notes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | Eastern Cape | Communal dip tanks (various) | Larval immersion test (LIT) | AM; SP; OP | Amitraz; cypermethrin; chlorfenvinphos | Resistance at 3/45 (AM), 1/45 (SP), 8/36 (OP) | [43] |
| 2013 | Mpumalanga | Unspecified (communal) | LTT/LPT bioassay | SP | (Not specified) | One SP-resistant population | [106] |
| 2006–2017 | Eastern Cape | Near Alexandria | LIT (lab submissions) | AM; OP; SP | Amitraz; chlorfenvinphos; cypermethrin | Notable multi-resistant population | [43] |
| 2019–2022 | KwaZulu-Natal | Various sites | On-animal field assays + lab | OP; FIP; SP; AM; ML | Chlorfenvinphos; fipronil; deltamethrin; amitraz; ivermectin | Phenotypic resistance observed | [106] |
| 2019–2022 | Mpumalanga | Various sites | On-animal field assays + lab | OP; FIP; SP; AM; ML | As above | Phenotypic resistance observed | [106] |
| 2019–2022 | Western Cape | Various sites | On-animal field assays + lab | OP; FIP; SP; AM; ML | As above | Phenotypic resistance observed | [106] |
| 2019–2022 | Eastern Cape | Various sites | On-animal field assays + lab | OP; FIP; SP; AM; ML | As above | Phenotypic resistance observed | [106] |
| 2023 | Eastern Cape | King Sabata Dalindyebo | AIT and LIT | AM; SP | Amitraz; deltamethrin | RR up to ~3 (AM) and ~14 (SP) | [42] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makwarela, T.G.; Seoraj-Pillai, N.; Malatji, D.P.; Nangammbi, T.C. Adaptation and Invasion Dynamics of Rhipicephalus microplus in South Africa: Ecology, Resistance, and Management Implications. Insects 2025, 16, 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121204
Makwarela TG, Seoraj-Pillai N, Malatji DP, Nangammbi TC. Adaptation and Invasion Dynamics of Rhipicephalus microplus in South Africa: Ecology, Resistance, and Management Implications. Insects. 2025; 16(12):1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121204
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakwarela, Tsireledzo Goodwill, Nimmi Seoraj-Pillai, Dikeledi Petunia Malatji, and Tshifhiwa Constance Nangammbi. 2025. "Adaptation and Invasion Dynamics of Rhipicephalus microplus in South Africa: Ecology, Resistance, and Management Implications" Insects 16, no. 12: 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121204
APA StyleMakwarela, T. G., Seoraj-Pillai, N., Malatji, D. P., & Nangammbi, T. C. (2025). Adaptation and Invasion Dynamics of Rhipicephalus microplus in South Africa: Ecology, Resistance, and Management Implications. Insects, 16(12), 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16121204