SIT-ia: A Software-Hardware System to Improve Male Sorting Efficacy for the Sterile Insect Technique
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drosophila suzukii Colony
2.2. Classification Algorithms
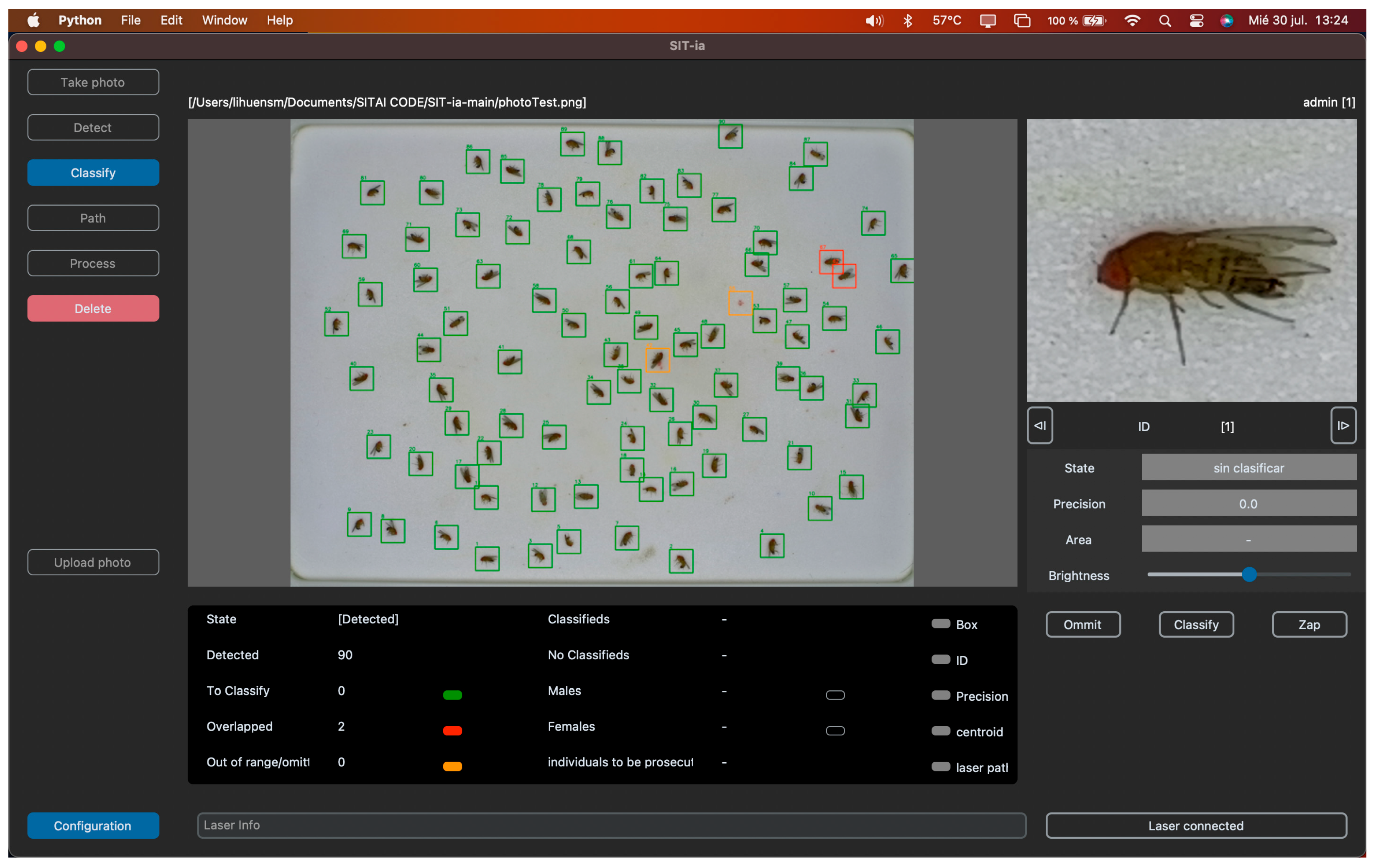
2.3. Software Design and Hardware Used
2.4. Route Optimization
2.5. System Performance
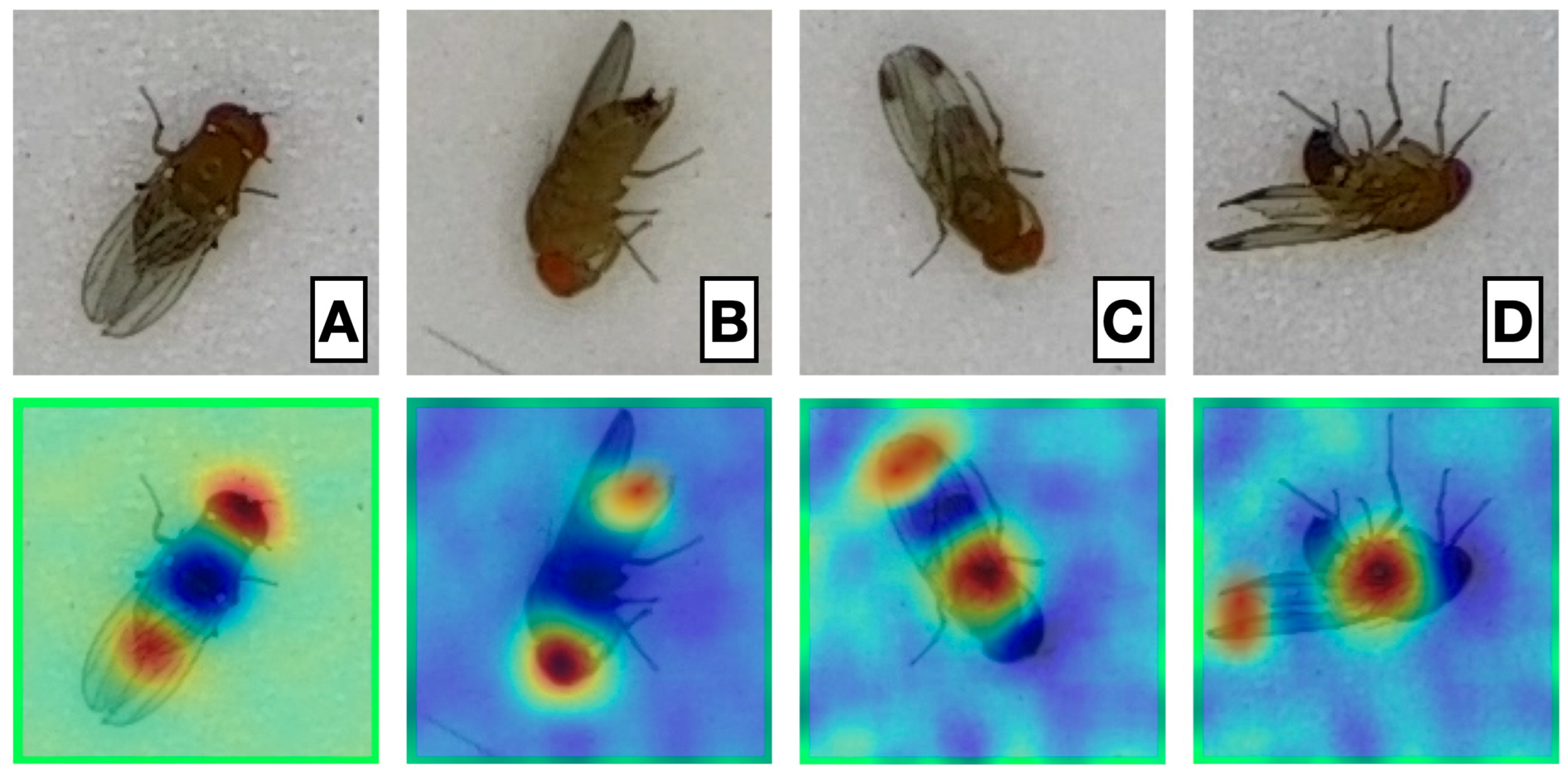
2.6. Model Explainability
3. Results
3.1. Classification Algorithms
3.2. Software Design and Implementation
3.3. Route Optimization
3.4. System Performance
3.5. Explainability
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SWD | Spotted Wing Drosophila |
| SIT | Sterile Insect Technique |
| ACO | Ant Colony Optimization |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CVPR | Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition |
| GSS | Genetic Sexing Strain |
| GUI | Graphical User Interface |
| PMLR | Proceedings of Machine Learning Research |
| RISE | Randomized Input Sampling for Explanation of Black-box Models |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| VGG | Visual Geometry Group (deep CNN architecture) |
| IAEA | International Atomic Energy Agency |
References
- Shackleton, R.T.; Shackleton, C.M.; Kull, C.A. The role of invasive alien species in shaping local livelihoods and human well-being: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 229, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, P.C.; Berec, L.; Liebhold, A.M. Exploiting Allee effects for managing biological invasions. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suckling, D.M.; Tobin, P.C.; McCullough, D.G.; Herms, D.A. Combining tactics to exploit Allee effects for eradication of alien insect populations. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, V.A.; Hendrichs, J.; Robinson, A.S. Sterile Insect Technique: Principles and Practice in Area-Wide Integrated Pest Management; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2021; p. 1216. [Google Scholar]
- Klassen, W.; Curtis, C.F. History of the sterile insect technique. In Sterile Insect Technique; Dyck, V.A., Hendrichs, J., Robinson, A.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Homem, R.A.; Mateos-Fierro, Z.; Jones, R.; Gilbert, D.; Mckemey, A.R.; Slade, G.; Fountain, M.T. Field suppression of spotted wing drosophila (SWD) (Drosophila suzukii Matsumura) using the sterile insect technique (SIT). Insects 2022, 13, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemer, S.; Mateos-Fierro, Z.; Brough, B.; Deakin, G.; Moar, R.; Carvalho, J.P.; Homem, R.A. Suppression of Spotted Wing Drosophila, Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura), in Raspberry Using the Sterile Insect Technique. Insects 2025, 16, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, S.L. When more is less: Mosquito population suppression using sterile, incompatible and genetically modified male mosquitoes. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dame, D.A.; Curtis, C.F.; Benedict, M.Q.; Robinson, A.S.; Knols, B.G. Historical applications of induced sterilisation in field populations of mosquitoes. Malar. J. 2009, 8 (Suppl. S2), S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, A.S.; Van Heemert, C. Ceratitis capitata—A suitable case for genetic sexing. Genetica 1982, 58, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddall, A.; Harvey-Samuel, T.; Chapman, T.; Leftwich, P.T. Manipulating insect sex determination pathways for genetic pest management: Opportunities and challenges. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 867851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Rayes, D.; Yang, M.; Akbari, O.S. Fluorescent-based sex-separation technique in major invasive crop pest, Drosophila suzukii. GEN Biotechnol. 2025, 4, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Scott, M.J. Evaluation of additional Drosophila suzukii male-only strains generated through remobilization of an FL19 transgene. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 829620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuizen, A.; Hemming, J.; Suh, H. Detection and classification of insects on stick-traps in a tomato crop using faster R-CNN. In Proceedings of the Netherlands Conference on Computer Vision, ’s-Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands, 26–27 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, M.C.F.; Leandro, M.E.D.; Valero, C.; Coronel, L.C.P.; Bazzo, C.O.G. Automatic detection and monitoring of insect pests—A review. Agriculture 2020, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosjen, P.P.J.; Kellenberger, B.; Kooistra, L.; Green, D.R.; Fahrentrapp, J. Deep learning for automated detection of Drosophila suzukii: Potential for UAV-based monitoring. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2994–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-López, G.I.; Valenzuela-Carrasco, G.; Toledo-Mesa, E.; Juárez-Durán, M.; Tapia-McClung, H.; Pérez-Staples, D. Determination of the physiological age in two tephritid fruit fly species using artificial intelligence. J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischel, D.M. Classification of the Sex of Drosophila Suzukii with Pre-Trained Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Le, K. An Overview of VGG16 and NiN Models. Available online: https://lekhuyen.medium.com/an-overview-of-vgg16-and-nin-models-96e4bf398484 (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Proceedings of Machine Learning Research (PMLR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Python Software Foundation. Python (Version 3.12). Available online: https://www.python.org/ (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Pandas Development Team. Pandas. Available online: https://pandas.pydata.org/ (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- OpenCV Team. OpenCV. Available online: https://opencv.org/ (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- The Linux Foundation. PyTorch. Available online: https://pytorch.org/ (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Messina, E.R.; Kramer, T.R.; Proctor, F.M. The NIST RS274NGC Interpreter, version 3; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Grupo de Ecología de Insectos GEPI. User Manual for SIT-ia. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/18S10qzuk6494w6m8Co41-sla4XFRZVZM/view?usp=sharing (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Dorigo, M.; Stützle, T. Ant colony optimization: Overview and recent advances. In Handbook of Metaheuristics, 2nd ed.; Gendreau, M., Potvin, J.-Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 311–351. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Bach, S.; Binder, A.; Montavon, G.; Klauschen, F.; Müller, K.-R.; Samek, W. On pixel-wise explanations for non-linear classifier decisions by layer-wise relevance propagation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsiuk, V.; Das, A.; Saenko, K. RISE: Randomized input sampling for explanation of black-box models. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.07421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendón, P.; McInnis, D.; Lance, D.; Stewart, J. Medfly (Diptera: Tephritidae) genetic sexing: Large-scale field comparison of males-only and bisexual sterile fly releases in Guatemala. J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Automation for Tsetse Mass Rearing for Use in Sterile Insect Technique Programmes. In Final Report of a Co-Ordinated Research Project 1995–2001; IAEA-TECDOC-1353; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zacarés, M.; Salvador-Herranz, G.; Almenar, D.; Tur, C.; Argilés, R.; Bourtzis, K.; Bossin, H.; Pla, I. Exploring the potential of computer vision analysis of pupae size dimorphism for adaptive sex sorting systems of various vector mosquito species. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11 (Suppl. S2), 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argilés-Herrero, R.; Salvador-Herranz, G.; Parker, A.G.; Zacarés, M.; Fall, A.G.; Gaye, A.M.; Nawaz, A.; Takáč, P.; Vreysen, M.J.B.; de Beer, C.J. Near-infrared imaging for automated tsetse pupae sex sorting in support of the sterile insect technique. Parasite 2023, 30, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.T.; Mamai, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Upscaling the production of sterile male mosquitoes with an automated pupa sex sorter. Sci. Robot. 2024, 9, eadj6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pérez, M.I.; Faulhaber, B.; Williams, M.; Brosa, J.; Aranda, C.; Pujol, N.; Talavera, S. A novel optical sensor system for the automatic classification of mosquitoes by genus and sex with high levels of accuracy. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patt, J.M.; Makagon, A.; Norton, B.; Marvit, M.; Rutschman, P.; Neligeorge, M.; Salesin, J. An optical system to detect, surveil, and kill flying insect vectors of human and crop pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, R.; Medici, A.; Puggioli, A.; Balestrino, F.; Carrieri, M. Pilot Field Trials with Aedes albopictus Irradiated Sterile Males in Italian Urban Areas. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamai, W.; Bueno-Masso, O.; Wallner, T.; Nikièma, S.A.; Meletiou, S.; Deng, L.; Balestrino, F.; Yamada, H.; Bouyer, J. Efficiency assessment of a novel automatic mosquito pupae sex separation system in support of area-wide male-based release strategies. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashatola, T.; Ndo, C.; Koekemoer, L.L.; Dandalo, L.C.; Wood, O.R.; Malakoane, L.; Poumachu, Y.; Lobb, L.N.; Kaiser, M.; Bourtzis, K.; et al. A review on the progress of sex-separation techniques for sterile insect technique applications against Anopheles arabiensis. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11 (Suppl. S2), 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, M.; Buitenhuis, R.; Murphy, G.; Scott-Dupree, C.D. Development of a mechanical sexing system to improve the efficacy of an area-wide sterile insect release programme to control American serpentine leafminer (Diptera: Agromyzidae) in Canadian ornamental greenhouses. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malefaki, A.X.; Valanides, N.; Manganaris, G.A.; DeVetter, L.W.; Papadaki, S.; Krokida, M.; Angelis-Dimakis, A. A comprehensive assessment of life cycle environmental impact and economic feasibility of different red raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) cultivation systems. Clean. Circ. Bioecon. 2025, 11, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Neural Network Architectures Model | Depth (Layers) | Key Architectural Features | Precision (Validation) | Precision (Test) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG16 | 16 | Simple stack of 13 convolutional + 3 fully connected layers. | 98.27% | 97.22% |
| VGG19 | 19 | Similar to VGG16 but with additional convolutional layers in the first three blocks. | 97.40% | 96.53% |
| ResNet50 | 50 | Residual learning blocks with skip connections. | 97.83% | 97.22% |
| ResNet101 | 101 | Same as ResNet50 but with more residual blocks. | 95.67% | 97.22% |
| ResNet152 | 152 | Same as ResNet50 but with more residual blocks. | 95.53% | 88.89% |
| MobileNetV2 | ~53 | Inverted residual blocks with linear bottlenecks. | 95.96% | 91.67% |
| EfficientNet | From 237 to 813 (B0–B7) | Uses compound scaling to uniformly balance network width, depth, and resolution. | 95.38% | 95.83% |
| CNN6 (Custom) | 6 | Four convolutional (ReLU) + max-pooling layers, followed by two fully connected layers. | 96.95% | 98.61% |
| Method | Generation Time [Seconds] | Path Length [Pixels] | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Optimization | 0.002 (±0.0008) | 38,113 (±14,289) | – |
| Greedy Algorithm | 0.29 (±0.08) | 30,265 (±8554) | 56% |
| Local Search | 0.56 (±0.16) | 28,423 (±8033) | 58% |
| Ant Colony | 6.58 (±1.86) | 22,893 (±6470) | 66% |
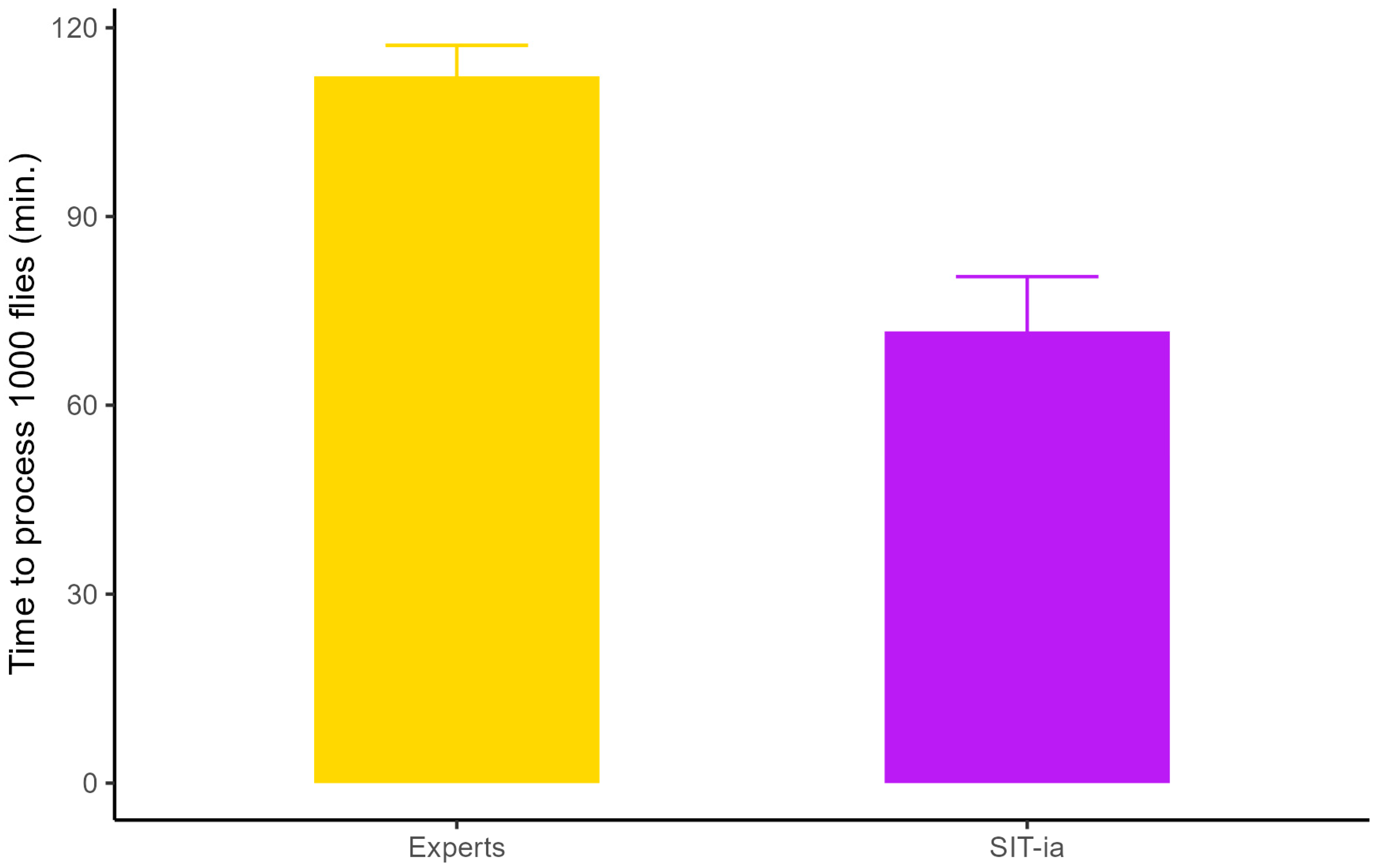
| Worker | Replicates | Flies per Plate | Preparation (Minutes) | Sex-Sorting (Minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experts | 21 | 224 (±53) | 3.8 (±2.0) | 21.3 (±6.9) |
| SIT-ia | 14 | 123 (±43) | 5.8 (±3.4) | 2.8 (±2.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de la Vega, G.; Smith, L.; Soria-Mercier, L.; Edwards, W.; Triñanes, F.; Masagué, S.; Corley, J. SIT-ia: A Software-Hardware System to Improve Male Sorting Efficacy for the Sterile Insect Technique. Insects 2025, 16, 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111108
de la Vega G, Smith L, Soria-Mercier L, Edwards W, Triñanes F, Masagué S, Corley J. SIT-ia: A Software-Hardware System to Improve Male Sorting Efficacy for the Sterile Insect Technique. Insects. 2025; 16(11):1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111108
Chicago/Turabian Stylede la Vega, Gerardo, Luciano Smith, Lihuen Soria-Mercier, Wilson Edwards, Federico Triñanes, Santiago Masagué, and Juan Corley. 2025. "SIT-ia: A Software-Hardware System to Improve Male Sorting Efficacy for the Sterile Insect Technique" Insects 16, no. 11: 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111108
APA Stylede la Vega, G., Smith, L., Soria-Mercier, L., Edwards, W., Triñanes, F., Masagué, S., & Corley, J. (2025). SIT-ia: A Software-Hardware System to Improve Male Sorting Efficacy for the Sterile Insect Technique. Insects, 16(11), 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111108







