Biocontrol Potential of a Commercially Available Predator Rhyzobius lophanthae Blaisdell (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) Against Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Liviidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Maintenance of Rhyzobius lophanthae
2.2. Maintenance of Diaphorina citri Colony and Field Populations
2.3. Mortality of D. citri Eggs and Nymphs Exposed to R. lophanthae
2.4. Predation Capacity of R. lophanthae on D. citri Nymphs
2.5. Field Evaluation of the Release Rates of R. lophanthae Adults on D. citri Immatures
2.6. Field Evaluation of the R. lophanthae Adult Survival at Two Densities of D. citri Immatures
2.7. Release of R. lophanthae Adults in a Citrus Orchard
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
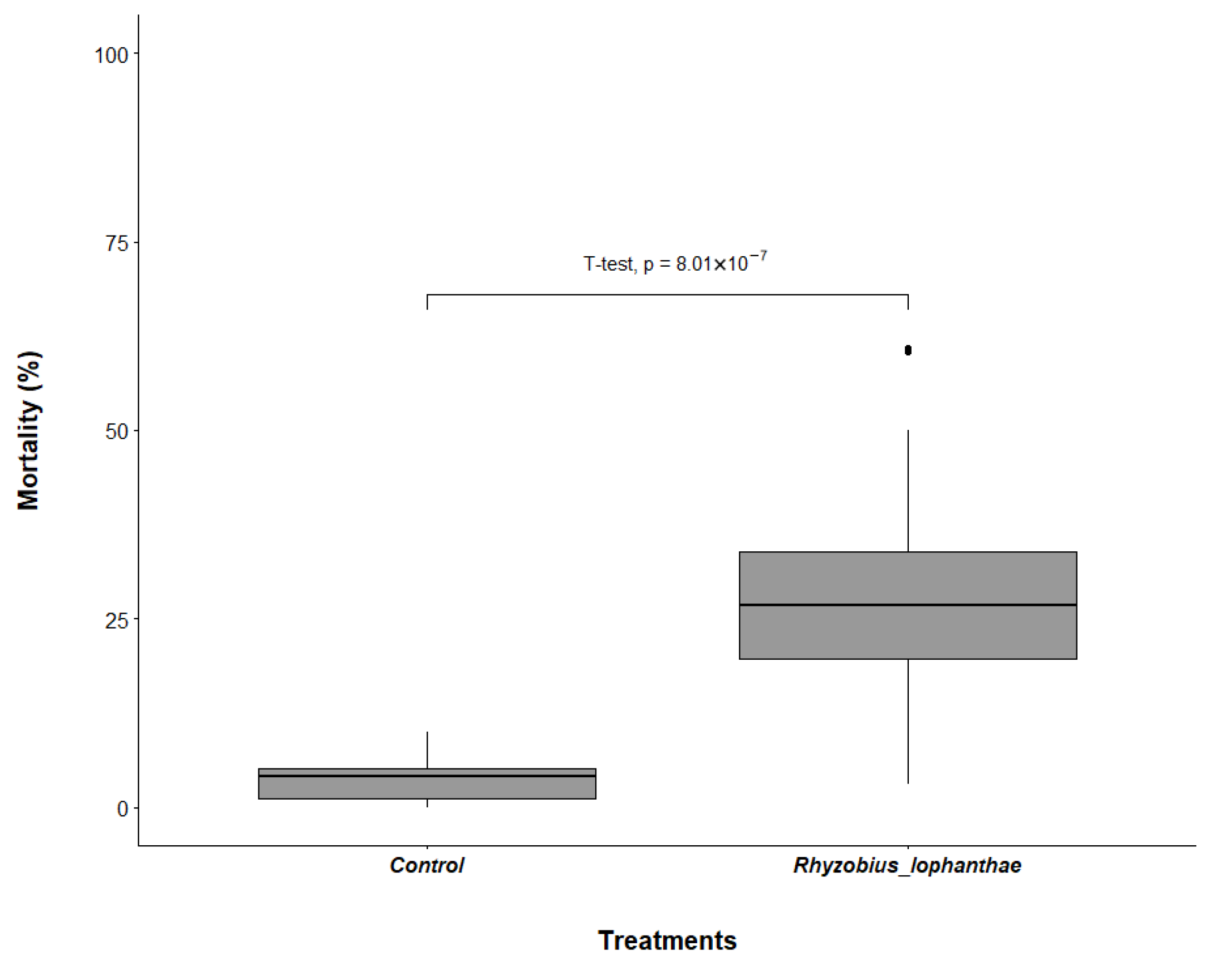
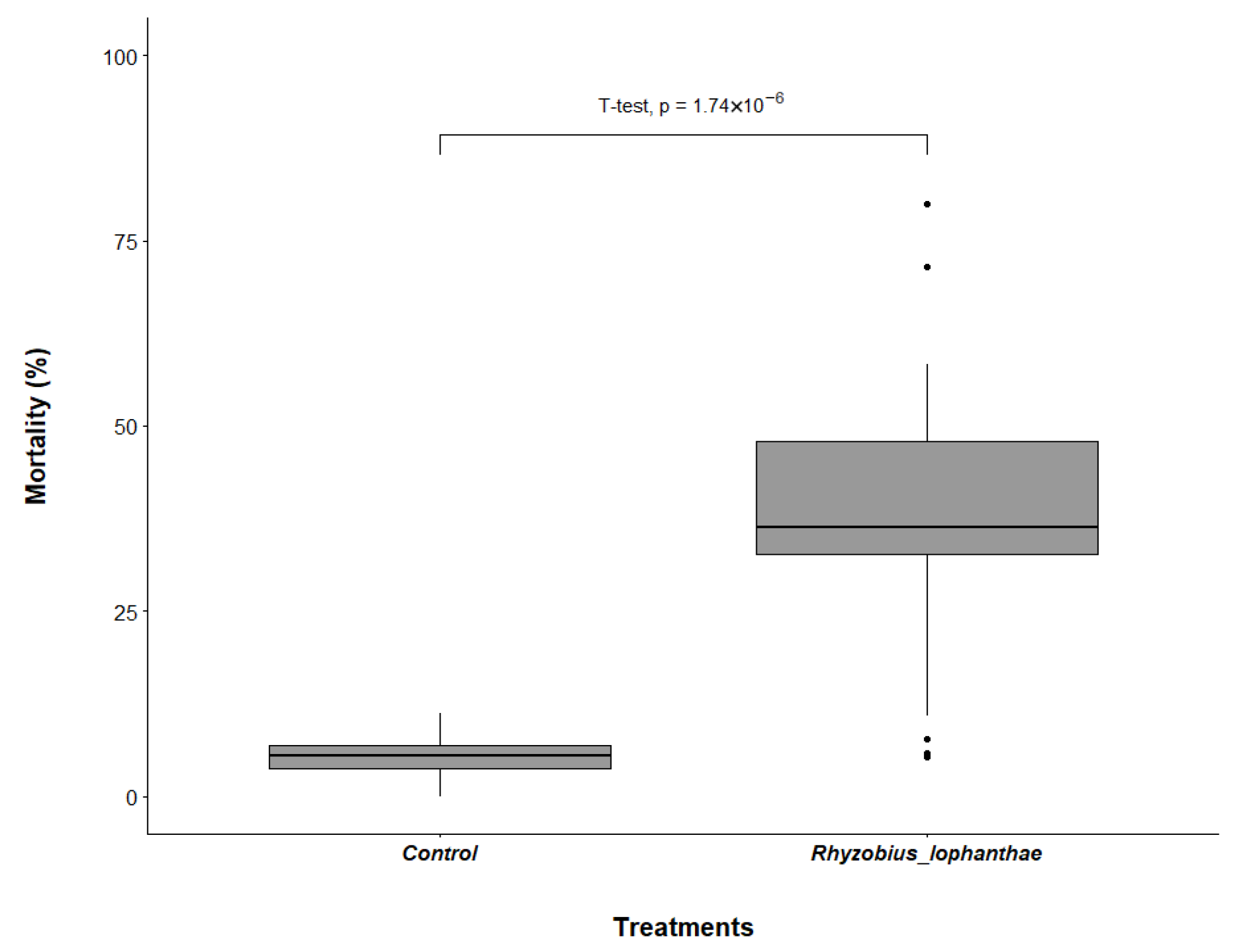
3.1. Rhyzobius lophanthae Predation of D. citri Eggs and Nymphs
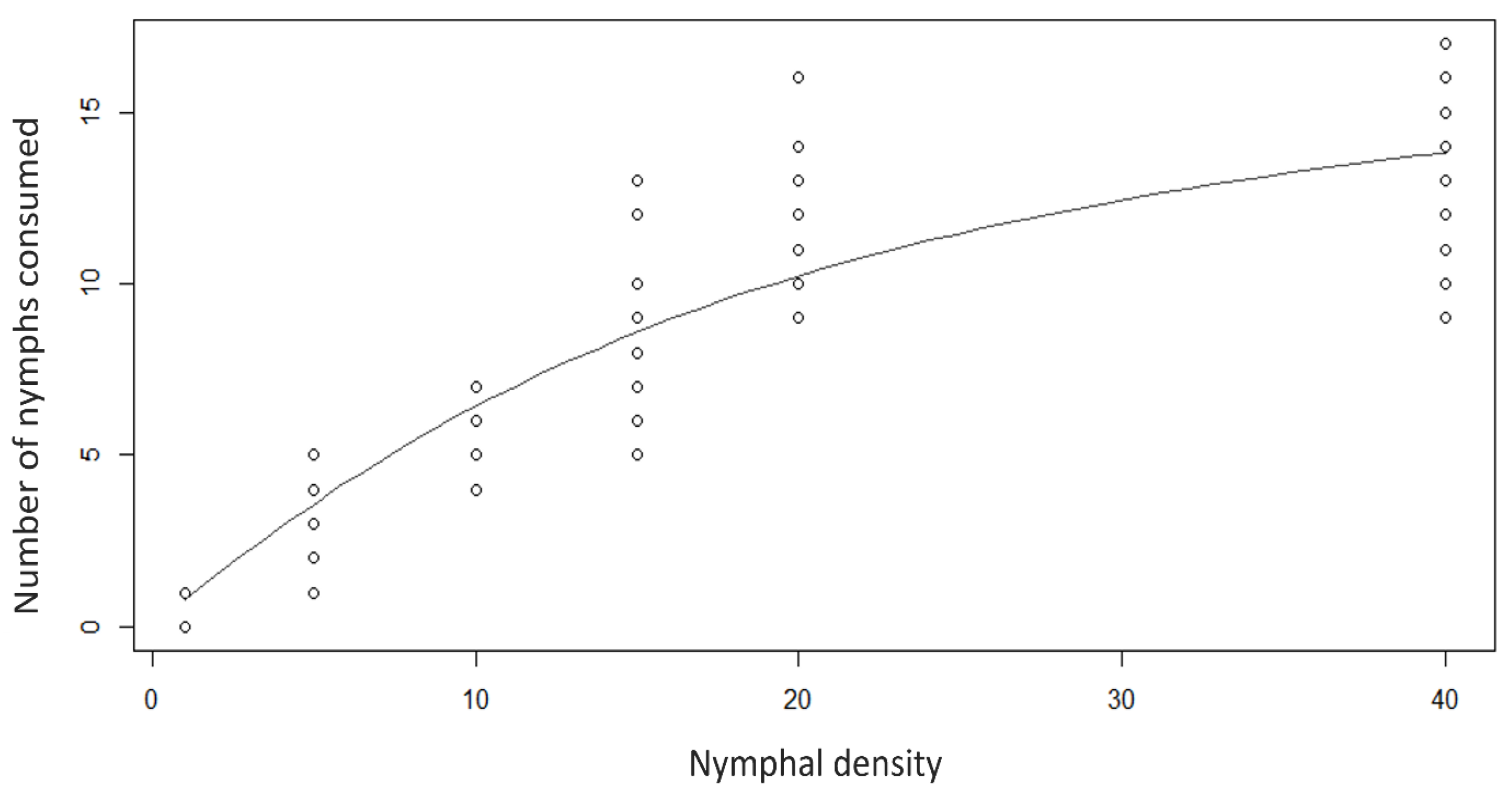
3.2. Rhyzobius lophanthae Predation Capacity at Different Densities of D. citri Immatures
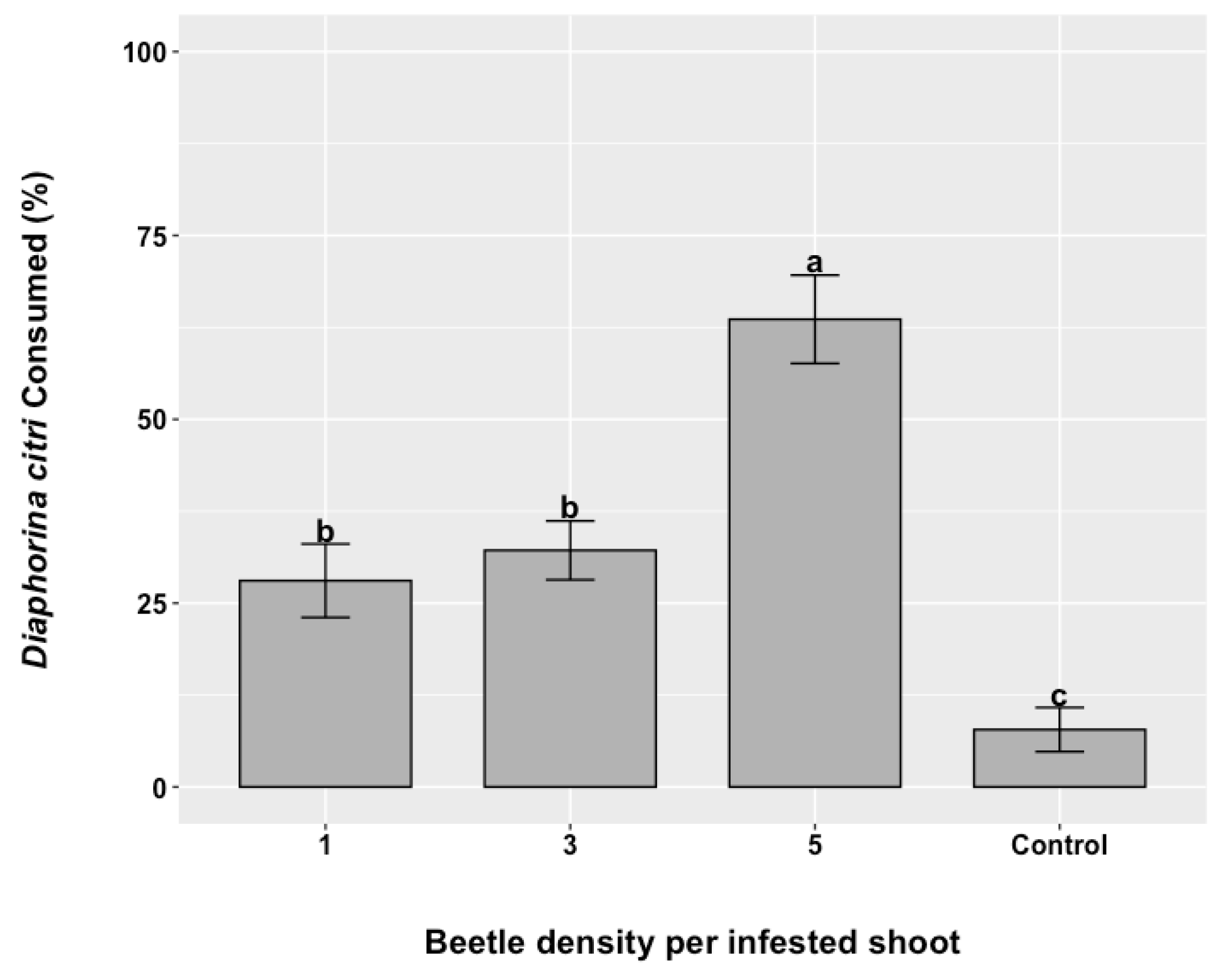
3.3. Diaphorina citri Suppression at Three Release Rates of R. lophanthae
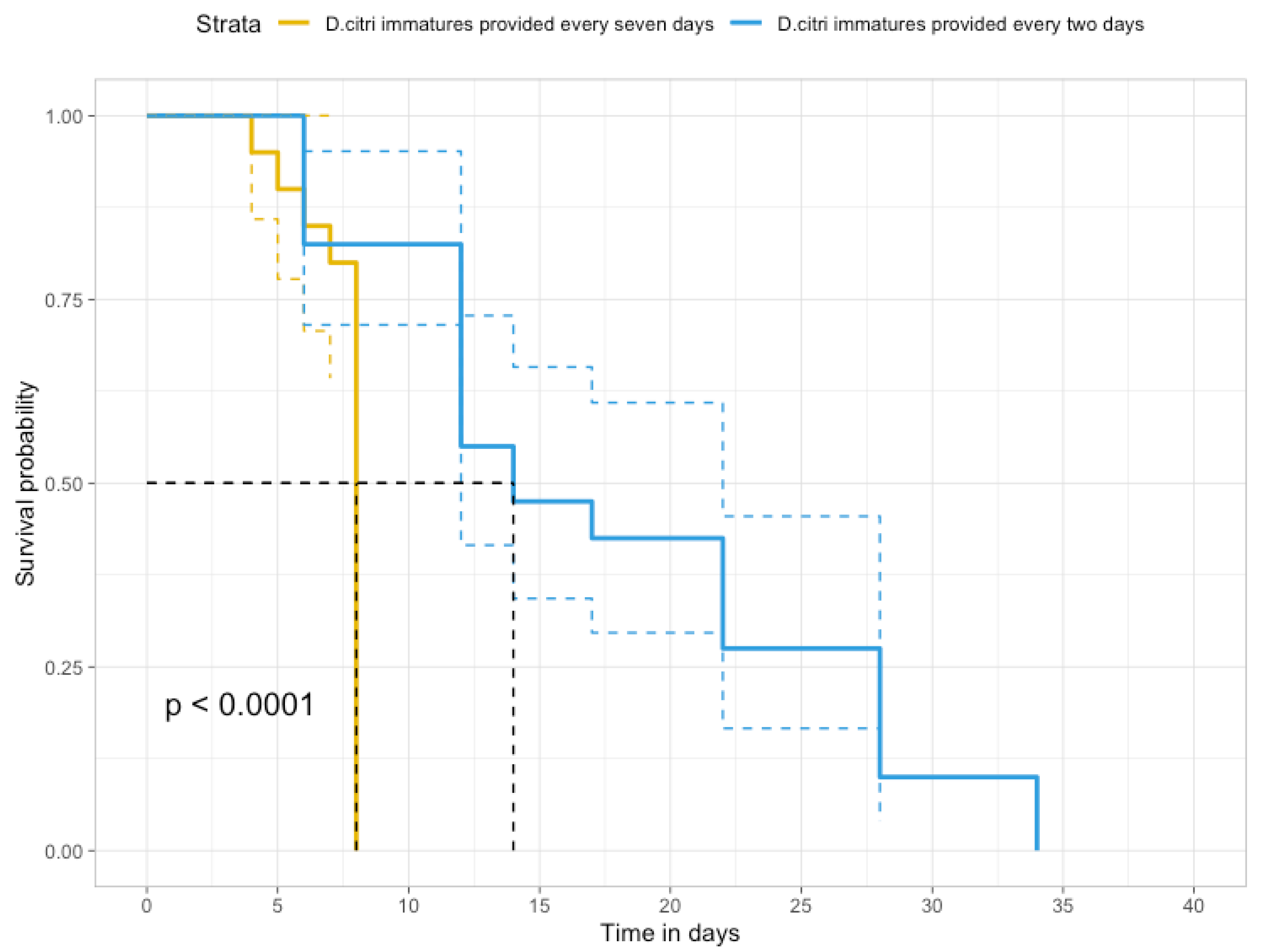
3.4. Rhyzobius lophanthae Survival at Two Levels of Diaphorina citri Populations, and Recovery from an Open Release in a Citrus Orchard
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bové, J.M. Huanglongbing: A destructive, newly-emerging, century-old disease of citrus. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 88, 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, J.A.; Stansly, P.A. Asian Citrus Psyllid: Biology, Ecology and Management of the Huanglongbing Vector; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2020; p. 352. ISBN 9781786394088. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, J.; Gottwald, T.; Setamou, M. Status of huanglongbing (hlb) outbreaks in Florida, California and Texas. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2020, 45, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, J.P. Biological control of Asian citrus psyllid (Homoptera: Psyllidae) in Florida. A preliminary report. Entomol. News 2002, 113, 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud, J.P.; Olsen, L.E. Suitability of Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri, as prey for ladybeetles. Biol. Control 2004, 49, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, J.A.; Stansly, P.A. Exclusion techniques reveal significant biotic mortality suffered by Asian citrus psyllid Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) populations in Florida citrus. Biol. Control 2009, 50, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, J.A.; Rogers, M.E.; Hall, D.G.; Stansly, P.A. Incidence of invasive Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) and its introduced parasitoid Tamarixia radiata (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) in Florida citrus. J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, J.P. Numerical response of Olla v-nigrum (Mulsant) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to infestations of Asian citrus psyllid (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) in Florida. Fla. Entomol. 2001, 84, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, C.W. Citrus: Current status of biological control in Florida. In Biological Control in Agricultural IPM Systems; Hoy, M.A., Herzog, D.C., Eds.; Academic: Orlando, FL, USA, 1985; pp. 481–499. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud, J.P. Natural mortality of Asian citrus psyllid (Homoptera: Psyllidae) in central Florida. Biol. Control 2004, 29, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, J.A.; Stansly, P.A. Dormant season foliar sprays of broad-spectrum insecticides: An effective component of integrated management for Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) in citrus orchards. Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, J.A.; Kostyk, B.; Stansly, P.A. Insecticidal suppression of Asian citrus psyllid Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae) vector of huanglongbing pathogens. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzo, C.; Qureshi, J.A.; Stansly, P.A. Insecticide sprays, natural enemy assemblages and predation on Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2014, 104, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Mann, R.S.; Rogers, M.E.; Stelinski, L.L. Insecticide resistance in field populations of Asian citrus psyllid in Florida. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanga, L.H.B.; Eason, J.; Haseeb, M.; Qureshi, J.; Stansly, P. Monitoring for insecticide resistance in Asian citrus psyllid (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) populations in Florida. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 109, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, J.A.; Szczepaniec, A.; Eubanks, M.D. The effects of sugarcane aphid density in sorghum on predation by lady beetles and lacewings. Biol. Control 2019, 129, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnó, J.; Molina, P.; Aparicio, Y.; Denis, C.; Gabarra, R.; Riudavets, J. Natural enemies associated with Tuta absoluta and functional biodiversity in vegetable crops. Biol. Control 2021, 66, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, D.; DeBach, P. Diaspididae. In Introduction Parasitoids and Predators of Arthropod Pest and Weeds: A World Review; USDA Agricultural Handbook No. 480; Clausen, C.P., Ed.; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Stathas, G.J. The effect of temperature on the development of the predator Rhyzobius lophanthae and its phenology in Greece. Biol. Control 2000, 45, 439–451. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, D.; Carlson, J. Fortuitous establishment of Rhyzobius lophanthae (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) and Aphytis lingnanesis (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) in South Texas on the Cycad Aulacaspis Scale, Aulacaspis yasumatsui (Hemiptera: Diaspididae). Southwest. Entomol. 2009, 34, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, J.Y.; Luck, R.F. Scale morphology effects on feeding behavior and biological control potential of Rhyzobius lophanthae (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1995, 88, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathas, G.J. Rhyzobius lophanthae prey consumption and fecundity. Phytoparasitica 2000, 28, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathas, G.J. Studies on morphology and biology of immature stages of the predator Rhyzobius lophanthae Blaisdell (Col.: Coccinellidae). Anz. Für Schädlingskunde J. Pest Sci. 2001, 74, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.R.; Cave, R.D. Pesticide susceptibility of Cybocephalus nipponicus and Rhyzobius lophanthae (Coleoptera: Cybocephalidae, Coccinellidae). Fla. Entomol. 2006, 89, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, C.R.; Sadof, C.S. Residual toxicity of insecticides to Chrysoperla rufilabris and Rhyzobius lophanthae predators as biocontrol agents of pine needle scale. Crop Prot. 2020, 130, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, H.T.; Meats, A.; Beattie, G.A.C.; Spooner-Hart, R. Ant-coccid mutualism in citrus canopies and its effect on natural enemies of red scale, Aonidiella aurantii (Maskell) (Hemiptera: Diaspididae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2014, 104, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloush, A.H.; Omkar, V.R.; Soares, A.O. Life-history attributes and biocontrol potential of the Purple coccidophagous ladybird, Rhyzobius lophanthae (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae). Bull. Insectology 2025, 78, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Marco, F.; Gebiola, M.; Simmons, G.S.; Stouthamer, R. Native, naturalized and commercial predators evaluated for use against Diaphorina citri. Crop Prot. 2022, 155, 105907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.G.; Albrigo, L.G. Estimating the relative abundance of flush shoots in citrus with implications on monitoring insects associated with flush. HortScience 2007, 42, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, J.A. Abiotic and biotic regulators of the Asian citrus psyllid populations. In Asian Citrus Psyllid: Biology, Ecology and Management of the Huanglongbing Vector; Qureshi, J.A., Stansly, P.A., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2020; pp. 88–100. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, J.A.; Stansly, P.A. Integrated approaches for managing the Asian citrus psyllid Diaphorina citri (Homoptera: Psyllidae) in Florida. Proc. Fla. State Hortic. Soc. 2007, 120, 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Monzo, C.; Arevalo, H.P.; Jones, M.M.; Vanacloch, P.; Croxton, S.D.; Qureshi, J.A.; Stansly, P.A. Sampling methods for detection and monitoring of the Asian citrus psyllid (Hemiptera: Psyllidae). Environ. Entomol. 2015, 44, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelder, A.J.A.; Wedderburn, R.W.M. Generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1972, 135, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinde, J.; Demétrio, C.G.B. Overdispersion: Models and estimation. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 1998, 27, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, D.W.; Barrios-O’Neill, D.; Bovy, H.; Paterson, R. Frair-Package: Tools for Functional Response Analysis in R. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/frair/frair.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Juliano, S.A. Nonlinear curve fitting: Predation and functional response curves. Des. Anal. Ecol. Exp. 2001, 2, 178–196. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, D.W.; Paterson, R.A.; Bovy, H.C.; Barrios-O’Neill, D. Frair: An R package for fitting and comparing consumer functional responses Poisot T [ed.]. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D. Random Search and Insect Population Models. J. Anim. Ecol. 1972, 41, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajulee, M.N.; Shrestha, R.B.; Leser, J.F.; Wester, D.B.; Blanco, C.A. Evaluation of the functional response of selected arthropod predators on bollworm eggs in the laboratory and effect of temperature on their predation efficiency. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Qureshi, J.; Zhou, X.; Pu, Z.; Chen, G.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H. Predation and functional response of the multi- coloured Asian ladybeetle Harmonia axyridis on the adult Asian citrus psyllid Diaphorina citri. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2019, 29, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadi, H.; Parizi, E.M.; Allahyari, H.; Enkegaard, A. Assessment of the biological control capability of Hippodamia variegata (Col.: Coccinellidae) using functional response experiments. J. Pest Sci. 2011, 84, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, F.J.; Hanks, J.B. Host plant alters the shape of the functional response of an aphid predator (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Environ. Entomol. 1998, 27, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uiterwaal, S.F.; DeLong, J.P. Multiple factors, including arena size, shape the functional responses of ladybird beetles. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 2429–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Y.; Shah, F.M.; Rubing, X.; Razaq, M.; Yabo, M.; Xihong, L.; Zhou, X. Functional response of Harmonia axyridis preying on Acyrthosiphon pisum nymphs: The effect of temperature. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoddle, M.S.; Pandey, R. Host range testing of Tamarixia radiata (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) sourced from the Punjab of Pakistan for classical biological control of Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae: Euphyllurinae: Diaphorinini) in California. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, D.; Ciomperlik, M. Biological control using the ectoparasitoid, Tamarixia radiata, against the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri, in the Lower Rio Grande Valley of Texas. Southwest. Entomol. 2017, 42, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.; Sétamou, M. Parasitism of Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae) by Tamarixia radiata (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) on residential citrus in Texas: Importance of colony size and instar composition. Biol. Control 2022, 165, 104796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rugno, G.R.; Qureshi, J.A. Biocontrol Potential of a Commercially Available Predator Rhyzobius lophanthae Blaisdell (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) Against Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Liviidae). Insects 2025, 16, 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111083
Rugno GR, Qureshi JA. Biocontrol Potential of a Commercially Available Predator Rhyzobius lophanthae Blaisdell (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) Against Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Liviidae). Insects. 2025; 16(11):1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111083
Chicago/Turabian StyleRugno, Gabriel Rodrigo, and Jawwad A. Qureshi. 2025. "Biocontrol Potential of a Commercially Available Predator Rhyzobius lophanthae Blaisdell (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) Against Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Liviidae)" Insects 16, no. 11: 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111083
APA StyleRugno, G. R., & Qureshi, J. A. (2025). Biocontrol Potential of a Commercially Available Predator Rhyzobius lophanthae Blaisdell (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) Against Diaphorina citri Kuwayama (Hemiptera: Liviidae). Insects, 16(11), 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111083





