Simple Summary
The bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis produces protein toxins that are able to control the mosquito Aedes aegypti, which is a vector of several human diseases. Understanding the mechanism of action of these toxins is necessary for both prolonging the effectiveness of bioinsecticides based on this bacterium and to potentially create new products. We have used a relatively new approach involving mutated toxins to indicate that eight different toxins appear to bind to the same cell surface receptor in the target insect. This result not only enhances our knowledge of host–pathogen interactions in this particular system but also indicates a greater commonality in the evolution of these toxins than was previously appreciated.
Abstract
A variety of pesticidal proteins derived from the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis exhibit activity against the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti and are used to control this insect vector. Several of these proteins, including Cry1Ca and Cry2Aa, additionally have activity against lepidopteran insects. Furthermore, the specificity of Cry2Aa has recently been shown to depend on domain I of the Cry protein, whereas it is generally recognized that domain II is the primary specificity-determining domain. This work has made use of disabled forms of three Cry proteins (Cry2Aa, Cry1Ca and Cry11Aa) and one naturally non-active protein (Cry2Ab) in an in vivo competition assay to investigate whether Cry2Aa and the dual-active Cry1Ca share a common receptor with the other pesticidal proteins. It was found that despite their differing specificities and potential modes of action, all of the Aedes-active proteins tested made use of a common receptor, although evidence is presented that Cry2Aa can use multiple receptors. When additional toxins (Cry41Aa, Cry1Aa, Cry1Ac) with no activity against this mosquito were tested, they too were found to share the same receptor, suggesting that Cry toxins may have evolved to utilize a common set of receptors in insects but that additional factors determine species specificity.
1. Introduction
Pesticidal proteins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis and other bacteria have long been used as biological insecticides to target crop pests and vectors of human disease. These proteins are generally pore-forming toxins which act on the midgut tissues of the host following ingestion and can either kill the insect outright or allow the bacterium to invade and colonize [1]. Individual proteins show specificity to particular orders or species of insect and although several factors can influence this specificity, the primary determinant is based on the interaction of the toxin with a receptor on the surface of the midgut cells [2]. Loss or mutation of these receptors can result in the insect acquiring resistance to the toxin, and if multiple toxins share the same receptor, then cross-resistance is observed [3]. Aedes aegypti is a mosquito capable of transmitting a number of diseases such as dengue, yellow fever, chikungunya and Zika, and is able to spread further afield as a result of human movement and climate change [4]. Products based on strains of B. thuringiensis subsp. israelensis (Bti) have successfully been used for decades to control this pest; fortunately, the insect has not managed to evolve resistance to the bacterium [5]. It has been suggested that the lack of resistance to Bti is due to the fact that it produces multiple toxins that can act in synergy, and so multiple mutations would be required to induce a resistance phenotype [6]. Various researchers have attempted to identify the receptors utilized by the individual toxins of Bti. Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) emerged as a strong candidate for the Cry11Aa toxin when a demonstration of binding between the two proteins was supplemented with the observation that knockdown of ALP1 by RNAi increased the tolerance of the insect larvae to Cry11Aa [7]. Subsequent work involving transgenic mosquitoes expressing a heat-inducible dsALP1RNA also observed a decrease in susceptibility to Cry11Aa upon induction [8]. However, a CRISPR-Cas9 generated knockout of ALP did not alter the insect’s susceptibility to either Cry11Aa, Cry4Aa or Cry4Ba [9]. That same study also found that knocking out the A. aegypti cadherin-like protein (CAD) did not alter susceptibility to the above three toxins. This seemed to contradict a previous finding that CAD could act as a receptor for Cry11Aa [10]. Regarding Cry4Ba, the ALP1 RNAi experiment described above [7] observed an increased tolerance to this toxin, whereas the inducible dsALP1RNA experiment [8] did not. Ectopic expression of ALP in Sf9 cells conferred susceptibility to Cry4Ba, and this strongly indicates its role as a functional receptor for this toxin [11]. Ectopic expression of two Aminopeptidase isoforms (AaeAPN2778 and AaeAPN2783) indicated that both could act as receptors for Cry4Ba, whereas the knocking out of one or both of two APN isoforms (APN1 and APN2) did not alter the susceptibility of larvae towards either Cry4Ba or Cry11Aa [12]. No clear picture has thus emerged concerning the functional receptors for the Bti toxins in A. aegypti. More recently, so-called Disabled Insecticidal Proteins (DIPs) have been used to investigate the receptor-binding preferences of Bt toxins [13]. These are mutated toxins that can no longer form pores but whose receptor-binding properties are largely unaltered. By performing in vivo competition assays, the effect of a DIP on the toxicity of a non-mutated toxin can indicate which toxins share common receptors. In this work we have used various DIPs to study the in vivo interactions between a number of different toxins with activity towards A. aegypti. In particular, we were interested in Cry2Aa. It has long been established that while Cry2Aa has activity against A. aegypti, the closely related Cry2Ab does not [14]. We identified that the differential specificity is associated with domain I of the protein [15,16], whereas specificity generally associates with domain II, and we wondered if this was reflected in Cry2Aa binding to a different type of receptor than the other toxins active against this mosquito.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Plasmids
We have previously described the expression systems used for Cry2Aa, Cry2Ab Cry1Ac, Cry1Ca, Cry11Aa, Cry4Aa and Cry41Aa [17,18]. For Cry1Aa and Cry4Ba, the gene encoding Cry2Aa in the respective plasmid was replaced with the open reading frames for these two other genes.
2.2. Toxin Preparation and Mosquito Bioassay
Recombinant Bt strains were grown in half-strength LB medium for 72 h at 30 °C, 180 rpm. Cells, spores and crystals were recovered by centrifugation, resuspended in water and sonicated to break open unlysed cells. Following further centrifugation (and a 2nd round of sonication if required), spores and crystals were resuspended in water. The purity and concentration of each toxin was assessed by SDS PAGE and densitometry, using BSA as a standard. To assess the likelihood of the introduced mutations affecting the structural instability of the toxins, all crystals were viewed under a phase-contrast microscope to check that the mutants maintained the same crystal shape as the wild-type. The solubilization of the crystals in alkali and the resistance of the solubilized toxin to digestion by 1 mg/mL trypsin was performed to confirm that the mutants had not undergone any significant structural changes. Mosquito assays were performed using third-instar larvae. Five larvae were placed in water in a 24-well cell culture plate. Toxin was added and the volume made up to 3 mL. 20 wells (ie 100 larvae) were used for each experiment. The larvae were incubated at 27 °C with a 16:8 light/day photoperiod for 24 h. For the in vivo competition assays, sufficient toxin was added to produce around 70% death and then various concentrations of competitor were added. For each experiment, the controls were wells with just the toxin, wells with no toxin and wells with the highest concentration of competitor. Experiments were abandoned if either of the latter two controls gave greater than 10% mortality. Assays were repeated at least three times to ensure consistent results. A competitor was considered to have completely inhibited the activity of a toxin if the relative mortality dropped below 20% at 100xfold excess. If the relative mortality dropped to 50–60%, but no lower, then inhibition was considered partial. To rule out non-specific effects, competition assays were also performed with excess amounts of BSA equivalent to the concentrations of the competitors used. BSA had no effect on the activity of the toxins.
3. Results
In order to undertake the in vivo competition assays, DIP variants of Cry2Aa and Cry1Ca were first created. The Cry2Aa DIP (G119C_N123A_L156C_R160A) was based on the equivalent Cry2Ab DIP [13] since these four amino acids are conserved between the two proteins. The Cry1Ca DIP (N98C_D143C) was also created based on a previously reported design [13]. Neither DIP was found to have any activity against A. aegypti larvae.
3.1. Cry2AaDIP and Cry2Ab Inhibit the Activity of Cry2Aa to Different Extents
Figure 1 shows that when Cry2Aa DIP was fed to the larvae alongside Cry2Aa, there was a dose-dependent inhibition of activity. With a 100-fold excess of the DIP, an almost complete inhibition was observed. This observation is consistent with the model that DIPs are able to compete for binding with the native toxin but are not able to go on and cause toxicity. When present in large excesses they should displace virtually all binding of the native protein. In contrast, while excesses of Cry2Ab–which itself has no activity–caused some inhibition of Cry2Aa activity, they did not fully block activity. Such a result is consistent with the possibility that Cry2Aa can bind to multiple receptors, only one of which is blocked by Cry2Ab.
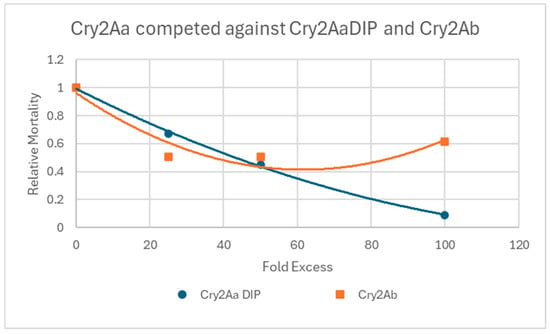
Figure 1.
In vivo competition assay between Cry2Aa and Cry2Ab. Representative data normalized to the activity of Cry2Aa alone.
3.2. Interactions Between Other A. aegypti-Active Toxins
Although Cry1Ca is best known as a leipdopteran-active toxin, its activity against A. aegypti has been previously reported [19]. Because of this unusual activity for a Cry1 toxin, we were interested in how this would interact with more traditional mosquitocidal toxins. Cry11Aa, Cry4Aa and Cry4Ba are all toxins produced by the Bt israelensis strain used commercially to control mosquitoes and all three have known activity against A. aegypti [20]. As anticipated, the Cry1CaDIP completely inhibited the activity of Cry1Ca (Table 1). It also completely inhibited the activity of Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa. In contrast, but in common with the result seen above with Cry2Ab, Cry1CaDIP could only partially inhibit the activity of Cry2Aa. Both Cry2Aa DIP and Cry2Ab were able to completely inhibit the activity of Cry4Aa, Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa. These data suggest that the five active toxins all shared the same receptor(s), with Cry2Aa potentially having an additional one.

Table 1.
In vivo competition results. The active toxins in the left-hand column (colored green) were competed against the proteins in the top row (colored pink). ND = not determined.
3.3. Cry11AaDIP and Cry41Aa Also Only Partially Inhibit Cry2Aa
A model in which Cry1Ca, Cry2Aa, Cry4Aa, Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa all share a common receptor would predict that a Cry11AaDIP would inhibit the activity of all these toxins—although for Cry2Aa, only partially. To test this hypothesis, the Cry11AaE100A variant was made based on a previous study of this mutant [21]. Table 1 shows that this DIP followed the same pattern as the other inactive proteins, in particular only partially inhibiting the activity of Cry2Aa. We had previously reported that the Cry41Aa Bt toxin with activity against some human cancer cells could block the activity of Cry1Ca in A. aegypti [18]. Since Cry1Ca appeared to use the same receptor as the other mosquitocidal toxins, we hypothesized that Cry41Aa would be able to also block the activity of these toxins, as indeed it could (Table 1).
3.4. Cry1Aa and Cry1Ac Could Also Inhibit the Activity of the Mosquitocidal Toxins
The observation that multiple Cry proteins—including two native toxins with no A. aegypti activity—could all inhibit the activity of the active toxins led us to wonder whether other toxins with no mosquitocidal activity would have the same effect. To test this, the lepidopteran-active Cry1Aa and Cry1Ac toxins were tested against Cry4Ba and were both found to completely inhibit its activity when present in excess.
4. Discussion
Although it is accepted that Bt toxins must bind to a cell surface receptor in order to efficiently go on and form a pore in the cell membrane, defining and identifying receptors is not straightforward. The first receptor to be identified was an aminopeptidase from Manduca sexta that was initially found as a binding partner of Cry1Ac [22]. A semi-purified preparation of this protein was also found to allow Cry1Ac-induced pore formation when incorporated into lipid vesicles [23]. In general, though binding per se is not a reliable indicator of receptor function since toxins have been shown to be able to bind to a wide range of different proteins, including intracellular ones such as actin that are extremely unlikely to be functional receptors [24]. Showing that RNAi of a putative receptor reduces the susceptibility to toxins [7] provides strong support, but it should be borne in mind that knockdown of non-receptor genes may also indirectly affect susceptibility [25]. More recently CRISPR-Cas9 knockouts have been widely used to characterize receptors [9] but perhaps the most powerful means of demonstrating receptor function is to show that ectopic expression in an otherwise non-susceptible cell makes that cell susceptible to the toxin [26]. Although the binding of toxins to other proteins is not always a reliable method for receptor identification, binding competition assays have long been used to predict whether different toxins might bind to the same receptor, and for determining the likelihood of cross-resistance [27]. To complement these in vitro binding assays, in vivo competition assays using Disabled Insecticidal Proteins (DIPs) have provided an additional means of investigating toxin–receptor interactions [13]. An underlying principle of these in vivo competition assays is that if a DIP form of a toxin inhibits the activity of a functional toxin, then it is assumed that they interact with the same receptor. Of course, other explanations are possible such as a direct interaction between the two toxin proteins. Based on the above principle, our data indicate that all of the toxins we tested against Aedes aegypti can bind to the same receptor, with the possibility that Cry2Aa can additionally bind to a different one. Whether this ability of Cry2Aa to bind to a different receptor is related to the role of its domain I in determining the differential activity of Cry2Aa and Cry2Ab to this mosquito [15,16,17] remains to be determined. Although all the toxins that we tested appear to bind to the same receptor, some of them (Cry1Aa, Cry1Ac and Cry41Aa) show no activity to A. aegypti despite being toxic to other hosts. There are numerous factors that can influence toxicity and specificity [2] but since competition for receptor binding has been observed, factors such as proteolytic instability or sequestration are unlikely to be the cause of non-toxicity. Although receptor binding is considered to be a pre-requisite for pore-formation in vivo, binding itself may not be sufficient for pore-formation or toxicity. It is quite feasible that a toxin can bind to a receptor in a way that prevents another toxin from binding to it, but that some aspect of this binding is not conducive to pore-formation. For example, if the binding position means that the pore-forming domain I is too far from or in the wrong orientation with respect to the membrane, then the ability to insert into the membrane may be hampered [28]. One of the reasons why Bti has proved to be such a successful biomosquitocide is that despite its extensive use, field resistance has not been consistently observed [29]. A strategy for delaying/preventing the development of resistance has been to use products containing multiple toxins that bind to different receptors. A target insect then has to acquire mutations in multiple receptors to show resistance [30]. It is somewhat surprising then that our data indicate that the three main Cry toxins of Bti (Cry11Aa, Cry4Aa and Cry4Ba) all utilize the same receptor. A separate hypothesis as to why mosquitoes have not developed resistance to Bti is the presence of the Cyt1Aa toxin which can interact and synergize with the Cyt1Aa toxin in a number of ways [31,32]. If indeed there is a single receptor for Cry11Aa, Cry4Aa and Cry4Ba in A. aegypti, it is not clear what that is. As discussed above, previous attempts to identify Cry toxin receptors in Bti have produced a confusing set of results.
5. Conclusions
The use of Disabled Insecticidal Proteins has indicated that multiple Cry toxins—both with and without activity towards A. aegypti—all share the same receptor in this mosquito. One of the toxins (Cry2Aa) may additionally utilize a second receptor. The observation that so many of the toxins can interact with the same receptor may reflect an evolutionary history in which Cry toxins bind to a common set of membrane proteins; however, subtle changes in the nature of this binding, or their ability to penetrate the membrane, has resulted in specificity towards particular insects.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.I. and N.C.; methodology, N.I. and N.C.; investigation, N.I.; writing—original draft preparation, N.I. and N.C.; writing—review and editing, N.C.; supervision, N.C.; project administration, N.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the involvement of the following undergraduate and master’s students in the generation of data: Luke Barden, Joe Everett, Manaratut Hakim, Nanthanut Piya-Aksornsak, Safwan Rana, Alice Wang, Shelly Wang and Lauren Wilson. We would like to thank Infravec2 (https://infravec2.eu/ (accessed on: 13 February 2021) for supplying Aedes aegypti eggs.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Schnepf, E.; Crickmore, N.; Van Rie, J.; Lereclus, D.; Baum, J.; Feitelson, J.; Zeigler, D.R.; Dean, D.H. Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 775–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Crickmore, N. Specificity determinants for Cry insecticidal proteins: Insights from their mode of action. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 142, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Heckel, D.G.; Ferre, J. Mechanisms of Resistance to Insecticidal Proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, M.U.G.; Reiner, R.C., Jr.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Gilbert, M.; Pigott, D.M.; Yi, D.; Johnson, K.; Earl, L.; Marczak, L.B.; et al. Past and future spread of the arbovirus vectors Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, K.D.S.; Crespo, M.M.; Araujo, A.P.; da Silva, R.S.; de Melo-Santos, M.A.V.; de Oliveira, C.M.F.; Silva-Filha, M. Long-term exposure of Aedes aegypti to Bacillus thuringiensis svar. israelensis did not involve altered susceptibility to this microbial larvicide or to other control agents. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, M.C.; Jiannino, J.A.; Federici, B.A.; Walton, W.E. Synergy between toxins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis and Bacillus sphaericus. J. Med. Entomol. 2004, 41, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jimenez, A.I.; Reyes, E.Z.; Cancino-Rodezno, A.; Bedoya-Perez, L.P.; Caballero-Flores, G.G.; Muriel-Millan, L.F.; Likitvivatanavong, S.; Gill, S.S.; Bravo, A.; Soberon, M. Aedes aegypti alkaline phosphatase ALP1 is a functional receptor of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa toxins. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Aimanova, K.; Gill, S.S. Functional characterization of Aedes aegypti alkaline phosphatase ALP1 involved in the toxicity of Cry toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis and jegathesan. Peptides 2017, 98, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, S.; Gallegos, A.S.; Pelaez-Aguilar, A.E.; Sanchez, J.; Gomez, I.; Soberon, M.; Bravo, A. CRISPR-Cas9 knockout of membrane-bound alkaline phosphatase or cadherin does not confer resistance to Cry toxins in Aedes aegypti. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Aimanova, K.G.; Fernandez, L.E.; Bravo, A.; Soberon, M.; Gill, S.S. Aedes aegypti cadherin serves as a putative receptor of the Cry11Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Biochem. J. 2009, 424, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechklar, M.; Tiewsiri, K.; Angsuthanasombat, C.; Pootanakit, K. Functional expression in insect cells of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked alkaline phosphatase from Aedes aegypti larval midgut: A Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin receptor. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, X.; He, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, W.; Ou, L.; Yang, Z.; Guan, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Knockout of Two Cry-Binding Aminopeptidase N Isoforms Does Not Change Susceptibility of Aedes aegypti Larvae to Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa Toxins. Insects 2021, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerga, A.; Evdokimov, A.G.; Moshiri, F.; Haas, J.A.; Chen, M.; Clinton, W.; Fu, X.; Halls, C.; Jimenez-Juarez, N.; Kretzler, C.N.; et al. Disabled insecticidal proteins: A novel tool to understand differences in insect receptor utilization. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 105, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widner, W.R.; Whiteley, H.R. Two highly related insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki possess different host range specificities. J. Bacteriol. 1989, 171, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Zhang, F.; Chen, G.; Joseph, L.; Barqawi, A.; Evans, J.; Song, F.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Crickmore, N. A natural hybrid of a Bacillus thuringiensis Cry2A toxin implicates Domain I in specificity determination. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 150, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goje, L.J.; Elmi, E.D.; Bracuti, A.; Courty, T.; Rao, T.; Alzahrani, F.A.; Crickmore, N. Identification of Aedes aegypti specificity motifs in the N-terminus of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry2Aa pesticidal protein. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 174, 107423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ay Alzahrani, F.; Crickmore, N. N-terminal proteolysis determines the differential activity of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry2A toxins towards Aedes aegypti. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2024, 204, 108100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryce-Sharron, N.; Nasiri, M.; Powell, T.; West, M.J.; Crickmore, N. A shared receptor suggests a common ancestry between an insecticidal Bacillus thuringiensis Cry protein and an anti-cancer parasporin. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Villarreal, S.E.; Garcia-Montelongo, M.; Ibarra, J.E. Insecticidal Activity of a Cry1Ca toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner (Firmicutes: Bacillaceae) and Its Synergism with the Cyt1Aa Toxin Against Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2020, 57, 1852–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crickmore, N.; Bone, E.J.; Williams, J.A.; Ellar, D.J. Contribution of the individual components of the delta-endotoxin crystal to the mosquitocidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 131, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, D.; Rodriguez-Almazan, C.; Munoz-Garay, C.; Portugal, L.; Perez, C.; de Maagd, R.A.; Bakker, P.; Soberon, M.; Bravo, A. Dominant negative phenotype of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab, Cry11Aa and Cry4Ba mutants suggest hetero-oligomer formation among different Cry toxins. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, P.J.; Crickmore, N.; Ellar, D.J. The receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis CrylA(c) delta-endotoxin in the brush border membrane of the lepidopteran Manduca sexta is aminopeptidase N. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 11, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangadala, S.; Walters, F.S.; English, L.H.; Adang, M.J. A mixture of Manduca sexta aminopeptidase and phosphatase enhances Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal CryIA(c) toxin binding and 86Rb(+)-K+ efflux in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10088–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, M.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; McNall, R.J.; Andacht, T.; Adang, M.J. Identification of novel Cry1Ac binding proteins in midgut membranes from Heliothis virescens using proteomic analyses. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayra-Pardo, C.; Raymond, B.; Gulzar, A.; Rodriguez-Cabrera, L.; Moran-Bertot, I.; Crickmore, N.; Wright, D.J. Novel genetic factors involved in resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in Plutella xylostella. Insect Mol. Biol. 2015, 24, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Endo, H.; Adegawa, S.; Kikuta, S.; Sato, R. Functional characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry toxin receptors explains resistance in insects. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 4474–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester, V.; Granero, F.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Malvar, T.; Ferre, J. Integrative model for binding of Bacillus thuringiensis toxins in susceptible and resistant larvae of the diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, H. Molecular and Kinetic Models for Pore Formation of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry Toxin. Toxins 2022, 14, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreau, G.; Stalinski, R.; David, J.P.; Despres, L. Monitoring resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis in the field by performing bioassays with each Cry toxin separately. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2013, 108, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressel, J.; Gassmann, A.J.; Owen, M.D. How well will stacked transgenic pest/herbicide resistances delay pests from evolving resistance? Pest. Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canton, P.E.; Zanicthe Reyes, E.Z.; Ruiz de Escudero, I.; Bravo, A.; Soberon, M. Binding of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Cry4Ba to Cyt1Aa has an important role in synergism. Peptides 2011, 32, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, C.; Fernandez, L.E.; Sun, J.; Folch, J.L.; Gill, S.S.; Soberon, M.; Bravo, A. Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Cyt1Aa synergizes Cry11Aa toxin by functioning as a membrane-bound receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18303–18308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).