Effect of Solvents on the Structure of the Gut Microbiota of Honeybees (Apis mellifera)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Honeybee and Chemicals
2.2. Effects of Pesticide Cosolvents on Honeybee Survival, Pollen Consumption, and Body Weight
2.3. Quantification and Structural Analysis of the Gut Microbial Community
2.4. In Vitro Growth Assay of Gut Bacteria Under Cosolvent Exposure
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cosolvent Exposure Does Not Significantly Affect Honeybee Survival, Pollen Consumption, or Body Weight
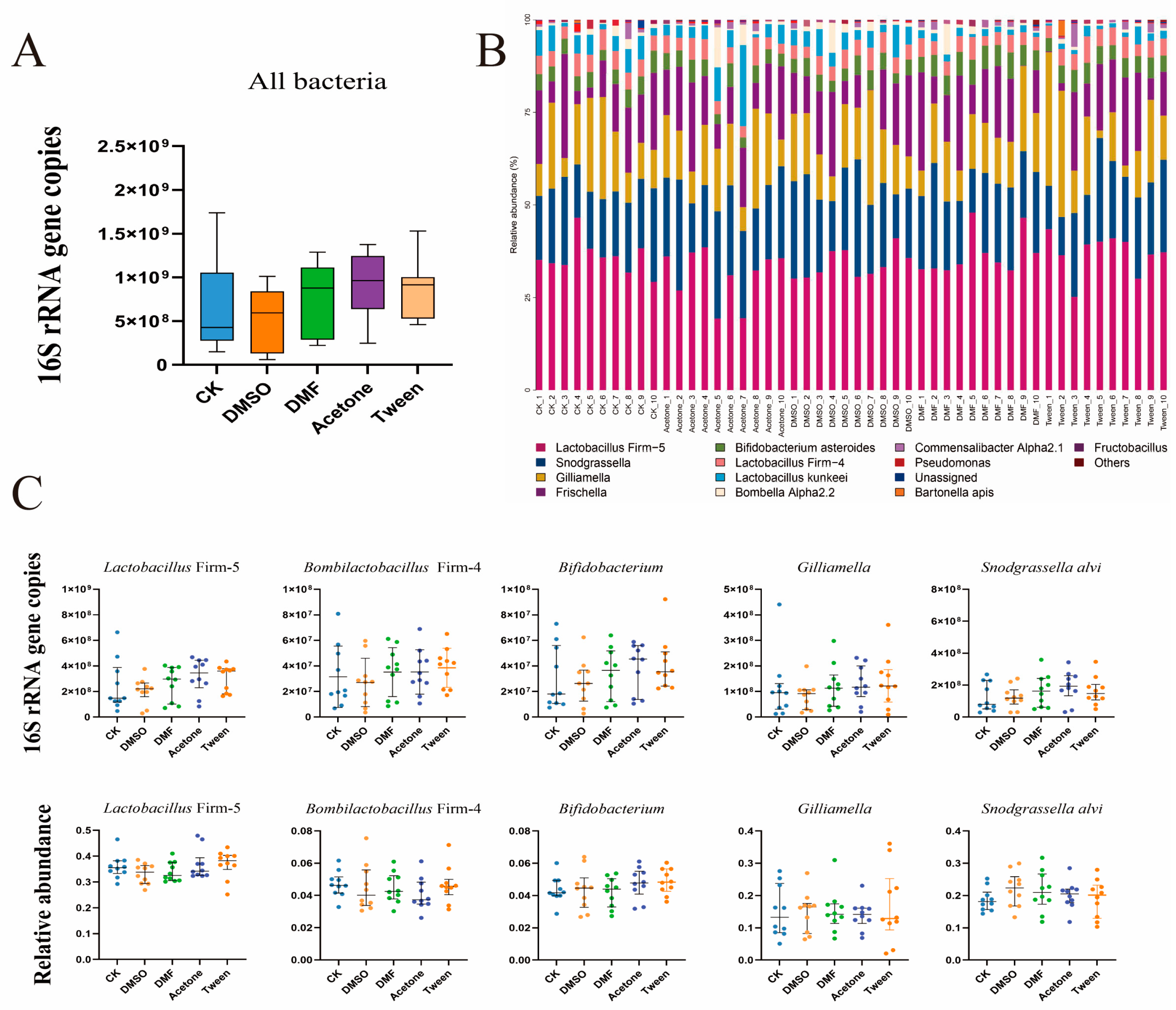
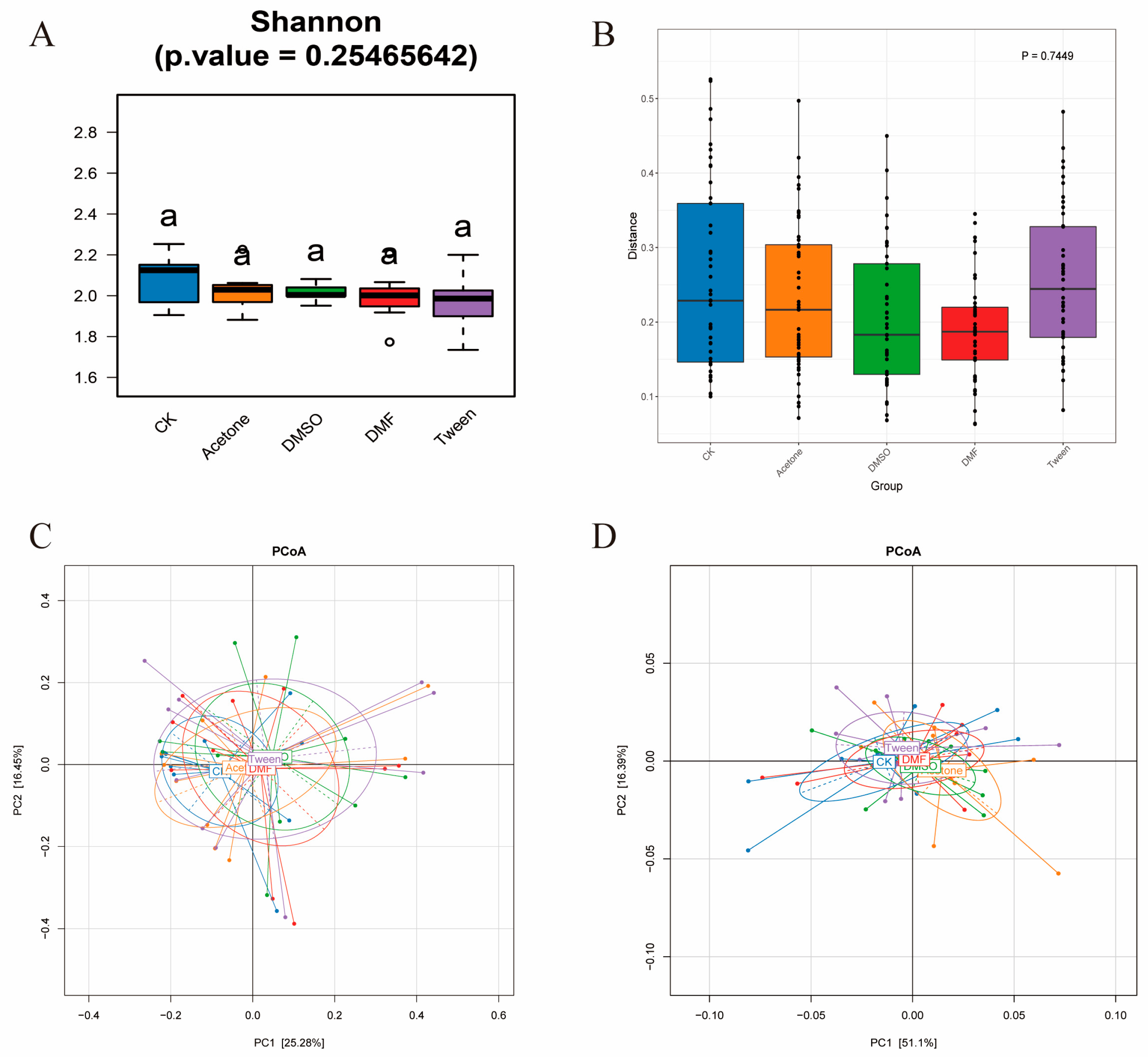
3.2. In Vivo Exposure to Cosolvents Does Not Significantly Alter Gut Microbiome Size or Composition
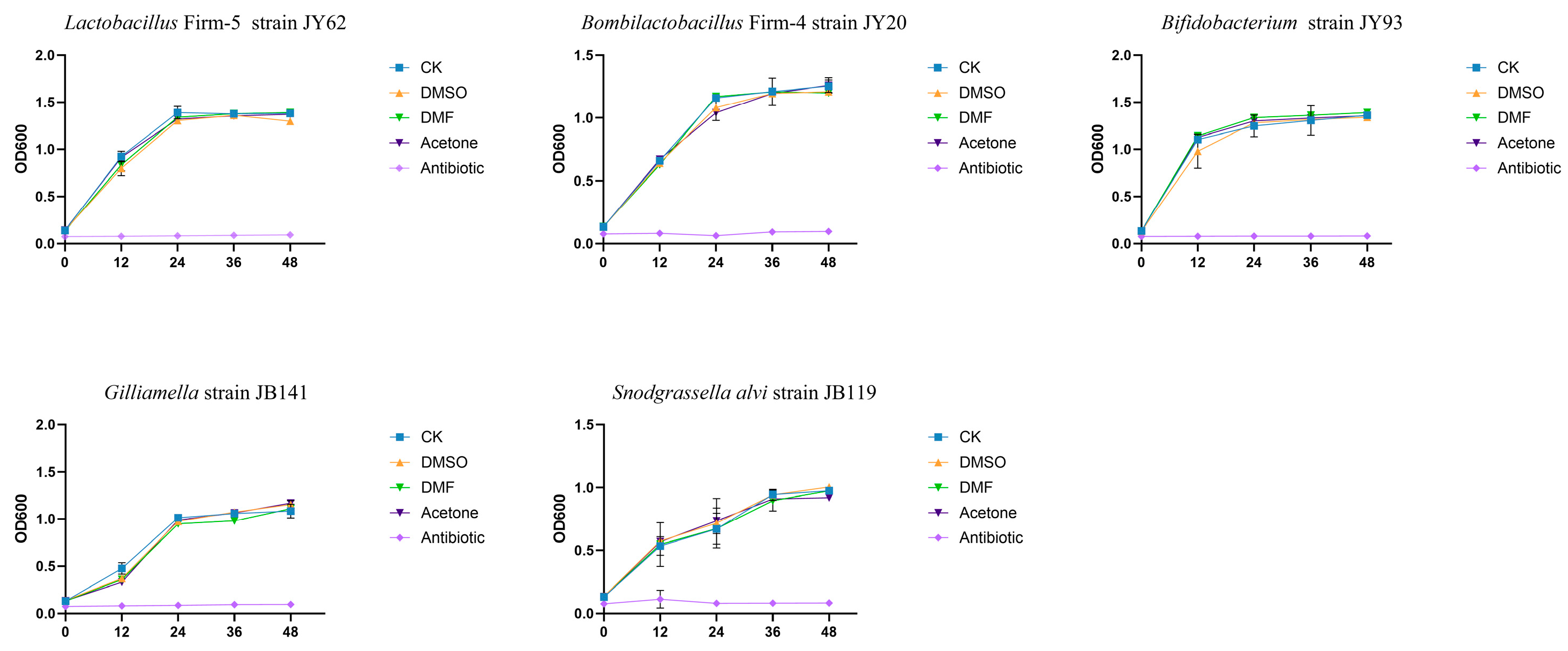
3.3. In Vitro Exposure to Pesticide Cosolvents Does Not Inhibit the Growth of Dominant Gut Symbionts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DMF | Dimethylformamide |
| OD600 | Optical density at 600 nm |
| PCoA | Principal coordinate analysis |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
References
- Goulson, D.; Nicholls, E.; Botías, C.; Rotheray, E.L. Bee declines driven by combined stress from parasites, pesticides, and lack of flowers. Science 2015, 347, 1255957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsky, J.; Joshi, N.K. Impact of biotic and abiotic stressors on managed and feral bees. Insects 2019, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.; Preetha, G.; Stanley, J.; Preetha, G. Pesticide toxicity to pollinators: Exposure, toxicity and risk assessment methodologies. In Pesticide Toxicity to Non-Target Organisms: Exposure, Toxicity and Risk Assessment Methodologies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 153–228. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, K.; Duca, R.C.; Lovas, S.; Creta, M.; Scheepers, P.T.; Godderis, L.; Ádám, B. Systematic review of comparative studies assessing the toxicity of pesticide active ingredients and their product formulations. Environ. Res. 2020, 181, 108926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, D.; Briggs, G. Physicochemical properties of adjuvants: Values and applications. Weed Technol. 2000, 14, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, P.J.; Rees, R.; Stock, D. Interactions Between Adjuvants, Agrochemicals and Target Organisms; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Cai, M.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Niu, Q.; Ji, T. Atrazine exposure can dysregulate the immune system and increase the susceptibility against pathogens in honeybees in a dose-dependent manner. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesnage, R.; Antoniou, M.N. Ignoring adjuvant toxicity falsifies the safety profile of commercial pesticides. Front. Public Health 2018, 5, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straw, E.A.; Thompson, L.J.; Leadbeater, E.; Brown, M.J. ‘Inert’ingredients are understudied, potentially dangerous to bees and deserve more research attention. Proc. R. Soc. B 2022, 289, 20212353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, B.; Walker, E.; Johnson, R.M. Toxicity of spray adjuvants and tank mix combinations used in almond orchards to adult honey bees (Apis mellifera). J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullin, C.A. Effects of ‘inactive’ingredients on bees. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 10, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straw, E.A.; Brown, M.J. Co-formulant in a commercial fungicide product causes lethal and sub-lethal effects in bumble bees. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullin, C.A.; Chen, J.; Fine, J.D.; Frazier, M.T.; Frazier, J.L. The formulation makes the honey bee poison. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 120, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrzycki, P.; Giffard, H.; Aupinel, P.; Belzunces, L.P.; Chauzat, M.-P.; Classen, C.; Colin, M.E.; Dupont, T.; Girolami, V.; Johnson, R.; et al. Standard methods for toxicology research in Apis mellifera. J. Apic. Res. 2013, 52, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 245: Honey Bee (Apis Mellifera L.), Chronic Oral Toxicity Test (10-Day Feeding). In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zheng, M.; Cai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Niu, Q.; Ji, T. Possible interactions between gut microbiome and division of labor in honey bees. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e11707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, N.A. Genomics of the honey bee microbiome. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 10, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymann, K.; Moran, N.A. The role of the gut microbiome in health and disease of adult honey bee workers. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 26, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, M.Z.; Poulain, A.J.; Forrest, J.R. Pesticide-induced disturbances of bee gut microbiotas. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 46, fuab056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, Z.; Xu, J.; Ma, G.; Pan, Y.; Cai, M.; Lin, Z.; Ji, T.; Wang, K. Impact of Atrazine on Sucrose Sensitivity in Honey Bees. Insects 2025, 16, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, H.; Fan, R.-L.; Lin, Z.-G.; Niu, Q.-S.; Wang, Z.; Ji, T. Effect of carbendazim on honey bee health: Assessment of survival, pollen consumption, and gut microbiome composition. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.C.; Chang, H.C.; Wu, W.Y.; Chen, Y.W. Impaired olfactory associative behavior of honeybee workers due to contamination of imidacloprid in the larval stage. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christen, V.; Schirrmann, M.; Frey, J.E.; Fent, K. Global transcriptomic effects of environmentally relevant concentrations of the neonicotinoids clothianidin, imidacloprid, and thiamethoxam in the brain of honey bees (Apis mellifera). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7534–7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doublet, V.; Labarussias, M.; de Miranda, J.R.; Moritz, R.F.; Paxton, R.J. Bees under stress: Sublethal doses of a neonicotinoid pesticide and pathogens interact to elevate honey bee mortality across the life cycle. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 969–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymann, K.; Shaffer, Z.; Moran, N.A. Antibiotic exposure perturbs the gut microbiota and elevates mortality in honeybees. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2001861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DesJardins, N.S.; Macias, J.; Soto Soto, D.; Harrison, J.F.; Smith, B.H. ‘Inert’co-formulants of a fungicide mediate acute effects on honey bee learning performance. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piechowicz, B.; Łaś, S.; Łaś, M.; Łuc, K.; Zaręba, L.; Kobylarz, D.; Kuliga, A.; Grodzicki, P.; Zienkiewicz, A.; Romerowicz-Misielak, M. The effects of deltamethrin (a synthetic pyrethroid insecticide), an anionic surfactant alone, and a co-formulated mixture of these substances on the honeybee (Apis mellifera) temperature preference, CO2 emission, and expression of detoxification-related genes. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2025, 65, 187–199. [Google Scholar]
- Tomé, H.V.; Clark, S.L.; Jorgenson, B.C.; Kimmel, S.; Wenzel, B.; Gimeno, C.; Porch, J.; Patnaude, M.R.; Schmidt, K.; Deslandes, L.; et al. Chronic larval and adult honey bee laboratory testing: Which dietary additive should be considered when a test substance is not solubilized in acetone? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 268, 115718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desclos le Peley, V.; Grateau, S.; Moreau-Vauzelle, C.; Raboteau, D.; Chevallereau, C.; Requier, F.; Aupinel, P.; Richard, F.J. Experimental ecotoxicology procedures interfere with honey bee life history. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, S.; Jarratt, N.; Harkin, S.; Thompson, H.; Coulson, M. Effects of solvent on the toxicity of dimethoate in a honey bee in vitro larval study. Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.W.; Fahrbach, S.E. Subtle effects of acetone and amitraz on sucrose sensitivity and recall in honey bees. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 20867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunçer, S.; Gurbanov, R. Non-growth inhibitory doses of dimethyl sulfoxide alter gene expression and epigenetic pattern of bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Wang, D.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Niu, J.; Hong, Y.; Drlica, K.; Zhao, X. Dimethyl sulfoxide protects Escherichia coli from rapid antimicrobial-mediated killing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5054–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jin, W.; Sun, C.; Gao, S.-H.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q.; Han, S.-F.; Tu, R.; Latif, M.A.; Wang, Q. Microbial degradation of N, N-dimethylformamide by Paracoccus sp. strain DMF-3 from activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Pan, J.; Cai, S.; Chen, L.; Cai, T.; Ji, X.-M. Biosynthesis of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) by N, N-dimethylformamide degrading strain Paracoccus sp. PXZ: A strategy for resource utilization of pollutants. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 129318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyrda, G.; Boniewska-Bernacka, E.; Man, D.; Barchiewicz, K.; Słota, R. The effect of organic solvents on selected microorganisms and model liposome membrane. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 3225–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, A. Diversity and ecology of organic solvent tolerant microorganisms. In Extremophiles Handbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 945–970. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, S.; Pandey, A.; Castro, G.R. Organic solvent adaptation of Gram positive bacteria: Applications and biotechnological potentials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jori, G.; Brown, S.B. Photosensitized inactivation of microorganisms. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2004, 3, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, A.; Molina, L.; Fillet, S.; Krell, T.; Bernal, P.; Muñoz-Rojas, J.; Ramos, J.-L. Solvent tolerance in Gram-negative bacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aono, R.; Tsukagoshi, N.; Miyamoto, T. Evaluation of the growth inhibition strength of hydrocarbon solvents against Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas putida grown in a two-liquid phase culture system consisting of a medium and organic solvent. Extremophiles 2001, 5, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.J.; de Bont, J.A. Adaptation mechanisms of microorganisms to the toxic effects of organic solvents on membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Biomembr. 1996, 1286, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta-Maté, A.; Renelies-Hamilton, J.; Kryger, P.; Jensen, A.B.; Sinotte, V.M.; Poulsen, M. Resistance and vulnerability of honeybee (Apis mellifera) gut bacteria to commonly used pesticides. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 717990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakumanu, M.L.; Reeves, A.M.; Anderson, T.D.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Williams, M.A. Honey bee gut microbiome is altered by in-hive pesticide exposures. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Ma, J.; Ji, T.; Zhang, H.; Yin, L. Effect of Solvents on the Structure of the Gut Microbiota of Honeybees (Apis mellifera). Insects 2025, 16, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111076
Wang K, Ma J, Ji T, Zhang H, Yin L. Effect of Solvents on the Structure of the Gut Microbiota of Honeybees (Apis mellifera). Insects. 2025; 16(11):1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111076
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kang, Jinmeng Ma, Ting Ji, Haibo Zhang, and Ling Yin. 2025. "Effect of Solvents on the Structure of the Gut Microbiota of Honeybees (Apis mellifera)" Insects 16, no. 11: 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111076
APA StyleWang, K., Ma, J., Ji, T., Zhang, H., & Yin, L. (2025). Effect of Solvents on the Structure of the Gut Microbiota of Honeybees (Apis mellifera). Insects, 16(11), 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111076





