Synergistic Effects of Beauveria bassiana and Insecticides for Integrated Management of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Strains and Pesticides
2.2. Determination of Median Lethal Concentration of Highly Virulent Strains
2.3. Assessment of Compatibility Between Beauveria bassiana and Insecticides
2.3.1. Preparation of Insecticide Solutions
2.3.2. Effect of Insecticides on Spore Germination of B. bassiana Bb-33
2.3.3. Effect of Insecticides on Colony Growth of B. bassiana Bb-33
2.3.4. Effect of Insecticides on Spore Production of B. bassiana Bb-33
2.4. Synergistic Effect and Greenhouse Evaluation
2.4.1. Toxicity of B. bassiana Combined with Chemical Insecticides Against B. dorsalis
2.4.2. Greenhouse Control Experiment of B. dorsalis Adults
2.4.3. Greenhouse Control Experiment of B. dorsalis Pupae
2.5. Data Analysis and Processing
3. Results
3.1. Lethal Concentration of B. bassiana Bb-33
3.2. Effects of Pesticides on Spore Germination of B. bassiana Bb-33
3.3. Colony Growth of B. bassiana Bb-33 Affected by Pesticides
3.4. Sporulation Yield of B. bassiana Bb-33 Affected by Pesticides
3.5. Screening of Pesticides with Good Compatibility with B. bassiana
3.6. Combined Toxicity and Co-Toxicity Coefficient of B. bassiana and Pesticides
3.7. Evaluation of a Compound Formulation for Controlling B. dorsalis Adults
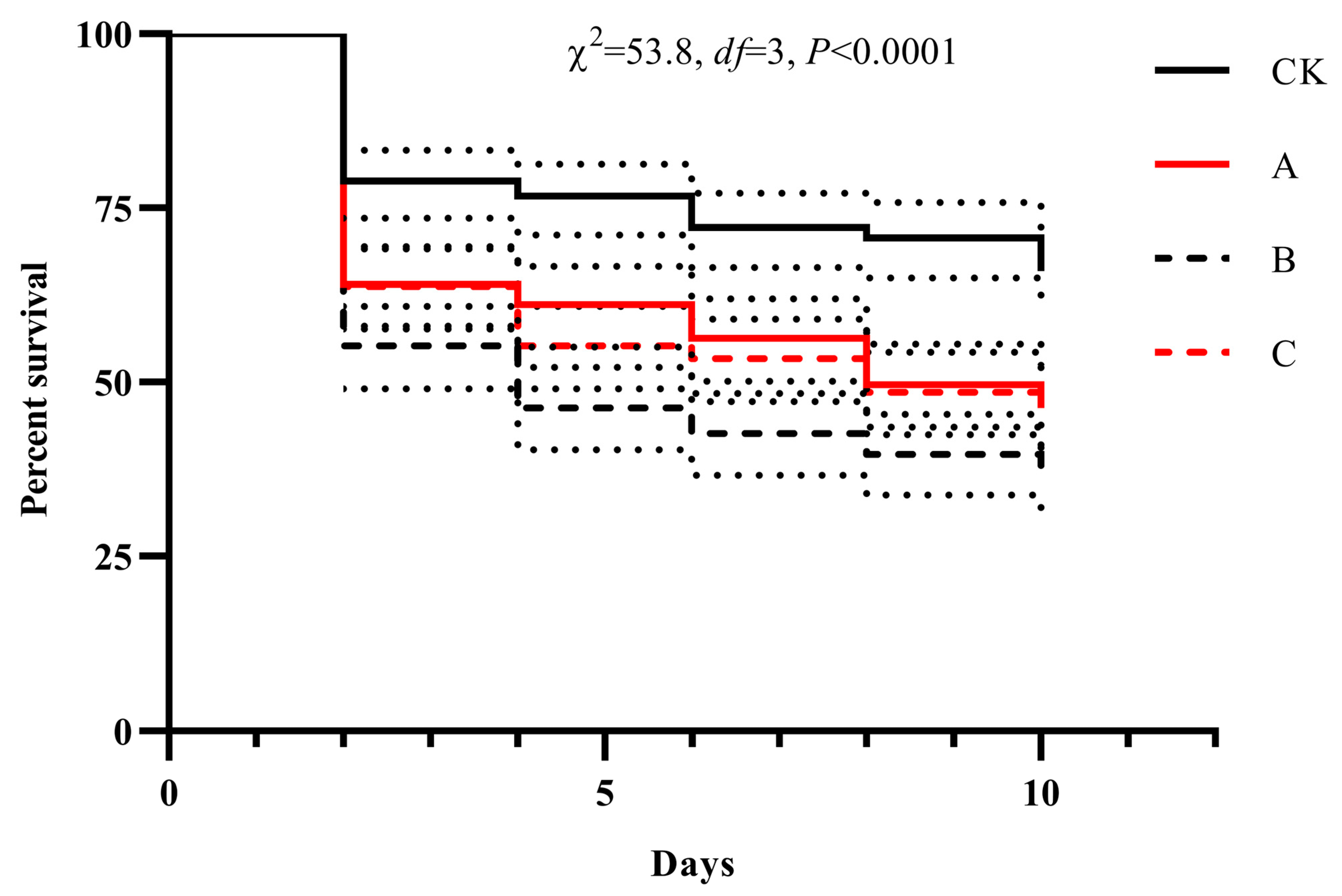
3.8. Evaluation of a Compound Formulation for Controlling B. dorsalis Pupae
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clarke, A.R.; Armstrong, K.F.; Carmichael, A.E.; Milne, J.R.; Raghu, S.; Roderick, G.K.; Yeates, D.K. Invasive phytophagous pests arising through a recent tropical evolutionary radiation: The Bactrocera dorsalis complex of fruit flies. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2005, 50, 293–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohino, T.; Hallman, G.J.; Grout, T.G.; Clarke, A.R.; Follett, P.A.; Cugala, D.R.; Tu, D.M.; Murdita, W.; Hernandez, E.; Pereira, R.; et al. Phytosanitary Treatments Against Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae): Current Situation and Future Prospects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 110, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Shang, M.Q.; Teng, Z.W.; Tan, X.M.; Guo, Y.J.; Meng, J.; Wan, F.H.; Zhou, H.X. Analysis of Invasive Distribution and Spread Trends of Bactrocera dorsalis. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2020, 5212, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, A.; Kriticos, D.; Leriche, A. The current and future potential geographical distribution of the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2007, 97, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, M. Cultural Measures as Management Option Against Fruit Flies Pest (Tephritidae: Diptera) in Garden or Farm and Territories. Int. J. Anim. Biol. 2015, 1, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, D.J.; Xu, Y.J.; Lei, W.; Cheng, D.F.; Qi, Y.; Zeng, L.; Lu, Y.Y. Invasion, expansion, and control of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.C.; Feng, H.T. Development of resistance to spinosad in oriental fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) in laboratory selection and cross-resistance. J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.D. The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekesi, S.; Dimibi, S.; Maniania, N.K. The role of entomopathogenic fungi in the integrated management of fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) with emphasis on species occurring in Africa. Biophys. J. 2007, 75, 2996–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, G. Review on safety of the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana and Beauveria brongniartii. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 553–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaronski, S.T. Ecological factors in the inundative use of fungal entomopathogens. BioControl 2010, 55, 159–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, L.A.; Grzywacz, D.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Frutos, R.; Brownbridge, M.; Goettel, M.S. Insect pathogens as biological control agents: Back to the future. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 132, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintela, E.D.; McCoy, C.W. Synergistic Effect of Imidacloprid and Two Entomopathogenic Fungi on the Behavior and Survival of Larvae of Diaprepes abbreviatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in Soil. J. Econ. Entomol. 1998, 91, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Zhou, X.P.; Xiao, Z.P.; Wu, S.L.; Cai, H.L.; Kai, T.; Zeng, W.A.; Li, J.J.; Xu, Q.X.; Zai, G. Synergistic interaction of Beauveria bassiana (Vuillemin) with Emamectin benzoate improves its pathogenicity against Spodoptera litura (Fabricius). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2023, 43, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, Z.Z. Compatibility of Beauveria bassiana to Some Chemical Insecticides and Herbicides. Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2001, 27, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.F.; Xie, T.; Jing, L.L.; Hong, B.; Jia, Y.X. Consistency of Beauveria bassiana with Eight Pesticides and Their Indoor Joint Toxicities to Bemisia tabaci. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2021, 30, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirapara, I.M.; Jethva, D.M.; Desai, A.V.; Patel, D.H. Compatibility of Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) vuillemin with different insecticides and fungicides. Indian J. Entomol. 2023, 85, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.J.; Wang, Y.; Pei, H.Y.; Yu, H.C. Study on Fitness of Beauveria bassiana Strain Bb170428 with 12 Low-toxic Insecticides. North. Hortic. 2022, 18, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Johnson, E.R. Analysis of Joint Action of Insecticides Against House Flies. J. Econ. Entomol. 1960, 53, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, W.X.; Wang, H.F.; Cheng, P.; Wang, H.W.; Guo, X.X.; Gong, M.Q.; Liu, L.J. Observation on the Control Effect of Beauveria bassiana on Vector Mosquitoes. J. Pathog. Biol. 2021, 16, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, T.S.; Rodrigo, A.P.; Souza, I.M.; Silva, G.G.; Soares, M.A.; Santos, J.B.D. Herbicides and bio-inputs: Compatibility and challenges for sustainable agriculture. Chemosphere 2024, 369, 143878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Z.Y.; Tong, W.; Sun, P.; Zeng, H.L.; Ye, S.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Long, Y.M. Research progress in infection characteristics and application of Beauveria bassiana. Microbiol. China 2023, 50, 3187–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.B.; Zhao, Y.D.; Zhou, X.L.; Shen, H.M. Biocompatibility between Acremonium hansfordii and common acaricides and the synergistic effect. J. Plant Prot. 2012, 38, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wei, Z.H.; Li, J.B.; Ge, Y.L. The Effect and Prospect of Mixed use of Fungal Insecticides and Chemical Insecticides. J. Agric. Catastr. Res. 2020, 10, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainab, B.; Asam, R.M.; Samy, S.; Zeeshan, M.M.; Sohail, A.; Sami, U. In vitro synergy of entomopathogenic fungi and differential-chemistry insecticides against armyworm Spodoptera litura Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2022, 42, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelizza, S.A.; Scorsetti, A.C.; Fogel, M.N.; Pacheco-Marino, S.G.; Stenglein, S.A.; Cabello, M.N.; Lang, C.E. Compatibility between entomopathogenic fungi and biorational insecticides in toxicity against Ronderosia bergi under laboratory conditions. BioControl 2015, 60, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luigia, M.V.; Caroline, Z.; Tommaso, A.; Anita, G.; Joachim, K. Herbicide exposure alters the effect of the enthomopathogen Beauveria bassiana on immune gene expression in mealworm beetles. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Jiang, L.; Hong, B.; Wang, X.P.; Jia, Y.X. Virulence and Field Control Effect of Beauveria bassiana Mixed with Matrine against Bemisia tabaci. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2019, 28, 830–836. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/61.1220.S.20190514.1242.038 (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Mota, L.H.C.; Silva, W.D.; Sermarini, R.A.; Demétrio, C.G.B.; Bento, J.M.S.; Delalibera, I. Autoinoculation trap for management of Hypothenemus hampei (Ferrari) with Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) in coffee crops. Biol. Control. 2017, 111, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zou Di Sun, S.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Wei, D.D. Screening of Highly Virulent Beauveria bassiana Strains Against Bactrocera dorsalis and Synergistic Effects of Their Mixed Application with Abamectin and Beta-Cypermethrin. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2025, 1–16. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1832.Q.20250422.1147.003 (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Kotta-Loizou, I.; Coutts, R.H. Studies on the Virome of the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria bassiana Reveal Novel dsRNA Elements and Mild Hypervirulence. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Hong, B.; Wang, X.P.; Jia, Y.X. Compatibility of chemical pesticides with Beauveria bassiana and synergistic control effect on Trialeurodes vaporariorum. J. Plant Prot. 2018, 44, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Insecticide | Category | LC50 (mg/L) | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spinosad 92% | Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor (nAChR) Allosteric Modulators | 7.48 | Huazhong Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China |
| Emamectin benzoate 95% | GABA Receptor Inhibitors | 1.77 | Huazhong Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China |
| Avermectin 96% | GABA Receptor Inhibitors | 8.86 | Huazhong Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China |
| Thiamethoxam 97% | Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor (nAChR) Agonists | 71.09 | Huazhong Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China |
| Beta-cypermethrin 96% | Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Inhibitors | 112.95 | Huazhong Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China |
| Imidacloprid 96% | Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor (nAChR) Agonists | 255.99 | Huazhong Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China |
| Insecticide | Spore Germination Inhibition Rate (%) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LC50 (Lethal) | 0.2 × LC50 (Sublethal) | 0.1 × LC50 (Sub-Sublethal) | |
| Emamectin benzoate | 10.16 ± 0.64 D | 7.05 ± 0.48 A | 5.18 ± 0.70 A |
| Spinosad | 13.15 ± 0.38 D | 11.11 ± 0.21 A | 7.13 ± 0.61 A |
| Beta-cypermethrin | 46.71 ± 1.17 B | 9.03 ± 0.84 A | 7.31 ± 0.33 A |
| Avermectin | 15.00 ± 0.75 D | 7.54 ± 1.00 A | 7.30 ± 1.08 A |
| Imidacloprid | 97.39± 0.61 A | 10.20 ± 0.23 A | 5.43 ± 0.74 A |
| Thiamethoxam | 26.89± 1.02 C | 8.15 ± 0.51 A | 7.46 ± 0.22 A |
| Insecticide | Mycelial Growth Inhibition Rate (%) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LC50 (Lethal) | 0.2 × LC50 (Sublethal) | 0.1 × LC50 (Sub-Sublethal) | |
| Emamectin benzoate | 12.26 ± 0.81 A | 6.39 ± 0.27 B | 4.75 ± 0.51 A |
| Spinosad | 13.00 ± 1.20 A | 9.51 ± 1.55 AB | 3.45 ± 0.77 A |
| Beta-cypermethrin | 11.71 ± 0.94 A | 12.01 ± 0.58 AB | 8.18 ± 0.53 A |
| Avermectin | 14.75 ± 0.66 A | 10.96 ± 0.98 AB | 7.84 ± 0.65 A |
| Imidacloprid | 15.67 ± 0.64 A | 13.31 ± 0.61 A | 8.18 ± 1.42 A |
| Thiamethoxam | 16.95 ± 1.13 A | 7.96 ± 1.69 AB | 3.10 ± 1.07 A |
| Insecticide | Sporulation Inhibition Rate (%) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LC50 (Lethal) | 0.2 × LC50 (Sublethal) | 0.1 × LC50 (Sub-Sublethal) | |
| Emamectin benzoate | 36.33 ± 1.19 C | 22.71 ± 0.65 D | 12.24 ± 1.21 D |
| Spinosad | 47.88 ± 0.75 BC | 38.02 ± 3.39 B | 27.84 ± 1.86 BC |
| Beta-cypermethrin | 63.19 ± 1.89 A | 46.95 ± 1.08 AB | 34.37 ± 2.46 AB |
| Avermectin | 54.11 ± 1.20 AB | 39.10 ± 1.09 BC | 24.54 ± 1.51 BC |
| Imidacloprid | 63.63 ± 0.31 A | 53.68 ± 1.82 A | 39.50 ± 1.90 A |
| Thiamethoxam | 52.97 ± 1.36 A | 29.77 ± 1.10 CD | 22.24 ± 2.43 C |
| Ratio | Slope ± SE | LC50 (mg/L) | 95% Confidence Interval | Chi-Square Test | CTC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A a:B b = 1:9 | 8.16 ± 1.03 | 1.11 | 0.99–1.21 | 2.48 | 175.11 |
| A:B = 1:4 | 12.77 ± 1.75 | 1.74 | 1.59–1.86 | 1.26 | 123.87 |
| A:B = 1:1 | 7.95 ± 0.69 | 5.33 | 4.91–5.75 | 0.45 | 60.05 |
| A:B = 4:1 | 3.76 ± 3.00 | 9.40 | 6.15–11.53 | 1.69 | 66.12 |
| A:B = 9:1 | 1.43 ± 1.00 | 18.70 | —— | 0.93 | 48.44 |
| Treatment Area | Insect Fruit Percentage e | Fruit Falling Percentage e | Emergence Percentage e |
|---|---|---|---|
| A a | 18.47 ± 12.47 B | 62.35 ± 0.12 B | 91.11 ± 0.64 A |
| B b | 9.80 ± 1.56 C | 51.08 ± 0.14 C | 79.26 ± 0.98 B |
| C c | 16.05 ± 8.07 B | 57.65 ± 0.03 BC | 83.33 ± 0.64 B |
| CK d | 36.00 ± 5.72 A | 79.72 ± 0.05 A | 91.48 ± 0.74 A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zha, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, Z.; Cai, W. Synergistic Effects of Beauveria bassiana and Insecticides for Integrated Management of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Insects 2025, 16, 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101067
Wang X, Li Y, Zha Y, Tian Y, Wang J, Li H, Zhu Z, Cai W. Synergistic Effects of Beauveria bassiana and Insecticides for Integrated Management of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Insects. 2025; 16(10):1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101067
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaole, Yunfei Li, Yuping Zha, Yubin Tian, Jing Wang, Hanbing Li, Zhihui Zhu, and Wanlun Cai. 2025. "Synergistic Effects of Beauveria bassiana and Insecticides for Integrated Management of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae)" Insects 16, no. 10: 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101067
APA StyleWang, X., Li, Y., Zha, Y., Tian, Y., Wang, J., Li, H., Zhu, Z., & Cai, W. (2025). Synergistic Effects of Beauveria bassiana and Insecticides for Integrated Management of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Insects, 16(10), 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101067







