Comparative Transcriptomics Unveils Pathogen-Specific mTOR Pathway Modulation in Monochamus alternatus Infected with Entomopathogenic Fungi
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Fungus Inoculate onto JPS
2.3. Quantification of EPF Pathogenicity
2.4. Dual RNA-Seq and Data Analysis
2.5. Gene Expression Quantification Assay
2.6. Rapamycin and Torin-1 Treatment
2.7. RNA Interference (RNAi) Assay
3. Results
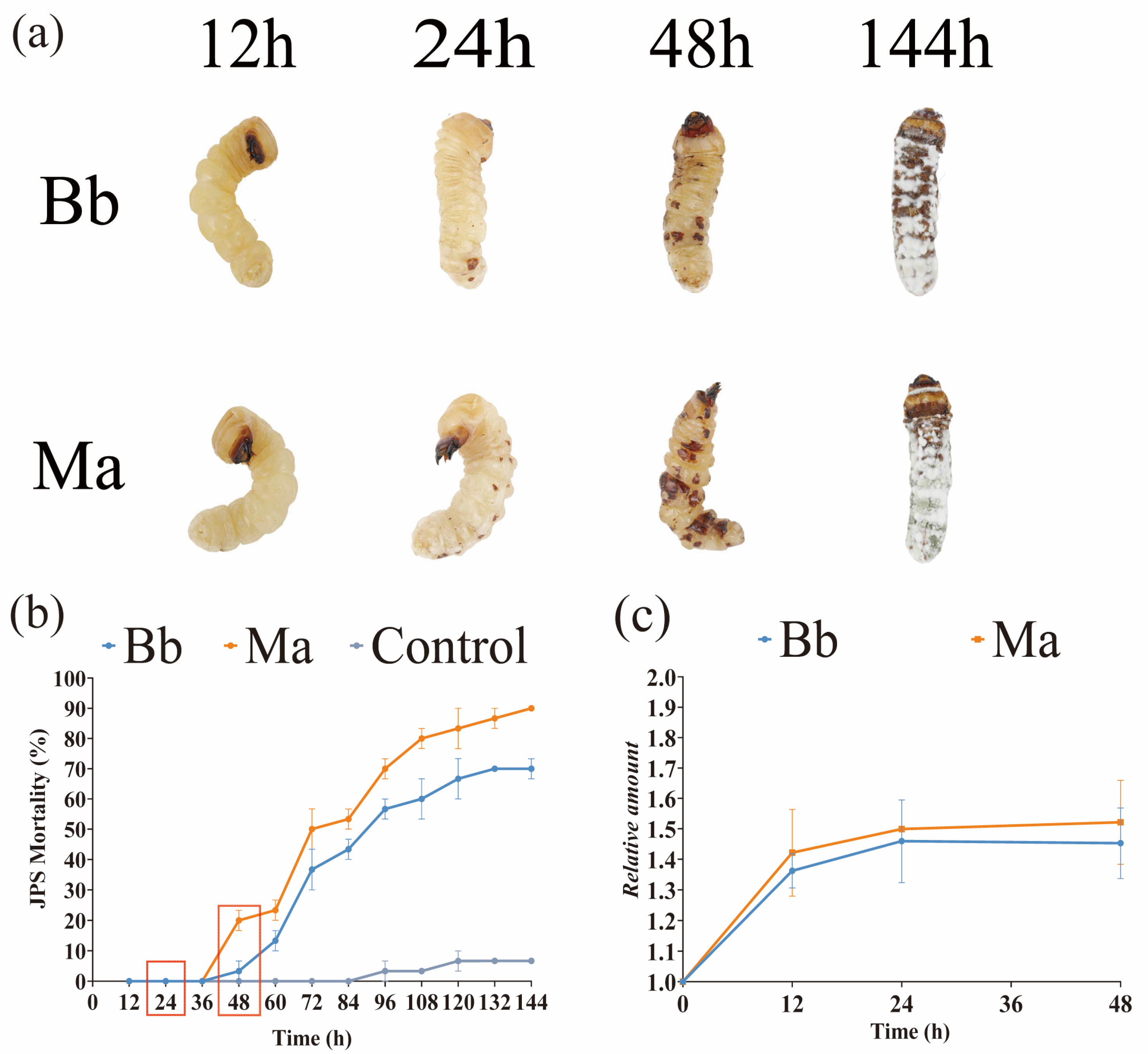
3.1. Comparative Pathogenicity Dynamics Between Bb and Ma in JPS Larvae
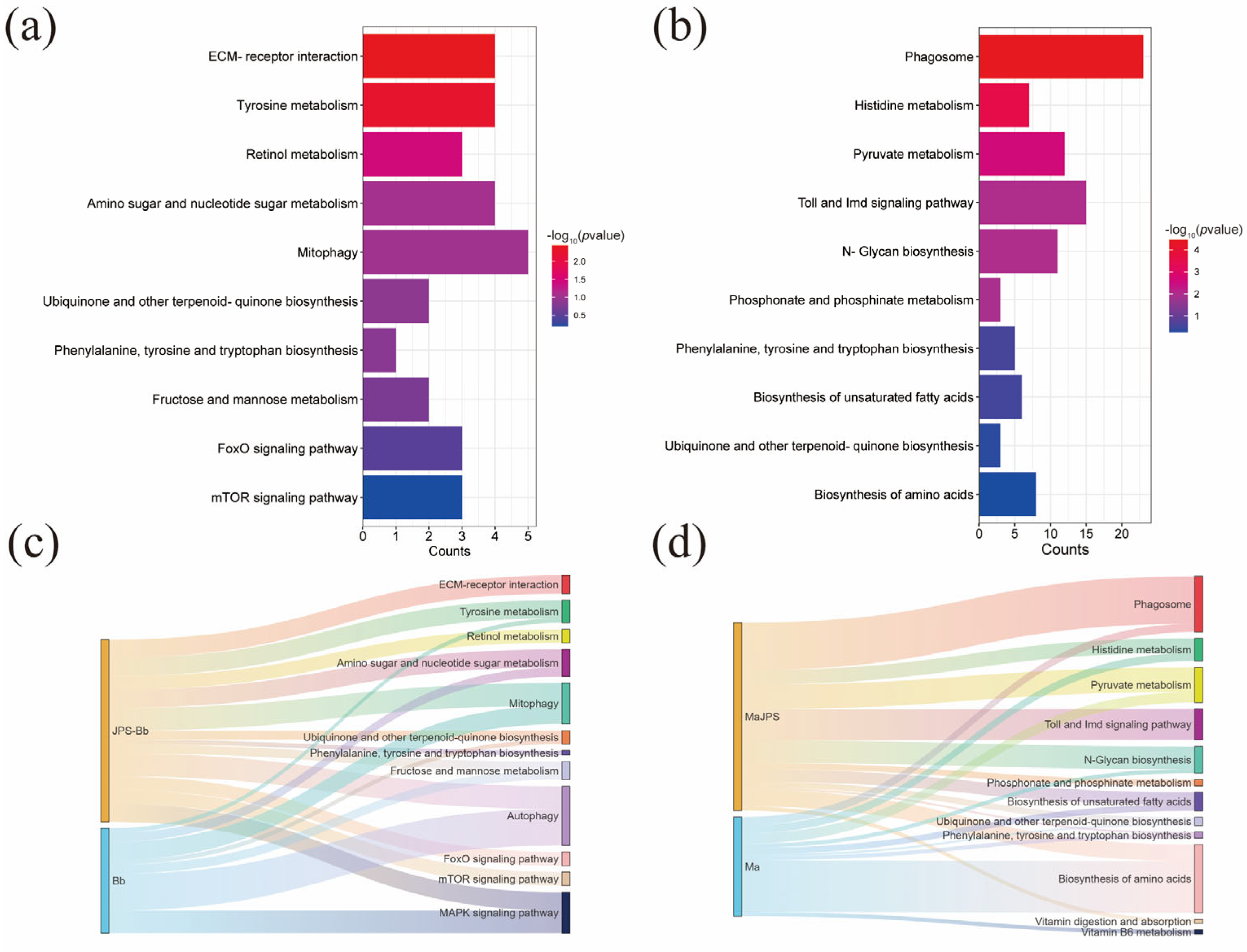
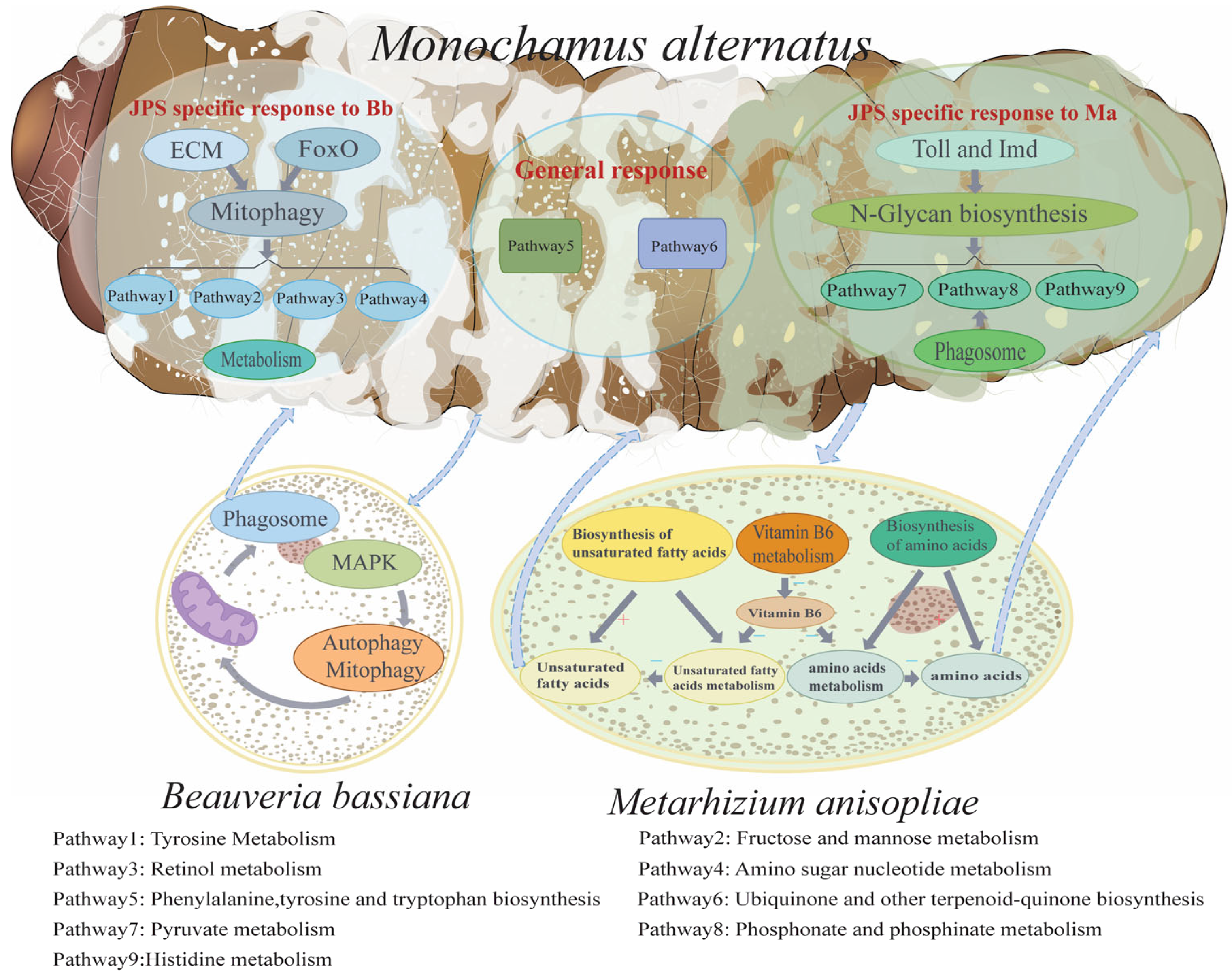
3.2. Transcriptomic Basis of Differential Host–Pathogen Interactions
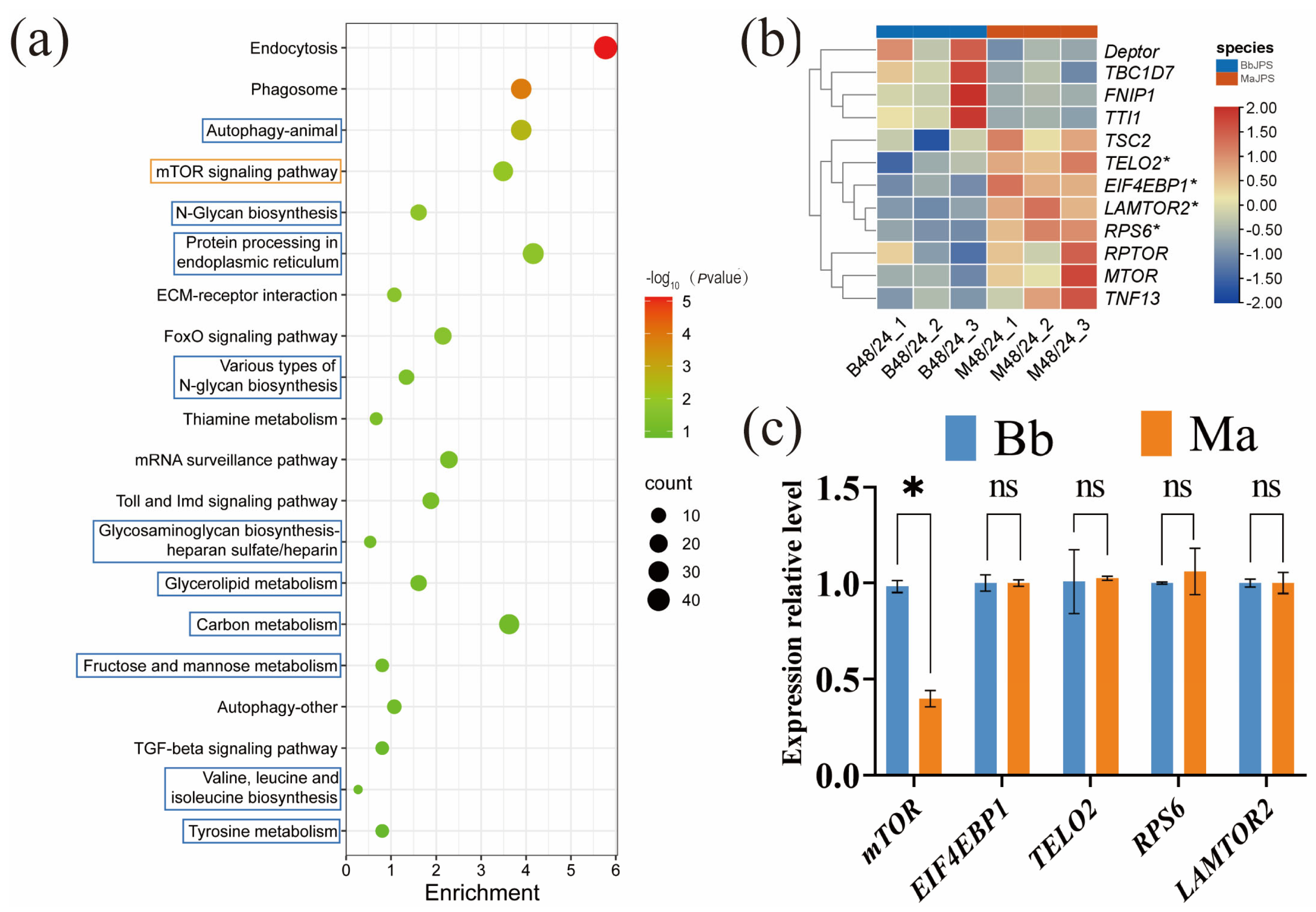
3.3. Differential mTOR Pathway Regulation Underlies Divergent Mortality Outcomes
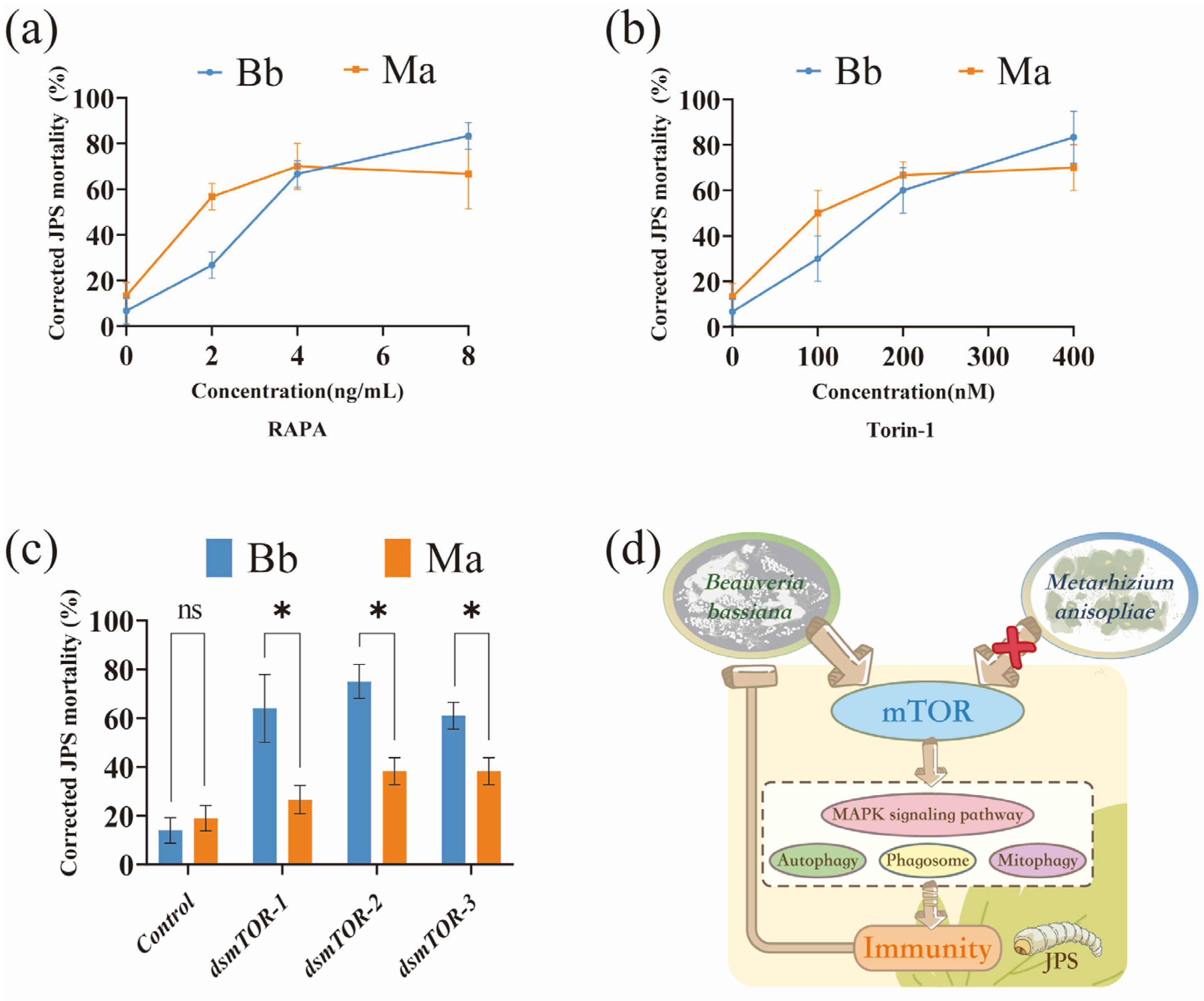
3.4. mTOR Signaling Is Critical for Host Defense Against Bb and Exhibits Pathogen-Specific Vulnerability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, L.; Mota, M.; Vieira, P.; Butcher, R.A.; Sun, J. Interspecific communication between pinewood nematode, its insect vector, and associated microbes. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ma, Y.; Duan, W.; Fan, Q.; Sun, J.; Wang, C. Pinewood nematode induced changes in the assembly process of gallery microbiomes benefit its vector beetle’s development. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0141224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Chen, L.; Yu, W.; Cai, S.; Su, S.; Xiao, X.; Tang, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, D.; Fang, Y.; et al. The novel nematicide chiricanine A suppresses Bursaphelenchus xylophilus pathogenicity in Pinus massoniana by inhibiting Aspergillus and its secondary metabolite, sterigmatocystin. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1257744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yu, M.; Sun, Z.; Pan, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, X.; Zhao, R.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X. Biomass-Based, Dual Enzyme-Responsive Nanopesticides: Eco-friendly and Efficient Control of Pine Wood Nematode Disease. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 13781–13793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Choi, I.S.; Lee, S.; Hwang, I.M.; Chun, H.H.; Wi, S.G.; Shin, T.Y.; Kim, J.C.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.; et al. Advanced strategy to produce insecticidal destruxins from lignocellulosic biomass Miscanthus. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B. Entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae play roles of maize (Zea mays) growth promoter. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maina, U.M.; Galadima, I.B.; Gambo, F.M.; Zakaria, D. A review on the use of entomopathogenic fungi in the management of insect pests of field crops. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hixson, B.; Huot, L.; Morejon, B.; Yang, X.; Nagy, P.; Michel, K.; Buchon, N. The transcriptional response in mosquitoes distinguishes between fungi and bacteria but not Gram types. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.L.; Vianna, M.F.; Scorsetti, A.C.; Ferreri, N.; de Abajo, J.M.; Troncozo, M.I.; Pelizza, S.A. Entomopathogenic Fungi as Dual Control Agents against Two Phytopathogens and the Lepidopteran Pest Rachiplusia nu in Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr). J. Fungi 2024, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.G.; Son, J.-K.; Lee, B.-H.; Cho, J.H.; Ren, Y. Comparison of Ethanedinitrile (C2N2) and Metam Sodium for Control of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchidae) and Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in Naturally Infested Logs at Low Temperatures. J. Econ. Èntomol. 2014, 107, 2055–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.-Q.; Cai, Q.-D.; Deng, M.-Z.; Huang, Q.; Peng, H.-J. Scorpion neurotoxin AaIT-expressing Beauveria bassiana enhances the virulence against Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. AMB Express 2017, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, D. Diversity of soil fungi and entomopathogenic fungi in subtropical mountain forest in southwest China. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2024, 16, e13267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petlamul, W.; Prasertsan, P. Evaluation of Strains of Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana against Spodoptera litura on the Basis of Their Virulence, Germination Rate, Conidia Production, Radial Growth and Enzyme Activity. Mycobiology 2012, 40, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batta, Y.A. Invert emulsion: Method of preparation and application as proper formulation of entomopathogenic fungi. MethodsX 2016, 3, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, C.J.; Rouhier, M.F.; Hillyer, J.F. Chemical Control of Mosquitoes and the Pesticide Treadmill: A Case for Photosensitive Insecticides as Larvicides. Insects 2022, 13, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Liu, X.; Peng, G.; Xia, Y.; Cao, Y. Recent Advancements in Pathogenic Mechanisms, Applications and Strategies for Entomopathogenic Fungi in Mosquito Biocontrol. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, S. Insect Pathogenic Fungi: Genomics, Molecular Interactions, and Genetic Improvements. Annu. Rev. Èntomol. 2017, 62, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirmohammadi, M.; Talaei-Hassanloui, R.; Moosa-Kazemi, S.H.; Rassi, Y.; Rahimi, S.; Fatemi, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Arandian, M.H.; Jafari, R.; Golzan, S.R.; et al. Evaluation of the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria bassiana on Different Stages of Phlebotomus papatasi (Diptera: Psychodidae), Vector of Zoonotic Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Iran. J. Arthropod-Borne Dis. 2023, 17, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Qiu, X.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Han, R.; Schubert, M. Evaluation of Reference Genes for Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR Studies of Physiological Responses in the Ghost Moth, Thitarodes armoricanus (Lepidoptera, Hepialidae. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Silva, C.S.; Muniz, E.R.; Lima, V.H.; Bernardo, C.C.; Arruda, W.; Castro, R.N.; Gôlo, P.S.; Angelo, I.C.; Fernandes, É.K.K. Cuticular Lipids as a First Barrier Defending Ixodid Ticks against Fungal Infection. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Tripathi, A.; Dwivedi, S.; Lal, K.; Jhang, T. Deciphering the mechanisms, hormonal signaling, and potential applications of endophytic microbes to mediate stress tolerance in medicinal plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1250020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, Z.; Huang, S.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lv, T.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y. Fus3/Kss1-MAP kinase and Ste12-like control distinct biocontrol-traits besides regulation of insect cuticle penetration via phosphorylation cascade in a filamentous fungal pathogen. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 2611–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Y.; Liu, C.; He, R.; Wang, R.; Qu, L. Detection and Identification of Novel Intracellular Bacteria Hosted in Strains CBS 648.67 and CFCC 80795 of Biocontrol Fungi Metarhizium. Microbes Environ. 2022, 37, ME21059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, W.; Lu, Y.; Kang, Q.; Sui, L.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, X.; Li, Q. Hypovirulence-associated mycovirus epidemics cause pathogenicity degeneration of Beauveria bassiana in the field. Virol. J. 2023, 20, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Deng, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Luo, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y. Multifunctional role of a fungal pathogen-secreted laccase 2 in evasion of insect immune defense. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 1256–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, K.M.S.; Hue, S.M. Mode of Infection of Metarhizium spp. Fungus and Their Potential as Biological Control Agents. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, T.; Aimanianda, V.; Bischoff, E.; Brito-Fravallo, E.; Eiglmeier, K.; Riehle, M.M.; Vernick, K.D.; Mitri, C. Genetics and immunity of Anopheles response to the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae overlap with immunity to Plasmodium. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pan, H.; Li, M.; Wu, W.; Yu, X. Comprehensive insights into host-pathogen interaction between brown planthopper and a fungal entomopathogen by dual RNA sequencing. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 4903–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Yuan, C.; Lu, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, C.-Y.; Zhang, P.; Dobens, L.; Zou, Z.; Wang, C.; et al. Prophenoloxidase-Mediated Ex Vivo Immunity to Delay Fungal Infection after Insect Ecdysis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, A.J.; Förstner, K.U.; Amman, F.; Barquist, L.; Chao, Y.; Schulte, L.N.; Müller, L.; Reinhardt, R.; Stadler, P.F.; Vogel, J. Dual RNA-seq unveils noncoding RNA functions in host-pathogen interactions. Nature 2016, 529, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhan, F.; Zeng, L.; Sun, Y.; Fu, S.; Fang, Y.; Lin, X.; Lin, H.; Su, J.; Cai, S.; et al. Arginine accumulation suppresses heat production during fermentation of the biocontrol fungus Beauveria bassiana. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 91, e0213424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusova, T.; Ciufo, S.; Fedorov, B.; O’nEill, K.; Tolstoy, I. RefSeq microbial genomes database: New representation and annotation strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D553–D559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. feature Counts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, J.D.; Tibshirani, R. Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9440–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Araki, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Kawashima, S.; Okuda, S.; Tokimatsu, T.; et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D480–D484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Wang, R.; Nanaei, H.A.; Wang, J.; Hu, D.; Jiang, Y. RGD v2.0: A major update of the ruminant functional and evolutionary genomics database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1091–D1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, F.-F.; Fu, L.-Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.-T.; Wang, Q.; Rao, X.-J. Identification of 35 C-Type Lectins in the Oriental Armyworm, Mythimna separata (Walker). Insects 2021, 12, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Li, L.; Pan, S.; Liu, Z.; Fan, J.; Tang, M. Adaptive Reproductive Strategies of an Ectoparasitoid Sclerodermus guani under the Stress of Its Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria bassiana. Insects 2023, 14, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisnik, M.; Walker, D.M. Bat Cutaneous Microbial Assemblage Functional Redundancy Across a Host-Mediated Disturbance. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, J.; Aboul-Enein, B.H.; Duchnik, E. Exercise-induced oxidative stress and melatonin supplementation: Current evidence. J. Physiol. Sci. 2021, 71, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Liu, F. Transcriptome Analysis to Identify Responsive Genes under Sublethal Concentration of Bifenazate in the Diamondback Moth, Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus, 1758) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Wang, J.; Xie, J.; Jiang, D.; Keyhani, N.O. The Elongator Subunit Elp3 Regulates Development, Stress Tolerance, Cell Cycle, and Virulence in the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria bassiana. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A.J.; Ezcurra, M.; Flanagan, C.E.; Summerfield, A.C.; Piper, M.D.; Gems, D.; Alic, N. Nutritional Programming of Lifespan by FOXO Inhibition on Sugar-Rich Diets. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-Q.; Liu, C.; Cai, Z.; Xie, Q.; Hu, T.; Duan, M.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Tang, Q. High-mobility group AT-hook 1 promotes cardiac dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy via autophagy inhibition. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, L.; Bertini, L.; Bonato, A.; Villanova, N.; Caruso, C.; Caruso, M.; Bernini, R.; Tirone, F. Role of Hydroxytyrosol and Oleuropein in the Prevention of Aging and Related Disorders: Focus on Neurodegeneration, Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction and Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, G.; Qiu, X.; Wang, X. Metabolomic Analysis of the Takifugu Obscurus Gill under Acute Hypoxic Stress. Animals 2022, 12, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiyin, H.; Na, N.; Han, X.; Fang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lou, W.; Yang, X. BRSK2 induced by nutrient deprivation promotes Akt activity in pancreatic cancer via downregulation of mTOR activity. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44669–44681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, R.K.; Vladimer, G.I.; Snijder, B.; Müller, A.C.; Rebsamen, M.; Bigenzahn, J.W.; Moskovskich, A.; Sabler, M.; Stefanovic, A.; Scorzoni, S.; et al. A time-resolved molecular map of the macrophage response to VSV infection. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 2016, 2, 16027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barilari, M.; Bonfils, G.; Treins, C.; Koka, V.; De Villeneuve, D.; Fabrega, S.; Pende, M. ZRF1 is a novel S6 kinase substrate that drives the senescence programme. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 736–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Cock, H.R.; Devinsky, O.; Joshi, C.; Miller, I.; Roberts, C.M.; Sanchez-Carpintero, R.; Checketts, D.; Sahebkar, F. Time to onset of cannabidiol treatment effect and resolution of adverse events in tuberous sclerosis complex: Post hoc analysis of randomized controlled phase 3 trial GWPCARE6. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, G.A. The role of mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) complexes signaling in the immune responses. Nutrients 2013, 5, 2231–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Hu, J.H.; Liu, D.R. Aptazyme-embedded guide RNAs enable ligand-responsive genome editing and transcriptional activation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15939. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, R.; Llewellyn, T.; Downes, E.; Oddy, J.; MacIntosh, C.; Kallow, S.; Panis, B.; Dickie, J.B.; Gaya, E. Seed Banks as Incidental Fungi Banks: Fungal Endophyte Diversity in Stored Seeds of Banana Wild Relatives. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 643731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, H.; He, J.; Zhang, C.; Shan, R.; Chen, H.; Wu, T.; Sun, Q.; Zeng, L.; Zhan, F.; Fang, Y.; et al. Comparative Transcriptomics Unveils Pathogen-Specific mTOR Pathway Modulation in Monochamus alternatus Infected with Entomopathogenic Fungi. Insects 2025, 16, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101006
Guan H, He J, Zhang C, Shan R, Chen H, Wu T, Sun Q, Zeng L, Zhan F, Fang Y, et al. Comparative Transcriptomics Unveils Pathogen-Specific mTOR Pathway Modulation in Monochamus alternatus Infected with Entomopathogenic Fungi. Insects. 2025; 16(10):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101006
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Haoran, Jinghong He, Chuanyu Zhang, Ruiyang Shan, Haoyuan Chen, Tong Wu, Qin Sun, Liqiong Zeng, Fangfang Zhan, Yu Fang, and et al. 2025. "Comparative Transcriptomics Unveils Pathogen-Specific mTOR Pathway Modulation in Monochamus alternatus Infected with Entomopathogenic Fungi" Insects 16, no. 10: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101006
APA StyleGuan, H., He, J., Zhang, C., Shan, R., Chen, H., Wu, T., Sun, Q., Zeng, L., Zhan, F., Fang, Y., Qu, G., Lin, C., Cai, S., & Su, J. (2025). Comparative Transcriptomics Unveils Pathogen-Specific mTOR Pathway Modulation in Monochamus alternatus Infected with Entomopathogenic Fungi. Insects, 16(10), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16101006





