Involvement of Inwardly Rectifying Potassium (Kir) Channels in the Toxicity of Flonicamid to Drosophila melanogaster
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Fly Strains
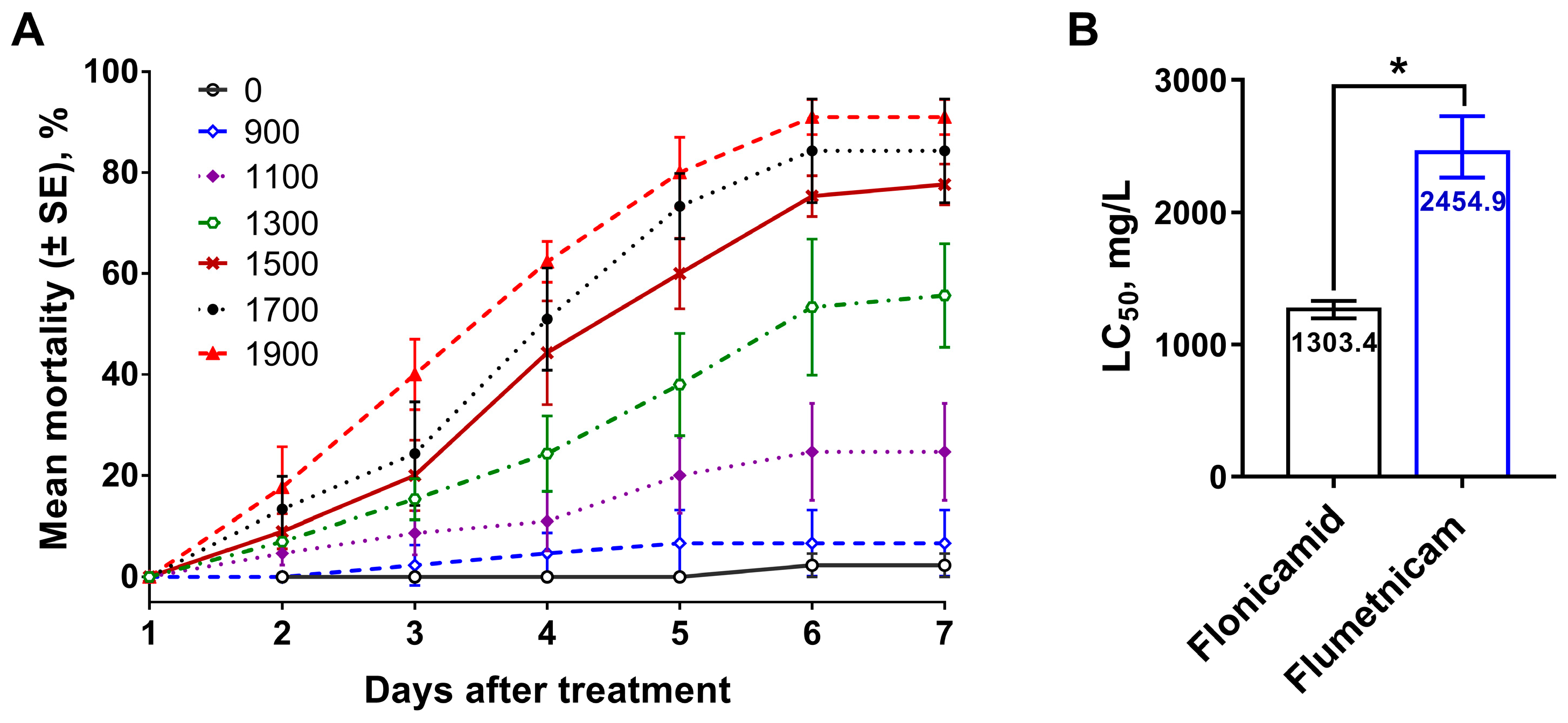
2.3. Susceptibility Bioassay in D. melanogaster
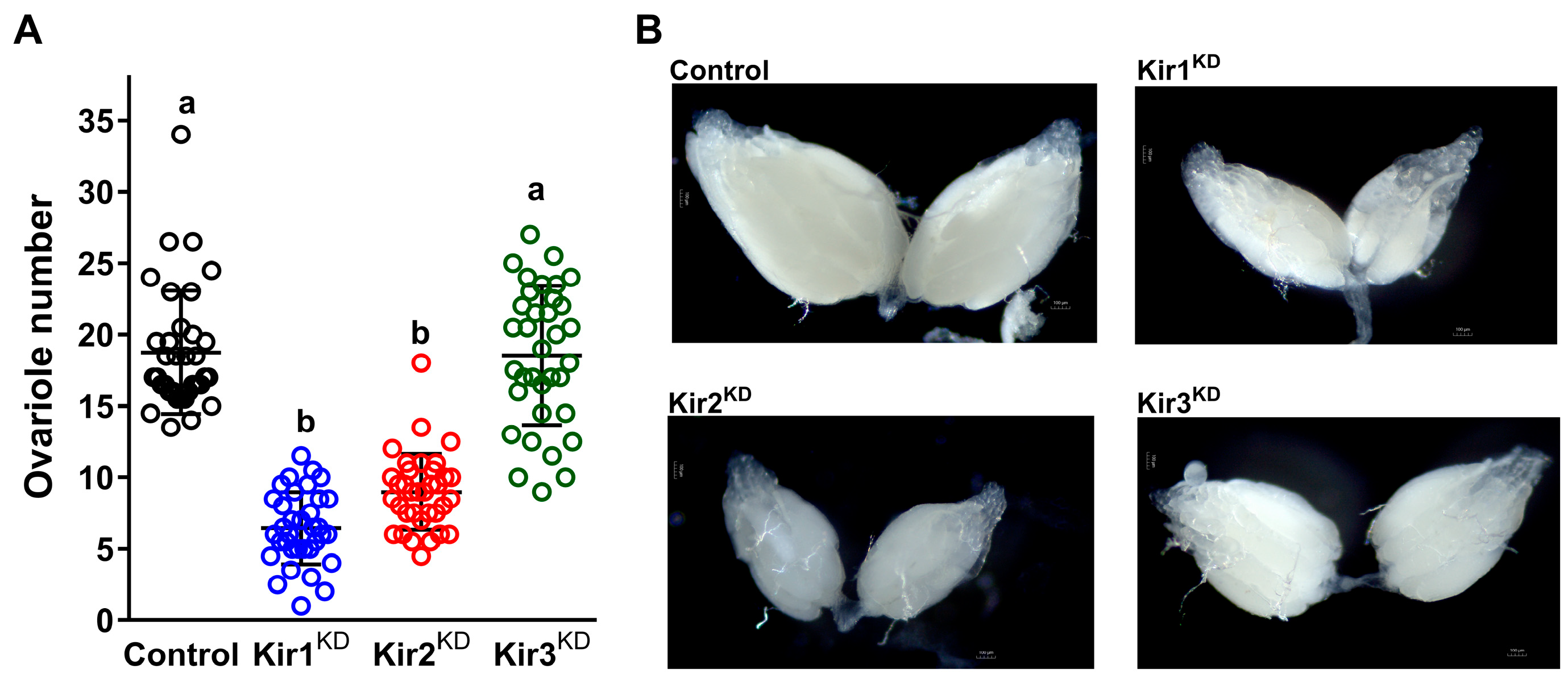
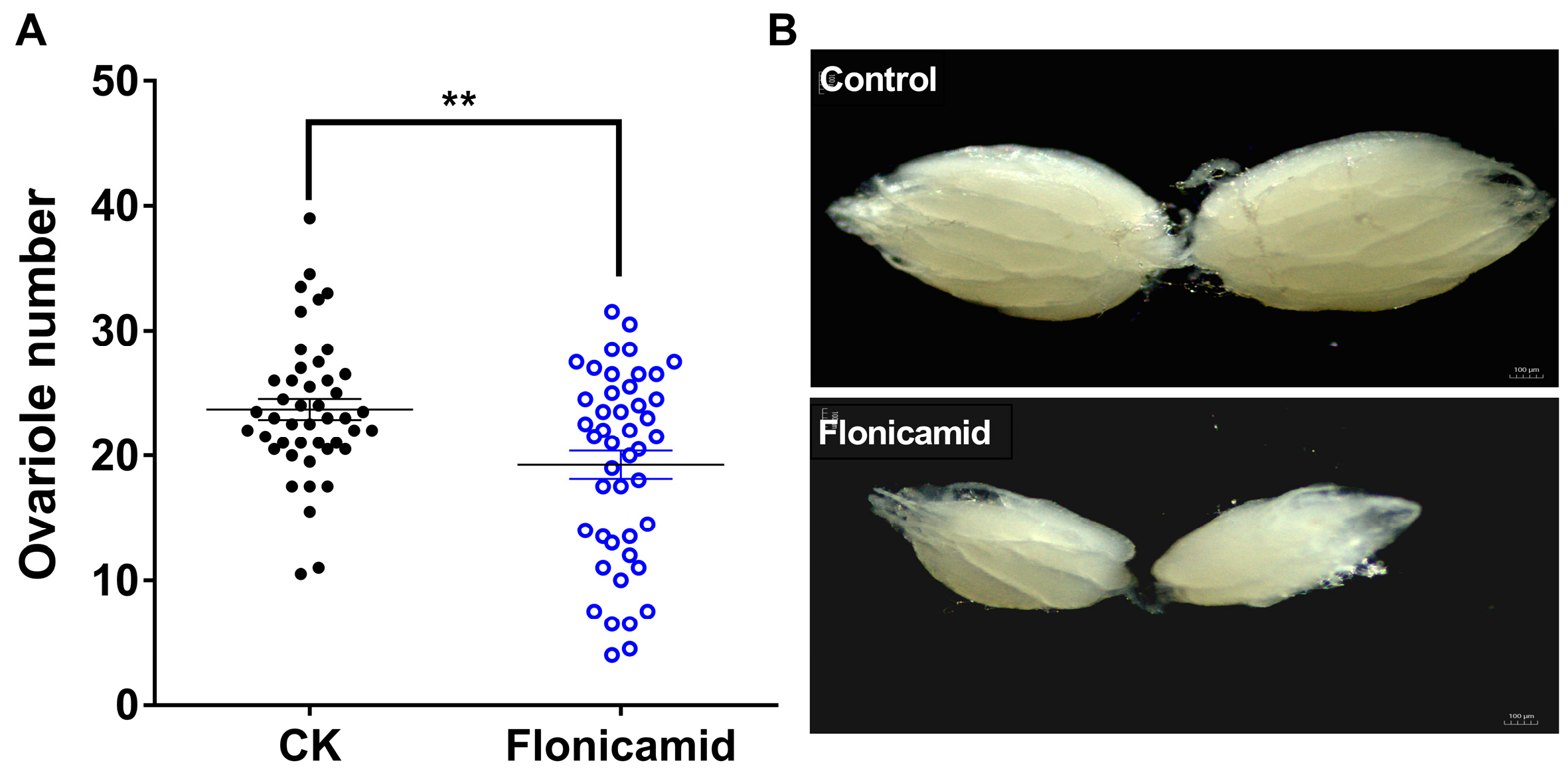
2.4. The Ovariole Number Assay
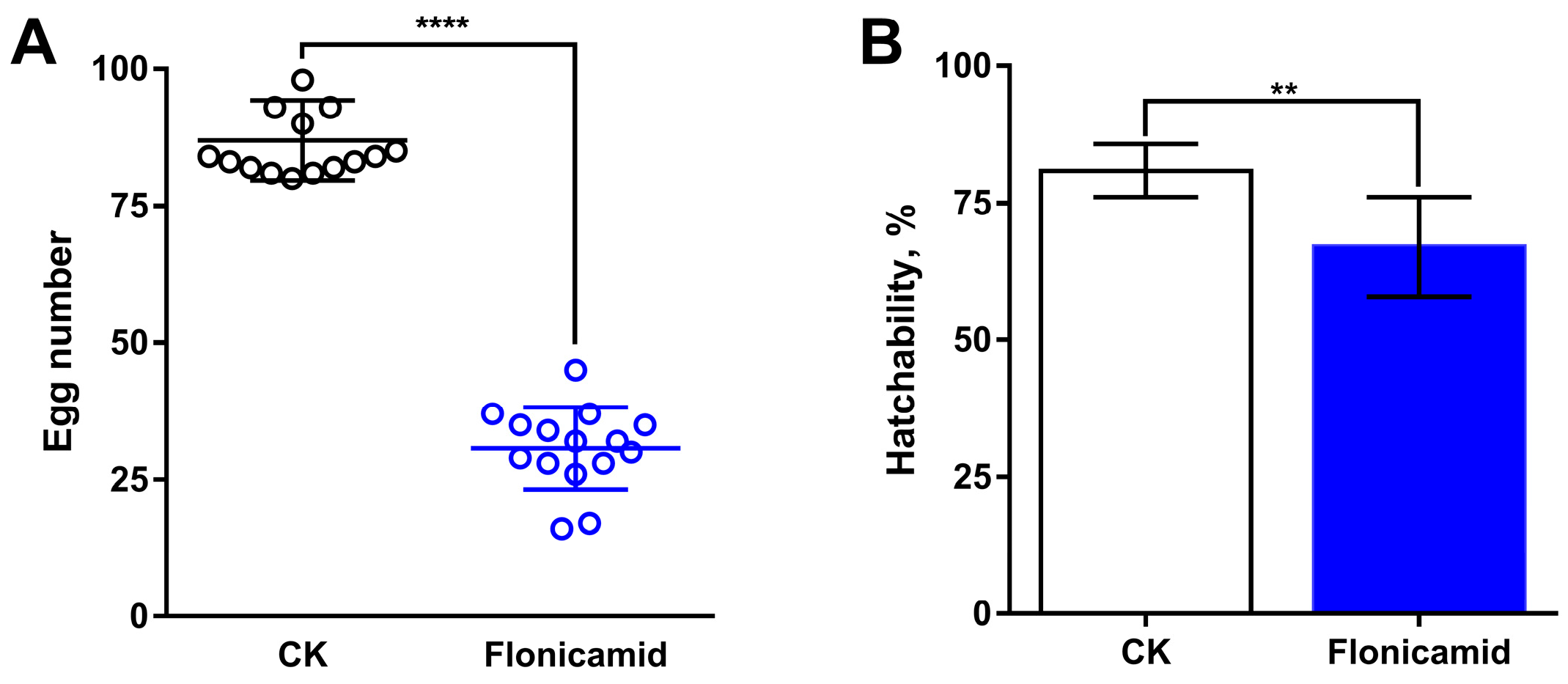
2.5. The Fecundity and Hatchablity Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
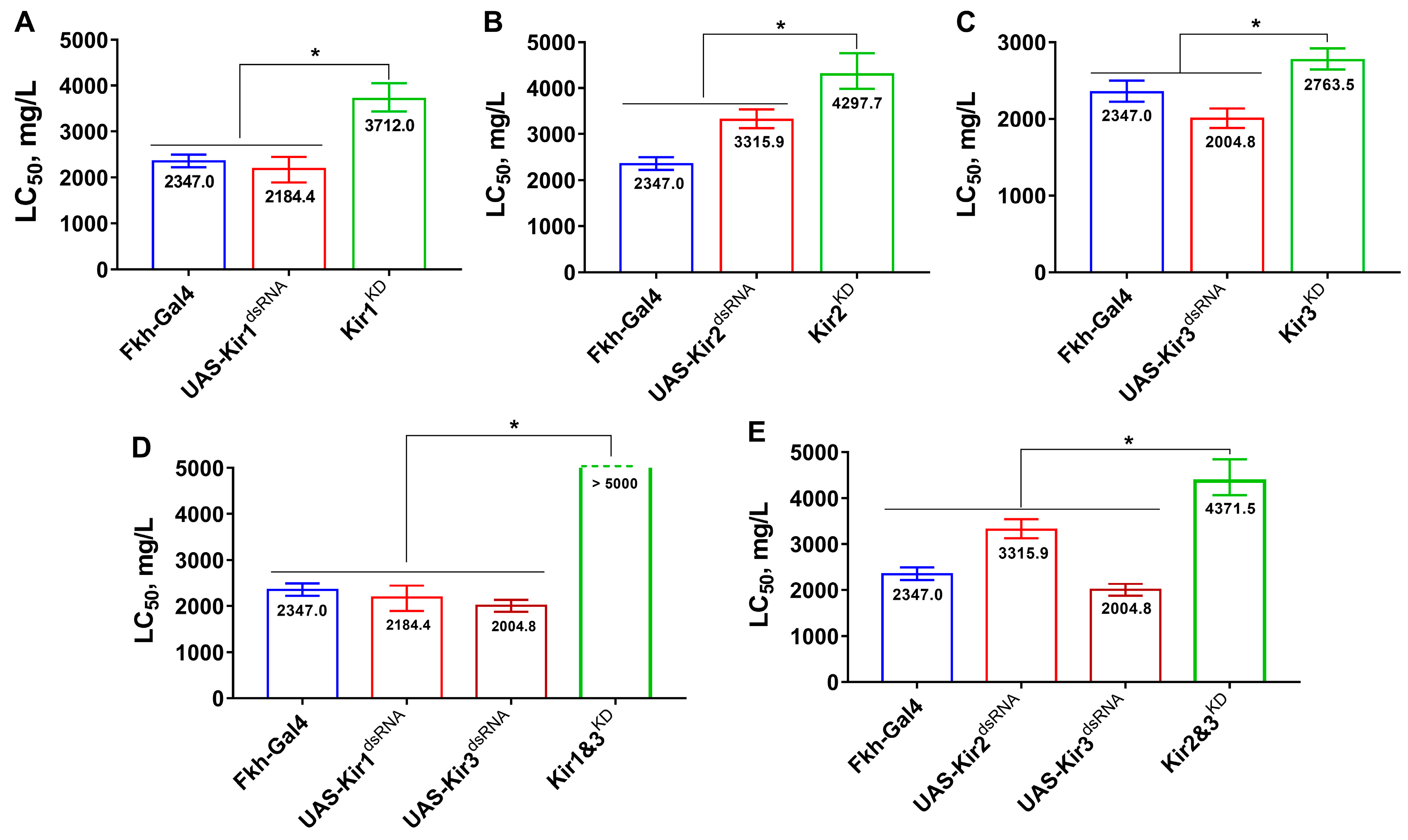
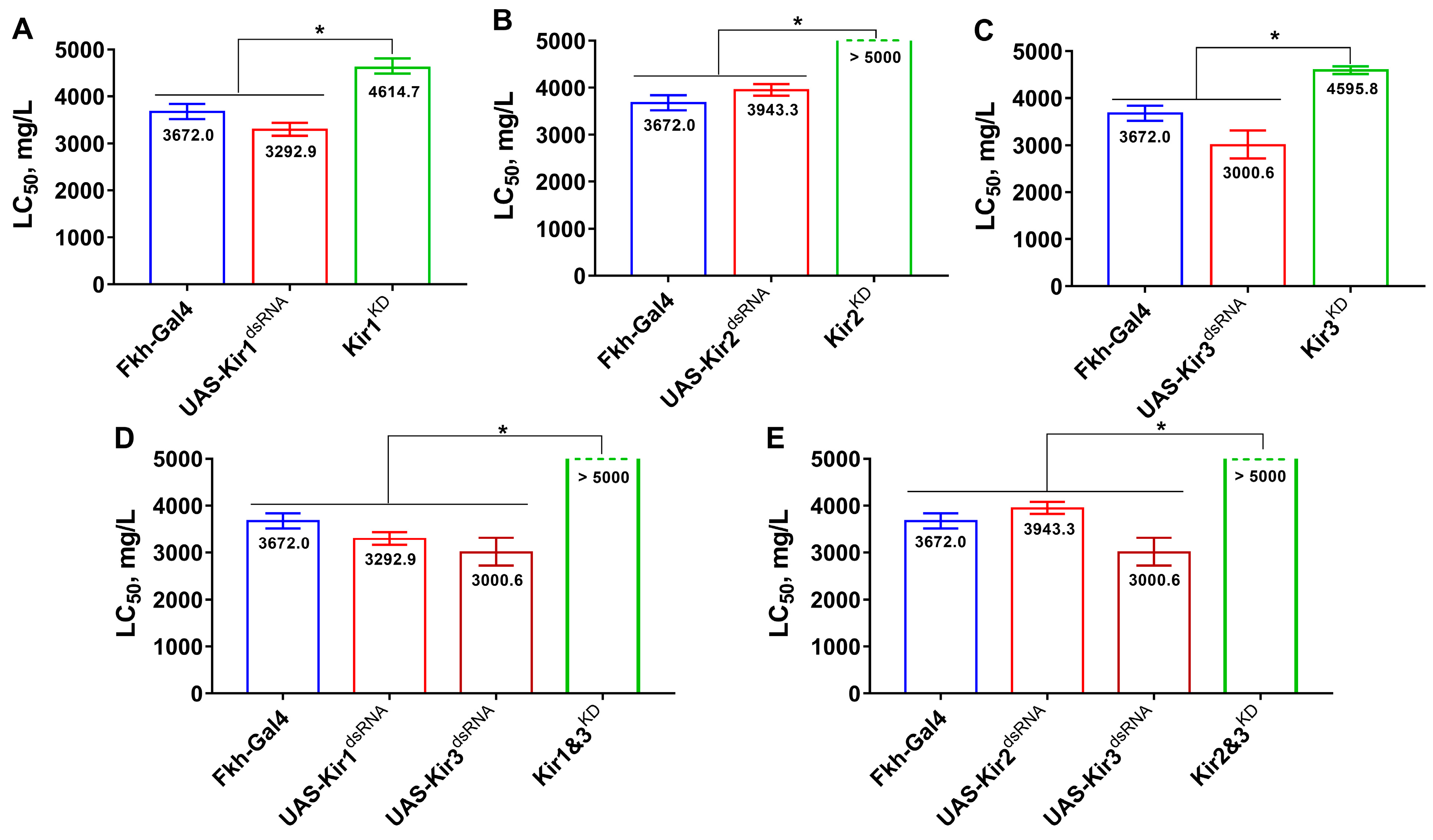
3. Results
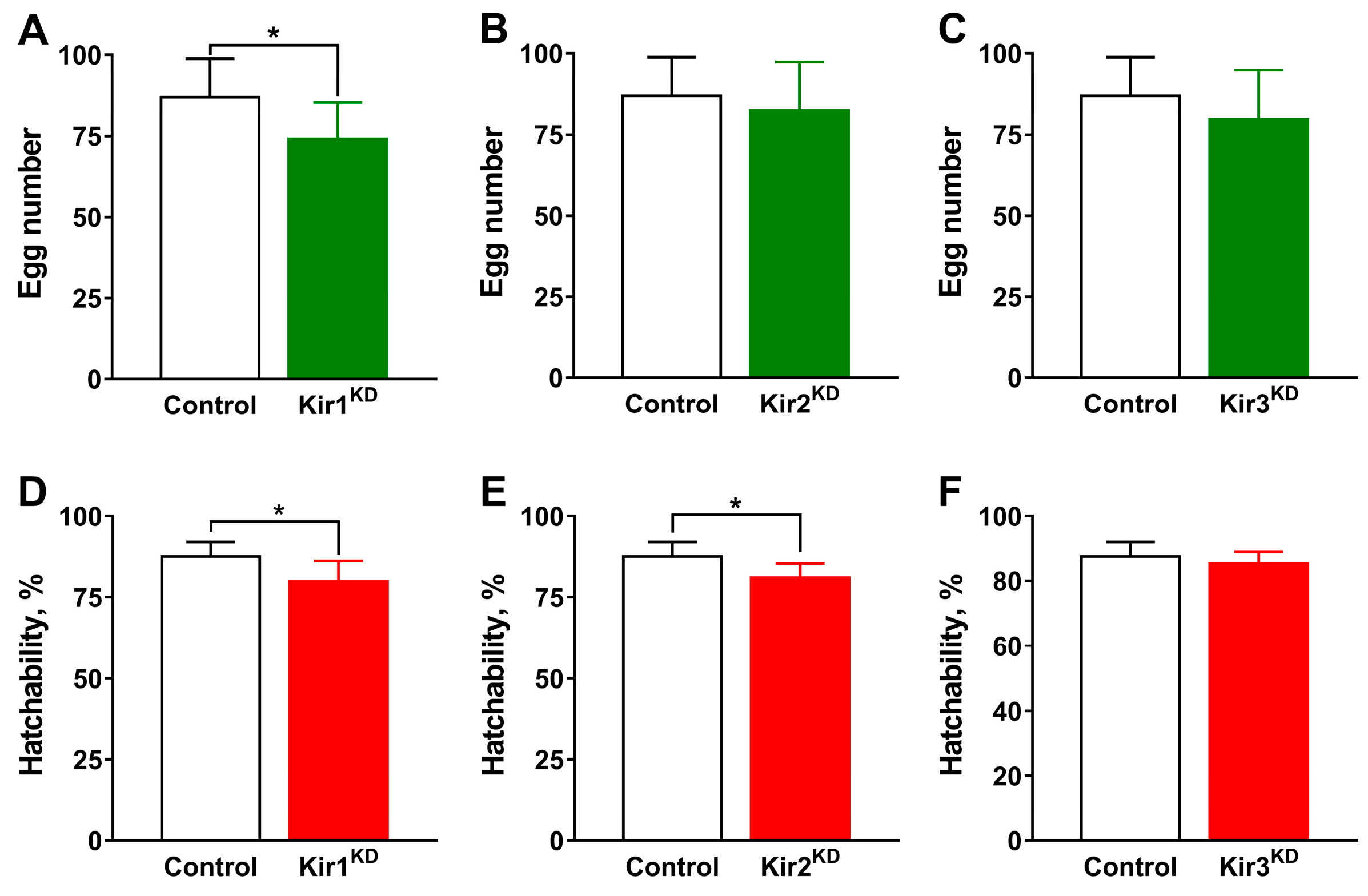
3.1. Knockdown of Kir Genes Reduces Fly’s Susceptibility to Flonicamid and Its Metabolite
3.2. Knockdown of Kir Genes Impairs Ovarian Development in D. melanogaster
3.3. Flonicamid Inhibits Ovarian Development in D. melanogaster
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morita, M.; Ueda, T.; Yoneda, T.; Koyanagi, T.; Haga, T. Flonicamid, a novel insecticide with a rapid inhibitory effect on aphid feeding. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, M.; Yoneda, T.; Akiyoshi, N. Research and development of a novel insecticide, flonicamid. J. Pestic. Sci. 2014, 39, 179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-R.; Koo, H.-N.; Yoon, C.; Kim, G.-H. Sublethal effects of flonicamid and thiamethoxam on green peach aphid, Myzus persicae and feeding behavior analysis. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2011, 54, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roditakis, E.; Fytrou, N.; Staurakaki, M.; Vontas, J.; Tsagkarakou, A. Activity of flonicamid on the sweet potato whitely Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) and its natural enemies. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.-N.; Lee, S.-W.; Yun, S.-H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, G.-H. Feeding response of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii, to sublethal rates of flonicamid and imidacloprid. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2015, 154, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, K.; Noor, M.; Backus, E.A.; Hussain, A.; Ali, A.; Peng, W.; Zhang, H. The toxicity of flonicamid to cotton leafhopper, Amrasca biguttula (Ishida), is by disruption of ingestion: An electropenetrography study. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Mo, Y.; Wu, B.; Yi, T.; Yang, Z. Toxicity of flonicamid to Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae) and its identification and expression of Kir channel genes. Insects 2024, 15, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterov, A.; Spalthoff, C.; Kandasamy, R.; Katana, R.; Rankl, N.B.; Andres, M.; Jahde, P.; Dorsch, J.A.; Stam, L.F.; Braun, F.J.; et al. TRP channels in insect stretch receptors as insecticide targets. Neuron 2015, 86, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, R.; London, D.; Stam, L.; von Deyn, W.; Zhao, X.; Salgado, V.L.; Nesterov, A. Afidopyropen: New and potent modulator of insect transient receptor potential channels. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 84, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, R.; Costea, P.I.; Stam, L.; Nesterov, A. TRPV channel nanchung and TRPA channel water witch form insecticide-activated complexes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 149, 103835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Wells, J.; Gross, A.D.; Jiang, S.; Demares, F.; Clements, J.S.; Carlier, P.R.; Bloomquist, J.R. Toxicity, mode of action, and synergist potential of flonicamid against mosquitoes. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 151, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spalthoff, C.; Salgado, V.L.; Theis, M.; Geurten, B.R.H.; Göpfert, M.C. Flonicamid metabolite 4-trifluoromethylnicotinamide is a chordotonal organ modulator insecticide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 4802–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, L.; Wu, W.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Montell, C.; Huang, J. An insecticide target in mechanoreceptor neurons. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Pisupati, A.; Jegla, T.; Crook, M.; Mickolajczyk, K.J.; Shorey, M.; Rohan, L.E.; Billings, K.A.; Rolls, M.M.; Hancock, W.O.; et al. Nicotinamide is an endogenous agonist for a C. elegans TRPV OSM-9 and OCR-4 channel. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, S.; Martinez, M.T.; Ruiz, A.F.; Hanna-Rose, W.; Thompson, G.A. Nicotinamide inhibits aphid fecundity and impacts survival. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insecticide Resistance Action Committee. IRAC Mode of Action Classification Scheme Ver. 10.5. Available online: https://irac-online.org/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- ISO. Flumetnicam—A New Common Name for a Nicotinamide Insecticide from Syngenta Crop Protection Provisionally Approved by ISO. Available online: https://news.agropages.com/News/NewsDetail---50397.htm (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Ren, M.; Niu, J.; Hu, B.; Wei, Q.; Zheng, C.; Tian, X.; Gao, C.; He, B.; Dong, K.; Su, J. Block of Kir channels by flonicamid disrupts salivary and renal excretion of insect pests. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 99, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piermarini, P.M.; Denton, J.S.; Swale, D.R. The molecular physiology and toxicology of inward rectifier potassium channels in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2022, 67, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhier, M.F.; Raphemot, R.; Denton, J.S.; Piermarini, P.M. Pharmacological validation of an inward-rectifier potassium (Kir) channel as an insecticide target in the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trigueros, R.R.; Hopkins, C.; Denton, J.; Piermarini, P. Pharmacological inhibition of inward rectifier potassium channels induces lethality in larval Aedes aegypti. Insects 2018, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Davis, J.A.; Swale, D.R. Chemical inhibition of Kir channels reduces salivary secretions and phloem feeding of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii (Glover). Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2725–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Macaluso, K.R.; Foil, L.D.; Swale, D.R. Inward rectifier potassium (Kir) channels mediate salivary gland function and blood feeding in the lone star tick, Amblyomma americanum. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Guerrero, F.; Pérez de León, A.A.; Foil, L.D.; Swale, D.R. Small-molecule inhibitors of inward rectifier potassium (Kir) channels reduce bloodmeal feeding and have insecticidal activity against the horn fly (Diptera: Muscidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2020, 57, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphemot, R.; Rouhier, M.F.; Hopkins, C.R.; Gogliotti, R.D.; Lovell, K.M.; Hine, R.M.; Ghosalkar, D.; Longo, A.; Beyenbach, K.W.; Denton, J.S.; et al. Eliciting renal failure in mosquitoes with a small-molecule inhibitor of inward-rectifying potassium channels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swale, D.R.; Engers, D.W.; Bollinger, S.R.; Gross, A.; Inocente, E.A.; Days, E.; Kanga, F.; Johnson, R.M.; Yang, L.; Bloomquist, J.R.; et al. An insecticide resistance-breaking mosquitocide targeting inward rectifier potassium channels in vectors of Zika virus and malaria. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Swale, D.R. Inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) channels represent a critical ion conductance pathway in the nervous systems of insects. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aretz, C.D.; Morwitzer, M.J.; Sanford, A.G.; Hogan, A.M.; Portillo, M.V.; Kharade, S.V.; Kramer, M.; McCarthey, J.B.; Trigueros, R.R.; Piermarini, P.M.; et al. Discovery and characterization of 2-nitro-5-(4-(phenylsulfonyl) piperazin-1-yl)-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl) anilines as novel inhibitors of the Aedes aegypti Kir1 (AeKir1) channel. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saelao, P.; Hickner, P.V.; Bendele, K.G.; Pérez de León, A.A. Phylogenomics of tick inward rectifier potassium channels and their potential as targets to innovate control technologies. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 647020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashinson, V.; Hopkins, C.R. Novel inhibitors of the renal inward rectifier potassium channel of the mosquito vector Aedes aegypti. Future Med. Chem. 2021, 13, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aretz, C.D.; Kharade, S.V.; Chronister, K.; Rusconi Trigueros, R.; Martinez Rodriguez, E.J.; Piermarini, P.M.; Denton, J.S.; Hopkins, C.R. Further SAR on the (phenylsulfonyl)piperazine scaffold as inhibitors of the Aedes aegypti Kir1 (AeKir) channel and larvicides. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyenbach, K.W.; Yu, Y.; Piermarini, P.M.; Denton, J. Targeting renal epithelial channels for the control of insect vectors. Tissue Barriers 2015, 3, e1081861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, W.; Ashburner, M.; Hawley, R.S. Drosophila Protocols; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Long Island, NY, USA, 2000; p. xiv. 697p. [Google Scholar]
- Kodandaram, M.H.; Kumar, Y.B.; Banerjee, K.; Hingmire, S.; Rai, A.B.; Singh, B. Field bioefficacy, phytotoxicity and residue dynamics of the insecticide flonicamid (50 WG) in okra [Abelmoschus esculenta (L) Moench]. Crop Prot. 2017, 94, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalthoff, C.; Salgado, V.L.; Balu, N.; David, M.D.; Hehlert, P.; Huang, H.; Jones, J.E.; Kandasamy, R.; Knudsen, G.A.; Lelito, K.R.; et al. The novel pyridazine pyrazolecarboxamide insecticide dimpropyridaz inhibits chordotonal organ function upstream of TRPV channels. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 1635–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, H.; ul Haq, I.; Ullah, F.; Khan, S.; Yaseen, A.; Shah, S.H.; Tariq, K.; Güncan, A.; Desneux, N.; Liu, X. Impact of sublethal concentrations of flonicamid on key demographic parameters and feeding behavior of Schizaphis graminum. Ecotoxicology 2023, 32, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibino, H.; Inanobe, A.; Furutani, K.; Murakami, S.; Findlay, I.; Kurachi, Y. Inwardly rectifying potassium channels: Their structure, function, and physiological roles. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 291–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raphemot, R.; Rouhier, M.F.; Swale, D.R.; Days, E.; Weaver, C.D.; Lovell, K.M.; Konkel, L.C.; Engers, D.W.; Bollinger, S.R.; Hopkins, C.; et al. Discovery and characterization of a potent and selective inhibitor of Aedes aegypti inward rectifier potassium channels. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; McComic, S.; Chen, R.; Kim, W.T.H.; Gaithuma, A.K.; Mooney, B.; Macaluso, K.R.; Mulenga, A.; Swale, D.R. ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channels regulate secretion of pro-feeding salivary proteins in the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doring, F.; Wischmeyer, E.; Kuhnlein, R.P.; Jackle, H.; Karschin, A. Inwardly rectifying K+ (Kir) channels in Drosophila. A crucial role of cellular milieu factors Kir channel function. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25554–25561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Z.; Li, H.-S. Inwardly rectifying potassium channels in Drosophila. Acta Physiol. Sinica 2012, 64, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raphemot, R.; Estevez-Lao, T.Y.; Rouhier, M.F.; Piermarini, P.M.; Denton, J.S.; Hillyer, J.F. Molecular and functional characterization of Anopheles gambiae inward rectifier potassium (Kir1) channels: A novel role in egg production. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, T.; Guo, H.; Qiao, J.; Su, J. Involvement of Inwardly Rectifying Potassium (Kir) Channels in the Toxicity of Flonicamid to Drosophila melanogaster. Insects 2025, 16, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16010069
Liu X, Gao Y, Liu T, Guo H, Qiao J, Su J. Involvement of Inwardly Rectifying Potassium (Kir) Channels in the Toxicity of Flonicamid to Drosophila melanogaster. Insects. 2025; 16(1):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16010069
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xuan, Yuying Gao, Tengfei Liu, Hailiang Guo, Jizu Qiao, and Jianya Su. 2025. "Involvement of Inwardly Rectifying Potassium (Kir) Channels in the Toxicity of Flonicamid to Drosophila melanogaster" Insects 16, no. 1: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16010069
APA StyleLiu, X., Gao, Y., Liu, T., Guo, H., Qiao, J., & Su, J. (2025). Involvement of Inwardly Rectifying Potassium (Kir) Channels in the Toxicity of Flonicamid to Drosophila melanogaster. Insects, 16(1), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16010069





