Simple Summary
Although our knowledge of the interactions between the underground and aboveground communities of organisms is growing, little is known about the impact of soil predatory mites on aboveground communities of plants, herbivores and their natural enemies. Blattisocius mali is a polyphagous predatory mite that disperses on the bodies of drosophilid fruit flies, on which it feeds; after disembarkment, it also preys on their eggs. This mite is mostly associated with soil or litter, but it has also been found in fruit and seed storage sites and on plants. In our tests, the starved predatory females readily fed on various stages of the common herbivores two-spotted spider mite and western flower thrips as well as the fruit fly Drosophila hydei. The predator came from cultures fed on acarid mites, and its identity was validated molecularly. Although B. mali shows the potential to prey upon herbivorous insects and mites, to determine whether it can also effectively reduce their population densities, further studies, including tests on the predator’s survival, fecundity and prey preference, are required.
Abstract
Research in recent years has shown that some species of predatory mites, considered to be typically associated with soil and litter, can also be found on plants. Such species include Blattisocius mali, which is an effective predator of acarid mites, nematodes and the eggs of moths and which can disperse by means of drosophilid fruit flies. Apart from soil and litter or storage, it has also been recorded on the bark of apple trees and the leaves of strawberries, thus suggesting its possible predation of/feeding on herbivorous mites and insects. Our goal was to examine whether B. mali could consume different development stages of two polyphagous herbivores, the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae, and the western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis, as well as the drosophilid fruit fly Drosophila hydei. In 24 h cage tests, single, starved B. mali females consumed all types of prey offered, i.e., the eggs, males and females of spider mites; the first-instar larvae and prepupae of thrips; and the eggs and first-instar larvae of fruit flies. The potential for B. mali to prey upon these insects and mites was confirmed. However, to estimate whether it can also effectively reduce their population, additional tests on the predator’s survival, fecundity and prey preference are needed.
1. Introduction
There is a growing body of evidence concerning interactions between the underground and aboveground communities of organisms and the significant implications of these interactions for both community- and ecosystem-level properties [1,2]. With respect to this, the effect of soil predatory mites on aboveground communities including plants, herbivores and their natural enemies is still poorly understood [3].
Blattisocius mali (Oudemans) is an effective predator of acarid mites, nematodes and the eggs of the potato tuber moth [4,5,6,7]. It belongs to Blattisociidae, a family of predatory mites recorded in soil and on plants, associated with insects, rodents and birds. Species of the genus Blattisocius Keegan are a distinctive group that commonly inhabit storage facilities and feed on mites and insect eggs [8,9]. Although generally regarded as edaphic, they can visit plants; for example, B. dendriticus Berlese has been noted on the leaves of lychee [10], leaves/twigs/flowers of some citrus trees [11] and leaflets of strawberries [3]. So far, B. mali has been found in soil from agricultural fields [7,12] and in storage sites of grass seeds, potatoes and fresh and dried fruit [4,5,13,14] as well as on the bark of apple trees [15] and on strawberry leaves [16]. The presence of this predator on plants suggests that it may also prey upon herbivorous insects and mites. Interestingly, recent studies on Drosophila melanogaster Meigen and D. hydei Sturtevant have shown that B. mali females can not only disperse by means of drosophilid fruit flies but also feed on their bodies during transportation, and they may also prey on their eggs after disembarkment [9,17]. As predatory mites transported by insects can prey upon the juvenile stages of their carriers, mostly eggs and larvae [18,19,20], it was suspected that B. mali may also feed on both the eggs and larvae of drosophilids.
Our aim was to examine whether B. mali can prey upon the various development stages of two phytophages, the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch, and the western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande), as well as on the drosophilid fruit fly D. hydei. Two-spotted spider mites and western flower thrips are highly polyphagous herbivores which can also be serious pests of many crop plants [21,22,23,24]. Both species can be preyed upon by phytoseiid mites. However, as thrips prepupae and pupae hide in soil, apart from phytoseiids, some edaphic laelapid mites, e.g., Gaeolaelaps aculeifer (Canestrini) and Stratiolaelaps scimitus (Womersley), are recommended for thrips control [21,25,26]. Drosophila hydei is a cosmopolitan, omnivorous fruit fly commonly found in woodlands but also near or in human dwellings [27,28,29].
In this paper, we examined the 24 h feeding rate of starved B. mali females on the eggs, males and females of spider mites, first-instar larvae and prepupae of thrips as well as the eggs and first-instar larvae of fruit flies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Material and General Methods
All insects and mites were obtained from and maintained in the Section of Applied Entomology, Department of Plant Protection at Warsaw University of Life Sciences (WULS). Blattisocius mali was reared using a mixture of bran and various stages of the mould mite Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Schrank) fed on yeast, following Michalska et al. [9,17]. The species of predatory mite was identified morphologically by Prof. D.J. Gwiazdowicz and then confirmed molecularly by sequencing the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene fragment (COI, DNA barcode) using a method previously described by Dabert et al. [30].
The western flower thrip, F. occidentalis, was reared on cucumber plants cv. ‘Skierniewicki’ in a glasshouse, while the two-spotted spider mite, T. urticae, was reared on plants of the common bean cv. ‘Ferrari’ in a growth chamber at 23 °C, 70–75% RH and 16/8 h (L/D) photoperiod.
As in previous studies by Michalska et al. [9,17], we used the flightless form of the fruit fly D. hydei, commercially distributed as a live pet food. The population of D. hydei was maintained on the standard fruit fly medium based on cornmeal, molasses, yeast and propionic acid in an incubator at 25 °C with a 12/12 (L/D) photoperiod.
For the experiments, we used glass cages with conical chambers of 0.8 cm and 0.3 cm diameter [9,17] or plexiglass detached leaf cages similar to those described by Tashiro [31] and Michalska and Studnicki [32] but consisting of only two plates (98 mm × 74 mm × 6 mm) with a central hole within the upper plate 20 mm in diameter and sealed from above with a square of ‘breathing’ dialysis cellulose membrane (Sigma-Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany, D-9402) (Figure 1). The membrane was attached to the upper plate by means of paraffin, and the edges of the membrane were additionally pressed against the plate with plasticine. Detached ‘clean’ bean leaves cv. ‘Ferrari’ with the main vein running down the middle or cucumber leaf (cv. ‘Skierniewicki’) squares (ca. 70 mm × 70 mm) were placed onto the lower plate of the plexiglass cages along with a piece of wet gauze with the underside face up. A rubber band gasket sealed the upper plate and the central hole, with a leaf forming a leaf chamber. The leaves were moistened by means of a dental cotton roll, which was placed in a container filled with water and which touched the gauze through a hole in the bottom plate (Figure 1).
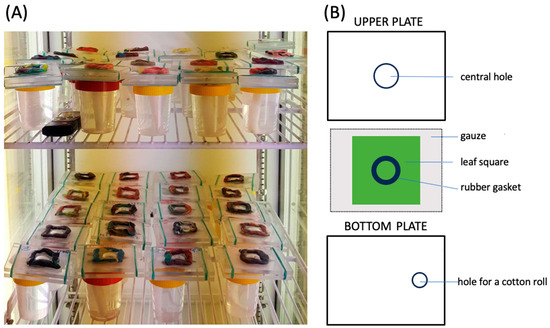
Figure 1.
Plexiglass detached leaf cages used in the experiments. (A) Cages put onto containers filled with water and moistened by means of dental cotton rolls. (B) Plan view of detached leaf cage elements. For details, see Materials and Methods section.
All experiments were carried out for 24 h within an incubator at 23 °C, 70–75% RH and 16/8 h (L/D) photoperiod using one-day-starved B. mali females. For starvation, females were put singly into the glass cages and kept there for the next 24 h. Cages with starving mites were kept in a desiccator, which provided a humidity of 75–80% RH [9,17]. The desiccator was maintained in an incubator at 23 °C and with a 16/8 h (L/D) photoperiod.
All mites and insects were randomly selected and transferred using a fine brush. All manipulations and observations were made under an Olympus SZX 12 dissecting microscope fitted with an Olympus Highlight 3100 cold light source. Apart from treatment combinations, we prepared the control cages (without predator), and the same number of replications was carried out for both. All life stages of insects and mites were given to the predator in ad libitum numbers. The prey numbers per cage were based on the results of our previous pilot tests. After 24 h, from the moment of releasing the predator into the cage, the number of dead prey individuals were counted. On rare occasions, predators were found dead, and such replications were excluded from further analysis. Similarly, the dead prey individuals were counted in the control cages. In the cases of spider mites and fruit flies, the eggs with visible chorion collapse were considered dead.
2.2. Experiments
For the test on B. mali feeding on spider mite eggs, we used ‘1.5-day’ eggs produced by spider mite females randomly selected from a population and placed on single detached bean leaves 36 h prior to the test in Petri dishes (9 cm diameter) lined up with wet cotton. The Petri dishes, each with 10 spider mite females, were kept in an incubator at 23 °C, 70–75% RH and 16/8 h (L/D) photoperiod. For the test, we used plexiglass cages with a detached bean leaf, and each cage had n = 20 spider mite eggs evenly distributed on a leaf arena. For both treatment and control combinations, N = 30 replications were made.
For the experiment on predators feeding on spider mite adults, we used either females, n = 15 individuals per plexiglass cage with detached bean leaf, or males, also n = 15 individuals per cage. Both the treatment and control combination were repeated, N = 28 times with the spider mite females and N = 26 times with the spider mite males. As spider mite females laid eggs during the test, we also examined the number of consumed (totally deflated) eggs as well as the total number of eggs (including those deflated) laid by females within each cage. On this basis, for treatment combination, the mean total number of eggs laid (and offered) per cage and the mean number of destroyed eggs per cage were calculated.
The first-instar thrips larvae (n = 12 individuals per cage) and prepupae (n = 3 individuals per cage), were tested in plexiglass cages with a square of the detached cucumber leaf. The larvae were directly collected from the infested leaves of cucumber plants grown in glasshouses. We selected the first-instar larvae at their very early stage, when they were still whitish in colour. To obtain prepupae, we placed the larvae in plexiglass cages with cucumber leaves (5 individuals per cage) and kept them for the next 5–6 days in an incubator at 23 °C, 70–75% RH and 16/8 h (L/D) photoperiod. Both treatment and control combinations with either the first-instar thrips larvae or prepupae were replicated N = 22 times.
The test of B. mali feeding on fruit fly eggs was conducted using ‘8-hour’ eggs of the flightless D. hydei and following the procedure developed by Michalska et al. [9]. The eggs were obtained from random fruit fly females released into Petri dishes half-filled with 0.75% agar medium with the addition of grape juice and yeast [33]. For egg laying, the Petri dishes with flies were kept in an incubator in darkness at 25 °C for 8 h. For the test, the eggs were first rinsed with a drop of distilled water (to remove agar residues) and then placed in glass cages (n = 40 eggs/cage). For both treatment and control combination, N = 16 replications were carried out.
In the pilot test, we estimated that the duration of the first-instar larvae of the flightless fruit fly D. hydei was around 48 h. Therefore, the test of B. mali feeding on first-instar fruit fly larvae was undertaken using ‘12-h’ larvae of the flightless D. hydei so that the larvae remained at the first-instar stage until the end of the test. Our experiment was conducted following the ‘spoon method’ developed by [34], with slight modifications. The spoon was previously filled with 0.75% agar medium with the addition of grape juice and yeast [33]. For egg laying, each spoon was covered with fresh yeast and kept along with 9- to 18-day-old flies for 20–24 h in a half-pint bottle in an incubator with a 12/12 (L/D) photoperiod at 25 °C. Then, the spoons were removed from the bottles and kept in the incubator, in the same conditions as previously, for 32–34 h. Each spoon was removed and the larvae were washed into a Petri dish with distilled water. For the test, the ‘12-h’ larvae were placed in glass cages, n = 20 larvae per cage. Both the treatment and control combination were replicated N = 16 times.
To protect the fruit fly eggs and larvae from drying out during the tests, the filter paper at the bottom of each glass cage was heavily moistened and additionally sealed with Scotch tape to maintain humidity inside the cage.
Statistical analysis was performed using R 4.2.1 software [35]. In order to compare the number of dead T. urticae males and dead F. occidentalis larvae or prepupae in combination with a B. mali female or without a predator, the one-factor generalized linear model (GLM) was applied, which enabled us to analyse the count data without their prior transformation. Due to frequent ‘0’ records of dead individuals in the control combination, the model was based on a zero infinite Poisson distribution [36]. When there was no destroyed prey in the control (only ‘zero’ records), such as in the case of drosophilid eggs and larvae as well as eggs and females of T. urticae, statistical analysis was not performed. The data are given as mean ± SE and the accepted level of significance is p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
Among the five barcoded predatory mite specimens, we found only one COI haplotype (GenBank acc. no. OQ825956), which differed by 2.7% (SD 0.7) from B. mali sequences found in specimens collected in Israel (MW344275–MW344284). Resolving whether this genetic distance can indicate a cryptic species is impossible without testing more Blattisocius species to determine the barcoding gap for the COI marker in the genus and confirming the results with nuclear DNA data. However, in mites, the barcoding gap is usually at a level of >10% (e.g., [37,38,39]), which supports the same-species hypothesis. Moreover, the only COI sequences published for other Blattisocius species, i.e., B. tarsalis (Berlese) (MK270529.1) and B. keegani Fox (MH120211.1), differ >34% between all three species in the analysed fragment.
This is the first report on predation of the species from the Blattisocius genera on herbivorous mites and insects (Figure 2). Although frequently recorded in soil, litter and fruit or vegetable storage sites, B. mali was first found on and described from the bark of the apple tree [4,5,7,12,14]. Moreover, it has also been collected from leaves of strawberries infested by two phytophagous mites, i.e., T. urticae and Phytonemus pallidus Banks [16]. It has been suggested that the appearance of B. mali on plants might not have been accidental but connected with the predator’s foraging. The two herbivores may be part of its diet, but this aspect was not investigated by the authors. The daily (mostly nocturnal) movement of the edaphic predatory mites B. dendriticus and Proctolaelaps pygmaeus (Muller) from organic mulch to strawberry plants was detected by Esteca et al. [3]. According to the authors, B. dendriticus, previously known to feed on acarid mites, might have been attracted by the presence of Ty. Neiswanderi Johnston and Bruce on strawberry leaves. However, T. urticae cohabited these plants. Thus, one cannot exclude that, as in the case of B. mali, spider mites could also be prey for this predatory mite. The probable association of B. dendriticus with another herbivorous mite, the lychee erinose mite, Aceria litchii (Keifer), which forms erinea on lychee leaves, was reported by Waite and Gerson [10]. However, its feeding on this eriophyid has not been confirmed.

Figure 2.
A female of Blattisocius mali feeding on (A) a male of the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae, (B) a first-instar larva of the western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis, and (C) a first-instar larva of the fruit fly Drosopila hydei.
The feeding rates of B. mali on T. urticae eggs, males and females are presented in Table 1. These rates appear close to those found for some generalist phytoseiid mites. For example, 24 h starved, random females of Amblyseius swirski Athias-Henriot and Neoseiulus californicus (McGregor) (obtained from the commercial Spical and Swirski-Mite Koppert biopreparates and mass-reared on T. urticae) exposed to 30 eggs aged 0–24 h of T. urticae consumed on average 14.83 and 8.84 eggs, respectively, within 24 h at ca. 25 °C [40]. In another study at 25 °C, newly mated, gravid females of the Japanese strain of N. californicus consumed on average 12.83 eggs (age unspecified), 6.4 males and 2.43 females of T. urticae per day (out of 20 prey individuals offered each day) in 7 consecutive days [41]. In our study, single, starved and random B. mali females, which had no previous experience with tetranychids, consumed on average 10.93 out of 20 spider mite eggs offered (0–36 h old), and when exposed to 15 spider mite females, they ate 1.96 females on average, plus 0.82 out of 68.12 eggs oviposited on average per cage (Table 1). We also noted on average 2.81 spider mite males destroyed per cage. However, the mean number of males consumed by the predator was probably slightly lower, considering that some males in the control also died during the test, though in much lower numbers than in treatment cages (GLM: χ2 = 35.098, df = 1, p < 0.0001). It should be emphasized that in the test with spider mite eggs, we did not examine the effect of the presence of webbing on the foraging efficiency of B. mali. Under natural conditions, spider mite eggs are often hidden under the web and laid in it, especially in the presence of predators [42]. Among phytoseiids, there are species that can move easily among dense strands of the web, while others can cope with it to a lesser extent or are even hindered by it and are usually considered ineffective predators of Tetranychus species [43,44]. In our tests with spider mite females, the web was clearly seen, and we noted a few cases of B. mali females that got stuck and died in the web. Thus, the extent to which webbing affects B. mali foraging and predation on T. urticae should be evaluated in further research.

Table 1.
Mean number (±SE, min.–max.) of prey individuals destroyed in cages with hungry Blattisocius mali females after 24 h exposure to various stages of the two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae, the western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis, and the fruit fly Drosophila hydei.
For the biological control of F. occidentalis against the aboveground larval stages of thrips, several generalist phytoseiids are recommended, including Amblydromalus limonicus (Garman and McGregor), A. swirski and Neoseiulus cucumeris (Oudemans) [45]. Van Houten et al. [46] tested seven phytoseiid species previously fed on pollen. At 25 °C on cucumber leaf discs with 12 F. occidentalis at their first larval stage, the mean feeding rates ranged from 0.5 to 6.9 thrips larvae/day, with the highest rates of 6.9 larvae for A. limonicus, 6.0 larvae for N. cucumeris and 4.4 larvae for Iphiseius degenerans Berlese. In another study [47], A. swirski was mass-reared on a mixture of pollen and spider mite eggs, and when exposed to 15 first-instar larvae of F. occidentalis at 25–27 °C, they consumed even more thrips on average, i.e., 9.9 larvae per day. In our study, the predation rate on thrips larvae appears to be lower than for the recommended phytoseiids (Table 1). The mean number of first-instar larvae destroyed in treatment cages was 4.73. However, the predation rate of hungry B. mali might have been slightly lower, considering that we also detected some mortality of thrips in control cages (GLM: χ2 = 43.816, df = 1, p < 0.0001) (Table 1).
Our observations and the test also showed that B. mali females can attack and consume the prepupae of F. occidentalis. However, we offered the predatory females only three prepupae per cage and also recorded quite high thrips mortality in the control, almost half as high as that recorded in the treatment (GLM: χ2 = 3.9282, df = 1, p = 0.0475) (Table 1). Thus, the potential feeding rates obtained in the test might have been underestimated, as there may have also been dead prepupae in some cages, which the predator may have fed on instead of live individuals. For comparison, when offered 5 pupae of F. occidentalis at ca 25 °C, starved S. scimitus females consumed on average 1.38 pupae during 24 h [48]. Interestingly, this edaphic mite can also prey on thrips larvae on the bottom leaves of cucumber and eggplants [49]. Although it is likely that B. mali could control both above- and belowground stages of this pest, further studies are needed, including experiments on its effectiveness against thrips larvae, prepupae and pupae directly in the crop.
Previous studies have shown that B. mali can not only feed on drosophilids during dispersal but also prey on their eggs [9,17]. In the test with 15 ‘8-hour’ eggs of D. hydei, 24 h starved predatory females consumed on average 6 fly eggs in 10 h, 3 of which were only partially consumed. Interestingly, some B. mali females returned to the partially fed eggs after some time and only then consumed them completely [9]. In this study, B. mali females were given 40 eggs of this fly and, within 24 h, ate on average 17 eggs, among which 5.38 ± 0.46 eggs were only partially consumed. Moreover, we demonstrated for the first time that B. mali can consume fruit fly larvae. When given 20 first-instar larvae of D. hydei, a starved female consumed on average 10.19 larvae per day (Table 1). Most larvae were consumed totally, i.e., 9.19 ± 0.49, whereas only a few larvae, i.e., 1 ± 0.32 were fed on to a lesser extent. Voracity of the edaphic predatory mites on drosophilid development stages was also examined by Esteca [50] using D. suzukii Magtsumura and 2-day-old gravid females of Macrocheles embersoni Azevedo, Castilho & Berto, M. muscadomesticae (Scopoli), P. bicklei (Bram) and S. scimitus previously fed with nematodes. When exposed to 20 fly eggs or 10 first-instar D. suzukii larvae for 10 days, the predatory females ate at 25 °C on average 2–10 eggs or 4–7 larvae per day. In these studies, however, mites were not starved before the experiment, and far fewer fruit fly eggs or larvae were offered than in our tests, which may have been the reason for the lower feeding rate in these species compared to B. mali. Interestingly, they also consumed the second- and third-instar larvae and, with the exception of M. muscadomesticae, the pupae of D. suzukii.
It should be emphasized that, in natural conditions, some drosophilid eggs and larvae may be buried in the substrate. Esteca [50] found that only S. scimitus was able to access D. suzukii eggs embedded in fruit. Thus, to assess the potential negative effect of B. mali on the fitness of its drosophilid host, more research is needed, taking into account the predation of this mite on all development stages of fruit flies exposed to it or hidden in the substrate.
In summary, this study revealed the potential for B. mali to prey upon various stages of phytophagous insects and mites as well as drosophilid fruit flies. Females starved for 24 h, previously fed on acarid mites and unfamiliar with other prey types, readily attacked and consumed the adults and eggs of two-spotted spider mites, the first-instar larvae and prepupae of western flower thrips and both the eggs and first-instar larvae of the fruit fly D. hydei. The 24 h feeding rate of B. mali on spider mites did not differ from that estimated for some polyphagous phytoseiids. Similarly, B. mali daily feeding rates on eggs and young larvae of D. hydei were comparable to those estimated for other edaphic predatory mites consuming eggs and larvae of D. suzukii. Only the voracity of the predator towards the larvae or prepupae of thrips was markedly lower than that found for some phytoseiid and laelapid mites. Undoubtedly, much more research is needed to estimate whether thrips, spider mites or drosophilids could be alternative prey for this mite. Future studies should be concerned with not only B. mali survival, fecundity and life cycle when feeding on theses insect and mites but also the predator’s prey preference and performance when foraging in their habitat.
So far, Blattisocius mali has been regarded as a potential bioagent of acarid mites, nematodes and potato tuber moths [4,5,6,7]. Interestingly, when B. mali fed on the mould mite T. putrescentiae, its intrinsic rate of population increase (r) was much higher than that of B. dendriticus or G. aculeifer, which are both recommended for the control of this acarid mite [4,51,52]. Thus, B. mali may be a promising alternative to G. aculeifer in the protection of bulbs of ornamental plants or cucumber plant seedlings against acarid mites [52,53], where it could additionally feed on spider mites or thrips. One also cannot exclude its potential in controlling both the adult population and offspring of drosophilid pests such as D. suzukii [54].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.M.; methodology, K.M., M.K.J., P.N., D.M., A.M., K.Z. and M.W.; software, M.S.; validation, K.M., M.S., M.K.J., A.M. and M.W.; formal analysis, M.S. and K.M.; investigation, M.K.J., P.N., D.M., K.Z., A.M. and K.M.; resources, K.M., M.S. and M.W.; data curation, K.M., M.S. and M.W.; writing—original draft preparation, K.M., M.K.J. and M.S.; writing—review and editing, K.M. and M.W.; visualization, K.M., M.S. and M.W.; supervision, K.M.; project administration, K.M.; funding acquisition, K.M., M.S. and M.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study are available by email request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Our special thanks go to D.J. Gwiazdowicz (Poznań University of Life Sciences) for morphological identification of Blattisocius mali and M. Dabert (Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań) for DNA barcoding analysis. We also thank Hanna Załęska for technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wardle, D.A. The Influence of Biotic Interactions on Soil Biodiversity. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 870–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinen, R.; Biere, A.; Harvey, J.A.; Bezemer, T.M. Effects of Soil Organisms on Aboveground Plant-Insect Interactions in the Field: Patterns, Mechanisms and the Role of Methodology. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cássia Neves Esteca, F.; Rodrigues, L.R.; De Moraes, G.J.; Júnior, I.D.; Klingen, I. Mulching with Coffee Husk and Pulp in Strawberry Affects Edaphic Predatory Mite and Spider Mite Densities. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 76, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirayeshfar, F.; Safavi, S.A.; Sarraf-moayeri, H.R.; Messelink, G.J. Active and Frozen Host Mite Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Acari: Acaridae) Influence the Mass Production of the Predatory Mite Blattisocius mali (Acari: Blattisociidae): Life Table Analysis. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2021, 26, 2096–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, J.R.; Gamez, M.; Cabello, T. Potential of the Blattisocius mali Mite (Acari: Blattisociidae) as a Biological Control Agent of Potato tubermoth (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) in Stored Potatoes. Potato Res. 2020, 63, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano-Rojas, Y.; Gallego, J.R.; Gamez, M.; Garay, J.; Hernandez, J.; Cabello, T. Evaluation of Trichogramma cacaeciae (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) and Blattisocius mali (Mesostigmata: Blattisociidae) in the Post-Harvest Biological Control of the Potato Tuber moth (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae): Use of Sigmoid Functions. Agriculture 2022, 12, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amal, A.; Yassin, E.M.A.; El-Bahrawy, A.F.; El-Sharabasy, H.M.; Kamel, M.S. Biology of Blattisocius mali (Oudemans) (Acari: Gamasida: Ascidae) Feeding on Different Diets under Laboratory Conditions. Egypt. Vet. Med. Soc. Parasitol. J. (EVMSPJ) 2020, 16, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes, G.J.; Venancio, R.; dos Santos, V.L.V.; Paschoal, A.D. Potential of Ascidae, Blattisociidae and Melicharidae (Acari: Mesostigmata) as Biological Control Agents of Pest Organisms. In Prospects for Biological Control of Plant Feeding Mites and Other Harmful Organisms; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 33–75. [Google Scholar]
- Michalska, K.; Mrowińska, A.; Studnicki, M.; Jena, M.K. Feeding Behaviour of the Mite Blattisocius mali on Eggs of the Fruit Flies Drosophila melanogaster and D. hydei. Diversity 2023, 15, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, G.K.; Gerson, U. The Predator Guild Associated with Aceria litchii (Acari: Eriophyidae) in Australia and China. Entomophaga 1994, 39, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childers, C.C.; Ueckermann, E.A. Non-Phytoseiid Mesostigmata within Citrus Orchards in Florida: Species Distribution, Relative and Seasonal Abundance within Trees, Associated Vines and Ground Cover Plants and Additional Collection Records of Mites in Citrus Orchards. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 65, 331–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karg, W. Acari (Acarina) Milben Unterordnung Anactinochaeta (Parasitiformes) Die Freilebenden Gamasina (Gamasides) Raubmilben; VEB Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Chmielwski, W. Skład Gatunkowy i Nasilenie Występowania Akarofauny w Nasionach Traw Przechowalnianych. Pr. Nauk. Inst. Ochr. Roślin 1971, 8, 201–215. [Google Scholar]
- Çakmak, I.; Faraji, F.; Çobanoğlu, S. A Checklist and Key to the Ascoidea and Phytoseioidea (except Phytoseiidae) Species of Turkey with Three New Species Records (Acari: Mesostigmata). Turk. J. Entomol. 2011, 35, 575–586. [Google Scholar]
- Oudemnans, A.C. Acarologische Aanteekeningen C. Entomol. Ber. 1931, 8, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Petrova, V.; Salmane, I.; Çudare, Z. The Predatory mite (Acari, Parasitiformes: Mesostigmata (Gamasina); Acariformes: Prostigmata) Community in Strawberry Agrocenosis. Acta Univ. Latv. 2004, 676, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Michalska, K.; Mrowińska, A.; Studnicki, M. Ectoparasitism of the Flightless Drosophila melanogaster and D. hydei by the Mite Blattisocius mali (Acari: Blattisociidae). Insects 2023, 14, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beresford, D.V.; Sutcliffe, J.F. The Effect of Macrocheles muscaedomesticae and M. subbadius (Acarina: Macrochelidae) Phoresy on the Dispersal of Stomoxys calcitrans (Diptera: Muscidae). Syst. Acarol. Acarol. Spec. Publ. 2009, 23, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Gasparini, O.; Kilner, R.M. Friend or Foe: Inter-specific Interactions and Conflicts of Interest within the Family. Ecol. Entomol. 2015, 40, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, L.T.; Penoni, L.R.; Horn, C.J.; Polak, M. Physical and Physiological Costs of Ectoparasitic Mites on Host Flight Endurance. Ecol. Entomol. 2015, 40, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Guo, J.; Reitz, S.R.; Lei, Z.; Wu, S. A Global Invasion by the Thrip, Frankliniella occidentalis: Current Virus Vector Status and Its Management. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 626–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CABI. Tetranychus Urticae (Two-Spotted Spider Mite); CABI Compendium: Wallingford, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, S. Frankliniella Occidentalis (Western Flower Thrips); CABI Compendium: Walingford, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Q. Spider Mites. In Mites of Greenhouses-Identification, Biology and Control; CABI: Walingford, UK, 2003; pp. 47–86. [Google Scholar]
- Buitenhuis, R.; Shipp, J.L. Influence of Plant Species and Plant Growth Stage on Frankliniella Occidentalis Pupation Behaviour in Greenhouse Ornamentals. J. Appl. Entomol. 2008, 132, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta, G.M.; Deere, J.A.; Messelink, G.J.; Muñoz-Cárdenas, K.; Janssen, A. Review: Predatory Soil Mites as Biocontrol Agents of above- and below-Ground Plant Pests. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2022, 87, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, W.; Shorrocks, B. Breeding Site Specificity in the Domestic Species of Drosophila. Oecologia 1977, 29, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuk, P.L.T. The Species of the Drosophila Repleta Group in Northwestern Europe with Special Reference to the Netherlands (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Entomol. Ber. 1993, 53, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D. Carnivory in the Larvae of Drosophila melanogaster and Other Drosophila Species. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabert, M.; Bigoś, A.; Witaliński, W. DNA Barcoding Reveals Andropolymorphism in Aclerogamasus Species (Acari: Parasitidae). Zootaxa 2011, 3015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, H. Self-Watering Acrylic Cages for Confining Insects and Mites on Detached Leaves12. J. Econ. Entomol. 1967, 60, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, K.; Studnicki, M. Behavioural Responses of Females of the Eriophyoid mite, Aculops allotrichus, to the Presence of Injured Conspecifics. Int. J. Acarol. 2021, 47, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, C.D.; Wuller, J.M.; Elgin, S.C.R. Raising Large Quantities of Drosophila for Biochemical Experiments. Methods Cell Biol. 1994, 44, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso, B.; Godoy-Herrera, R.; Mora, W. The Development of Larval Movement Patterns in Drosophila. Heredity 1987, 58, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing (ver. 4.2.1); R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N. A Beginner’s Guide to Zero-Inflated Models with R.; Highland Statistics: Newburgh, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fajfer, M.; Melnikov, D.; Dabert, M. Three New Species of the Genus Pterygosoma Peters, 1849 (Acariformes: Pterygosomatidae) from Agamid lizards (Sauria: Agaminae) with DNA Barcode Data. Syst. Parasitol. 2016, 93, 791–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracka, A.; Dabert, M. The Cereal Rust Mite Abacarus hystrix (Acari: Eriophyoidea) Is a Complex of Species: Evidence from Mitochondrial and Nuclear DNA Sequences. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2010, 100, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabert, J.; Mironov, S.V.; Dabert, M. The Explosive Radiation, Intense Host-Shifts and Long-Term Failure to Speciate in the Evolutionary History of the Feather Mite Genus Analges (Acariformes: Analgidae) from European Passerines. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2022, 195, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyazi, R.; Altunc, Y.E.; Soysal, M. Amblyseius swirskii ve Neoseiulus californicus (Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae)’un Tüketim Kapasitesine Avın Yumurta Yaşının Etkisi. Türk Tarım ve Doğa Bilimleri Dergisi 2018, 5, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Canlas, L.J.; Amano, H.; Ochiai, N.; Takeda, M. Biology and Predation of the Japanese Strain of Neoseiulus californicus (McGregor) (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2006, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lemos, F.; Sarmento, R.A.; Pallini, A.; Dias, C.R.; Sabelis, M.W.; Janssen, A. Spider Mite Web Mediates Anti-Predator Behaviour. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2010, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McMurtry, J.A.; Croft, B.A. Life Styles of Phytoseiid Mites and Their Roles as Biological Control Agents. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1997, 42, 291–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurtry, J.A.; de Moraes, G.; Sourassou, N. Revision of the Lifestyles of Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and Implications for Biological Control Strategies. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2013, 18, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, M.; Van Houten, Y.; Hoogerbrugge, H.; Bolckmans, K. Amblydromalus limonicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae) as a Biocontrol Agent: Literature Review and New Findings. Acarologia 2013, 53, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houten, Y.M.; Rijn, P.C.J.; Tanigoshi, L.K.; Stratum, P.; Bruin, J. Preselection of Predatory Mites to Improve Year-Round Biological Control of Western Flower Thrips in Greenhouse Crops. Entomol. Exp. Et Appl. 1995, 74, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannou, I.D.; Hanna, R. Clarifying the Identity of Amblyseius swirskii and Amblyseius rykei (Acari: Phytoseiidae): Are They Two Distinct Species or Two Populations of One Species? Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2011, 53, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, E.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Z. Evaluation of Stratiolaelaos scimitus and Neoseiulus barkeri for Biological Control of Thrips on Greenhouse Cucumbers. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Lei, Z. Interactions between Foliage- and Soil-Dwelling Predatory mites and Consequences for Biological Control of Frankliniella occidentalis. BioControl 2016, 61, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteca, F.d.C.N. Environmental Management Strategies for Pest Control in Strawberry Crop. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, Piracicaba, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Asgari, F.; Safavi, S.A.; Moayeri, H.R.S. Life Table Parameters of the Predatory mite, Blattisocius mali Oudemans (Mesostigmata: Blattisociidae), Fed on Eggs and Larvae of the Stored Product Mite, Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Schrank). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest. Control. 2022, 32, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Q. Acarid Mites. In Mites of Greenhouses-Identification, Biology and Control; CABI: Walingford, UK, 2003; pp. 141–158. [Google Scholar]
- Lesna, I.; Sabelis, M.; Conijn, C. Biological Control of the Bulb Mite, Rhizoglyphus Robini, by the Predatory mite, Hypoaspis aculeifer, on Lilies: Predator-Prey Interactions at Various Spatial Scales. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCS. Invasive Insect Pests: The Spotted Wing Drosophila; National Centre for Climate Services: Zurich, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).