Phylogenetic Analysis of the Genus Planaphrodes Hamilton (Hemiptera, Cicadellidae, Aphrodinae) Based on Morphological Characteristics, with Revision of Species from China, Korea and Japan
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Taxa and Terminology
2.2. Taxon Sampling and Morphological Characters
- 0.
- Microsculpture of crown and pronotum: 0, glabrous (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 1A,D); 2, finely striate; 1, shagreened (Figures 4A–G,I and 5A–D).
- 1.
- Width of head: 0, wider than pronotum (Figures 4A–G,I and 5A–D); 1, narrower than pronotum.
- 2.
- Crown: 0, blunt, almost parallel-margined; 1, slightly produced (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 1A,D); 2, strongly produced or elongate (Figures 4A–G,I and 5A–D); (State: 0, strongly narrower than midwidth of pronotum; 1, same as midwidth of pronotum; 2, significantly wider than midwidth of pronotum).
- 3.
- Vertex: 0, crown rounded to face, transition poorly delimited (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 1B,E); 1, with anterior margin strongly carinate, transition from crown to face well delimited (Figures 4H and 5E–D).
- 4.
- Crown anterior margin: 0, unicolorous or without spots (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 1A,D); 1, with numerous small bright spots (Figures 4A–G,I and 5A–D).
- 5.
- Crown: 0, slightly convex, smooth (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 1A,D); 1, flat, with distinct medial carina and two slightly elevated keels behind the ocelli (Figures 4A–G,I and 5A–D).
- 6.
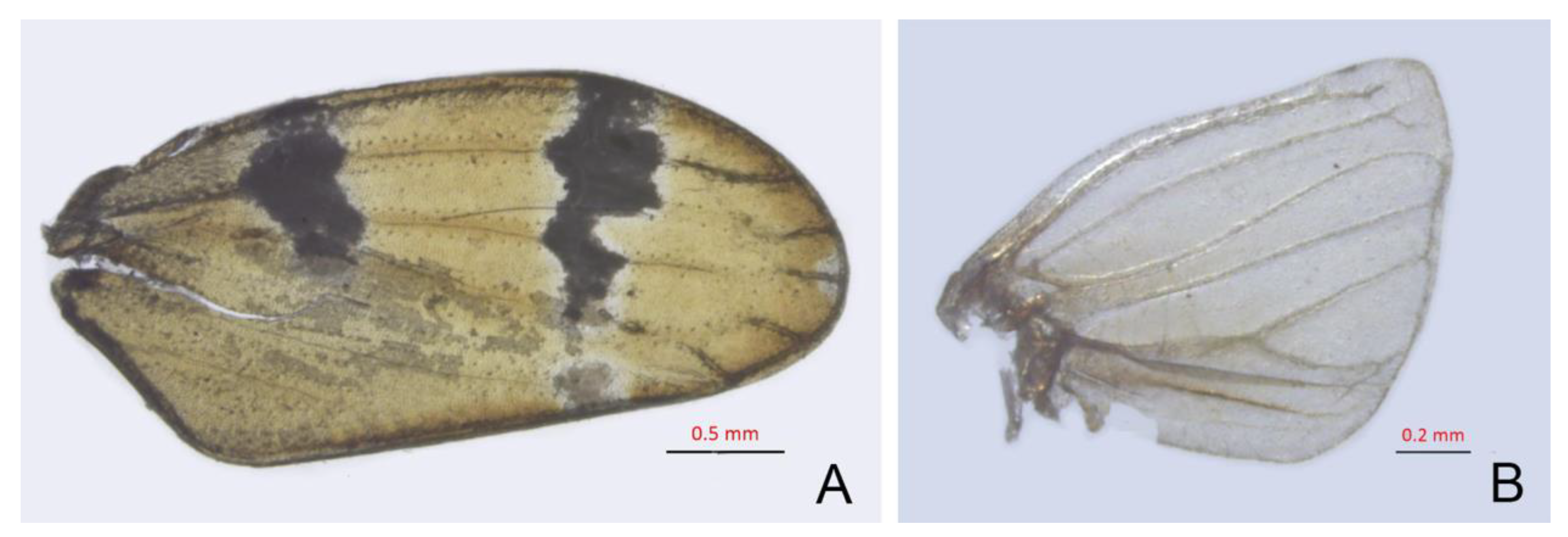
- Wings: 0, transparent, membranous (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 1B,E); 1, opaque, leathery (Figures 4H, 5E–H and 11A).
- 7.
- Venation: 0, not elevated (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 1B,E); 1, elevated (Figures 4H and 5E–H).
- 8.
- Genital capsule: 0, cylindrical (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2A); 1, conical (Figures 6D, 9B,C, 14B,15B and 16B).
- 9.
- Lobes of the pygofer posterior margin: 0, significantly produced, rounded (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2A); 1, absent; 2, folded into cavity, forming a partially sclerotized barrier, like an interconnecting membrane in some leafhoppers, with strigate sculpture (Figures 6A,B, 9A, 14A, 15A and 16A).
- 10.
- Pygofer lobe posterior margin: 0, with papillae or microsetae (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2A); 1, without papillae or microsetae (Figures 6A,B, 9A, 14A, 15A and 16A).
- 11.
- Setae of pygofer: 0, 2 rows of large macrosetae near the base of lobe (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2A); 1, macrosetae in irregular tuft surrounding anal tube; 2, microsetae, scattered (Figure 14A,B).
- 12.
- Pygofer appendage: 0, inner, a small ventrad angular projection (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2B); 1, outer, posteroventrally directed harpoon-shaped process; 2, a curved dorsal tarpering process; 3, outer, a posteriorly directed swollen and curved dorsal hook–shaped process (Figure 6C).
- 13.
- Valve shape: 0, approximately rectangular (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2C); 1, expanded sickle shaped; 2, depressed trapezoidal (Figures 6E, 9D, 14C, 15C and 16C).
- 14.
- Subgenital plate shape: 0, broad with apex rounded (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2C); 1, ligulate with apex attenuate (Figures 6E, 9D, 14C, 15C and 16C).
- 15.
- Setae on subgenital plate: 0, two rows of large submarginal setae and several rows of hairlike setae mesally (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2C); 1, long setae, submarginal and mesal; 2, short setae, submarginal and at apex; 3, microsetae, scattered (Figures 9D and 14C).
- 16.
- Style shape: 0, S-shaped (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2D); 1, crescent-shaped, slenderer, significantly bent; 2, crescent-shaped, not bent (Figures 9E,F and 14D); 3, crescent-shaped, broader, significantly bent (Figures 6F,G, 15D and 16D).
- 17.
- Style apophysis apex: 0, acuminate, with foot-like extension (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2D); 1, blunt, slightly expanded then tapering; 2, blunt, uniform width; 3, blunt, strongly expanded; 4, obliquely truncate, broadened (Figures 9E,F and 14D); 5, blunt, strongly bent and expanded (Figures 6F,G, 15D and 16D).
- 18.
- Style apophysis ventral margin: 0, without denticles or areoles (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2D); 1, with denticles, areoles absent; 2, with denticles and areolate submargin (Figures 6F,G, 9E,F, 14D, 15D and 16D).
- 19.
- Connective: 0, Y-shaped with a short median anterior lobe (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2D); 1, Y-shaped with posterior stem divided; 2, Y-shaped without median anterior lobe (Figures 6F,G, 9E,F, 14D, 15D and 16D).
- 20.
- Aedeagus dorsal apodeme: 0, significantly longer than 1/2 length of aedeagal shaft (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2F,H); 1, almost 1/2 length of aedeagal shaft (Figures 7A–F, 9G,H, 14F, 15F and 16F).
- 21.
- Aedeagal shaft: 0, cylindrical (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2E,G); 1, flattened laterally (Figures 7G,H, 9I,J, 14E, 15E and 16E).
- 22.
- Aedeagal shaft dorsal lamella: 0, present (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2F,H); 1, absent (Figures 7A–F, 9G,H, 14F, 15F and 16F).
- 23.
- Shape of aedeagal shaft in lateral view: 0, straight, evenly broad (Figure 9G,H); 1, slightly curved, thin, atrium widened, shaft tapering; 2, arcuate, base evenly broad, apical 1/2 gradually tapering; 3, straight, uniformly slender; 4, straight, thin, slightly broader in middle than at both ends (Table 2: Aedeagus lateral view of P. elongatus, P. iranicus and P. nisamiana); 5, straight, broad, apical 1/3 abruptly tapered (Figure 14F); 6, slightly curved, strongly widened in middle 1/3 (Figures 7A–F, 15F and 16F).
- 24.
- Aedeagal shaft apical denticles: 0, absent (Figures 7G,H, 9I,J, 14E, 15E and 16E); 1, present (Table 2: Aedeagus caudal view of P. bifasciatus).
- 25.
- 26.
- Apical spines of aedeagus: 0, long, thin petal-shaped; 1, long, broad petal-shaped; 2, short spine; 3, tiny hook-like (Figures 7A–F, 9G,H, 14F, 15F and 16F); 4, widened hook (Table 2: Aedeagus lateral view of P. angulaticeps and P. iranicus).
- 27.
- Apical spines of aedeagus, position: 0, arising laterally (Figure 14E,F); 1, arising caudally (Figures 7A–H, 9G–J, 15E,F and 16E,F).
- 28.
- Apical spines of aedeagus, orientation: 0, directed posteroventrad (Figures 7A–H, 9G–J, 15E,F and 16E,F); 1, directed ventrad; 2, directed anteroventrad (Figure 14E,F).
- 29.
- Lateral processes of aedeagus: 0, short spine (Figures 9G,H and 14F); 1, large crescent-shaped process; 2, spinule (Figures 7A–F, 15F and 16F); 3, triangle (Table 2: Aedeagus lateral view of P. nisamiana).
- 30.
- Lateral processes of aedeagus, orientation: 0, divergent laterally, anteroventrad (Table 2: Aedeagus lateral and caudal view of P. bifasciatus, P. monticola, P. vallicola); 1, directed anteroventrad (Figures 7A–H, 9G–J, 14E,F, 15E,F and 16E,F); 2, posteroventrad.
- 31.
- Caudal processes of aedeagus: 0, absent (Table 2: Aedeagus lateral view of P. vallicola); 1, slender spines (Table 2: Aedeagus lateral view of P. bifasciatus, P. elongatus, P. iranicus, P. nisamiana); 2, poorly developed tooth (Table 2: Aedeagus lateral view of P. mondicus); 3, tiny tooth (Figures 7A–F, 15F and 16F); 4, large shark fin (Figures 9G,H and 14F).
- 32.
- Bases of caudal processes of aedeagus: 0, separated; 1, connected (Figures 7G,H, 9I,J, 15E and 16E); 2, fused for most of length (Figure 14E Table 2: Aedeagus caudal view of P. lusitanicus).
- 33.
- Relative distance between lateral and caudal processes of aedeagus: 0, lateral processes much higher than caudal processes (Table 2: Aedeagus lateral view of P. angulaticeps, P. araxicus, P. modicus and P. monticola); 1, lateral processes slightly higher than caudal processes (Figure 14F); 2, lateral processes and caudal processes at the same level (Figure 9G,H); 3, lateral processes lower than caudal processes Figures 7A–F, 15F and 16F) (0, processes with bases well separated, greater than the lateral processes length; 1, processes with bases close to each other, tips of lateral processes not reaching base of caudal processes).
- 34.
- Dorsal processes of aedeagus: 0, absent (Figures 9G,H and 14F); 1, acute triangle (Figure 15F); 2, obtuse triangle (Figure 16F); 3, tooth (Table 2: Aedeagus lateral view of P. bifasciatus, P. monticola and P. nigritus); 4, long and strongly divergent process (Figure 7A–F and Table 2: Aedeagus lateral view of P. vallicola).
- 35.
- Dorsal processes of aedeagus orientation: 0, directed posteroventrad (Figures 15E,F and 16E,F); 1, directed downward (Table 2: Aedeagus lateral and caudal view of P. bifasciatus, P. monticola, P. nigritus); 2, directed dorsad (Figure 7A–F and Table 2: Aedeagus lateral and caudal view of P. vallicola);
- 36.
- Relative positions of dorsal and lateral processes of aedeagus: 0, dorsal processes higher than lateral processes (Figures 7A–F, 9G,H, 15E,F and 16E,F); 1, dorsal processes lower than lateral processes (Table 2: Aedeagus lateral view of P. monticola).
- 37.
- Shape of gonopore: 0, circle (Liang et al. 2021 [35], Figure 2E,G); 1, willow leaf shaped; 2, flat ellipse; 3, teardrop-shaped (Figures 7G,H, 9I,J, 14E,F, 15E,F and 16E,F).
- 38.
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
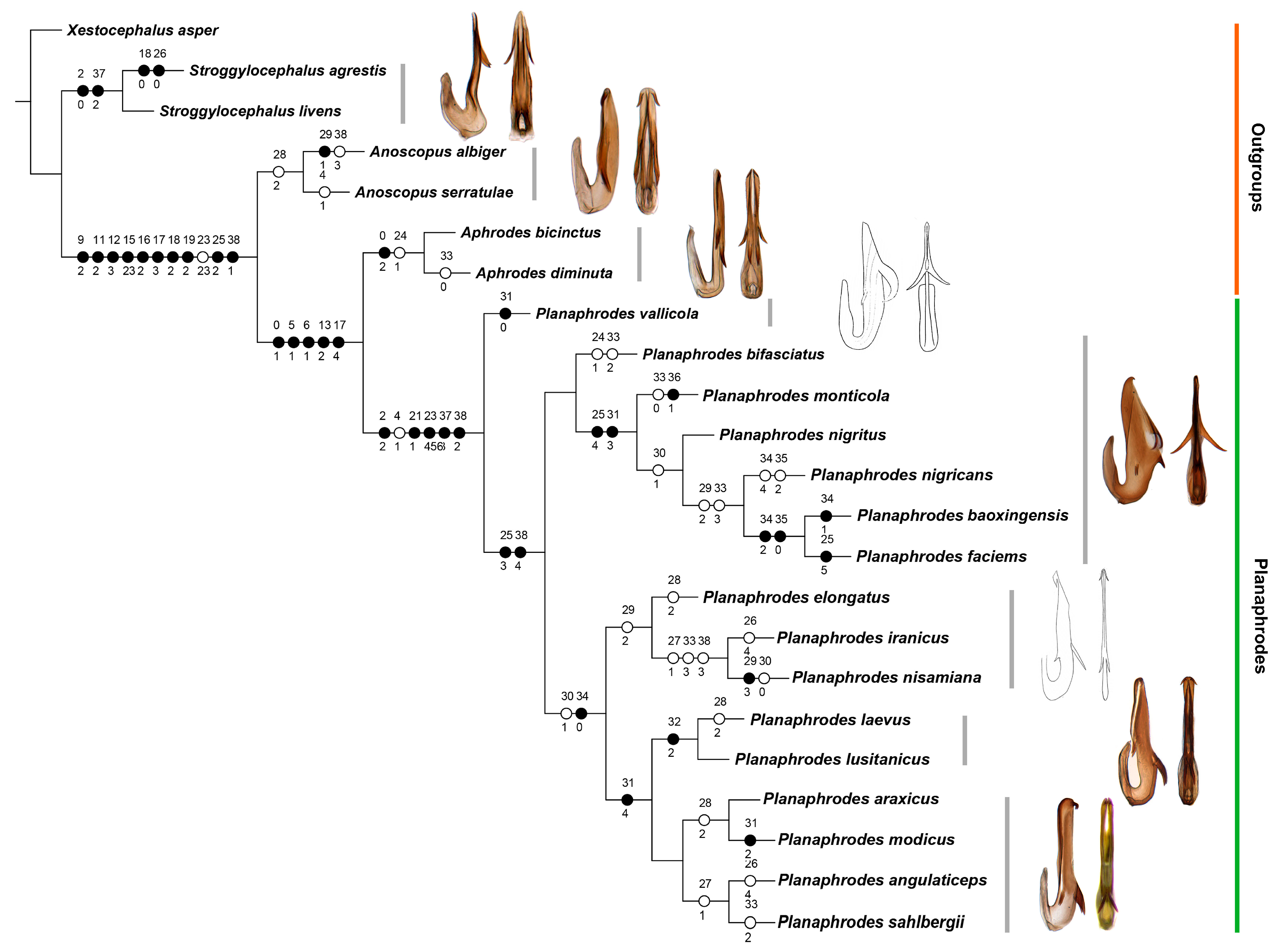
3. Results
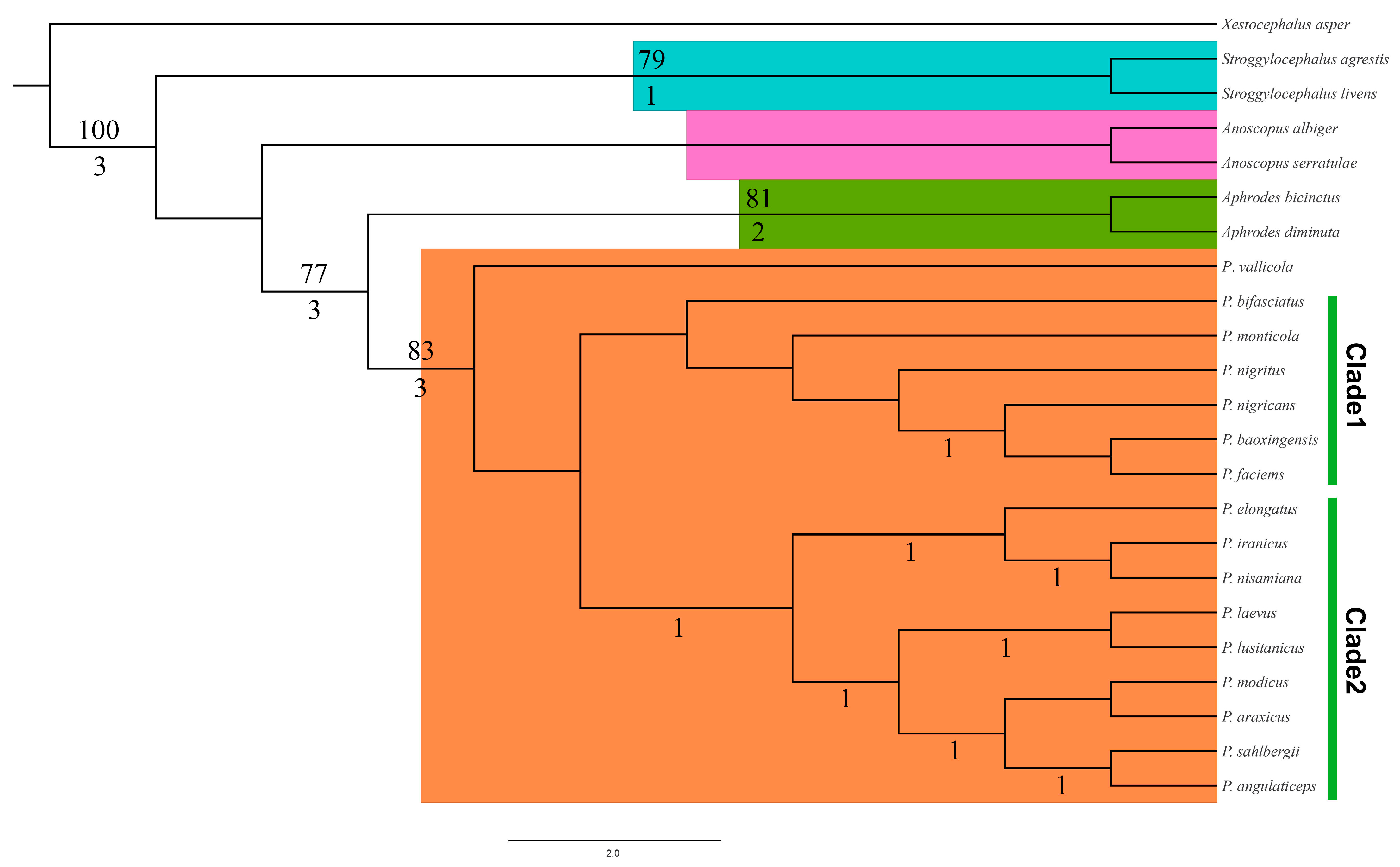
3.1. Phylogeny
3.2. Systematics
3.2.1. Tribe Aphrodini
3.2.2. Genus Planaphrodes Hamilton, 1975
3.2.3. Checklist of Species of Planaphrodes Hamilton
3.2.4. Key to Species of the Genus Planaphrodes
- 1.
- Aedeagal shaft with more than three pairs of processes (Figures 7A–F, 15F and 16F)...... 2
- -
- Aedeagal shaft with less than or equal to three pairs of processes (Figures 9G,H and 14F)...........................................................................................................................................6
- 2.
- Lateral processes of aedeagus situated higher than caudal processes (Figure 14F).... 3
- -
- Lateral processes of aedeagus situated lower than caudal processes (Figures 7A–F, 15F and 16F)...........................................................................................................................................4
- 3.
- Dorsal processes of aedeagus situated higher than lateral processes..............P. nigritus
- -
- Dorsal processes of aedeagus situated lower than lateral processes........... P. monticola
- 4.
- Aedeagal shaft with five pairs of retrorse processes (Figure 16F).....P. faciems sp. nov.
- -
- Aedeagal shaft with four pairs of retrorse spines (Figures 7A–F and 15F)..................5
- 5.
- Dorsal processes of aedeagus long and strongly divergent, curved laterally (Figure 7G,H).................................................................................................................... P. nigricans
- -
- Dorsal processes of aedeagus short, not strongly divergent, directed posteriorly (Figure 15E).............................................................................................. P. baoxingensis sp. nov.
- 6.
- Aedeagal shaft with two pairs of retrorse processes......................................... P. vallicola
- -
- Aedeagal shaft with three pairs of retrorse processes (Figures 9G,H and 14F)............. 7
- 7.
- Aedeagal shaft with apical denticles.............................................................. P. bifasciatus
- -
- Aedeagal shaft with apical spines (Figures 7A–F, 9G,H, 14F, 15F and 16F).................. 8
- 8.
- Aedeagal shaft slender in lateral view, slightly widened near middle......................... 9
- -
- The width of aedeagal shaft moderate in lateral view.................................................... 11
- 9.
- Lateral processes of aedeagus situated higher than caudal processes.......... P. elongatus
- -
- Lateral processes of aedeagus situated lower than caudal processes........................... 10
- 10.
- Apical retrorse spines of aedeagus tiny, hook-like........................................... P. iranicus
- -
- Apical retrorse spines of aedeagus strongly widened, hook-like................. P. nisamiana
- 11.
- Aedeagal shaft with almost uniform width in lateral view (Figure 9G,H).................12
- -
- Aedeagal shaft apical 1/3 obviously tarpered in lateral view (Figure 14F).................13
- 12.
- Aedeagus with apical retrorse spines arising ventrally (Figure 9G,H)....... P. sahlbergii
- -
- Aedeagus with apical retrorse spines arising laterally.................................... P. araxicus
- 13.
- Aedeagus with caudal process short and poorly developed........................... P. modicus
- -
- Aedeagus with caudal process shark fin-like and well developed............................... 14
- 14.
- Aedeagus with apical retrorse spines strongly widened hook-like......... P. angulaticeps
- -
- Aedeagus with apical retrorse spines tiny hook- like.................................................... 15
- 15.
- Aedeagus with apical spines directed ventrad down................................... P. lusitanicus
- -
- Aedeagus with apical spines directed dorsad down (Figure 14F)..................... P. laevus
3.3. Taxonomy
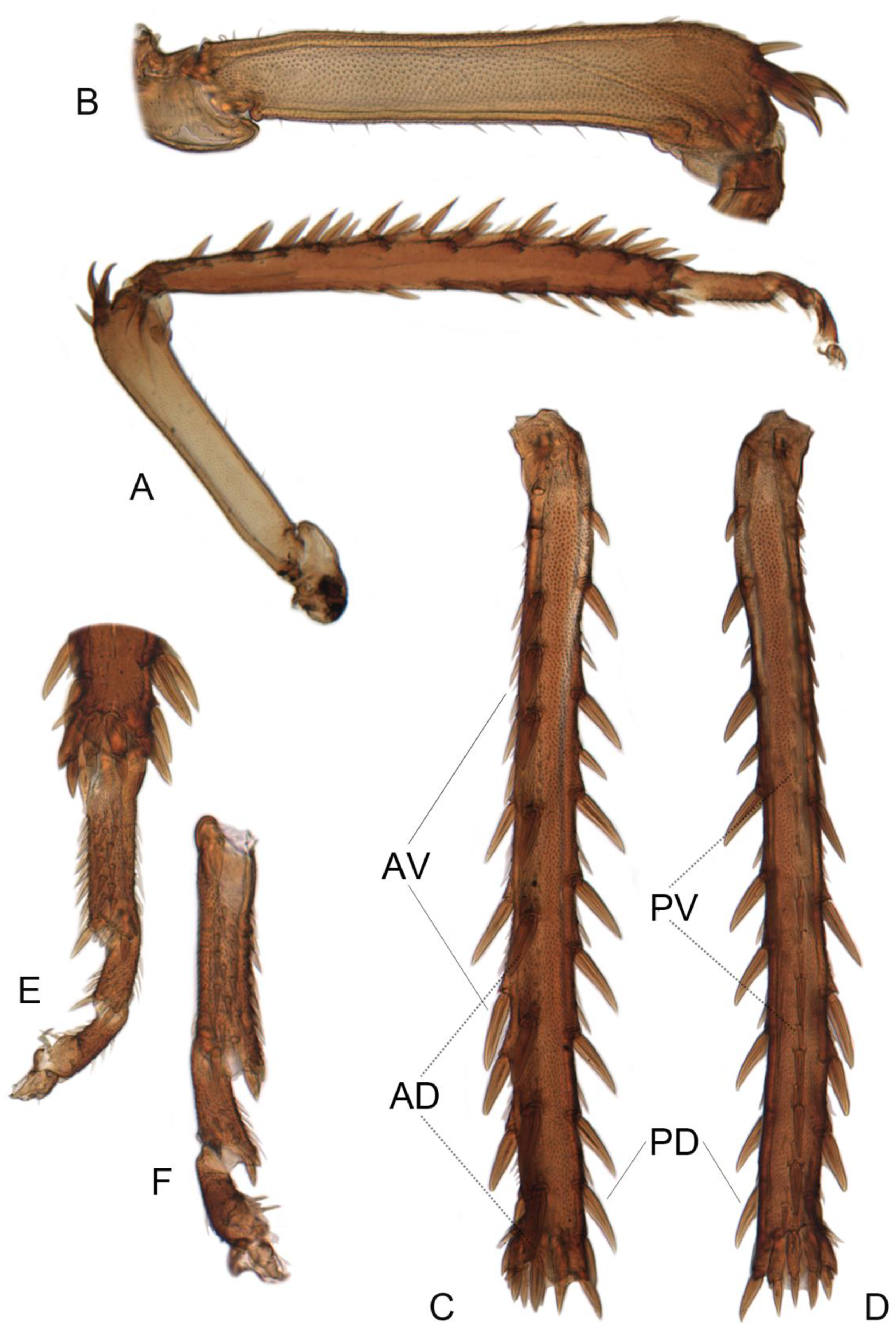
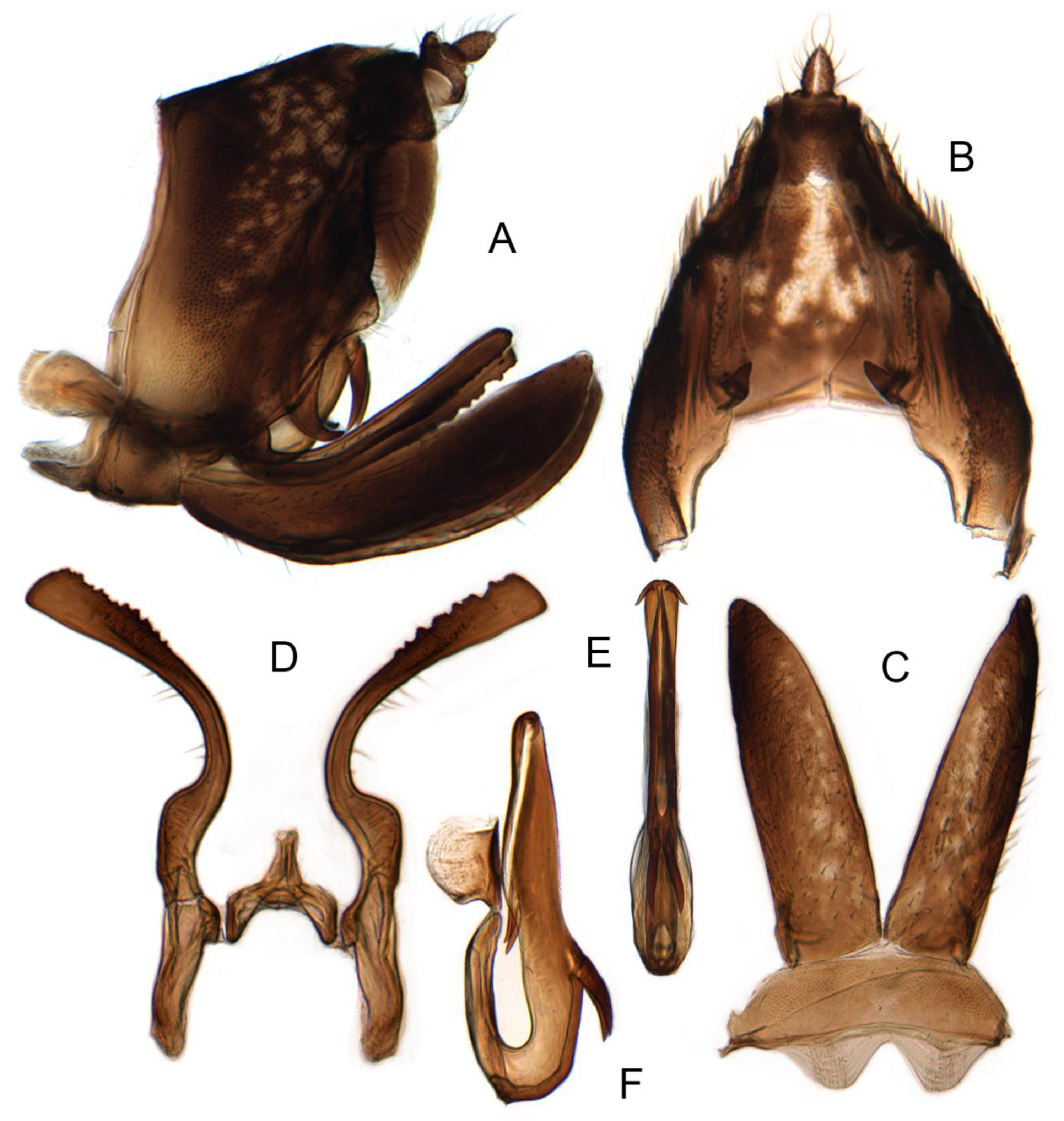
3.3.1. Planaphrodes nigricans (Matsumura, 1912) (Figure 4A–I, Figure 5M, Figure 6A–G and Figure 7A–H)
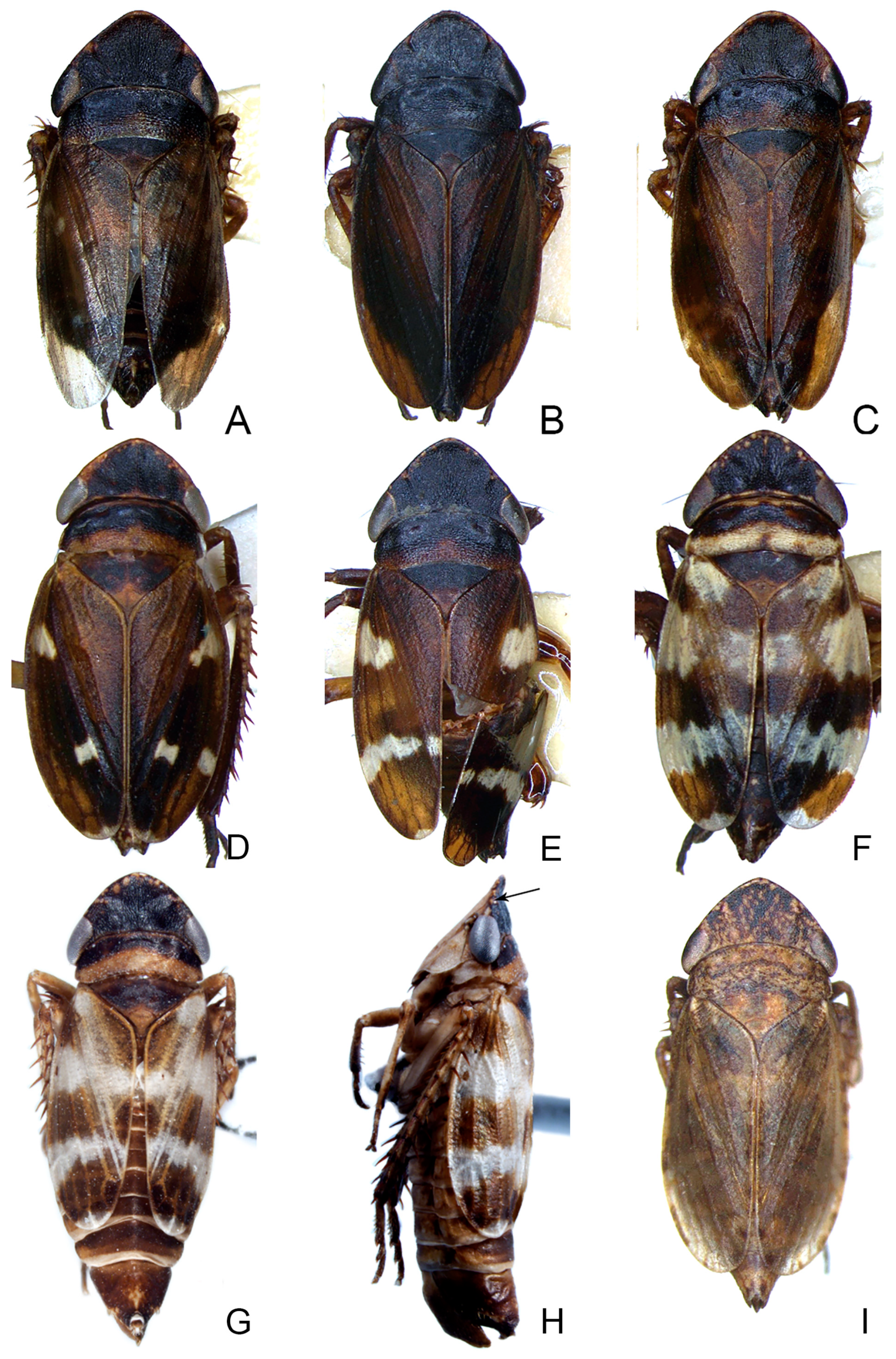


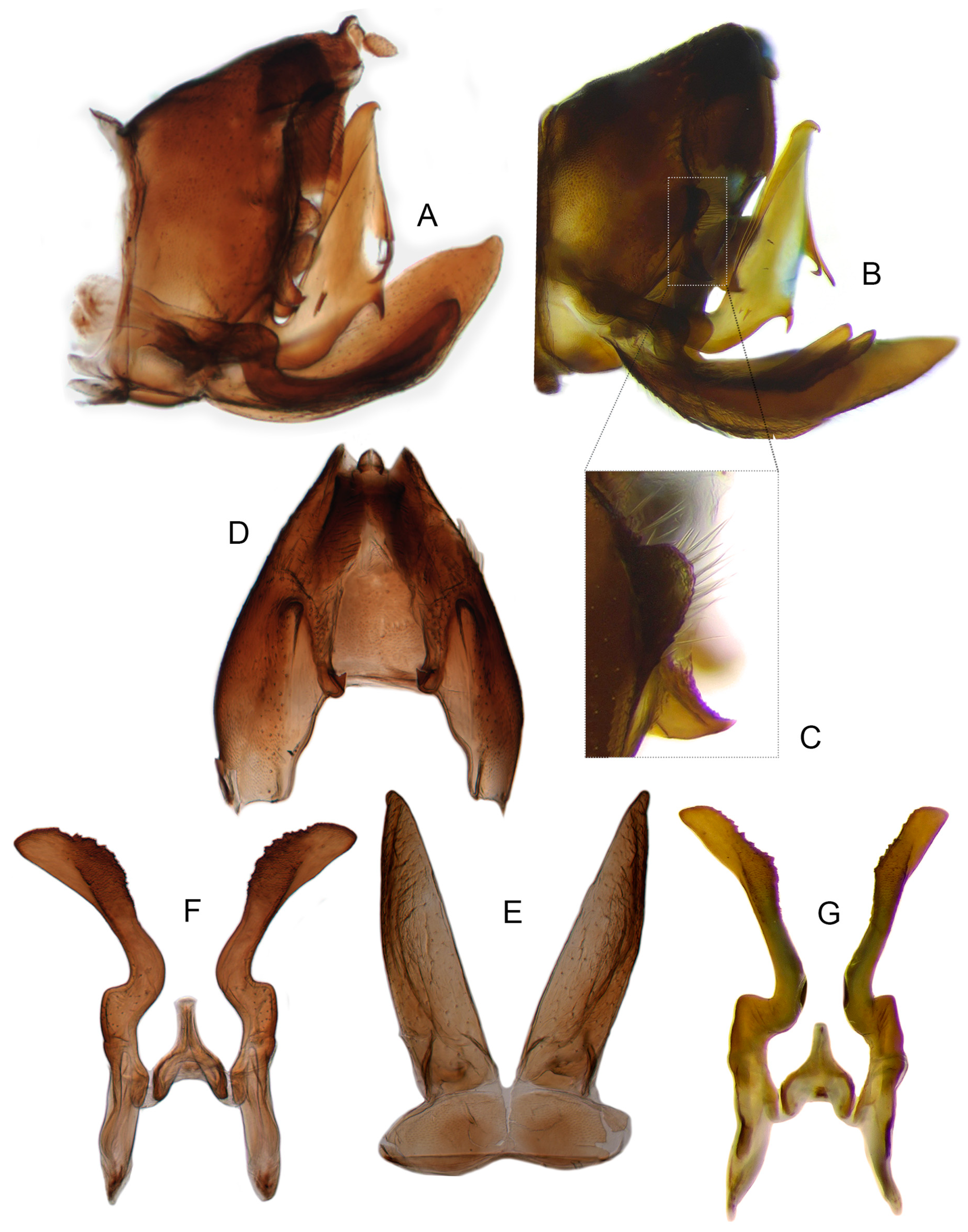
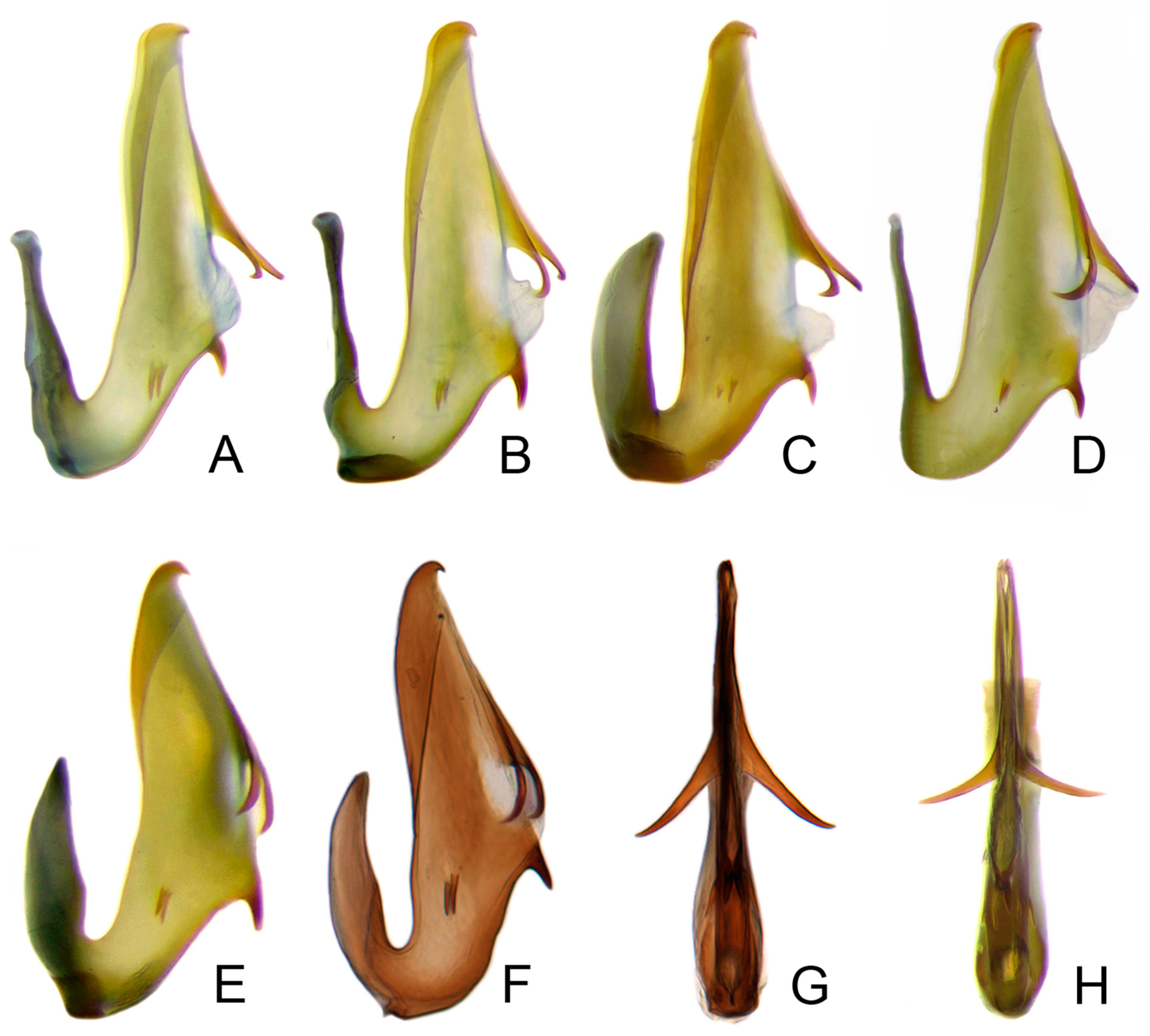
3.3.2. Planaphrodes Sahlbergii (Signoret, 1879) (Figure 5N,O, Figure 8A–K, Figure 9A–J and Figure 10A–I)

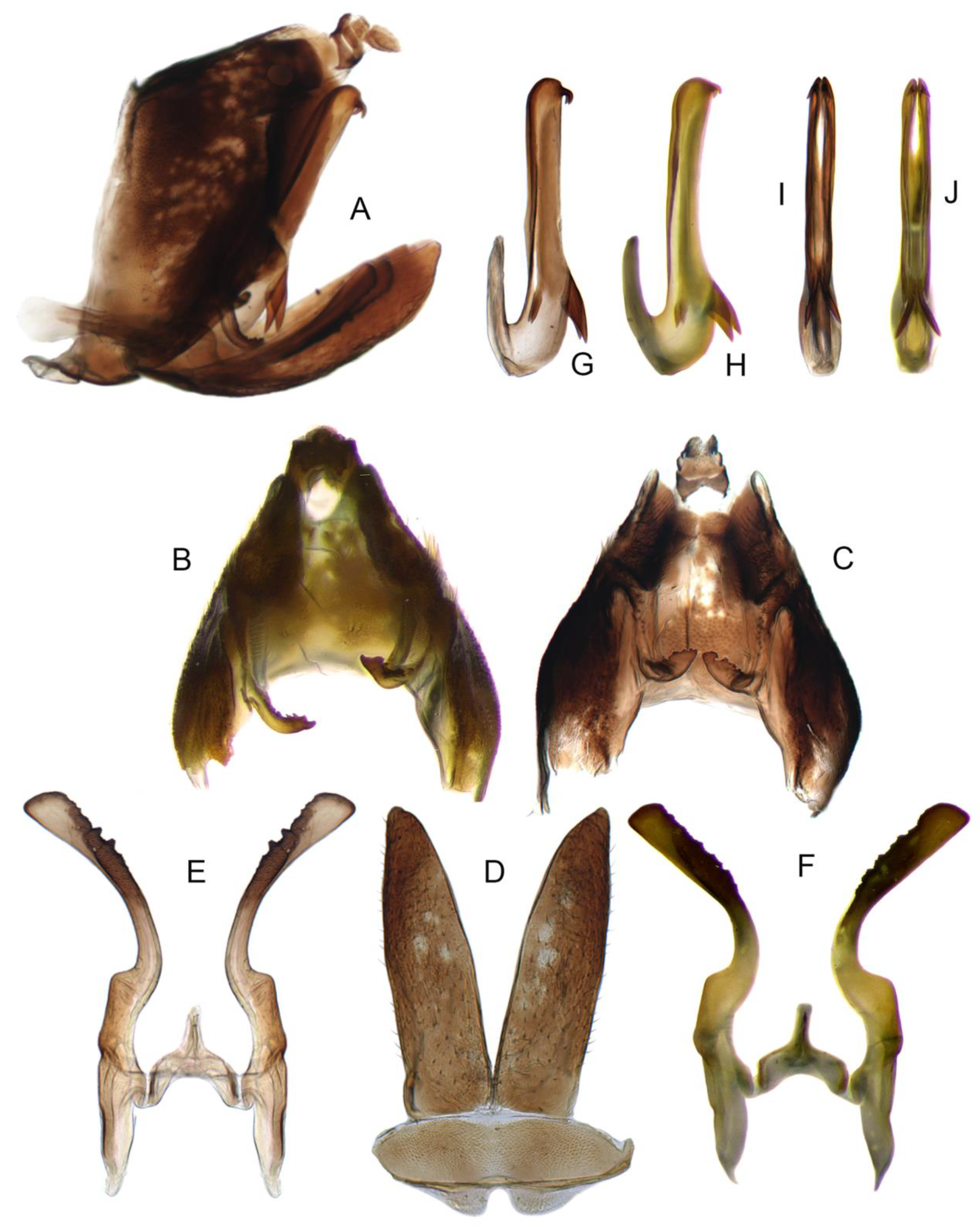
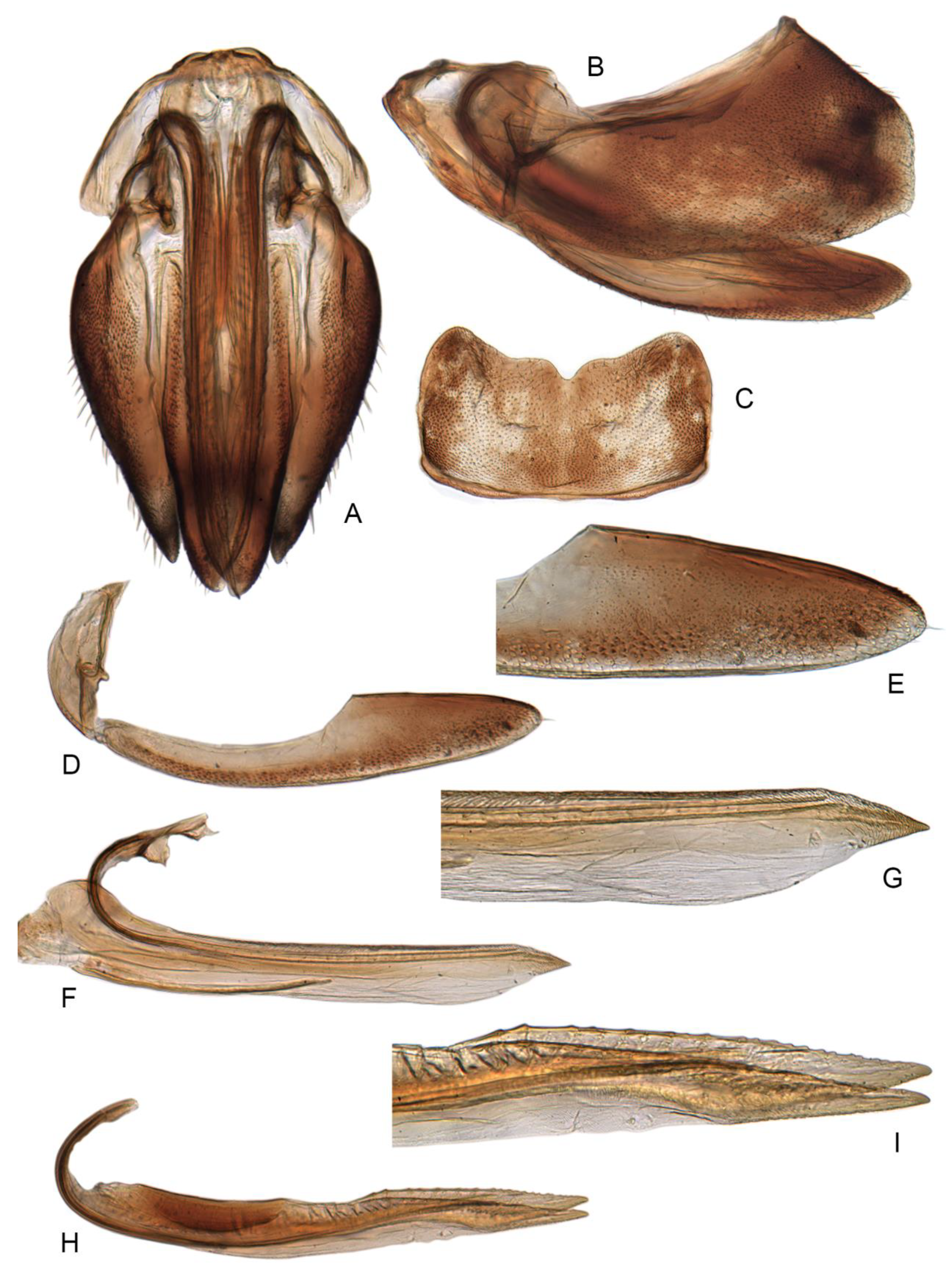
3.3.3. Planaphrodes bifasciatus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Figure 5A,E,I, Figure 11A,B, Figure 12A–C and Figure 13A–F)

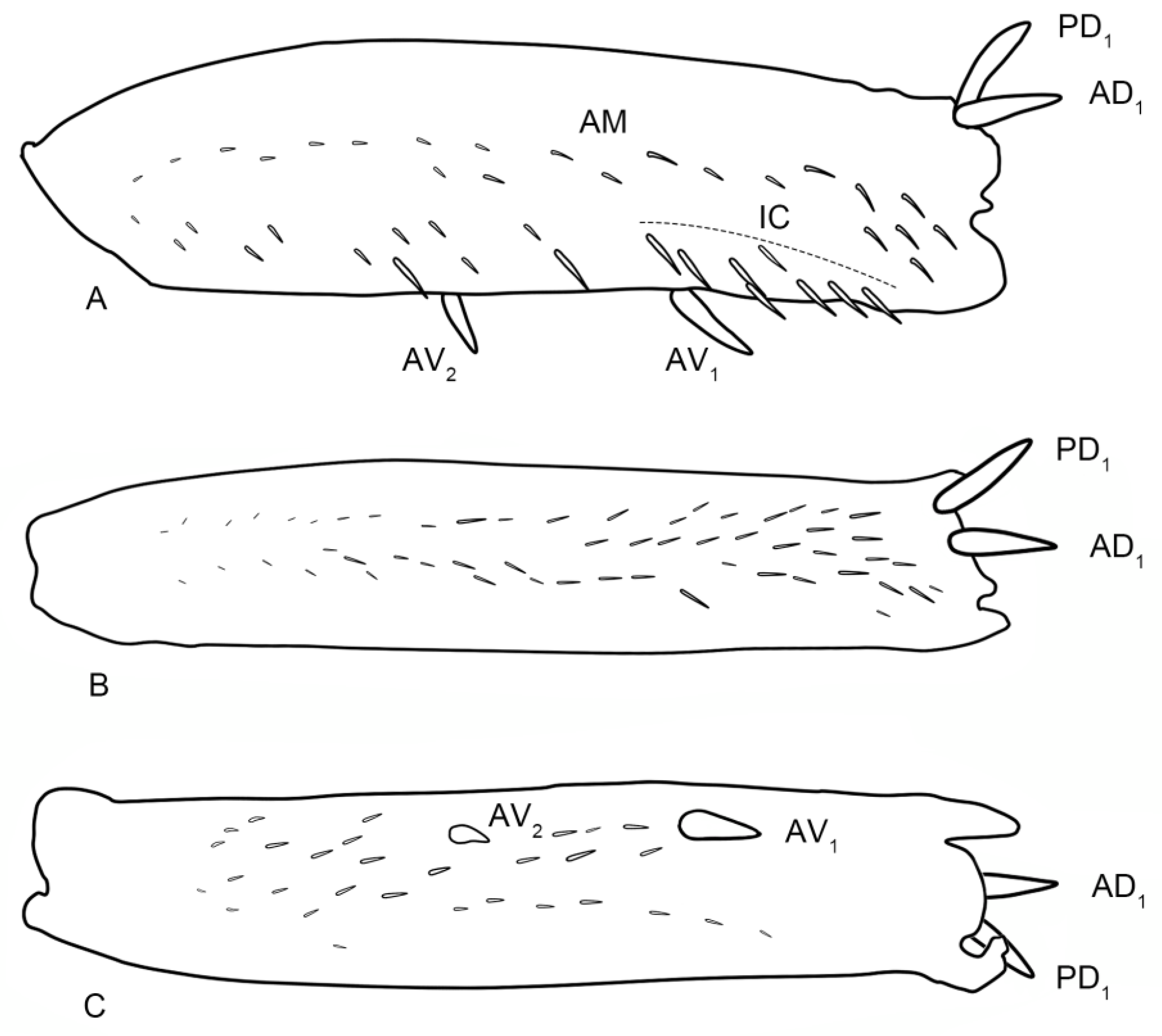
3.3.4. Planaphrodes laevus (Rey, 1891) n. rec from China (Figure 5B,F,J and Figure 14A–F)
3.3.5. Planaphrodes baoxingensis Liang & Dai, sp. nov. (Figure 5C,G,K and Figure 15A–F)

3.3.6. Planaphrodes faciems Liang & Dai, sp. nov. (Figure 5D,H,L and Figure 16A–F)

4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Auchenorrhyncha Database. Available online: https://proceps.github.io/auchenorrhyncha/#/ (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Whitcomb, R.F.; Kramer, J.; Coan, M.E.; Hicks, A.L. Ecology and Evolution of Leafhopper—Grass Host Relationships in North American Grasslands. Curr. Top. Vector Res. 1987, 4, 121–178. [Google Scholar]
- Ossiannilsson, F. The Auchenorrhyncha (Homoptera) of Fennoscandia and Denmark. II. The families Cicadidae, Cercopidae, Membracidae and Cicadellidae (excl. Deltocephalinae). Fauna Entomol. Scand. 1981, 7, 223–593. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmino, A.; Bückle, C. Revision of Errhomeninae and Aphrodinae (Hemiptera, Cicadomorpha) in Italy with remarks on their variability and distribution in adjacent regions and description of three new taxa. Zootaxa 2015, 3906, 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielson, M.W. The Leafhopper Vectors of Phytopathogenic Viruses (Homoptera, Cicadellidae) Taxonomy, Biology and Virus Transmission. Tech. Bull. United States Dep. Agric. 1968, 1382, 1–386. [Google Scholar]
- Hemiptera-Phytoplasma-Plant Biological Interaction Database. Available online: http://trivellone.speciesfile.org/ (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Hamilton, K.G.A. A review of the Northern Hemisphere Aphrodina (Rhynchota: Homoptera: Cicadellidae), with special reference to the Nearctic fauna. Can. Entomol. 1975, 107, 1009–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Quesne, W.J. Some taxonomic changes and additions in the British Cicadellidae (Hemiptera) including a new species and subspecies. Proc. R. Entomol. Soc. Lond. 1964, 33, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anufriev, G.A.; Danzig, E.M.; Emeljanov, A.F.; Golub, V.B.; Kanyukova, E.V.; Kerzhner, I.M.; Konovalova, Z.A.; Pashchenko, N.F.; Tshernova, G.P.; Vinokurov, N.N. Suborder Cicadinea (Auchenorrhyncha). In Keys to the Insects of the Far East of the USSR; Nauka Publishing House: Leningrad, Russia, 1988; Volume 2, pp. 12–495. [Google Scholar]
- Emeljanov, A.F. Leafhoppers (Homoptera, Auchenorryncha) from the Mongolian People’s Republic based mainly on materials of the Soviet-Mongolian zoological expeditions (1967–1969). Insects Mong. 1977, 5, 96–195. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, S. Die Acocephalinen und Bythoscopinen Japans. J. Sapporo Agric. Coll. 1912, 4, 279–325. [Google Scholar]
- Dlabola, J. Eine neue Dictyophara Art aus Kaschmir. Atti Del Mus. Civ. Di Stor. Nat. Di Trieste 1960, 22, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dlabola, J. Ergebnisse der zoologischen Forschungen von Dr. Z. Kaszab in der Mongolei. 54; Homoptera, Auchenorrhyncha. Acta Faun. Entomol. Musei Natl. Pragae 1965, 11, 79–136. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Anufriev, G.A. Leafhoppers (Homoptera, Auchenorrhyncha, Cicadellidae) of the Kurile Islands. Trans. Zool. Inst. 1977, 70, 10–36. [Google Scholar]
- Anufriev, G.A. Les cicadellides, de le Territoire Maritime. Horae Soc. Entomol. Unionis Sov. 1978, 60, 1–215. [Google Scholar]
- Choe, K.R. Three new species of leafhoppers (Cicadellidae, Homoptera) from Korea. Korean J. Plant Prot. 1981, 20, 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Logvinenko, V.N. New leafhoppers of the family Cicadellidae (Auchenorrhyncha) from Transcaucasia. Entomol. Obozr. 1983, 62, 83–90. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Cantoreanu, M. Eine neue Cycaden-art: Aphrodes dobrogicus n. sp. aus Rumanien. Rev. Roum. De Biol. Ser. De Zool. 1968, 13, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Emeljanov, A.F. Suborder Cicadinea (Auchenorrhyncha). InKeys to the Insects of the European USSR. Apterygota, Palaeoptera, Hemimetabola; Smithsonian Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 1964; Volume 1, pp. 337–437. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gnezdilov, V.M. To the knowledge of the faunistic complexes of the Cicadina (Homoptera) in the main plant formations of the Northwestern Caucasus. Entomol. Obozr. 2000, 79, 794–811. [Google Scholar]
- Tishechkin, D.Y. Calling signal pattern vs. genitalia morphology in Planaphrodes Hamilton, 1975 (Homoptera: Auchenorrhyncha: Cicadellidae: Aphrodinae)—Which trait evolves faster? Russ. Entomol. J. 2019, 28, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshanin, V.T. Verzeichnis der Palaarktischen Hemipteren, mit Besonderer Berücksichtigung Ihrer Verteilung im Russischen Reiche. II. Band Homoptera. I. Lieferung; Annuaire du Musee Zoologique de l’Academie Imperiale des Sciences: St. Petersburg, Russia, 1906; Volume 11, Chapter i–xvi; pp. 1–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, M. Notes on some Manchurian Homoptera, collected by Mr. K. Kikuchi. Entomol. World 1933, 1, 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobi, A. Zur Kenntnis der Insekten von Mandschuko. 12. Beitrag. Eine Homopterenfaunula der Mandschurei (Homoptera: Fulgoroidea, Cercopoidea & Jassoidea). Arb. Auf Morphol. Und Taxon. Von Entomolgie 1943, 10, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, M.S.; Kamitani, S.; Ohara, N. Family Cicadellidae. In Catalogue of the Insects of Japan 4 (Paraneoptera); Entomological Society of Japan: Nara, Japan, 2016; pp. 264–322. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.J.; Huh, E.Y. Homoptera (suborder Auchenorrhyncha). Economic Insects of Korea 19. Insecta Koreana Suppl. 2001, 26, 1–461. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, C.H. Keys to the families of Cicadomorpha and subfamilies and tribes of Cicadellidae (Hemiptera: Auchenorrhyncha). Fla. Entomol. 2005, 88, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logvinenko, V.N. New species of leafhoppers (Homoptera: Auchenorrhyncha) from the Caucasus and Moldavia. Entomol. Obozr. 1966, 45, 401–410. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Logvinenko, V.N. New species of cicades (Auchenorrhyncha, Cicadellidae) from Caucasus. Zool. Zhurnal. 1971, 50, 589–592. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, P.D. Notes Homopterologiques I. Remarques sur Quelques Cicadellidae du Portugal Avec la Description de Quatre Especes Nouvelles, 2nd ed.; Archives do Museu Bocage: Lisbon, Portugal, 1968; Volume 2, pp. 9–23. [Google Scholar]
- Dlabola, J. Taxonomische und chorologische Ergänzungen der Zikadenfauna von Anatolien, Iran, Afghanistan und Pakistan (Homoptera, Auchenorrhyncha). Sb. Faun. Pr. Entomol. Odelini Nar. Mus. V Pr. 1971, 14, 115–138. [Google Scholar]
- Mitjaev, I.D. A new species and subspecies of leafhoppers (Homoptera, Cicadellidae) from North Kazakhstan. Inst. Zool. Acad. Sci. Kazakh SSR 1979, 58, 1738–1741. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, C.H.; Dmitriev, D.A.; Rakitov, R.A.; Takiya, D.M.; Webb, M.D.; Zahniser, J.N. Phylogeny of Cicadellidae (Hemiptera: Cicadomorpha: Membracoidea) based on morphological characters. In Proceedings of the 13th International Auchenorrhyncha Congress Abstracts, Vaison la Romain, France, 28 June–2 July 2010; pp. 48–49. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, R.K.; Dietrich, C.H.; Walden, K.K.O.; Gordon, E.; Sweet, A.D.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Petersen, M.; Simon, C.; Takiya, D.M.; Johnson, K.P. Phylogenomics of Auchenorrhyncha (Insecta: Hemiptera) using transcriptomes: Examining controversial relationships via degeneracy coding and interrogation of gene conflict. Syst. Entomol. 2019, 45, 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.L.; Dietrich, C.H.; Dai, W. Remarkable Species Diversity of the Leafhopper Genus Xestocephalus (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae: Aphrodinae) in Thailand. Insects 2021, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribaut, H. Homoptères Auchénorrhynques. II (Jassidae), Faune de France; Lechevalier: Paris, France, 1952; Volume 57, pp. 1–474. [Google Scholar]
- Goloboff, P.A.; Farris, J.S.; Nixon, K.C. TNT, a free program for phylogenetic analysis. Cladistics 2008, 24, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WinClada Ver. 1.00.08. Available online: http://www.cladistics.com/ (accessed on 10 August 2012).
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Harris, A.J.; Blair, C.; He, X.J. RASP (reconstruct ancestral state in phylogenies): A tool for historical biogeography. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 87, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahniser, J.N.; Dietrich, C.H. A review of the tribes of Deltocephalinae (Hemiptera: Auchenorrhyncha: Cicadellidae). Eur. J. Taxon. 2013, 45, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.H.; Allen, J.M.; Lemmon, A.R.; Lemmon, E.M.; Takiya, D.M.; Evangelista, O.; Walden, K.K.; Grady, P.G.; Johnson, K.P. Anchored hybrid enrichment-based phylogenomics of leafhoppers and treehoppers (Hemiptera: Cicadomorpha: Membracoidea). Insect Syst. Divers. 2017, 1, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.H.; Dmitriev, D.A.; Takiya, D.M.; Thomas, M.J.; Webb, M.D.; Zahniser, J.N.; Zhang, Y.L. Morphology-based phylogenetic analysis of Membracoidea (Hemiptera: Cicadomorpha) with placement of fossil taxa and description of a new subfamily. Insect Syst. Divers. 2022, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J. Acucephalus. Br. Entomol. 1836, 13, 620–621. [Google Scholar]
- Linnaeus, C., II. Hemiptera. In Systema Naturae: Per Regna Tria Naturae, Secundum Classes, Ordines, Genera, Species Cum Characteribus, Differentiis, Synonymis, Locis; Stock Holmiae: Salvii, Italia, 1758; Volume 1, pp. 1–824. [Google Scholar]
- Lethierry, L.F. Homoptères nouveaux d’Europe et des contrées voisines. Ann. De La Société Entomol. De Belg. 1876, 19, lxxvi–lxxxviii. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, C. Observations sur quelques Hémiptères-Homoptères et descriptions d’espèces nouvelles ou peu connues. Rev. D’entomologie Publiée Par La Société Française D’entomologie 1891, 10, 240–256. [Google Scholar]
- Logvinenko, V.N. New Forms of Leafhoppers from the Crimea. Dopovidi Akad. Nauk Ukrayins’ Koyi RSR (Ser. B) 1965, 11, 1526–1530, (In Ukrainian with English and Russian summaries). [Google Scholar]
- Kirschbaum, C.L. Die Cicadinen der gegend von Wiesbaden und Frankfurt A. M. nebst einer anzahl neuer oder Schwer zu unterscheidender Arten aus anderen Gegenden Europa’s Tabellarisch Beschrieben. Jahrbücher Des Ver. Für Nat. Im Herzogthum Nassau 1868, 21–22, 1–202. [Google Scholar]
- Signoret, V. Essai sur les Jassides Stål, Fieb. et plus particulièrement sur les Acocéphalides Puton. 1re partie. Ann. De La Société Entomol. De Fr. 1879, 9, 47–92. [Google Scholar]
- Logvinenko, V.N. Novyi vid tsikadki roda afrodes—Aphrodes (Auchenorrhyncha, Cicadellidae)—S Kavkoza. Vestn. Zool. 1967, 1, 69–71. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kato, M. Homoptera. Zoko Genshoku Nihon Konchu zukan. Kosei-Kaku 1933, 4, 1–9. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, T. A tentative check list of the superfamily Cicadelloidea of Japan (Homoptera). Scinetific Rep. Matsuyama Agric. Coll. 1953, 11, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Esaki, T.; Ito, S. A Tentative Catalogue of Jassoidea of Japan and Her Adjacent Territories; Japan Society for the Promotion of Science: Tokyo, Japna, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf, Z.P. General Catalogue of the Homoptera. Fascicle VI. Cicadelloidea. Part 8. Aphrodidae; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Nast, J. Palaearctic Auchenorrhyncha (Homoptera). In An Annotated Check List; Polish Scientific Publisher: Warszawa, Polish, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, T. Cicadelloidea. In Iconographia Insectorum Japonicorum; Hokuryukan Company: Tokyo, Japan, 1965; Volume 3, Chapter 116–128; pp. 58–64. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.E.; Kwon, Y.J. Studies on the spittlebugs, leafhoppers and planthoppers (Homoptera, Hemiptera, Auchenorrhyncha). Nat. Life 1977, 7, 55–111. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.E.; Kwon, Y.J. A check list of the Auchenorrhyncha from Korea (Homoptera). In Ilustrated Flora and Fauna of Korea, Insecta (VII); Ministry of Education: Seoul, Republic of Koera, 1979; Volume 23, pp. 799–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Puton, A. Homoptera Am. Serv. (Gulaerostria Zett. Fieb.) Sect. 1. Auchenorrhyncha Dumér. Cicadina Burm. Catalogue des Hémiptères (Hétéroptères, Cicadines et Psyllides) de la Faune Paléarctique, 3rd ed.; Imprimerie le Blanc-Hardel: Caen, France, 1886; pp. 3–100. [Google Scholar]
- Oshanin, V.T. Katalog der Paläarktischen Hemiptera (Heteroptera, Homoptera-Auchenorrhynche und Psylloideae); R. Friedländer & Sohn: Berlin, Germany, 1912; pp. 1–187. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, T. Aphrodesguttatus (Matsumura) (Cicadellidae) collected on Salidago altissima L. (Compositae). Rostria 1976, 26, 187. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.E. Illustrated Flora and Fauna of Korea, Insecta (VII); Ministry of Education: Seoul, Republic of Koera, 1979; Volume 23, pp. 1–1070. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, K. Hemiptera, (a) Homoptera. In A Check List of Japanese Insects; The Entomological Laboratory, Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, the Japan Wildlife Research Center: Fukuoka, Japan, 1989; Volume 1, pp. 82–151. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.I.; Kwon, Y.J.; Paek, J.C.; Lee, S.M.; Chu, H.Y. Homoptera (Order 21). In Check List of Insects from Korea. Entomological Society of Korea & Korean Society of Applied Entomology; Kon-Kuk University Press: Seoul, Republic of Koera, 1994; pp. 82–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kuoh, C.L. Homoptera: Cicadelloidea. In The Comprehensive Scientific Expedition to the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, Insects of Xizang; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1981; Volume 1, pp. 195–219. [Google Scholar]
- Kuoh, C.L. Homoptera: Cicadelloidea. In The Comprehensive Scientific Expedition to the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, Insects of the Hengduan Mountains Region; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1992; Volume 1, pp. 243–316. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, P.; Shen, X.C. Homoptera: Cicadellidae. In Insect of the Mountains Taihang and Tongbai Regions; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 269–279. [Google Scholar]
- De Geer, C. Cinquième mémoire. Des Cigales Mémoires Pour Serv. À L’histoire Des Insects 1773, 3, 1–696. [Google Scholar]
- Fabricius, J.C. Rhyngota. In Systema Entomologiae: Sistens Insectorum Classes, Ordines, Genera, Species, Adiectis Synonymis, Locis, Descriptionibus, Observationibus; Officina Libraria Kortii: Flensbvrgi et Lipsiae, Germany, 1775; pp. 1–816. [Google Scholar]
- Gmelin, J.F. Insecta Hemiptera. Caroli a Linné. In Systema Naturae per Regna Tria Naturae, Secundum Classes, Ordines, Genera, Species, Cum Characteribus, Differentiis, Synonymis, Locis; Impensis G. E. Beer: Lipsiae, Germany, 1789; Volume 1, pp. 1517–2224. [Google Scholar]
- Germar, E.F. Bemerkungen über einige Gattungen der Cicadarien. Mag. Der Entomol. 1821, 4, 1–106. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, J. A Guide to an Arrangement of British Insects: Being a Catalogue of All the Named Species Hitherto Discovered in Great Britain and Ireland; London, UK, 1829; pp. 1–256. Available online: https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/46860 (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Li, Z.Z.; Wang, L.M. Agricultural and Forestry Insect Fauna of Guizhou Vol. 4. Guizhou; Science and Technology Publishing House: Guiyang, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Herrich-Schäffer, G.A.W. Acucephalus Bifasciatus, Acucephalus Dispar, Jassus Abdominalis, Jassus Pallens, Jassus Cephalotes, Jassus Simplex, Jassus Proteus. Dtschl. Insecten 1834, 125, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.F. Order XV. Homoptera. Catalogus Insectorum Sinensium; Fan Memorial Institute of Biology: Beijing, China, 1935; Volume 2, pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Herrich-Schäffer, G.A.W. Homoptera. Nomenclator entomologicus: Verzeichniss der europäischen Insecten, zur Erleichterung des Tauschverkehrs mit Preisen versehen. Friedrich Pustet 1835, 1–4, 1–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zetterstedt, J.W. Famils. Perlariae Zatr. In Ordo III. Hemiptera, Insecta Lapponica Descripta; Lipsiae: Voss, Norway, 1840; Volume 1, Chapter i–vi; pp. 1–314. [Google Scholar]
- Amyot, C.J.B.; Audinet-Serville, J.G. Homoptères. Homoptera Latr. In Histoire Naturelle des Insectes, Hémiptères; Librairie Encyclopédique de Roret: Paris, France, 1843; pp. 1–676. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, T.A. An essay towards a knowledge of British Homoptera. Entomol. Mon. Mag. 1865, 2, 145–146. [Google Scholar]
- Fieber, F.X. Katalog der europäischen Cicadinen, nach Originalien mit Benützung der neuesten Literatur. Carl Gerold’s Sohn 1872, i–iv, 1–19. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Bachmetjew, P.I. Experimentelle entomologische Studien vom physikaliisich- chemischen Standpunkt aus. Temp. Bei Insekten 1901, 1, 1–944. [Google Scholar]
- Bierman, C.J.H. Cicadologische Aanteekeningen III. Entomol. Ber. 1907, 2, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmänner, B. Die Hemipterenfauna des Schweizerischen Nationalparkes (Heteropteren und Cicadinen). Denkschr. Der Schweiz. Nat. Ges. 1924, 60, 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Blöte, H.C. De nederlandsche Jassidae uit het Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie. Zool. Meded. 1927, 10, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.T. Preliminary study on leafhoppers and those disease transmitted by leafhoppers in Gansu Province (II). Gansu Agric. Sci. Technol. 1988, 29, 19–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lallemand, V. Revision des Cercopinae (Hemiptera Homoptera) Première partie. Mémoires De L’institut R. Des Sci. Nat. De Belg. 1949, 32, 1–193. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Nast, J. The Auchenorrhyncha (Homoptera) of Europe. Ann. Zool. Warszawa 1987, 40, 535–661. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L. A Taxonomic Study of Chinese Cicadellidae (Homoptera); Tianze Eldonejo: Yangling, China, 1990; pp. 1–218. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Eversmann, E.F. Insecta Wolgam fluvium inter et montes Uralenses observata, Rhynchota. Mémoires De La Société Impériale Des Amis Des Sci. Nat. 1837, 10, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yersin, A. Extraits d’une lettre addressée à M. L. Brisout sur les Orthoptères et quelques Hémiptères des environs d’Hyères en Provence. Ann. De La Société Entomol. De Fr. 1856, 4, 737–748. [Google Scholar]
- Kusnezov, V. Beitrag zur Kenntnis der transbaikalischen Homopteren fauna. Wien. Entomol. Ztg. 1929, 46, 157–185. [Google Scholar]
- Dubovsky, G.K. Cicadina (Auchnorrhyncha) of the Fergana Valley; IZDATELSTVO. FAN.: Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 1966. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mitjaev, I.D. New and little-known species of Cicadinae (Homoptera: Auchenorrhyncha) from East Kazakhstan. Entomologicheskoe 1967, 46, 712–723. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Koçak, A.Ö. Nomenclatural note on Homoptera. Priamus 1981, 1, 41. [Google Scholar]

| Species | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xestocephalus asper | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0 | 0 |
| Aphrodes bicinctus | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| Aphrodes diminuta | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| Anoscopus albiger | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 3 |
| Anoscopus serratulae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| Stroggylocephalus agrestis | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 0 |
| Stroggylocephalus livens | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 0 |
| Planaphrodes angulaticeps | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes araxicus | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes baoxingensis | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes bifasciatus | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 3 | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes elongatus | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ? | ? | 1 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | - | - | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes faciems | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes iranicus | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ? | ? | 1 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | - | - | 3 | 3 |
| Planaphrodes laevus | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | ? | ? | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | - | - | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes lusitanicus | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 2 | 4 | 2 | ? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | - | - | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes modicus | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ? | ? | ? | ? | 3 | ? | ? | ? | 2 | 4 | 2 | ? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes monticola | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes nigricans | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes nigritus | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes nisamiana | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ? | 1 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 2 | 4 | 2 | ? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | - | - | 3 | 3 |
| Planaphrodes sahlbergii | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | - | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| Planaphrodes vallicola | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 3 | ? | ? | ? | 2 | 4 | 2 | ? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 2 | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | 4 | 2 | - | 3 | 2 |
| Species Name | Aedeagus, Lateral View | Aedeagus, Caudal View | Style | Species Name | Aedeagus, Lateral View | Aedeagus, Caudal Views | Style |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| angulaticeps | 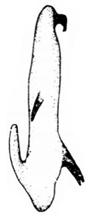 | 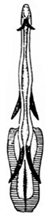 | 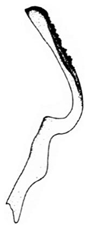 | araxicus |  |  | |
| baoxingensis |  |  | 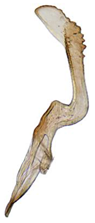 | bifasciatus | 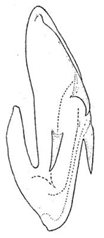 | 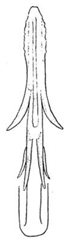 | |
| elongatus |  |  | faciems |  |  |  | |
| iranicus | 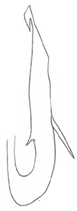 |  | laevus |  |  |  | |
| lusitanicus | 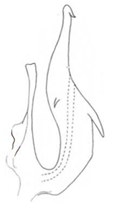 |  | 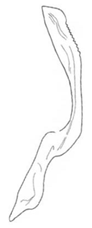 | modicus |  | 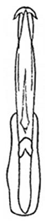 | 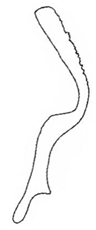 |
| monticola |  | 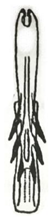 | 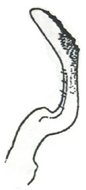 | nigricans |  |  |  |
| nigritus | 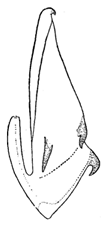 | 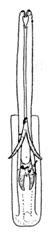 | nisamiana | 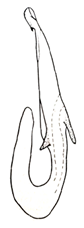 |  | 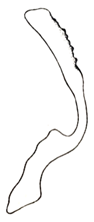 | |
| sahlbergii |  |  |  | vallicola | 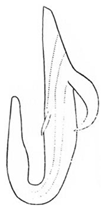 | 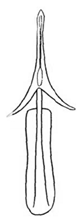 | 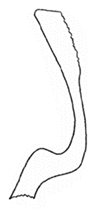 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Z.; Kwon, J.-H.; Hayashi, M.; Dietrich, C.H.; Dai, W. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Genus Planaphrodes Hamilton (Hemiptera, Cicadellidae, Aphrodinae) Based on Morphological Characteristics, with Revision of Species from China, Korea and Japan. Insects 2023, 14, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14030291
Liang Z, Kwon J-H, Hayashi M, Dietrich CH, Dai W. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Genus Planaphrodes Hamilton (Hemiptera, Cicadellidae, Aphrodinae) Based on Morphological Characteristics, with Revision of Species from China, Korea and Japan. Insects. 2023; 14(3):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14030291
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Zonglei, Jin-Hyung Kwon, Masami Hayashi, Christopher H. Dietrich, and Wu Dai. 2023. "Phylogenetic Analysis of the Genus Planaphrodes Hamilton (Hemiptera, Cicadellidae, Aphrodinae) Based on Morphological Characteristics, with Revision of Species from China, Korea and Japan" Insects 14, no. 3: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14030291
APA StyleLiang, Z., Kwon, J.-H., Hayashi, M., Dietrich, C. H., & Dai, W. (2023). Phylogenetic Analysis of the Genus Planaphrodes Hamilton (Hemiptera, Cicadellidae, Aphrodinae) Based on Morphological Characteristics, with Revision of Species from China, Korea and Japan. Insects, 14(3), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14030291






