Simple Summary
The patterns and causes of biodiversity variations along environmental gradients are hot topics for ecologists and biogeographers. Leaf miners are the specific insect guild that feed and live inside plant leaves. Although altitudinal diversity trends have been studied for many insect groups, few scientists have focused on the elevational diversity pattern of leaf-mining insects. To the best of our knowledge, there are no reports on the elevational distribution of leaf miners in China. Moreover, all previous work on the elevational change of leaf miners only focused on their abundance or species richness, without further analyses on their diversity indices, especially on phylogenetic diversity and functional diversity. The diversity of the leaf-mining insects on one dominant oak species in Central China was thus investigated through Hill numbers. The oak species hosted rich leaf miner species, and different leaf miners showed different elevational preferences. Most diversity metrics of leaf miners generally followed hump-shaped mid-peak elevational patterns.
Abstract
The species composition and diversity pattern of leaf miners on dominant trees in China are poorly understood. Using Hill-based diversity metrics, the elevational patterns of taxonomic, phylogenetic, and functional diversity for leaf miners on Quercus variabilis Blume at Baotianman were systematically analyzed. Leaf mine types belonged to ten genera and seven families. Different leaf miners had different elevational preferences. Most taxonomic and phylogenetic Hill diversity indices had typical hump-shaped elevational patterns, with a peak at the middle elevation of approximately 875 m. No functional Hill diversity indices presented significant linear or nonlinear trends with altitude. The driving factors behind the elevational distribution patterns of leaf miners require further work.
1. Introduction
The patterns and causes of biodiversity variations along environmental gradients are hot topics in ecology and biogeography [1,2,3,4]. The elevation gradient includes the gradient effects of various environmental factors, such as temperature, moisture, and light [5]. Therefore, studying elevational biodiversity change is essential for exploring the influencing factors behind biodiversity-environmental gradient relationships [3,6]. For host-specific herbivorous insects, their elevational distribution is also affected by their host plants’ elevational distribution [7,8,9,10]. The diversity of most herbivorous insects shows the following elevational patterns: (1) diversity peaks at lower elevations; (2) diversity peaks at middle elevations; (3) diversity peaks at higher elevations; and (4) diversity has no apparent relationship with elevation [10,11,12,13,14]. In the current research on the elevational patterns of herbivorous insects, exophagous insects are relatively well studied, while endophagous insect research is mainly concentrated on wood-boring insects and gall-forming insects [7,15,16].
Leaf-mining insects are another important endophagous group. They feed and live inside host plant leaves during either young or whole larval stages [17,18,19,20,21]. More than 10,000 leaf-mining species are found in approximately 50 families belonging to the four largest orders of Insecta: Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Diptera, and Hymenoptera [21]. However, the number of leaf-mining species is far higher than what is currently known [21]. The feeding trails of leaf miners are known as leaf mines [21]. The mine characteristics are usually family- or genus-specific [22], which are valuable clues for insect identification. The mines can remain on the leaves for a long time, and some mine traces are kept in fossil leaves. According to leaf mines, both ecologists and paleontologists can reconstruct the feeding habits, life history, and interspecific relationships of leaf-mining insects [23,24,25,26,27,28]. Moreover, most leaf-mining insects are monophagous or oligophagous, with high host specificity [28,29]. Therefore, leaf-mining insects can be used as model organisms to study species interactions, coevolution, and environmental adaptation [30,31,32,33].
There are fewer studies focusing on the elevational distribution of leaf-mining insects, most of which are on the population density of a single species, usually an important pest [34,35,36]. Diversity at the community level is rarely analyzed for leaf-mining insects at different elevations [37,38]. Leaf-mining insects are sensitive to environmental changes, and how elevation affects the distribution of leaf-mining insect communities is poorly understood [37,38]. Elevational variation in climatic factors [34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43], plant characteristics [37,38,41,42,43,44,45,46], natural enemies [36,42,43], and human activities [35], may contribute differently to the elevational distribution of leaf miners. Furthermore, some factors have been implicated as the underlying causes of elevational diversity [12], such as source-sink dynamics [47] and evolutionary history [48], which may also affect the distribution of leaf-mining insects.
Fagaceae plants are widely distributed, consisting of 900–1000 species in 7–12 genera [49]. Many Fagaceae plants are the dominant species in forest communities in the Northern Hemisphere, covering tropical, subtropical, and temperate climate zones [50]. According to the ‘plant apparency hypothesis’, such dominant plants are susceptible targets to leaf-mining insects [51,52,53]. For instance, Quercus robur hosts 36 leaf-mining species in the UK [54]; Q. crispula hosts over 12 leaf-mining species and Q. dentata hosts 9 species in Japan [55,56,57]; Q. falcata hosts 18 species, Q. nigra hosts 17 species and Q. hemisphaerica hosts 15 species in northern Florida; and oaks host 15 genera and nine families of leaf miners, while a single oak species can have 2 to 18 leaf miners in California [58]. To date, more than 400 leaf-mining insects have been globally discovered on Fagaceae plants, and they cover nearly all the typical leaf-mining families (Xiaohua Dai et al., unpublished data).
Chinese cork oak (Q. variabilis) is one of the most extensively distributed deciduous broad-leaved tree species in East Asia [59,60]. Its distribution latitude is from 22° to 42° N, and its continuous distribution range is from 24.43° to 40.25° N, covering the southern subtropical, central subtropical, northern subtropical, warm temperate, and medium temperate zones [61,62]. The vertical distribution of Q. variabilis is from 50 m to 3000 m [60]. Similar to other Fagaceae plants, leaf-mining insects are diverse on Q. variabilis [63].
To the best of our knowledge, there are no reports on the elevational distribution of leaf miners in China. Moreover, all previous work on the elevational change of leaf miners only involved their abundance or species richness, without further analyses on their diversity indices, especially on phylogenetic diversity and functional diversity. In our study, we used Q. variabilis as an example to explore the relationships between elevation and the following: (i) the abundance of different leaf miners; (ii) the taxonomic diversity of leaf miners; (iii) the phylogenetic diversity of leaf miners; and (iv) the functional diversity of leaf miners. We intended to answer the following questions: (i) Are the elevational patterns of leaf-mining insects the same as those of other herbivorous insects? (ii) Do their elevational distributions fit the “mid domain model”, “monotonic decreasing model”, or “monotonic increasing model”? (iii) Do different diversity metrics respond differently to elevation?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
Baotianman (33°20′~33°36′ N, 111°47′~112°04′ E, 500~1845 m a.s.l) is located in Neixiang County in southwestern Henan Province, Central China (Figure 1). It is at the southern slope of the Funiu Mountains in the eastern extension of the Qinling Mountains (the natural boundary between South and North China) [64]. It has a continental monsoon climate with four distinct seasons [64], with an average annual temperature of 15.1 °C, an average annual precipitation of approximately 900 mm, an average annual evaporation of 991.6 mm, and an average annual relative humidity of 68% [65,66,67,68]. The climate is between the northern subtropical and warm temperate zones [64,69]. The corresponding vegetation transitions from deciduous broadleaf forest to evergreen broad-leaved forest [70]. Baotianman National Nature Reserve has rich species, with 223 families, 1002 genera, 2771 species of plants, and over 1700 species of animals, including 1500 species of insects [71]. Q. variabilis is one of the primary constructive and dominant species in Baotianman and the surrounding areas [64,67,68,72,73].
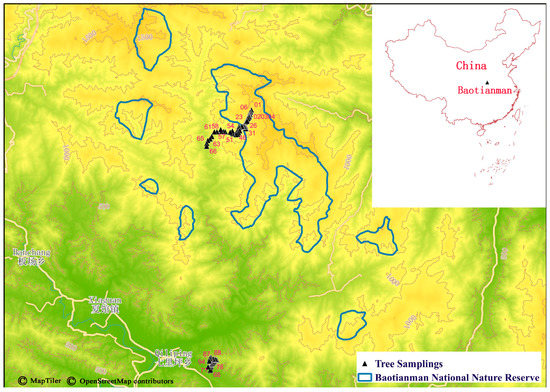
Figure 1.
Sampling areas of leaf mines on Quercus variabilis Blume at Baotianman, Henan. The numbers in pink indicate the order of tree samplings. The reserve boundary was provided by Baotianman National Nature Reserve Administrative Bureau. The map was constructed using QGIS 3.26.3 [74]. QGIS MapTiler Plugin can obtain OpenStreetMap data from the OpenMapTiles project (openstreetmap.org). The base maps, terrain, and contours for this plugin are available from the MapTiler Cloud under the Open Database License.
2.2. Sampling of Leaves with Mines
In September 2020, according to the known distribution areas of Q. variabilis and the map information (Figure 1), we set up two transects from 300 to 1350 m a.s.l at Baotianman, i.e., Baotianman Scenic Area (600 m–1350 m) and Houyemiao, Qiliping County (300 m–600 m). Part of the first transect was inside the experimental zone of Baotianman National Nature Reserve. The two transects form a continuous elevation gradient (Figure S1). First, we tried to find some flat plots at certain altitudes to perform the investigation. However, the slopes are very steep in the Baotianman Scenic Area, and the highway is meandering. Q. variabilis trees are scattered along the highway, especially in regions of human disturbance. Therefore, we walked on the highway from the mountain top to the mountain foot to sample leaves with mines present from nearly all accessible Q. variabilis trees. The distances between two neighboring sampled trees were relatively even (mean ± SD: 111 ± 111 m, with a range of 0–561 m, SD: mean = 1 indicating an even distribution), although we did not plan it that way. There are almost no Q. variabilis trees along the highway in the valley area due to high human disturbance. Therefore, we have to set up another low-altitude transect at Houyemiao. At the Houyemiao transect, Q. variabilis trees are also scattered except on the mountain top. Therefore, we also tried to sample the trees evenly along the mountain road at Houyemiao (distance between two sampled neighbors, mean ± SD: 79 ± 64 m, with a range of 9–221 m, SD: mean = 0.81 indicating a nearly even distribution). We carried out continuous sampling along the whole elevational range from 300 m to 1350 m.
Most sampled Q. variabilis trees were saplings (tree height between 2 and 3 m), so we collected all leaves with leaf mines from the whole saplings. For some adult trees (tree height > 3 m), we collected all mined leaves from only accessible branches (branch height to the ground < 3 m, analogous to one tree sapling) without using additional long-reach pruning tools. The sampled trees were labeled consecutively as 01, 02, 03… 92, 93, 94 (Table S1). Occasionally, there were two or three trees located in the same place, and we only kept one tree with the richest leaf mines. However, we also analyzed the mining diversity pattern with or without the removal of tree samplings at the same location, and the results were almost the same. The location and elevation of each tree sample was measured and recorded with the Aowei Interactive Map app and a Garmin GPS device. Leaf samples with leaf mines were placed in plastic self-sealable bags, and each bag was blown with the appropriate gas to ensure the freshness of the sampled leaves.
2.3. Leaf Mine Classification
Due to long-term coevolution and interspecific differentiation, leaf miners have formed various mine forms, reflected in the feeding parts and mine shape [17,18,24,75]. For example, different leaf-mining larvae may feed on different vertical leaf parts and make leaf mines of various depths [18,76], including upper-surface mines in the palisade mesophyll [77], lower-surface mines in the sponge mesophyll [78], epidermal mines in the epidermis [79], and full-depth mines consuming both palisade and spongy mesophyll tissues [21]. Leaf mine shapes can be divided into three main categories: linear mines, blotch mines, and linear blotch mines [18]. Linear mines are caused by the consistent one-directional feeding of leaf-mining larvae; blotch mines are made when larvae feed in multiple directions; and linear blotch mines are transitional types between linear mines and blotch mines [18].
Based on the above and other leaf mine characteristics (Table S2) of known insect inducers from publications, websites, and our previous rearing records, the corresponding leaf-mining insect groups in our collections were preliminarily identified. Then, we consulted leaf miner experts (see Acknowledgments for names and institutes) to verify the identification. By far, we could only identify the leaf mine to the genus level. Ten leaf mine types and their related genera of leaf-mining insects on Q. variabilis at Baotianman were then obtained: LM01 (Acrocercops), LM03 (Caloptilia), LM05 (Dactylispa), LM06 (Ectoedemia), LM08 (Phyllonorycter), LM10 (Stigmella), LM11 (Tischeria), LM12 (Trachys), LM15 (Chrysopeleia), and LM19 (Profenusa) (Table S3). Sample leaves with the same leaf mine type were scanned together with an EPSON 10000XL, and the scanned images were saved.
2.4. Leaf Mine Area Measurement
Twenty leaves with one complete mine image were selected for each leaf mine type, and the mining part was filled in red (or a color that differed markedly from the healthy part of the leaf), while the other leaf part was filled in green with Adobe Photoshop 2021 (CS5.1). The processed pictures were then imported into WinFolia 2016b Pro (Regent Instruments Canada Inc., Quebec City, QC, Canada). Setting green as the healthy color, red as the mine color, and white as the background color, the area of the mining part for each mine type could be calculated from the leaf area and health rate: leaf mine area = leaf area ∗ (1 − health rate). The area of each leaf mine type was the average value of twenty leaves (Table S2). For the leaf mine type without twenty leaf samples in this investigation, we use additional Q. variabilis leaf samples with the corresponding mine type in other years.
2.5. Data Analysis
2.5.1. Taxonomic Hill Diversity of Leaf Mines
Based on the number of each leaf mine type on each Q. variabilis tree (Table S1), the following taxonomic Hill diversity indices of leaf mines were calculated for each tree individual with the “hillR” R package [80]. The taxonomic Hill numbers through different orders (q values) have different meanings: (1) q = 0, species richness and it reflects the diversity of all species; (2) q = 1, Shannon entropy index and it reflects the diversity of common species; and (3) q = 2, inverse Simpson’ dominant index and it reflects the diversity of dominant species [80,81,82].
2.5.2. Phylogenetic Hill Diversity of Leaf Mines
The taxonomic status (~Order/Superfamily/Family/Genus) of the leaf-mining insect groups on each leaf mine type (Table S3) was used to obtain the phylogenetic tree (Figure S2) using the ‘as.phylo.formula’ function of the “ape” R package [83]. The following phylogenetic Hill numbers of leaf mines were then computed for each tree individual by the “hillR” R package [80]. The phylogenetic Hill numbers through different orders (q values) are also closely related to different phylogenetic diversity indices: (1) q = 0, the phylogenetic Hill number is related to Faith’s phylogenetic diversity; (2) q = 1, the phylogenetic Hill number is related to Allen’s phylogenetic entropy; and (3) q = 2, the phylogenetic Hill number is related to Rao’s quadratic entropy [82,84,85,86].
2.5.3. Functional Hill Diversity of Leaf Mines
Based on the functional characteristics of each leaf mine type (Table S2), the trait-clustering dendrogram among different leaf mine types was constructed by “FD” R package [87,88] (Figure S3). The following functional Hill numbers through different orders (q values) of leaf mines were then calculated for each tree individual by the “hillR” R package [80]: (1) q = 0, FAD (functional attribute diversity); (2) q = 1, the related functional diversity index is still unclear; and (3) q = 2, the function Hill number is related to Rao’s quadratic entropy and weighted Gini–Simpson’s index [82,89,90,91]
2.5.4. Elevational Diversity Pattern
A piecewise model is a regression model used to clarify whether the relationship between one or more explanatory variables is piecewise linear [92]. The value corresponding to the turning point in the piecewise fitting process is the break point [93]. The “segmented” R package provides tools for estimating and summarizing generalized linear models with piecewise relationships, and there are no restrictions on the number of segmented variables and the number of change points [93]. Regression splines are used to estimate break points (knots in spline terminology) when the sample point interval is known [93], and splines with a single break point can be useful statistical tools for modeling linear predictors in generalized linear models [94]. In addition, there are four other ways to evaluate break points [92]. The piecewise model is especially appropriate for our consecutive samplings along the elevational gradient.
The relationship between each Hill diversity index and the corresponding elevation of each sampled tree was fitted with the piecewise linear model. When the piecewise relationship was not significant (p > 0.1), the simple linear model was alternatively used for the fitting. All fittings were run with the “segmented” R package [92,93,95,96]. In some cases, nonlinear regressions might be more appropriate to fit the above relationships. The nonlinear fitting results with a number of models, such as linear, quadratic, power, exponential, Von Bertalanffy, Michaelis–Menten, logistic, Gompertz, Gaussian, and Hill, were quickly checked with the Past software [97] and appropriate models were selected according to the curves, AIC values and R-squared values.
2.5.5. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
The presence of spatial autocorrelation in geospatial data might make non-significant regression relationships show false significant results [98,99,100,101]. Therefore, potential spatial autocorrelation in the elevational distribution of leaf mine diversity indices should be considered. The latitude and longitude of each sample tree were converted to the planar XY position (unit: m) using the “PBSmapping” R package [102]. Based on the planar coordinates of each tree, the ‘modifiedttest’ function in the “SpatialPack” R package [103] was used to assess the spatial autocorrelation between taxonomic, phylogenetic, or functional Hill numbers and elevation. The modified t test corrects the Pearson’s correlation for spatial autocorrelation based on Dutilleul’s method [104,105]. The ‘modifiedttest’ function also provides Moran’s index for both spatial variables [103].
2.5.6. Community Similarity Analysis
The community similarity index of leaf mine types and elevation differences between each tree pair (j, k) were calculated and output as matrices using Past 4.11 [97]. Community similarity was measured as the Bray-Curtis index (djk) as follows: where xmn is the abundance of leaf mine type n on tree m. The lower triangular portion of each matrix was extracted using the “gdata” R package [106]. The relationship between the community similarity index and elevation differences was then fitted with the simple linear model.
The above taxonomic diversity, phylogenetic diversity, and functional diversity analyses, model fitting and community similarity analyses were carried out with R 4.2.1 [107] in the graphic interface of RStudio [108].
3. Results
3.1. Number of Leaf Mine Types at Different Transects
In total, there were 3713 leaf mines and ten leaf mine types (i.e., ten leaf-mining genera) on 89 individuals of Q. variabilis at Baotianman along an elevational gradient from 300 m to 1350 m (Table 1, Tables S4 and S5). The number of leaf mine types per tree was mean ± SD: 4.6 ± 1.2. The maximum number of leaf mine types per tree was seven, while the minimum number of leaf mine types per tree was one. Phyllonorycter was present in nearly all sampled trees (88/89). In the Baotianman Scenic Area (600–1350 m a.s.l), there were a total of nine leaf mine types, without Dactylispa. The number of leaf mine types per tree was mean ± SD: 4.5 ± 1.1. At Houyemiao, Qiliping County (300–600 m a.s.l), there were a total of nine leaf mine types, without Caloptilia. The number of leaf mine types per tree was mean ± SD: 4.6 ± 1.4. There were no significant differences between the mean number of leaf mine types per tree among the two transects (t = 0.773, p = 0.442 > 0.05).

Table 1.
Detailed information of the two transects for leaf mine sampling on Quercus variabilis at Baotianman.
3.2. Elevational Pattern of Mine Numbers
Within the elevational range from 300 m to 1350 m, the total number of leaf mines on Q. variabilis had no apparent elevational pattern (p > 0.1). However, the individual numbers of different leaf mine types presented different elevational patterns. The numbers of Ectoedemia and Stigmella mines significantly decreased with elevation (piecewise model: PEctoedemia = 0.021 < 0.05, PStigmella = 0.057 < 0.1) (Figure 2). For Ectoedemia, the piecewise model was better than the nonlinear quadratic model (AICpiecewise: 363 < AICquadratic: 481). The number of Chrysopeleia mines significantly increased with elevation (PChrysopeleia = 0.015 < 0.05) (Figure 3). The number of Phyllonorycter mines had a minimum value at middle elevations of 786 m (PPhyllonorycter = 0.029 < 0.05) (Figure 3). In contrast, the numbers of Acrocercops, Tischeria, and Profenusa mines had no apparent elevational patterns (p > 0.1). The rare leaf mine types Caloptilia and Dactylispa occasionally existed in high- and low-elevation areas, respectively, while Trachys was more common at low altitudes.
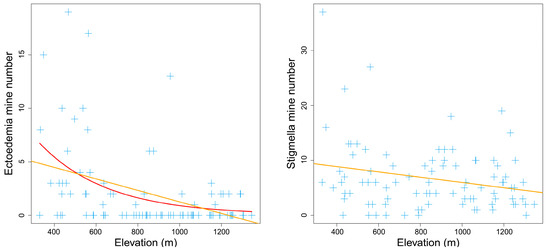
Figure 2.
Elevation decreasing pattern of mine numbers on Quercus variabilis Blume. The orange line was fitted with the piecewise linear model, while the red line was fitted with the nonlinear quadratic model.
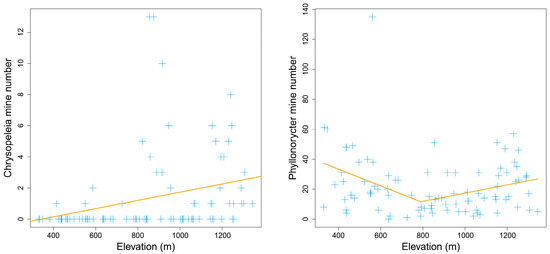
Figure 3.
Elevation increasing and V-shaped pattern of mine numbers on Quercus variabilis Blume. The orange line was fitted with the piecewise linear model.
3.3. Elevational Pattern of Taxonomic Hill Diversity
There was no significant spatial autocorrelation between any taxonomic Hill numbers and elevation (q = 0: F = 0.0085, DF = 175.4, p = 0.927 > 0.1; q = 1: F = 0.0186, DF = 31.3, p = 0.893 > 0.1; q = 2: F = 0.0203, DF = 19.6, p = 0.888 > 0.1). Most Moran’s indices of each taxonomic Hill number were generally around 0, indicating unapparent spatial autocorrelation of taxonomic Hill diversity (Table S6).
Both the piecewise model and the nonlinear model showed that most taxonomic Hill numbers peaked at the middle elevation of about 900 m (Figure 4). For Shannon entropy index (q = 1), the piecewise model was better than the nonlinear quadratic model (AICpiecewise: 224 < AICquadratic: 227). For inverse Simpson’ dominant index (q = 2), the piecewise model was also better than the nonlinear quadratic model (AICpiecewise: 210 < AICquadratic: 215).
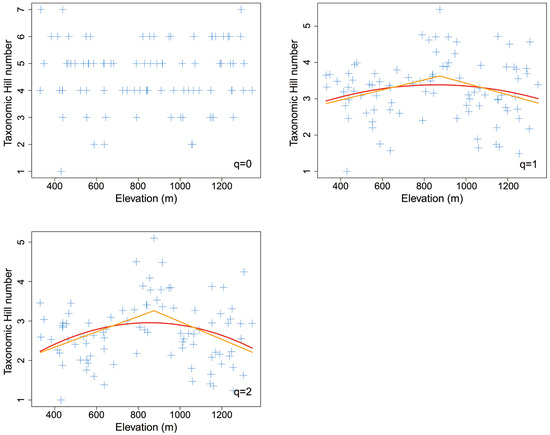
Figure 4.
The elevational pattern of taxonomic Hill numbers for leaf mines on Quercus variabilis Blume. The orange line was fitted with the piecewise linear model, while the red line was fitted with the nonlinear quadratic model.
Piecewise linear models indicated that both Shannon entropy index (q = 1) and inverse Simpson’ dominant index (q = 2) peaked at the middle elevation of 875 m, showing significant hump-shaped elevational patterns (p < 0.1) (Table 2). In contrast, taxonomic species richness (q = 0) did not show apparent elevational patterns (p > 0.1) (Figure 4).

Table 2.
Piecewise linear relationships between leaf mine diversity and elevation.
3.4. Elevational Pattern of Phylogenetic Hill Diversity
There was no significant spatial autocorrelation between any phylogenetic Hill numbers and elevation (q = 0: F = 0.612, DF = 53.8, p = 0.438 > 0.1; q = 1: F = 0.268, DF = 14.0, p = 0.613 > 0.1; q = 2: F = 0.185, DF = 12.1, p = 0.675 > 0.1). Most Moran’s indices of each phylogenetic Hill number were generally around 0, indicating unapparent spatial autocorrelation of phylogenetic Hill diversity (Table S6).
Both the piecewise model and the nonlinear model showed that most phylogenetic Hill numbers reached a maximum at the middle elevation of about 900 m (Figure 5). For Allen’s phylogenetic entropy (q = 1), the piecewise model was better than the nonlinear quadratic model (AICpiecewise: 396 < AICquadratic: 401). For Rao’s quadratic entropy (q = 2), the piecewise model was also better than the nonlinear quadratic model (AICpiecewise: 363 < AICquadratic: 372).
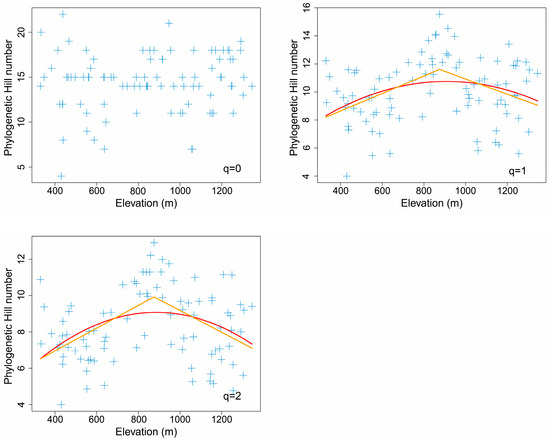
Figure 5.
The elevational pattern of phylogenetic Hill numbers for leaf mines on Quercus variabilis Blume. The orange line was fitted with the piecewise linear model, while the red line was fitted with the nonlinear quadratic model.
Piecewise linear models indicated that both Allen’s phylogenetic entropy (q = 1) and Rao’s quadratic entropy (q = 2) peaked at the middle elevation of 875 m, showing significant hump-shaped elevational patterns (p < 0.1) (Table 2). In contrast, Faith’s phylogenetic diversity (q = 0) did not show apparent elevational patterns (p > 0.1) (Figure 5).
3.5. Elevational Pattern of Functional Hill Diversity
There was no significant spatial autocorrelation between any functional Hill numbers and elevation (q = 0: F = 0.100, DF = 145.5, p = 0.752 > 0.1; q = 1: F = 0.493, DF = 40.4, p = 0.487 > 0.1; q = 2: F = 0.518, DF = 27.6, p = 0.478 > 0.1). Most Moran’s indices of each functional Hill number were generally around 0, indicating unapparent spatial autocorrelation of functional Hill diversity (Table S6). No functional Hill diversity indices showed significant linear or nonlinear trends with elevation (p > 0.1, Table 2, Figure 6).
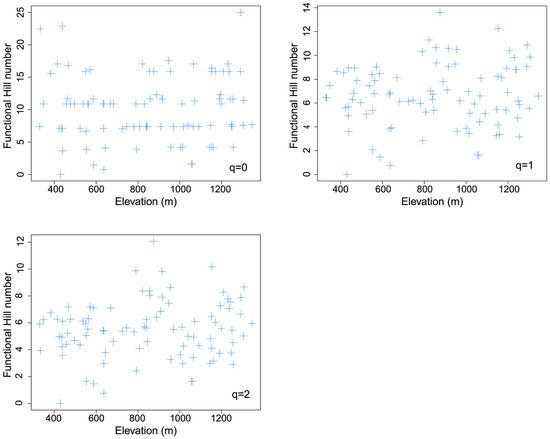
Figure 6.
The elevational pattern of different total functional diversity indices for leaf mines on Quercus variabilis Blume.
3.6. Relationship between Leaf Mine Community Similarity and Elevation Difference
The similarity of leaf mine communities on Q. variabilis at Baotianman showed no apparent relationship with elevation difference (p > 0.1).
4. Discussion
Seven families and ten genera of leaf-mining insects were collected in this study (Table 1 and Table S3), including Acrocercops (Gracillariidae), Caloptilia (Gracillariidae), Dactylispa (Chrysomelidae), Ectoedemia (Nepticulidae), Phyllonorycter (Gracillariidae), Stigmella (Nepticulidae), Tischeria (Tischeriidae), Trachys (Buprestidae), Stilbosis (Cosmopterigidae), and Profenusa (Tenthredinidae), which have been discovered on Q. variabilis at Baotianman, supporting the hypothesis that dominant plants should have rich leaf miners [51].
The abundance and diversity along the elevational gradient varied for different animal groups. There were nine elevational diversity modes for birds, including increasing, decreasing, mid-peak, mid-valley, low-plateau, low-valley, high-plateau, high-valley, and nonsignificant modes [1,109]. Mid-peak is the dominant elevational diversity mode for nonflying small mammals [110,111]. Decreasing and mid-peak are the two main elevational diversity trends for bats [111]. Decreasing is the dominant elevational diversity trend for reptiles [111,112]. The elevational diversity patterns of geometrid moths could have decreased, mid-peak, and other complicated shapes [113]. Without regard to the specific leaf-mining species, the total number of leaf mines on Q. variabilis at Baotianman had no apparent elevational patterns, but the number of leaf mines on Nothofagus pumilio was negatively correlated with elevation [46]. With the increase in elevation difference, the similarity of the leaf miner community on Q. variabilis at Baotianman also showed no apparent pattern.
Different leaf-mining insect groups on Q. variabilis at Baotianman had different elevation preferences, and their abundance also reflected different altitudinal distribution patterns. The abundance of Ectoedemia and Stigmella had a peak at low elevations and decreased with increasing elevation. Similarly, the populations of Leucopteru coffeellu were larger at low elevations [36,42]. Both Liriomyza sativae and L. trifolli were more abundant in mid-low elevational domains [39]. The distributions of Coptodisca lucifluella and Phytomyza ilicis were also negatively correlated with elevation [34,43]. In contrast, the individual numbers of L. huidobrensis, Caloptilia bryonoma, Lyonetia lechrioscia and one unidentified leaf miner on Doryphora sassafras were predominant at high altitudes [37,39,40], such as Chrysopeleia in our study. The presence of Tuta absoluta and Platynotocis angulipennis showed no altitudinal trends [37,44], similar to Acrocercops, Tischeria, and Profenusa in our study. The abundance of Phyllonorycter was lowest at middle altitudes. Such a mid-valley pattern is not typical in leaf-mining insects.
Different leaf miners may have different ecological niches and perform differently under different environmental conditions. For example, some leaf-mining species only survive, develop, or reproduce in cooler places, while others adapt to warmer places, which may explain their differences in elevational distribution [34,38,40,42]. Precipitation at different altitudes may affect the population load of leaf miners [38,42,43]. Different climatic factors could also interact to change the altitudinal pattern of leaf miners [38]. The quantity and quality of plants and the pressure of natural enemies may alter the elevational pattern of leaf miners [38,42,43]. Climates can have indirect impacts on leaf miners through their effects on host plants and natural enemies at different elevations [38,42,43]. However, some leaf miners are highly adaptative and can expand their elevational range [39,44]. Human management could also alter leaf miners’ elevational distribution pattern [35,44]. In addition, the same leaf miner may show different shapes of elevational distribution curves in different places, especially when the elevational ranges are very different [36,42].
The taxonomic species richness of leaf-mining insects may decrease with altitude [38] or have no altitudinal trends [37,38]. In our study, the species richness (q = 0) of leaf miners on Q. variabilis did not vary significantly with elevation, but the Shannon entropy index (q = 1) and the inverse Simpson dominant index (q = 2) showed mid-peak distribution patterns. Such hump-shaped trends are common in invertebrates [114,115,116] and vertebrates [11,110,111,117,118].
The Faith’s phylogenetic diversity (q = 0) of leaf miners on Q. variabilis at Baotianman also did not vary significantly with elevation. However, all other phylogenetic Hill numbers (q = 1 and q = 2) of leaf mines peaked at middle elevations, similar to the results of some plants but different from many other animals. At the global scale, the Faith’s phylogenetic diversity of birds along elevation gradients is dominated by a low-plateau pattern, while the MPD (mean phylogenetic distance) of birds along elevation gradients is dominated by low-plateau pattern, mid-peak pattern, and high-valley pattern [109]. However, both sesPD (standardized effect size of Faith’s phylogenetic diversity) and sesMPD (standardized effect size of mean phylogenetic distance) of birds generally increased with increasing elevation [109]. In a temperate mountain forest in China, both the sesMPD and the Faith’s phylogenetic diversity of moths increased with increasing elevation [113].
None of the functional Hill numbers of leaf miners on Q. variabilis at Baotianman changed significantly with altitude. In contrast, the FRic (functional richness) and FDis (functional dispersion) of birds along elevational gradients were dominated by mid-peak and low-plateau patterns [109]. Both sesFRic (standardized effect size of functional richness) and sesFDis (standardized effect size of functional dispersion) of birds generally increased with increasing elevation [109].
Different components (taxonomic, phylogenetic or functional) of leaf mine diversity did not respond to the elevational gradient consistently. Such inconsistent patterns are also found in some previous biodiversity studies [119].
In conclusion, different leaf-mining insect groups might adapt to different elevational ranges, and the hump-shaped distribution pattern was typical in leaf-mine diversity along the elevational gradient. By far, we could identify the leaf mine to only the genus level. In the future, we will try to rear the leaf-mining insects and identify them with DNA barcodes. We can also further connect the distribution of leaf mine diversity with the variation in ecological factors and plant traits along the elevational gradient. Therefore, we can better understand the patterns and mechanisms of biodiversity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/insects14010007/s1, Figure S1: Sampling trees of leaf mines on Quercus variabilis Blume at Baotianman, Henan. Figure S2: Phylogenetic tree of leaf-mining insects on Quercus variabilis Blume. Figure S3: Clustering dendrogram of leaf-mining insects on Quercus variabilis Blume based on functional traits. Table S1: Number of different mine types on Quercus variabilis Blume at different elevations. Table S2: Functional characteristics of different leaf mine types on Quercus variabilis Blume. Table S3: Taxonomic status of different leaf mine types on Quercus variabilis Blume. Table S4: Number of leaf miner genera on Quercus variabilis Blume at different altitudes in the Baotianman Scenic Area. Table S5: Number of leaf miner genera on Quercus variabilis Blume at different altitudes at Houyemiao, Qiliping County. Table S6 Moran’s index output from the ‘modifiedttest’ function in the “SpatialPack” R package.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.D.; data curation, X.C., X.D. and X.L.; formal analysis, X.C., M.Z., L.C., J.X. and X.D.; funding acquisition, J.X., X.D.; investigation, L.C., X.D. and X.L.; methodology, X.C., X.D.; project administration, X.D.; resources, X.D., X.L.; software, X.C., X.D.; supervision, X.D.; validation, X.C., M.Z., L.C., J.X. and X.D.; visualization, X.C., X.D.; writing—original draft, X.C.; writing—review and editing, X.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41971059, 32260282, and 31760173).
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting this study’s findings are available in the Supplementary Materials. The R codes are available on request from the corresponding author, X.D.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Charley Eiseman (Northfield, MA, USA), Lukáš Sekerka (National Museum, Prague, Czech Republic), Jonas Rimantas Stonis (State Research Institute Nature Research Centre, Vilnius, Lithuania), Willem N. Ellis (Amsterdam, The Netherlands), and Erik J. van Nieukerken (Naturalis Biodiversity Center, Leiden, The Netherlands) for their kind help with leaf mine identification.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- McCain, C.M. Global analysis of bird elevational diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodkinson, I.D. Terrestrial insects along elevation gradients: Species and community responses to altitude. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2005, 80, 489–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.-Y.; Tang, Z.-Y. A review on the elevational patterns of plant species diversity. Biodivers. Sci. 2004, 12, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, S.M.D. Elevational diversity patterns of small mammals on Mount Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2001, 10, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, K.J. Global patterns in biodiversity. Nature 2000, 405, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coince, A.; Cordier, T.; Lengelle, J.; Defossez, E.; Vacher, C.; Robin, C.; Buee, M.; Marcais, B. Leaf and root-associated fungal assemblages do not follow similar elevational diversity patterns. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanche, K.R.; Ludwig, J.A. Species richness of gall-inducing insects and host plants along an altitudinal gradient in Big Bend National Park, Texas. Am. Midl. Nat. 2001, 145, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakadai, R.; Murakami, M.; Hirao, T. Effects of phylogeny, leaf traits, and the altitudinal distribution of host plants on herbivore assemblages on congeneric Acer species. Oecologia 2014, 175, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, X.; Petry, W.K.; Mooney, K.A.; Rasmann, S.; Abdala-Roberts, L. Elevational gradients in plant defences and insect herbivory: Recent advances in the field and prospects for future research. Ecography 2018, 41, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, J.H.; MacGarvin, M.; Heads, P.A. Effects of altitude on the abundance and species richness of insect herbivores on bracken. J. Anim. Ecol. 1987, 56, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbek, C. The role of spatial scale and the perception of large-scale species-richness patterns. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 8, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, N.J.; Rahbek, C. The patterns and causes of elevational diversity gradients. Ecography 2012, 35, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, G.; Süssenbach, D.; Fiedler, K. Unique elevational diversity patterns of geometrid moths in an Andean montane rainforest. Ecography 2003, 26, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogues-Bravo, D.; Araujo, M.B.; Romdal, T.; Rahbek, C. Scale effects and human impact on the elevational species richness gradients. Nature 2008, 453, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.W.; Lara, A.C.F. Diversity of Indonesian gall-forming herbivores along altitudinal gradients. Biodivers. Lett. 1993, 1, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.W.; Price, P.W. Biogeographical gradients in galling species richness: Tests of hypotheses. Oecologia 1988, 76, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, J.G.; Frost, S.W.; Tothill, B.H. Leaf-Mining Insects; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1928. [Google Scholar]
- Hering, E.M. Biology of the Leaf Miners; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, L. The Ecology and Continuous Control of Liriomyza Sativae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, R.J.; Hughes, L. Leaf miners: The hidden herbivores. Austral Ecol. 2010, 35, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csóka, G. Leaf Mines and Leaf Miners; Hungarian Forest Research Institute: Budapest, Hungary, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.H.; Dai, X.H.; Xu, J.S. Influences of leaf-mining insects on their host plants: A review. Collect. Bot. 2015, 34, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K. Leaf mines as visual defensive signals to herbivores. Oikos 2010, 119, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilf, P.; Labandeira, C.C.; Johnson, K.R.; Ellis, B. Decoupled plant and insect diversity after the end-Cretaceous extinction. Science 2006, 313, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labandeira, C.C.; Dilcher, D.L.; Davis, D.R.; Wagner, D.L. Ninety-seven million years of angiosperm-insect association: Paleobiological insights into the meaning of coevolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12278–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Vaamonde, C.; Wikstrom, N.; Labandeira, C.; Godfray, H.C.; Goodman, S.J.; Cook, J.M. Fossil-calibrated molecular phylogenies reveal that leaf-mining moths radiated millions of years after their host plants. J. Evol. Biol. 2006, 19, 1314–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krassilov, V. Mine and gall predation as top down regulation in the plant–insect systems from the Cretaceous of Negev, Israel. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2008, 261, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hespenheide, H.A. Bionomics of leaf-mining insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1991, 36, 535–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, V.; Basset, Y. Host specificity of insect herbivores in tropical forests. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, S. Associations of leaf miners and leaf gallers with island plants of different residency histories. J. Biogeogr. 2010, 37, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Chen, B.; Wei, J.N.; Liu, T.X. Roles of thermal adaptation and chemical ecology in Liriomyza distribution and control. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2009, 54, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollár, J.; Hrubík, P. The mining species on woody plants of urban environments in the West Slovak area. Acta Entomol. Serbica 2009, 14, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Connor, E.F.; Taverner, M.P. The evolution and adaptive significance of the leaf-mining habit. Oikos 1997, 79, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggetti, L.; Raranciuc, S.; Chiaba, C.; Vischi, M.; Zandigiacomo, P. Altitude affects the distribution and abundance of two non-native insect pests of the common walnut. J. Appl. Entomol. 2019, 143, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.; Kandel, P.; Bhatta, D.; Pandit, V.; Felton, G.W.; Rajotte, E.G. Insect herbivore populations and plant damage increase at higher elevations. Insects 2021, 12, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuelher, E.D.S.; de Oliveira, E.E.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Magalhaes, L.C. Occurrence of coffee leaf-miner (Leucoptera coffeella) influenced by season and altitude. Acta Sci.-Agron. 2003, 25, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Maunsell, S.C.; Burwell, C.J.; Morris, R.J.; McDonald, W.J.F.; Edwards, E.D.; Oberprieler, R.G.; Kitching, R.L. Elevational turnover in the composition of leaf miners and their interactions with host plants in Australian subtropical rainforest. Austral Ecol. 2016, 41, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.W.; Castro, F.M.C.; Faria, M.L.; Marques, E.S.A.; Greco, M.K.B. Effects of hygrothermal stress, plant richness, and architecture on mining insect diversity. Biotropica 2004, 36, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foba, C.N.; Salifu, D.; Lagat, Z.O.; Gitonga, L.M.; Akutse, K.S.; Fiaboe, K.K. Species composition, distribution, and seasonal abundance of Liriomyza leafminers (Diptera: Agromyzidae) under different vegetable production systems and agroecological zones in Kenya. Environ. Entomol. 2015, 44, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.; Barekye, A.; Joseph, E.; Gerald, K.; Innocent, U.; Sarah, K. Management of potato leaf miner in Uganda. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 14, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairstow, K.A.; Clarke, K.L.; McGeoch, M.A.; Andrew, N.R. Leaf miner and plant galler species richness on Acacia: Relative importance of plant traits and climate. Oecologia 2010, 163, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestel, D.; Dickschen, F.; Altieri, M.A. Seasonal and spatial population loads of a tropical insect: The case of the coffee leaf-miner in Mexico. Ecol. Entomol. 1994, 19, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, K.J.; Genney, D.R.; Thurlow, M.; Hartley, S.E. The geographical range structure of the holly leaf-miner. IV. Effects of variation in host-plant quality. J. Anim. Ecol. 2004, 73, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinyanjui, G.; Khamis, F.M.; Ombura, F.L.O.; Kenya, E.U.; Ekesi, S.; Mohamed, S.A. Distribution, abundance and natural enemies of the invasive tomato leafminer, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) in Kenya. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2021, 111, 658–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, M.V.; van Nieukerken, E.J.; Zverev, V.; Zvereva, E.L. Abundance and diversity of birch-feeding leafminers along latitudinal gradients in northern Europe. Ecography 2013, 36, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibaldi, L.A.; Kitzberger, T.; Chaneton, E.J. Environmental and genetic control of insect abundance and herbivory along a forest elevational gradient. Oecologia 2011, 167, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, M.; Hofmann, S.; Kromer, T.; Cicuzza, D.; Kluge, J. The impact of sterile populations on the perception of elevational richness patterns in ferns. Ecography 2011, 34, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machac, A.; Janda, M.; Dunn, R.R.; Sanders, N.J. Elevational gradients in phylogenetic structure of ant communities reveal the interplay of biotic and abiotic constraints on diversity. Ecography 2011, 34, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Bartholomew, B. Fagaceae. In Flora of China; Wu, Z.Y., Raven, P.H., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 314–400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z. Fossils of the Fagaceae and their implications in systematics and biogeography. Acta Phytotaxon Sin. 1999, 37, 369–385. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Long, C.; Xu, J.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Bater. Are dominant plant species more susceptible to leaf-mining insects? A case study at Saihanwula Nature Reserve, China. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 7633–7648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Duffy, K.J.; Guo, Q. Global pattern of plant utilization across different organisms: Does plant apparency or plant phylogeny matter? Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeny, P. Plant Apparency and Chemical Defense; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Claridge, M.F.; Wilson, M.R. Insect herbivore guilds and species-area relationships: Leafminers on British trees. Ecol. Entomol. 1982, 7, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H. Differential resource utilization and co-occurrence of leaf miners on oak (Quercus dentata). Ecol. Entomol. 1991, 16, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Hattori, K.; Ishida, T.A.; Sato, H.; Kimura, M.T. Population dynamics of leafminers on a deciduous oak Quercus dentata. Acta Oecologica 2008, 34, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.A.; Hattori, K.; Kimura, M.T. Abundance of leafminers and leaf area loss by chewing herbivores in hybrids between Quercus crispula and Quercus dentata. Can. J. Res. 2004, 34, 2501–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opler, P.A.; Davis, D.R. The Leaf Mining Moths of the Genus Cameraria Associated with Fagaceae in California (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae); Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Kang, H.; Sun, X.; Yin, S.; Du, H.; Yamanaka, N.; Gapare, W.; Wu, H.X.; Liu, C. Phylogeography of Quercus variabilis based on chloroplast DNA sequence in East Asia: Multiple glacial refugia and Mainland-migrated island populations. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y. Chinese Cork Oak; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.F.; Liu, J.F.; Gao, W.Q.; Deng, Y.P.; Ni, Y.Y.; Xiao, Y.H.; Kang, F.F.; Wang, Q.; Lei, J.P.; Jiang, Z.P. Defense pattern of Chinese cork oak across latitudinal gradients: Influences of ontogeny, herbivory, climate and soil nutrients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Knag, H.; Zhuang, h.; Liu, C. Variations of Quercus variabilis leaf traits in relation to climatic factors at regional scale. Chin. J. Ecol. 2010, 29, 2309–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Dai, X.; Liao, C.; DiSkus, A.; Stonis, J.R. Discovery of Ulmaceae-feeding Tischeriidae (Lepidoptera, Tischerioidea), Tischeria ulmella sp. nov., and the first report of the Quercus-feeding T. naraensis Sato in China. Zootaxa 2018, 4399, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Peng, C.; Yang, B.; Song, H.; Li, Q.; Jiang, L.; Wei, G.; Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Contrasting soil bacterial community, diversity, and function in two forests in China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. The charcteristics of flora of seed plants in Baotianman. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 1996, 16, 329–335. [Google Scholar]
- Du, B.; Ji, H.; Peng, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, C. Altitudinal patterns of leaf stoichiometry and nutrient resorption in Quercus variabilis in the Baotianman Mountains, China. Plant Soil 2016, 413, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Liu, S.R.; Liu, C.J.; Wang, H.; Luan, J.W.; Liu, X.J.; Guo, X.W.; Niu, B.L. Soil bacterial and fungal richness and network exhibit different responses to long-term throughfall reduction in a warm-temperate oak forest. Forests 2021, 12, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, P.K.; Yuan, Z.L.; Ye, Y.Z. The relationships among topographically-driven habitats, dominant species and vertical layers in temperate forest in China. Russ. J. Ecol. 2019, 50, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Peng, C.H.; Liu, S.R.; Liu, X.J.; Li, P.; Song, H.X.; Yuan, M.S.; Wang, M. Variation in soil methane fluxes and comparison between two forests in China. Forests 2018, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z. Plant community diversity in Baotianman National Reserve, Henan Province. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, M.; Duan, W.; Pan, Y. Study on space characteristics of biodiversity in Baotianman Natural Reserve, Neixiang County. J. Henan For. Sci. Technol. 1999, 19, 10–12+14. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z. Study on niche of main population of Quercus variabilis (Fagaceae) forest in Henan province. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 1999, 19, 511–518. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, R.; Xiao, W. Community characteristics of Quercus variabilis forest and species diversity in Baotianman, Henan Province. J. Plant Resour. Environ. 1998, 7, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- QGIS.org. QGIS Geographic Information System; QGIS Association: Beaverton, OR, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, K.A.; Steyskal, G.C. Manual of the Agromyzidae (Diptera) of the United States; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.H.; Xu, J.S.; Ding, X.L. Circular distribution pattern of plant modulars and endophagous herbivory within tree crowns: The impact of roadside light conditions. J. Insect Sci. 2013, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.W.; Welter, S.C.; Toscano, N.C.; Ting, P.; Trumble, J.T. Reduction of tomato leaflet photosynthesis rates by mining activity of Liriomyza sativae (Diptera: Agromyzidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1983, 76, 1061–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrella, M.P.; Jones, V.P.; Youngman, R.R.; Lebeck, L.M. Effect of leaf mining and leaf stippling of Liriomyza spp. on photosynthetic rates of Chrysanthemum. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, F.; Trifilo, P.; Gullo, M.A. Does citrus leaf miner impair hydraulics and fitness of citrus host plants? Tree Physiol. 2013, 33, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D. hillR: Taxonomic, functional, and phylogenetic diversity and similarity through Hill Numbers. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Gotelli, N.J.; Hsieh, T.C.; Sander, E.L.; Ma, K.H.; Colwell, R.K.; Ellison, A.M. Rarefaction and extrapolation with Hill numbers: A framework for sampling and estimation in species diversity studies. Ecol. Monogr. 2014, 84, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.H.; Chen, C.F.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, X.X. Taxonomic, phylogenetic, and functional diversity of ferns at three differently disturbed sites in Longnan County, China. Diversity 2020, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Chiu, C.H.; Jost, L. Phylogenetic diversity measures based on Hill numbers. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 3599–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiasu, R.C.; Guiasu, S. The weighted Gini-Simpson index: Revitalizing an old index of biodiversity. Int. J. Ecol. 2012, 2012, 478728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliberté, E.; Legendre, P.; Shipley, B. FD: Measuring Functional Diversity from Multiple Traits, and Other Tools for Functional Ecology. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/FD/index.html (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Laliberte, E.; Legendre, P. A distance-based framework for measuring functional diversity from multiple traits. Ecology 2010, 91, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.H.; Chao, A. Distance-based functional diversity measures and their decomposition: A framework based on Hill numbers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.; Kinzig, A.; Langridge, J. Plant attribute diversity, resilience, and ecosystem function: The nature and significance of dominant and minor species. Ecosystems 1999, 2, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiasu, R.C.; Guiasu, S. The weighted quadratic index of biodiversity for pairs of species: A generalization of Rao’s index. Nat. Sci. 2011, 3, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggeo, V.M. Estimating regression models with unknown break-points. Stat. Med. 2003, 22, 3055–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggeo, V.M.R. Segmented: An R package to fit regression models with boken-line relationships. R. News 2008, 8, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Stasinopoulos, D.M.; Rigby, R.A. Detecting break points in generalised linear models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 1992, 13, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggeo, V.M.R. Testing with a nuisance parameter present only under the alternative: A score-based approach with application to segmented modelling. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2016, 86, 3059–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggeo, V.M.R. Interval estimation for the breakpoint in segmented regression: A smoothed score-based approach. Aust. N. Zeal. J. Stat. 2017, 59, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.D.; Lu, L.; Luo, T.H.; Zhou, H.Z. Elevational gradient in species richness pattern of epigaeic beetles and underlying mechanisms at east slope of Balang Mountain in southwestern China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, N.J.; Lessard, J.-P.; Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Dunn, R.R. Temperature, but not productivity or geometry, predicts elevational diversity gradients in ants across spatial grains. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2007, 16, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormann, C.F.; McPherson, J.M.; Araújo, M.B.; Bivand, R.; Bolliger, J.; Carl, G.; Davies, R.G.; Hirzel, A.; Jetz, W.; Kissling, W.D.; et al. Methods to account for spatial autocorrelation in the analysis of species distributional data: A review. Ecography 2007, 30, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, T.F.; Diniz-Filho, J.A.F.; Bini, L.M. SAM: A comprehensive application for Spatial Analysis in Macroecology. Ecography 2010, 33, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnute, J.T.; Boers, N.; Haigh, R. PBSmapping 2.70.3: User’s Guide Revised from Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences; Fisheries and Oceans Canada: Nanaimo, BC, Canada, 2017; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Vallejos, R.; Osorio, F.; Bevilacqua, M. Spatial Relationships Between Two Georeferenced Variables: With Applications in R; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Clifford, P.; Richardson, S.; Hemon, D. Assessing the significance of the correlation between two spatial processes. Biometrics 1989, 45, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutilleul, P. Modifying the t test for assessing the correlation between two spatial processes. Biometrics 1993, 49, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnes, G.R.; Bolker, B.; Gorjanc, G.; Grothendieck, G.; Korosec, A.; Lumley, T.; MacQueen, D.; Magnusson, A.; Rogers, J. gdata: Various R Programming Tools for Data Manipulation. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/gdata/index.html (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Montaño-Centellas, F.A.; McCain, C.; Loiselle, B.A.; Grytnes, J.A. Using functional and phylogenetic diversity to infer avian community assembly along elevational gradients. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2019, 29, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCain, C.M. Elevational gradients in diversity of small mammals. Ecology 2005, 86, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCain, C.M.; Grytnes, J.A. Elevational Gradients in Species Richness. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences (ELS); John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- McCain, C.M. Global analysis of reptile elevational diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Sang, W.; Hausmann, A.; Axmacher, J.C. High phylogenetic diversity is preserved in species-poor high-elevation temperate moth assemblages. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.; Chey, V.K. Explaining the elevational diversity pattern of geometrid moths from Borneo: A test of five hypotheses. J. Biogeogr. 2008, 35, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, T.; McCain, C.M. A systematic review of global drivers of ant elevational diversity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.; McCain, C.M.; Axmacher, J.C.; Ashton, L.A.; Bärtschi, F.; Brehm, G.; Choi, S.W.; Cizek, O.; Colwell, R.K.; Fiedler, K.; et al. Elevational species richness gradients in a hyperdiverse insect taxon: A global meta-study on geometrid moths. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2016, 26, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Kelt, D.A.; Sun, Z.; Liu, H.; Hu, L.; Ren, H.; Wen, J. Global variation in elevational diversity patterns. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.C.; DuBay, S.; Zhangshang, M.; Cheng, Y.W.; Liu, Z.W.; Li, D.R.; Ran, J.H.; Wu, Y.J. Seasonal elevational patterns and the underlying mechanisms of avian diversity and community structure on the eastern slope of Mt. Gongga. Divers. Distrib. 2022, 28, 2459–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guariento, E.; Strutzenberger, P.; Truxa, C.; Fiedler, K. The trinity of ecological contrasts: A case study on rich insect assemblages by means of species, functional and phylogenetic diversity measures. BMC Ecol. 2020, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).