Short Neuropeptide F and Its Receptor Regulate Feeding Behavior in Pea Aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
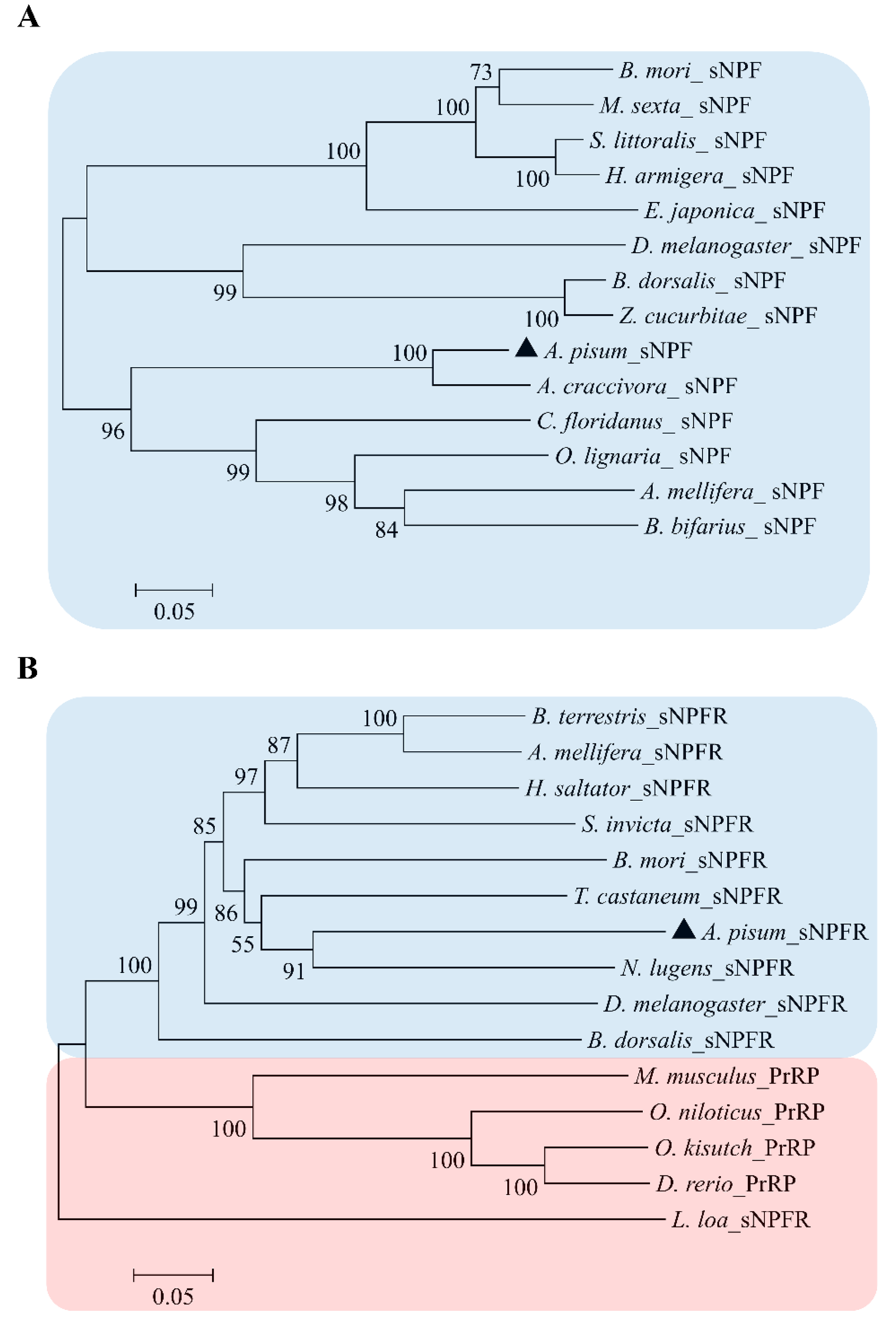
2.2. Identification of Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Stage- and Tissue-Specific Expression Profile of A. pisum sNPF/sNPFR via qRT-PCR
2.4. Transcript Pattern during Feeding and Starvation Stress via qRT-PCR
2.5. Double-Stranded RNA Synthesis and Injection
2.6. Transcript Expression after RNAi
2.7. EPG Analysis of Aphid Feeding Behavior
2.8. Survival and Reproduction Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
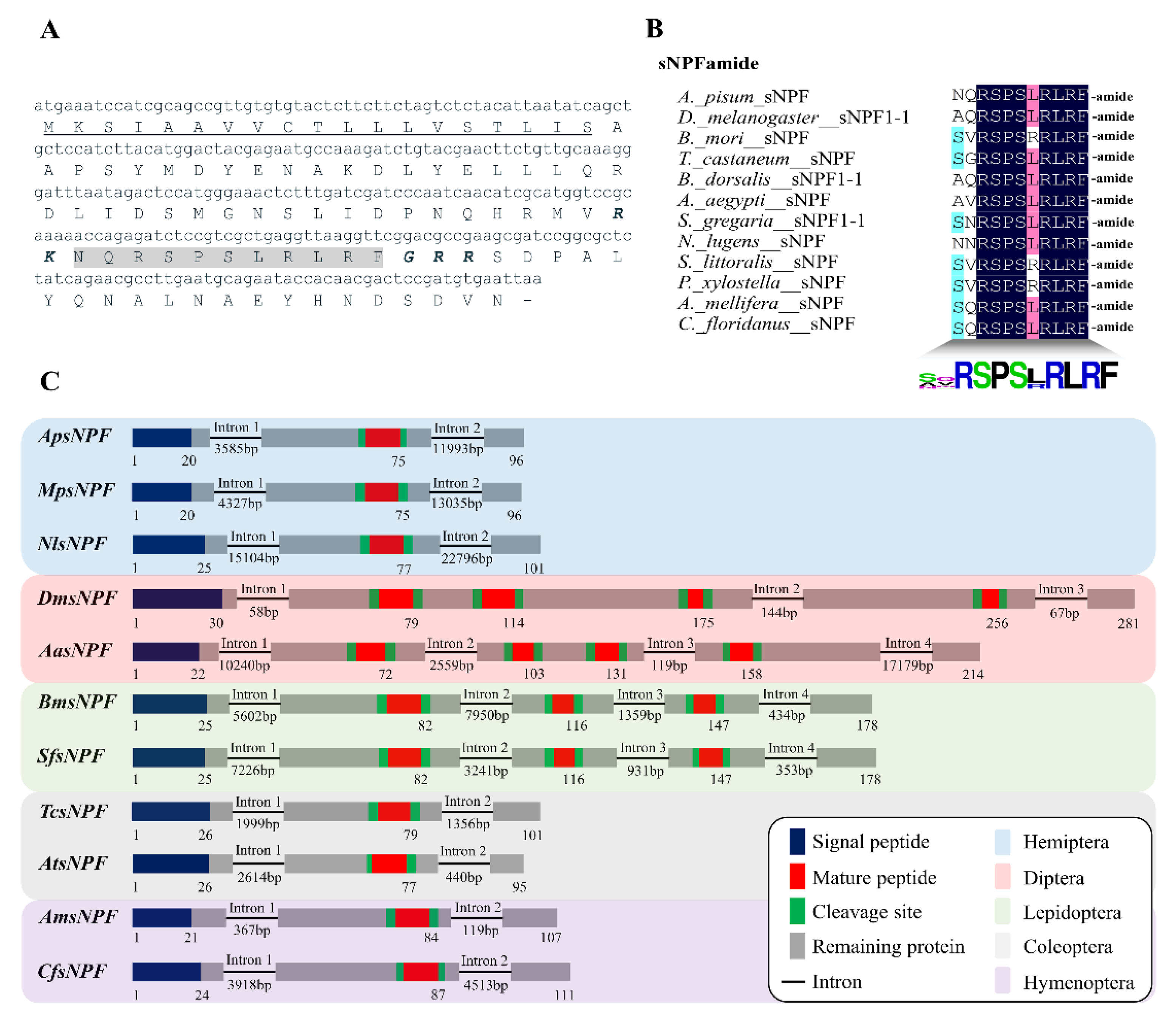
3.1. Characterization of ApsNPF and Its Receptor
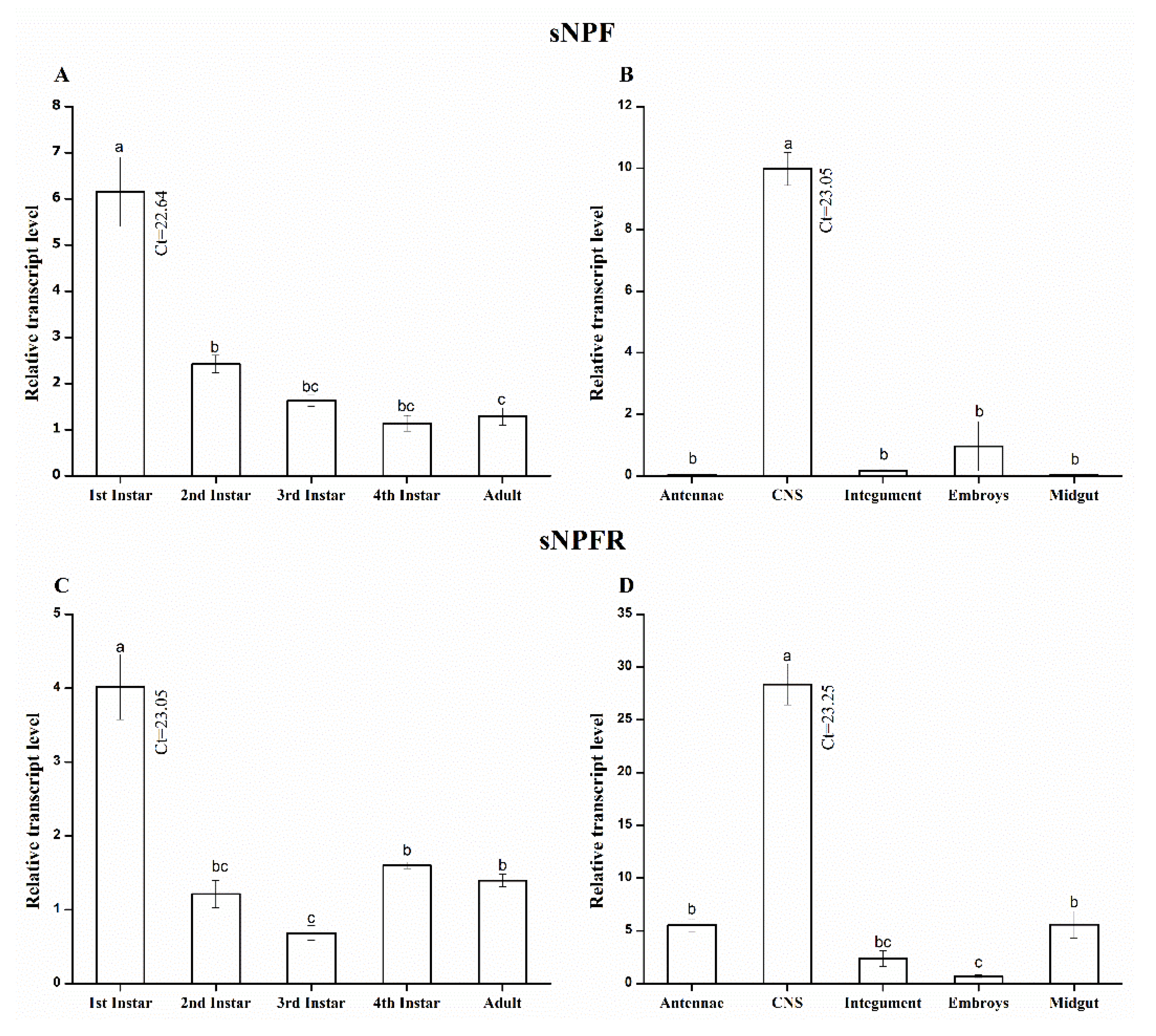
3.2. Stage- and Tissue-Specific qRT-PCR Analysis Shows a Spatiotemporal Transcript Expression of A. pisum sNPF/sNPFR
3.3. Transcript Expression during Feeding and Starvation Stress
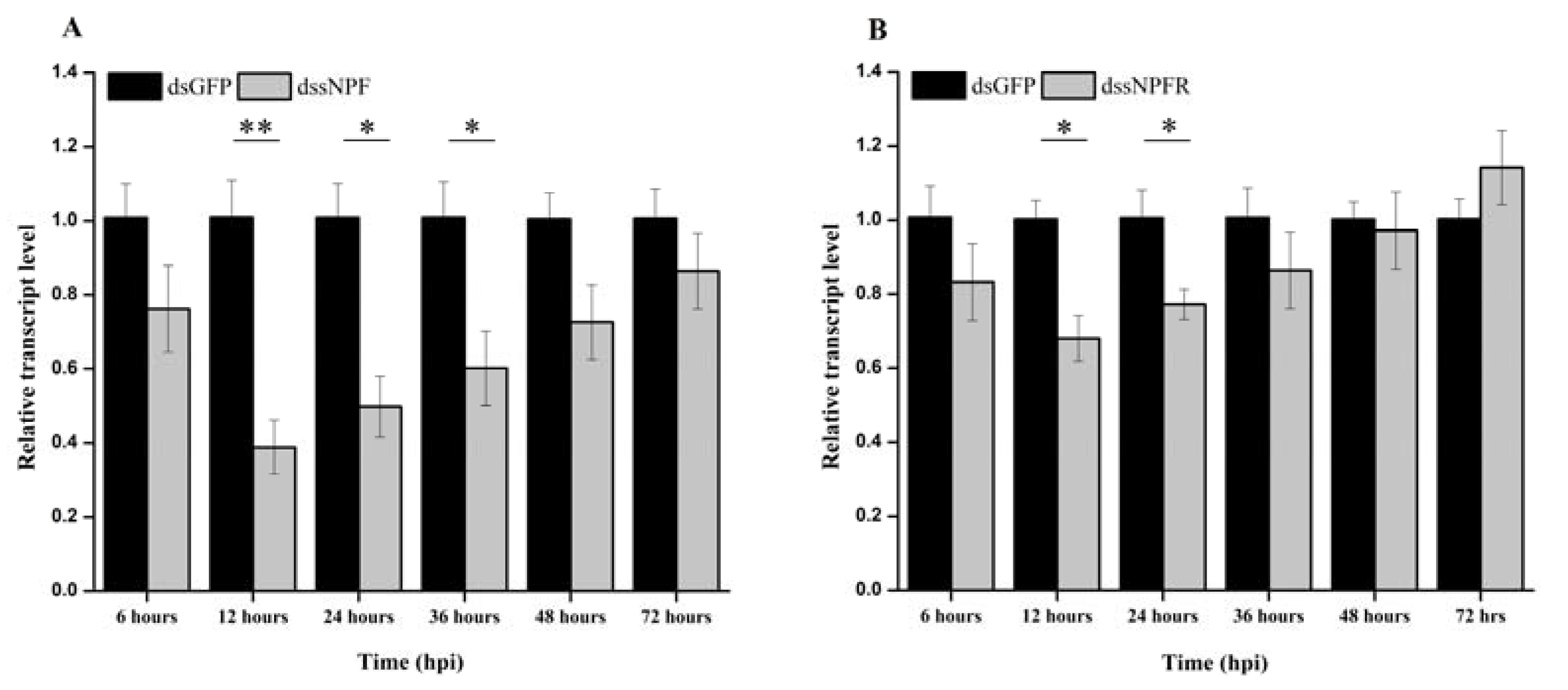
3.4. RNAi-Mediated Silencing of ApsNPF and ApsNPFR via dsRNA Injection
3.5. Effect on Feeding Behavior after ApsNPF and ApsNPFR Silencing
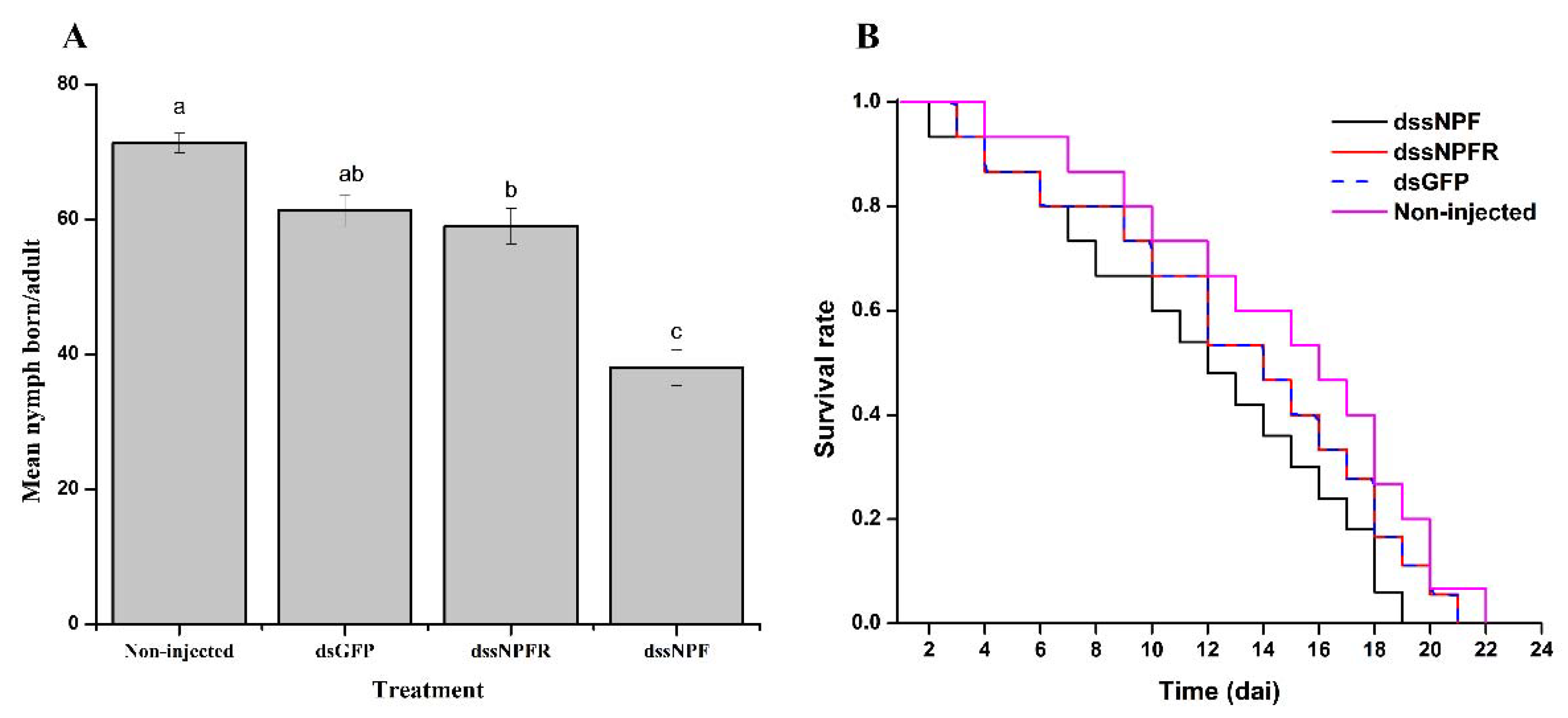
3.6. Effect of sNPF Silencing on Aphid Reproduction and Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jékely, G. Global view of the evolution and diversity of metazoan neuropeptide signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8702–8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Nachman, R.J.; Gui, S.; Piot, N.; Kaczmarek, K.; Zabrocki, J.; Dow, J.A.T.; Davies, S.; Smagghe, G. Efficacy and biosafety assessment of neuropeptide CAPA analogues against the peach-potato aphid (Myzus persicae). Insect Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, A.J. Feeding, hunger, satiety and serotonin in invertebrates. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spittaels, K.; Verhaert, P.; Shaw, C.; Johnston, R.N.; Devreese, B.; Van Beeumen, J.; De Loof, A. Insect neuropeptide F (NPF)-related peptides: Isolation from Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata) brain. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1996, 26, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeck, J.V. Neuropeptides and their precursors in the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster. Peptides 2001, 22, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Reale, V.; Chatwin, H.; Kennedy, K.; Venard, R.; Ericsson, C.; Yu, K.; Evans, P.D.; Hall, L.M. Functional characterization of a neuropeptide F-like receptor from Drosophila melanogaster. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nässel, D.R.; Wegener, C. A comparative review of short and long neuropeptide F signaling in invertebrates: Any similarities to vertebrate neuropeptide Y signaling? Peptides 2011, 32, 1335–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, I.; Meeusen, T.; Huybrechts, R.; De Loof, A.; Schoofs, L. Characterization of the short neuropeptide F receptor from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 297, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nässel, D.R.; Enell, L.E.; Santos, J.G.; Wegener, C.; Johard, H.A.D. A large population of diverse neurons in the Drosophila central nervous system expresses short neuropeptide F, suggesting multiple distributed peptide functions. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Nakane, T.; Ohara, A.; Morooka, N.; Konuma, T.; Nagai, C.; Nagasawa, H. Effects of starvation on brain short neuropeptide F-1, -2, and -3 levels and short neuropeptide F receptor expression levels of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Q.; Cao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yan, L.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, N.; Huang, H. Bombyx neuropeptide G protein-coupled receptor A7 is the third cognate receptor for short neuropeptide F from silkworm. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 20599–20612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dillen, S.; Verdonck, R.; Zels, S.; Van Wielendaele, P.; Broeck, J.V. Identification of the short neuropeptide F precursor in the desert locust: Evidence for an inhibitory role of sNPF in the control of feeding. Peptides 2014, 53, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillen, S.; Zels, S.; Verlinden, H.; Spit, J.; van Wielendaele, P.; Broeck, J.V. Functional characterization of the short neuropeptide F receptor in the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garczynski, S.F.; Crim, J.W.; Brown, M.R. Characterization and expression of the short neuropeptide F receptor in the African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Peptides 2007, 28, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Predel, R.; Neupert, S.; Hauser, F.; Tanaka, Y.; Cazzamali, G.; Williamson, M.; Arakane, Y.; Verleyen, P.; Schoofs, L.; et al. Genomics, transcriptomics, and peptidomics of neuropeptides and protein hormones in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knapek, S.; Kahsai, L.; Winther, Å.M.E.; Tanimoto, H.; Nässel, D.R. Short neuropeptide F acts as a functional neuromodulator for olfactory memory in Kenyon cells of Drosophila mushroom bodies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 5340–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.B.; Gui, S.H.; Xu, L.; Pei, Y.X.; Smagghe, G.; Wang, J.J. The short neuropeptide F modulates olfactory sensitivity of Bactrocera dorsalis upon starvation. J. Insect Physiol. 2017, 99, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahsai, L.; Martin, J.; Winther, Å.M.E. Neuropeptides in the Drosophila central complex in modulation of locomotor behavior. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 2256–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerstiaensa, A.N.J.A.; Benfekihb, L.; Zouitenc, H.; Verhaerta, P.; De Loofa, A.; Schoofsa, L. Led-NPF-1 stimulates ovarian development in locusts. Peptides 1999, 20, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Chen, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Su, S.; Chen, M. Expression patterns and functional analysis of the short neuropeptide F and NPF receptor genes in Rhopalosiphum padi. Insect Sci. 2020, 28, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Hiruma, K. Short neuropeptide F (sNPF) is a stage-specific suppressor for juvenile hormone biosynthesis by corpora allata, and a critical factor for the initiation of insect metamorphosis. Dev. Biol. 2014, 393, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, R.; Wang, B.; Giribaldi, M.G.; Ayres, J.; Thomas, J.B.; Montminy, M. Neuronal energy-sensing pathway promotes energy balance by modulating disease tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3307–E3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Shi, W.; Li, L.; Zheng, Z.; Li, T.; Bai, W.; Zhao, Z. Regulation of sleep by the short neuropeptide F (sNPF) in Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Donelson, N.C.; Vecsey, C.G.; Guo, F.; Rosbash, M.; Griffith, L.C. Short Neuropeptide F Is a Sleep-Promoting Inhibitory Modulator. Neuron 2013, 80, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.; Holy, T.E.; Taghert, P.H. A Series of Suppressive Signals within the Drosophila Circadian Neural Circuit Generates Sequential Daily Outputs. Neuron 2017, 94, 1173–1189.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selcho, M.; Millán, C.; Palacios-Muñoz, A.; Ruf, F.; Ubillo, L.; Chen, J.; Bergmann, G.; Ito, C.; Silva, V.; Wegener, C.; et al. Central and peripheral clocks are coupled by a neuropeptide pathway in Drosophila. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; You, K.H.; Choo, J.K.; Han, Y.M.; Yu, K. Drosophila short neuropeptide F regulates food intake and body size. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 50781–50789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ament, S.A.; Velarde, R.A.; Kolodkin, M.H.; Moyse, D.; Robinson, G.E. Neuropeptide Y-like signalling and nutritionally mediated gene expression and behaviour in the honey bee. Insect Mol. Biol. 2011, 20, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagata, S.; Morooka, N.; Matsumoto, S.; Kawai, T.; Nagasawa, H. Effects of neuropeptides on feeding initiation in larvae of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 172, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, C.M.; Ko, K.I.; Jafari, A.; Wang, J.W. Presynaptic facilitation by neuropeptide signaling mediates odor-driven food search. Cell 2011, 145, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, M.R.; Klowden, M.J.; Crim, J.W.; Young, L.; Shrouder, L.A.; Lea, A.O. Endogenous regulation of mosquito host-seeking behavior by a neuropeptide. J. Insect Physiol. 1994, 40, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogenhout, S.A.; Ammar, E.; Whitfield, A.E.; Redinbaugh, M.G. Insect vector interactions with persistently transmitted viruses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2008, 46, 327–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reyes, M.L.; Laughton, A.M.; Parker, B.J.; Wichmann, H.; Fan, M.; Sok, D.; Hrček, J.; Acevedo, T.; Gerardo, N.M. The influence of symbiotic bacteria on reproductive strategies and wing polyphenism in pea aphids responding to stress. J. Anim. Ecol. 2019, 88, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huybrechts, J.; Bonhomme, J.; Minoli, S.; Prunier-Leterme, N.; Dombrovsky, A.; Abdel-Latief, M.; Robichon, A.; Veenstra, J.A.; Tagu, D. Neuropeptide and neurohormone precursors in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yun, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, M.; Liu, X.; Wu, W.; Li, B. Identification of G protein-coupled receptors in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Genomics 2013, 102, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2-A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kapustin, Y.; Souvorov, A.; Tatusova, T.; Lipman, D. Splign: Algorithms for computing spliced alignments with identification of paralogs. Biol. Direct 2008, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Xie, Y.; Ma, J.; Luo, X.; Nie, P.; Zuo, Z.; Lahrmann, U.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. IBS: An illustrator for the presentation and visualization of biological sequences. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3359–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakabachi, A.; Shigenobu, S.; Sakazume, N.; Shiraki, T.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Carninci, P.; Ishikawa, H.; Kudo, T.; Fukatsu, T. Transcriptome analysis of the aphid bacteriocyte, the symbiotic host cell that harbors an endocellular mutualistic bacterium, Buchnera. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5477–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Qu, M.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.W.; Liu, T.X. Expression of neuropeptide F gene and its regulation of feeding behavior in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mclean, D.L.; Kinsey, M.G. A technique for electronically recording aphid feeding and salivation. Nature 1964, 202, 1358–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjallingii, W.F. Electronic recording of penetration behavior by aphids. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1978, 24, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, E.; Tjallingii, W.F. Aphid activities during sieve element punctures. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1994, 72, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarria, E.; Cid, M.; Garzo, E.; Fereres, A. Excel Workbook for automatic parameter calculation of EPG data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2009, 67, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenstra, J.A. Peptidergic paracrine and endocrine cells in the midgut of the fruit fly maggot. Cell Tissue Res. 2009, 336, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caers, J.; Peymen, K.; Van Hiel, M.B.; Van Rompay, L.; Van Den Abbeele, J.; Schoofs, L.; Beets, I. Molecular characterization of a short neuropeptide F signaling system in the tsetse fly, Glossina morsitans morsitans. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 235, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenstra, J.A.; Lambrou, G. Isolation of a noval RFamide peptide from the midgut of the American cockroach, Periplaneta Americana. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 213, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, M.A.; Diesner, M.; Schachtner, J.; Na, D.R. Multiple neuropeptides in the Drosophila antennal lobe suggest complex modulatory circuits. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010, 3380, 3359–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, K.I.; Root, C.M.; Lindsay, S.A.; Zaninovich, O.A.; Shepherd, A.K.; Wasserman, S.A.; Kim, S.M.; Wang, J.W. Starvation promotes concerted modulation of appetitive olfactory behavior via parallel neuromodulatory circuits. eLife 2015, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Kwon, O.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kwon, K.; Min, K.J.; Jung, S.A.; Kim, A.K.; You, K.H.; Tatar, M.; Yu, K. Drosophila short neuropeptide F signalling regulates growth by ERK-mediated insulin signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Will, T.; Vilcinskas, A. The structural sheath protein of aphids is required for phloem feeding. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 57, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Tissue Specificity | Parameters | dsGFP | dssNPF | dssNPFR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epidermis | Time of start of EPG to 1st probe (s) | 2.91 ± 0.05 c | 14.41 ± 2.14 a | 8.20 ± 0.86 b |
| Epidermis and mesophyll | Time from 1st probe to 1st E2 (s) | 7621 ± 1424 b | 11786 ± 865 a | 10290 ± 590 ab |
| Duration of 1st probe (s) | 2084 ± 153 a | 1583 ± 153 b | 1699 ± 97 ab | |
| Duration of the non-probe period before the 1st E (s) | 1365 ± 61 b | 1749 ± 120 a | 1688 ± 108 a | |
| Number of probes to the 1st E | 8.2 ± 0.34 a | 7.5 ± 0.27 a | 7.65 ± 0.20 a | |
| Number of F | 2.35 ± 0.35 a | 1.25 ± 0.23 b | 1.55 ± 0.32 ab | |
| Total duration of F (s) | 62.0 ± 9.6 a | 39.3 ± 8.9 a | 41.9 ± 9.5 a | |
| Mean duration of F (s) | 27.3 ± 5.1 a | 23.6 ± 5.8 a | 19. 8 ± 5.2 a | |
| All tissues | Time from 1st probe to 1st sustained E2 (>10 min) (s) | 8298 ± 1530 b | 13649 ± 772 a | 11078 ± 630 ab |
| Number of probes | 12.35 ± 0.33 a | 10.8 ± 0.40 b | 11.05 ± 0.40 b | |
| Total probing time (s) | 28617 ± 43 a | 23157 ± 733 b | 24121 ± 453 b | |
| Number of short probes (C < 3 min) (s) | 5.69 ± 0.47 a | 6.47 ± 1.24 a | 6.13 ± 0.41 a | |
| Number of C | 10.4 ± 0.83 a | 9.45 ± 0.54 a | 9.75 ± 0.56 a | |
| Total duration of C (s) | 9847 ± 932 b | 12631 ± 809 a | 12443 ± 829 a | |
| Mean duration of C (s) | 847 ± 37 a | 734 ± 43 a | 757 ± 40 a | |
| Number of np | 9.15 ± 0.78 b | 12.7 ± 1.22 a | 12.1 ±1.05 ab | |
| Total duration of np (s) | 3054 ± 298 a | 3920 ± 397 a | 3717 ± 359 a | |
| Mean duration of np (s) | 264 ± 28 a | 403 ± 50 a | 364 ± 88 a | |
| Total duration of no phloem phase (s) | 18729 ± 981 b | 22248 ± 1025 a | 21661 ± 1119 a |
| Tissue Specificity | Parameters | dsGFP | dssNPF | dssNPFR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epidermis and mesophyll | Time from start of EPG to 1st E2 (s) | 8151 ± 1600 b | 12703 ± 754 a | 10633 ± 619 ab |
| All tissues | Time from start of EPG to 1st E2 (s) | 9005 ± 1646 b | 13724 ± 816 a | 11194 ± 824 ab |
| Time from start of EPG to 1st sustained E2 (> 10 min) (s) | 9615 ± 1744 b | 14424 ± 821 a | 13411 ± 583 a | |
| Phloem | Number of E1 | 4.60 ± 0.29 a | 3.55 ± 0.25 b | 3.70 ± 0.31 b |
| Number of E2 | 4.35 ± 0.31 a | 3.15 ± 0.34 b | 3.35 ± 0.34 b | |
| Number of single E1 | 0.60 ± 0.11 b | 1.15 ± 0.18 a | 1.00 ± 0.12 ab | |
| Number of sustained E2 (> 10 min) | 2.40 ± 0.19 a | 1.75 ± 0.19 b | 1.95 ± 0.15 ab | |
| Total duration of E (s) | 10530 ± 1014 a | 6025 ± 1014 b | 7563 ± 1085 b | |
| Total duration of E1 (s) | 265 ± 28 a | 184 ± 20 b | 191 ± 26 b | |
| Total duration of E2 (s) | 11674 ± 1301 a | 5788 ± 1031 b | 7181 ± 1021 b | |
| Mean duration of E1 (s) | 65.8 ± 4.33 a | 59.9 ± 2.90 a | 63.9 ± 1.79 a | |
| Mean duration of E2 (s) | 5933 ± 467 a | 2872 ± 1020 b | 3412 ± 1008 b | |
| Duration of 1st E (s) | 5172 ± 347 a | 2842 ± 519 b | 3228 ± 1021 ab | |
| Duration of the longest E2 (s) | 8543 ± 1236 a | 4096 ± 1027 b | 5112 ± 1146 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amir, M.B.; Shi, Y.; Cao, H.; Ali, M.Y.; Ahmed, M.A.; Smagghe, G.; Liu, T.-X. Short Neuropeptide F and Its Receptor Regulate Feeding Behavior in Pea Aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum). Insects 2022, 13, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13030282
Amir MB, Shi Y, Cao H, Ali MY, Ahmed MA, Smagghe G, Liu T-X. Short Neuropeptide F and Its Receptor Regulate Feeding Behavior in Pea Aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum). Insects. 2022; 13(3):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13030282
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmir, Muhammad Bilal, Yan Shi, Hehe Cao, Muhammad Yasir Ali, Muhammad Afaq Ahmed, Guy Smagghe, and Tong-Xian Liu. 2022. "Short Neuropeptide F and Its Receptor Regulate Feeding Behavior in Pea Aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum)" Insects 13, no. 3: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13030282
APA StyleAmir, M. B., Shi, Y., Cao, H., Ali, M. Y., Ahmed, M. A., Smagghe, G., & Liu, T.-X. (2022). Short Neuropeptide F and Its Receptor Regulate Feeding Behavior in Pea Aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum). Insects, 13(3), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13030282








