First Discovery of Vespa velutina nigrithorax du Buysson (Hymenoptera: Vespidae), an Invasive Hornet in the Feces of the Yellow-Throated Marten in South Korea
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hulme, P.E. Trade, transport and trouble: Managing invasive species pathways in an era of globalization. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziska, L.H.; Blumenthal, D.M.; Runion, G.B.; Hunt, E.R.; Diaz-Soltero, H. Invasive species and climate change: An agronomic perspective. Clim. Chang. 2011, 105, 13–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimpel, G.E.; Cock, M.J. Shifting paradigms in the history of classical biological control. BioControl 2018, 63, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lenteren, J.C. Success in biological control of arthropods by augmentation of natural enemies. In Biological Control: Measures of Success; Gurr, G., Wratten, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 77–103. [Google Scholar]
- Van Lenteren, J.C. The state of commercial augmentative biological control: Plenty of natural enemies, but a frustrating lack of uptake. BioControl 2012, 57, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, D.A.; Wratten, S.D.; Gurr, G.M. Habitat management to conserve natural enemies of arthropod pests in agriculture. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 175–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.J.; Bauer, L.S.; Abell, K.J.; Ulyshen, M.D.; Van Driesche, R.G. Population dynamics of an invasive forest insect and associated natural enemies in the aftermath of invasion: Implications for biological control. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Sasiprapa, W.; Taekul, C.; Kondo, T. Unsung heroes: Fixing multifaceted sustainability challenges through insect biological control. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2020, 40, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beggs, J.R.; Brockerhoff, E.G.; Corley, J.C.; Kenis, M.; Masciocchi, M.; Muller, F.; Rome, Q.; Villemant, C. Ecological effects and management of invasive alien Vespidae. BioControl 2011, 56, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.; Choi, M.B. Interspecific hierarchies from aggressiveness and body size among the invasive alien hornet, Vespa velutina nigrithorax, and five native hornets in South Korea. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulay, R.; Arnan, X.; Cerda, X.; Retana, J. The ecological benefits of larger colony size may promote polygyny in ants. J. Evol. Biol. 2014, 27, 2856–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffaker, C.B. Biological Control; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, S.; Kawashima, M.; Kosaka, H. First record of occurrence of Xenos moutoni (Strepsiptera: Stylopidae), an important parasite of hornets (Hymenoptera: Vepidae: Vespa), in Korea. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2011, 14, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga-Ch, D.; Sarmiento, C.E. Parasitoids of Polistes myersi Bequaert, 1934 (Vespidae, Polistinae). Sociobiology 2020, 67, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabar, M.; Danci, A.; McCann, S.; Schaefer, P.; Gries, G. New findings on life history traits of Xenos peckii (Strepsiptera: Xenidae). Can. Entomol. 2014, 146, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrouzet, E.; Gevar, J.; Dupont, S. A scientific note about a parasitoid that can parasitize the yellow-legged hornet, Vespa velutina nigrithorax, in Europe. Apidologie 2015, 46, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayama, K.; Kosaka, H.; Makino, S. The first record of infection and sterilization by the nematode Sphaerularia in hornets (Hymenoptera, Vespidae, Vespa). Insectes Soc. 2007, 54, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemant, C.; Zuccon, D.; Rome, Q.; Muller, F.; Poinar, G.O., Jr.; Justine, J.L. Can parasites halt the invader? Mermithid nematodes parasitizing the yellow-legged Asian hornet in France. PeerJ 2015, 3, e947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.H.; An, S.L.; Lee, J.W. Review of Korean Latibulus (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae: Cryptinae) and a key to the world species. Can. Entomol. 2012, 144, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, K.; Sayama, K.; Choi, J.Y. Intraspecific color variation in Sphecophaga vesparum (Curtis) and subspecific status of the far eastern population (Hyemnoptera: Ichneumonidae). Jpn. J. Entomol. 1997, 65, 536–540. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.J.; Tan, J.L.; Lee, B.W.; Oh, S.H.; Choi, M.B. Discovery of a trigonalid wasp, Bareogonalos xibeidai (Hymenoptera: Trigonalyidae), reared from nests of Vespula koreensis koreensis (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in South Korea. J. Asia Pac. Biodivers. 2020, 13, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, S. New taxa of the genus Bareogonalos from Asia with further information on the tribe Nomadinini (Hymenoptera, Trigonalidae). Halteres 2014, 5, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.L.; Van Achterberg, C.; Tan, Q.Q.; Zhao, L.P. New species of Trigonalyidae (Hymenoptera) from NW China. ZooKeys 2017, 698, 17–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, I.K.; Kwon, O.; Choi, M.B. Two species of Elasmus japonicus Ashmead and Elasmus polistis Burks (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) reared form nests of Polistes (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in Korea. J. Asia Pac. Biodivers. 2016, 9, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, M.; Yamane, S. Biology of the Vespine Wasps; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, S.J. Occurrence of the Pyralid Moth Hypsopygia mauritialis (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae) in the nests of Vespa affinis (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Jpn. J. Entomol. 1992, 60, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki, M. Eagles Hawks Falcons; Heibon-sha: Tokyo, Japan, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Macià, F.X.; Menchetti, M.; Corbella, C.; Grajera, J.; Vila, R. Exploitation of the invasive Asian hornet Vespa velutina by the European honey buzzard Pernis apivorus. Bird Study 2019, 66, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Wilson, G. Factors affecting populations of social wasps, Vespula species, in England (Hymenoptera). Proc. R. Entomol. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Gen. Entomol. 1946, 21, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trap-Lind, I. Observations on a honey buzzard digging out a wasp’s nest. Br. Birds 1962, 55, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Spradbery, J.P. Wasps: An Account of the Biology and Natural History of Social and Solitary Wasps; Sidgwick & Jackson: London, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, J.F. Comparative and adaptive aspects of vespine nest construction. In Proceedings of the 8th International Congress IUSSI, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 5 September 1977; pp. 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, R. Social Wasps: Their Biology and Control; Rentokil Libr: East Grinstead, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.B.; Woo, D.; Choi, T.Y. Composition of the insect diet in feces of yellow-throated marten, Martes flavigula, in Jirisan National Park, South Korea. J. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 38, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, W.J.; Spencer, W.D.; Barrett, R.H. Relationship between food habits and activity patterns of pine martens. Mammal 1983, 64, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Choi, M.B.; Moon, T.Y. Occurrence of Vespa velutina Lepeletier from Korea, and a revised key for Korean Vespa species (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Entomolog. Res. 2006, 36, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, Y.; Kim, J.B.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, C.J.; Kwon, O.; Choi, M.B. Quantitative analysis of research topics and public concern on V. velutina as invasive species in Asian and European countries. Entomolog. Res. 2019, 49, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Jung, C. Risk prediction of the distribution of invasive hornet, Vespa velutina nigrothorax in Korea using CLIMEX model. J. Apicult. 2016, 31, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, A.; Negrisolo, E.; Bonomi, J.; Zulian, Z.; Cappa, F.; Bortolotti, L.; Mutinelli, F. Recent confirmation of a single haplotype in the Italian population of Vespa velutina. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 2811–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Takahashi, J. Discovery of a worker of Vespa velutina (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) from Tsuhima Island, Japan (Japanese with English summary). Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2014, 17, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Haxaire, J.; Bouguet, J.P.; Tamisier, J.P. Vespa velutina Lepeletire, 1836, une redoutable novueauté pour la faune de France (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Bull. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 2006, 111, 535–538. [Google Scholar]
- Husemann, M.; Sterr, A.; Maack, S.; Abraham, R. The northernmost record of the Asian hornet Vespa velutina nigrithorax (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Evol. Syst. 2020, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rome, Q.; Villemant, C. Le Frelon Asiatique Vespa velutina. Inventaire National du Patrimoine Naturel—Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle. Available online: http://frelonasiatique.mnhn.fr/home (accessed on 18 October 2020).
- Requier, F.; Rome, Q.; Chiron, G.; Decante, D.; Marion, S.; Menard, M.; Muller, F.; Villemant, C.; Henry, M. Predation of the invasive Asian hornet affects foraging activity and survival probability of honey bees in Western Europe. J. Pest. Sci. 2019, 92, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cini, A.; Cappa, F.; Petrocelli, I.; Pepiciello, I.; Bortolotti, L.; Cervo, R. Competition between the native and the introduced hornets Vespa crabro and Vespa velutina: A comparison of potentially relevant life-history traits. Ecol. Entomol. 2018, 43, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.B.; Kim, T.G.; Kwon, O. Recent trends in wasp nest removal and Hymenoptera stings in South Korea. J. Medic. Entomol. 2019, 56, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Takahashi, R.; Harada, R.; Matsuo, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Takahashi, J.I. Reproductive interference by alien hornet Vespa velutina threatens the native populations of Vespa simillima in Japan. Sci. Natur. 2019, 106, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioy, S.; Laurino, D.; Capello, M.; Romano, A.; Manino, A.; Porporato, M. Effectiveness and selectiveness of traps and baits for catching the invasive hornet Vespa velutina. Insects 2020, 11, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milanesio, D.; Saccani, M.; Maggiora, R.; Laurino, D.; Porporato, M. Recent upgrades of the harmonic radar for the tracking of the Asian yellow-legged hornet. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 4599–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, P.J.; Ford, S.M.; Poidatz, J.; Thiery, D.; Osborne, J.L. Searching for nests of the invasive Asian hornet (Vespa velutina) using radio-telemetry. Comm. Biol. 2018, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchi, L.; Derijard, B. Options for the biological and physical control of Vespa velutina nigrithorax (Hym.: Vespidae) in Europe: A review. J. Appl. Entomol. 2018, 142, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, K.S.; Heo, J.H.; Choi, M.B.; Yoon, H.J.; Hong, I.P.; Korea Apicultural Agriculture Cooperative; Korea Forest Service. Korean Beekeeping Industry and Save Honeybees Movement in Korea; Incheon National University Press: Incheon, Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, D.H.; Seomun, H.; Song, D.J.; Choi, E.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Cho, C.U.; Song, B.C.; Yang, D.H. Analysis of Asiatic black bear’s foods by using scats in the Jirisan National Park. Kor. J. Environ. Ecol. 2016, 30, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Biological Resources. Available online: https://species.nibr.go.kr/home/mainHome.do?cont_link=011&subMenu=011013&contCd=011013001001 (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/ (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- Woo, D.G. A Study on Ecological Characteristics and Conservation of Yellow-Throated Marten (Martes flavigula) in Temperate Forests of Korea. Ph.D. Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jedrzejewska, B.; Jedrejewski, W. Predation in Vertebrate Communities: The Bialowieza Primeval Forest as a Case Study; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, M.E. Vespine Wasps of the World: Behaviour, Ecology & Taxonomy of the Vespinae; Siri Scientific Press: Manchester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Song, W.; Lee, M.J. Habitat potential mapping of marten (Martes flavigula) and leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis) in South Korea using artificial neural network machine learning. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.; Woo, D.; Yang, B.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Jeong, W.; Choi, D. Management of Ecological Corridor to Conserve Wildlife Population (III); National Institute of Environmental Research: Incheon, Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.B.; Newman, C.; Xu, W.T.; Buesching, C.D.; Zalewski, A.; Kaneko, Y.; Macdonald, D.W.; Xie, Z.Q. Biogeographical variation in the diet of Holarctic martens (genus Martes, Mammalia: Carnivora: Mustelidae): Adaptive foraging in generalists. J. Biogeogr. 2010, 38, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slauson, K.M.; Zielinski, W.J. Seasonal specialization in diet of the Humboldt marten (Martes caurina humboldtensis) in California and the importance of prey size. J. Mammalog. 2017, 98, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlikowski, T.; Olszewski, P.; Piekarska-Boniecka, H.; Pawlikowski, K. Diversity of social wasp communities (Hymenoptera: Polistinae and Vespinae) in the agricultural landscape of Central Poland. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2016, 68, 553–556. [Google Scholar]
- Prowse, T.A.A.; Cassey, P.; Ross, J.V.; Pfitzner, C.; Wittmann, T.A.; Thomas, P. Dodging silver bullets: Good CRISPR gene-drive design is critical for eradicating exotic vertebrates. Proc. R. Soc. B 2017, 284, 20170799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alphey, L.; Benedict, M.; Bellini, R.; Clark, G.G.; Dame, D.A.; Service, M.W.; Dobson, S.L. Sterile-insect methods for control of mosquito-borne diseases: An analysis. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Wu, Y.; Liang, X.; Liang, Y.; Pan, X.; Linchao, H.; Sun, Q.; et al. Incompatible and sterile insect techniques combined to eliminate mosquitoes. Nature 2019, 572, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seomun, H. Analysis of Asiatic Black Bears’s Foods by Using Feces. Master’s Thesis, Kookmin University, Seoul, Korea, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.J.; Kim, T.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, S.H.; Han, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Oh, H.S. A case study of the habitat expansion of the Asiatic black bear (Ursus thibetanus ussuricus). Kor. J. Environ. Biol. 2019, 37, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
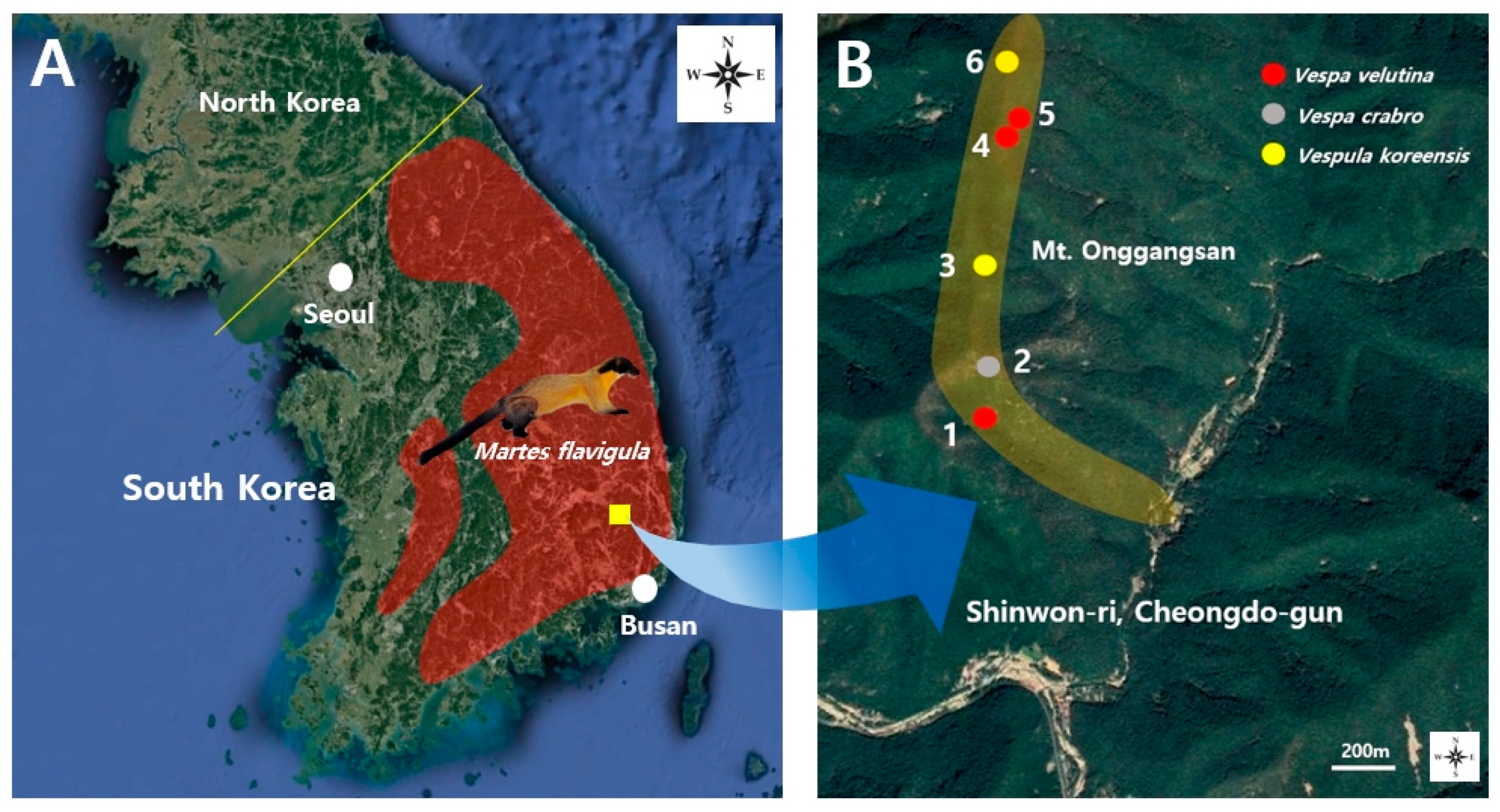
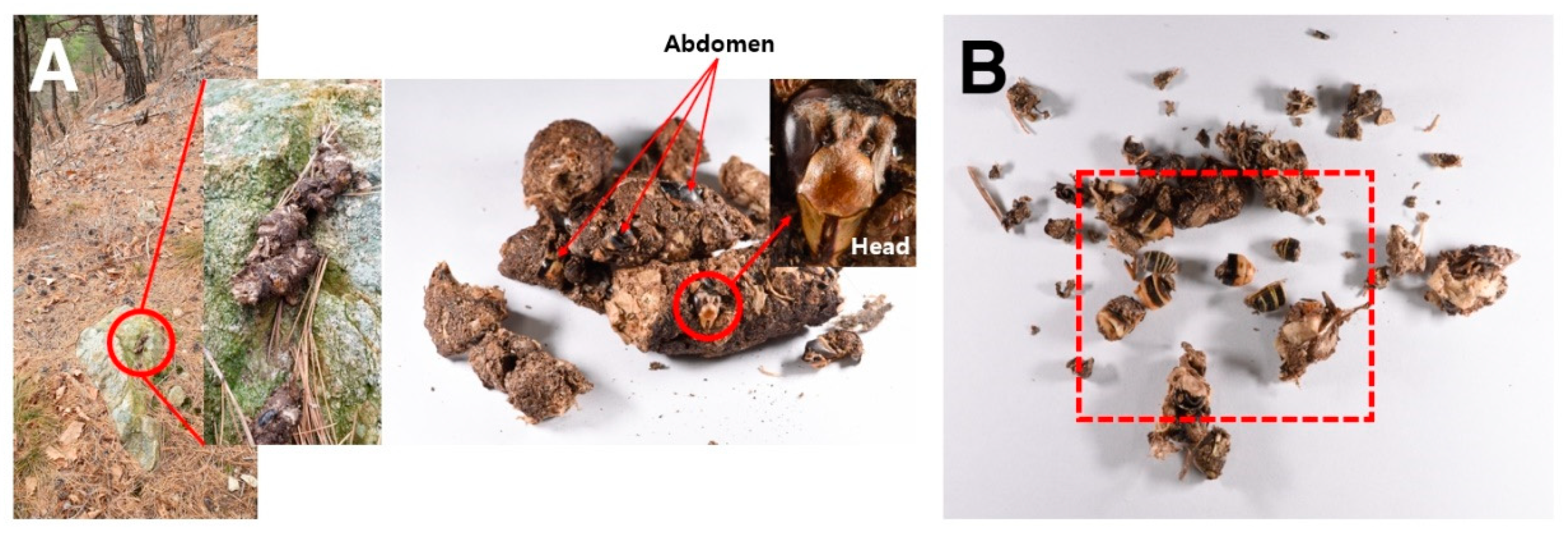
| Fecal Collection Area | Coordinates | Altitude (m) | Date of Collection | Identification | Sex and Caste | Number of Individuals | * Number of Fecal Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N35°40′52.06″ E129°00′03.62″ | 501 | 11/13 | Vespa velutina | Female | 1 | 1 |
| Male | 2 | ||||||
| 2 | N35°40′56.22″ E129°00′03.76″ | 593 | 10/23 | Vespa crabro | Female | 2 | 1 |
| 3 | N35°41′07.06″ E129°00′05.52″ | 583 | 11/13 | Vespula koreensis | Queen | 4 | 1 |
| Male | 2 | ||||||
| 4 | N35°41′21.13″ E129°00′11.73″ | 716 | 11/13 | Vespa velutina | Male | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | N35°41′24.50″ E129°00′14.40″ | 728 | 12/4 | Vespa velutina | Queen | 1 | 1 |
| Wasp | 1 | ||||||
| 6 | N35°41′41.87″ E129°00′20.81″ | 722 | 10/23 | Vespula koreensis | Queen | 3 | 1 |
| Male | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, C.-J.; Choi, M.B. First Discovery of Vespa velutina nigrithorax du Buysson (Hymenoptera: Vespidae), an Invasive Hornet in the Feces of the Yellow-Throated Marten in South Korea. Insects 2021, 12, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12040296
Kim C-J, Choi MB. First Discovery of Vespa velutina nigrithorax du Buysson (Hymenoptera: Vespidae), an Invasive Hornet in the Feces of the Yellow-Throated Marten in South Korea. Insects. 2021; 12(4):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12040296
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Chang-Jun, and Moon Bo Choi. 2021. "First Discovery of Vespa velutina nigrithorax du Buysson (Hymenoptera: Vespidae), an Invasive Hornet in the Feces of the Yellow-Throated Marten in South Korea" Insects 12, no. 4: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12040296
APA StyleKim, C.-J., & Choi, M. B. (2021). First Discovery of Vespa velutina nigrithorax du Buysson (Hymenoptera: Vespidae), an Invasive Hornet in the Feces of the Yellow-Throated Marten in South Korea. Insects, 12(4), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12040296






