Performance of a Native Butterfly and Introduced Moth on Native and Introduced Lineages of Phragmites australis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Collection and Propagation
2.2. Insect Collection and Rearing
2.3. Field Surveys for Rhizedra lutosa
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Poanes viator Larvae Fed Leaves
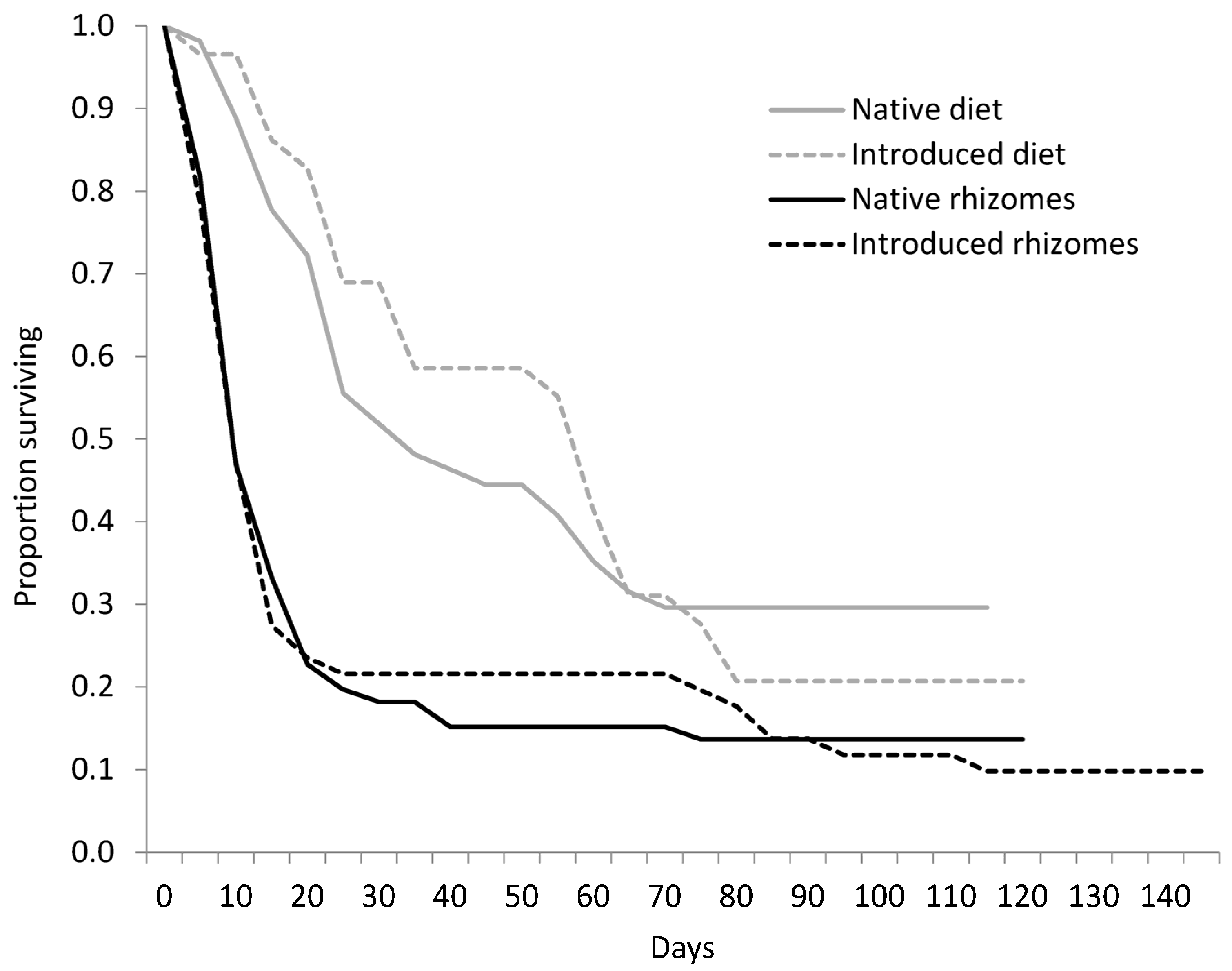
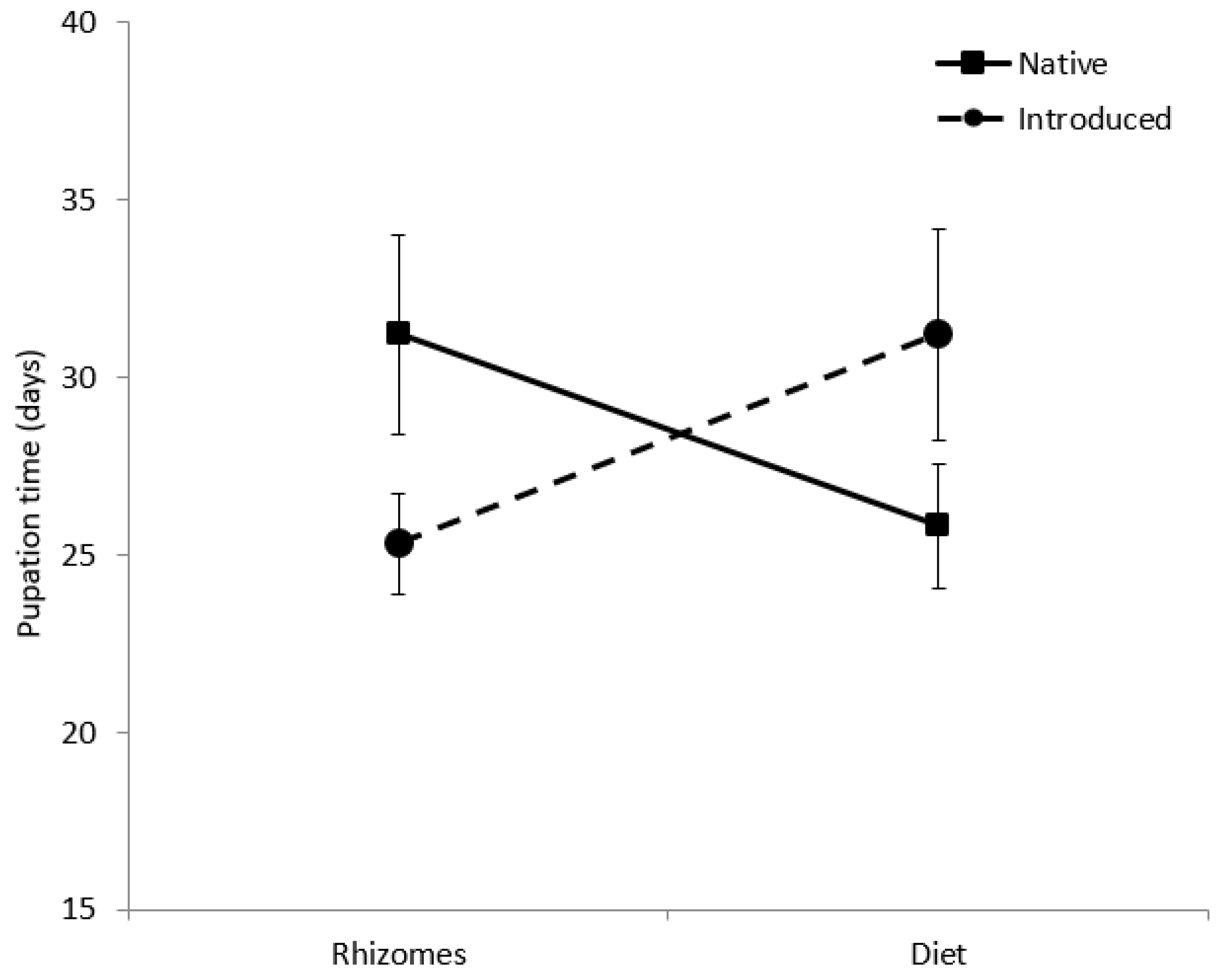
3.2. Rhizedra lutosa Larvae Fed Rhizomes or Diet
3.3. Field Surveys for Rhizedra lutosa
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambert, A.M.; Saltonstall, K.; Long, R.; Dudley, T.L. Biogeography of Phragmites australis lineages in the southwestern United States. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 2597–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltonstall, K. Cryptic invasion by a non-native genotype of the common reed, Phragmites australis, into North America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2445–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chambers, R.M.; Meyerson, L.A.; Saltonstall, K. Expansion of Phragmites australis into tidal wetlands of North America. Aquat. Bot. 1999, 64, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerson, L.A.; Lambert, A.M.; Saltonstall, K. A tale of three lineages: Expansion of common reed (Phragmites australis) in the U.S. Southwest and gulf coast. Invasive Plant Sci. Manag. 2010, 3, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossey, B.; Casagrande, R.A. Biological control of invasive Phragmites may safeguard native Phragmites and increase wetland conservation values. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 2753–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossey, B.; Häfliger, P.; Tewksbury, L.; Dávalos, A.; Casagrande, R.A. Host specificity and risk assessment of Archanara geminipuncta and Archanara neurica, two potential biocontrol agents for invasive Phragmites australis in North America. Biol. Control 2018, 125, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewksbury, L.; Casagrande, R.A.; Blossey, B.; Hafliger, P.; Schwarzlander, M. Potential for biological control of Phragmites australis in North America. Biol. Control 2002, 23, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossey, B.; Endriss, S.B.; Casagrande, R.; Häfliger, P.; Hinz, H.; Dávalos, A.; Brown-Lima, C.; Tewksbury, L.; Bourchier, R.S. When misconceptions impede best practices: Evidence supports biological control of invasive Phragmites. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cronin, J.T.; Kiviat, E.; Meyerson, L.A.; Bhattarai, G.P.; Allen, W.J. Biological control of invasive Phragmites australis will be detrimental to native P. australis. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 2749–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, G.P.; Meyerson, L.A.; Cronin, J.T. Geographic variation in apparent competition between native and invasive Phragmites australis. Ecology 2017, 98, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cronin, J.T.; Bhattarai, G.P.; Allen, W.J.; Meyerson, L.A. Biogeography of a plant invasion: Plant–herbivore interactions. Ecology 2015, 96, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kendall, R.O. Larval food plants and distribution notes for three Texas Hesperiidae. J. Lepid. Soc. 1966, 20, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, A.M. Notes on the biology of Poanes viator (Hesperiidae) with the description of a new subspecies. J. Res. Lepid. 1970, 9, 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Gochfeld, M.; Burger, J. Butterflies of New Jersey; Rutgers University Press: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- van der Toorn, J.; Mook, J.H. The influence of environmental factors and management on stands of Phragmites australis. I. Effects of burning, frost and insect damage on shoot density and shoot size. J. Appl. Ecol. 1982, 19, 477–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, T.L.; Schweitzer, D.F. Rhizedra lutosa (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) newly introduced to North America. Entomol. News 1991, 102, 130–132. [Google Scholar]
- Casagrande, R.A.; Balme, G.; Blossey, B. Rhizedra lutosa, a natural enemy of Phragmites australis in North America. Estuaries 2003, 26, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkola, K.; Lafontaine, J.D. Recent introductions of riparian noctuid moths from the Palearctic region to North America, with the first report of Apamea unanimis (Huebner) (Noctuidae; Amphipyrinae). J. Lepid. Soc. 1994, 48, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Balme, G. Insects on Phragmites australis. Master’s Thesis, University of Rhode Island, Kingston, RI, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lambertini, C.; Mendelssohn, I.A.; Gustafsson, M.H.G.; Olesen, B.; RIIS, T.; Sorrell, B.K.; Brix, H. Tracing the origin of Gulf Coast Phragmites (Poaceae): A story of long-distance dispersal and hybridization. Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.M.; Casagrande, R.A. Susceptibility of native and non-native common reed to the non-native mealy plum aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) in North America. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, W.J.; Young, R.E.; Bhattarai, G.P.; Croy, J.R.; Lambert, A.M.; Meyerson, L.A.; Cronin, J.T. Multitrophic enemy escape of invasive Phragmites australis and its introduced herbivores in North America. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 3419–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.M.; Winiarski, K.; Casagrande, R.A. Distribution and impact of exotic gall flies (Lipara sp.) on native and exotic Phragmites australis. Aquat. Bot. 2007, 86, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalucki, M.P.; Clarke, A.R.; Malcolm, S.B. Ecology and behavior of first instar larval lepidoptera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 361–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyi, A.; Zalucki, M.P.; Titmarsh, I.J. An experimental study of early stage survival of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on cotton. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1991, 81, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titmarsh, I.J. Mortality of Immature Lepidoptera: A Case Study with Heliothis Species (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Agricultural Crops on the Darling Downs. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Queensland, St Lucia, Australia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, E.E.; Gosnell, S.; Hallagan, C.; Otten, K.E.; Slayter, L.; Murphy, S.M. Performance of Western tent caterpillar (Malacosoma californicum) on two common host plants, including a new host plant record. J. Lepid. Soc. 2016, 70, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.S.; Rodrigues, D.; Stireman, J.O., III; Carrière, Y. Roles of food quality and enemy-free space in host use by a generalist insect herbivore. Ecology 2004, 85, 2747–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenbaum, M.R.; Zangerl, A.R. Chemical phenotype matching between a plant and its insect herbivore. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13743–13748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyerson, L.A.; Saltonstall, K.; Windham, L.; Kiviat, E.; Findlay, S. A comparison of Phragmites australisin freshwater and brackish marsh environments in North America. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 8, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, I.; Cooper, D.R. An inland population of Poanes viator (Hesperiidae) associated with Phragmites australis, the common reed. J. Lepid. Soc. 2005, 59, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Häfliger, P.; Teyssiere, S. Evaluating the Potential for Biological Control of Common Reed, Phragmites Australis; Annual Report 2003; CABI Bioscience, Switzerland Centre: Delémont, Switzerland, 2004; Unpublished report. [Google Scholar]
- Bossdorf, O.; Schroder, S.; Prati, D.; Auge, H. Palatability and tolerance to simulated herbivory in native and introduced populations of Alliaria petiolata (Brassicaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2004, 91, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemann, E.; Rogers, W.E. Reduced resistance of invasive varieties of the alien tree Sapium sebiferum to a generalist herbivore. Oecologia 2003, 135, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Siemann, E.; Zou, J.; Wheeler, G.S.; Carrillo, J.; Ding, J. Lower resistance and higher tolerance of invasive host plants: Biocontrol agents reach high densities but exert weak control. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, D.A. The Role of trichomes in plant defense. Q. Rev. Biol. 1973, 48, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, V.; Cuda, J.P.; Overholt, W.A.; Williams, D.A.; Wheeler, G.S. Effect of host-plant genotypes on the performance of three candidate biological control agents of Schinus terebinthifolius in Florida. Biol. Control 2008, 47, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, N.; Rausher, M.D. The effects of host-plant genotype on herbovire population dynamics. Ecology 2000, 81, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awmack, C.S.; Leather, S.R. Host plant quality and fecundity in herbivorous insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 817–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Rossi, D.; Rank, N.; Strong, D.R. Potential for self-defeating biological control? Variation in herbivore vulnerability among invasive Spartina genotypes. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 1640–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Plant Species | Native Status | N | Larval Duration of Individuals Not Reaching Pupation (Days ± SD) | Larval Duration of Individuals Reaching Pupation (Days ± SD) | N Pupated | Pupal Weight (g) | Pupal Duration (Days) | N Eclosed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phragmites australis | ||||||||
| Haplotype M (RI) | Introduced | 11 | 13.6 ± 14.6 | - | 0 | - | - | - |
| Haplotype M (NY) | Introduced | 11 | 8.3 ± 3.9 | - | 0 | - | - | - |
| Haplotype E (ME) | Native | 11 | 8.6 ± 2.2 | - | 0 | - | - | - |
| Haplotype E (NY) | Native | 12 | 8.4 ± 8.1 | 49.6 ± 11.8 | 3 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 13.0 ± 1.4 | 2 |
| Haplotype AB (RI) | Native | 13 | 10.3 ± 9.2 | 78.5 ± 6.4 | 2 | 0.34 ± 0.04 | 12.0 ± 1.4 | 2 |
| Zizania aquatica | Native | 13 | 16.6 ± 10.3 | 52.0 ± 1.0 | 3 | 0.32 ± 0.07 | 13.7 ± 1.5 | 3 |
| Plant Species | Initial N | N Died in Larval Stage | N Entering Diapause | N Pupated | N Eclosed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phragmites australis | |||||
| Haplotype M (RI) | 11 | 7 | 4 | 0 | - |
| Haplotype M (NY) | 11 | 8 | 3 | 0 | - |
| Haplotype E (ME) | 11 | 7 | 4 | 0 | - |
| Haplotype E (NY) | 12 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 2 |
| Haplotype AB (RI) | 13 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Zizania aquatica | 13 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Native plants | 49 | 30 | 12 | 7 | 7 |
| Introduced plants | 22 | 15 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Haplotype | Native Status | N | Larval Duration of Individuals Not Reaching Pupation (Days ± SD) | Larval Duration of Individuals Reaching Pupation (Days ± SD) | N Pupated | Pupal Weight (g) | Pupal Duration (days) | N Eclosed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R. lutosa fed rhizomes | ||||||||
| Haplotype M (RI) | Introduced | 25 | 24.0 ± 37.1 | 122.0 ± 16.3 | 4 | 0.47 ± 0.03 | 24.0± 2.8 | 3 |
| Haplotype M (NY) | Introduced | 27 | 15.1 ± 22.9 | 82 | 1 | no data | 25 | 1 |
| Haplotype E (ME) | Native | 32 | 9.2 ± 7.7 | 106.3 ± 11.0 | 3 | 0.62 ± 0.07 | 27.3 ± 2.1 | 3 |
| Haplotype E (NY) | Native | 22 | 13.0 ± 8.6 | 100.0 ± 8.8 | 4 | 0.46 ± 0.08 | 29.5 ± 5.7 | 4 |
| Haplotype AB (RI) | Native | 11 | 33.7 ± 46.5 | 119.0 ± 7.1 | 2 | 0.29 ± 0.08 | 38 | 1 |
| Native haplotypes | 66 | 11.3 ± 11.3 | 106.3 ± 11.2 | 9 | 0.48 ± 0.15 | 29.6 ± 5.4 | 8 | |
| Introduced haplotype | 51 | 19.3 ± 30.0 | 114.0 ± 22.8 | 5 | 0.52 ± 0.07 | 25.3 ± 2.5 | 4 | |
| R. lutosa fed diet | ||||||||
| Haplotype M (RI) | Introduced | 28 | 48.4 ± 36.8 | 66.2 ± 13.7 | 6 | 0.74 ± 0.11 | 31.2 ± 6.7 | 5 |
| Haplotype E (NY) | Native | 27 | 31.7 ± 24.2 | 80.4 ± 19.8 | 9 | 0.64 ± 0.16 | 24.6 ± 5.4 | 8 |
| Haplotype AB (RI) | Native | 28 | 33.1 ± 527.2 | 73.8 ± 25.0 | 7 | 0.73 ± 0.21 | 27.6 ± 4.5 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lambert, A.M.; Tewksbury, L.A.; Casagrande, R.A. Performance of a Native Butterfly and Introduced Moth on Native and Introduced Lineages of Phragmites australis. Insects 2021, 12, 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121102
Lambert AM, Tewksbury LA, Casagrande RA. Performance of a Native Butterfly and Introduced Moth on Native and Introduced Lineages of Phragmites australis. Insects. 2021; 12(12):1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121102
Chicago/Turabian StyleLambert, Adam M., Lisa A. Tewksbury, and Richard A. Casagrande. 2021. "Performance of a Native Butterfly and Introduced Moth on Native and Introduced Lineages of Phragmites australis" Insects 12, no. 12: 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121102
APA StyleLambert, A. M., Tewksbury, L. A., & Casagrande, R. A. (2021). Performance of a Native Butterfly and Introduced Moth on Native and Introduced Lineages of Phragmites australis. Insects, 12(12), 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121102






