Metabolic Resistance in Permethrin-Resistant Florida Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mosquito Egg Collection
2.2. Mosquito Rearing
2.3. Permethrin Susceptibility Assay
2.4. Permethrin Metabolic Resistance Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Permethrin Susceptiblity
3.2. Permethrin Metabolic Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brady, O.J.; Hay, S.I. The Global Expansion of Dengue: How. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowman, L.R.; Donegan, S.; McCall, P.J. Is Dengue Vector Control Deficient in Effectiveness or Evidence? Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soderlund, D.; Bloomquist, J. Neurotoxic Actions of Pyrethroid Insecticides. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1989, 34, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estep, A.; Sanscrainte, N.; Waits, C.; Bernard, S.; Lloyd, A.; Lucas, K.; Buckner, E.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Morreale, R.; Conti, L.; et al. Quantification of permethrin resistance and kdr alleles in Florida strains of Aedes aegypti (L.) and Aedes albopictus (Skuse). PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EPA. Permethrin, Resmethrin, d-Phenothrin (Sumithrin): Synthetic Pyrethroids for Mosquito Control. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/mosquitocontrol/permethrin-resmethrin-d-phenothrin-sumithrinr-synthetic-pyrethroids-mosquito-control (accessed on 12 February 2021).
- Parker, C.; Ramirez, D.; Thomas, C.; Connelly, R.C. Baseline Susceptibility Status of Florida Populations of Aedes aegypti (Diperta: Culicide) and Aedes albopictus. J. Med. Entomol. 2020, 57, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. 22nd Report by the Expert Committee of Insecticides. WHO Tech. Rep. Ser. 1976, 585, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Georghiou, G.; Taylor, C. Factors Influencing the Evolution of Resistance. In Pesticide Resistance: Strategies and Tactics for Management; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; pp. 157–169. [Google Scholar]
- Amelia-Yap, Z.; Chen, C.; Sofian-Azirun, M.; Low, V. Pyrethroid resistance in the dengue vector Aedes aegypti in Southeast Asia: Present situation and prospects for management. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, N.; Berenbaum, M. Insecticide Resistance in Mosquitoes: Impact, Mechanisms, and Research Directions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.; Ismail, H.; Chandor-Proust, A.; Paine, M. Role of cytochrome P450s in insecticide resistance: Impact on the control of mosquito-borne diseases and use of insecticides on Earth. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faucon, F.; Dusfour, I.; Gaude, T.; Navratil, V.; Boyer, F.; Chandre, F.; Sirisopa, P.; Thanispong, K.; Juntarajumnong, W.; Poupardin, R.; et al. Identifying genomic changes associated with insecticide resistance in the dengue mosquito Aedes aegypti by deep targeted sequencing. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1347–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamita, S.; Mulligan, S.; Cornel, A.; Hammock, B. Quantification of GST and esterase activities in pyrethrin-resistant mosquitoes using pyrethroid-like fluorescent substrates. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 2016, 62, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucon, F.; Gaude, T.; Dusfour, I.; Navratil, V.; Corbel, V.; Juntarajumnong, W.; Girod, R.; Poupardin, R.; Boyer, F.; Reynaud, S.; et al. In the hunt for genomic markers of metabolic resistance to pyrethroids in the mosquito Aedes aegypti: An integrated next-generation sequencing approach. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yang, P.; Jiang, F.; Cui, N.; Ma, E.; Qiao, C.; Cui, F. Transcriptomic and phylogenetic analysis of Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus for three detoxification gene families. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xing, D.; Yan, T.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, T. Identification of genes involved in pyrethroid-, propoxur-, and dichlorvos- insecticides resistance in the mosquitoes, Culex pipiens complex (Diptera: Culicidae). Acta Trop. 2016, 157, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.S.; Kim, H.C.; Klein, T.A.; Ju, Y.R. Insecticide resistance and cytochrome-P450 activation in unfed and blood-fed laboratory and field populations of. J. Pest. Sci. 2017, 90, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, N.; Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, D.; Shen, B.; Zhu, C. Identification and classification of differentially expressed genes in pyrethroid-resistant Culex pipiens pallens. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2019, 294, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namountougou, M.; Simard, F.; Baldet, T.; Diabaté, A.; Ouédraogo, J.B.; Martin, T.; Dabiré, R.K. Multiple insecticide resistance in Anopheles gambiae s.l. populations from Burkina Faso, West Africa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balmert, N.; Rund, S.; Ghazi, J.; Zhou, P.; Duffield, G. Time-of-day specific changes in metabolic detoxification and insecticide resistance in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. J. Insect Physiol. 2014, 64, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolfi, A.; Poulton, B.; Anthousi, A.; Macilwee, S.; Ranson, H.; Lycett, G. Functional genetic validation of key genes conferring insecticide resistance in the major African malaria vector, Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25764–25772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machani, M.G.; Ochomo, E.; Zhong, D.; Zhou, G.; Wang, X.; Githeko, A.K.; Yan, G.; Afrane, Y.A. Phenotypic, genotypic and biochemical changes during pyrethroid resistance selection in Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeu, M.; Mulamba, C.; Weedall, G.; Wondji, C. A differential expression of pyrethroid resistance genes in the malaria vector Anopheles funestus across Uganda is associated with patterns of gene flow. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poupardin, R.; Reynaud, S.; Strode, C.; Ranson, H.; Vontas, J.; David, J. Cross-induction of detoxification genes by environmental xenobiotics and insecticides in the mosquito Aedes aegypti: Impact on larval tolerance to chemical insecticides. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcombe, S.; Poupardin, R.; Darriet, F.; Reynaud, S.; Bonnet, J.; Strode, C.; Brengues, C.; Yebakima, A.; Ranson, H.; Corbel, V.; et al. Exploring the molecular basis of insecticide resistance in the dengue vector Aedes aegypti: A case study in Martinique Island (French West Indies). BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saavedra-Rodriguez, K.; Suarez, A.F.; Salas, I.F.; Strode, C.; Ranson, H.; Hemingway, J.; Black, W.C. Transcription of detoxification genes after permethrin selection in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insect Mol. Biol. 2012, 21, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelia-Yap, Z.; Sofian-Azirun, M.; Chen, C.; Suana, I.; Lau, K.; Elia-Amira, N.; Haziqah-Rashid, A.; Tan, T.; Lim, Y.; Low, V. Pyrethroids Use: Threats on Metabolic-Mediated Resistance Mechanisms in the Primary Dengue Vector Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemingway, J.; Ranson, H. Insecticide resistance in insect vectors of human disease. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J. Cytochromes P450 and insecticide resistance. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 29, 757–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, B.; Pignatelli, P.; Nikou, D.; Paine, M. Pinpointing P450s Associated with Pyrethroid Metabolism in the Dengue Vector, Aedes aegypti: Developing New Tools to Combat Insecticide Resistance. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasai, S.; Komagata, O.; Itokawa, K.; Shono, T.; Ng, L.; Kobayashi, M.; Tomita, T. Mechanisms of Pyrethroid Resistance in the Dengue Mosquito Vector, Aedes aegypti: Target Site Insensitivity, Penetration, and Metabolism. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lumjuan, N.; Rajatileka, S.; Changsom, D.; Wicheer, J.; Leelapat, P.; Prapanthadara, L.; Somboon, P.; Lycett, G.; Ranson, H. The role of the Aedes aegypti Epsilon glutathione transferases in conferring resistance to DDT and pyrethroid insecticides. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paeporn, P.; Supaphathom, K.; Srisawat, R.; Komalamisra, N.; Deesin, V.; Ya-umphan, P.; Lemming Sawat, S. Biochemical detection of pyrethroid resistance mechanism in Aedes aegypti in Ratchaburi province, Thailand. Trop. Biomed. 2004, 21, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grigoraki, L.; Balabanidou, V.; Meristoudis, C.; Miridakis, A.; Ranson, H.; Swevers, L.; Vontas, J. Functional and immunohistochemical characterization of CCEae3a, a carboxylesterase associated with temephos resistance in the major arbovirus vectors Aedes aegypti and Ae. albopictus. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 74, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corbel, V.; N’Guessan, R. Distribution, Mechanisms, Impact and Management of Insecticide Resistance in Malaria Vectors: A Pragmatic Review. In Anopheles Mosquitoes-New Insights into Malaria Vectors; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tchigossou, G.; Djouaka, R.; Akoton, R.; Riveron, J.; Irving, H.; Atoyebi, S.; Moutairou, K.; Yessoufou, A.; Wondji, C. Molecular basis of permethrin and DDT resistance in an Anopheles funestus population from Benin. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seixas, G.; Grigoraki, L.; Weetman, D.; Vicente, J.; Silva, A.; Pinto, J.; Vontas, J.; Sousa, C. Insecticide resistance is mediated by multiple mechanisms in recently introduced Aedes aegypti from Madeira Island (Portugal). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parker, C.; Ramirez, D.; Connelly, C.R. State-wide survey of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) in Florida. J. Vector Ecol. 2019, 44, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuno, G. Early History of Laboratory Breeding of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) Focusing on the Origins and Use of Selected Strains. J. Med. Entomol. 2010, 47, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brogdon, W.G.; McAllister, J.C. Simplification of adult mosquito bioassays through use of time-mortality determinations in glass bottles. J. Am. Mosq. Control. Assoc. 1998, 14, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- CDC—Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CONUS Manual for Evaluating Insecticide Resistance in Mosquitoes Using the CDC Bottle Bioassay Kit. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mosquitoes/pdfs/CONUS-508.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2021).
- Abbott, W.S. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Am. Mosq. Control. Assoc. 1925, 3, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aïzoun, N.; Aïkpon, R.; Padonou, G.G.; Oussou, O.; Oké-Agbo, F.; Gnanguenon, V.; Ossè, R.; Akogbéto, M. Mixed-function oxidases and esterases associated with permethrin, deltamethrin and bendiocarb resistance in Anopheles gambiae s.l. in the south-north transect Benin, West Africa. Parasit Vectors 2013, 6, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dadzie, S.K.; Chabi, J.; Asafu-Adjaye, A.; Owusu-Akrofi, O.; Baffoe-Wilmot, A.; Malm, K.; Bart-Plange, C.; Coleman, S.; Appawu, M.A.; Boakye, D.A. Evaluation of piperonyl butoxide in enhancing the efficacy of pyrethroid insecticides against resistant Anopheles gambiae s.l. in Ghana. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okia, M.; Hoel, D.F.; Kirunda, J.; Rwakimari, J.B.; Mpeka, B.; Ambayo, D.; Price, A.; Oguttu, D.W.; Okui, A.P.; Govere, J. Insecticide resistance status of the malaria mosquitoes: Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles funestus in eastern and northern Uganda. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, L.M.; Rašić, G.; Peatey, C.L.; Hugo, L.E.; Beebe, N.W.; Devine, G.J. Identifying the fitness costs of a pyrethroid-resistant genotype in the major arboviral vector Aedes aegypti. Parasit Vectors 2020, 13, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, W.R. Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 1989, 43, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.; Kasai, S.; Scott, J. Pyrethroid resistance in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus: Important mosquito vectors of human diseases. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 133, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.; Tyagi, R.; Kasai, S.; Scott, J. CYP-mediated permethrin resistance in Aedes aegypti and evidence for trans-regulation. PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badolo, A.; Sombie, A.; Pignatelli, P.; Sanon, A.; Yameogo, F.; Wangrawa, D.; Kanuka, H.; McCall, P.; Weetman, D. Insecticide resistance levels and mechanisms in Aedes aegypti populations in and around Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, C.S.; Vythilingam, I.; Liew, J.W.; Wong, M.L.; Wan-Yusoff, W.S.; Lau, Y.L. Enzymatic and molecular characterization of insecticide resistance mechanisms in field populations of Aedes aegypti from Selangor, Malaysia. Parasit Vectors 2019, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethuan, S.; Jirakanjanakit, N.; Saengtharatip, S.; Chareonviriyaphap, T.; Kaewpa, D.; Rongnoparut, P. Biochemical studies of insecticide resistance in Aedes (Stegomyia) aegypti and Aedes (Stegomyia) albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) in Thailand. Trop. Biomed. 2007, 24, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Polson, K.A.; Brogdon, W.G.; Rawlins, S.C.; Chadee, D.D. Characterization of insecticide resistance in Trinidadian strains of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Acta Trop. 2011, 117, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, V.L.; Chen, C.D.; Lee, H.L.; Tan, T.K.; Chen, C.F.; Leong, C.S.; Lim, Y.A.; Lim, P.E.; Norma-Rashid, Y.; Sofian-Azirun, M. Enzymatic characterization of insecticide resistance mechanisms in field populations of Malaysian Culex quinquefasciatus say (Diptera: Culicidae). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Astari, S.; Tan, M. Resistance of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) in 2006 to pyrethroid insecticides in Indonesia and its association with oxidase and esterase levels. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 10, 3688–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Putra, R.E.; Ahmad, I.; Prasetyo, D.B.; Susanti, S.; Rahayu, R.; Hariani, N. Detection of insecticide resistance in the larvae of some Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) strains from Java, Indonesia to Temephos, Malathion and Permethrin. Int. J. Mosq. Res. 2016, 3, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, K.J.; Bales, R.B.; McCoy, K.; Weldon, C. Oxidase, esterase, and KDR-associated pyrethroid resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus field collections of Collier County, Florida. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2020, 36, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayati, A.A.; Vatandoost, H.; Ladonni, H.; Townson, H.; Hemingway, J. Molecular evidence for a kdr-like pyrethroid resistance mechanism in the malaria vector mosquito Anopheles stephensi. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2003, 17, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, N. Resistance in the mosquito, Culex quinquefasciatus, and possible mechanisms for resistance. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2005, 61, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunning, R.V.; Moores, G.D.; Devonshire, A.L. Inhibition of resistance related esterase by piperonyl butoxide in Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctoidae) and Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). In Piperonyl Butoxide: The Insecticide Synergist; Jones, G., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1998; pp. 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Young, S.J.; Gunning, R.V.; Moores, G.D. The effect of piperonyl butoxide on pyrethroid-resistance-associated esterases in Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pest. Manag. Sci. 2005, 61, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, S.J.; Gunning, R.V.; Moores, G.D. Effect of pretreatment with piperonyl butoxide on pyrethroid efficacy against insecticide-resistant Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and Bemisia tabaci (Sternorrhyncha: Aleyrodidae). Pest. Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
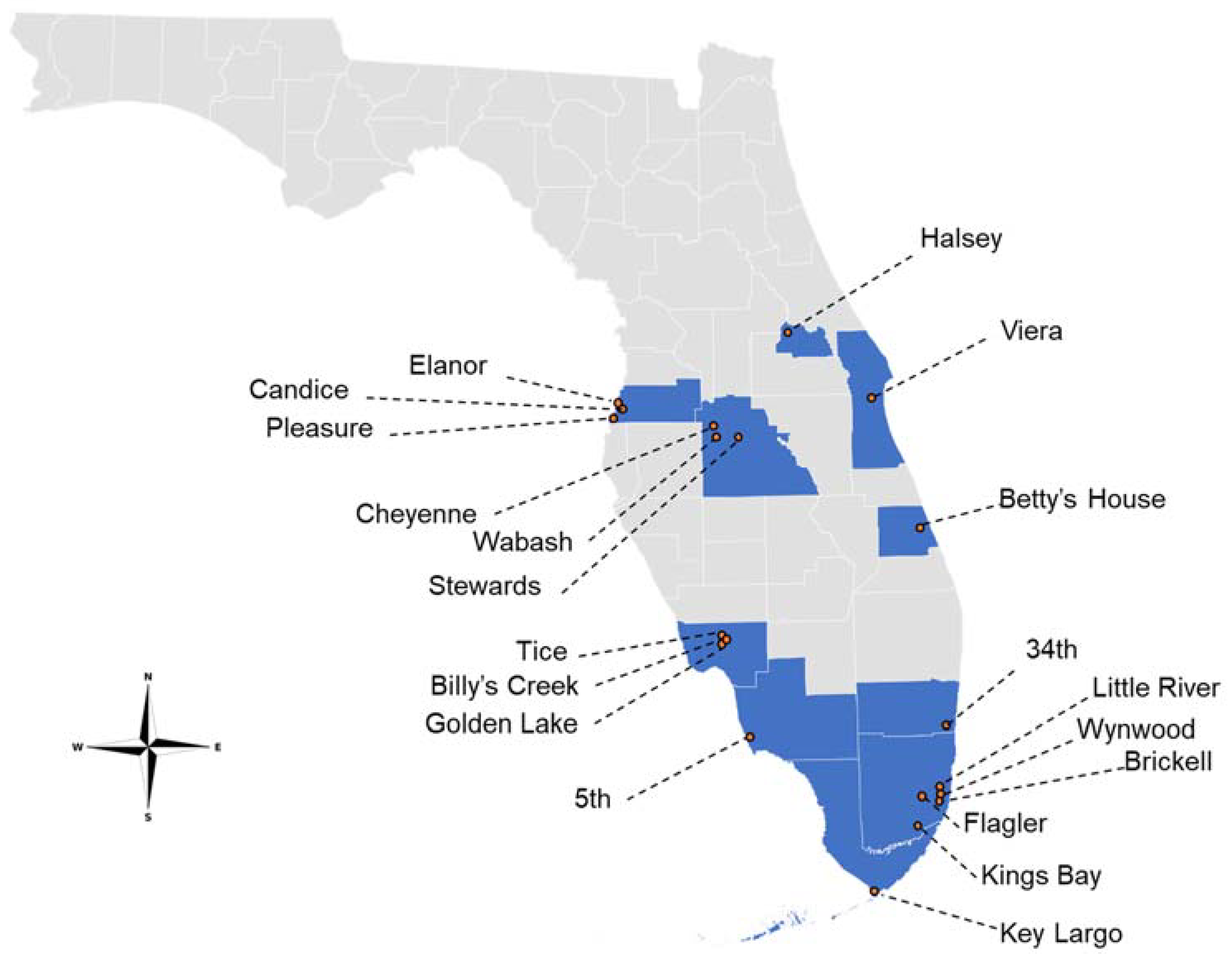
| County | Site | Latitude | Longitude | Date Collected | Collector |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brevard | Viera | 28.24641 | −80.73662 | 10–11/2019 | C. McDowell |
| Broward | 34th | 26.035359 | −80.178085 | 10/2020 | T. Hamilton |
| Collier | 5th | 26.14090 | −81.803287 | 10/2020 | R. Bales |
| Lee | Billy’s Creek | 26.660952 | −81.811921 | 08/2020 | K. Tyler-Julian |
| Lee | Golden Lake | 26.65284 | −81.81183 | 08/2020 | K. Tyler-Julian |
| Lee | Tice | 26.67116 | −81.811934 | 10/2020 | K. Tyler-Julian |
| Miami Dade | Brickell | 25.7586 | −80.19819 | 06–07/2020 | J. Medina |
| Miami Dade | Flagler | 25.77342 | −80.28567 | 09–11/2019 | J. Medina |
| Miami Dade | Kings Bay | 25.63456 | −80.29749 | 09–11/2019 | J. Medina |
| Miami Dade | Little River | 25.83762 | −80.19921 | 07–08/2019 | J. Medina |
| Miami Dade | Wynwood | 25.80475 | −80.19776 | 07–08/2019 | J. Medina |
| Monroe | Key Largo | 25.131444 | −80.405158 | 06/2020 | C. Pruszynski |
| Pasco | Candice | 28.261939 | −82.705499 | 09–10/2020 | A. Janusauskaite |
| Pasco | Elanor | 28.322423 | −82.706873 | 09–10/2020 | A. Janusauskaite |
| Pasco | Pleasure | 28.186338 | −82.745269 | 09–10/2020 | A. Janusauskaite |
| Polk | Cheyenne | 28.14449 | −82.00326 | 08/2020 | J. Mosley |
| Polk | Stewards | 28.04472 | −81.77675 | 08/2020 | J. Mosley |
| Polk | Wabash | 28.04866 | −81.99078 | 08/2020 | J. Mosley |
| Seminole | Halsey | 28.82609 | −81.335136 | 10/19–01/20 | T. Jones |
| St. Lucie | Betty’s House | 27.411226 | −80.336365 | 08/2020 | B. Starke |
| Chemical | Diagnostic Dose (μg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Permethrin | 43 |
| Diethyl maleate (DM) | 80 |
| Piperonyl butoxide (PBO) | 400 |
| S.S.S-tributyl phosphorotrithioate (DEF) | 125 |
| County | Site | DT (min) | % Mortality at DT | Resistance Status | Generation Tested |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brevard | Viera | 10 | 6 | R | F1 |
| Broward | 34th | 10 | 21 | R | F0 |
| Collier | 5th | 10 | 0 | R | F1 |
| Lee | Billy’s Creek | 10 | 1 | R | F1 |
| Lee | Golden Lake | 10 | 38 | R | F1 |
| Lee | Tice | 10 | 7 | R | F1 |
| Miami Dade | Brickell | 10 | 1 | R | F2 |
| Miami Dade | Flagler | 10 | 0 | R | F1 |
| Miami Dade | Kings Bay | 10 | 0 | R | F2 |
| Miami Dade | Little River | 15 | 11 | R | F1 |
| Miami Dade | Wynwood | 10 | 5 | R | F1 |
| Monroe | Key Largo | 10 | 15 | R | F2 |
| Pasco | Candice | 10 | 55 | R | F2 |
| Pasco | Elanor | 10 | 13 | R | F1 |
| Pasco | Pleasure | 10 | 4 | R | F1 |
| Polk | Cheyenne | 10 | 0 | R | F1 |
| Polk | Stewards | 10 | 11 | R | F2 |
| Polk | Wabash | 10 | 2 | R | F2 |
| Seminole | Halsey | 10 | 42 | R | F2 |
| St. Lucie | Betty’s House | 10 | 1 | R | F1 |
| County | Site | Insecticide | No. Tested | % Mortality (30 min) | X2 | Critical p Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brevard | Viera | Permethrin | 75 | 26 | - | - | - |
| PBO + Permethrin | 83 | 74 | 37.8 | 0.013 | 7.90 × 10−10 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 63 | 84 | 47.3 | 0.01 | 6.15 × 10−12 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 100 | 87 | 69.8 | 0.008 | <2.2 × 10−16 | ||
| Broward | 34th | Permethrin | 100 | 81 | - | - | - |
| PBO + Permethrin | 115 | 77 | 0.42 | 0.025 | 5.17 × 10−1 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 131 | 72 | 2.24 | 0.008 | 1.35 × 10−1 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 104 | 77 | 0.52 | 0.017 | 4.72 × 10−1 | ||
| Collier | 5th | Permethrin | 87 | 38 | - | - | - |
| PBO + Permethrin | 108 | 41 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 6.90 × 10−1 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 104 | 63 | 12.37 | 0.01 | 4.37 × 10−4 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 107 | 26 | 3.08 | 0.025 | 7.93 × 10−2 | ||
| Lee | Billy’s Creek | Permethrin | 134 | 57 | - | - | - |
| PBO + Permethrin | 134 | 71 | 5.83 | 0.025 | 1.57 × 10−2 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 117 | 92 | 40.44 | 0.008 | 2.03 × 10−10 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 143 | 87 | 30.65 | 0.01 | 3.09 × 10−8 | ||
| Golden Lake | Permethrin | 117 | 91 | - | - | - | |
| PBO + Permethrin | 99 | 85 | 2.29 | 0.025 | 1.31 × 10−1 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 127 | 98 | 4.62 | 0.01 | 3.16 × 10−2 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 119 | 92 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 7.81 × 10−1 | ||
| Tice | Permethrin | 143 | 57 | - | - | - | |
| PBO + Permethrin | 120 | 33 | 15.33 | 0.01 | 9.03 × 10−5 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 104 | 43 | 4.31 | 0.017 | 3.79 × 10−2 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 112 | 27 | 22.78 | 0.008 | 1.82 × 10−6 | ||
| Miami-Dade | Brickell | Permethrin | 132 | 58 | - | - | - |
| PBO + Permethrin | 102 | 77 | 10.16 | 0.008 | 1.43 × 10−3 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 84 | 62 | 0.4 | 0.017 | 5.28 × 10−1 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 99 | 59 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 8.78 × 10−1 | ||
| Flagler | Permethrin | 72 | 82 | - | - | - | |
| PBO + Permethrin | 96 | 83 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 8.14 × 10−1 | ||
| DEF +Permethrin | 93 | 91 | 3.27 | 0.017 | 7.08 × 10−2 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 88 | 58 | 10.61 | 0.013 | 1.13 × 10−3 | ||
| Kings Bay | Permethrin | 120 | 50 | - | - | - | |
| PBO + Permethrin | 97 | 57 | 0.97 | 0.008 | 3.25 × 10−1 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 81 | 49 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 9.32 × 10−1 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 114 | 45 | 0.65 | 0.013 | 4.20 × 10−1 | ||
| Little River | Permethrin | 85 | 98 | - | - | - | |
| PBO + Permethrin | 97 | 89 | 5.52 | 0.01 | 1.88 × 10−2 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 93 | 85 | 8.76 | 0.008 | 3.08 × 10−3 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 92 | 91 | 3.33 | 0.013 | 6.79 × 10−2 | ||
| Wynwood | Permethrin | 131 | 58 | - | - | - | |
| PBO + Permethrin | 156 | 84 | 23.87 | 0.01 | 1.03 × 10−6 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 127 | 88 | 26.7 | 0.008 | 5.05 × 10−8 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 142 | 83 | 23.04 | 0.013 | 1.59 × 10−6 | ||
| Monroe | Key Largo | Permethrin | 135 | 84 | - | - | - |
| PBO + Permethrin | 99 | 74 | 3.57 | 0.05 | 5.90 × 10−2 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 124 | 100 | 21.75 | 0.01 | 3.41 × 10−6 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 122 | 94 | 6.7 | 0.025 | 9.76 × 10−3 | ||
| Pasco | Elanor | Permethrin | 102 | 70 | - | - | - |
| PBO + Permethrin | 105 | 88 | 10.03 | 0.008 | 1.54 × 10−3 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 100 | 86 | 7.84 | 0.01 | 5.12 × 10−3 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 75 | 80 | 2.43 | 0.013 | 1.19 × 10−1 | ||
| Pleasure | Permethrin | 122 | 59 | - | - | - | |
| PBO + Permethrin | 118 | 63 | 0.34 | 0.025 | 5.58 × 10−1 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 111 | 73 | 5.02 | 0.01 | 2.50 × 10−2 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 112 | 55 | 0.32 | 0.05 | 5.72 × 10−1 | ||
| Candice | Permethrin | 46 | 91 | - | - | - | |
| PBO + Permethrin | 122 | 98 | 4.83 | 0.017 | 2.80 × 10−2 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 93 | 98 | 3.19 | 0.025 | 7.40 × 10−2 | ||
| Polk | Cheyenne | Permethrin | 95 | 14 | - | - | - |
| PBO + Permethrin | 125 | 70 | 68.07 | 0.013 | <2.2 × 10−16 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 139 | 88 | 129.73 | 0.008 | <2.2 × 10−16 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 128 | 78 | 90.59 | 0.01 | <2.2 × 10−16 | ||
| Stewards | Permethrin | 122 | 85 | - | - | - | |
| PBO + Permethrin | 124 | 93 | 3.54 | 0.025 | 6.00 × 10−2 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 52 | 69 | 5.95 | 0.01 | 1.47 × 10−2 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 106 | 85 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 9.43 × 10−1 | ||
| Wabash | Permethrin | 134 | 49 | - | - | - | |
| PBO + Permethrin | 120 | 41 | 1.81 | 0.05 | 1.78 × 10−1 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 115 | 72 | 13.53 | 0.013 | 2.35 × 10−4 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 145 | 32 | 8.2 | 0.017 | 4.20 × 10−3 | ||
| Seminole | Halsey | Permethrin | 127 | 82 | - | - | - |
| PBO + Permethrin | 118 | 93 | 7.11 | 0.008 | 7.69 × 10−3 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 95 | 83 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 8.06 × 10−1 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 79 | 85 | 0.29 | 0.017 | 5.87 × 10−1 | ||
| St. Lucie | Betty’s House | Permethrin | 117 | 40 | - | - | - |
| PBO + Permethrin | 110 | 55 | 5.3 | 0.01 | 2.12 × 10−2 | ||
| DEF + Permethrin | 127 | 52 | 3.41 | 0.013 | 6.49 × 10−2 | ||
| DM + Permethrin | 118 | 64 | 7.87 | 0.008 | 5.02 × 10−3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schluep, S.M.; Buckner, E.A. Metabolic Resistance in Permethrin-Resistant Florida Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Insects 2021, 12, 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100866
Schluep SM, Buckner EA. Metabolic Resistance in Permethrin-Resistant Florida Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Insects. 2021; 12(10):866. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100866
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchluep, Sierra M., and Eva A. Buckner. 2021. "Metabolic Resistance in Permethrin-Resistant Florida Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae)" Insects 12, no. 10: 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100866
APA StyleSchluep, S. M., & Buckner, E. A. (2021). Metabolic Resistance in Permethrin-Resistant Florida Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Insects, 12(10), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100866






