Expressional Localization and Functionally Identifying an RNA Editing Enzyme BmADARa of the Silkworm Bombyx mori
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silkworms, Vectors and Cell Strains
2.2. RNA Isolation, RT-PCR and Cloning of the Full-Length cDNA of BmADAR
2.3. Sequence Analysis
2.4. Overexpression of BmADARa and Preparation of the Polyclonal Antibody
2.5. Extraction of Total Proteins from Larval Tissue and Adenosine Deaminase Activity Assay
2.6. Construction of Recombinant Plasmids and Identification of Recombinant Bacmids
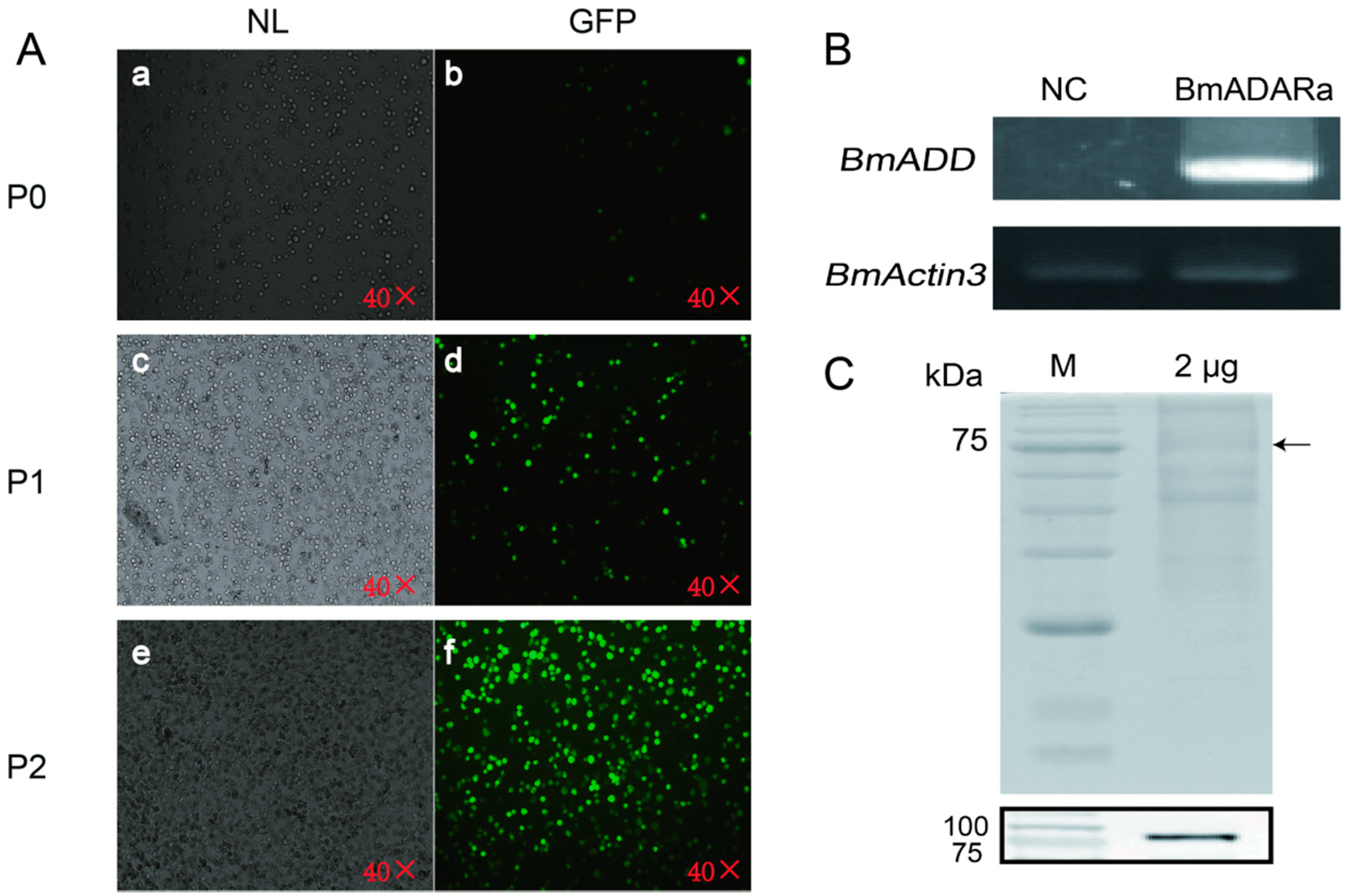
2.7. Expression and Purification of Recombinant BmADARa in BmN Cells
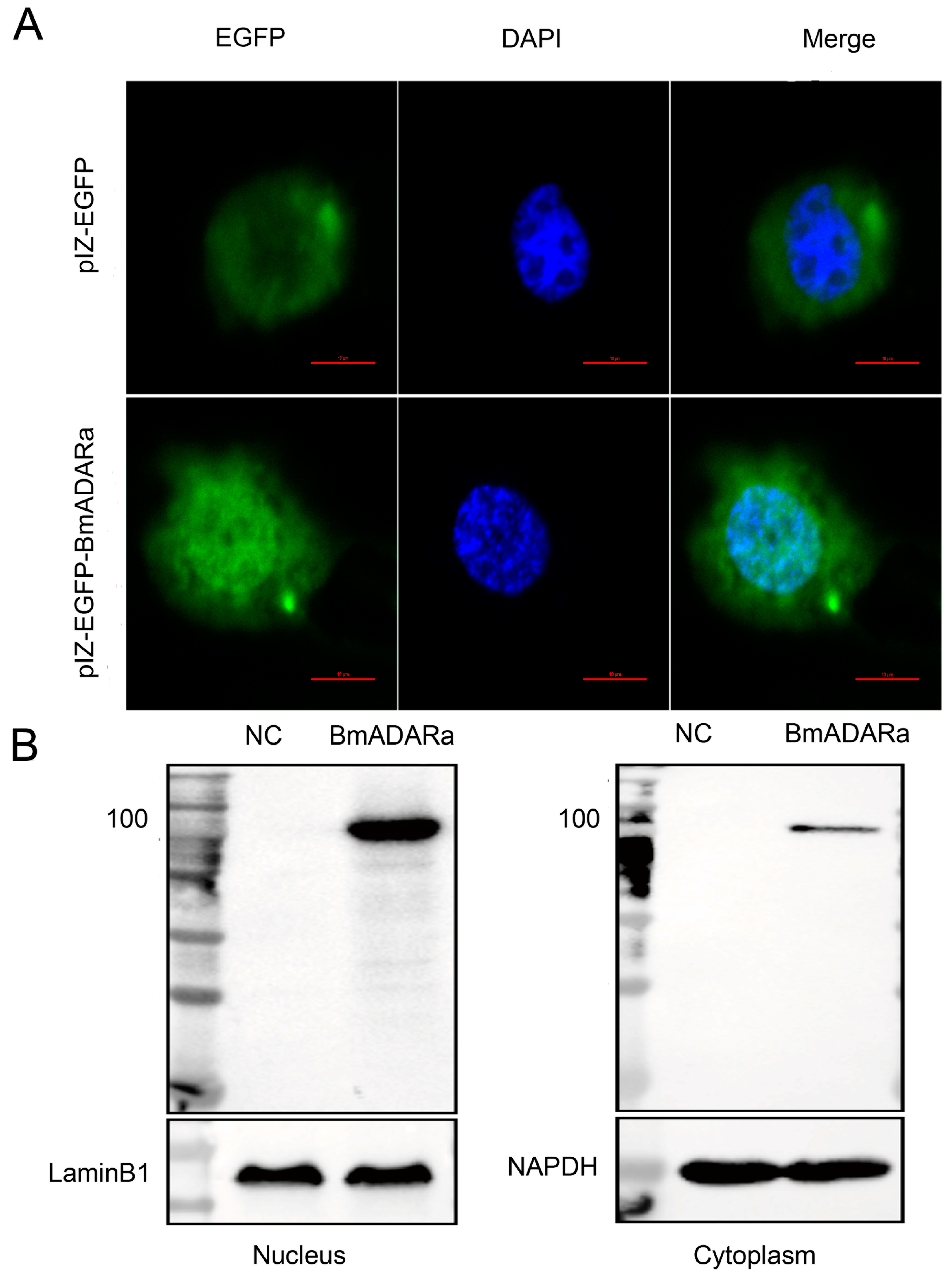
2.8. Subcellular Localization of BmADARa
2.9. Overexpression of BmSyt I and Co-Expression with BmADARa
2.10. Western Blot
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Cloning of BmADAR
3.2. Expression Pattern of BmADAR Transcripts and Sequence Analysis of BmADARa
3.3. Over-Expression of BmADARa and Adenosine Deaminase Activity
3.4. Subcellular Localization of BmADARa and Its Editing Function on BmSyt I
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benne, R.; Van den Burg, J.; Brakenhoff, J.P.; Sloof, P.; Van Boom, J.H.; Tromp, M.C. Major transcript of the frameshifted coxII gene from trypanosome mitochondria contains four nucleotides that are not encoded in the DNA. Cell 1986, 46, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, Q. Origins and evolution of ADAR-mediated RNA editing. Iubmb Life 2009, 61, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladino, M.J.; Keegan, L.P.; O’Connell, M.A.; Reenan, R.A. A-to-I pre-mRNA editing in Drosophila is primarily involved in adult nervous system function and integrity. Cell 2000, 102, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behm, M.; Wahlstedt, H.; Widmark, A.; Eriksson, M.; Öhman, M. Accumulation of nuclear ADAR2 regulates adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing during neuronal development. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.; Jantsch, M.F.; Licht, K. The editor’s I on disease development. Trends Genet. 2019, 35, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikura, K. Functions and regulation of RNA editing by ADAR deaminases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikura, K. Editing the message from A to I. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 962–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, C.; Barbon, A.; Barlati, S. Activity regulation of adenosine deaminases acting on RNA (ADARs). Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 45, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.E.; Bahn, J.H.; Yang, Y.; Lin, X.; Tran, S.; Yang, E.W.; Quinones-Valdez, G.; Xiao, X. RNA editing in nascent RNA affects pre-mRNA splicing. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reenan, R.A.; Hanrahan, C.J.; Ganetzky, B. The mle (napts) RNA helicase mutation in Drosophila results in a splicing catastrophe of the para Na+ channel transcript in a region of RNA editing. Neuron 2000, 25, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reenan, R.A. Molecular determinants and guided evolution of species-specific RNA editing. Nature 2005, 434, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, D.P.; Zhang, H.J.; Zhao, P.; Lin, Y.; Xia, Q.Y.; Xiang, Z.H. Identification and expression pattern of the chemosensory protein gene family in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Khan, A. Adar RNA editing-dependent and -independent effects are required for brain and innate immune functions in Drosophila. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Tian, N.; Cao, J.; Liang, J.; Yang, Z.; Lv, J. RNA editing and alternative splicing of the insect nAChR subunit alpha6 transcript: Evolutionary conservation, divergence and regulation. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lv, J.; Gui, B.; Yin, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y. A-to-I RNA editing alters less-conserved residues of highly conserved coding regions: Implications for dual functions in evolution. RNA 2008, 14, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daimon, T.; Katsuma, S.; Iwanaga, M.; Kang, W.; Shimada, T. The BmChi-h gene, a bacterial-type chitinase gene of Bombyx mori, encodes a functional exochitinase that plays a role in the chitin degradation during the molting process. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 35, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Macri, D.; Srivastava, I.; McPherson, C.; Felberbaum, R.; Post, P.; Cox, M. Complete study demonstrating the absence of rhabdovirus in a distinct Sf9 cell line. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, M.; Jouraku, A.; Toyoda, A.; Yokoi, K.; Minakuchi, Y.; Katsuma, S.; Fujiyama, A.; Kiuchi, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Shimada, T. High-quality genome assembly of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 107, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.J.; Zhong, X.; Lin, X.Y.; Huang, X.H.; Yu, X.Q. Characterization of a novel Manduca sexta beta-1, 3-glucan recognition protein (βGRP3) with multiple functions. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 52, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fang, Q.; Qian, C.; Wang, F.; Yu, X.Q.; Ye, G. Inhibition of host cell encapsulation through inhibiting immune gene expression by the parasitic wasp venom calreticulin. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, L.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Meng, Y. D181A site-mutagenesis enhances both the hydrolyzing and transfructosylating activities of BmSUC1, a novel β-fructofuranosidase in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.C.; Cao, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, L.Z.; Meng, F.; Zhu, X.Z. Modulating effect of adenosine deaminase on function of adenosine A1 receptors. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Weisman, M.I.; Caiolfa, V.R.; Parola, A.H. Adenosine deaminase-complexing protein from bovine kidney. Isolation of two distinct subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 5266–5270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Daimon, T.; Taguchi, T.; Meng, Y.; Katsuma, S.; Mita, K.; Shimada, T. Beta-fructofuranosidase genes of the silkworm, Bombyx mori: Insights into enzymatic adaptation of B. mori to toxic alkaloids in mulberry latex. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 15271–15279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H. Identification of A-to-I RNA Editing Sites of Invertebrate Kv2 Genes and Preliminary Study on Their Formation Mechanisms. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Gong, M.; Shu, R.; Li, X.; Gao, J.; Meng, Y. Molecular and enzymatic characterization of two enzymes BmPCD and BmDHPR involving in the regeneration pathway of tetrahydrobiopterin from the silkworm Bombyx mori. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B: Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 186, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Quan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Expression and functional analysis of storage protein 2 in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Int. J. Genom. 2013, 2013, 145450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Shi, L.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, T.; Jiang, S.; Gao, J.; Meng, Y. BmSUC1 is essential for glycometabolism modulation in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2018, 1861, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepson, J.E.; Reenan, R.A. RNA editing in regulating gene expression in the brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2008, 1779, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, L.P.; McGurk, L.; Palavicini, J.P.; Brindle, J.; Paro, S.; Li, X.; Rosenthal, J.J.; O’Connell, M.A. Functional conservation in human and Drosophila of Metazoan ADAR2 involved in RNA editing: Loss of ADAR1 in insects. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7249–7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, L.; Khan, A.; Vukic, D.; O’Connell, M. ADAR RNA editing below the backbone. RNA 2017, 23, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.; Vissel, B. The essential role of AMPA receptor GluR2 subunit RNA editing in the normal and diseased brain. Front. Moecularl Neurosci. 2012, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, J.; Yoon, J.; Baek, K. Analysis of two promoters that control the expression of the GTP cyclohydrolase I gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Cells 2009, 27, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Beal, P.A. Adenosine deaminases that act on RNA (ADARs). Enzymes 2017, 41, 215–268. [Google Scholar]
- Novakova, M.; Dolezal, T. Expression of Drosophila adenosine deaminase in immune cells during inflammatory response. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capiotti, K.M.; Siebel, A.M.; Kist, L.W.; Bogo, M.R.; Bonan, C.D.; Da Silva, R.S. Hyperglycemia alters E-NTPDases, ecto-5’-nucleotidase, and ectosolic and cytosolic adenosine deaminase activities and expression from encephala of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Purinergic Signal. 2016, 12, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, S.; Gommans, W.M. Identification of a selective nuclear import signal in adenosine deaminases acting on RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 5822–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcucci, R.; Brindle, J.; Paro, S.; Casadio, A.; Hempel, S.; Morrice, N.; Bisso, A.; Keegan, L.P.; Del Sal, G.; O’Connell, M.A. Pin1 and WWP2 regulate GluR2 Q/R site RNA editing by ADAR2 with opposing effects. Embo J. 2011, 30, 4211–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraud, P.; Banerjee, S.; Mohamed, W.I.; Jantsch, M.F.; Allain, F.H.-T. A bimodular nuclear localization signal assembled via an extended double-stranded RNA-binding domain acts as an RNA-sensing signal for transportin 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E1852–E1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wells, K.S.; Emeson, R.B. Substrate-dependent Contribution of Double-stranded RNA-binding Motifs to ADAR2 Function. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 3211–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, C.E. Adenosine deaminases acting on RNA (ADARs) are both antiviral and proviral. Virology 2011, 411, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamers, M.M.; van den Hoogen, B.G.; Haagmans, B.L. ADAR1: “Editor-in-Chief” of Cytoplasmic Innate Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefl, R.; Xu, M.; Skrisovska, L.; Emeson, R.B.; Allain, F.H. Structure and specific RNA binding of ADAR2 double-stranded RNA binding motifs. Structure 2006, 14, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikura, K.; Yoo, C.; Kim, U.; Murray, J.M.; Estes, P.A.; Cash, F.E.; Liebhaber, S.A. Substrate specificity of the dsRNA unwinding/modifying activity. Embo J. 1991, 10, 3523–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.E.; Butler, M.D.; Pan, Q.; Ruvkun, G. Trans-splicing in C. elegans generates the negative RNAi regulator ERI-6/7. Nature 2008, 455, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.D.; McFarland, K.N.; Darnell, S.B.; Huizenga, M.N.; Sangrey, G.R.; Cha, J.H.; Pierce, R.C.; Sadri-Vakili, G. ADAR2-dependent GluA2 editing regulates cocaine seeking. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 20, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; O’Brien, P.J.; Chen, C.X.; Cho, D.S.; Murray, J.M.; Nishikura, K. Altered G protein-coupling functions of RNA editing isoform and splicing variant serotonin2C receptors. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, C.; Jiang, S.; Gong, M.; Min, Q.; Fan, M.; Gao, J.; Meng, Y. Expressional Localization and Functionally Identifying an RNA Editing Enzyme BmADARa of the Silkworm Bombyx mori. Insects 2020, 11, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080523
Ye C, Jiang S, Gong M, Min Q, Fan M, Gao J, Meng Y. Expressional Localization and Functionally Identifying an RNA Editing Enzyme BmADARa of the Silkworm Bombyx mori. Insects. 2020; 11(8):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080523
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Chongjun, Song Jiang, Meixia Gong, Qin Min, Manli Fan, Junshan Gao, and Yan Meng. 2020. "Expressional Localization and Functionally Identifying an RNA Editing Enzyme BmADARa of the Silkworm Bombyx mori" Insects 11, no. 8: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080523
APA StyleYe, C., Jiang, S., Gong, M., Min, Q., Fan, M., Gao, J., & Meng, Y. (2020). Expressional Localization and Functionally Identifying an RNA Editing Enzyme BmADARa of the Silkworm Bombyx mori. Insects, 11(8), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080523