Behavioral Responses of Western Flower Thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis) to Visual and Olfactory Cues at Short Distances
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. WFT Rearing
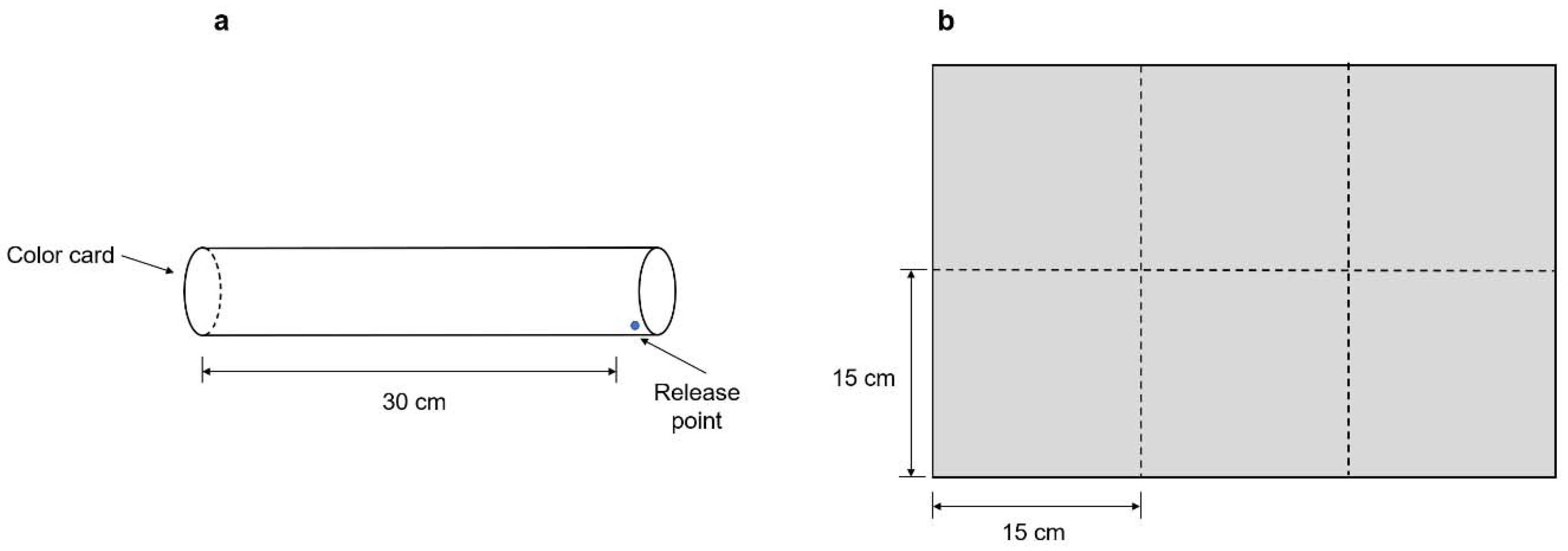
2.2. Distance Effect on Cue Perception
2.3. Color Preference
2.4. Geometric Preference Assay
2.5. Visual Cues Versus Olfactory Cues at A Short Distance
2.6. Plant Volatile Collection and Analysis
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
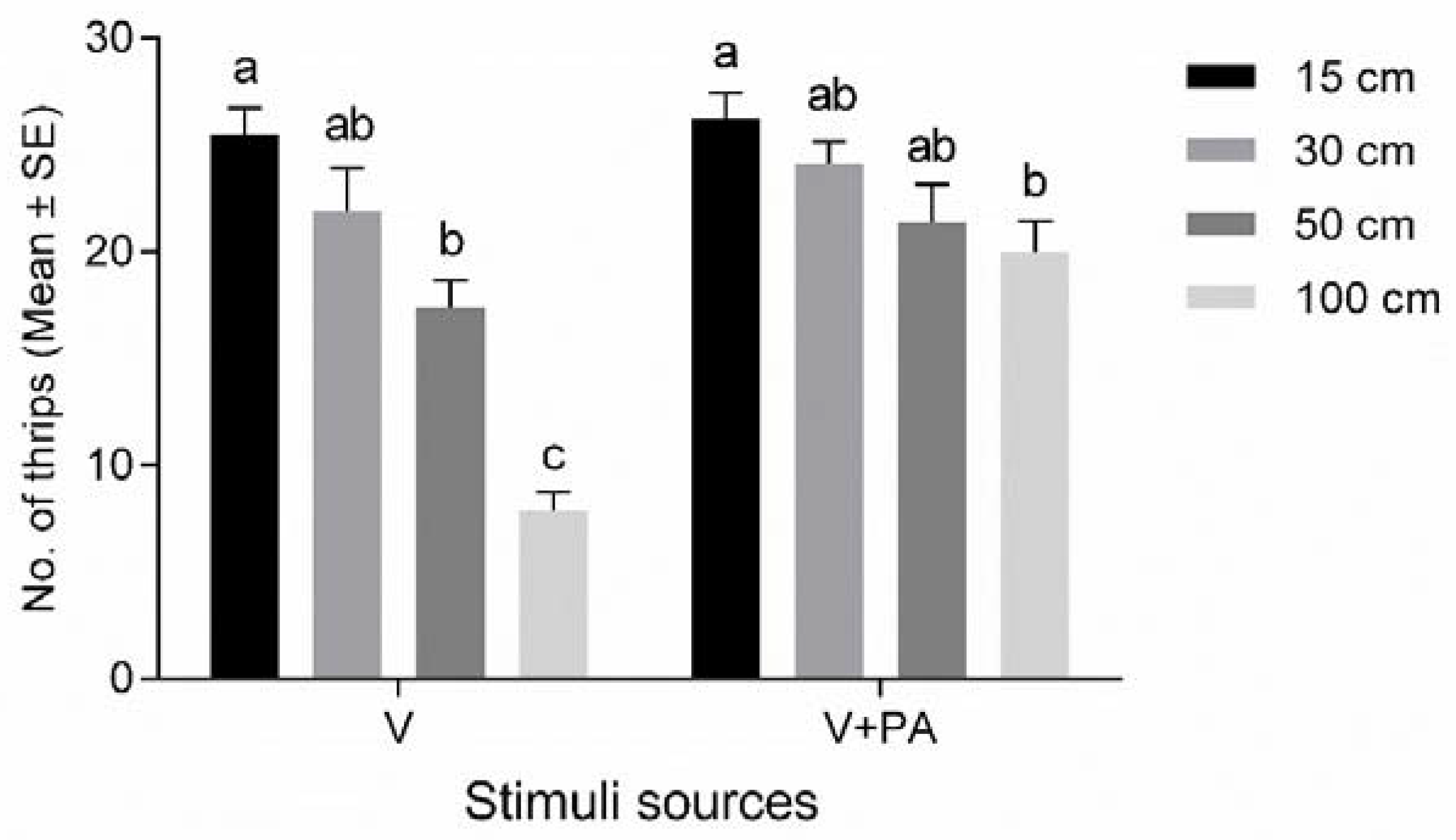
3.1. Distance Effect on Cue Perception
3.2. Visual Cues Used in Short Distances
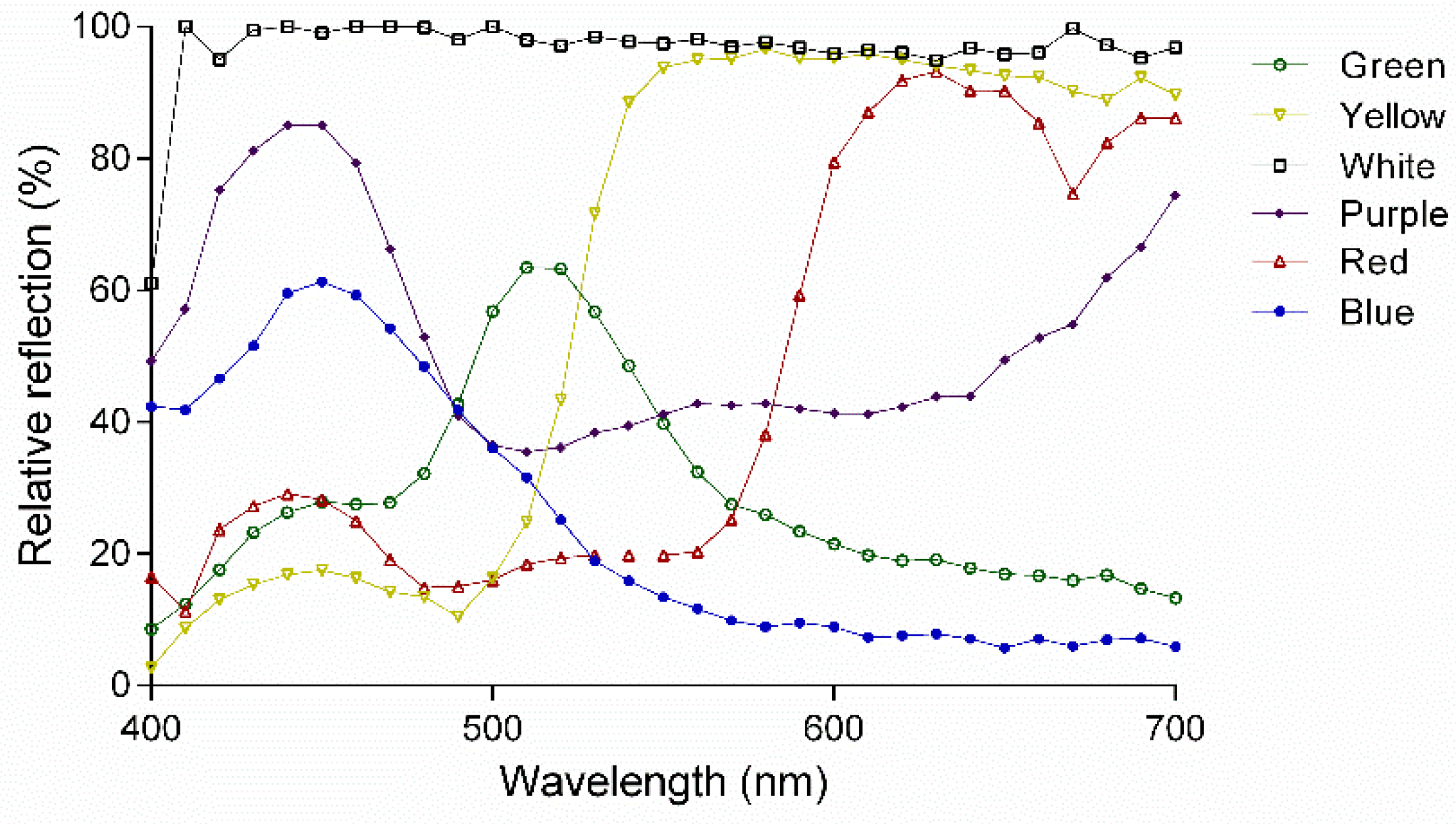
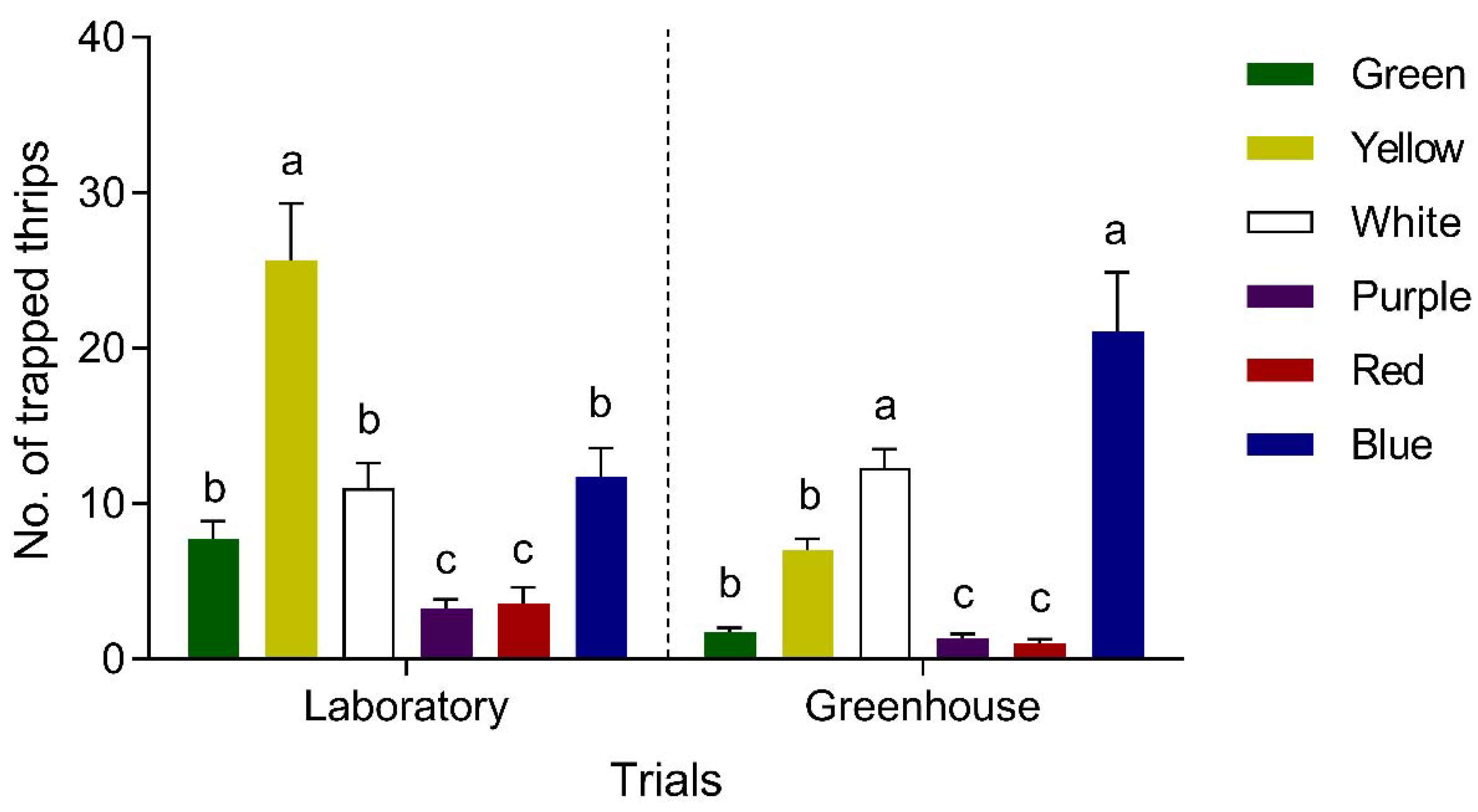
3.2.1. Color Preference
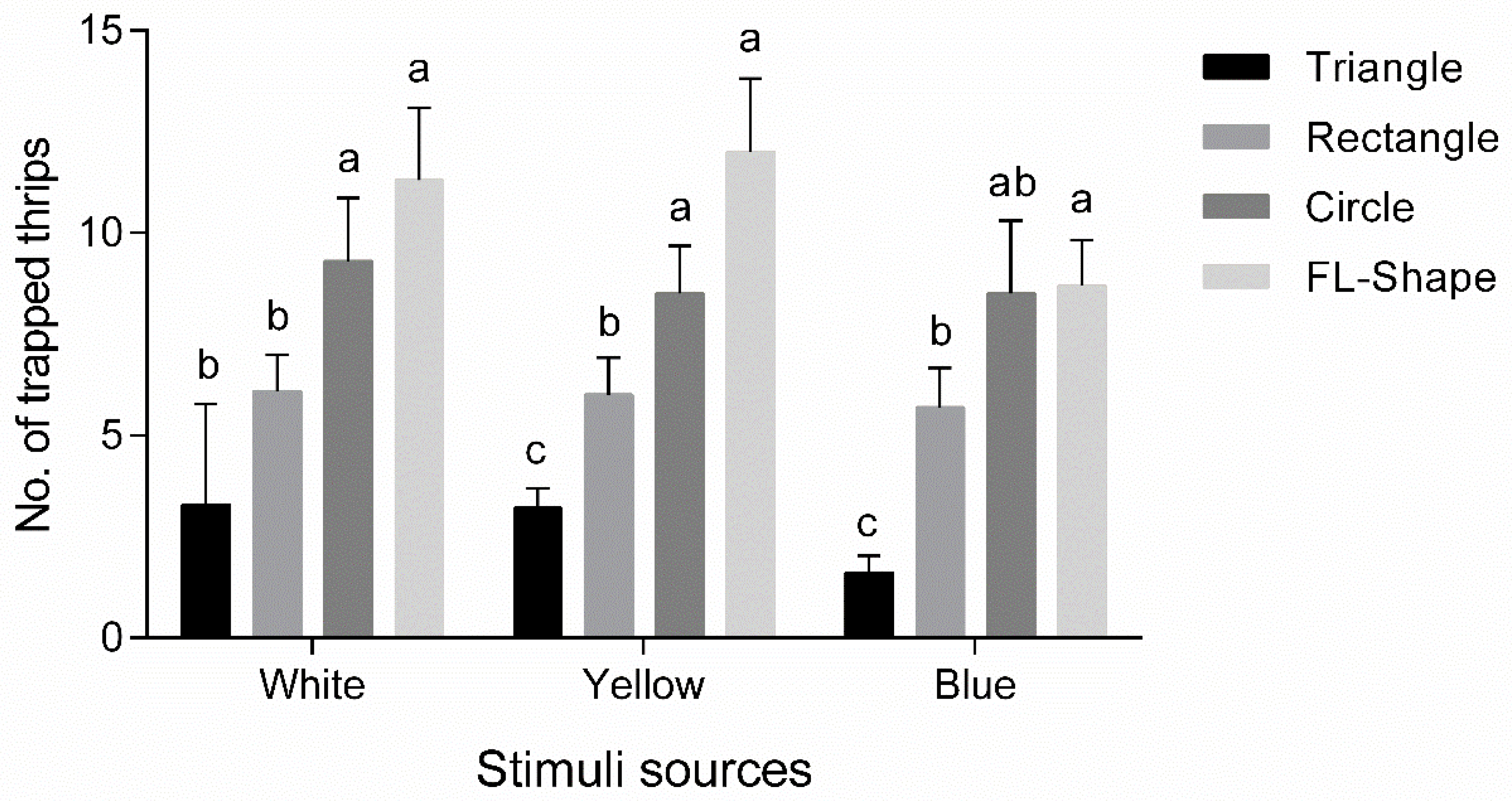
3.2.2. Geometric Preference Assay
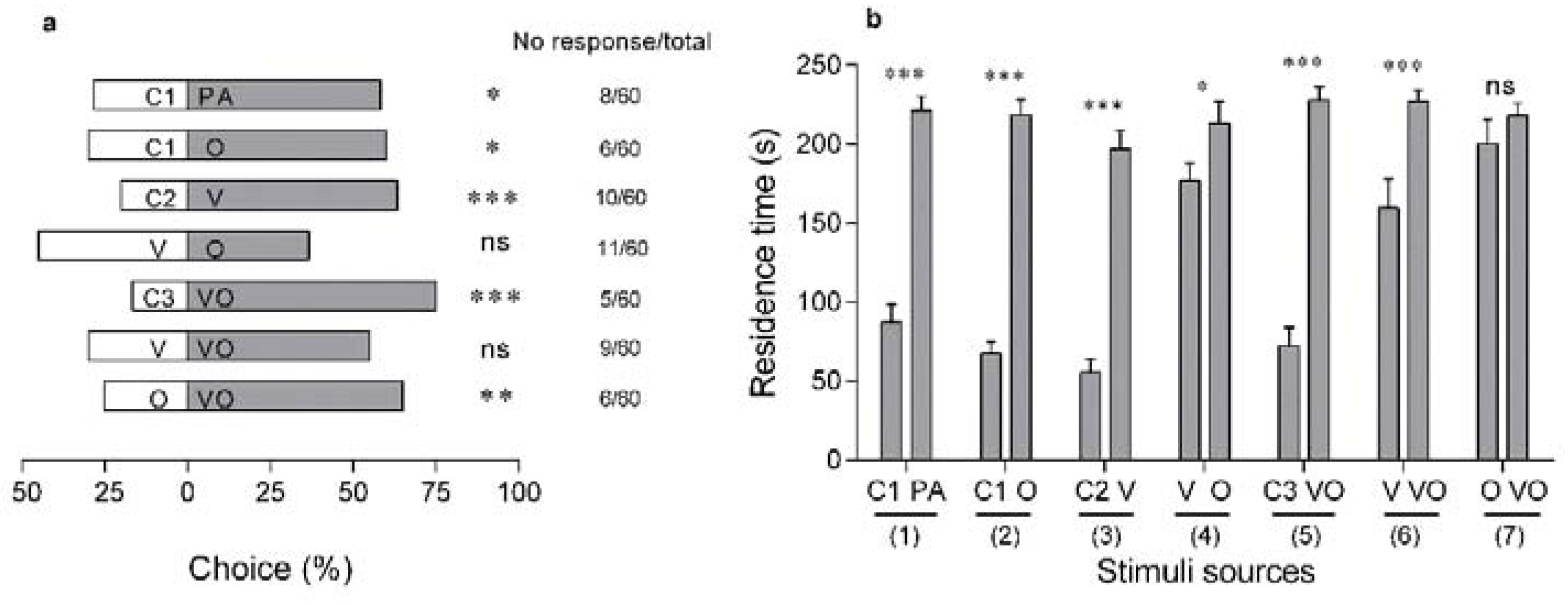
3.3. Visual Cues Versus Olfactory Cues at A Short Distance
3.4. Plant Volatile Collection and Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirk, W.D.J.; Terry, L.I. The spread of the western flower thrips Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande). Agric. Forest Entomol. 2003, 5, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, S.R. Biology and ecology of the western flower thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae): The making of a pest. Fla. Entomol. 2009, 92, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, S.R.; Gao, Y.; Lei, Z. Thrips: Pests of concern to China and the United States. J. Integr. Agric. 2011, 10, 867–892. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.; Hereward, J.P.; Walter, G.H.; Wilson, L.J.; Furlong, M.J. Seasonal abundance of cotton thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) across crop and non-crop vegetation in an Australian cotton producing region. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 256, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lei, Z.; Reitz, S.R. Western flower thrips resistance to insecticides: Detection, mechanisms and management strategies. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Tang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xing, Z.; Lei, Z.; Gao, Y. A decade of a thrips invasion in China: Lessons learned. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, B.P.; Lim, U.T. Behavioral response of western flower thrips to visual and olfactory cues. J. Insect Behav. 2011, 24, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K. Host-plant selection mechanisms and behavioural manipulation strategies of phytophagous insects. Acta Eco. Sinica. 2008, 28, 5113–5122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, T.J.A.; Wadhams, L.J.; Woodcock, C.M. Insect host location: A volatile situation. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, R.; Hilker, M. The relevance of background odor in resource location by insects: A behavioral approach. BioScience 2008, 58, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschier, E.H.; de Kogel, W.J.; Visser, J.H. Assessing the attractiveness of volatile plant compounds to western flower thrips Frankliniella occidentalis. J. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 26, 2643–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otieno, J.A.; Stukenberg, N.; Weller, J.; Poehling, H.M. Efficacy of LED-enhanced blue sticky traps combined with the synthetic lure Lurem-TR for trapping of western flower thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis). J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopy, R.J.; Owens, E.D. Visual detection of plants by herbivorous insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1983, 28, 337–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kogel, W.J.; Koschier, E.H. Thrips responses to plant odours. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Thysanoptera; Marullo, R., Mound, L., Eds.; CSIRO Entomology: Canberra, Australia, 2002; pp. 189–190. [Google Scholar]
- Vernon, R.S.; Gillespie, D.R. Spectral responsiveness of Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) determined by trap catches in greenhouses. Environ. Entomol. 1990, 19, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteson, N.; Terry, I.; Ascoli-Christensen, A.; Gilbert, C. Spectral efficiency of the western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis. J. Insect Physiol. 1992, 38, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearsall, I.A. Flower preference behaviour of western flower thrips in the Similkameen Valley, British Columbia, Canada. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2000, 95, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubos, C.R.; Liburd, O.E. Effect of trap color on captures of grape root borer (Lepidoptera: Sesiidae) males and non-target insects. J. Agric. Urban. Entomol. 2008, 25, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straw, N.A.; Williams, D.T.; Green, G. Influence of sticky trap color and height above ground on capture of alate Elatobium abietinum (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in Sitka Spruce Plantations. Environ. Entomol. 2011, 40, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, E.H. Effect of trap color and orientation on the capture of Aphelinus mali (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae), a parasitoid of woolly apple aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieske, L.K.; Raffa, K.F. Evaluation of visual and olfactory cues for sampling three thrips species (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in deciduous forests of the northern United States. J. Econ. Entomol. 2003, 96, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, B.P.; Lim, U.T. Circular yellow sticky trap with black background enhances attraction of Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2010, 45, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharekhani, G.H.; Ghorbansyahi, S.; Saber, M.; Bagheri, B. Influence of the colour and height of sticky traps in attraction of Thrips tabaci (Lindeman) (Thysanoptera, Thripidae) and predatory thrips of family Aeolothripidae on garlic, onion and tomato crops. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2014, 47, 2270–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, N.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Lei, Z. The phototaxis behavior of Thrips tabaci and trapping effect of different wavelength sticky cards in the field. Sci. Agric. Sinica. 2019, 52, 1721–1732. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, L.; Chang, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H. Attraction effect of different colored cards on thrips Frankliniella intonsa in cowpea greenhouses in China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.; Yang, P.X.; Yao, Y.J.; Luo, Z.X.; Cai, X.M.; Chen, Z.M. Effect of trap color, height, and orientation on the capture of yellow and stick tea thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) and nontarget insects in tea gardens. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Zhi, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, R.; Wang, C.; Shang, B.; Gao, Y. Behavioral responses of Frankliniella occidentalis to floral volatiles combined with different background visual cues. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2018, 12, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, B.P.; Lim, U.T. Use of flower model trap to reduce the infestation of greenhouse whitefly on tomato. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2008, 11, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulson, D. Foraging strategies of insects for gathering nectar and pollen, and implications for plant ecology and evolution. Perspect. Plant Ecol. 1999, 2, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, J.P.; Moore, C.J.; Zalucki, M.P.; Cribb, B.W. Insect odour perception: Recognition of odour components by flower foraging moths. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 2035–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguso, R.A. Wake up and smell the roses: The ecology and evolution of floral scent. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 39, 549–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Lu, L.; Xiu, C.; Geng, H.; Cai, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Williams III, L.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Wu, K. Volatile fragrances associated with flowers mediate host plant alternation of a polyphagous mirid bug. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riffell, J.A.; Lei, H.; Abrell, L.; Hildebrand, J.G. Neural basis of a pollinator’s buffet: Olfactory specialization and learning in Manduca sexta. Science 2013, 339, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teulon, D.A.J.; Hollister, B.; Butler, R.C.; Cameron, E.A. Colour and odour responses of flying western flower thrips: Wind tunnel and greenhouse experiments. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1999, 93, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, B.P.; Lim, U.T. Evaluation of chrysanthemum flower model trap to attract two Frankliniella thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2008, 11, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, D.S.; Gregory, W.A.; Tanigoshi, L.K. Flight response of Aphytis melinus (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) and Scirtothrips citri (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) to trap color, size, and shape. Environ. Entomol. 1984, 13, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, J.L. Vision should not be overlooked as an important sensory modality for finding host plants. Environ. Entomol. 2011, 40, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, B.P.; Kárpáti, Z.; Nagy, A.; Szarukán, I.; Csabai, J.; Koczor, S.; Tóth, M. Development of a female-targeted lure for the box tree moth Cydalima perspectalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae): A preliminary report. J. Chem. Ecol. 2019, 45, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, C. Dispersal of adult cabbage root fly (Erioischia brassicae (Bouche)) in relation to a Barassica crop. J. Appl. Ecol. 1974, 11, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, S.; Collier, R.H. Host-plant selection by insects—A theory based on ‘appropriate/inappropriate landings’ by pest insects of cruciferous plants. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2000, 96, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tava, A.; Pecetti, L. Volatiles from Medicago sativa complex flowers. Phtochemisty 1997, 45, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teulon, D.A.J.; Davidson, M.M.; Hedderley, D.I.; James, D.E.; Fletcher, C.D.; Larsen, L.; Green, V.C.; Perry, N.B. 4-Pyridyl carbonyl and related compounds as thrips lures: Effectiveness for onion thrips and New Zealand flower thrips in field experiments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6198–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteson, N.A.; Terry, L.I. Response to color by male and female Frankliniella occidentalis during swarming and non-swarming behavior. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1992, 63, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natwick, E.T.; Byers, J.A.; Chu, C.; Lopez, M.; Henneberry, T.J. Early detection and mass trapping of Frankliniella occidentalis, and Thrips tabaci in vegetable crops. Southwest Entomol. 2007, 32, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsgaard, H.F. Coloured sticky traps for Frankhiella occidentalis (Pergande) (Thysanoptera, Thripidae) in glasshouses. J. Appl. Entomol. 1989, 107, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoddle, M.S.; Robinson, L.; Morgan, D. Attraction of thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae and Aeolothripidae) to colored sticky cards in a California avocado orchard. Crop Prot. 2002, 21, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antignus, Y. Manipulation of wavelength-dependent behaviour of insects: An IPM tool to impede insects and restrict epidemics of insect-borne viruses. Virus Res. 2000, 71, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. The expression of three opsin genes from the compound eye of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) is regulated by a circadian clock, light conditions and nutritional status. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, M.M.; Butler, R.C.; Teulon, D.A.J. Starvation period and age affect the response of female Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) to odor and visual cues. J. Insect Physiol. 2006, 52, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | Retention Time | Relative Content (%) 1 |
|---|---|---|
| (Z)-3-hexenyl acetate | 8.89 | 17.3 ± 1.7 |
| (E)-2-hexenyl acetate | 9.071 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| 3-methylcyclohex-2-en-1-ol | 9.317 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| d-limonene | 9.493 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| phenylacetaldehyde | 9.753 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| (E)-β-ocimene | 9.786 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| methyl phenethyl ether | 10.482 | 10.8 ± 0.4 |
| methyl benzoate | 10.782 | 0.1 ± 0.0 |
| nonanal | 10.937 | 1.2 ± 0.0 |
| phenethyl alcohol | 11.138 | 29.9 ± 1.0 |
| 4-methoxystyrene | 11.944 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| 1,4-dimethoxybenzene | 12.105 | 0.5 ± 0.1 |
| (Z)-3-hexenyl butanoate | 12.475 | 0.3 ± 0.0 |
| methyl salicylate | 12.731 | 0.9 ± 0.1 |
| decanal | 12.894 | 1.1 ± 0.1 |
| ethyl nicotinate | 13.083 | 0.4 ± 0.0 |
| (Z)-3-hexenyl isovalerate | 13.41 | 0.3 ± 0.0 |
| phenethyl acetate | 13.801 | 7.3 ± 0.6 |
| 2-undecanone | 14.46 | 1.3 ± 0.1 |
| 1-acetoxynonane | 14.731 | 22.0 ± 1.9 |
| germacrene D | 17.833 | 0.9 ± 0.1 |
| 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol | 18.061 | 4.0 ± 0.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; Wu, S.; Xing, Z.; Xu, R.; Cai, W.; Lei, Z. Behavioral Responses of Western Flower Thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis) to Visual and Olfactory Cues at Short Distances. Insects 2020, 11, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030177
Ren X, Wu S, Xing Z, Xu R, Cai W, Lei Z. Behavioral Responses of Western Flower Thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis) to Visual and Olfactory Cues at Short Distances. Insects. 2020; 11(3):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030177
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xiaoyun, Shengyong Wu, Zhenlong Xing, Ruirui Xu, Wanzhi Cai, and Zhongren Lei. 2020. "Behavioral Responses of Western Flower Thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis) to Visual and Olfactory Cues at Short Distances" Insects 11, no. 3: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030177
APA StyleRen, X., Wu, S., Xing, Z., Xu, R., Cai, W., & Lei, Z. (2020). Behavioral Responses of Western Flower Thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis) to Visual and Olfactory Cues at Short Distances. Insects, 11(3), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030177





