Transcriptome Profiling Revealed Potentially Critical Roles for Digestion and Defense-Related Genes in Insects’ Use of Resistant Host Plants: A Case Study with Sitobion Avenae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aphid Sample Collection and Colony Establishment
2.2. Fitness Bioassays of Both S. Avenae Biotypes on Wheat and Barley
2.3. RNA Sampling and Sequencing
2.4. Transcriptome Assembly and Annotation
2.5. Analysis of Gene Expression Patterns
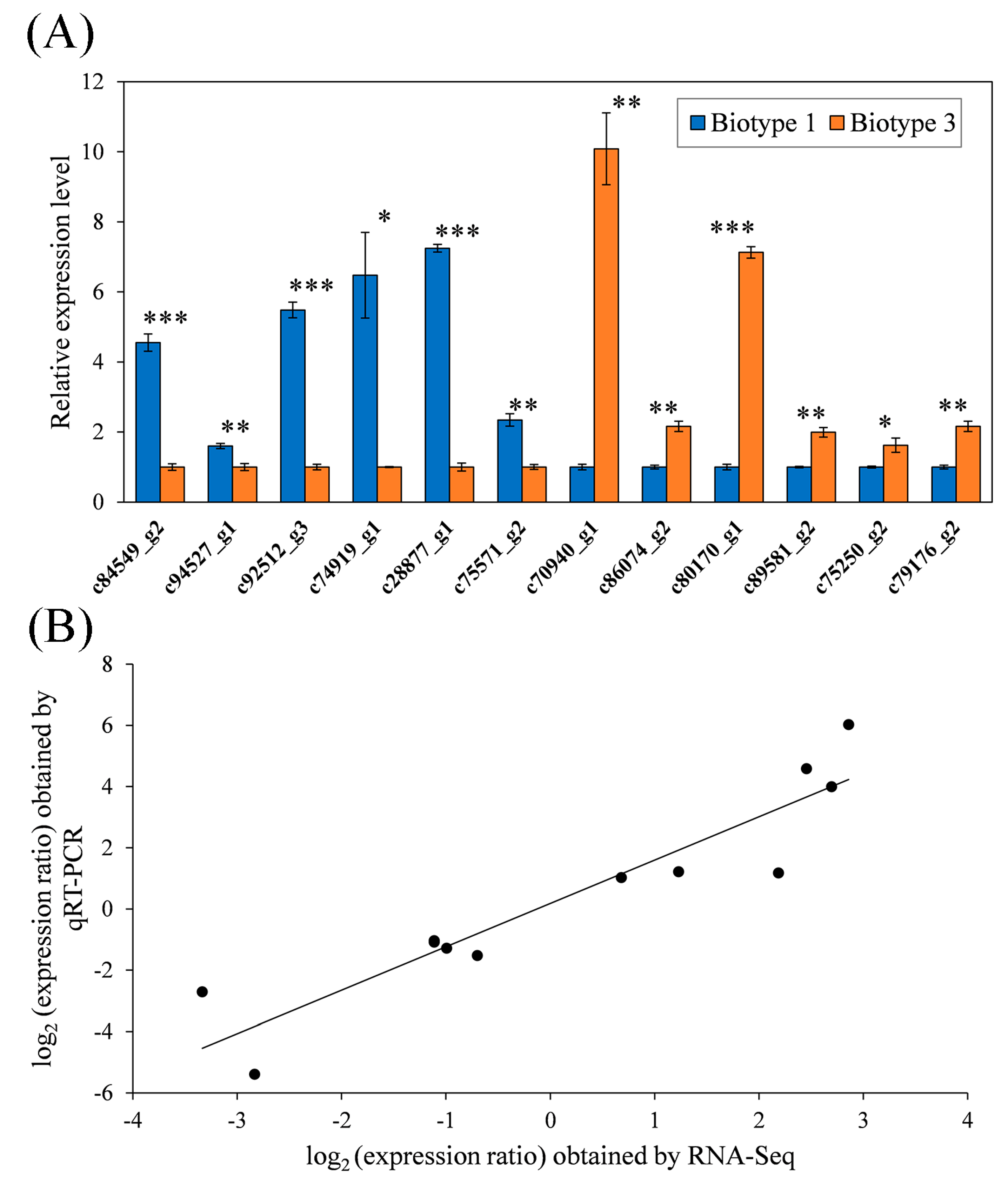
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
3. Results
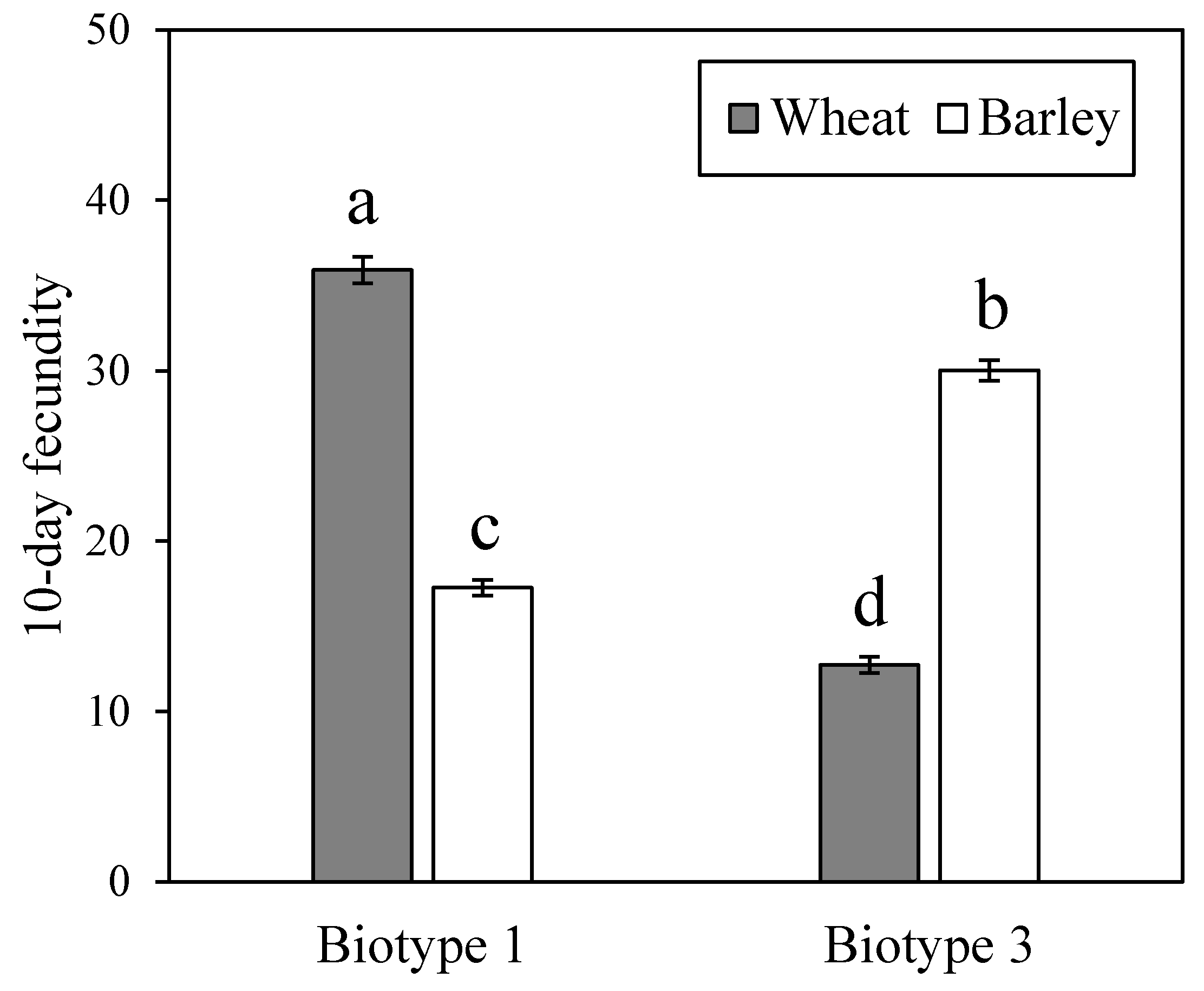
3.1. Fitness Performance of Two S. Avenae Biotypes on Wheat and Barley
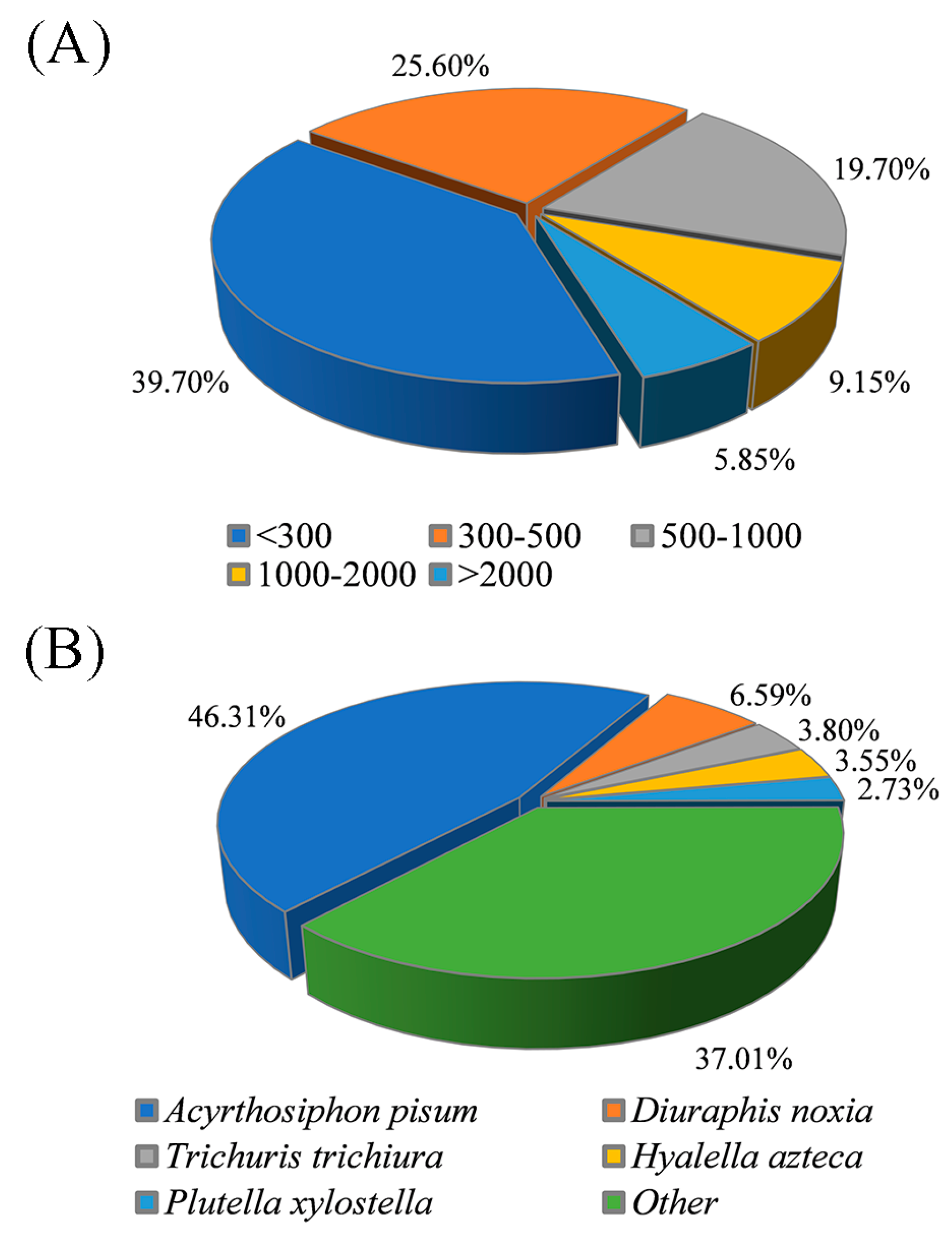
3.2. De Novo Assembly and Transcriptome Annotation
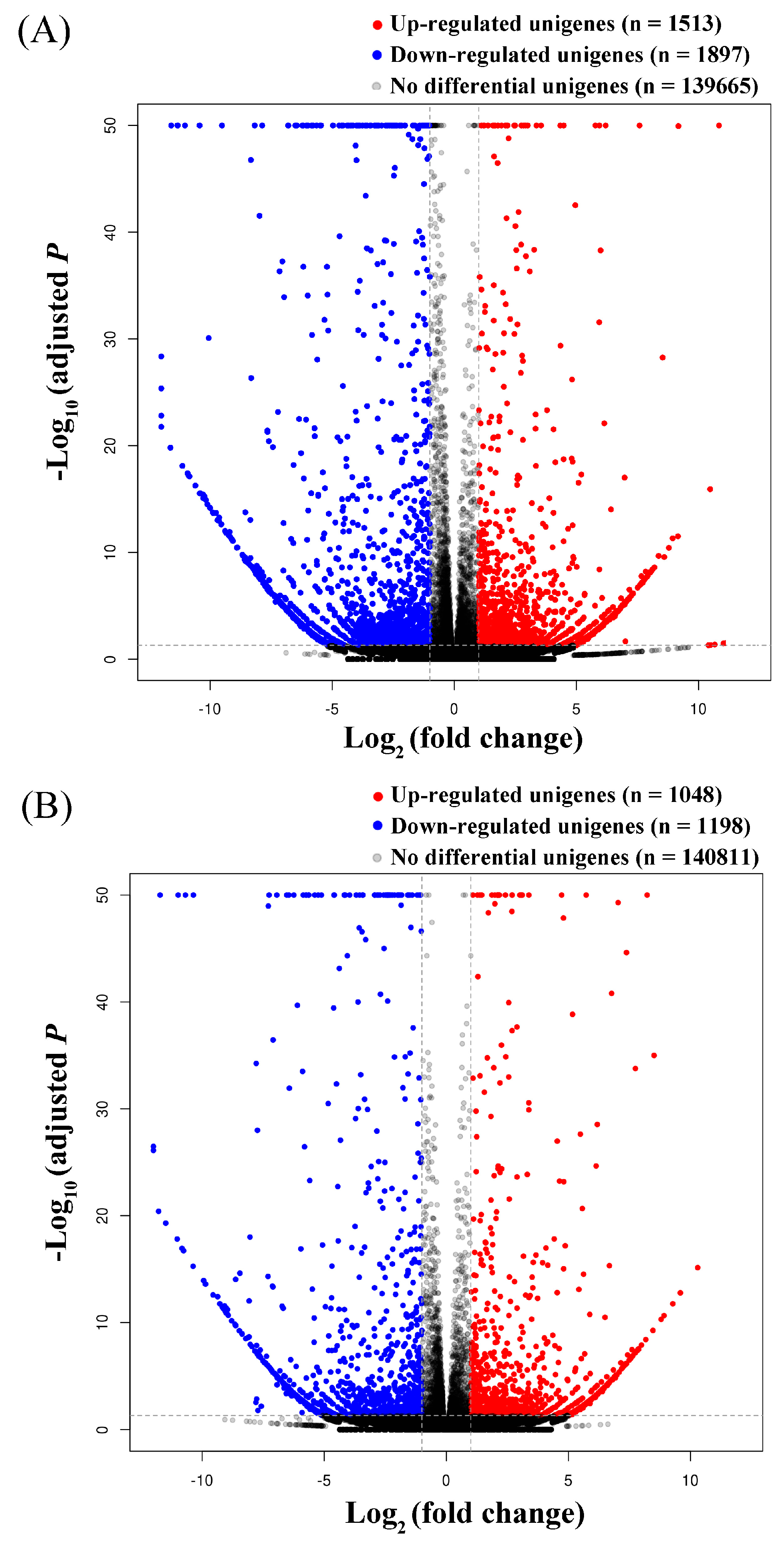
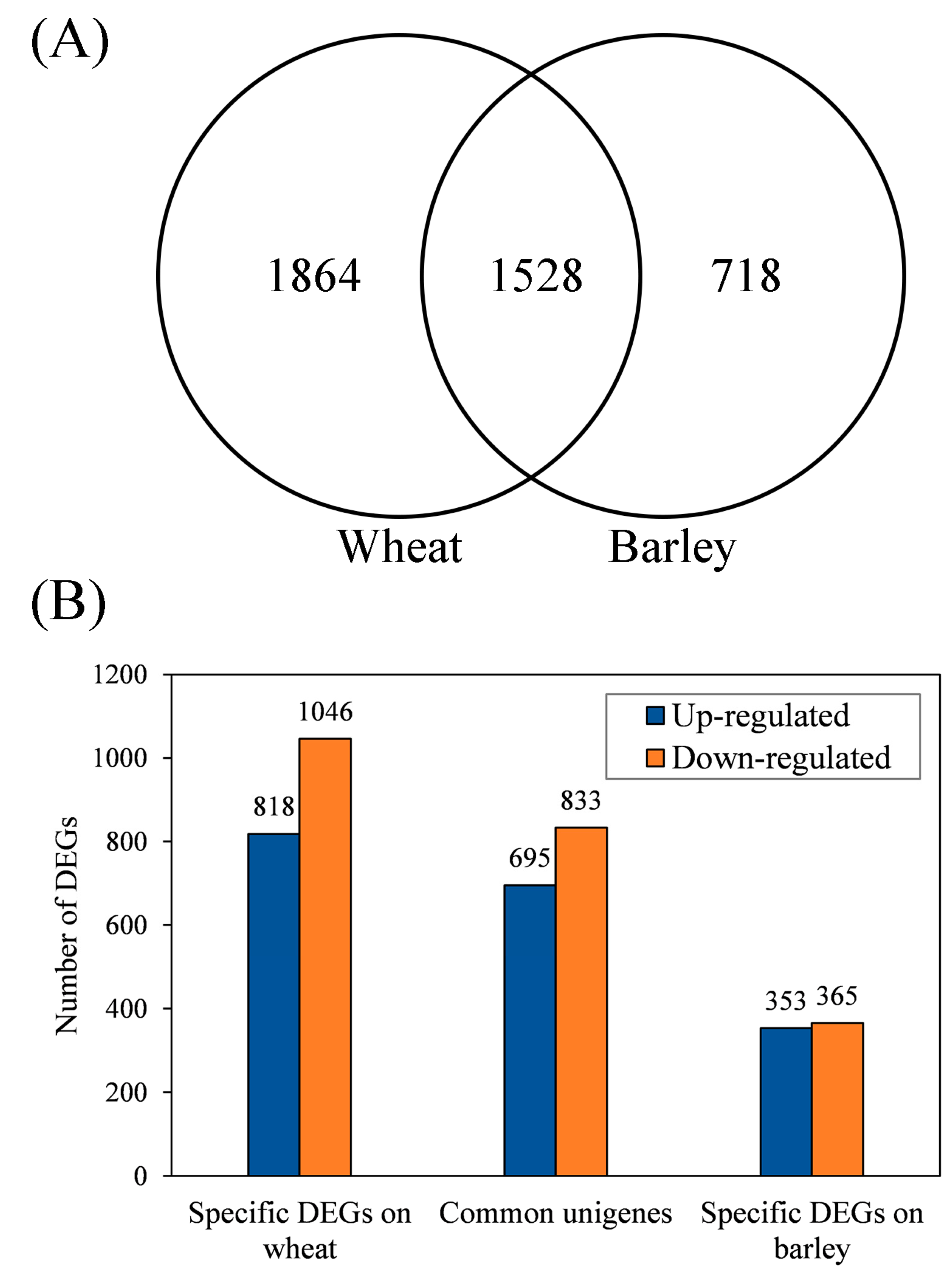
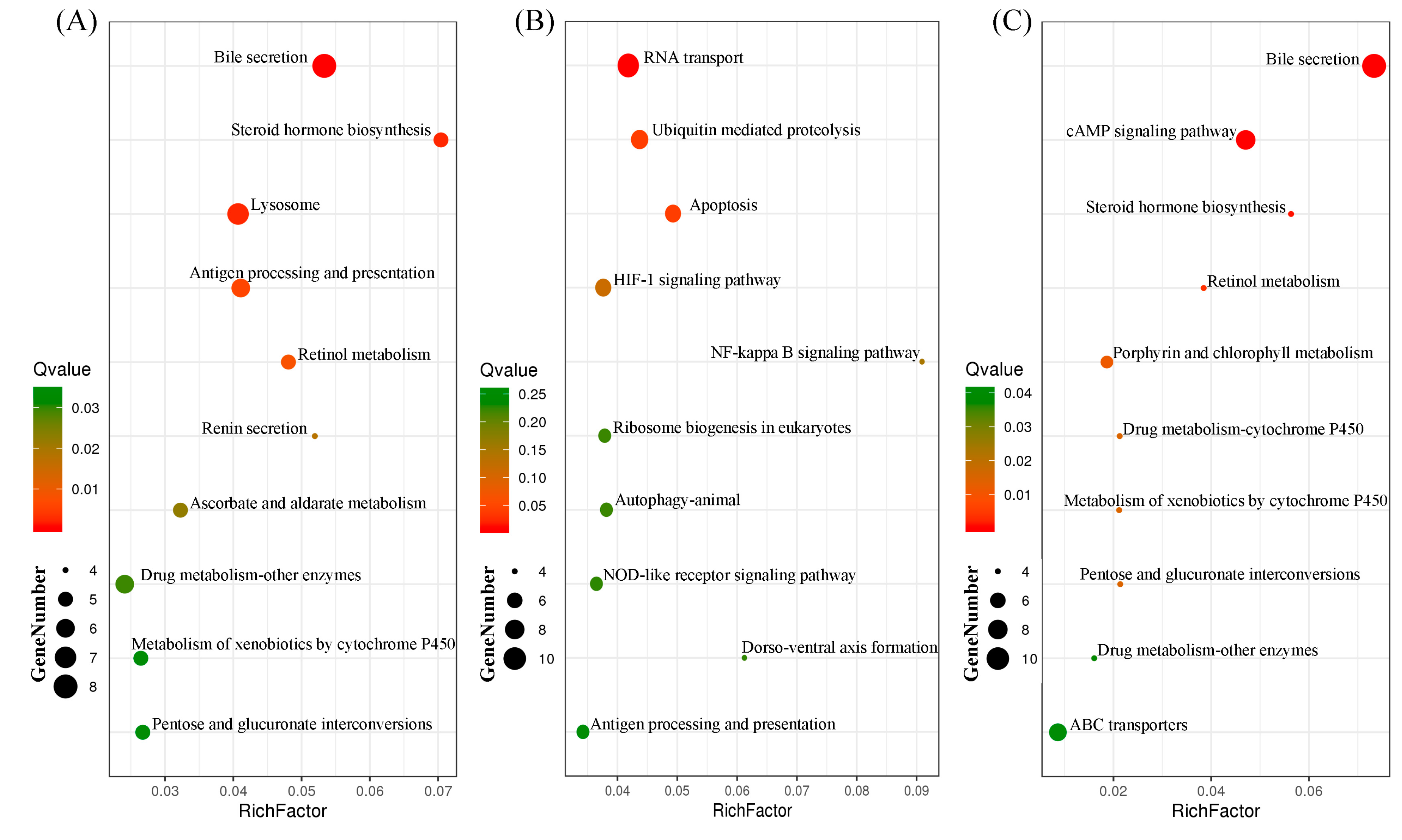
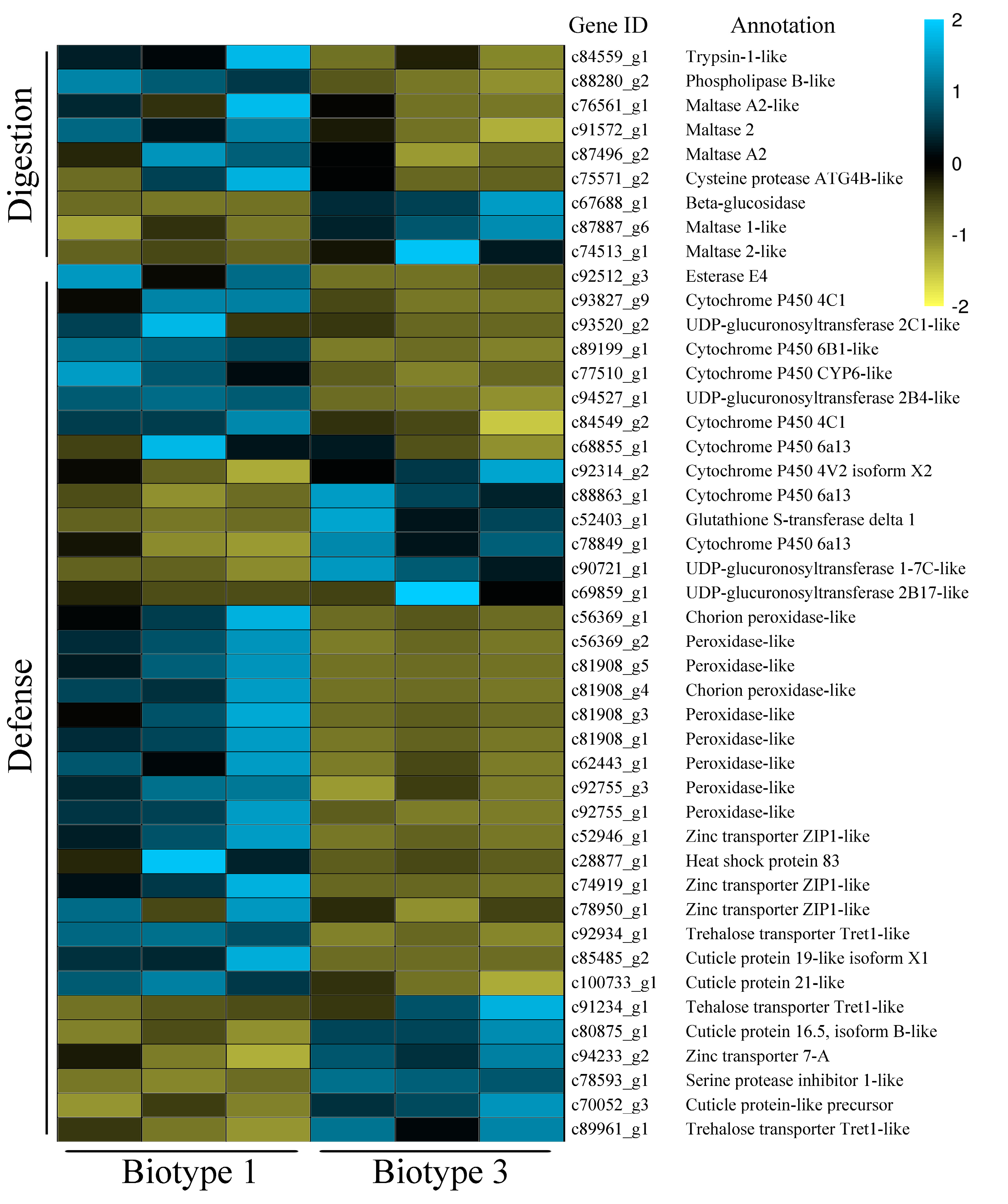
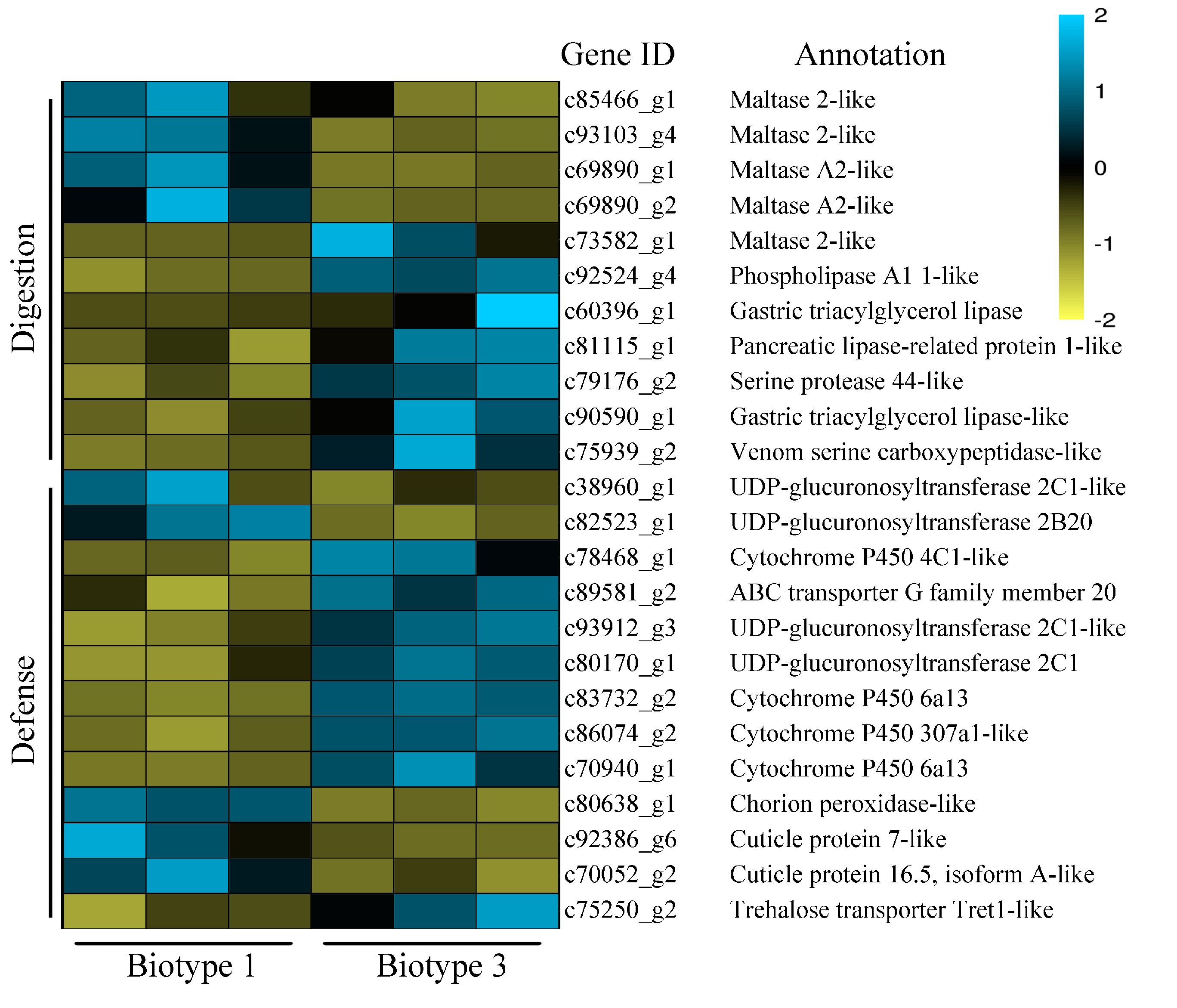
3.3. Identification of Common and Specific DEGs (Differentially Expressed Genes) and Enrichment Analyses
3.4. Validation of RNA-Seq Data by qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
4.1. Divergence of Aphid Biotypes
4.2. Molecular Factors Underlying Aphids’ Use of Resistant Host Plants
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCarville, M.T.; O’Neal, M.E. Measuring the benefit of biological control for single gene and pyramided host plant resistance for Aphis glycines (Hemiptera: Aphididae) management. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, R.; Michel, A. Molecular Adaptations of Aphid Biotypes in Overcoming Host-Plant Resistance. In Short Views on Insect Genomics and Proteomics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 75–93. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Liu, D. Differential performance of Sitobion avenae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) clones from wheat and barley with implications for its management through alternative cultural practices. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, N.; Li, C.; Shi, X. Identification and Genetic Differentiation of Sitobion avenae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) Biotypes in China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, A.P.; Mittapalli, O.; Mian, M.R. Evolution of Soybean Aphid Biotypes: Understanding and Managing Virulence to Host-Plant Resistance. In Soybean-Molecular Aspects of Breeding; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sōgawa, K. The rice brown planthopper: Feeding physiology and host plant interactions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1982, 27, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, R.H.; Cambron, S.E.; Flanders, K.L.; Bosque-Perez, N.A.; Clement, S.L.; Ohm, H.W. Biotype composition of Hessian fly (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) populations from the southeastern, midwestern, and northwestern United States and virulence to resistance genes in wheat. J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-S.; Hill, C.B.; Hartman, G.L.; Mian, M.; Diers, B.W. Discovery of soybean aphid biotypes. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccoud, J.; Ollivier, A.; Plantegenest, M.; Simon, J.-C. A continuum of genetic divergence from sympatric host races to species in the pea aphid complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7495–7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccoud, J.; Mahéo, F.; de La Huerta, M.; Laurence, C.; Simon, J.C. Genetic characterisation of new host-specialised biotypes and novel associations with bacterial symbionts in the pea aphid complex. Insect Conserv. Divers. 2015, 8, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.M.; Chuang, W.P. Plant resistance to aphid feeding: Behavioral, physiological, genetic and molecular cues regulate aphid host selection and feeding. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, S.P.; Shaw, K.L. Insect speciation rules: Unifying concepts in speciation research. Annu. Rev. Entomol 2014, 59, 339–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouhaud, P.; Gautier, M.; Gouin, A.; Jaquiéry, J.; Peccoud, J.; Legeai, F.; Mieuzet, L.; Smadja, C.M.; Lemaitre, C.; Vitalis, R. Identifying genomic hotspots of differentiation and candidate genes involved in the adaptive divergence of pea aphid host races. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 3287–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osbourn, A.E.; Qi, X.; Townsend, B.; Qin, B. Dissecting plant secondary metabolism-constitutive chemical defences in cereals. New Phytol. 2003, 159, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicker, D.; Schulz, M. Benzoxazinones in Plants: Occurrence, Synthetic Access, and Biological Activity. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 27, pp. 185–232. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Fang, T.; Pu, G.; Sun, X.; Zhou, X.; Cai, Q. Xenobiotic metabolism of plant secondary compounds in the English grain aphid, Sitobion avenae (F.)(Hemiptera: Aphididae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 107, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.-Q.; Zhang, M.-X.; Yu, J.-Y.; Jin, Y.; Ling, B.; Du, J.-P.; Li, G.-H.; Qin, Q.-M.; Cai, Q.-N. Glutathione S-transferase of brown planthoppers (Nilaparvata lugens) is essential for their adaptation to gramine-containing host plants. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, S.S.; Rinker, D.C.; Gerardo, N.M.; Abbot, P. Transcriptional profile and differential fitness in a specialist milkweed insect across host plants varying in toxicity. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 6742–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, R.; Shi, X. Transcriptional Responses in Defense-Related Genes of Sitobion avenae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) Feeding on Wheat and Barley. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 112, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.-N.; Han, Y.; Cao, Y.-Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Bi, J.-L. Detoxification of gramine by the cereal aphid Sitobion avenae. J. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 35, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loayza-Muro, R.; Figueroa, C.C.; Niemeyer, H.M. Effect of Two Wheat Cultivars Differing in Hydroxamic Acid Concentration on Detoxification Metabolism in the Aphid Sitobion avenae. J. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 26, 2725–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Quisenberry, S.S. Possible roles of esterase, glutathione S-transferase, and superoxide dismutase activities in understanding aphid-cereal interactions. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2003, 108, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzanowski, G.; Leszczyński, B.; Czerniewicz, P.; Sytykiewicz, H.; Matok, H.; Krzyżanowski, R.; Sempruch, C. Effect of phenolic acids from black currant, sour cherry and walnut on grain aphid (Sitobion avenae F.) development. Crop. Prot. 2012, 35, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouhaud, P.; Peccoud, J.; Mahéo, F.; Mieuzet, L.; Jaquiéry, J.; Simon, J.C. Genomic regions repeatedly involved in divergence among plant-specialized pea aphid biotypes. J. Evol. Biol 2014, 27, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Crops: An Identification and Information Guide; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fekih, I.B.; Jensen, A.B.; Boukhris-Bouhachem, S.; Pozsgai, G.; Rezgui, S.; Rensing, C.; Eilenberg, J. Virulence of Two Entomophthoralean Fungi, Pandora neoaphidis and Entomophthora planchoniana, to Their Conspecific (Sitobion avenae) and Heterospecific (Rhopalosiphum padi) Aphid Hosts. Insects 2019, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kloos, S.; Mora-Ramírez, I.; Romeis, J.; Brunner, S.; Li, Y.; Meissle, M. Transgenic Winter Wheat Expressing the Sucrose Transporter HvSUT1 from Barley does not Affect Aphid Performance. Insects 2019, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcuera, L.; Argandona, V.; Pena, G.; Perez, F.; Niemeyer, H. Effect of a Benzoxazinone from Wheat on Aphids. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Insect-Plant Relationships, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1–4 March 1982; pp. 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Niemeyer, H.M. Hydroxamic acids derived from 2-hydroxy-2 H-1, 4-benzoxazin-3 (4 H)-one: Key defense chemicals of cereals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1677–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.X.; Liu, D.G.; Chen, H.; Meng, X.X. Fitness traits and underlying genetic variation related to host plant specialization in the aphid Sitobion avenae. Insect Sci. 2014, 21, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, D.; Wang, D.; Shi, X.; Simon, J.-C. Molecular and quantitative genetic differentiation in Sitobion avenae populations from both sides of the Qinling Mountains. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Shi, X.; Dai, P.; Liu, D.; Dai, X.; Shang, Z.; Ge, Z.; Meng, X. Comparison of fitness traits and their plasticity on multiple plants for Sitobion avenae infected and cured of a secondary endosymbiont. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, D.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, R.; Shi, X. Clonal Diversity and Genetic Differentiation of Sitobion avenae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) From Wheat and Barley in China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute, S. Base SAS 9.4 Procedures Guide: Statistical Procedures; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q. Trinity: Reconstructing a full-length transcriptome without a genome from RNA-Seq data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talón, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, J.H.; Roper, S.; Vahter, P. Dynamic complementarities in innovation strategies. Res. Policy 2014, 43, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Mao, X.; Huang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Dong, S.; Kong, L.; Gao, G.; Li, C.-Y.; Wei, L. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39 (suppl. 2), W316–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyres, I.; Jaquiéry, J.; Sugio, A.; Duvaux, L.; Gharbi, K.; Zhou, J.J.; Legeai, F.; Nelson, M.; Simon, J.C.; Smadja, C.M. Differential gene expression according to race and host plant in the pea aphid. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 4197–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-H.; Chen, J.-L.; Cheng, D.-F.; Sun, J.-R.; Liu, Y.; Francis, F. Discovery of English grain aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) biotypes in China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvarov, B.P. Insect nutrition and metabolism: A summary of the literature. Trans. R. Entomol. Soc. Lond. 1929, 76, 255–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, W.; Ferreira, C.; De Bianchi, A. Distribution of digestive enzymes among the endo-and ectoperitrophic spaces and midgut cells of Rhynchosciara and its physiological significance. J. Insect Physiol. 1979, 25, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.P.; Terra, W.R. α-galactosidase activity in ingested seeds and in the midgut of Dysdercus peruvianus (Hemiptera: Pyrrhocoridae). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1997, 34, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabadi, M.; Bandani, A.R.; Dastranj, M. Salivary digestive enzymes of the wheat bug, Eurygaster integriceps (Insecta: Hemiptera: Scutelleridae). Compt. R. Biol. 2014, 337, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terra, W.R.; Ferreira, C. Biochemistry and molecular biology of digestion. In Insect Molecular Biology and Biochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 365–418. [Google Scholar]
- Weidlich, S.; Hoffmann, K.H.; Woodring, J. Secretion of lipases in the digestive tract of the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. Arch. Insect Biochem. 2015, 90, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.-D.; Su, Y.-L.; Zhao, Q.-Y.; Xia, W.-Q.; Liu, S.-S.; Wang, X.-W. Transcriptomic analyses reveal the adaptive features and biological differences of guts from two invasive whitefly species. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, M.; Murat, S.; Clark, A.G.; Gouppil, G.; Blais, C.; Matzkin, L.M.; Guittard, É.; Yoshiyama-Yanagawa, T.; Kataoka, H.; Niwa, R. Mutations in the neverland gene turned Drosophila pachea into an obligate specialist species. Science 2012, 337, 1658–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, W.R.; Dillwith, J.W.; Puterka, G.J. Salivary proteins of Russian wheat aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, S.J.; Hartson, S.D.; Puterka, G.J. Proteomic analysis of secreted saliva from Russian Wheat Aphid (Diuraphis noxia Kurd.) biotypes that differ in virulence to wheat. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2252–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, S.J.; Puterka, G.J. Variation in the salivary proteomes of differentially virulent greenbug (Schizaphis graminum Rondani) biotypes. J. Proteom. 2014, 105, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.-C.; d’Alencon, E.; Guy, E.; Jacquin-Joly, E.; Jaquiery, J.; Nouhaud, P.; Peccoud, J.; Sugio, A.; Streiff, R. Genomics of adaptation to host-plants in herbivorous insects. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2015, 14, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadway, R.M. Dietary regulation of serine proteinases that are resistant to serine proteinase inhibitors. J. Insect Physiol. 1997, 43, 855–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losvik, A.; Beste, L.; Mehrabi, S.; Jonsson, L. The protease inhibitor CI2c gene induced by bird cherry-oat aphid in barley inhibits green peach aphid fecundity in transgenic Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyati, P.; Bandani, A.R.; Fitches, E.; Gatehouse, J.A. Protein digestion in cereal aphids (Sitobion avenae) as a target for plant defence by endogenous proteinase inhibitors. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.; Wei, C. De novo comparative transcriptome analysis of a rare cicada, with identification of candidate genes related to adaptation to a novel host plant and drier habitats. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, M.; Dietrich, C.H.; He, Z.; Wei, C. Comparative sialotranscriptome analysis of the rare Chinese cicada Subpsaltria yangi, with identification of candidate genes related to host-plant adaptation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zúñiga, G.E.; Argandoña, V.H.; Niemeyer, H.M.; Corcuera, L.J. Hydroxamic acid content in wild and cultivated Gramineae. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 2665–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argandoña, V.H.; Zuñiga, G.E.; Corcuera, L.J. Distribution of gramine and hydroxamic acids in barley and wheat leaves. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 1917–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollina, V.; Kushalappa, A.C.; Choo, T.M.; Dion, Y.; Rioux, S. Identification of metabolites related to mechanisms of resistance in barley against Fusarium graminearum, based on mass spectrometry. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 77, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, T.; Scholz, B.; Peter, S.; Engel, K.-H. Metabolite profiling of barley: Influence of the malting process. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.H.; Newbigin, E.; Tester, M.; Bacic, A.; Roessner, U. Metabolic responses to salt stress of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cultivars, Sahara and Clipper, which differ in salinity tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 4089–4103. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Vasanthan, T.; Temelli, F. Analysis of phenolic acids in barley by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4352–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmak, S.; Jonnala, R.S.; MacRitchie, F. Effect of genetic variation on phenolic acid and policosanol contents of Pegaso wheat lines. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 48, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczynski, B.; Dixon, A. Resistance of cereals to aphids: The interaction between hydroxamic acids and glutathione S-transferases in the grain aphid Sitobion avenae (F.)(Hom., Aphididae). J. Appl. Entomol. 1992, 113, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczynski, B.; Matok, H.; Dixon, A. Resistance of cereals to aphids: The interaction between hydroxamic acids and UDP-glucose transferases in the aphid Sitobion avenae (Homoptera: Aphididae). J. Chem. Ecol. 1992, 18, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawada, K.; Lohar, M.K. Effect of gramine on the fecundity, longevity and probing behaviour of the greenbug, Schizaphis graminum (Rondani). Berichte Ohara Instituts Fuer Landwirtsch. Biol. Okayama Univ. 1989, 19, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, M.; Corcuera, L. Effect of environment on gramine content in barley leaves and susceptibility to the aphid Schizaphis graminum. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 3237–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustamani, M.A.; Kanehisa, K.; Tsumuki, H.; Shiraga, T. Additional observations on aphid densities and gramine contents in barley lines. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1992, 27, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcuera, L.J. Biochemical basis for the resistance of barley to aphids. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuvesson, S.; Johansson, M. Does indole alkaloid gramine confer resistance in barley to aphid Rhopalosiphum padi? J. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 26, 233–255. [Google Scholar]
- Hofman, J.; Hofmanova, O. 1, 4-Benzoxazine Derivatives in Plants: Sephadex Fractionation and Identification of a New Glucoside. Eur. J. Biochem. 1969, 8, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, H.M. Hydroxamic acids (4-hydroxy-1, 4-benzoxazin-3-ones), defence chemicals in the Gramineae. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 3349–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, L.; Niemeyer, H.M.; Jonsson, L.M. Partial purification and characterization of a hydroxamic acid glucoside β-D-glucosidase from maize. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 2609–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givovich, A.; Sandström, J.; Niemeyer, H.; Pettersson, J. Presence of a hydroxamic acid glucoside in wheat phloem sap, and its consequences for performance of Rhopalosiphum padi (L.)(Homoptera: Aphididae). J. Chem. Ecol. 1994, 20, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Fall, L.A.; Solomon, P.S. Role of cereal secondary metabolites involved in mediating the outcome of plant-pathogen interactions. Metabolites 2011, 1, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameters | Wheat | Barley | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biotype 1 | Biotype 3 | Biotype 1 | Biotype 3 | |
| Raw reads | 25,989,771–28,117,345 | 26,056,761–28,490,615 | 26,108,796–29,031,747 | 28,413,038–40,153,204 |
| Clean reads | 25,482,373–27,506,078 | 25,567,593–27,982,220 | 25,669,614–28,512,017 | 27,900,884–39,420,648 |
| Clean base pairs (Gb) | 3.85–4.28 | 4.19–5.91 | 3.82–4.13 | 3.84–4.2 |
| Error (%) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Q20 (%) | 98.76–98.80 | 98.66–98.79 | 98.72–98.80 | 98.70–98.78 |
| Q30 (%) | 96.49–96.58 | 96.18–96.58 | 96.32–96.59 | 96.40–96.56 |
| GC (%) | 40.04–40.99 | 40.19–40.34 | 40.38–40.46 | 39.70–39.96 |
| Total number of unigenes | 143,058 | |||
| Total length of unigenes (nt) | 95,512,520 | |||
| Mean length of unigenes (nt) | 358 | |||
| N50 of unigenes | 1012 | |||
| Mapped reads (%) | 71.67–72.46 | 72.80–72.84 | 72.46–73.23 | 72.22–73.14 |
| GO | Term Type a | Go Description | DE | Total | p-Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0006259 | P | DNA metabolic process | 32 | 1042 | <0.001 | 0.001 |
| GO:0006508 | P | Proteolysis | 27 | 987 | <0.001 | 0.039 |
| GO:0015074 | P | DNA integration | 17 | 313 | <0.001 | 0 |
| GO:0005488 | F | Binding | 178 | 9929 | 0.001 | 0.036 |
| GO:0003676 | F | Nucleic acid binding | 95 | 4051 | <0.001 | 0.001 |
| GO:0008233 | F | Peptidase activity | 30 | 945 | <0.001 | 0.017 |
| GO:0070011 | F | Peptidase activity, acting on L-amino acid peptides | 28 | 847 | <0.001 | 0.017 |
| GO:0004175 | F | Endopeptidase activity | 17 | 462 | 0.001 | 0.036 |
| GO:0008236 | F | Serine-type peptidase activity | 13 | 279 | <0.001 | 0.023 |
| GO:0017171 | F | Serine hydrolase activity | 13 | 279 | <0.001 | 0.023 |
| GO:0015020 | F | Glucuronosyltransferase activity | 7 | 81 | <0.001 | 0.021 |
| GO:0008194 | F | UDP-glycosyltransferase activity | 7 | 107 | 0.001 | 0.044 |
| GO:0004523 | F | RNA-DNA hybrid ribonuclease activity | 5 | 50 | 0.001 | 0.036 |
| GO | Term Type a | Go Description | DE | Total | p-Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0006950 | P | Response to stress | 15 | 553 | <0.001 | 0.043 |
| GO:0006979 | P | Response to oxidative stress | 8 | 140 | <0.001 | 0.02 |
| GO:0018205 | P | Peptidyl-lysine modification | 7 | 121 | <0.001 | 0.039 |
| GO:0098754 | P | Detoxification | 7 | 136 | <0.001 | 0.042 |
| GO:0098869 | P | Cellular oxidant detoxification | 7 | 136 | <0.001 | 0.042 |
| GO:1990748 | P | Cellular detoxification | 7 | 136 | <0.001 | 0.042 |
| GO:0009636 | P | Response to toxic substance | 7 | 137 | <0.001 | 0.042 |
| GO:0016573 | P | Histone acetylation | 5 | 62 | <0.001 | 0.042 |
| GO:0006475 | P | Internal protein amino acid acetylation | 5 | 71 | <0.001 | 0.043 |
| GO:0018393 | P | Internal peptidyl-lysine acetylation | 5 | 71 | <0.001 | 0.043 |
| GO:0018394 | P | Peptidyl-lysine acetylation | 5 | 71 | <0.001 | 0.043 |
| GO:0034655 | P | Nucleobase-containing compound catabolic process | 5 | 74 | 0.001 | 0.048 |
| GO:0006473 | P | Protein acetylation | 5 | 75 | 0.001 | 0.048 |
| GO:0043543 | P | Protein acylation | 5 | 76 | 0.001 | 0.048 |
| GO:0008285 | P | Negative regulation of cell proliferation | 4 | 13 | <0.001 | 0.005 |
| GO:0042127 | P | Regulation of cell proliferation | 4 | 17 | <0.001 | 0.008 |
| GO:0008283 | P | Cell proliferation | 4 | 19 | <0.001 | 0.009 |
| GO:0003676 | F | Nucleic acid binding | 68 | 4051 | <0.001 | 0.048 |
| GO:0008234 | F | Cysteine-type peptidase activity | 10 | 197 | <0.001 | 0.032 |
| GO:0004601 | F | Peroxidase activity | 7 | 118 | <0.001 | 0.045 |
| GO:0016684 | F | Oxidoreductase activity | 7 | 130 | <0.001 | 0.048 |
| GO:0004197 | F | Cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | 5 | 55 | <0.001 | 0.045 |
| GO | Term Type a | Go Description | DE | Total | p-Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0034204 | P | Lipid translocation | 2 | 8 | <0.001 | 0.039 |
| GO:0045332 | P | Phospholipid translocation | 2 | 8 | <0.001 | 0.039 |
| GO:0097035 | P | Regulation of membrane lipid distribution | 2 | 8 | <0.001 | 0.039 |
| GO:0015748 | P | Organophosphate ester transport | 2 | 12 | <0.001 | 0.055 |
| GO:0015914 | P | Phospholipid transport | 2 | 12 | <0.001 | 0.055 |
| GO:0016705 | F | Oxidoreductase activity | 4 | 171 | 0.007 | 0.078 |
| GO:0005548 | F | Phospholipid transporter activity | 2 | 8 | 0.002 | 0.030 |
| GO:0003840 | F | Gamma-glutamyltransferase activity | 2 | 14 | 0.003 | 0.065 |
| GO:0005319 | F | Lipid transporter activity | 2 | 20 | 0.003 | 0.078 |
| GO:0016755 | F | Transferase activity | 2 | 21 | 0.003 | 0.078 |
| GO:0004824 | F | Lysine-trna ligase activity | 2 | 22 | 0.004 | 0.078 |
| GO:0004012 | F | Phospholipid-translocating atpase activity | 2 | 8 | 0.001 | 0.03 |
| Gene ID | Annotation | Wheat a | Barley b | Gene ID | Annotation | Wheat a | Barley b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log2 (Fold Change) | Log2 (Fold Change) | Log2 (Fold Change) | Log2 (Fold Change) | ||||
| c68224_g2 | Beta-galactosidase isoform X2 | 1.67 | 1.72 | c93888_g2 | Pancreatic lipase-related protein 1-like | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| c4428_g1 | Alpha-mannosidase-like 2 | 4.06 | 5.49 | c70849_g1 | Pancreatic lipase-related protein 2-like | −2.46 | −1.97 |
| c86944_g1 | Serine protease K12H4.7 | 2.1 | 2.14 | c88297_g5 | Phospholipase YOR022C | −8.35 | −8.97 |
| c84329_g2 | Serine protease 44-like | 2.16 | 2.09 | c88297_g1 | Phospholipase YOR022C | −8.35 | −8.99 |
| c93201_g1 | Serine proteinase stubble-like isoform X1 | 1.02 | 1.24 | c92524_g1 | Phospholipase A1 1-like | 1.65 | 1.9 |
| c90736_g1 | Hormone-sensitive lipase | 3.51 | 6.39 | c47889_g1 | Maltase A2-like | 4.84 | 7.38 |
| c78349_g1 | Lipase 3-like | 3.34 | 2.58 | c75939_g1 | Carboxypeptidase CG4572_56.1 | 5.26 | 7.38 |
| c91806_g1 | Pancreatic lipase-related protein 2-like | 1.6 | 2.02 | c91663_g1 | Venom serine carboxypeptidase-like | 3.36 | 4.54 |
| c81636_g2 | Cytochrome P450 6a13 | 1.87 | 2.77 | c75860_g1 | Alkaline phosphatase 4 | 1.67 | 1.69 |
| c84461_g2 | Cytochrome P450 4V2-like | 2.64 | 2.45 | c80317_g2 | Esterase E4-like | −1.69 | −1.54 |
| c94592_g2 | Cytochrome P450 4C1-like | 1.15 | 2.17 | c89160_g1 | Esterase FE4-like isoform X2 | −2.37 | −1.83 |
| c85949_g2 | Cytochrome P450 6a13 isoform X2 | 1.85 | 1.42 | c73140_g3 | Esterase E4-like | 3.21 | 4.02 |
| c82801_g1 | Cytochrome P450 4C1-like | −1.85 | −1.24 | c92686_g1 | Esterase FE4-like | 2.22 | 3.04 |
| c92410_g3 | Cytochrome P450 6k1 | −1.65 | −1.42 | c88468_g2 | Laccase-5 | −2.24 | −1.49 |
| c81321_g1 | Cytochrome P450 6k1-like isoform X1 | −1.54 | −1.47 | c86869_g2 | Peroxidase-like | −2.35 | −1.47 |
| c92410_g2 | Cytochrome P450 6k1-like isoform X2 | −2.52 | −2.21 | c86704_g2 | Peroxidase-like | −1.63 | −1.69 |
| c94328_g3 | Venom carboxylesterase-6-like | −1.44 | −1.04 | c91728_g2 | Peroxidase-like | −1.34 | −1.73 |
| c87374_g1 | Glutathione S-transferase-like | −1.21 | −1.06 | c86869_g1 | Peroxidase-like isoform X2 | −3.63 | −3.57 |
| c83325_g1 | Glutathione S-transferase omega-1-like | −1.81 | −2.29 | c58802_g1 | Peroxidase | −5.56 | −5.86 |
| c89912_g1 | Glutathione S-transferase-like | 2.84 | 3.01 | c81908_g2 | Peroxidase-like | −12.42 | −8.48 |
| c89445_g1 | UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2B2 | 2.01 | 2.15 | c87544_g2 | Superoxide dismutase | −4.71 | −5.12 |
| c91825_g1 | UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2B7-like | 1.15 | 1.83 | c92840_g2 | Serine protease inhibitor 5 | −1.16 | −1.36 |
| c91399_g1 | UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2B4-like | −3.32 | −2.18 | c65501_g1 | Cuticle protein 7-like | −6.68 | −6.57 |
| c89981_g2 | UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2B20-like | −2.65 | −2.32 | c81826_g1 | Cuticle protein 7-like | 5.94 | 4.8 |
| c89981_g3 | UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2B1-like | −3.11 | −2.41 | c69395_g1 | Heat shock protein 68-like | −4.76 | −2.38 |
| c79169_g2 | UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2B17-like | −1.97 | −2.71 | c91730_g6 | Trehalose transporter Tret1-like | −2.51 | −3.55 |
| c72511_g1 | ABC transporter G family member 23 | 2.23 | 2.8 | c19378_g1 | Trehalose transporter Tret1 | −1.32 | −1.13 |
| c93663_g1 | Alkaline phosphatase 4 | 1.62 | 2.1 | c87097_g1 | Trehalose transporter Tret1 | −1.81 | −1.44 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Shi, X.; Liu, D.; Yang, Y.; Shang, Z. Transcriptome Profiling Revealed Potentially Critical Roles for Digestion and Defense-Related Genes in Insects’ Use of Resistant Host Plants: A Case Study with Sitobion Avenae. Insects 2020, 11, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020090
Wang D, Shi X, Liu D, Yang Y, Shang Z. Transcriptome Profiling Revealed Potentially Critical Roles for Digestion and Defense-Related Genes in Insects’ Use of Resistant Host Plants: A Case Study with Sitobion Avenae. Insects. 2020; 11(2):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020090
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Da, Xiaoqin Shi, Deguang Liu, Yujing Yang, and Zheming Shang. 2020. "Transcriptome Profiling Revealed Potentially Critical Roles for Digestion and Defense-Related Genes in Insects’ Use of Resistant Host Plants: A Case Study with Sitobion Avenae" Insects 11, no. 2: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020090
APA StyleWang, D., Shi, X., Liu, D., Yang, Y., & Shang, Z. (2020). Transcriptome Profiling Revealed Potentially Critical Roles for Digestion and Defense-Related Genes in Insects’ Use of Resistant Host Plants: A Case Study with Sitobion Avenae. Insects, 11(2), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020090





