Rearing Trissolcus japonicus and Trissolcus mitsukurii for Biological Control of Halyomorpha halys
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Origin of Insects
2.2. Survival Analysis
2.3. Parasitization Tests
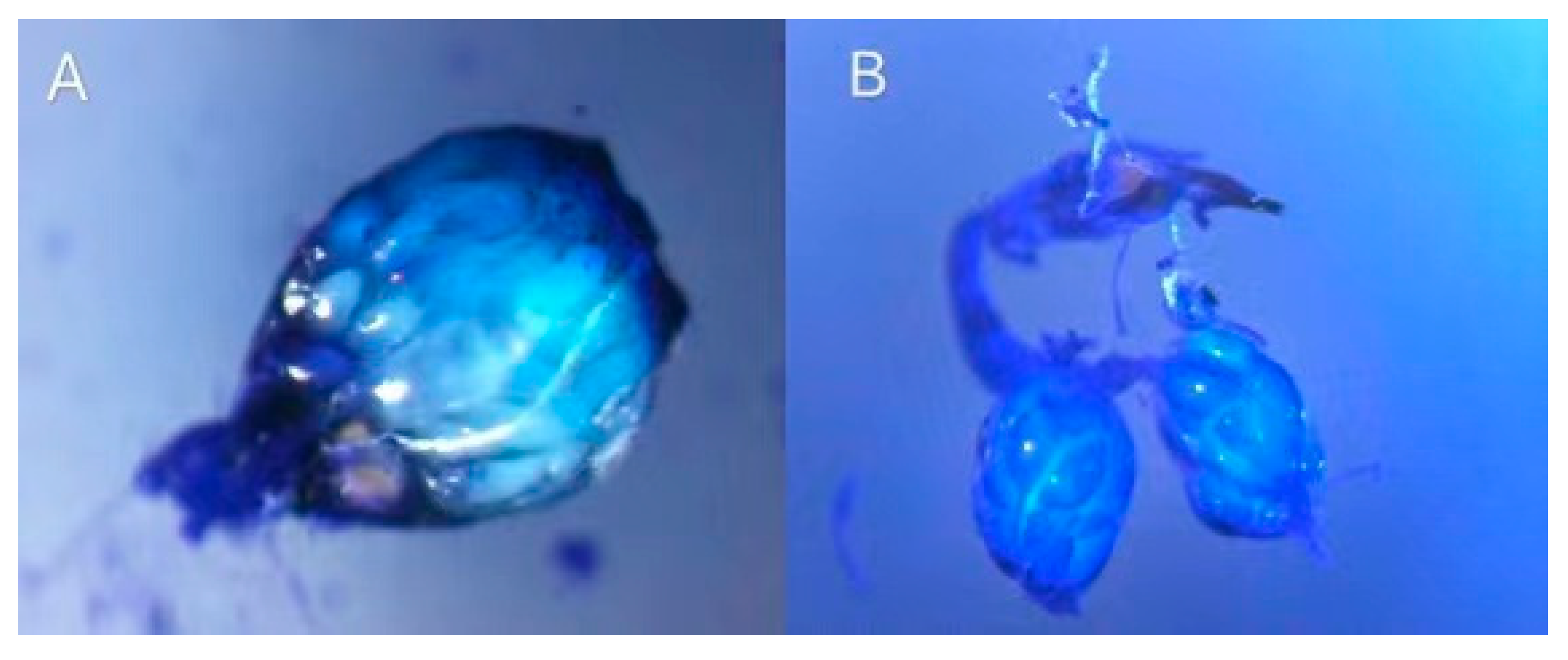
2.4. Assessment of Ovaries and Egg Load
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
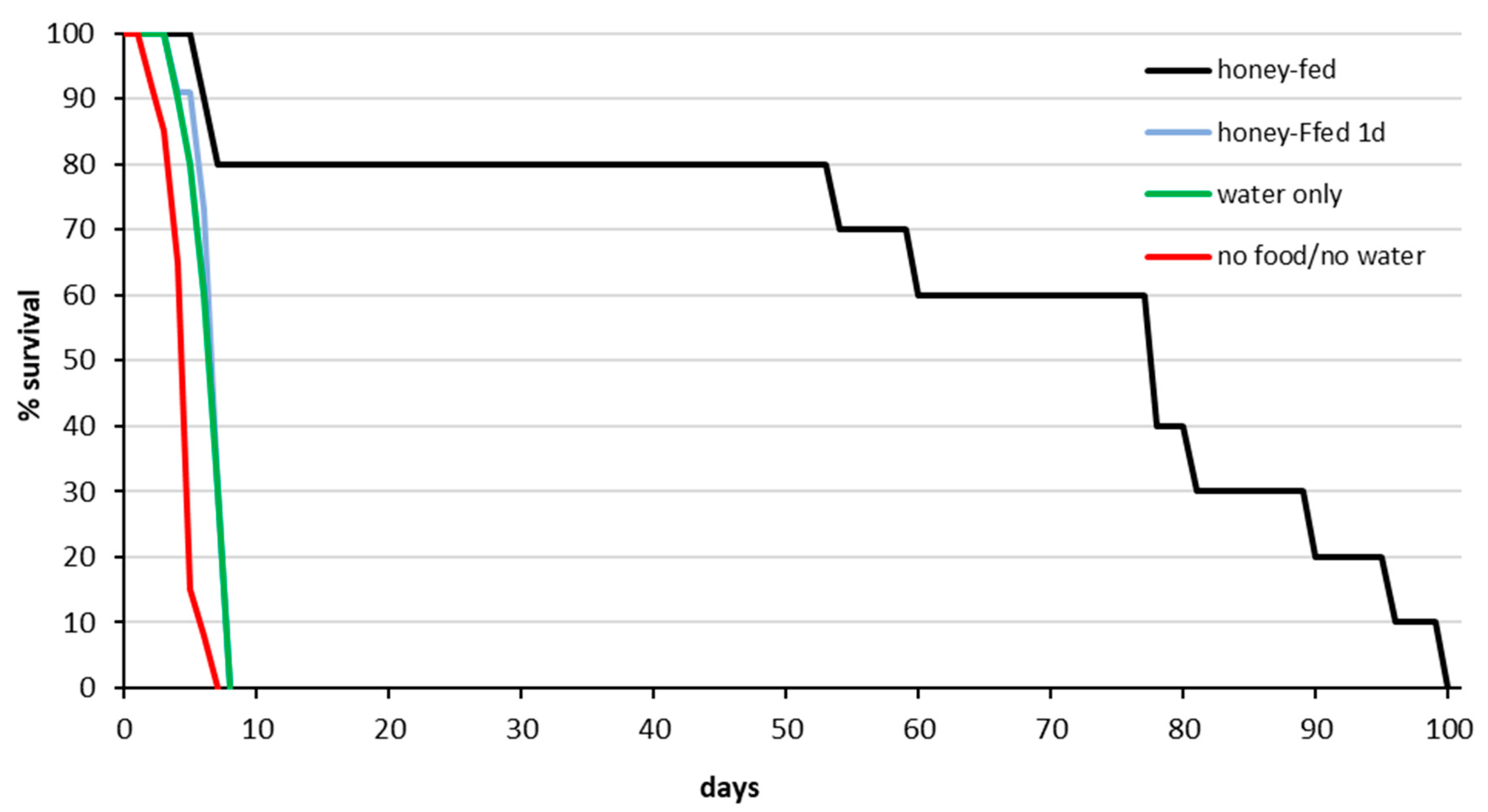
3.1. Survival Analysis
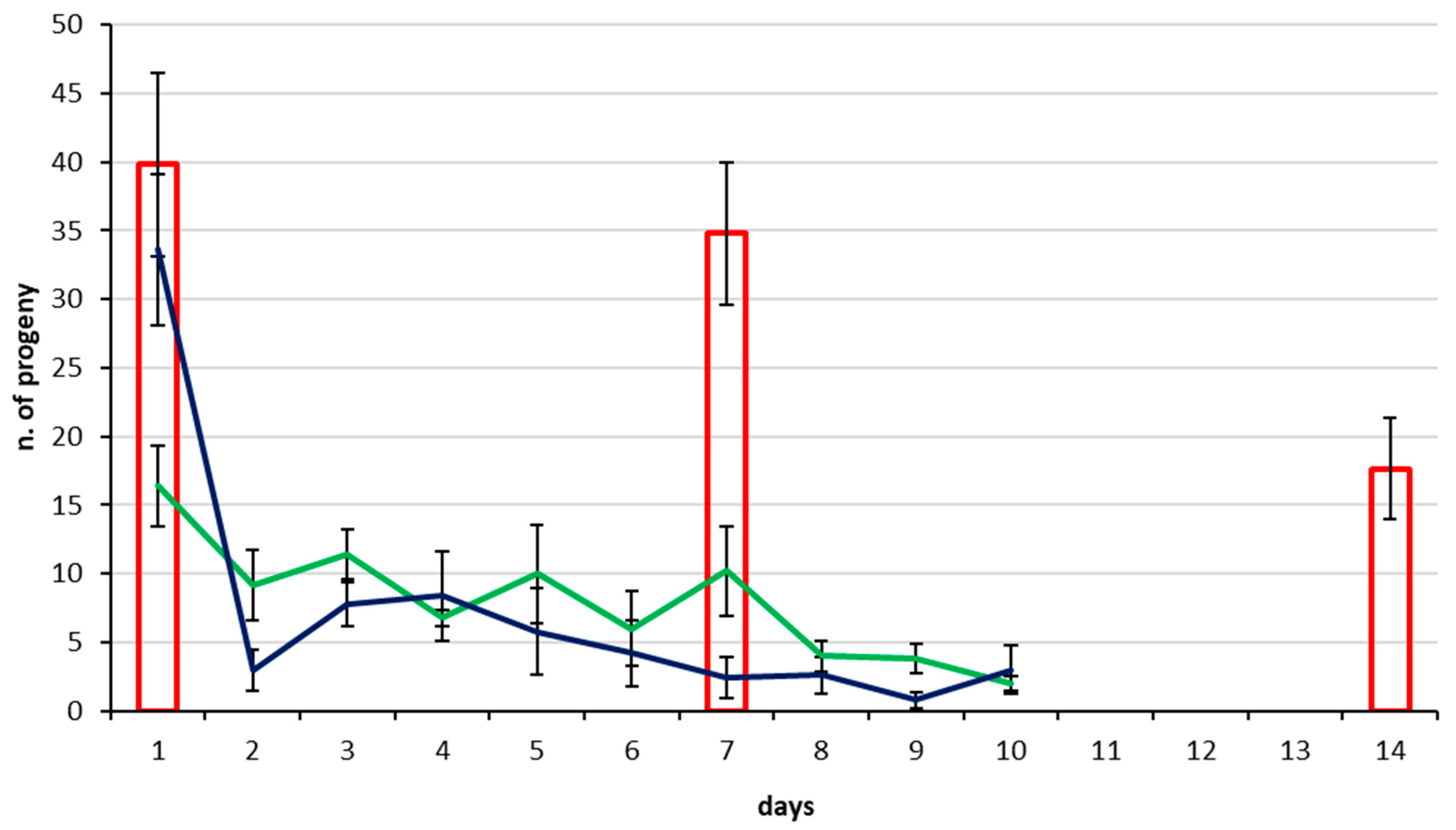
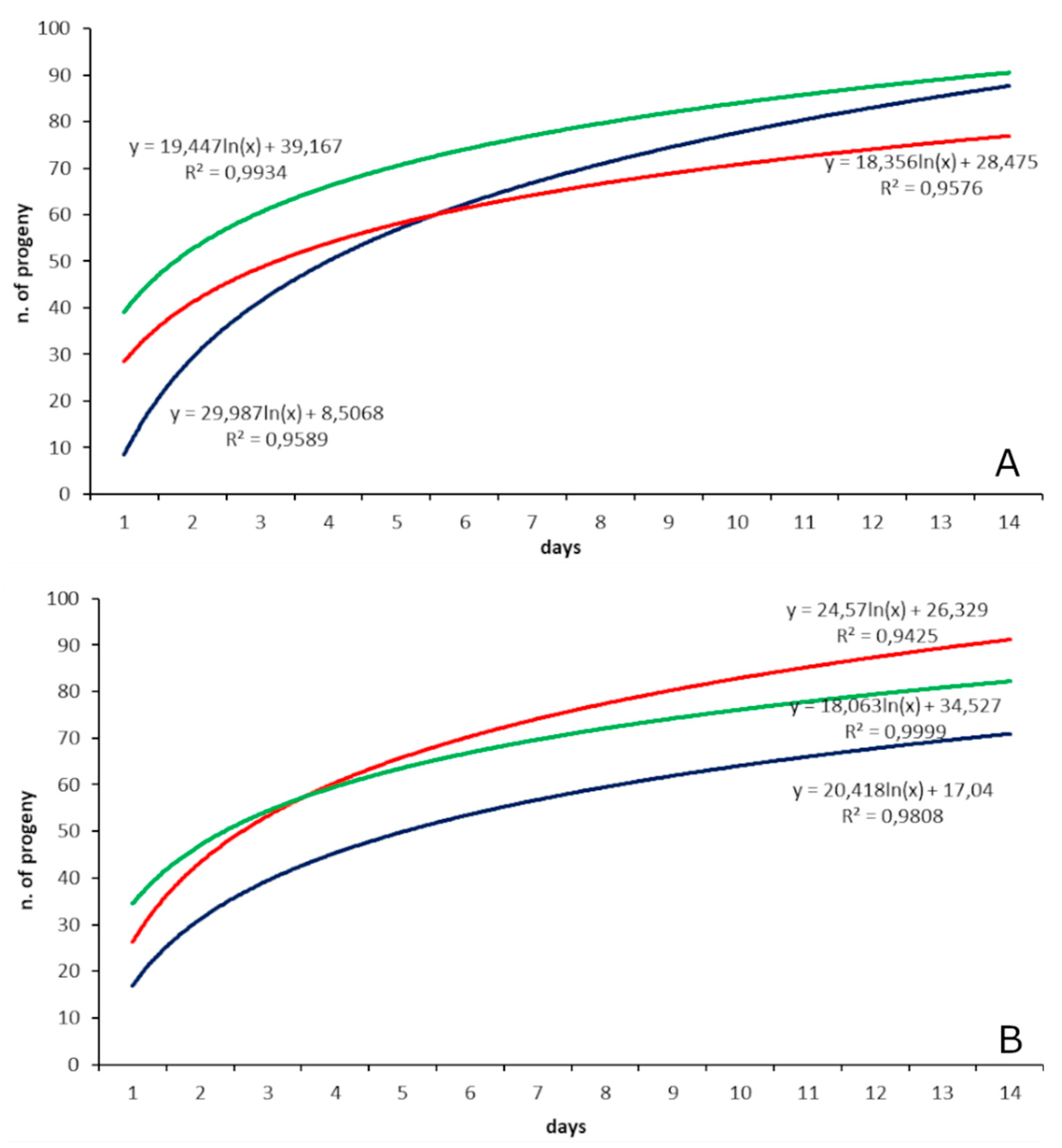
3.2. Parasitization Tests
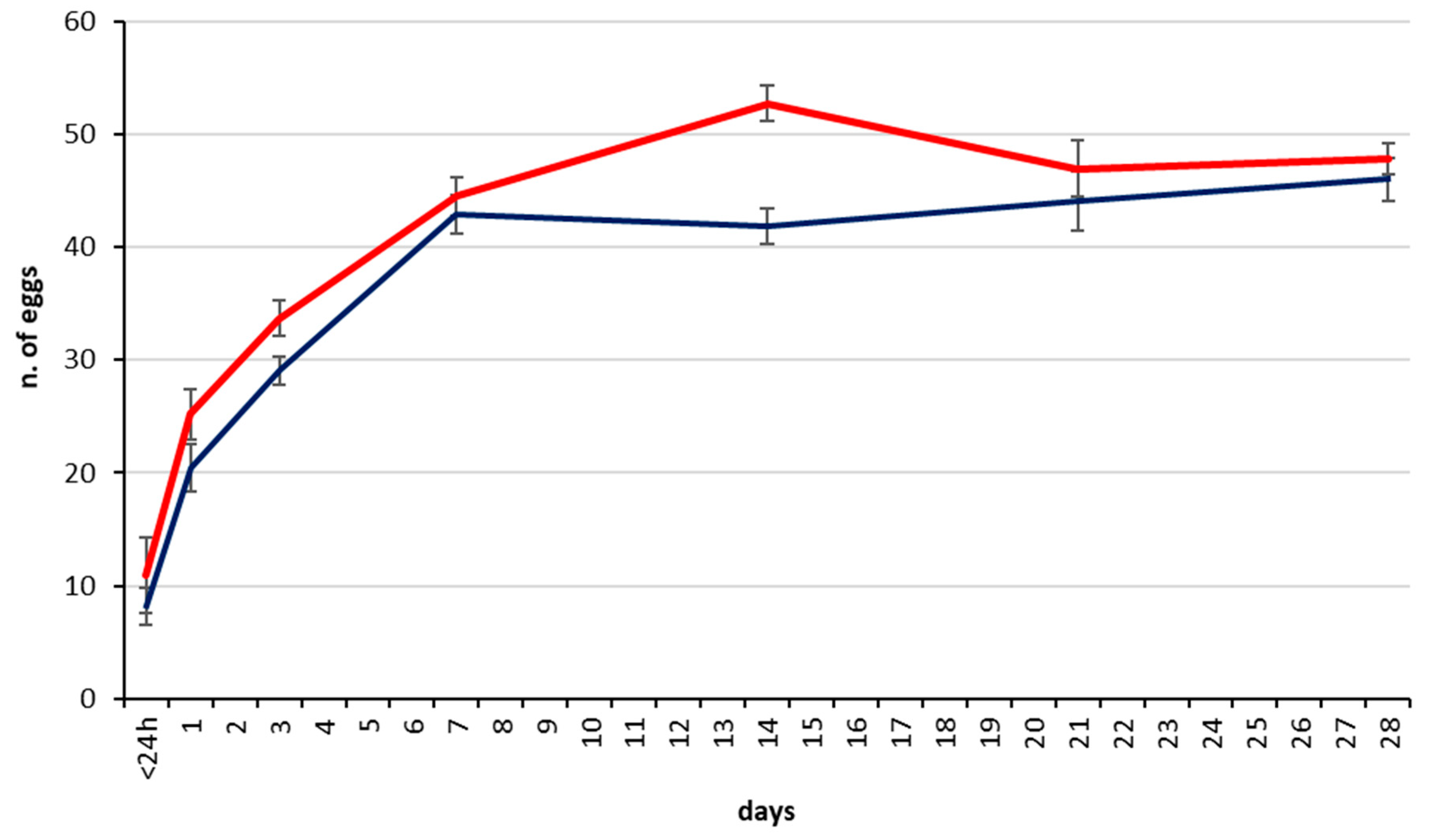
3.3. Egg Load in the Ovary
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leskey, T.C.; Nielsen, A.L. Impact of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug in North America and Europe: History, biology, ecology, and management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 599–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leskey, T.C.; Short, B.D.; Butler, B.R.; Wright, S.E. Impact of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål), in mid-Atlantic tree fruit orchards in the United States: Case studies of commercial management. Psyche 2012, 2012, 535062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leskey, T.C.; Hamilton, G.C.; Nielsen, A.L.; Polk, D.F.; Rodriguez-Saona, C.; Bergh, J.C.; Herbert, D.A.; Kuhar, T.P.; Pfeiffer, D.; Dively, G.P.; et al. Pest status of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys in the USA. Outlooks Pest Manag. 2012, 23, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brust, G.; Rane, K. Transmission of the Yeast Eremothecium coryli to Fruits and Vegetables by the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug. 2013. Available online: https://extension.umd.edu/learn/transmission-yeast-eremothecium-coryli-fruits-and-vegetables-brown-marmorated-stink-bug (accessed on 2 August 2020).
- Rice, K.; Bergh, C.; Bergman, E.; Biddinger, D.; Dieckhoff, C.; Dively, G.; Fraser, H.; Gariepy, T.; Hamilton, G.; Haye, T.; et al. Biology, ecology, and management of brown marmorated stink bug (Halyomorpha halys). J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2014, 5, A1–A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Yao, Y.X.; Qiu, L.F.; Li, Z.X. A new species of Trissolcus (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) parasitizing eggs of Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in China with comments on its biology. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2009, 102, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedstrom, C.; Lowenstein, D.; Andrews, H.; Bai, B.; Wiman, N. Pentatomid host suitability and the discovery of introduced populations of Trissolcus japonicus in Oregon. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Gariepy, T.; Mason, P.; Gillespie, D.; Talamas, E.J.; Haye, T. Seasonal parasitism and host specificity of Trissolcus japonicus in northern China. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avila, G.A.; Charles, J.G. Modelling the potential geographic distribution of Trissolcus japonicus: A biological control agent of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys. BioControl 2018, 63, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botch, P.S.; Delfosse, E.S. Host-Acceptance behavior of Trissolcus japonicus (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) reared on the invasive Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) and nontarget species. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 47, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffington, M.L.; Talamas, E.J.; Hoelmer, K.A. Team Trissolcus: Integrating taxonomy and biological control to combat the brown marmorated stink bug. Am. Entomol. 2018, 64, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, J.G.; Avila, G.A.; Hoelmer, K.A.; Hunt, S.; Gardner-Gee, R.; MacDonald, F.; Davis, V. Experimental assessment of the biosafety of Trissolcus japonicus in New Zealand, prior to the anticipated arrival of the invasive pest Halyomorpha halys. BioControl 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haye, H.; Moraglio, S.T.; Stahl, J.; Visentin, S.; Gregorio, T.; Tavella, L. Fundamental host range of Trissolcus japonicus in Europe. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 93, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konopka, J.K.; Haye, T.; Gariepy, T.D.; McNeil, J.N. Possible coexistence of native and exotic parasitoids and their impact on control of Halyomorpha halys. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 90, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milnes, J.M.; Beers, E.H. Trissolcus japonicus (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) causes low levels of parasitism in three North American pentatomids under field conditions. J. Insect Sci. 2019, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arakawa, R.; Namura, Y. Effects of temperature on development of three Trissolcus spp. (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae), egg parasitoids of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Entomol. Sci. 2002, 5, 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa, R.; Miura, M.; Fujita, M. Effects of host species on the body size, fecundity, and longevity of Trissolcus mitsukurii (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae), a solitary egg parasitoid of stink bugs. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2004, 39, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talamas, E.J.; Herlihy, M.V.; Dieckhoff, C.; Hoelmer, K.; Buffington, M.; Bon, M.-C.; Weber, D.C. Trissolcus japonicus (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera, Scelionidae) emerges in North America. J. Hymenopt. Res. 2015, 43, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabbatini Peverieri, G.; Talamas, E.; Bon, M.C.; Marianelli, L.; Bernardinelli, I.; Malossini, G.; Benvenuto, L.; Roversi, P.F.; Hoelmer, K. Two Asian egg parasitoids of Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Hemiptera, Pentatomidae) emerge in northern Italy: Trissolcus mitsukurii (Ashmead) and Trissolcus japonicus (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera, Scelionidae). J. Hymenopt. Res. 2018, 67, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, J.; Tortorici, F.; Pontini, M.; Bon, M.C.; Hoelmer, K.; Marazzi, C.; Tavella, L.; Haye, T. First discovery of adventive populations of Trissolcus japonicus (Ashmead) in Europe. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abram, P.K.; Talamas, E.J.; Acheampong, S.; Mason, P.G.; Gariepy, T.D. First detection of the samurai wasp, Trissolcus japonicus (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera, Scelionidae), in Canada. J. Hymenopt. Res. 2019, 68, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postali Parra, J.R. Mass Rearing of egg parasitoids for biological control programs. In Egg Parasitoids in Agroecosystems with Emphasis on Trichogramma; Cônsoli, F.L., Parra, J.R.P., Zucchi, R.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 267–292. [Google Scholar]
- Medal, J.; Smith, T.; Fox, A.; Santa Cruz, A.; Poplin, A.; Hodges, A. Rearing the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Fla. Entomol. 2012, 95, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.M.; Coffey, P.L.; Hamby, K.A.; Dively, G.P. Laboratory rearing of Halyomorpha halys: Methods to optimize survival and fitness of adults during and after diapause. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, H.; Lowenstein, D.M.; Wiman, N.G.; Wong, J.S.; Lee, J.C. Parasitism of frozen Halyomorpha halys eggs by Trissolcus japonicus: Applications for rearing and experimentation. Biocontrol. Sci. Technol. 2019, 29, 478–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.H.L.; Walz, M.A.; Oscienny, A.B.; Sherwood, J.L.; Abram, P.K. An effective cold storage method for stockpiling Halyomorpha halys eggs for field surveys and laboratory rearing of Trissolcus japonicus. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokyo, F.; Kiritani, K.; Nakasuji, F.; Shiga, M. Comparative biology of the two scelionid egg parasites of Nezara viridula L. (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1966, 1, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, L.; Yang, Z.; Tao, W. Biology and population dynamics of Trissolcus halyomorphae. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2007, 43, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Y.; Zhan, H.X.; Zhang, F.; Babendreier, D.; Zhong, Y.Z.; Lou, Q.Z.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.P. Development and fecundity of Trissolcus japonicus on fertilized and unfertilized eggs of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, M.L.; Dieckhoff, C.; Vinyard, B.T.; Hoelmer, K.A. Parasitism and predation on sentinel egg masses of the brown marmorated stink bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in three vegetable crops: Importance of dissections for evaluating the impact of native parasitoids on an exotic pest. Environ. Entomol. 2016, 45, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Y. Effect of temperature on development of egg parasitoid Trissolcus halyomorphae and the eggs of its host, Halyomorpha halys. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2004, 20, 64–66. [Google Scholar]
- Sabbatini Peverieri, G.; Furlan, P.; Simoni, S.; Strong, W.B.; Roversi, P.F. Laboratory evaluation of Gryon pennsylvanicum (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera, Platygastridae) as a biological control agent of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann (Heteroptera, Coreidae). Biol. Control 2012, 61, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Funayama, K. A new rearing method using carrots as food for the brown-marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2006, 41, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Species | Treatment | n. Progeny/Female | Sex Ratio (% of Females) | Develop. Time Males (d) | Develop. Time Females (d) | Emergence Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trissolcus japonicus | 1 d × 10 d | 79.8 (63–88) a | 84.6(71.3–90.9) a | 11.3 (9–15) a | 12.2 (11–15) a | 98.5 |
| 7 d × 10 d | 73.4 (40–121) a | 78.3 (71.9–85.5) b | 11.2 (10–14) a | 12.2 (11–14) a | 98.9 | |
| 7 d × 3 w | 85.2 (46–121) a | 91.4 (88.4–95.4) a | 11.1 (10–13) a | 12.0 (11–15) a | 99.63 | |
| Trissolcus mitsukurii | 1 d × 10 d | 63.0 (52–75) a | 88.1 (75.9–94.3) a | 11.3 (11–13) a | 12.3 (11–14) a | 94.60 |
| 7 d × 10 d | 83.0 (56–103) a | 89.8 (85.7–91.3) a | 11.5 (11–13) a | 12.5 (11–15) a | 95.42 | |
| 7 d × 3 w | 77.2 (66–90) a | 88.5 (84.4–94.6) a | 11.5 (10–13) a | 12.0 (12–13) b | 96.63 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabbatini-Peverieri, G.; Dieckhoff, C.; Giovannini, L.; Marianelli, L.; Roversi, P.F.; Hoelmer, K. Rearing Trissolcus japonicus and Trissolcus mitsukurii for Biological Control of Halyomorpha halys. Insects 2020, 11, 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110787
Sabbatini-Peverieri G, Dieckhoff C, Giovannini L, Marianelli L, Roversi PF, Hoelmer K. Rearing Trissolcus japonicus and Trissolcus mitsukurii for Biological Control of Halyomorpha halys. Insects. 2020; 11(11):787. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110787
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabbatini-Peverieri, Giuseppino, Christine Dieckhoff, Lucrezia Giovannini, Leonardo Marianelli, Pio Federico Roversi, and Kim Hoelmer. 2020. "Rearing Trissolcus japonicus and Trissolcus mitsukurii for Biological Control of Halyomorpha halys" Insects 11, no. 11: 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110787
APA StyleSabbatini-Peverieri, G., Dieckhoff, C., Giovannini, L., Marianelli, L., Roversi, P. F., & Hoelmer, K. (2020). Rearing Trissolcus japonicus and Trissolcus mitsukurii for Biological Control of Halyomorpha halys. Insects, 11(11), 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110787








