Culturing-Enriched Metabarcoding Analysis of the Oryctes rhinoceros Gut Microbiome
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Source
2.2. Dissection and Microbiology
2.3. Cellulase Testing
2.4. Cultured Microbe Identification
2.5. Metabarcoding
3. Results
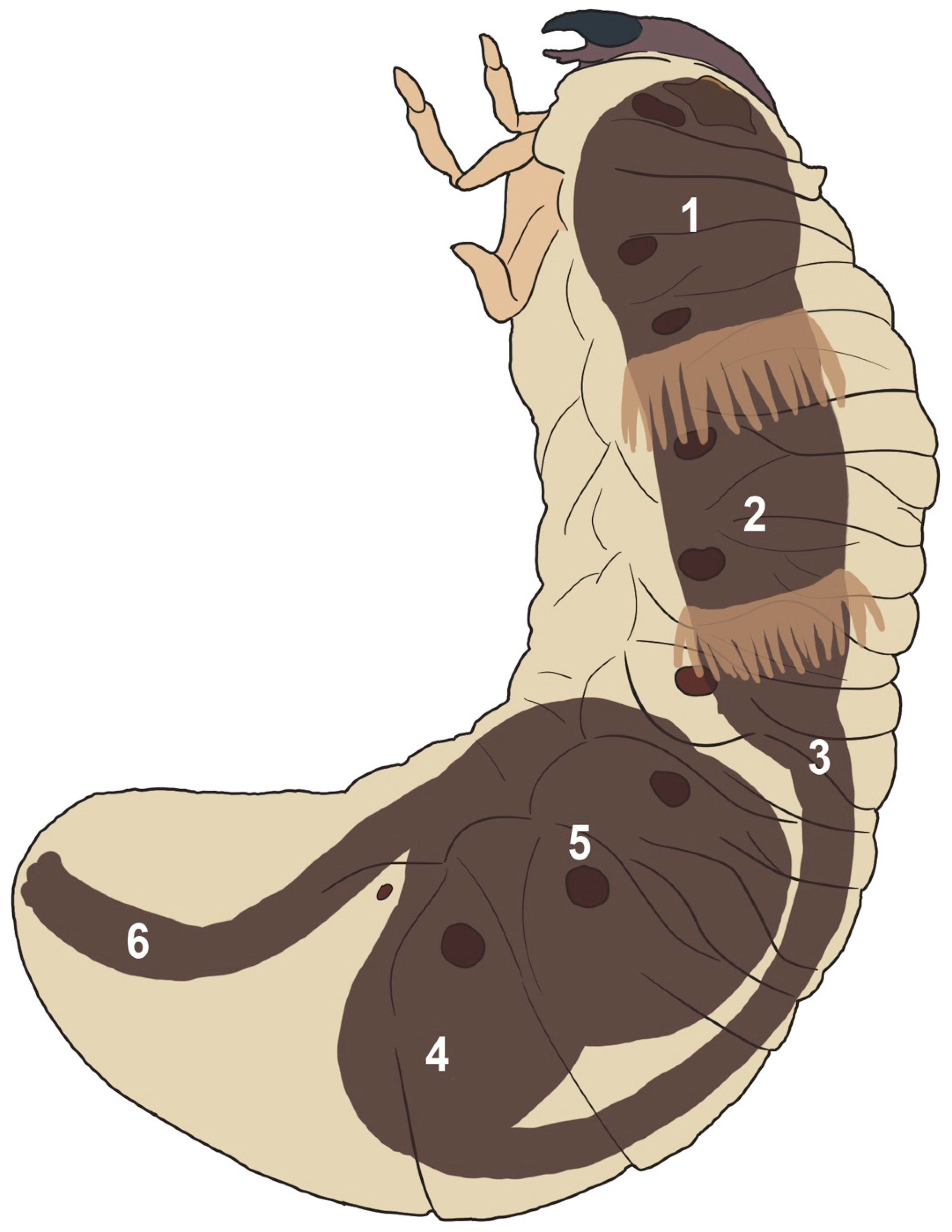
3.1. Anatomy
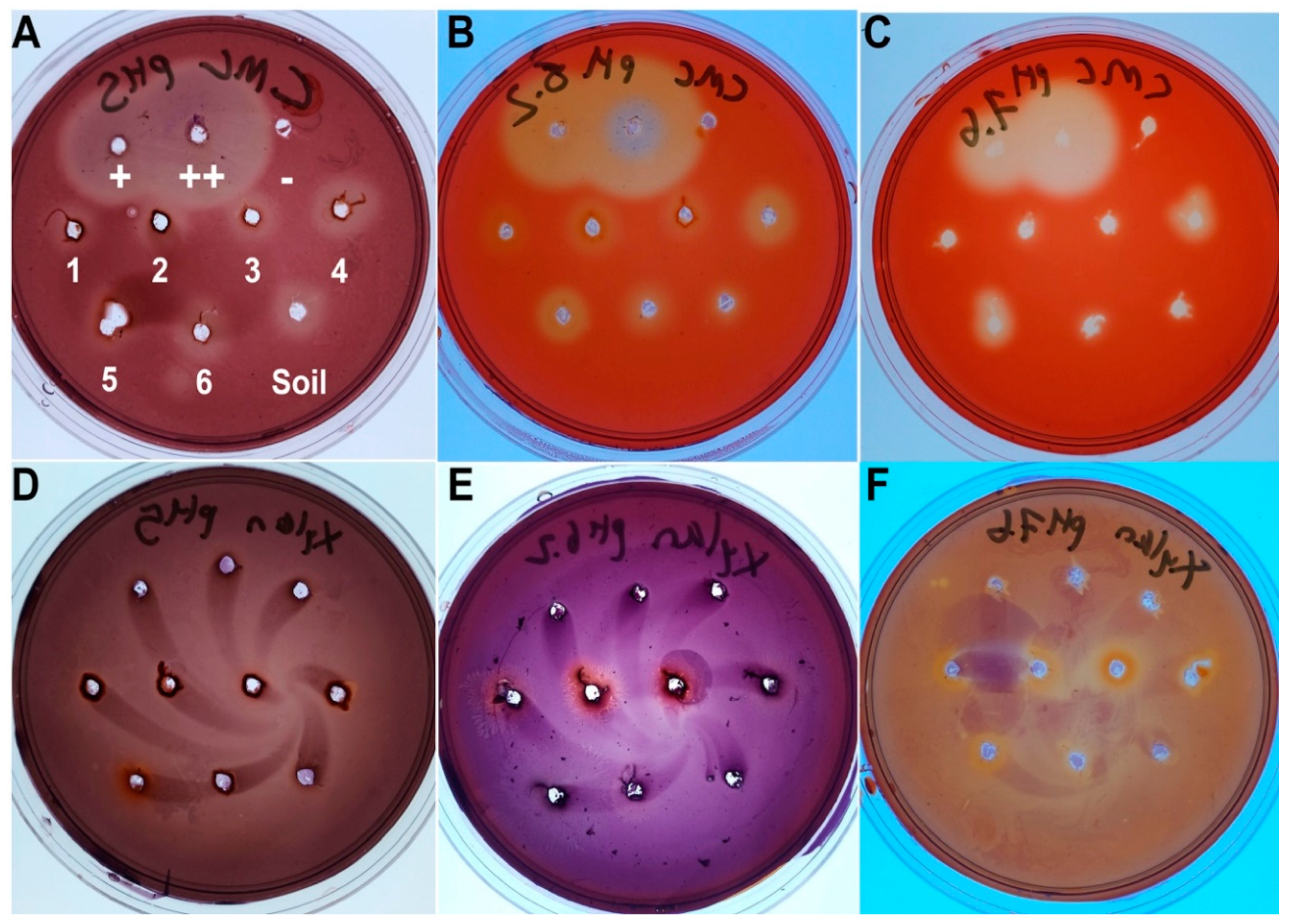
3.2. Cellulase and Xylanase Activity of the Gut
3.3. Cultured Microbes
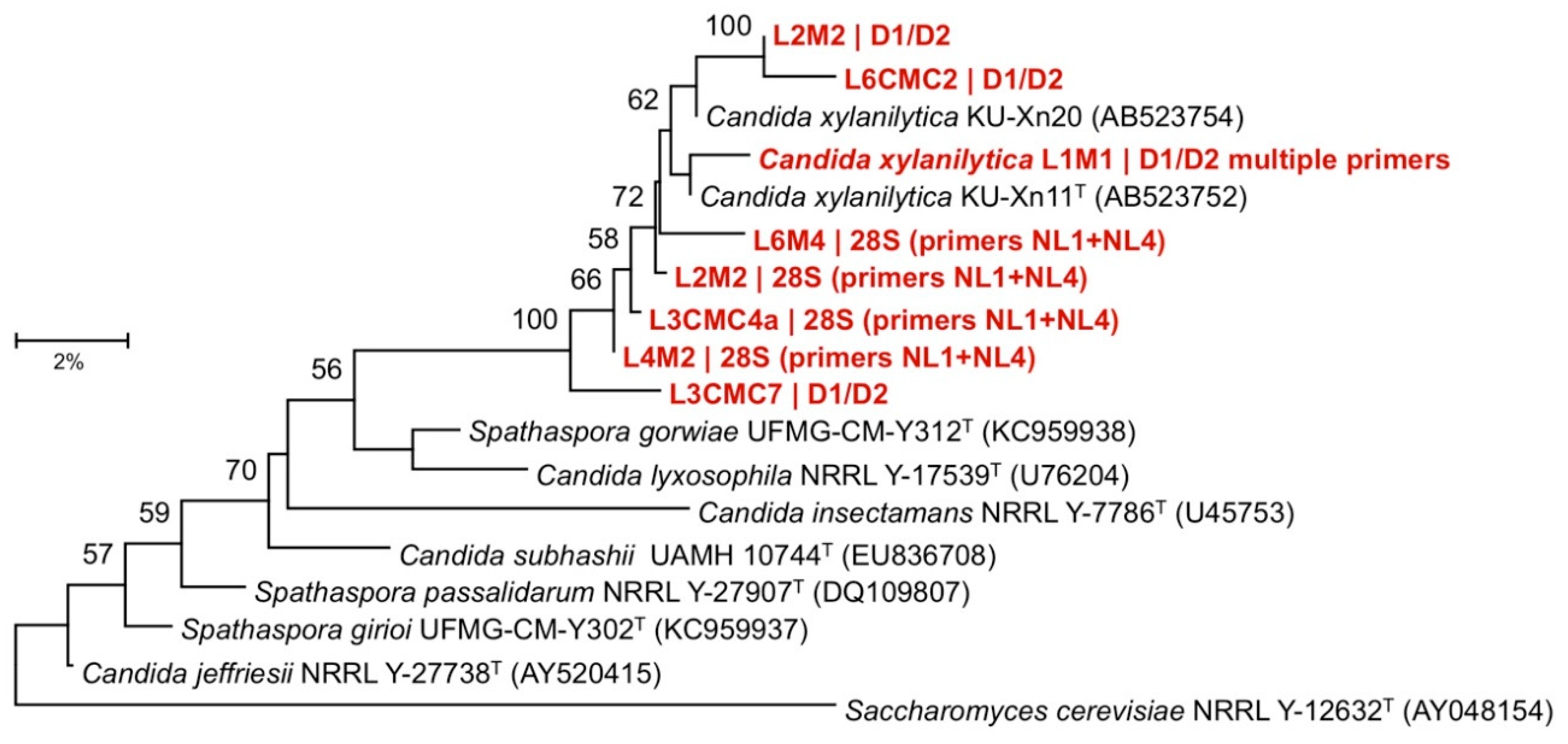
3.4. 16S Microbial Profiling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calderón-Cortés, N.; Quesada, M.; Watanabe, H.; Cano-Camacho, H.; Oyama, K. Endogenous Plant Cell Wall Digestion: A Key Mechanism in Insect Evolution. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 45–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Tokuda, G. Lignocellulose-degrading enzymes from termites and their symbiotic microbiota. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Rehman, K.u.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Li, W.; Cai, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z. Insect biorefinery: A green approach for conversion of crop residues into biodiesel and protein. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, W.S.; Ziganshina, E.E.; Shagimardanova, E.I.; Gogoleva, N.E.; Ziganshin, A.M. Comparison of intestinal bacterial and fungal communities across various xylophagous beetle larvae (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, A.; Danchin, E.G.; Pauchet, Y. Functional diversification of horizontally acquired glycoside hydrolase family 45 (GH45) proteins in Phytophaga beetles. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sudakaran, S.; Kost, C.; Kaltenpoth, M. Symbiont Acquisition and Replacement as a Source of Ecological Innovation. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.A.; Crawford, A.M.; Glare, T.R. Oryctes virus—time for a new look at a useful biocontrol agent. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2005, 89, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedford, G.O. Biology, ecology, and control of palm rhinoceros beetles. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1980, 25, 309–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, K.C.; Ooi, P.A.C.; Ho, C.T. Crop Pests and Their Management in Malaysia; Tropical Press: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1991; pp. ix + 242. [Google Scholar]
- Huger, A.M. The Oryctes virus: Its detection, identification, and implementation in biological control of the coconut palm rhinoceros beetle, Oryctes rhinoceros (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2005, 89, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yamamoto, M.; Ishibashi, J.; Taniai, K.; Yamakawa, M. Isolation, cDNA cloning and gene expression of an antibacterial protein from larvae of the coconut rhinoceros beetle, Oryctes rhinoceros. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 255, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomie, T.; Ishibashi, J.; Furukawa, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Sawahata, R.; Asaoka, A.; Tagawa, M.; Yamakawa, M. Scarabaecin, a novel cysteine-containing antifungal peptide from the rhinoceros beetle, Oryctes rhinoceros. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 307, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelomi, M.; Lin, S.-S.; Liu, L.-Y. Transcriptome and microbiome of coconut rhinoceros beetle (Oryctes rhinoceros) larvae. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desai, A.; Bhamre, P. Diversity of gut bacterial fauna of Oryctes monocerus linnaeus (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Bionano Front. 2012, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, W.S.; Ibrahim, R.A. Diversity and phylogenetic analysis of endosymbiotic bacteria of the date palm root borer Oryctes agamemnon (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sowole, A.D.; Awojobi, K.O.; Agboola, F.K. Purification and Characterization of Partially Purified Cellulolytic Enzyme Produced by Bacillys brevis Isolated from the Gut of Larva of Beetle, Oryctes rhinoceros (L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ife, Nigeria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sari, S.L.A.; Pangastuti, A.; Susilowati, A.; Purwoko, T.; Mahajoeno, E.; Hidayat, W.; Mardhena, I.; Panuntun, D.F.; Kurniawati, D.; Anitasari, R. Cellulolytic and hemicellulolytic bacteria from the gut of Oryctes rhinoceros larvae. Biodiversitas 2016, 17, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, I.R.; Wawan, W.; Hapsoh, H.; Sriwahyuni, S. Isolation and Identification of Cellulolytic and Lignolytic Bacteria from the Gut Oryctes rhinoceros L. Larvae Decomposition of Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunches. Indones J. Agric. Res. 2018, 1, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep Kumar, R.; John, A.; Kumar, P.; Dinesh Babu, K.V.; Evans, D.A. Larvicidal efficacy of Adiantobischrysene from Adiantum latifolium against Oryctes rhinoceros through disrupting metamorphosis and impeding microbial mediated digestion. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin-Ollivier, L.; Prior, R.N.; Laup, S. Simplified field key to identify larvae of some rhinoceros beetles and associated scarabs (Coleoptera: Scarabaeoidea) in Papua New Guinea coconut developments. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2000, 93, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teather, R.M.; Wood, P.J. Use of Congo red-polysaccharide interactions in enumeration and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria from the bovine rumen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jue, C.K.; Lipke, P.N. Determination of reducing sugars in the nanomole range with tetrazolium blue. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1985, 11, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Cortés, N.; Watanabe, H.; Cano-Camacho, H.; Zavala-Páramo, G.; Quesada, M. cDNA cloning, homology modelling and evolutionary insights into novel endogenous cellulases of the borer beetle Oncideres albomarginata chamela (Cerambycidae). Insect. Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMBOSS Merger. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.nl/cgi-bin/emboss/merger (accessed on 16 October 2020).
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinform 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “all-species living tree project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceja-Navarro, J.A.; Karaoz, U.; Bill, M.; Hao, Z.; White, R.A., 3rd; Arellano, A.; Ramanculova, L.; Filley, T.R.; Berry, T.D.; Conrad, M.E.; et al. Gut anatomical properties and microbial functional assembly promote lignocellulose deconstruction and colony subsistence of a wood-feeding beetle. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lu, M.; Xu, D.; Chen, L.; Sun, J. Sexual variation of bacterial microbiota of Dendroctonus valens guts and frass in relation to verbenone production. J. Insect Physiol. 2016, 95, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Deng, J.; Zhou, F.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Lu, M. Gut microbiota in an invasive bark beetle infected by a pathogenic fungus accelerates beetle mortality. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, M.; Gómez-Zurita, J.; Giorgi, A.; Epis, S.; Lozzia, G.; Bandi, C. Metamicrobiomics in herbivore beetles of the genus Cryptocephalus (Chrysomelidae): Toward the understanding of ecological determinants in insect symbiosis. Insect Sci. 2015, 22, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.P.; Vogel, H.; Heckel, D.G.; Vilcinskas, A.; Kaltenpoth, M. Burying beetles regulate the microbiome of carcasses and use it to transmit a core microbiota to their offspring. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzini, P.Z.N.; Ramond, J.-B.; Scholtz, C.H.; Sole, C.L.; Ronca, S.; Cowan, D.A. The Gut Microbiomes of Two Pachysoma MacLeay Desert Dung Beetle Species (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Scarabaeinae) Feeding on Different Diets. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasko, D.A.; Altherr, M.R.; Han, C.S.; Ravel, J. Genomics of the Bacillus cereus group of organisms. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.; Sheng, P.; Zhang, H. Isolation and identification of cellulolytic bacteria from the gut of Holotrichia parallela larvae (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 2563–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mereghetti, V.; Chouaia, B.; Montagna, M. New Insights into the Microbiota of Moth Pests. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jensen, G.; Hansen, B.; Eilenberg, J.; Mahillon, J. The hidden lifestyles of Bacillus cereus and relatives. Environ. Micobiol. 2003, 5, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Investigation of Gut-Associated Bacteria in Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) Larvae Using Culture-Dependent and DGGE Methods. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2015, 108, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römling, U. Cellulose biosynthesis in Enterobacteriaceae. In Cellulose: Molecular and Structural Biology; Brown, R.M., Jr., Saxena, I.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonmak, C.; Limtong, S.; Jindamorakot, S.; Am-In, S.; Yongmanitchai, W.; Suzuki, K.-i.; Nakase, T.; Kawasaki, H. Candida xylanilytica sp. nov., a xylan-degrading yeast species isolated from Thailand. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micobiol. 2011, 61, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadete, R.M.; Lopes, M.R.; Rosa, C.A. Yeasts Associated with Decomposing Plant Material and Rotting Wood. In Yeasts in Natural Ecosystems: Diversity; Buzzini, P., Lachance, M.-A., Yurkov, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 265–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C. The bacterium, Lysinibacillus sphaericus, as an insect pathogen. J. Invertebr. Path 2012, 109, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, T.J.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W.; Jaffe, S.P.; Fierer, N. Caterpillars lack a resident gut microbiome. PNAS 2017, 114, 9641–9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, H.; Tokuda, G. Cellulolytic systems in insects. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 609–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliot, A.; Kontsedalov, S.; Lebedev, G.; Brumin, M.; Cathrin, P.B.; Marubayashi, J.M.; Skaljac, M.; Belausov, E.; Czosnek, H.; Ghanim, M. Fluorescence in situ Hybridizations (FISH) for the Localization of Viruses and Endosymbiotic Bacteria in Plant and Insect Tissues. JoVE 2014, 84, e51030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Identity | Agar | Mean CFU/mg (# Samples) | # of Larvae | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Midgut | Hindgut | |||
| Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579 (99.72) | NA, CMC | 4.7 × 105 (3) | 5.5 × 105 (5) | 5 |
| Bacillus proteolyticus MCCC 1A00365 (99.79) | NA | 7.2 × 105 (1) | 0 | 1 |
| Bacillus toyonensis BCT-7112 (99.93) | NA | 5.0 × 104 (1) | 1.5 × 107 (1) | 1 |
| * Candida tropicalis ATCC 750 (99.65) | CMC | - (1) | 0 | 1 |
| * Candida xylanilytica KU-Xn11T (99.85) | NA, CMC | 9.9 × 106 (5) | 3.5 × 107 (3) | 5 |
| Citrobacter koseri LMG 5519 (99.44) | NA, CMC | - (2) | 3.1 × 108 (2) | 3 |
| Comamonas nitrativorans 23310 (99.15) | NA, CMC | - (2) | 7.4 × 107 (3) | 3 |
| Diaphorobacter aerolatus 8604S-37 like (97.38) | CMC | 0 | - (1) | 1 |
| Enterobacteriaceae (97.75) | NA, CMC | 3.5 × 107 (3) | 1.4 × 107 (3) | 3 |
| Klebsiella pneuomoniae DSM 30104 (99.44) | NA, CMC | 1.1 × 106 (1) | 6.8 × 107 (1) | 1 |
| Kluyvera georgiana ATCC 51603 (99.14) | NA, CMC | 3.5 × 106 (1) | 3.9 × 105 (1) | 1 |
| Lactococcus lactis NBRC 100933 like (96.45) | NA | 2.6 × 106 (1) | 0 | 1 |
| Lysinibacillus fusiformis NBRC 15717 (99.30) | NA, CMC | 1.7 × 105 (1) | 1.5 × 105 (4) | 4 |
| Pseudomonas citronellolis NBRC 103043 (98.59) | NA, CMC | 0 | 5.0 × 106 (1) | 1 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis NBRC 100911 (99.23) | NA | 5.0 × 103 (1) | 0 | 1 |
| Staphylococcus hominis GTC 1228 (99.65%) | NA | 0 | 1.7 × 106 (1) | 1 |
| Streptomyces costaricanus NBRC 100773 or S. murinus NBRC 14802 (99.64) | CMC | - (1) | - (1) | 1 |
| * Trichoderma virens DAOM 164916 (99.19) | CMC | - (1) | 0 | 1 |
| Sample | Absorbance at 470 nm | M Sugars |
|---|---|---|
| L1M1 | 1.23 | 0.1665 |
| L2M2 | 1.41 | 0.4398 |
| L3CMC4A | 1.19 | 0.1342 |
| L3CMC7 | 1.11 | 0.0871 |
| L4M2 | 0.99 | 0.0456 |
| L6M4 | 1.18 | 0.1271 |
| L6CMC2 | 1.36 | 0.3358 |
| Positive control | 1.3 | 0.2429 |
| Negative control | 0.54 | 0.0040 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shelomi, M.; Chen, M.-J. Culturing-Enriched Metabarcoding Analysis of the Oryctes rhinoceros Gut Microbiome. Insects 2020, 11, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110782
Shelomi M, Chen M-J. Culturing-Enriched Metabarcoding Analysis of the Oryctes rhinoceros Gut Microbiome. Insects. 2020; 11(11):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110782
Chicago/Turabian StyleShelomi, Matan, and Ming-Ju Chen. 2020. "Culturing-Enriched Metabarcoding Analysis of the Oryctes rhinoceros Gut Microbiome" Insects 11, no. 11: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110782
APA StyleShelomi, M., & Chen, M.-J. (2020). Culturing-Enriched Metabarcoding Analysis of the Oryctes rhinoceros Gut Microbiome. Insects, 11(11), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110782





