Effect of Cleaning Multiple-Funnel Traps on Captures of Bark and Woodboring Beetles in Northeastern United States
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment 1: Effect of Pollen/Dirt Accumulation on Surfactant-Treated and Non-Treated Traps on Trapping Efficacy
2.2. Experiment 2: Field Cleaning Traps-Effect of Pollen/Dirt Accumulation on Trap Efficacy
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1: Effect of Pollen/Dirt Accumulation on Surfactant-Treated and Non-Treated Traps on Trapping Efficacy
3.2. Experiment 2: Field Cleaning Traps-Effect of Pollen/Dirt Accumulation on Trap Efficacy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dodds, K.J.; DiGirolomo, M.F.; Fraver, S. Response of bark beetles and woodborers to tornado damage and subsequent salvage logging in northern coniferous forests of Maine, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, K.J.K.; Cognato, A.I.; Lightle, D.M.; Mosley, B.J.; Nielsen, D.G.; Herms, D.A. Species composition, seasonal activity, and semiochemical response of native and exotic bark and ambrosia beetles (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae) in northeastern Ohio. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, K.J.K.; Gilmore, D.W.; Haack, R.A.; Katovich, S.A.; Krauth, S.J.; Mattson, W.J.; Zasada, J.C.; Seybold, S.J. Application of semiochemicals to assess the biodiversity of subcortical insects following an ecosystem disturbance in a sub-boreal forest. J. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 35, 1384–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabaglia, R.J.; Cognato, A.I.; Hoebeke, E.R.; Johnson, C.W.; LaBonte, J.R.; Carter, M.E.; Vlach, J.J. Early detection and rapid response: A 10-year summary of the USDA Forest Service program of surveillance for non-native bark and ambrosia beetles. Am. Entomol. 2019, 65, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHIS. Exotic Wood Borer Bark Beetle National Survey Field Manual. Available online: http://download.ceris.purdue.edu/file/3290 (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Dodds, K.J.; Dubois, G.D.; Hoebeke, E.R. Trap type, lure placement, and habitat effects on Cerambycidae and Scolytinae (Coleoptera) catches in the northeastern United States. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, K.J.; Allison, J.D.; Miller, D.R.; Hanavan, R.P.; Sweeney, J. Considering species richness and rarity when selecting optimal survey traps: Comparisons of semiochemical baited flight intercept traps for Cerambycidae in eastern North America. Agric. For. Entomol. 2015, 17, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.E.; Poland, T.M.; McCullough, D.G.; Millar, J.G. A comparison of trap type and height for capturing cerambycid beetles (Coleoptera). J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIntosh, R.L.; Katinic, P.J.; Allison, J.D.; Borden, J.H.; Downey, D.L. Comparitive efficacy of five types of trap for woodborers in the Cerambycidae, Buprestidae and Siricidae. Agric. For. Entomol. 2001, 3, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, D.R.; Crowe, C.M.; Barnes, B.F.; Gandhi, K.J.K.; Duerr, D.A. Attaching lures to multiple-funnel traps targeting saproxylic beetles (Coleoptera) in pine stands: Inside or outside funnels? J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Duerr, D.A. Comparison of arboreal beetle catches in wet and dry collection cups with Lindgren multiple funnel traps. J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, P.; Nott, R.W. Response of Monochamus (Col., Cerambycidae) and some Buprestidae to flight intercept traps. J. Appl. Entomol. 2003, 127, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.E.; Mitchell, R.F.; Reagel, P.F.; Barbour, J.D.; Millar, J.G.; Hanks, L.M. Treating panel traps with a fluoropolymer enhances their efficiency in capturing cerambycid beetles. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, J.D.; Bhandari, B.D.; McKenney, J.L.; Millar, J.G. Design factors that influence the performance of flight intercept traps for the capture of longhorned beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) from the subfamilies Lamiinae and Cerambycinae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dodds, K.J. Effects of habitat type and trap placement on captures of bark (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) and longhorned (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) beetles in semiochemical-baited traps. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouget, C.; Brustel, H.; Brin, A.; Valladares, L. Evaluation of window flight traps for effectiveness at monitoring dead wood-associated beetles: The effect of ethanol lure under contrasting environmental conditions. Agric. For. Entomol. 2009, 11, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmeelk, T.C.; Millar, J.G.; Hanks, L.M. Influence of trap height and bait type on abundance and species diversity of cerambycid beetles captured in forests of east-central Illinois. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1750–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, K.J. Effects of trap height on captures of arboreal insects in pine stands of northeastern United States of America. Can. Entomol. 2014, 146, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Crowe, C.M.; Sweeney, J.D. Trap height affects catches of bark and woodboring beetles (Coleoptera: Curculionidae, Cerambycidae) in baited multiple-funnel traps in southeastern United States. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 113, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudinsky, J.A.; Daterman, G.E. Field studies on flight patterns and olfactory responses of ambrosia beetles in Douglas-fir forests of western Oregon. Can. Entomol. 1964, 96, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salom, S.M.; McLean, J.A. Flight behavior of scolytid beetle in response to semiochemicals at different wind speeds. J. Chem. Ecol. 1991, 17, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, B.S. A multiple funnel trap for scolytid beetles (Coleoptera). Can. Entomol. 1983, 115, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.L. The Bark and Ambrosia Beetles of North and Central America (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), a Taxonomic Monograph; Great Basin Naturalist Memoirs; Brigham Young University: Provo, UT, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Lingafelter, S.W. Illustrated Key to the Longhorned Woodboring Beetles of the Eastern United States; Coleopterists Society Miscellaneous Publication; Special Publication No. 3; Coleopterists Society: North Potomac, MD, USA, 2007; p. 206. [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet, Y.; Laplante, S.; Hammond, H.E.J.; Langor, D.W. Cerambycidae (Coleoptera) of Canada and Alaska: Identification Guide with Nomenclatural, Taxonomic, Distributional, Host-Plant, and Ecological Data; Nakladatelství Jan Farkač: Prague, Czech Republic, 2017; 300p. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, D.F.; Rabaglia, R.J.; Fairbanks, K.E.O.; Hulcr, J. North American Xyleborini north of Mexico: A review and key to genera and species (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Scolytinae). Zookeys 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for eduation and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, J.D.; Johnson, C.W.; Meeker, J.R.; Strom, B.L.; Butler, S.M. Effect of aerosol surface lubricants on the abundance and richness of selected forest insects captured in multiple-funnel and panel traps. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, J.; de Groot, P.; MacDonald, L.; Smith, S.; Cocquempot, C.; Kenis, M.; Gutowski, J.M. Host volatile attractants and traps for detection of Tetropium fuscum (F.), Tetropium castaneum L., and other longhorned beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Environ. Entomol. 2004, 33, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allison, J.D.; Redak, R.A. The impact of trap type and design features on survey and detection of bark and woodboring beetles and their associates: A review and meta-analysis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2017, 62, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |


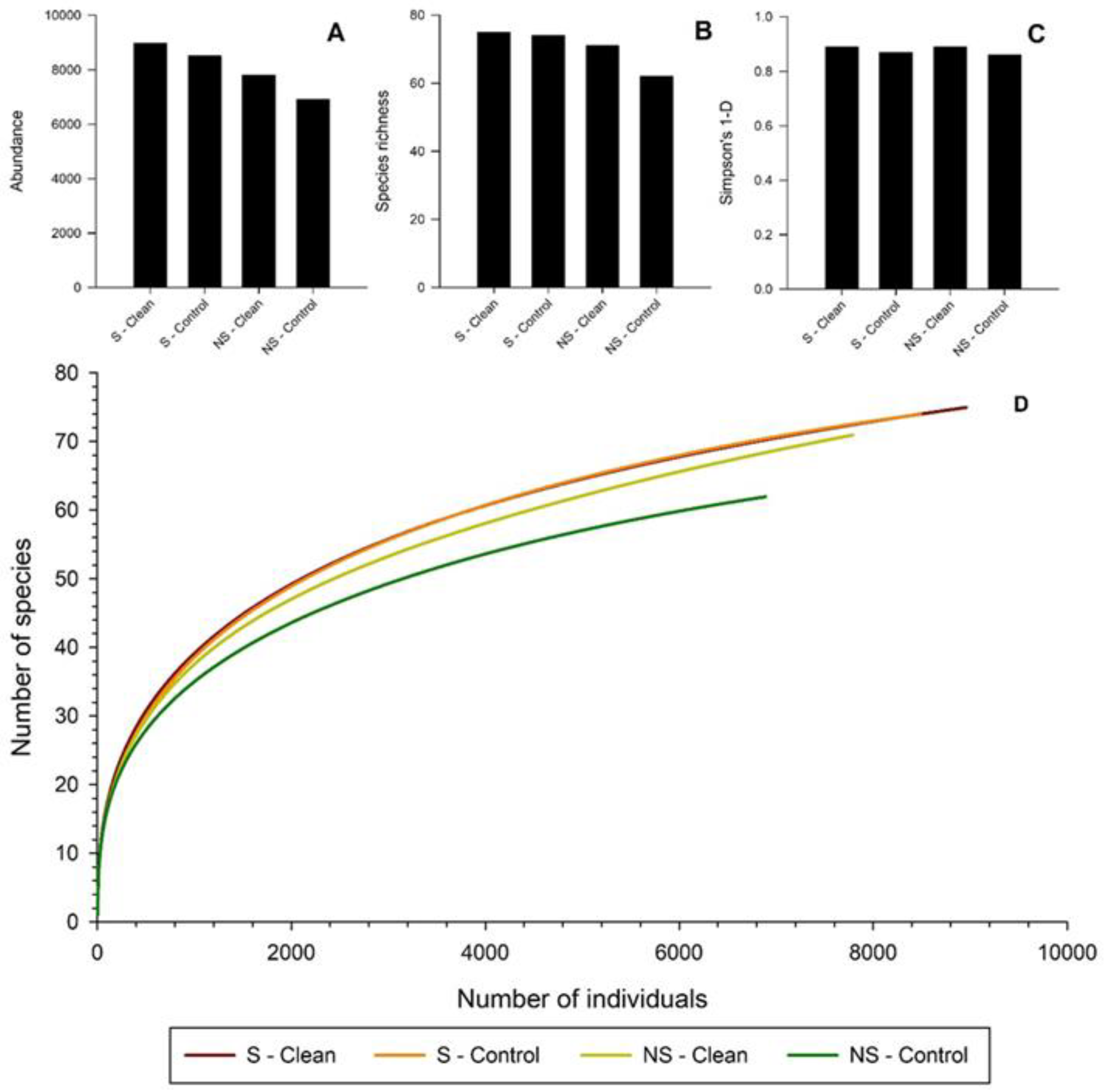
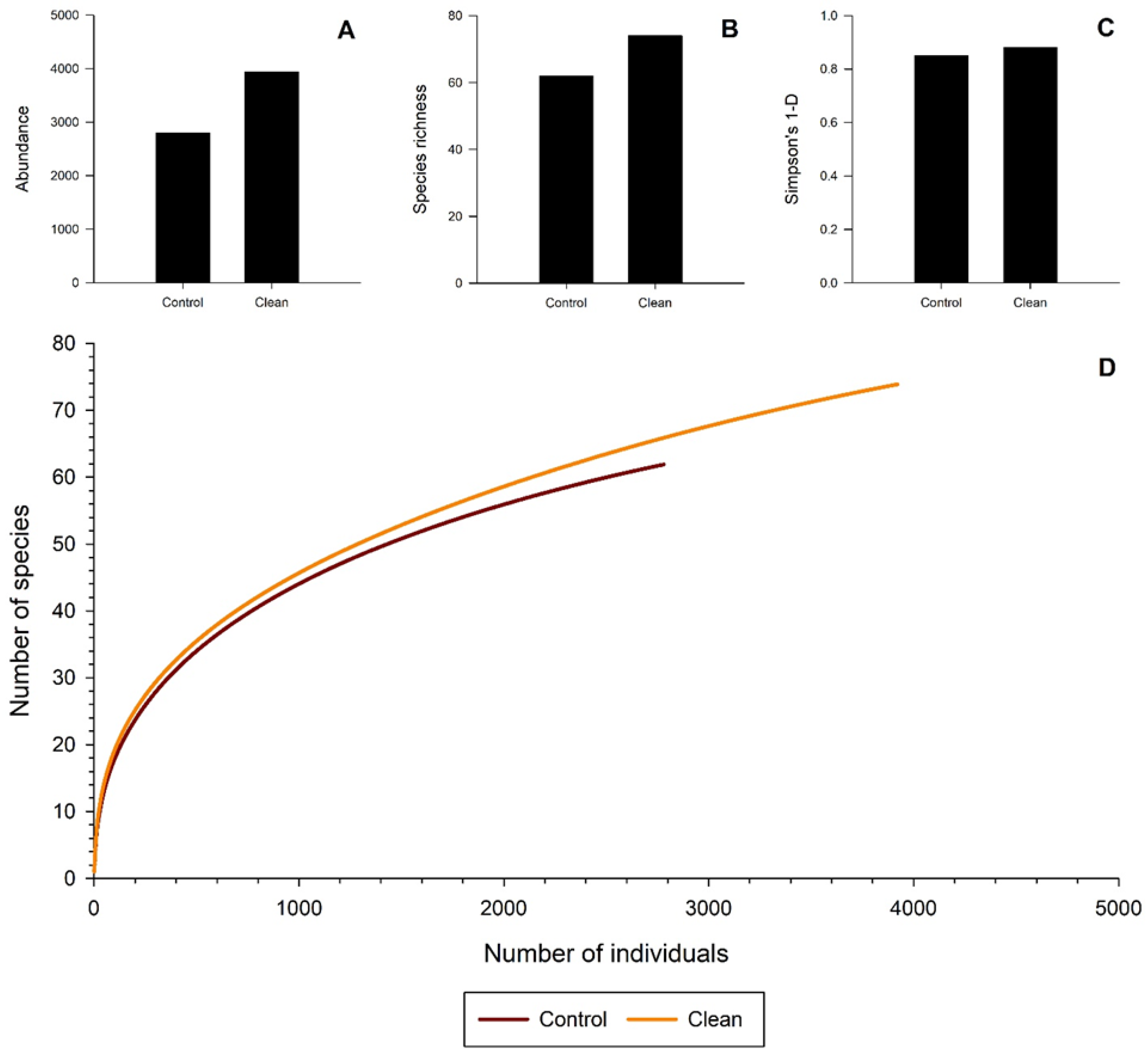
| Species | Surfactant Treated | No Surfactant Treatment | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean | Control | Clean | Control | ||
| Total beetles | 1217.2 ± 196.3 | 1113.4 ± 179.6 | 1020.5 ± 164.7 | 965.5 ± 155.8 | 0.2151 |
| Species richness | 38.5 ± 2.7 | 38.8 ± 2.7 | 35.5 ± 2.6 | 33. 4± 2.5 | 0.3 |
| Total bark beetles | 1018.0 ± 177.1 | 934.3 ± 162.5 | 919.9 ± 160.0 | 852.2 ± 148.3 | 0.6013 |
| Crypturgus alutaceus | 18.4 ± 6.7 | 9.8 ± 3.7 | 11.6 ± 4.3 | 9.2 ± 3.5 | 0.08 |
| Crypturgus pusillus | 139.7 ± 44.3 | 67.4 ± 21.5 | 111.4 ± 35.4 | 51.8 ± 16.6 | 0.06 |
| Dendroctonus valens | 111.6 ± 45.3 | 77.9 ± 31.7 | 75.9 ± 30.9 | 65.5 ± 26.7 | 0.2 |
| Dryocoetes autographus | 155.9 ± 29.9 | 218.2 ± 41.6 | 155.1 ± 29.7 | 248.9 ± 47.4 | 0.07 |
| Gnathotrichus materiarius | 56.3 ± 10.8 | 59.6 ± 11.4 | 60.6 ± 11.6 | 55.4 ± 10.6 | 0.9 |
| Hylastes opacus | 19.1 ± 4.3 | 13.7 ± 3.2 | 19.0 ± 4.3 | 16.0 ± 3.6 | 0.51 |
| Hylastes porculus | 30.6 ± 19.1 | 16.6 ± 10.5 | 24.3 ± 15.2 | 13.8 ± 8.7 | 0.3 |
| Ips grandicollis | 174.5 ± 24.3 | 219.8 ± 30.4 | 187.6 ± 26.1 | 173.5 ± 24.1 | 0.5 |
| Orthotomicus caelatus | 205.4 ± 52.6 | 171.2 ± 43.9 | 140.7 ± 36.1 | 127.9 ± 32.9 | 0.2 |
| Total Cerambycidae | 189.8 ± 23.5a | 180.2 ± 22.3a | 92.2 ± 11.7b | 114.5 ± 14.4b | 0.0001 |
| Asemum striatum | 32.1 ± 6.6ab | 47.5 ± 9.6a | 20.6 ± 4.4b | 26.8 ± 5.6ab | 0.01 |
| Monochamus scutellatus | 108.6 ± 19.5a | 84.6 ± 15.3ab | 45.2 ± 8.4b | 58.4 ± 10.7ab | 0.005 |
| Species | Control | Cleaned | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total beetles | 395.7 ± 41.1 | 556.7 ± 57.5 | 0.04 |
| Species richness | 29.2 ± 2.4 | 35.6 ± 2.7 | 0.08 |
| Total bark beetles | 191.7 ± 23.7 | 329.1 ± 40.2 | 0.007 |
| Dryocoetes autographus | 52.4 ± 8.4 | 73.7 ± 11.6 | 0.2 |
| Dendroctonus valens | 10.6 ± 2.2 | 25.9 ± 4.9 | 0.02 |
| Hylastes porculus | 10.3 ± 3.2 | 17.3 ± 5.2 | 0.09 |
| Ips grandicollis | 77.1 ± 14.3 | 108.7 ± 20.0 | 0.1 |
| Gnathotrichus materiarius | 12.6 ± 2.4 | 21.0 ± 3.7 | 0.06 |
| Orthotomicus caelatus | 13.3 ± 2.6 | 32.9 ± 5.8 | 0.008 |
| Pityophthorus puberulus | 2.9 ± 0.8 | 12.6 ± 2.5 | 0.003 |
| Total cerambycids | 201.1 ± 20.6 | 225.0 ± 23.0 | 0.5 |
| Acanthocinus obsoletus | 2.0 ± 0.7 | 6.9 ± 1.9 | 0.02 |
| Asemum striatum | 44.0 ± 5.6 | 56.1 ± 7.0 | 0.2 |
| Monochamus scutellatus | 110.3 ± 14.5 | 111.8 ± 14.7 | 0.9 |
| Monochamus complex | 12.6 ± 4.1 | 13.7 ± 4.4 | 0.9 |
| Monochamus notatus | 9.2 ± 2.3 | 7.2 ± 1.8 | 0.4 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dodds, K.J.; DiGirolomo, M.F. Effect of Cleaning Multiple-Funnel Traps on Captures of Bark and Woodboring Beetles in Northeastern United States. Insects 2020, 11, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100702
Dodds KJ, DiGirolomo MF. Effect of Cleaning Multiple-Funnel Traps on Captures of Bark and Woodboring Beetles in Northeastern United States. Insects. 2020; 11(10):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100702
Chicago/Turabian StyleDodds, Kevin J., and Marc F. DiGirolomo. 2020. "Effect of Cleaning Multiple-Funnel Traps on Captures of Bark and Woodboring Beetles in Northeastern United States" Insects 11, no. 10: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100702
APA StyleDodds, K. J., & DiGirolomo, M. F. (2020). Effect of Cleaning Multiple-Funnel Traps on Captures of Bark and Woodboring Beetles in Northeastern United States. Insects, 11(10), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100702





