Development and Evaluation of Sex Pheromone Mass Trapping Technology for Ectropis grisescens: A Potential Integrated Pest Management Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Field Site
2.2. Optimization of Sex Pheromone Mass Trapping Technology
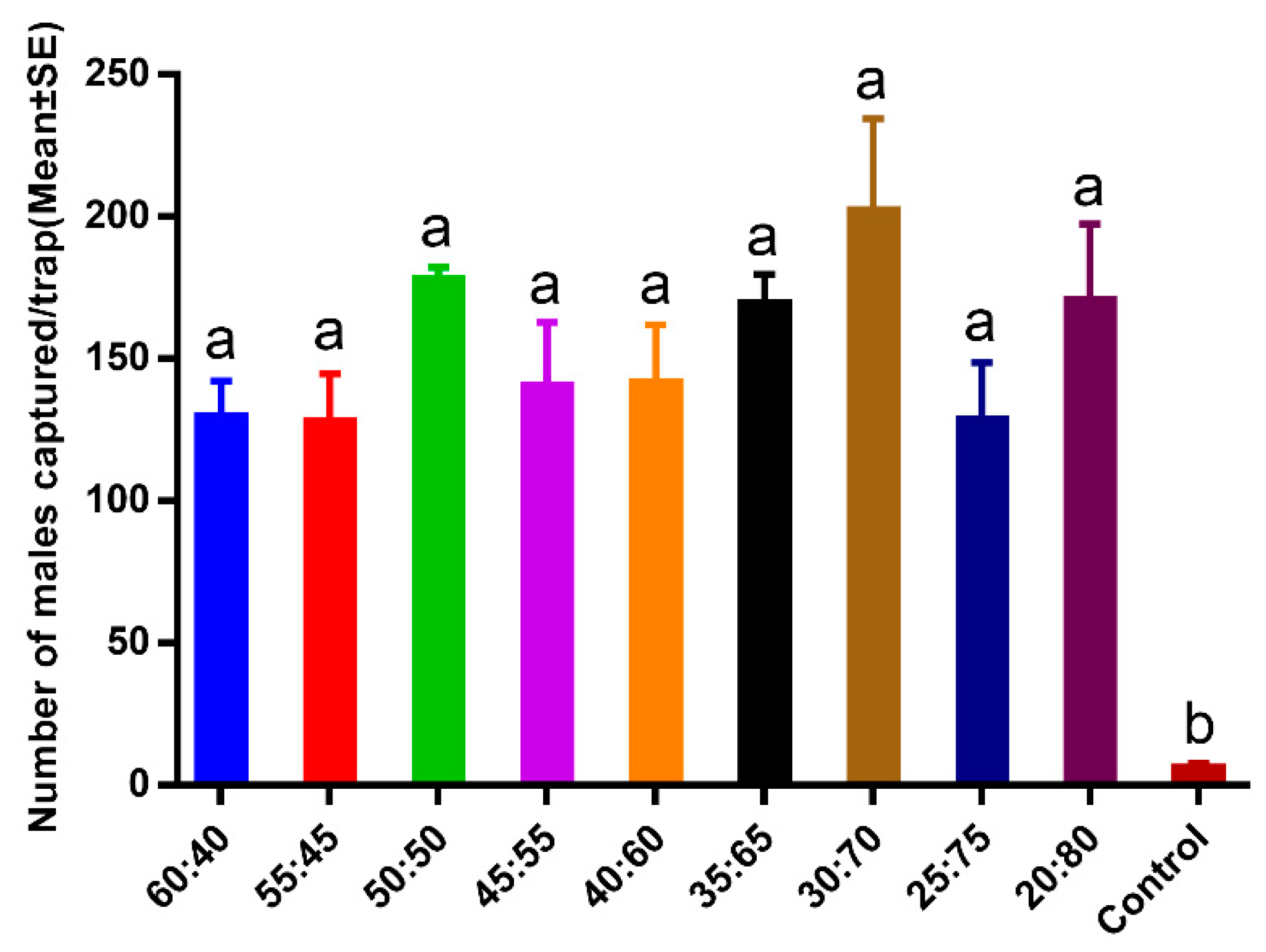
2.2.1. Pheromone Ratio Efficiency Experiment
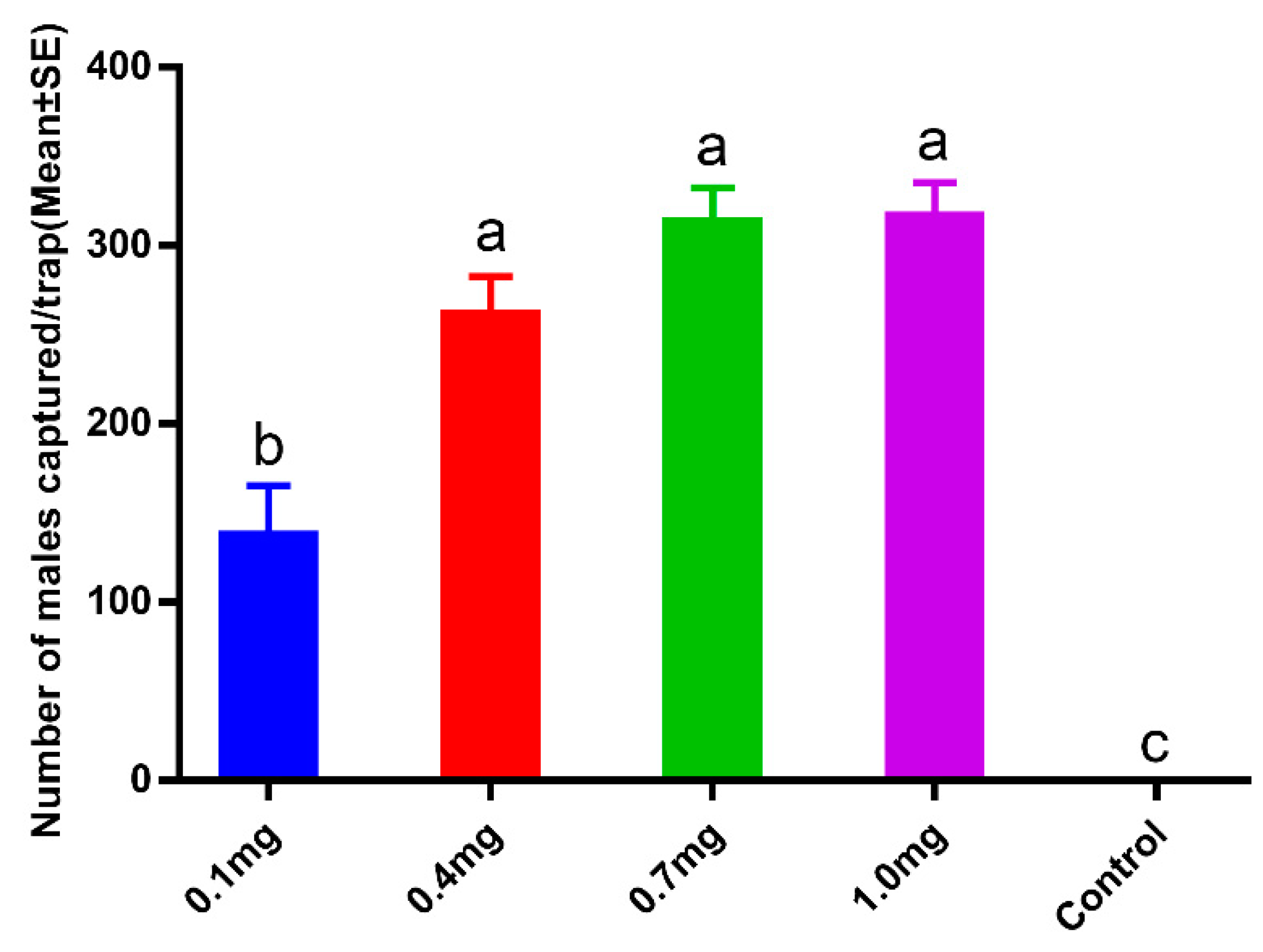
2.2.2. Pheromone Dosage Efficiency Experiment
2.2.3. Pheromone Dispenser Efficiency Experiments
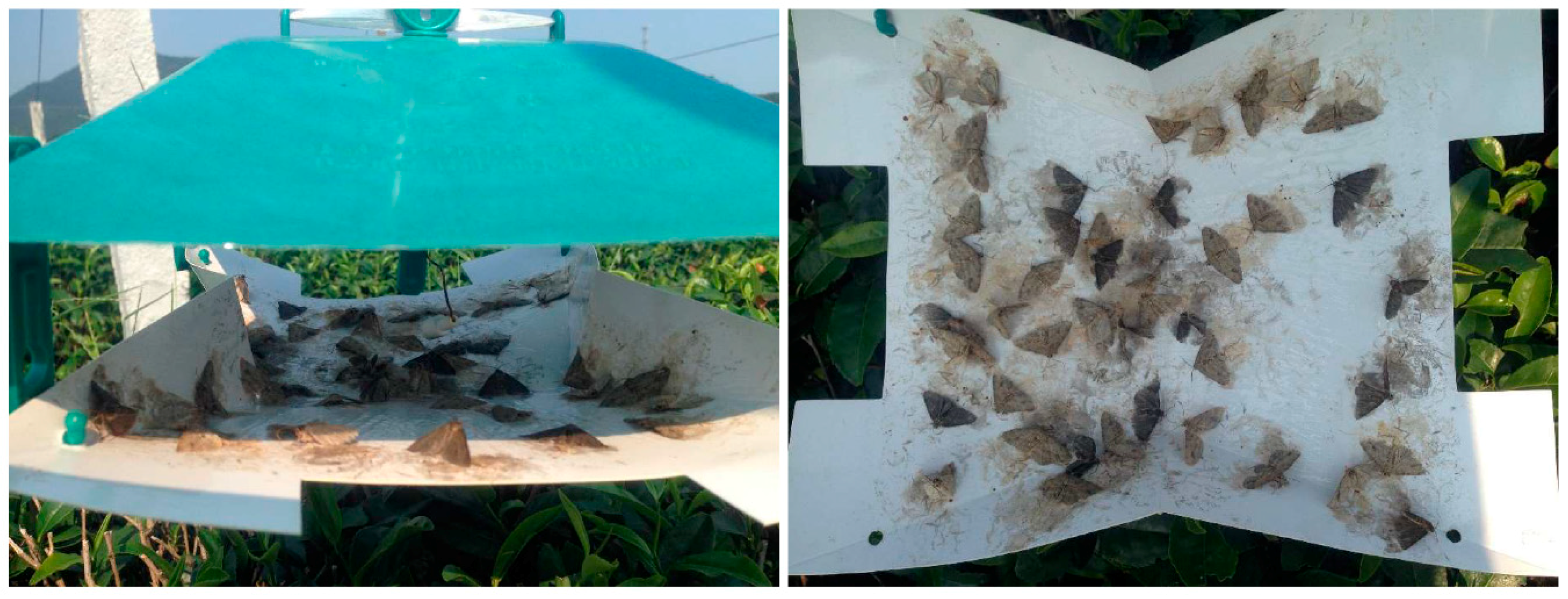
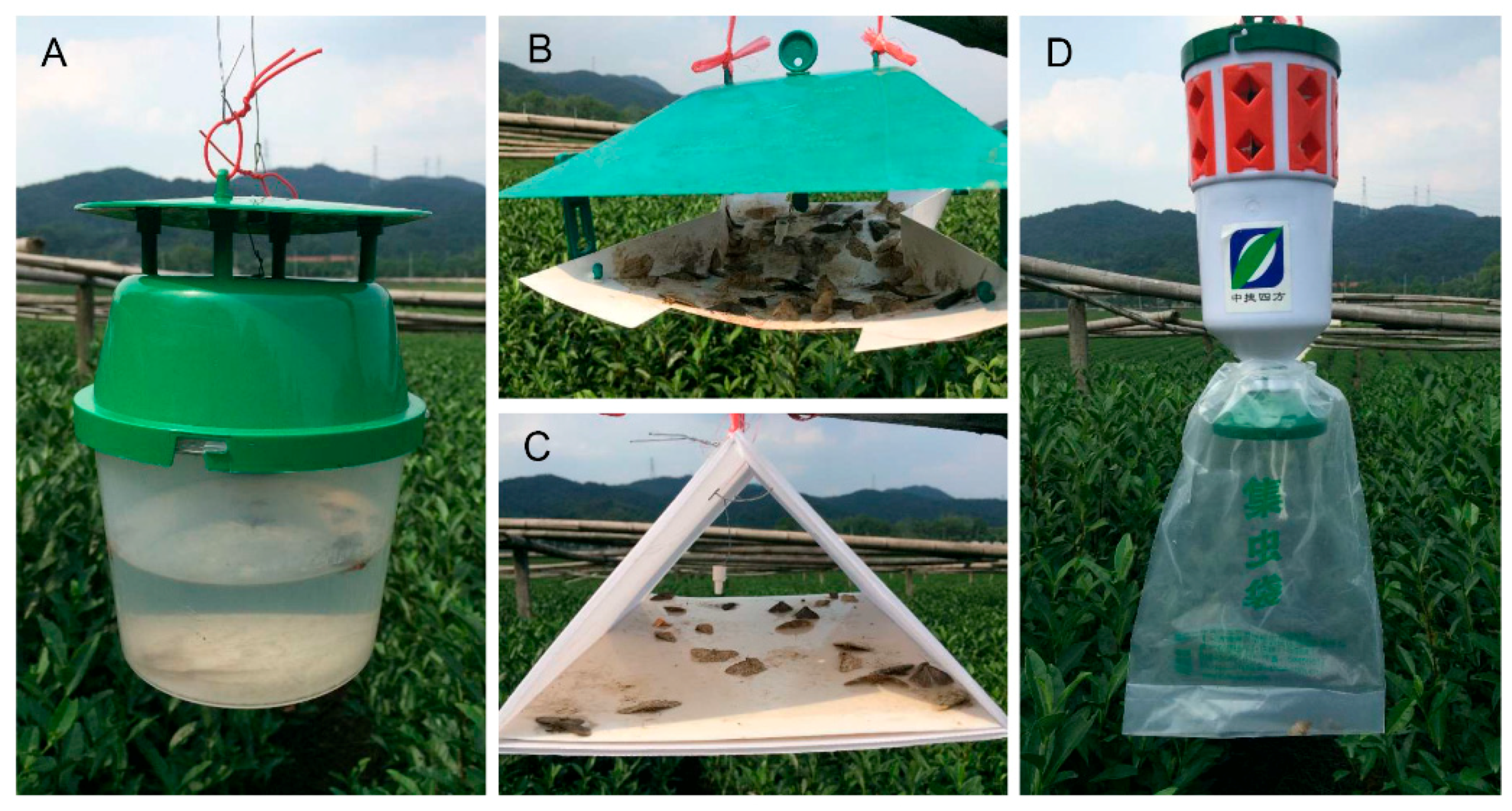
2.2.4. Pheromone Trap Efficiency Experiments
2.3. Field Efficacy of Sex Pheromone Mass Trapping
2.3.1. Investigation of Population Density of Adult Males
2.3.2. Estimation of Larva Control Efficiency
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Pheromone Ratio
3.2. Pheromone Dosage
3.3. Pheromone Dispensers
3.4. Pheromone Traps
3.5. Field Efficacy of Larger Plot Mass Trapping on Population Density of Adult Males
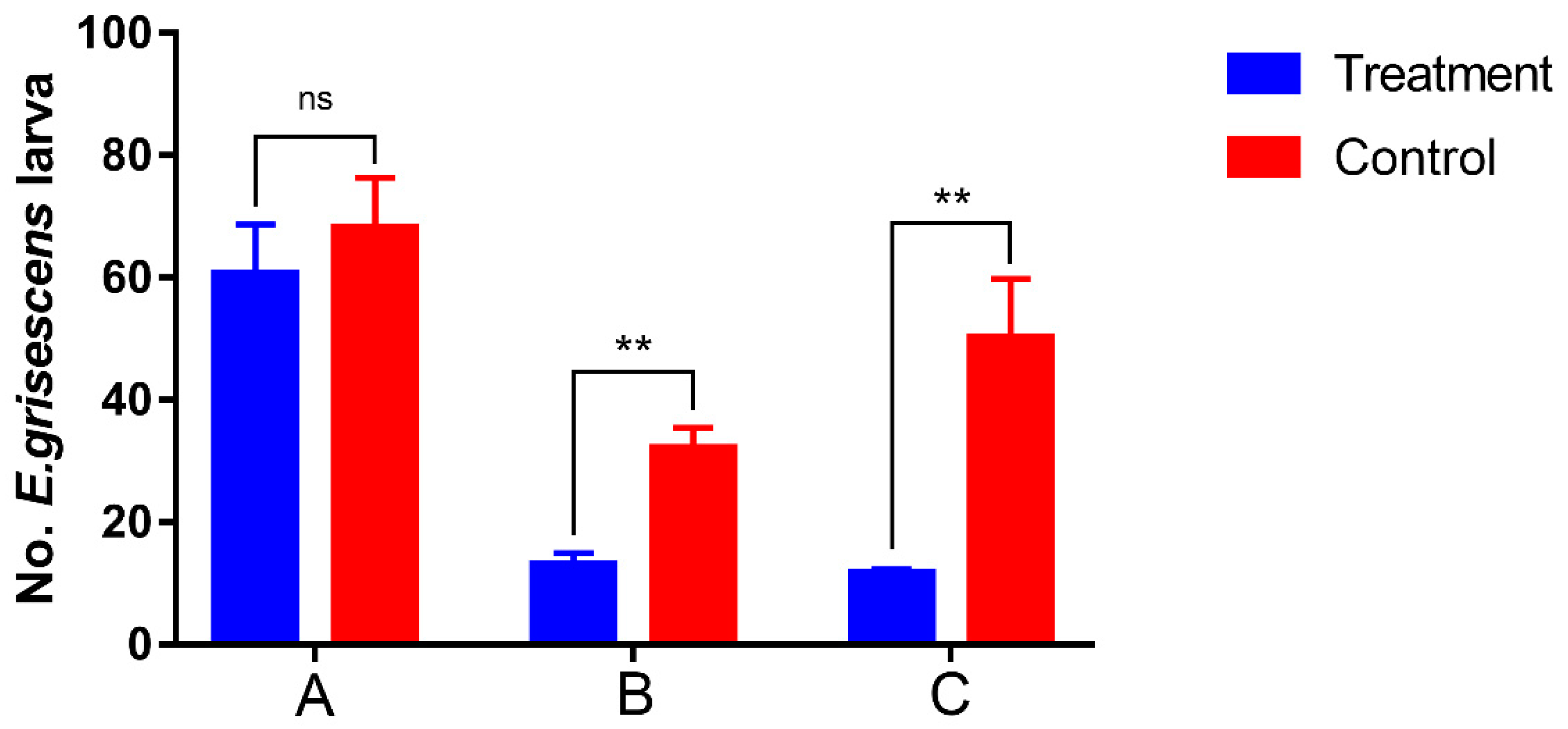
3.6. Efficiency of Large-Plot Mass Trapping for Larva Density Control
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, G.Y.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.X.; Yuan, Z.J.; Stanley, D.W.; Hu, C. Tea: Biological control of insect and mite pests in China. Biol. Control. 2014, 68, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.G.; Han, B.Y. The analysis on the fauna of tea insect pests in China and their regional occurrence. J. Tea Sci. 1999, 19, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.M.; Zhou, L.; Yang, M.; Luo, F.J.; Lou, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Sun, H.Z.; Wang, X.R. Index design and safety evaluation of pesticides application based on a fuzzy AHP model for beverage crops: Tea as a case study. Pest Manag Sci. 2019, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebhold, A.M.; Tobin, P.C. Population ecology of insect invasions and their management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2008, 53, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelinski, L.L.; Gut, L.J.; Miller, J.R. An attempt to increase efficacy of moth mating disruption by co-releasing pheromones with kairomones and to understand possible underlying mechanisms of this technique. Environ. Entomol. 2013, 42, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Knight, A.L.; Stelinski, L.L.; Hebert, V.; Gut, L.; Light, D.; Brunner, J. Evaluation of novel semiochemical dispensers simultaneously releasing pear ester and sex pheromone for mating disruption of codling moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 2012, 136, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, K.; Witjaksono; Fukumoto, T.; Mochizuki, F.; Yamamoto, M.; Ando, T. Mating disruption of the Japanese giant looper in tea gardens permeated with synthetic pheromone and related compounds. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2001, 100, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Ge, F.; Liu, X.H.; Feng, F.; Wang, L.J. Evaluation of mass-trapping for control of tea tussock moth Euproctis pseudoconspersa (Strand) (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) with synthetic sex pheromone in south China. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2005, 51, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Xiao, Q.; Yu, Y.G.; Wang, C.; Zhu, C.Q.; Sun, Z.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Wen, X.J. Analysis of tea geometrid (Ectropis grisescens) pheromone gland extracts using GC-EAD and GC×GC/TOFMS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3161–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.X.; Li, Z.Q.; Cai, X.M.; Bian, L.; Chen, Z.M. A primary study on sex pheromone of Ectropis grisescens. J. Tea Sci. 2016, 36, 537–543. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, T.; Ohsawa, H.; Ueno, T.; Kishi, H.; Okamura, Y.; Hashimoto, S. Hydrocarbons with a homoconjugated polyene system and their monoepoxy derivatives: Sex attractants of geometrid and noctuid moths distributed in Japan. J. Chem. Ecol. 1993, 19, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Shi, Y.H.; Liao, M.; Xiao, J.J.; Li, X.X.; Zhou, L.J.; Liu, C.W.; Liu, P.; Cao, H.Q. Laboratory and field evaluation of the aphidicidal activity of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) leaf extract and identification of the active components. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 3167–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, T. Mating disruption or mass trapping? Numerical simulation analysis of a control strategy for lepidopteran pests. Popul. Ecol. 2007, 49, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Inomata, S.; Yamamoto, M. Lepidopteran sex pheromones. In The Chemistry of Pheromones and Other Semiochemicals I; Schulz, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004; pp. 51–96. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.X.; Li, Z.Q.; Cai, X.M.; Bian, L.; Chen, Z.M. Evidence of premating isolation between two sibling moths: Ectropis grisescens and Ectropis obliqua (Lepidoptera: Geometridae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 2364–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cork, A.; De Souza, K.; Hall, D.R.; Jones, O.T.; Casagrande, E.; Krishnaiah, K.; Syed, Z. Development of PVC-resin-controlled release formulation for pheromones and use in mating disruption of yellow rice stem borer, Scirpophaga incertulas. Crop Prot. 2008, 27, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, W.L.; Glass, E.H.; Tette, J.; Comeau, A. Sex pheromone trapping for red-banded leaf roller control: Theoretical and actual. J. Econ. Entomol. 1970, 63, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassiou, C.G.; Kavallieratos, N.G.; Gakis, S.F.; Kyrtsa, L.A.; Mazomenos, B.E.; Gravanis, F.T. Influence of trap type, trap colour, and trapping location on the capture of the pine moth, Thaumetopoea pityocampa. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2007, 122, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cork, A.; Alam, S.N.; Rouf, F.M.A.; Talekar, N.S. Female sex pheromone of brinjal fruit and shoot borer, Leucinodes orbonalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae): Trap optimization and application in IPM trials. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2003, 93, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Ma, T.; Mao, T.F.; Guo, H.W.; Zhou, X.G.; Wen, X.J.; Xiao, Q. Application technology of the sex pheromone of the tea geometrid Ectropis grisescens (Lepidoptera: Geometridae). Int. J. Pest Manag. 2018, 64, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.; Peng, C.L.; Li, J.; Feng, C.H.; Li, P.; Du, Y.J. Optimization and field evaluation of the sex pheromone of Trichophysetis cretacea (Lepidoptera, Crambidae) for pest monitoring. J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 137, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinke, M.D.; Miller, J.R.; Gut, L.J. Potential of high-density pheromone-releasing microtraps for control of codling moth Cydia pomonella and obliquebanded leafroller Choristoneura rosaceana. Physiol. Entomol. 2012, 37, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, B.D.; Guédot, C.; Landolt, P.J. Mass-trapping codling moth, Cydia pomonella (Lepidopteran: Torticidae), using a kairomone lure reduces fruit damage in commercial apple orchards. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 1983–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Geng, S.; Chen, H.; Jung, C.; Wang, C.; Tu, H.; Zhang, J. Mass trapping of apple leafminer, Phyllonorycter ringoniella with sex pheromone traps in apple orchards. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, E.; Kovanci, O.B. Mass trapping low-density populations of Tuta absoluta with various types of traps in field-grown tomatoes. J. Plant Dis. Protect. 2016, 123, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarudin, N.; Ahmad, S.N.; Arshad, O.; Wahid, M.B. Pheromone mass trapping of bagworm moths, Metisa plana Walker (Lepidoptera: Psychidae), for its control in mature oil palms in Perak, Malaysia. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2010, 13, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyappa, C.; Raja Madhura Bhanu, K.; Chakravarthy, A.K.; Muttuvalli Seetharama, P.; Mangalgikar, P.; Ammagarahalli, B. Factors affecting catch of the black-headed caterpillar, Opisina arenosella Walker in sex pheromone-baited traps and evidence for population suppression by mass trapping. Orient. Insects 2018, 52, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Z.; Magsi, F.H.; Li, Z.; Cai, X.; Bian, L.; Liu, Y.; Xin, Z.; Xiu, C.; Chen, Z. Development and Evaluation of Sex Pheromone Mass Trapping Technology for Ectropis grisescens: A Potential Integrated Pest Management Strategy. Insects 2020, 11, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11010015
Luo Z, Magsi FH, Li Z, Cai X, Bian L, Liu Y, Xin Z, Xiu C, Chen Z. Development and Evaluation of Sex Pheromone Mass Trapping Technology for Ectropis grisescens: A Potential Integrated Pest Management Strategy. Insects. 2020; 11(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Zongxiu, Fida Hussain Magsi, Zhaoqun Li, Xiaoming Cai, Lei Bian, Yan Liu, Zhaojun Xin, Chunli Xiu, and Zongmao Chen. 2020. "Development and Evaluation of Sex Pheromone Mass Trapping Technology for Ectropis grisescens: A Potential Integrated Pest Management Strategy" Insects 11, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11010015
APA StyleLuo, Z., Magsi, F. H., Li, Z., Cai, X., Bian, L., Liu, Y., Xin, Z., Xiu, C., & Chen, Z. (2020). Development and Evaluation of Sex Pheromone Mass Trapping Technology for Ectropis grisescens: A Potential Integrated Pest Management Strategy. Insects, 11(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11010015




